Abstract
Bcl-2 is often upregulated in cancers to neutralize the BH3-only protein Bim at the mitochondria. BH3 mimetics (e.g. ABT-199 (venetoclax)) kill cancer cells by targeting Bcl-2’s hydrophobic cleft and disrupting Bcl-2/Bim complexes. Some cancers with elevated Bcl-2 display poor responses towards BH3 mimetics, suggesting an additional function for anti-apoptotic Bcl-2 in these cancers. Indeed, Bcl-2 via its BH4 domain prevents cytotoxic Ca2+ release from the endoplasmic reticulum (ER) by directly inhibiting the inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate receptor (IP3R). The cell-permeable Bcl-2/IP3R disruptor-2 (BIRD-2) peptide can kill these Bcl-2-dependent cancers by targeting Bcl-2’s BH4 domain, unleashing pro-apoptotic Ca2+-release events. We compared eight “primed to death” diffuse large B-cell lymphoma cell lines (DLBCL) for their apoptotic sensitivity towards BIRD-2 and venetoclax. By determining their IC50 using cytometric cell-death analysis, we discovered a reciprocal sensitivity towards venetoclax versus BIRD-2. Using immunoblotting, we quantified the expression levels of IP3R2 and Bim in DLBCL cell lysates, revealing that BIRD-2 sensitivity correlated with IP3R2 levels but not with Bim levels. Moreover, the requirement of intracellular Ca2+ for BIRD-2- versus venetoclax-induced cell death was different. Indeed, BAPTA-AM suppressed BIRD-2-induced cell death, but promoted venetoclax-induced cell death in DLBCL cells. Finally, compared to single-agent treatments, combining BIRD-2 with venetoclax synergistically enhanced cell-death induction, correlating with a Ca2+-dependent upregulation of Bim after BIRD-2 treatment. Our findings suggest that some cancer cells require Bcl-2 proteins at the mitochondria, preventing Bax activation via its hydrophobic cleft, while others require Bcl-2 proteins at the ER, preventing cytotoxic Ca2+-signaling events via its BH4 domain.
Keywords: apoptosis, anti-apoptotic Bcl-2, B-cell lymphoma, venetoclax, BIRD-2
INTRODUCTION
Diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL) and chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL) are amongst the most prevalent lymphoproliferative malignancies, characterized by an aggressive or indolent clinical behavior, respectively. A combination of chemo-, radio- and immunotherapy are currently used to treat patients suffering from non-Hodgkin lymphoma. Although the standard therapy varies according to the lymphoma subtype, often a cocktail of cytotoxic drugs in combination with an anti-CD20 monoclonal antibody (like rituximab®) is used in DLBCL. Still, a significant proportion of patients (29% of CD20-positive B-cell malignancies [1]) experiences side effects or relapse after rituximab® treatment due to tumorescape mechanisms like downregulation of CD20 protein expression [2]. Another important survival strategy of these B-cell malignancies is their upregulation of anti-apoptotic Bcl-2 proteins. Indeed, cancer cells are addicted to Bcl-2 for their survival due to their continuous and permanent ongoing apoptotic signaling [3]. Bcl-2 is the founding member of the Bcl-2 family. Along with Bcl-XL, Bcl-W, Bfl-1 and Mcl-1 it belongs to the anti-apoptotic members. These proteins are composed of four Bcl-2 homology (BH) domains. On the opposite side, the pro-apoptotic family members also consist out of 4 BH domains (like Bax and Bak) or have only one (the BH3-only proteins; like Bim) [4]. For many years it is known that anti-apoptotic Bcl-2 via its hydrophobic cleft, formed by the BH1-3, scaffolds and neutralizes pro-apoptotic members of the Bcl-2 family, including the executioner proteins, Bax and Bak, and the BH3-only proteins, like Bim [5]. Additionally, the BH4 domain of Bcl-2 prevented Bax activation by binding to its inactive conformation [6]. This situation where Bcl-2 is loaded with pro-apoptotic family members has been referred to as “primed to death” [7]. Insights into the binding of Bcl-2 with the pro-apoptotic members have spurred the development of the BH3 mimetics. These molecules mimic the BH3 domain of Bad, a sensitizer BH3-only protein thereby disrupting Bcl-2/Bim complexes and releasing Bim from the hydrophobic cleft of Bcl-2, which then results in Bax/Bak-mediated apoptosis in cancer cells but not in healthy cells [8, 9]. Nowadays, a Bcl-2-selective BH3-mimetic compound, ABT-199 (venetoclax) established by AbbVie is currently implemented to treat 17p-deleted CLL patients [10] without affecting platelet survival [11–13]. Unfortunately, some Bcl-2-dependent cancer cells are insensitive to BH3-mimetic compounds [11], likely due to low levels of Bim and/or of Bax/Bak. As such, at the level of the mitochondria, these cells are poorly “primed to death”. Moreover, patients suffering from these poorly-primed cancers also display poor responses to conventional chemotherapeutic drugs and thus seem hard to treat [14].
Interestingly, for treating cancer cells with upregulated Bcl-2 levels, which display reduced responses to chemotherapy/BH3 mimetics, Bcl-2’s function may be used in an alternative way, namely at the endoplasmic reticulum (ER), the main intracellular Ca2+-storage organelle [15, 16]. A major ER Ca2+-release pathway is formed by the inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate (IP3) receptor (IP3R), which impacts several cancer hallmarks, including cell death and survival [17]. During recent years, it became clear that an important part of Bcl-2’s anti-apoptotic properties is due to direct targeting and inhibition of IP3Rs [18–20]. Bcl-2/IP3R complex formation is dependent on Bcl-2’s BH4 domain, which targets the central, modulatory domain of all three IP3R isoforms [21–23]. Importantly, Bcl-2’s hydrophobic cleft is dispensable for IP3R-complex formation and IP3R inhibition [24]. Consistent with this, venetoclax does neither interfere with the binding of Bcl-2 to IP3Rs nor alleviate the inhibition of IP3R-mediated Ca2+ release by Bcl-2 [24, 25]. Also, a peptide tool comprising the Bcl-2-binding site on the IP3R (aa 1389-1408 of mouse IP3R1 in which Asp1403Asp1404 residues were changed into two Ala residues) was developed, called Bcl-2/IP3R disruptor-2 (BIRD-2) [26]. BIRD-2 targets the BH4 domain of Bcl-2, thereby disrupting Bcl-2/IP3R complexes and thus abolishing Bcl-2’s inhibitory action on the IP3R channel, but not Bcl-2/Bim complexes [18]. BIRD-2 by itself is sufficient to kill Bcl-2-dependent CLL and DLBCL cancer cells by provoking spontaneous, pro-apoptotic Ca2+ signals [26, 27]. Importantly, BIRD-2 does not cause a general cytotoxicity. Several cell types were found to be very resistant to BIRD-2, e.g. peripheral mononuclear blood cells [26], certain types of DLBCL cells [27], non-malignant cell lines, like WEHI7.2 T cells that express low endogenous Bcl-2 levels [26], and platelets (unpublished data). In addition, the cell-death properties of BIRD-2, which are in lymphoid malignancies accompanied by Bax and caspase-3 activation, also provoked a marked decrease in in vivo tumor growth in xenografted mouse models [28]. Remarkably, in these lymphoma cell lines susceptibility to BIRD-2-induced Ca2+ release and cell death correlated with the expression level of IP3R2. IP3R2 is the isoform with the highest sensitivity towards its ligand, IP3 [29]. Among DLBCL cancer cells, SU-DHL-4 cells displayed the highest IP3R2 level and highest BIRD-2 sensitivity, while OCI-LY-1 displayed the lowest IP3R2 level and lowest BIRD-2 sensitivity [27]. Interestingly, previous studies indicated that OCI-LY-1 were more sensitive to BH3 mimetics like the non-selective Bcl-2/Bcl-XL inhibitor ABT-737 [30] and the selective Bcl-2 inhibitor venetoclax [11] than SU-DHL-4. Yet, a more detailed analysis directly comparing and correlating the response of a larger set of different Bcl-2-dependent DLBCL cancer cells to BIRD-2 versus venetoclax has not been performed.
RESULTS
Heterogeneous responses in DLBCL cell lines towards venetoclax treatment
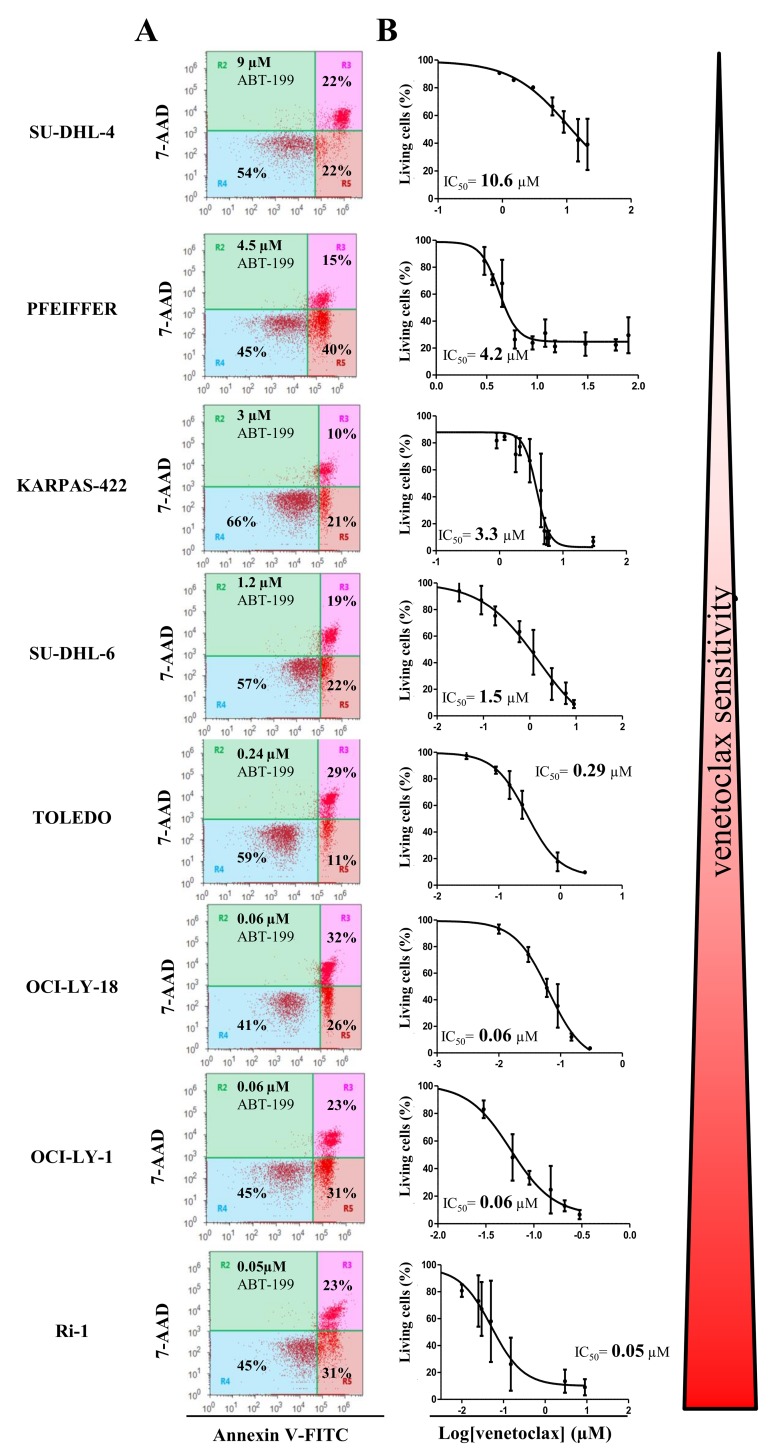
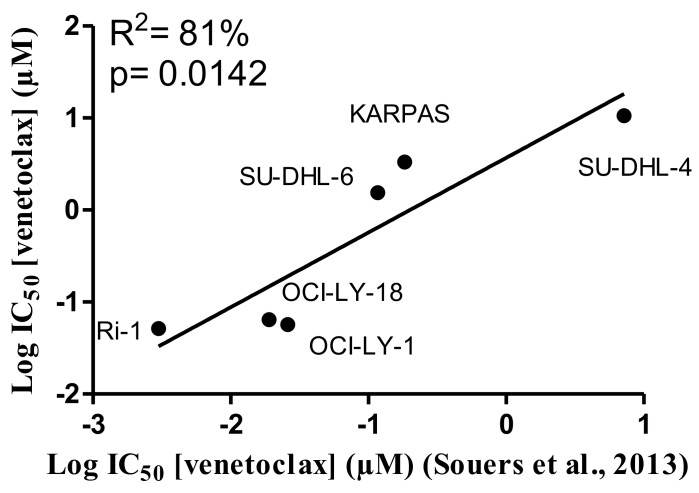
A collection of cancer cell lines mainly composed of germinal center DLBCL cells, which are highly dependent on Bcl-2 to survive the continuous and permanent death signaling, was used in the present study. Although, all the cells displayed high levels of Bcl-2 and were identified to be dependent on Bcl-2 for their survival [30], they differently responded to ABT-199 (venetoclax) treatment [11]. We wanted to validate the differential apoptotic sensitivity towards venetoclax in our collection of hematological cancer cell lines. To challenge our findings, we also included an internal (negative) control, i.e. a DLBCL cell line (PFEIFFER) that was not dependent on Bcl-2, but expresses high levels of Bfl-1 mRNA and therefore was described as being putatively Bfl-1 dependent [30]. Hence, we exposed the cells to increasing concentrations of venetoclax and determined the apoptosis fraction after 24 hours of venetoclax treatment (Figure 1A and 1B). The IC50 was determined, confirming the differential apoptotic sensitivities in these cell lines, listed from high to low sensitivity to venetoclax: Ri-1 (IC50= 0.05 μM), OCI-LY-1 (IC50= 0.06 μM), OCI-LY-18 (IC50= 0.06 μM), TOLEDO (IC50= 0.29 μM), SU-DHL-6 (IC50= 1.5 μM), KARPAS-422 (IC50= 3.3 μM), PFEIFFER (IC50= 4.2 μM) and SU-DHL-4 (IC50= 10.6 μM). Further, we wanted to validate our data set against the results obtained by Souers et al. [11]. These data revealed, using linear regression analysis, a strong and significant positive correlation (R2= 81%, Figure 2) between our experimentally obtained IC50 values and their IC50 values [11]. Hence, we could confirm and validate the heterogeneity and representativeness of our cell lines towards venetoclax.
Figure 1. The apoptotic response of eight different DLBCL cell lines towards venetoclax treatment.
(A) Representative dot plots from flow cytometric analysis of Annexin V-FITC/7-AAD stained SU-DHL-4, PFEIFFER, KARPAS-422, SU-DHL-6, TOLEDO, OCI-LY-18, OCI-LY-1, and Ri-1 cells, treated with venetoclax at a concentration (indicated in the left top corner of the dot plot) around its IC50 value during 24h (10 000 cells per analysis). (B) Concentration-response curves of the 8 different DLBCL cell lines after incubation with increasing concentrations of venetoclax for 24h. The apoptotic population was defined as the Annexin V-FITC/7-AAD-positive fraction. Data represented are average ± SD (N≥3).
Figure 2. Positive correlation between the IC50 values for venetoclax determined in this project and previously published IC50 values.
Linear regression analysis of the IC50 values obtained for venetoclax from the concentration-response curves of Figure 1 against the previously published results obtained by Souers et al. [11] for respectively six different DLBCL cell lines.
BIRD-2 sensitivity negatively correlated with venetoclax-induced apoptosis in DLBCL cells
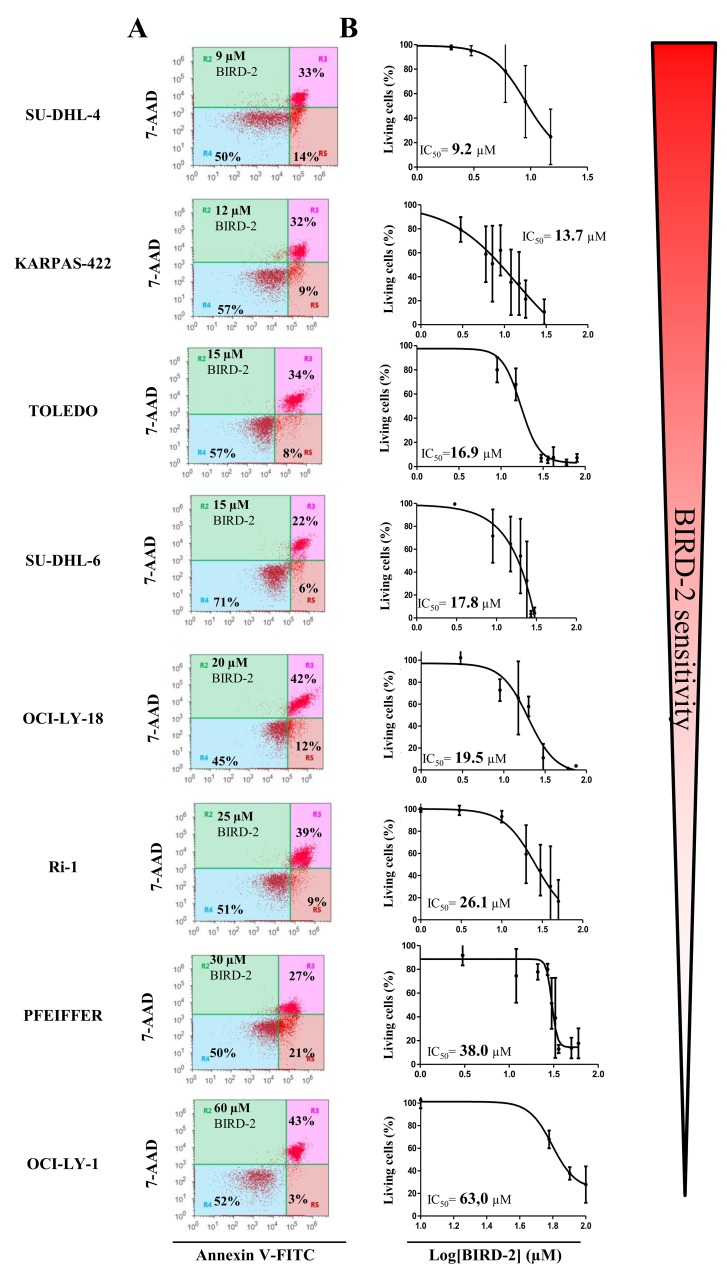
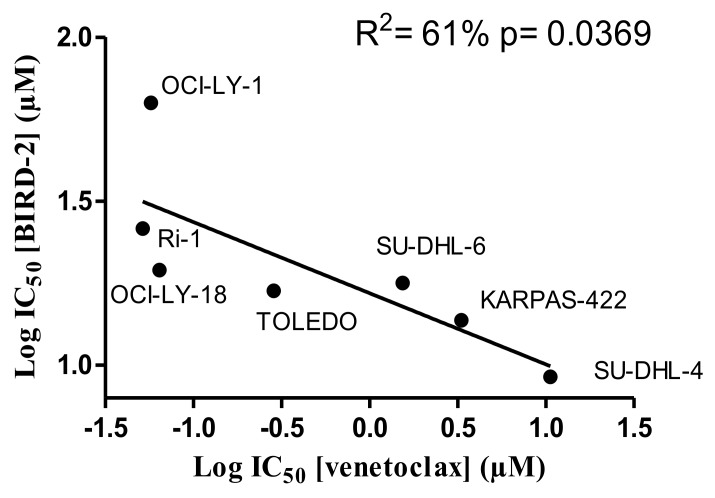
Since BIRD-2 and venetoclax target different domains of Bcl-2, i.e. the BH4 domain and the hydrophobic cleft, respectively, we next examined the sensitivity of these cells to BIRD-2. We therefore determined the IC50 values for BIRD-2-induced cell death (in the following rank order from high to low sensitivity to BIRD-2: SU-DHL-4 (IC50= 9.2 μM), KARPAS-422 (IC50= 13.7 μM), TOLEDO (IC50= 16.9 μM), SU-DHL-6 (IC50= 17.8 μM), OCI-LY-18 (IC50= 19.5 μM), Ri-1 (IC50= 26.1 μM), PFEIFFER (IC50= 38.0 μM) and OCI-LY-1 (IC50= 63 μM)) and correlated them with the IC50 values obtained for venetoclax-induced cell death. Interestingly, cells previously shown to be sensitive towards venetoclax (Ri-1, OCI-LY-1 and OCI-LY-18, Figure 1) were more resistant towards BIRD-2 treatment (Figure 3A and 3B) and vice versa. Moreover, plotting the log IC50 values of both compounds against each other for the Bcl-2-dependent cell lines revealed an opposite sensitivity between BIRD-2 and venetoclax-induced cell death (Figure 4). The correlation between BIRD-2 and venetoclax sensitivity was quantified by linear regression, showing a significant reciprocal correlation between BIRD-2 versus venetoclax sensitivity with a R2 value of 61%. Strikingly, the IC50 values for BIRD-2 and venetoclax in the Bfl-1-dependent cell line PFEIFFER did not follow this reciprocal sensitivity. This is consistent that the opposite correlation between both Bcl-2 inhibitors is valid for Bcl-2-dependent cancer cells, but not for cancer cells dependent on other Bcl-2-family members, like Bfl-1. This underpins the “on-target” effect of BIRD-2 and venetoclax tools.
Figure 3. Heterogeneity in the apoptotic response of eight different DLBCL cell lines towards BIRD-2 treatment.
(A) Representative dot plots from flow cytometric analysis of Annexin V-FITC/7-AAD-stained SU-DHL-4, KARPAS-422, SU-DHL-6, TOLEDO, OCI-LY-18, Ri-1, PFEIFFER and OCI-LY-1 cells, treated with BIRD-2 at a concentration (indicated in the left top corner of the dot plot) around its IC50 value, during 24h (10 000 cells per analysis). (B) Concentration-response curves of the different DLBCL cell lines after incubation with increasing concentrations of BIRD-2 for 24h. The apoptotic population was identified as the Annexin V-FITC/7-AAD-positive fraction. Data represented are average ± SD (N≥3).
Figure 4. The IC50 values of the analysed DLBCL cell lines indicate an opposite response to BIRD-2 versus venetoclax.
The different IC50 values were determined via the concentration-response curves (Figures 1 and 3) and the log IC50 values for BIRD-2 were plotted as a function of the log IC50 values for venetoclax. These IC50 values were subjected to statistical analysis via linear regression.
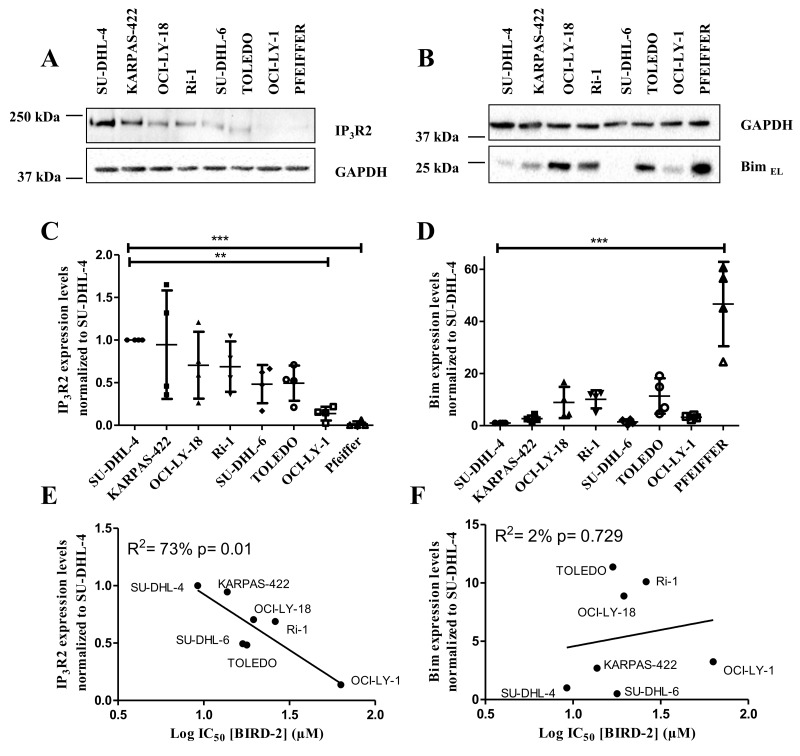
IP3R2 protein expression levels positively correlated with BIRD-2 sensitivity
Previously, our laboratory has provided evidence for the existence of a correlation between the BIRD-2-induced cell death and the IP3R2 expression levels [27]. We thereby showed that there was a good correlation with IP3R2, the IP3R isoform with the highest sensitivity for the endogenous ligand IP3 [29], but not with the other isoforms nor with the total IP3R level, pointing to a peculiar role of this IP3R2 isoform in cytotoxic Ca2+signaling. We also wanted to examine whether there was a correlation between the sensitivity towards BIRD-2 and the expression levels of the BH3-only protein Bim, which is active at the level of the mitochondria. Therefore, we quantified the expression levels of IP3R2 and BimEL, the most abundant isoform of Bim, in DLBCL cell lysates using immunoblotting (normalized to SU-DHL-4, Figure 5A-5D). These expression levels were plotted with respect to the IC50 values obtained for BIRD-2 for each cell line (Figure 5E-5F). These data revealed a significant positive correlation between the BIRD-2 sensitivity and IP3R2- expression levels (R2= 73% Figure 5E), but no correlation between the Bim-expression levels and BIRD-2 sensitivity was found (R2= 2%, Figure 5F). As a consequence, SU-DHL-4, KARPAS-422 and TOLEDO cells were good responders towards BIRD-2 (Figure 5E) due to their high IP3R2 expression levels (Figure 5C). On the other hand, OCI-LY-1 has a lower amount of IP3R2 (Figure 5C), which correlates with the low sensitivity to BIRD-2 (Figure 5E). Also, PFEIFFER expressed lower IP3R2 levels but its position in the plot showed a bad correlation with BIRD-2 sensitivity (data not shown).
Figure 5. Positive correlation between the IP3R2 levels and the BIRD-2 sensitivity.
(A-B) Representative western blots of the IP3R2 (A) and BimEL (B) expression levels. GAPDH was used as loading control. (C-D) Quantification of IP3R2 (C) and BimEL (D) expression levels. Data are represented as the average ± SD of N≥3 with ** p<0.01 and ***p<0.001 obtained via a repeated measure ANOVA with a Bonferroni’s post-hoc test versus SU-DHL-4. (E-F) Correlation between the expression levels of IP3R2 (E) and BimEL (F) with the IC50 values of BIRD-2, subjected to statistical analysis via linear regression.
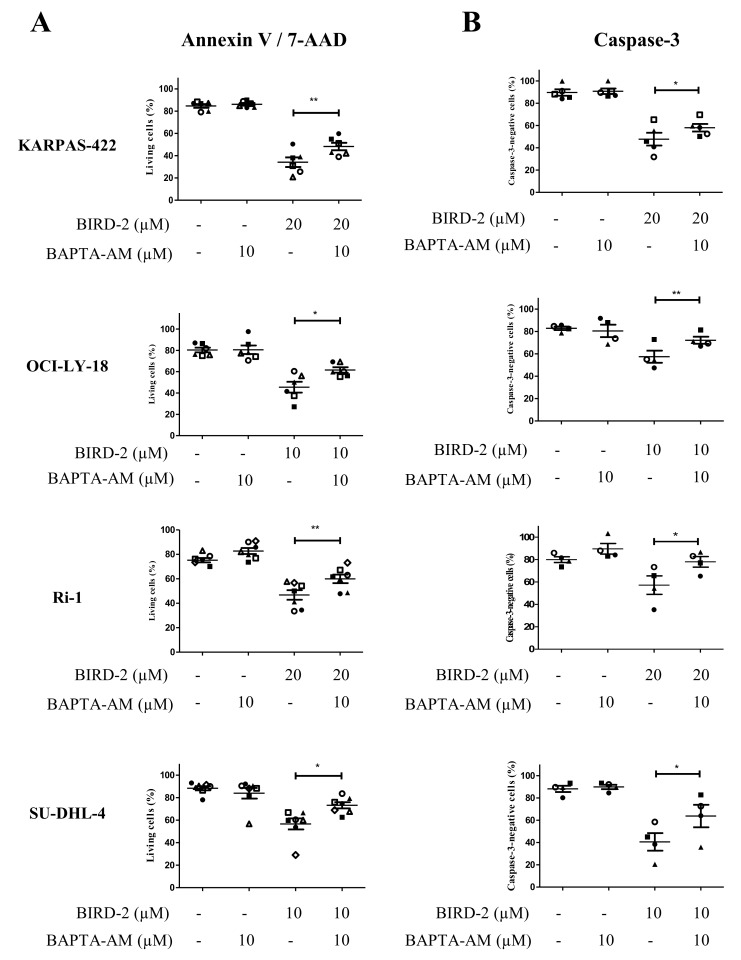
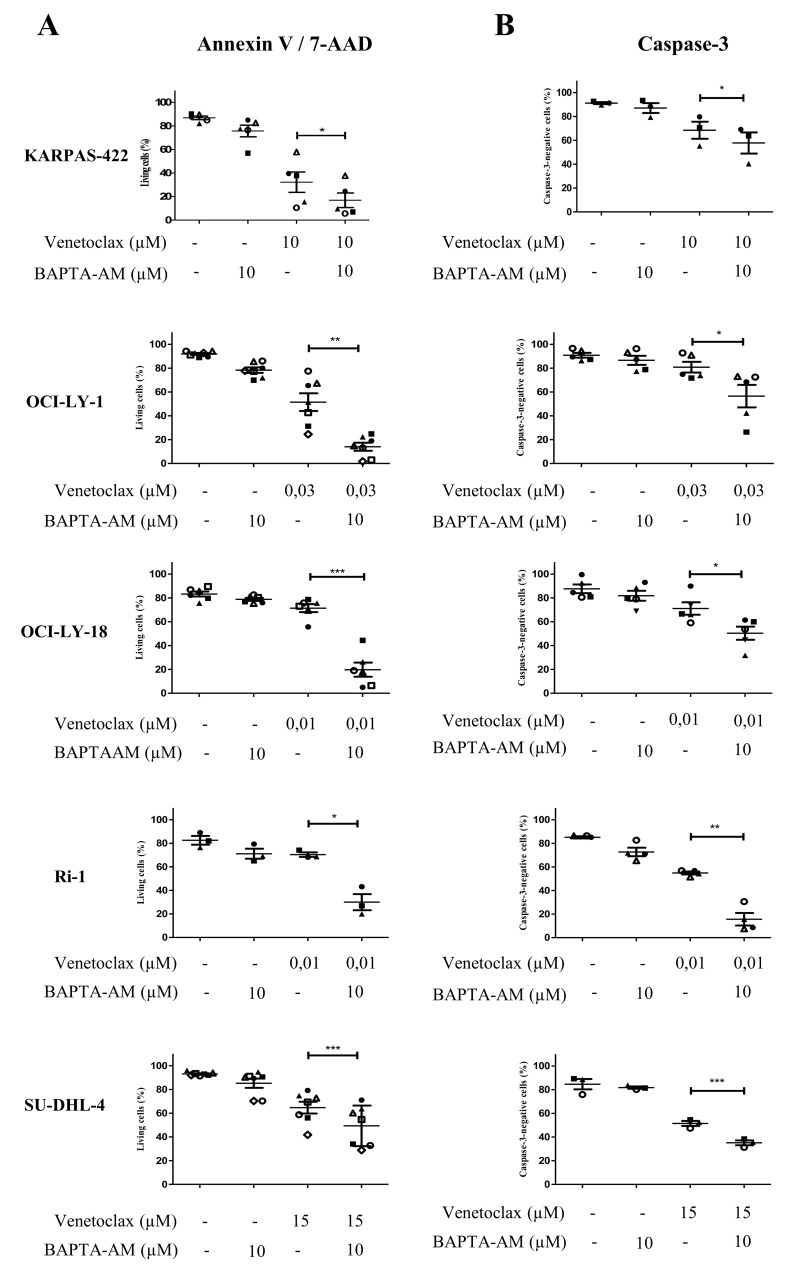
Intracellular Ca2+ is required for BIRD-2-, but not for venetoclax-induced cell death
In a previous study, we have already observed that the BIRD-2-induced apoptosis correlated with the BIRD-2-induced Ca2+ release [27]. This together with the observation that BIRD-2 positively correlates with the IP3R2-expression levels strongly suggest that intracellular Ca2+ is important for the BIRD-2-induced cell death. To explore the role of Ca2+ in BIRD-2- and venetoclax-induced cell death, we measured apoptosis while chelating intracellular Ca2+ using BAPTA-AM. We first validated that our BAPTA-AM treatment effectively chelated intracellular Ca2+ by assessing agonist-induced Ca2+ release in Fura-2-loaded SU-DHL-4 cells. Compared to untreated cells, cells pre-treated with BAPTA-AM for 2 hours displayed a severely reduced response to anti-IgG/IgM, a B-cell receptor agonist that results in IP3/Ca2+ signaling, thereby validating the effectiveness of BAPTA-AM (Supplementary Figure 1). Adding BAPTA-AM prior to BIRD-2 treatment significantly reduced the occurrence of cell death in KARPAS-422, OCI-LY-18, Ri-1 and SU-DHL-4 (Figure 6A). A similar protection by BAPTA-AM was observed when measuring apoptosis via a caspase-3 assay (Figure 6B). OCI-LY-1 could not be included in this analysis as the concentration of BIRD-2 needed to evoke cell death was too high to exclude additional off-target effects. Oppositely, chelating intracellular Ca2+ upon venetoclax treatment significantly enhanced single-agent induced cell death and caspase-3 activity in KARPAS-422, OCI-LY-1, OCI-LY-18, SU-DHL-4 and Ri-1 cells (Figure 7A and 7B). Interestingly, the cell death induced by BAPTA-AM in the presence of venetoclax seemed to correlate with their venetoclax sensitivity, as Ri-1, OCI-LY-1 and OCI-LY-18 were the most sensitive to BAPTA-AM and KARPAS-422 and SU-DHL-4 the least sensitive ones.
Figure 6. Intracellular Ca2+ has a primary role in the BIRD-2-induced cell death.
Analysis of Annexin V-FITC/7-AAD-negative cells (living cells (%), A) and caspase-3-negative cells (B) obtained using flow-cytometric analysis of KARPAS-422, OCI-LY-18, Ri-1 and SU-DHL-4 cells treated with or without BIRD-2 and 10 μM BAPTA-AM for 2h. Data are represented as mean ± SEM >3 independent experiments. Significance was obtained using a two-tailed paired t-test with * p< 0.05, **p<0.01.
Figure 7. Intracellular Ca2+ does not contribute to the venetoclax-induced cell death.
Analysis of Annexin V-FITC/7-AAD-negative cells (living cells (%), A) and caspase-3-negative cells (B) obtained using flow-cytometric analysis of KARPAS-422, OCI-LY-1, OCI-LY-18, Ri-1 and SU-DHL-4 cells treated with or without venetoclax and 10 μM BAPTA-AM for 4h. Data are represented as mean ± SEM >3 independent experiments. Significance was obtained using a two-tailed paired t-test with * p< 0.05, **p<0.01, ***p<0.001.
Hence, overall these findings suggest a different requirement for Ca2+ in the BIRD-2- or venetoclax-induced cell death.
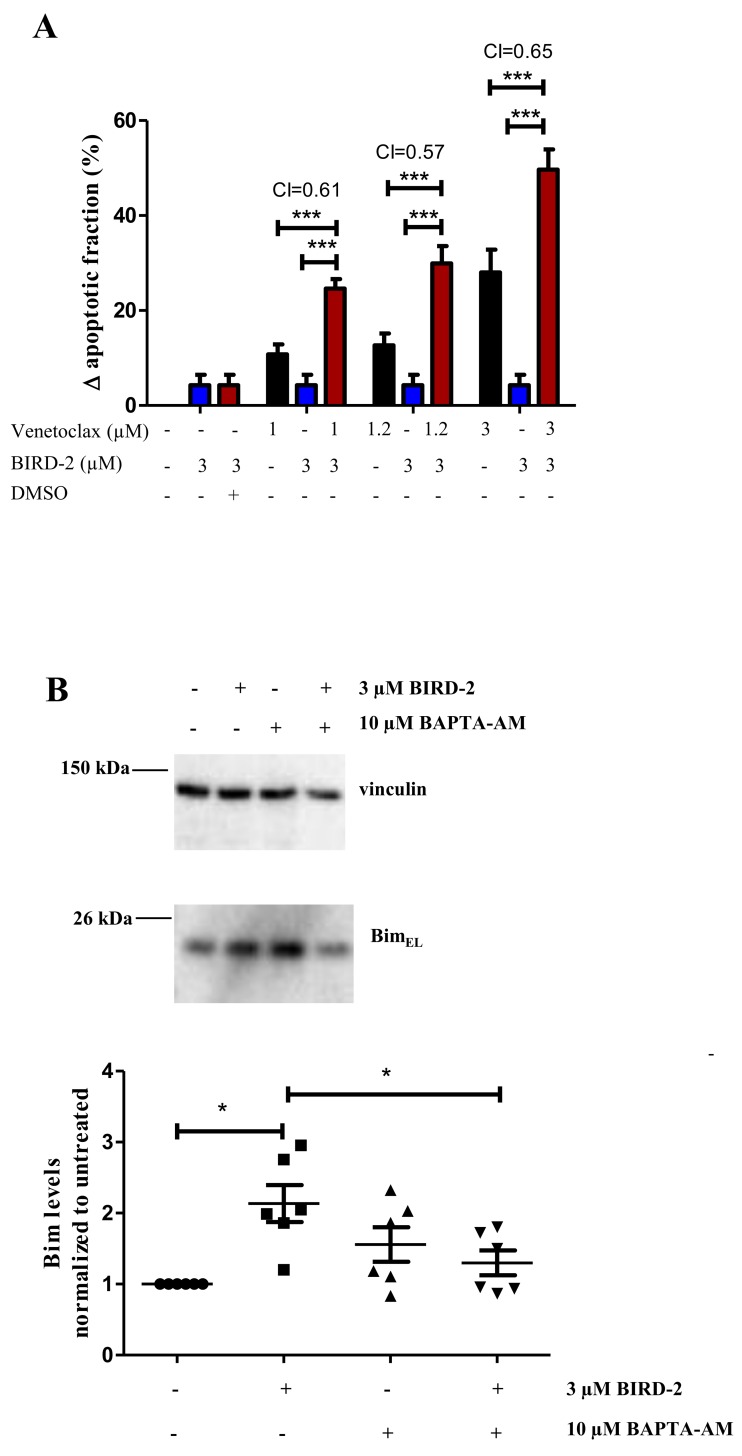
Synergistic killing of DLBCL cells by venetoclax and BIRD-2
Because BIRD-2 and venetoclax target different domains of Bcl-2, we tested whether combining these agents would synergistically induce cell death. Combining a submaximal concentration of BIRD-2 with increasing concentrations of venetoclax enhanced cell-death induction in the venetoclax-resistant SU-DHL-4 DLBCL cell line compared to single-agent treatment (Figure 8A). In order to determine mathematically whether it is a synergistic or additive effect, a combination index (CI) was measured. As a CI<1 indicates synergy, co-treatment of SU-DHL-4 with BIRD-2 and venetoclax consistently induced synergistic cytotoxicity at all concentration measured. Additionally, similar results were obtained when calculating the CI using the raw data set (Supplementary Figure 2) instead of the change in apoptotic fraction. Moreover, we demonstrated that treating the highly BIRD-2-sensitive SU-DHL-4 cell line with 3 μM BIRD-2, a concentration ineffective to trigger cell death by itself, significantly increased the Bim levels, thereby priming the cells for sensitivity to venetoclax (Figure 8B). Moreover, the BIRD-2-induced upregulation of Bim seemed to be Ca2+ dependent, since chelating intracellular Ca2+ with BAPTA-AM could suppress the BIRD-2-induced upregulation of Bim.
Figure 8. Synergistic effect of BIRD-2 and venetoclax in SU-DHL-4 cells, correlating to Bim upregulation in BIRD-2-treated SU-DHL-4 cells.
(A) SU-DHL-4 cells were treated for 24h with various concentrations of venetoclax alone (black bars), BIRD-2 alone (blue bars) or a combination of venetoclax/DMSO Ctrl (0.03%) and BIRD-2 (red bars). Cell death was measured using flow cytometry of Annexin V-FITC/7-AAD-stained cells and plotted as the BIRD-2- or venetoclax-induced apoptotic fraction. The combination index, calculated using the response additive method (CI= (Evenetoclax+ EBIRD-2)/Evenetoclax+BIRD-2) was measured as indication for synergistic or additive cell killing. Data are represented as average ± SEM of N=5. Statistical significance was determined with a two-way ANOVA with a Bonferroni post-hoc test comparing Evenetoclax or EBIRD-2 with Evenetoclax+BIRD-2 for the different venetoclax concentrations. (B) Representative western blots showing the BimEL-expression levels after 24h treatment of SU-DHL-4 cells with 3 μM BIRD-2 in the presence or absence of 10 μM BAPTA-AM. Vinculin was used as loading control. Data are represented as the average ± SD of N≥3 with * p<0.05 obtained via Wilcoxon signed rank test.
Together with the existence of a reciprocal correlation, these data underpin differences in the targets for apoptotic induction by BIRD-2 or venetoclax.
DISCUSSION
Anti-apoptotic Bcl-2 protects cancer cells from cell death by acting at the mitochondria, scaffolding Bim/Bak/Bax [6] and by acting at the ER, suppressing excessive IP3Rs activity [31]. Here, we used a collection of well-established Bcl-2-dependent DLBCL cell lines to assess the cell-death properties of two selective Bcl-2 inhibitors that target different domains of Bcl-2, namely ABT-199 (venetoclax), which targets the hydrophobic cleft of Bcl-2 and disrupts Bcl-2/Bim interactions [11], and BIRD-2, which targets the N-terminal BH4 domain of Bcl-2 and disrupts IP3R/Bcl-2 interactions [21]. Plotting the IC50 values for the apoptotic effect of both Bcl-2 inhibitors revealed a reciprocal sensitivity between venetoclax and BIRD-2 in the cancer cells dependent on Bcl-2 for their survival. This reciprocal sensitivity between venetoclax and BIRD-2 appeared to count for Bcl-2-dependent cancer cells, but not for Bfl-1-dependent cancer cells, as the Bfl-1-dependent cancer cell line PFEIFFER was relatively resistant to both venetoclax and BIRD-2. This correlates with previous work showing that increased transcript levels of Bfl-1 has been allocated to resistance to BH3 mimetics [32]. We also wish to note that the range of sensitivities of the different DLBCL cells obtained for BIRD-2 versus venetoclax are very different, being ∼6-fold different for BIRD-2, while being ∼200-fold different for venetoclax. The reason for this difference is not clear, but may relate to differences in uptake rate and mechanisms and in their underlying mechanism of action. In any case, the range of sensitivities obtained in this work for BIRD-2 and venetoclax are very similar to the ones previously reported in the literature [11, 27, 28, 33].
Though our study is the first to have systematically compared and correlated the sensitivity of a collection of DLBCL cell lines towards venetoclax versus BIRD-2 by performing complete and quantitative concentration-response analyses, previous studies have hinted towards such a concept. Indeed, previous work from our own lab focusing on SU-DHL-4 versus OCI-LY-1 and short-term apoptosis experiments showed that the venetoclax-sensitive OCI-LY-1 cells were resistant to 10 μM BIRD-2, while SU-DHL-4, a cell line less sensitive to venetoclax was sensitive to 10 μM BIRD-2 [27]. Follow-up work by Distelhorst and co-workers in multiple myeloma cells [28] and small cell lung carcinoma [34], using a single concentration of BIRD-2 and of BH3 mimetics, confirmed that cell lines more resistant to BH3 mimetics were more sensitive to BIRD-2 and vice versa. We now provide further insight in the reciprocal sensitivity of cancer cells to venetoclax versus BIRD-2. Previous work from Letai and co-workers showed that responsiveness to BH3 mimetics correlated with Bim levels and more particular with Bcl-2/Bim complex formation [30]. Here, we show that BIRD-2 sensitivity positively correlates with IP3R2 levels while there was no correlation with Bim levels. Hence, these data support the concept of the dual dependence of cancer cells on Bcl-2 for their survival with respect to the oncogenic signaling either by Bim upregulation or by IP3R2 upregulation. Of note, Bcl-2 also interacts with the regulatory and coupling domain of the IP3R isoform 1 and isoform 3 [22] and is able to form protein complexes with all three IP3R isoforms in Jurkat and WEHI7.2 T cells [18, 35]. This correlates with the high level of conservation of the 20-amino acid stretch encompassing the Bcl-2-binding site among the different IP3R isoforms [36–38]. However, in DLBCL cells, it seems that Bcl-2 interaction with the different IP3R isoforms is context dependent. In SU-DHL-4, Bcl-2 co-immunoprecipitated predominantly with IP3R2 when compared with IP3R3, while in OCI-LY-1 the reverse was observed [27]. The reason for this is not clear, but may indicate a differential modulation of IP3R isoforms and Bcl-2 in different cellular contexts. In any case, both the intracellular Ca2+ release and the apoptotic response induced by BIRD-2 correlated with IP3R2-expression levels but not with IP3R1- or IP3R3-expression levels. The binding of Bcl-2 to IP3R2, which displays the highest sensitivity to its ligand IP3, and the concomitant suppression of IP3R2 activity may enable cancer cell survival in two ways: (i) by preventing the occurrence of excessive, pro-apoptotic Ca2+-release events and (ii) by establishing low-level Ca2+ signaling that drives the mitochondrial metabolism of cancer cells [39, 40]. In addition to this, IP3R2 upregulation has been implicated in cellular senescence, a stable growth arrest that prevents the proliferation of malignant cells [41]. Therefore, the binding of Bcl-2 to IP3R2 may allow cancer cells to escape cellular senescence. The oncogenic mechanisms responsible for IP3R2 upregulation remain largely unknown, although a role for constitutive NFAT signaling may be part of the signaling mechanisms that cause IP3R2 upregulation [42]. Furthermore, it is also unknown which mechanisms or checkpoints are in place that are responsible for the ‘choice’ of upregulating Bim versus IP3Rs in response to oncogenic stress. It is conceivable that the upregulation of Bim or IP3R2 in cancer cells ought to be compensated by high anti-apoptotic Bcl-2 levels resulting in protein complexes with either Bim or IP3R2. Because the IP3R2 is an important mediator of the BIRD-2 susceptibility, we examined in more detail the role of intracellular Ca2+ in the BIRD-2- and venetoclax-induced cell death. We confirmed earlier work [27, 28], pinpointing to an important role for intracellular Ca2+ overload in BIRD-2-induced cell death, since intracellular Ca2+ buffering decreased caspase-3 activation in response to BIRD-2 treatment in different DLBCL cell lines. In addition to this, it is possible that BAPTA-AM can suppress BIRD-2-induced cell death by counteracting the upregulation of pro-apoptotic BH3-only protein Bim brought about by BIRD-2 treatment. In contrast, chelating intracellular Ca2+ enhanced the venetoclax-induced caspase-3 activation in different DLBCL cell lines. We have already elucidated previously that venetoclax did not trigger an acute Ca2+ release and that intracellular Ca2+ buffers did not protect against venetoclax-induced cell death in OCI-LY-1 and SU-DHL-4 cells [25]. Here we extended our earlier work to several DLBCL cell lines, firmly excluding an essential role for intracellular Ca2+ overload for venetoclax-induced cell death. On the contrary, it seems that DLBCL cells can be sensitized to venetoclax by buffering intracellular Ca2+. The mechanisms underlying the interplay between venetoclax and basal Ca2+ signals in DLBCL are not clear and will require further research. However, it is possible that BAPTA-AM treatment disturbs the balance between pro-apoptotic and anti-apoptotic Bcl-2-family members. For instance, ovarian cancer cells exposed to BAPTA-AM display a reduction in the protein levels of anti-apoptotic Mcl-1 [43]. Hence, such decreases in the levels of anti-apoptotic proteins and/or increases in the levels of pro-apoptotic proteins may account for the toxic effects of BAPTA-AM and/or sensitization towards BH3-mimetic drugs.
In addition, combing BIRD-2 with venetoclax enhanced cell demise compared to single treatment alone in a venetoclax-resistant DLBCL cell line. Hence, co-treatment with BIRD-2 could sensitize the cells towards venetoclax. Previous reports also indicated a synergistic effect between BIRD-2 and BH3 mimetics in melanoma [28] and lung cancer cells [34]. In melanoma cells prolonged exposure to BIRD-2 increased the protein levels of Bim in a Ca2+-dependent manner and consequently increased the sensitivity towards BH3 mimetics [28]. We here report that the BIRD-2-dependent upregulation of Bim also occurs in DLBCL cells in a Ca2+-dependent manner, thereby sensitizing these cancer cells towards venetoclax and thus likely underlying the synergism between BIRD-2 and venetoclax for inducing cell death in DLBCL cells. This synergism also establishes an interesting link between the “ER Ca2+ signaling” pathways and “mitochondrial BH3-only” pathways in apoptosis, where Ca2+ signals may not only by themselves trigger apoptosis, e.g. by mitochondrial Ca2+ overload, but may also affect the expression levels of other Bcl-2-family members, thereby modulating cell death. This intriguing link between Ca2+ signaling and Bcl-2-family members is further underpinned by the fact that venetoclax-induced cell death can be enhanced by intracellular Ca2+ chelation using BAPTA-AM.
Our collection of data is also consistent with the dual role of anti-apoptotic Bcl-2 being either inhibiting pro-apoptotic proteins or suppressing aberrant IP3-mediated Ca2+ release [31]. It may also indicate that different domains of Bcl-2 underlie Bcl-2’s differential role at the mitochondria (its hydrophobic cleft targetable by BH3-domain-like molecules) and at the ER (its BH4 domain targetable by IP3R-domain-derived molecules). Indeed, previous work indicated that the inhibition of IP3Rs by Bcl-2 critically depends on Bcl-2’s BH4 domain [21, 22], while Bcl-2’s hydrophobic cleft is dispensable for this [24]. Furthermore, by showing that the IP3R2 protein levels correlated with the sensitivity to BIRD-2 in the following rank order: KARPAS-422 > SU-DHL-4 > OCI-LY-18 > Ri-1 > SU-DHL-6 > TOLEDO > OCI-LY-1, we confirm the complex formation between IP3R2 and Bcl-2 as a major determinant for cancer cell addiction to Bcl-2 at the ER. However, other confounding factors might further influence the correlation between the IP3R2/Bim-expression levels with the BIRD-2 sensitivity. Indeed, recent reports have indicated that the activation of proto-oncogene like PKB/Akt can affect, by phosphorylation, both the IP3R function and ER Ca2+ homeostasis and thereby decreasing apoptotic events by dampening the mitochondrial Ca2+ rise [44, 45]. Moreover, this oncogenic PKB/Akt hyperactivity is often linked to the loss of PTEN in DLBCL cells [46]. It is not known whether PKB/Akt signaling affects all IP3R subtypes and particularly IP3R2 in the same way and thus could modulate BIRD-2-induced cell death.
Thus, cancer cells can exploit both of the anti-apoptotic actions of Bcl-2 to promote their survival, dependent on the challenging conditions operative in these cells, either by Bim upregulation or by IP3R2 upregulation. The type of addiction to Bcl-2 will dictate their apoptotic sensitivity to BH3 mimetics or BH4-domain-targeting compounds. Importantly, the chemotherapeutic response of cancer cells appears to correlate with the mitochondrial “primed to death” status of Bcl-2 and thus their sensitivity to BH3 mimetics [14, 47–49]. This indicates that patients displaying a poor response to chemotherapy will also display a weak response to BH3 mimetics, as they impinge on the same mitochondrial pathway. However, our data suggest that these “resistant” cancers might be targeted using BH4-domain-targeting tools like BIRD-2. This indicates that patients with a poor clinical response to chemotherapy due to poor mitochondrial priming may benefit from BH4-domain-antagonizing compounds, like BIRD-2. Further work is needed on the identification of BH4-domain-antagonizing molecules that are applicable in vivo. However, this area is also in vivid expansion, recently resulting in the development of BDA-366, a small molecule targeting the BH4 domain of Bcl-2 with very high affinity and selectivity compared to Bcl-XL [50]. The mechanism of action of BDA-366 appeared to involve a conformational switch of Bcl-2 from an anti-apoptotic to pro-apoptotic protein, thereby exposing its BH3 domain and acting as a Bax-activating protein. BDA-366 also disrupted IP3R/Bcl-2 complexes [51]. Yet, further work is required to validate whether BIRD-2 and BDA-366 share a common mechanism of action. As such, BDA-366 might be a first promising tool to elicit cell death in cancers that are more resistant to BH3 mimetics [50–52].
Overall, our data indicate that BH4-domain-antagonizing tools like BIRD-2 hold potential to kill Bcl-2-dependent cancer cells, in particular those that are more resistant to chemotherapy and precision medicines like venetoclax. By acting on a different functional domain of Bcl-2 than BH3 mimetics, these tools could provide additional opportunities to kill these cancers, and to be used as follow-up strategies to kill venetoclax-resistant or -relapsed cancers, or to participate in combination therapies with venetoclax via their ability to boost endogenous Bim levels.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Cells
SU-DHL-4, KARPAS-422, PFEIFFER, TOLEDO, SU-DHL-6, OCI-LY-1 and OCI-LY-18 DLBCL cell lines were kindly obtained from Dr. Anthony Letai (Dana-Farber Cancer Institute, Boston, Massachusetts, USA), who performed a complete “BH3 profiling” analysis of these cell lines [30]. The Ri-1 DLBCL cell line was ordered via DSMZ (Braunschweig, Germany). All these cell lines were authenticated by the University of Arizona Genetics Core (Tucson, AZ, USA) using autosomal short tandem repeat (STR) profiling via Science Exchange (www.scienceexchange.com). The results were validated using reference databases such as DSMZ (Germany) and sample profiles (allelic values) and electropherogram trace data were provided. All cell lines except one displayed a perfectly matched profile with 8 tested alleles (8/8), while for SU-DHL-6 cells 7/8 alleles matched. The apoptotic response of these cells to different venetoclax concentrations was validated and benchmarked against the published venetoclax IC50 values by Souers et al [11]. The SU-DHL-4, KARPAS-422, PFEIFFER, TOLEDO, Ri-1 and SU-DHL-6 DLBCL cell lines were cultured in suspension in RPMI-1640 media. The OCI-LY-1 and OCI-LY-18 DLBCL cell lines were cultured in suspension in Iscove modified Dulbecco medium (Invitrogen, Merelbeke, Belgium). All media were supplemented with 10% heat-inactivated fetal bovine serum, L-glutamine (100 × GlutaMAX, Gibco/Invitrogen, Merelbeke, Belgium) and penicillin and streptomycin (100 × Pen/Strep, Gibco/Invitrogen, Merelbeke, Belgium) and cultured at 37°C and 5% CO2.
Antibodies and reagents
Immunoblotting was performed with anti-GAPDH (Sigma-Aldrich, Munich, Germany), anti-vinculin (Sigma-Aldrich, Munich, Germany), anti-IP3R2 (Rbt02 [53]) and anti-Bim (Bioké, Leiden, The Netherlands).
BIRD-2 (RKKRRQRRRGGNVYTEIKCNSLLPLAAIVRV) (purity>85%) was purchased from LifeTein (South Plainfield, New Jersey, USA) and venetoclax from Active Biochem (Bonn, Germany).
Western blotting
DLBCL cells were washed with phosphate-buffered saline and incubated at 4°C with lysis buffer (20 mM Tris-HCl (pH 7.5), 150 mM NaCl, 1.5 mM MgCl2, 0.5 mM dithiothreitol, 1% Triton X-100, 1 tablet complete EDTA-free protease inhibitor per 50 ml (Thermo Scientific, Brussels, Belgium) for 30 min on a head-over-head rotor. Cell lysates were centrifuged for 5 minutes at 10 000 rpm. Twenty μg of protein sample was loaded on a NuPAGE 3-8% Tris-Acetate protein gel for the detection of the IP3R2 protein and for the detection of the Bim protein a NuPAGE 4-12% Bis-Tris protein gel (Life Technologies, Brussels, Belgium) was used for western blotting as previously described [22].
Apoptosis assay
After treatment (see figure legends for more information about the treatment, time and concentration) DLBCL cells (5 × 105 cells/ml) were pelleted by centrifugation, and incubated with Annexin V-FITC (Life Technologies, Brussels, Belgium) and 7-aminoactinomycin D (7-AAD) (Life Technologies, Brussels, Belgium) or with 2.5 μM NucviewTM 488 caspase-3 substrate (Biotium, CA, USA) for 15 or 30 minutes respectively. Cell suspensions were analyzed with an Attune® Acoustic Focusing Flow Cytometer (Applied Biosystems, Brussels, Belgium). Cell death was scored by quantifying the population of Annexin V-FITC-positive and 7-AAD positive cells or by quantifying the caspase-3 positive cells.
Cytosolic Ca2+ measurements in intact cell populations
SU-DHL-4 cells were loaded for 30 min with 1.25 μM Fura-2 AM at room temperature in modified Krebs solution (150 mM NaCl, 5.9 mM KCl, 1.2 mM MgCl2, 11.6 mM HEPES pH 7.3, 11.5 mM glucose and 1.5 mM CaCl2). Afterwards, 400 000 cells were seeded in poly-L-lysine coated 96-well plates (Greiner, Vilvoorde, Belgium) and incubated for at least 30 minutes in the absence of Fura-2 AM. Fluorescence was monitored on a FlexStation3 microplate reader (Molecular Devices, CA, USA) by alternately exciting the Ca2+ indicator at 340 and 380 nm and collecting emission fluorescence at 510 nm. After 60 seconds agonist-induced Ca2+ release was induced by adding 12 μg/ml anti-IgG/IgM (Sanbio, Uden, The Netherlands). All traces are shown as the ratio of emitted fluorescence of Fura-2 (F340/F380).
Statistical analysis
Results from the western blot analysis are expressed as average ± SD whereby N refers to the number of independent experiments. Significance was determined using a repeated measures one-way ANOVA with a Bonferroni’s post hoc test for the IP3R and Bim expression levels. Statistical significance of the Bim expression levels after BIRD-2 treatment in the absence or presence of BAPTA-AM was performed with a Wilcoxon signed rank test. Differences were considered significant at p<0.05. Correlation of the different IC50 values with each other and with the protein expression levels were statistically analysed via linear regression.
As indicative of synergy between BIRD-2 and venetoclax treatment the Combination Index (CI) was calculated by making the ratio of the theoretical sum of the individual effects (Evenetoclax+ EBIRD-2) with the effect of combining the treatments (Evenetoclax+BIRD-2). Statistical significance was determined with a two-way ANOVA with a Bonferroni post-hoc test comparing Evenetoclax or EBIRD-2 with Evenetoclax+BIRD-2 for the different venetoclax concentrations.
SUPPLEMENTARY MATERIALS FIGURES
ACKNOWLEDGMENTS AND FUNDING
We thank Marina Crabbé, Anja Florizoone, Kirsten Welkenhuyzen and Tomas Luyten for their excellent technical assistance. We are grateful to Dr. A. Letai for providing us with the B-cell lymphoma cells. We thank Annouschka Laenen for her advice and support during the statistical analysis. We are grateful to Dr. Martin D. Bootman for helpful discussions. This work was supported by a research grant from the Emmanuel van der Schueren Fund of the “Kom op tegen Kanker” Action and by grants from the Research Foundation - Flanders (FWO) (grants G.0634.13N, G.0C91.14N and G.0A34.16N), the Research Council - KU Leuven (OT14/101) and the Interuniversity Attraction Pole Program (IAP) (P7/13).
Footnotes
CONFLICTS OF INTEREST
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
REFERENCES
- 1.Hiraga J, Tomita A, Sugimoto T, Shimada K, Ito M, Nakamura S, Kiyoi H, Kinoshita T, Naoe T. Down-regulation of CD20 expression in B-cell lymphoma cells after treatment with rituximab-containing combination chemotherapies: its prevalence and clinical significance. Blood. 2009;113:4885–93. doi: 10.1182/blood-2008-08-175208. https://doi.org/10.1182/blood-2008-08-175208. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Davis TA, Czerwinski DK, Levy R. Therapy of B-cell lymphoma with anti-CD20 antibodies can result in the loss of CD20 antigen expression. Clin Cancer Res. 1999;5:611–5. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Letai AG. Diagnosing and exploiting cancer’s addiction to blocks in apoptosis. Nat Rev Cancer. 2008;8:121–32. doi: 10.1038/nrc2297. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrc2297. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Youle RJ, Strasser A. The BCL-2 protein family: opposing activities that mediate cell death. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2008;9:47–59. doi: 10.1038/nrm2308. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrm2308. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Chipuk JE, Moldoveanu T, Llambi F, Parsons MJ, Green DR. The BCL-2 family reunion. Mol Cell. 2010;37:299–310. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2010.01.025. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molcel.2010.01.025. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Barclay LA, Wales TE, Garner TP, Wachter F, Lee S, Guerra RM, Stewart ML, Braun CR, Bird GH, Gavathiotis E, Engen JR, Walensky LD. Inhibition of Pro-apoptotic BAX by a noncanonical interaction mechanism. Mol Cell. 2015;57:873–86. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2015.01.014. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molcel.2015.01.014. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Davids MS, Letai A. Targeting the B-cell lymphoma/leukemia 2 family in cancer. J Clin Oncol. 2012;30:3127–35. doi: 10.1200/JCO.2011.37.0981. https://doi.org/10.1200/JCO.2011.37.0981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Oltersdorf T, Elmore SW, Shoemaker AR, Armstrong RC, Augeri DJ, Belli BA, Bruncko M, Deckwerth TL, Dinges J, Hajduk PJ, Joseph MK, Kitada S, Korsmeyer SJ, et al. An inhibitor of Bcl-2 family proteins induces regression of solid tumours. Nature. 2005;435:677–81. doi: 10.1038/nature03579. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature03579. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Tse C, Shoemaker AR, Adickes J, Anderson MG, Chen J, Jin S, Johnson EF, Marsh KC, Mitten MJ, Nimmer P, Roberts L, Tahir SK, Xiao Y, et al. ABT-263: a potent and orally bioavailable Bcl-2 family inhibitor. Cancer Res. 2008;68:3421–8. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-07-5836. https://doi.org/10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-07-5836. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Green DR. A BH3 mimetic for killing cancer cells. Cell. 2016;165:1560. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2016.05.080. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cell.2016.05.080. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Souers AJ, Leverson JD, Boghaert ER, Ackler SL, Catron ND, Chen J, Dayton BD, Ding H, Enschede SH, Fairbrother WJ, Huang DC, Hymowitz SG, Jin S, et al. ABT-199, a potent and selective BCL-2 inhibitor, achieves antitumor activity while sparing platelets. Nat Med. 2013;19:202–8. doi: 10.1038/nm.3048. https://doi.org/10.1038/nm.3048. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Vandenberg CJ, Cory S. ABT-199, a new Bcl-2-specific BH3 mimetic, has in vivo efficacy against aggressive Myc-driven mouse lymphomas without provoking thrombocytopenia. Blood. 2013;121:2285–8. doi: 10.1182/blood-2013-01-475855. https://doi.org/10.1182/blood-2013-01-475855. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Vogler M, Dinsdale D, Dyer MJ, Cohen GM. ABT-199 selectively inhibits BCL2 but not BCL2L1 and efficiently induces apoptosis of chronic lymphocytic leukaemic cells but not platelets. Br J Haematol. 2013;163:139–42. doi: 10.1111/bjh.12457. https://doi.org/10.1111/bjh.12457. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Ni Chonghaile T, Sarosiek KA, Vo TT, Ryan JA, Tammareddi A, Moore Vdel G, Deng J, Anderson KC, Richardson P, Tai YT, Mitsiades CS, Matulonis UA, Drapkin R, et al. Pretreatment mitochondrial priming correlates with clinical response to cytotoxic chemotherapy. Science. 2011;334:1129–33. doi: 10.1126/science.1206727. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1206727. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Vervliet T, Parys JB, Bultynck G. Bcl-2 proteins and calcium signaling: complexity beneath the surface. Oncogene. 2016;35:5079–92. doi: 10.1038/onc.2016.31. https://doi.org/10.1038/onc.2016.31. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Bittremieux M, Parys JB, Pinton P, Bultynck G. ER functions of oncogenes and tumor suppressors: modulators of intracellular Ca2+ signaling. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2016;1863:1364–78. doi: 10.1016/j.bbamcr.2016.01.002. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbamcr.2016.01.002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Ivanova H, Kerkhofs M, La Rovere R, Bultynck G. ER-mitochondrial Ca2+ fluxes underlying cancer cell survival. Front Oncol. 2017;7:70. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2017.00070. https://doi.org/10.3389/fonc.2017.00070. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Rong Y, Distelhorst CW. Bcl-2 protein family members: versatile regulators of calcium signaling in cell survival and apoptosis. Annu Rev Physiol. 2008;70:73–91. doi: 10.1146/annurev.physiol.70.021507.105852. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev.physiol.70.021507.105852. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Akl H, Bultynck G. Altered Ca2+ signaling in cancer cells: proto-oncogenes and tumor suppressors targeting IP3 receptors. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2013;1835:180–93. doi: 10.1016/j.bbcan.2012.12.001. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbcan.2012.12.001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Vervliet T, Clerix E, Seitaj B, Ivanova H, Monaco G, Bultynck G. Modulation of Ca2+ signaling by anti-apoptotic Bcl-2 proteins at the ER-mitochondrial interface. Front Oncol. 2017;7:75. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2017.00075. https://doi.org/10.3389/fonc.2017.00075. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Rong YP, Bultynck G, Aromolaran AS, Zhong F, Parys JB, De Smedt H, Mignery GA, Roderick HL, Bootman MD, Distelhorst CW. The BH4 domain of Bcl-2 inhibits ER calcium release and apoptosis by binding the regulatory and coupling domain of the IP3 receptor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2009;106:14397–402. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0907555106. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.0907555106. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Monaco G, Decrock E, Akl H, Ponsaerts R, Vervliet T, Luyten T, De Maeyer M, Missiaen L, Distelhorst CW, De Smedt H, Parys JB, Leybaert L, Bultynck G. Selective regulation of IP3-receptor-mediated Ca2+ signaling and apoptosis by the BH4 domain of Bcl-2 versus Bcl-Xl. Cell Death Differ. 2012;19:295–309. doi: 10.1038/cdd.2011.97. https://doi.org/10.1038/cdd.2011.97. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Rong YP, Aromolaran AS, Bultynck G, Zhong F, Li X, McColl K, Matsuyama S, Herlitze S, Roderick HL, Bootman MD, Mignery GA, Parys JB, De Smedt H, et al. Targeting Bcl-2-IP3 receptor interaction to reverse Bcl-2’s inhibition of apoptotic calcium signals. Mol Cell. 2008;31:255–65. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2008.06.014. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molcel.2008.06.014. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Ivanova H, Ritaine A, Wagner L, Luyten T, Shapovalov G, Welkenhuyzen K, Seitaj B, Monaco G, De Smedt H, Prevarskaya N, Yule DI, Parys JB, Bultynck G. The trans-membrane domain of Bcl-2alpha, but not its hydrophobic cleft, is a critical determinant for efficient IP3 receptor inhibition. Oncotarget. 2016;7:55704–20. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.11005. https://doi.org/10.18632/oncotarget.11005. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Vervloessem T, Ivanova H, Luyten T, Parys JB, Bultynck G. The selective Bcl-2 inhibitor venetoclax, a BH3 mimetic, does not dysregulate intracellular Ca2+ signaling. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2017;1864:968–76. doi: 10.1016/j.bbamcr.2016.11.024. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbamcr.2016.11.024. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Zhong F, Harr MW, Bultynck G, Monaco G, Parys JB, De Smedt H, Rong YP, Molitoris JK, Lam M, Ryder C, Matsuyama S, Distelhorst CW. Induction of Ca2+-driven apoptosis in chronic lymphocytic leukemia cells by peptide-mediated disruption of Bcl-2-IP3 receptor interaction. Blood. 2011;117:2924–34. doi: 10.1182/blood-2010-09-307405. https://doi.org/10.1182/blood-2010-09-307405. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Akl H, Monaco G, La Rovere R, Welkenhuyzen K, Kiviluoto S, Vervliet T, Molgo J, Distelhorst CW, Missiaen L, Mikoshiba K, Parys JB, De Smedt H, Bultynck G. IP3R2 levels dictate the apoptotic sensitivity of diffuse large B-cell lymphoma cells to an IP3R-derived peptide targeting the BH4 domain of Bcl-2. Cell Death Dis. 2013;4:e632. doi: 10.1038/cddis.2013.140. https://doi.org/10.1038/cddis.2013.140. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Lavik AR, Zhong F, Chang MJ, Greenberg E, Choudhary Y, Smith MR, McColl KS, Pink J, Reu FJ, Matsuyama S, Distelhorst CW. A synthetic peptide targeting the BH4 domain of Bcl-2 induces apoptosis in multiple myeloma and follicular lymphoma cells alone or in combination with agents targeting the BH3-binding pocket of Bcl-2. Oncotarget. 2015;6:27388–402. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.4489. https://doi.org/10.18632/oncotarget.4489. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Vervloessem T, Yule DI, Bultynck G, Parys JB. The type 2 inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate receptor, emerging functions for an intriguing Ca2+-release channel. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2014;1853:1992–2005. doi: 10.1016/j.bbamcr.2014.12.006. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbamcr.2014.12.006. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Deng J, Carlson N, Takeyama K, Dal Cin P, Shipp M, Letai A. BH3 profiling identifies three distinct classes of apoptotic blocks to predict response to ABT-737 and conventional chemotherapeutic agents. Cancer Cell. 2007;12:171–85. doi: 10.1016/j.ccr.2007.07.001. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ccr.2007.07.001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Akl H, Vervloessem T, Kiviluoto S, Bittremieux M, Parys JB, De Smedt H, Bultynck G. A dual role for the anti-apoptotic Bcl-2 protein in cancer: mitochondria versus endoplasmic reticulum. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2014;1843:2240–52. doi: 10.1016/j.bbamcr.2014.04.017. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbamcr.2014.04.017. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Yecies D, Carlson NE, Deng J, Letai A. Acquired resistance to ABT-737 in lymphoma cells that up-regulate MCL-1 and BFL-1. Blood. 2010;115:3304–13. doi: 10.1182/blood-2009-07-233304. https://doi.org/10.1182/blood-2009-07-233304. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Phillips DC, Xiao Y, Lam LT, Litvinovich E, Roberts-Rapp L, Souers AJ, Leverson JD. Loss in MCL-1 function sensitizes non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma cell lines to the Bcl-2-selective inhibitor venetoclax (ABT-199) Blood Cancer J. 2015;5:e368. doi: 10.1038/bcj.2015.88. https://doi.org/10.1038/bcj.2015.88. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Greenberg EF, McColl KS, Zhong F, Wildey G, Dowlati A, Distelhorst CW. Synergistic killing of human small cell lung cancer cells by the Bcl-2-inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate receptor disruptor BIRD-2 and the BH3-mimetic ABT-263. Cell Death Dis. 2015;6:e2034. doi: 10.1038/cddis.2015.355. https://doi.org/10.1038/cddis.2015.355. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Chen R, Valencia I, Zhong F, McColl KS, Roderick HL, Bootman MD, Berridge MJ, Conway SJ, Holmes AB, Mignery GA, Velez P, Distelhorst CW. Bcl-2 functionally interacts with inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate receptors to regulate calcium release from the ER in response to inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate. J Cell Biol. 2004;166:193–203. doi: 10.1083/jcb.200309146. https://doi.org/10.1083/jcb.200309146. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Monaco G, Vervliet T, Akl H, Bultynck G. The selective BH4-domain biology of Bcl-2-family members: IP3Rs and beyond. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2013;70:1171–83. doi: 10.1007/s00018-012-1118-y. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00018-012-1118-y. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Bultynck G, Rossi D, Callewaert G, Missiaen L, Sorrentino V, Parys JB, De Smedt H. The conserved sites for the FK506-binding proteins in ryanodine receptors and inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate receptors are structurally and functionally different. J Biol Chem. 2001;276:47715–24. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M106573200. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M106573200. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Ivanova H, Luyten T, Decrock E, Vervliet T, Leybaert L, Parys JB, Bultynck G. The BH4 domain of Bcl-2 orthologues from different classes of vertebrates can act as an evolutionary conserved inhibitor of IP3 receptor channels. Cell Calcium. 2017;62:41–6. doi: 10.1016/j.ceca.2017.01.010. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ceca.2017.01.010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Cardenas C, Muller M, McNeal A, Lovy A, Jana F, Bustos G, Urra F, Smith N, Molgo J, Diehl JA, Ridky TW, Foskett JK. Selective vulnerability of cancer cells by inhibition of Ca2+ transfer from endoplasmic reticulum to mitochondria. Cell Rep. 2016;14:2313–24. doi: 10.1016/j.celrep.2016.02.030. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.celrep.2016.02.030. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Bultynck G. Onco-IP3Rs feed cancerous cravings for mitochondrial Ca2+ Trends Biochem Sci. 2016;41:390–3. doi: 10.1016/j.tibs.2016.03.006. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tibs.2016.03.006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Wiel C, Lallet-Daher H, Gitenay D, Gras B, Le Calve B, Augert A, Ferrand M, Prevarskaya N, Simonnet H, Vindrieux D, Bernard D. Endoplasmic reticulum calcium release through ITPR2 channels leads to mitochondrial calcium accumulation and senescence. Nat Commun. 2014;5:3792. doi: 10.1038/ncomms4792. https://doi.org/10.1038/ncomms4792. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Sankar N, deTombe PP, Mignery GA. Calcineurin-NFATc regulates type 2 inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate receptor (InsP3R2) expression during cardiac remodeling. J Biol Chem. 2014;289:6188–98. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M113.495242. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M113.495242. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Bonnefond ML, Lambert B, Giffard F, Abeilard E, Brotin E, Louis MH, Gueye MS, Gauduchon P, Poulain L, N’Diaye M. Calcium signals inhibition sensitizes ovarian carcinoma cells to anti-Bcl-xL strategies through Mcl-1 down-regulation. Apoptosis. 2015;20:535–50. doi: 10.1007/s10495-015-1095-3. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10495-015-1095-3. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44.Bononi A, Bonora M, Marchi S, Missiroli S, Poletti F, Giorgi C, Pandolfi PP, Pinton P. Identification of PTEN at the ER and MAMs and its regulation of Ca2+ signaling and apoptosis in a protein phosphatase-dependent manner. Cell Death Differ. 2013;20:1631–43. doi: 10.1038/cdd.2013.77. https://doi.org/10.1038/cdd.2013.77. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45.Marchi S, Marinello M, Bononi A, Bonora M, Giorgi C, Rimessi A, Pinton P. Selective modulation of subtype III IP3R by Akt regulates ER Ca2+ release and apoptosis. Cell Death Dis. 2012;3:e304. doi: 10.1038/cddis.2012.45. https://doi.org/10.1038/cddis.2012.45. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46.Pfeifer M, Grau M, Lenze D, Wenzel SS, Wolf A, Wollert-Wulf B, Dietze K, Nogai H, Storek B, Madle H, Dorken B, Janz M, Dirnhofer S, et al. PTEN loss defines a PI3K/AKT pathway-dependent germinal center subtype of diffuse large B-cell lymphoma. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2013;110:12420–5. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1305656110. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1305656110. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47.Colak S, Zimberlin CD, Fessler E, Hogdal L, Prasetyanti PR, Grandela CM, Letai A, Medema JP. Decreased mitochondrial priming determines chemoresistance of colon cancer stem cells. Cell Death Differ. 2014;21:1170–7. doi: 10.1038/cdd.2014.37. https://doi.org/10.1038/cdd.2014.37. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 48.Vo TT, Ryan J, Carrasco R, Neuberg D, Rossi DJ, Stone RM, Deangelo DJ, Frattini MG, Letai A. Relative mitochondrial priming of myeloblasts and normal HSCs determines chemotherapeutic success in AML. Cell. 2012;151:344–55. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2012.08.038. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cell.2012.08.038. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 49.Montero J, Sarosiek KA, DeAngelo JD, Maertens O, Ryan J, Ercan D, Piao H, Horowitz NS, Berkowitz RS, Matulonis U, Janne PA, Amrein PC, Cichowski K, et al. Drug-induced death signaling strategy rapidly predicts cancer response to chemotherapy. Cell. 2015;160:977–89. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2015.01.042. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cell.2015.01.042. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 50.Han B, Park D, Li R, Xie M, Owonikoko TK, Zhang G, Sica GL, Ding C, Zhou J, Magis AT, Chen ZG, Shin DM, Ramalingam SS, et al. Small-molecule Bcl-2 BH4 antagonist for lung cancer therapy. Cancer Cell. 2015;27:852–63. doi: 10.1016/j.ccell.2015.04.010. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ccell.2015.04.010. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 51.Vervloessem T, La Rovere R, Bultynck G. Antagonizing Bcl-2’s BH4 domain in cancer. Aging (Albany NY) 2015;7:748–9. doi: 10.18632/aging.100828. https://doi.org/10.18632/aging.100828. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 52.Liu Z, Wild C, Ding Y, Ye N, Chen H, Wold EA, Zhou J. BH4 domain of Bcl-2 as a novel target for cancer therapy. Drug Discov Today. 2015 doi: 10.1016/j.drudis.2015.11.008. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.drudis.2015.11.008. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 53.Parys JB, de Smedt H, Missiaen L, Bootman MD, Sienaert I, Casteels R. Rat basophilic leukemia cells as model system for inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate receptor IV, a receptor of the type II family: functional comparison and immunological detection. Cell Calcium. 1995;17:239–49. doi: 10.1016/0143-4160(95)90070-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.