Abstract
The repair of DNA double-stranded breaks (DNAdsb) through non-homologous end joining (NHEJ) is a prerequisite for the proper development of the central nervous system and the adaptive immune system. Yet, mice with Xlf or PAXX loss of function are viable and present with very mild immune phenotypes, although their lymphoid cells are sensitive to ionizing radiation attesting for the role of these factors in NHEJ. In contrast, we show here that mice defective for both Xlf and PAXX are embryonically lethal owing to a massive apoptosis of post-mitotic neurons, a situation reminiscent to XRCC4 or DNA Ligase IV KO conditions. The development of the adaptive immune system in Xlf−/−PAXX−/− E18.5 embryos is severely affected with the block of B- and T-cell maturation at the stage of IgH and TCRβ gene rearrangements, respectively. This damaging phenotype highlights the functional nexus between Xlf and PAXX, which is critical for the completion of NHEJ-dependent mechanisms during mouse development.
All living organisms are subjected to multitude sources of DNA damage during their lifespan, either as a result of external assault or endogenous physiological processes.1 Among endogenous sources of physiological DNAdsb is the somatic rearrangement of immunoglobulin (Ig) and TCR genes in B and T lymphocytes, respectively, during the diversification of the adaptive immune system through V(D)J recombination.2 DNA double-stranded breaks (DNAdsb) are considered the most toxic lesions. DNAdsbs are repaired by two main mechanisms: the homologous recombination (HR) in cycling cells, when a sister chromatid is available as DNA repair template, and the non-homologous end joining (NHEJ) during all phases of the cell cycle.
NHEJ proceeds via the simple religation of DNA ends without the need for a repair template.3 Briefly, the NHEJ is composed of seven core factors comprising the Ku70/80/DNA-PKcs (DNA-dependent protein kinase catalytic subunit) complex, which recognizes and protects the broken DNA ends, the Artemis endo/exonuclease, which participates, when needed, in processing the DNA ends and the XRCC4/DNA-Ligase IV/Xlf complex, which ultimately reseals the DNA break. The critical function of the NHEJ apparatus in various aspects of higher eukaryote development has been extensively perceived in several animal and human pathological conditions. As emblematic examples, loss of function of either XRCC4 or DNA ligase IV results in embryonic lethality in mice4, 5 and mutations in Artemis or DNA-PKcs result in severe combined immunodeficiency conditions in both men and mice, owing to aborted V(D)J recombination.6 In addition, defects in NHEJ results in genetic instability and the propensity to develop various types of cancers, notably leukemia and lymphomas.7
Recently, a new DNA repair factor, PAXX (PAralog of XRCC4 and Xlf, also known as C9orf142 or XLS), has been identified independently by three laboratories based on bioinformatics and biochemistry approaches.8, 9, 10 PAXX belongs to the XRCC4 superfamily and shows structural similarities with both XRCC4 and Xlf. PAXX is recruited to DNAdsb and is a physical interactor of the Ku/DNAPK complex, notably through its interaction with Ku70.11 Surprisingly, for a NHEJ factor, the deficiency of PAXX does not systematically result in an increased sensitivity to ionizing radiation (IR) and the results of the various DNA repair assays are highly controversial, depending on the experimental settings.8, 9, 10, 12, 13, 14, 15 This suggested a possible functional complementation of PAXX deficiency in certain conditions.
To analyze the role of PAXX during mouse development in vivo and identify a possible redundant function with another DNA repair factor, we created CRISPR/Cas9 PAXX mutant mouse lines. Although the sole inactivation of PAXX did not result in an overwhelming phenotype, the concomitant deletion of PAXX and Xlf had severe consequences resulting in embryonic lethality and arrest of V(D)J recombination in embryos. Altogether, these results are consistent with PAXX being a bona fide NHEJ factor and highlight the critical functional interplay between PAXX and Xlf during mouse development.
Results and discussion
Generation of PAXX KO mice
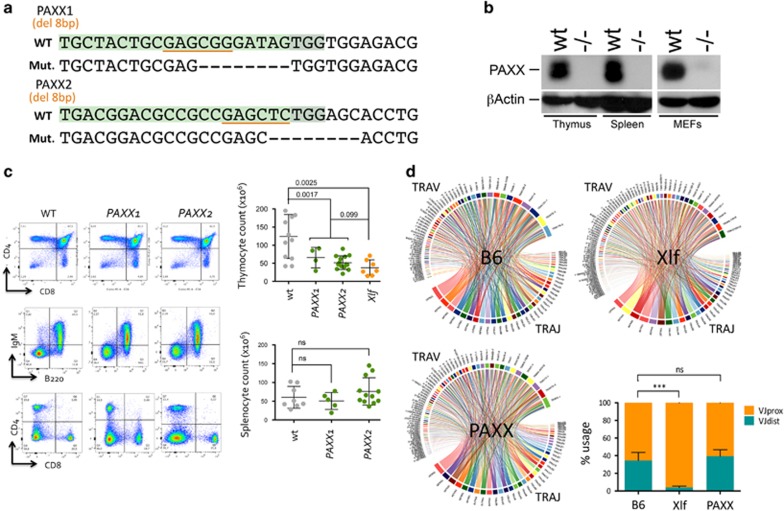
PAXX KO mice were generated using CRISPR/Cas9. Two guide RNA target sequences were selected in exon 1 (PAXX1) and exon 2 (PAXX2) of the murine PAXX gene (Figure 1a and Supplementary Figure S1A). The efficacy of the two gRNA was scored through the disappearance of restriction sites BsrBI and SacI upon transfection of MEFs with the pX330 vector expressing the gRNAs and Cas9 (Supplementary Figure S1B). To generate mutant mouse lines, zygotes were microinjected with pX330 according to the protocol of Mashiko et al.16 Thirteen and five F0 mice were obtained for PAXX1 and PAXX2, respectively. Tail DNA was analyzed by PCR and restriction digest (PCR-RE) to identify four PAXX1 and two PAXX2 F0 mutant mice showing clear retention of undigested DNA above background (Supplementary Figure S1C). F0 mice were crossed onto C57Bl/6 to segregate the various CRISPR/Cas9-generated mutant alleles. Two F0-derived F1 mice, #2 for PAXX1 and #14 were selected upon direct DNA sequencing of the mutant alleles. CRISPR/Cas9 mutagenesis resulted in an 8-bp deletion and subsequent frameshift in both cases (Figure 1a). Each line was backcrossed up to six times on C57Bl/6 to segregate away any off-target event outside of chromosome 2. Homozygous mutant mice were obtained by intercross of either PAXX1+/− or PAXX2+/− heterozygous founders. Homozygous mice were viable and were produced at Mendelian frequencies ruling out a major effect of PAXX deficiency during embryogenesis. The loss of function of the CRISPR/Cas9-generated PAXX mutant allele were ascertained by western blotting using protein extracts from thymus, spleen, and MEFs from PAXX2 mouse line. As shown in Figure 1b, PAXX protein expression was undetectable in PAXX2−/− mice, in contrast to wild-type littermates. We conclude that CRISPR/Cas9 mutagenesis resulted in complete PAXX loss of function.
Figure 1.
Design and immunophenotyping of PAXX KO mice. (a) Design of gRNA used to create CRISPR/Cas9 mutations in the PAXX gene. The BsrBI and SacI restriction enzyme sites used to screen for mutagenesis are underlined. The two lines PAXX1 and PAXX2 harbor an 8-bp deletion resulting in frameshift. (b) Western blot analysis confirming the PAXX loss of function in PAXX2 mutant mice, with the absent protein in the thymus, spleen, and MEFs. (c) Immunophenotyping of wt. (N=11), PAXX1 (N=4), PAXX2 (N=12), and Xlf (N=7) mice. FACS representation of thymocytes and splenocytes and representation of absolute count numbers. (d) Illustrative Circos-plot representations of TCRα repertoire in thymocytes from C57Bl/6, Xlf, and PAXX2 mice. Each chord line represents the association between one TRAV and one TRAJ segment as determined by TCRα transcript sequencing. Quantification of TCRα TRAV gene usage in C57Bl/6, Xlf, and PAXX2 mice. TCRα repertoire determination was repeated two times using an overall six PAXX2 KO, five C57Bl/6, and six Xlf KO mice. Statistical analyses were performed using Mann–Whitney non-parametric t-test using Prism v6 (***P < 0.001)
Normal development of the immune system in PAXX KO mice
Proficiency of the DNA Damage Response (DDR) machinery, in particular the NHEJ pathway, is critical for the appropriate development of B and T lymphocytes, owing to the generation of DNAdsb during the somatic DNA rearrangement of both Ig and TCR genes.6 Nevertheless, Xlf deficiency does not have a severe impact on the V(D)J recombination process and Xlf-deficient mice present with a very mild defect in their immune system, characterized mainly by a slight reduction in lymphocyte numbers and an increased in thymocyte apoptosis.17, 18 Qualitatively, this translates into a skewing in the TCRα repertoire with the under-representation of distal TRAV and TRAJ gene segments.17 Analysis of the immune system in both PAXX1 and PAXX2 KO mice revealed an overall normal development of T cells in the thymus, despite a statistically significant reduction in thymocyte numbers in the range of what observed in Xlf mice (Figure 1c). Mature B- and T-cell numbers in the spleen were comparable between PAXX mice and WT littermates. This is in general agreement with previously described PAXX mutant mice.12, 15 Analysis of the TCRα repertoire through 5’ RACE RT-PCR and next-generation sequencing revealed a well-diversified TCRα repertoire in PAXX mice, comparable to WT and Xlf animals (Figure 1d). However, in contrast to the important decrease in distal VαJα usage in Xlf thymocytes as previously described,17 thymocytes from PAXX mice did not show any skewing in the representation of these TCRα gene segments. From these observations, we conclude that PAXX loss of function does not have any detrimental impact on the V(D)J recombination process and/or the overall viability of thymocytes.
DNAdsb repair defect in PAXX KO mice
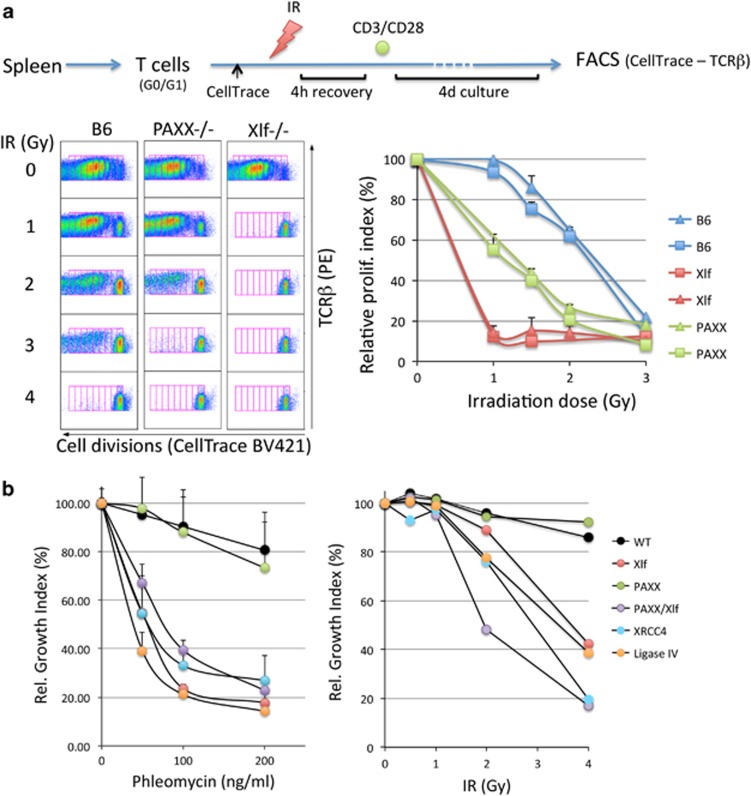
Given its homology with both XRCC4 and Xlf, PAXX is thought to intervene during DNA repair through NHEJ.8, 9, 10 T lymphocytes isolated from blood or spleen are mainly non-cycling resting cells which, as a result, utilize NHEJ to cope with DNAdsb when HR is operational only in cycling cells. We set up to analyze the role of PAXX during NHEJ through the survey of splenic T-cell sensitivity to IRs (Figure 2a). Ex vivo isolated resting splenic mature T cells were subjected to various doses of IR (0–4 Gy). After 4 h of recovery to allow for repair of IR-induced DNAdsb, cells were incubated with anti-CD3/anti-CD28-coated beads during 4 days, which activates and induces a strong proliferative response of T lymphocytes that can be readily quantified through the dilution of the CellTrace dye upon cell divisions. We used this readout as a mean to score the relative index of proliferation, and hence the cell survival, following IR. Using this protocol, T cells from Xlf mice showed an extreme sensitivity to IR as compared with WT (Figure 2a) with a fall in cell survival already at the first dose of 1 Gy, as expected for Xlf deficiency. PAXX-deficient T lymphocytes were also strikingly radiosensitive, although to a lesser extent than Xlf-defective T cells. In contrast, murine embryonic fibroblasts (MEFs) derived from PAXX mutants were resistant to either IR or the DNAdsb inducer Phleomycin with cell survival comparable to that of WT MEFs (Figure 2b), whereas MEFs defective for XRCC4, DNA-Ligase IV, or Xlf were highly sensitive as expected. This is in accord with the previously noted mild sensitivity of PAXX−/− MEFs to IR15 but contrasts with the results from Balmus et al.12 Ever since the identification of PAXX by three different groups, its implication in the DDR as judged by the sensitivity to genotoxic drugs or IR has been highly controversial, depending on the cell line analyzed in vitro, the experimental conditions, and the drugs used to inflict DNA damage.8, 9, 10 Interestingly, asynchronous PAXX-defective CH12 B-cell lines or v-Abl-transformed Pro-B-cell lines do not demonstrate any IR sensitivity above that of their wt counterparts, as we found in MEFs, and the concomitant PAXX and Xlf deficiency does not worsen the sensitivity caused by Xlf mutation alone in these cycling cells.13 In contrast, the synchronization of PAXX−/−/Xlf−/− v-Abl pro-B cells into the G1 phase of the cell cycle with either STI-571 (v-Abl kinase inhibitor) or PD033991 (CDK4/6 inhibitor) results in an extreme sensitivity to IR, well beyond that of Xlf−/− single mutants in the same conditions arguing for a unique role of PAXX in classical NHEJ when DNA damage occurs in G1, hence in the absence of functional HR. Our observation of an IR sensitivity of small resting, ex vivo purified T lymphocytes from PAXX−/− mice concords with this conclusion of a specific role of PAXX during C-NHEJ.
Figure 2.
DNA repair defect in PAXX KO mice. (a) Radiosensitivity assay performed on mature splenic T lymphocytes. For FACS analysis, doubling populations were scored in gates defined by the dilution of the CellTrace signal and the proliferative index calculated according to Roederer.26 The relative proliferative indexes were plotted for each sample according to the proliferation in the absence of IR and used to define the radiosensitivity level. The experiment was repeated twice with two mice per genotype each time. (b) Phleomycin and IR sensitivity on SV40-transformed MEFs. MEFs from XRCC4, DNA-Ligase IV, and Xlf KO mice were used as radiosensitive controls. The relative growth indexes were calculated by comparing the confluence of treated cells and non-treated cells during culture with real-time Incucyte monitoring (see Materials and Methods). This experiment was repeated three times
PAXX-Xlf interplay during neuronal development
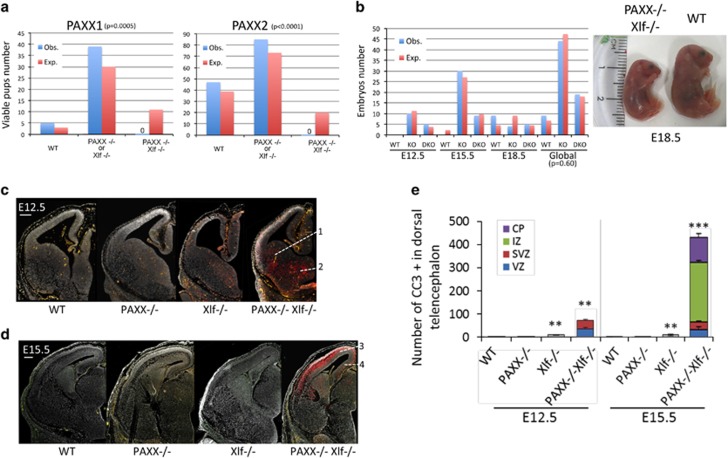
We next set up to evaluate the possible functional relationship between PAXX and Xlf during the DNA damage response (DDR) by generating doubly deficient mice through intercrossing either PAXX−/−Xlf+/− or PAXX+/−Xlf−/− animals. In no instance did we obtain PAXX−/−/Xlf−/− mice on a total of 176 newborns (44 PAXX1 and 132 PAXX2) obtained from crosses of various genotype combinations for which about 31 (11 PAXX1 and 20 PAXX2) were expected to harbor the PAXX−/−/Xlf−/− DKO genotype, arguing for an embryonic lethality of the concomitant inactivation of both factors (Figure 3a) as previously noted in two different studies.12, 15 The embryonic lethality was observed with both PAXX1 and PAXX2 mutant lines, excluding an off-target effect as responsible for this phenotype. Lived DKO embryos could be readily obtained in E18.5 mice downward (Figure 3b) arguing for a late embryonic lethality of DKO animals, similar to the previously described late embryonic lethality of XRCC4 and DNA Ligase IV KO mice.4, 5 Nevertheless, embryos at E18.5 usually appeared smaller than their heterozygous littermates (Figure 3b), confirming their overall abnormal development. The lethality of PAXX/Xlf DKO embryos was to us the first evidence of a functional interplay between PAXX and Xlf, the co-inactivation of which results in a major viability phenotype, when both single mutants do not present evidence for developmental defect (this study and Vera et al.17). In XRCC4 and DNA-Ligase IV KO mice, the embryonic lethality is caused by the massive apoptosis of post-mitotic neurons.4, 5 Likewise, the presence of numerous pyknotic nuclei and the cleaved-caspase 3 (CC3) immunostaining19 revealed a severe neuronal apoptosis in the brain of Xlf−/−PAXX−/− embryos (Figures 3c–e,Supplementary Figure S3) as previously reported.12, 15 This contrasted with the scarce apoptotic cells in the brains of Xlf−/− embryos and their absence in that of PAXX−/− embryos (Figures 3c–e, and Supplementary Figure S3A). The observation of a massive neuronal apoptosis in PAXX−/−Xlf−/− DKO whatever the type of PAXX1 or PAXX2 mutants used in intercrosses again ruled out a CRISPR/Cas9 off-target effect as responsible for this phenotype. Although apoptosis was detected in the regions where neural progenitors proliferate (that is, the ventricular (VZ) and subventricular zones (SVZ), surrounding the lateral hemispheres), it was most prominent in the regions that contain post-mitotic neurons. Indeed, consistent with the kinetics of neuronal production in the different brain structures, apoptosis was predominantly found in the ventral telencephalon at E12.5 (Figure 3a) and in the dorsal telencephalon at E15.5 (Figures 3b and c and Supplementary Figure S3B).
Figure 3.
Embryonic lethality and massive neuronal apoptosis in PAXX−/−Xlf−/− embryos. (a) Impaired development of PAXX−/−Xlf−/− DKO mice. No DKO mice were born from various combinations of PAXX1 or PAXX2 and Xlf crosses (44 and 132 pups, respectively). Statistical significance of the differences between the observed (Obs.) and expected (Exp.) genotype distributions was assessed by χ2-test. (b) Survival of PAXX−/−Xlf−/− embryos up to E18.5. Photograph showing the reduced size of PAXX−/−Xlf−/− E18.5 embryos. (c and d) Coronal sections of cerebral hemispheres of wt., PAXX−/−, Xlf−/−, and PAXX−/−Xlf−/− embryos collected at E12.5 (c) and E15.5 (d) and stained with 4’-6-Diamidino-2-phenylindole (DAPI; gray) and CC3 (red). Blood vessels are colored in orange. Scale bars: 200 μm. (c) At E12.5, apoptosis in PAXX−/−Xlf−/− embryos is massively detected in the intermediate zones (IZs) of the ganglionic eminences (1, 2) containing newly generated neurons for the striatum and the globus pallidus. (d) At E15.5, apoptosis in PAXX−/−Xlf−/− embryos is predominant in the IZ and the cortical plates (CPs) of the dorsal telencephalon containing newly generated post-mitotic neurons of the neocortex (3) and the hippocampus (4). (e) The bar graph shows the mean numbers per cortical slice of cleaved-caspase-3-positive cells±S.D. detected in the ventricular zone (VZ), subventricular zone (SVZ), IZ, and CP of the neocortex of wt., PAXX−/−, Xlf−/−, and PAXX−/−Xlf−/− embryos at E12.5 and E15.5. Data have been obtained from at least three embryos per group. Stars indicate the statistical significance in comparison to the wt controls. **P≤0.01, ***P≤0.001; Mann–Whitney test
PAXX-Xlf interplay during lymphoid development
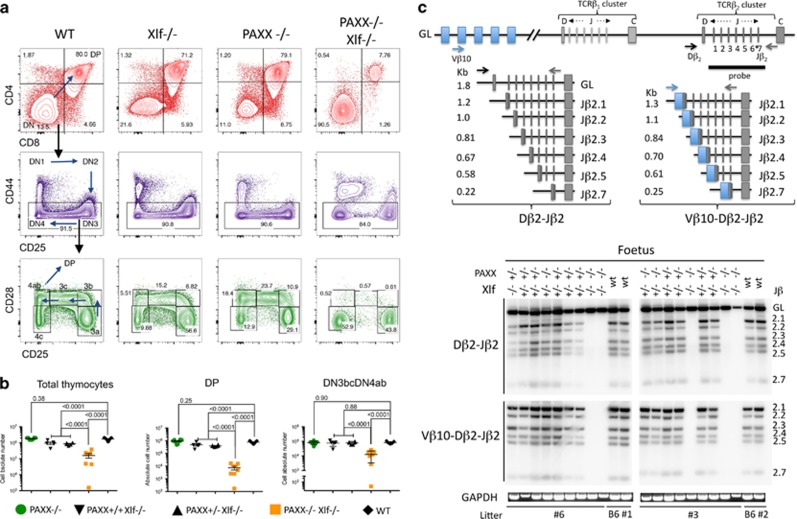
The profound impact of the concomitant deletion of PAXX and Xlf on the development of the central nervous system, resulting in late embryonic lethality, is highly reminiscent of both XRCC4 and DNA Ligase IV-deficient conditions, in which NHEJ is severely affected.4, 5 As a major defect in the development of the immune system is also one typical feature of these NHEJ-deficient murine models, we aimed at analyzing this question qualitatively and quantitatively in Xlf−/−PAXX−/− DKO embryos. TCR gene rearrangements begin around E13 and thymuses are easily recovered at E18.5, the gestation day we choose for this analysis. At E18.5, thymuses from wt mice contained 1.71 × 106 thymocytes on average (Figures 4a and b), a number that was not affected by the deletion of PAXX alone (1.84 × 106) but was significantly reduced around twofold in the context of Xlf KO (0.9 × 106, P<0.0001) as previously found in thymuses from 6- to 8-week-old mutant mice.17, 18 Strikingly, Xlf−/−PAXX−/− embryos exhibited a 10-fold decrease in thymocyte number (1.7 × 105, P<0.0001). This reduction in the total numbers of thymocytes was mainly accounted for by the loss of CD4+CD8+ double-positive (DP) thymocytes in Xlf−/−PAXX−/− mice when compared with wt mice (7.40 × 103 versus 7.75 × 105, P<0.0001), arguing for an abnormal maturation process. CD4−CD8− double-negative (DN) thymocytes, which precede the maturation to DP, can be further divided into various populations according to their differential expression of the CD44, CD25, and CD28 surface markers.20 In particular, the CD44−CD25+CD28+ (DN3b) fraction represents thymocytes that have undergone β-selection upon successful rearrangement of their TCR-β locus. They will subsequently progress to DN3c, DN4a, and DN4b, and ultimately to DP as depicted in Figure 4a. Analyses of these archetypical thymocyte populations in Xlf−/−PAXX−/− DKO E18.5 embryos revealed a major block at the transition DN3a to DN3b (Figures 4a and b), resulting in a significant decrease in the number of thymocytes from DN3b stage onward when compared with wt mice (1.3 × 104 versus 8.3 × 104, P<0.0001). This developmental arrest at the critical step of β-selection strongly suggested a possible impairment of V(D)J recombination at the TCR-β locus in thymocytes from Xlf−/−PAXX−/− embryos. TCR-β rearrangements involving Vβ10 and the Dβ2-Jβ2 cluster were analyzed by PCR in thymocytes from mice with various genotypes as depicted in Figure 4c. Rearrangements of Dβ2 or Vβ10Dβ2 segments to Jβ2 elements resulted in a ladder of PCR products identified by an intronic 3’Jβ2 probe the length of which depends on the Jβ2 element utilized during the recombination process. No detectable PCR product corresponding to either Dβ2Jβ or Vβ10Dβ2Jβ rearrangements could be detected in DNA from Xlf−/−PAXX−/− thymocytes (Figure 4c, lanes 8, 9,16, and 20), although they were readily identified in PAXX and Xlf single KO mice, attesting for the severely impaired V(D)J recombination process in the concomitant absence of PAXX and Xlf.
Figure 4.
V(D)J recombination defect and impaired development of thymocytes in PAXX−/−/Xlf−/− E18.5 embryos. (a) Immunostaining of thymocytes from wt, Xlf−/−, PAXX−/−, and PAXX−/−Xlf−/− E18.5 embryos. Upper panel (red) shows the important decrease in CD4+CD8+ DP in the thymus from PAXX−/−Xlf−/− embryos. DN (CD4−CD8−CD3−) thymocytes were subdivided into DN1–DN4 according to the expression of CD44 and CD25 (middle panel). Lower panel (green) shows the severe block at the transition DN3a (CD44−CD25+CD28−) to DN3b (CD44−CD25+CD28+) in PAXX−/−Xlf−/− embryos. B220+CD19+ FL cells were analyzed for the expression of CD43 that marks pro-B cells (middle panel). In the lower panel, cells were gated on the CD43+B220+CD19+ population and analyzed for iIgM expression. (b) Quantification of thymocyte subpopulations in the various PAXX/Xlf genotypes. Mann–Whitney test was used for statistical analysis. (c) PCR strategy to analyze TCRβ rearrangement according to Gartner et al.29 and autoradiogram of PCR products revealed with the TCR-Jβ probe demonstrating the absence of either Dβ-Jβ or VβDβJβ rearrangements in thymocytes from PAXX−/−Xlf−/− embryos. GAPDH-specific PCR was used as loading control
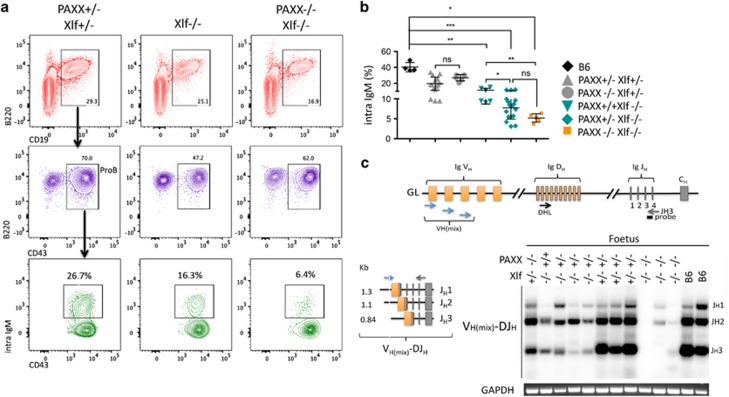
B-cell maturation in fetus takes place in the fetal liver (FL) with rearrangement and expression of the Ig heavy chain locus occurring around E17.5 at which time μH chain becomes detectable intracellularly.21 CD19+B220+ B-lineage cells were present in the FL of WT, Xlf−/− and PAXX−/−Xlf−/− E18.5 embryos, attesting for the normal B-cell lineage commitment in all conditions (Figure 5a). However, whereas ~20% of CD43+B220+ pro-B cells expressed the intracytoplasmic μH chain (iIgM) in FL of littermates PAXX+/−Xlf+/− embryos, this population represented only 5% of the CD43+B220+ population in the PAXX−/−Xlf−/− DKO embryos (Figures 5a and b), attesting for a major defect in either rearrangement or expression of the IgH locus in these embryos. Interestingly, a gradient of severity of this phenotype followed the severity of the genotype involved with a statistically significant contribution of Xlf KO on its own (Figure 5b). This could also be noticed in the fetal thymus with the partial block of Xlf−/− thymocytes at the DN3a stage when compared with wt embryos (Figure 4a). As for TCRβ rearragement in the thymus, we used a PCR approach to analyze the recombination of the IgH locus in B-commited cell within the FL. This analysis clearly demonstrated an almost complete absence of detectable VH–DJH rearrangement in FL from PAXX−/−Xlf−/− embryos (Figure 5c, lanes 9, 10, and 11) in contrast to wt animals. Interestingly, all embryos carrying the Xlf−/− genotype already demonstrated a decrease in V(D)J recombination efficiency, as judged by the decreased signal intensity of the PCR products, in line with the fall in IgM-expressing pro-B cells in these animals.
Figure 5.
V(D)J recombination defect and impaired B-cell development in PAXX−/−/Xlf−/− E18.5 embryos. (a) Immunostaining of FL cells from PAXX−/−Xlf−/−, Xlf−/−, and PAXX−/−Xlf−/− E18.5 embryos. In the lower panel, B-lineage cells were gated on CD43+B220+ population and analyzed for intracytoplasmic IgM (iIgM) staining. (b) Quantification of iIgM-positive cells among various PAXX/Xlf genotypes showing the severe deficit in PAXX−/−Xlf−/− embryos. (c) PCR strategy to analyze IgH rearrangement according to Schlissel et al.30 and autoradiogram of PCR products revealed with the JH3 probe demonstrating the profound defect of IgH rearrangement in FL cells from PAXX−/−Xlf−/− embryos. GAPDH-specific PCR was used as loading control
Our observations of an impaired V(D)J recombination in vivo in both B- and T-cell lineages in PAXX−/−Xlf−/− E18.5 embryos are in agreement with the reports of a similar malfunction in v-Abl-transformed pro-B-cell lines in vitro using chromosome-integrated V(D)J recombination substrates.13, 14, 15, 22 Altogether, these experiments demonstrate that, although Xlf and PAXX are largely dispensable for V(D)J recombination, their concomitant defect sharply impairs the rearrangement of the TCRβ and IgH loci in T- and B-cell lineages, respectively, resulting in the block of their maturation in the thymus and the FL. This is consistent with the single ever born PAXX−/−Xlf−/− mouse that had no thymus and had a microspleen.12 We anticipate that the conditional ablation of these two genes in the hematopoietic system to bypass the embryonic lethality should result in live animals with a severe combined immunodeficiency phenotype characterized by the absence of mature B and T lymphocytes.
We identified here a robust functional interplay in vivo between the two DNA repair factor paralogs Xlf and PAXX, as evidenced by the synthetic lethality of their concomitant defect owing to a massive apoptosis of post-mitotic neurons and the negative impact on V(D)J recombination in immature B and T lymphocytes. In that sense, PAXX−/−Xlf−/− DKO mice share most of the phenotypic characteristics of XRCC4 and DNA-Ligase IV single-mutant mice. The survival of post-mitotic neurons and the development of the adaptive immune system both rely on efficient NHEJ as demonstrated in several animal models and human conditions.6 The impairment of these two functions specifically in PAXX−/−Xlf−/− animals, therefore, confirms the role of PAXX as a bona fide NHEJ factor. Others and we have previously reported that Xlf, like PAXX, is largely dispensable during V(D)J recombination.17, 18 We have recently highlighted the relationship between RAG2 and Xlf as a mean to provide a two-tier mechanism ensuring the proper repair of DNAdsb generated during V(D)J recombination and, hence to avoid genetic instability.14 A similar functional interaction between PAXX and Xlf can be proposed to account for the unaffected V(D)J recombination in PAXX−/− mice as opposed to PAXX−/−Xlf−/− embryos. This would place PAXX on the same side as RAG2 in this safeguard mechanism. Accordingly, RAG2 and PAXX are epistatic, as their combined mutations do not impair V(D)J recombination in v-Abl pro-B cells in vitro.14 Likewise, whereas V(D)J recombination is severely compromised in ATM−/−Xlf−/− mice,23 it is efficient in ATM−/−RAG2cc mutated v-Abl cells,14 positioning ATM on the 'same side' as RAG2 and PAXX, opposite to Xlf. Indeed, ATM−/−PAXX−/− animals do not present defect in the development of their adaptive immune system beyond that of the sole ATM deficiency as expected according to this model.12
Materials and methods
gRNA design, cloning, and validation
Two guide RNA sequences were selected on exons 1 and 2 of the MuPAXX gene using the CRISPOR web tool (http://crispor.tefor.net/crispor.py).24 gRNA-overlapping restriction enzyme (RE) diagnostic sites near the Cas9 cleavage site were selected to facilitate mutagenesis screening and subsequent mouse genotyping (Supplementary Figures S1A and B). Double-stranded DNA oligonucleotides corresponding to the selected guide RNA were cloned into the pX330-U6-Chimeric_BB-CBh-hSpCas9 vector (the generous gift of Feng Zhang, Addgene, Cambridge MA, USA, #42230) according to Zhang lab’s recommendations.25 For mutagenesis scoring and mouse genotyping, genomic DNA surrounding the guide RNA target sequences were PCR-amplified (MuPAXX_F1: 5′-CAACCTTGAGTACCGCCCAT-3′, MuPAXX_R1: 5′-CAACCTTGAGTACCGCCCAT-3′, 500 bp) and the resulting PCR products digested with either BsrBI or SacI RE to analyze PAXX1 and PAXX2 mutagenesis, respectively (Supplementary Figure S1C and D). Undigested PCR products represent mutagenized DNA molecules. To validate CRISPR/Cas9 mutagenesis, the two gRNA expressing pX330 constructs were transfected into MEFs using the NEPA21 electroporator (Nepagene, Ichikawa-City, Chiba, Japan) with the following settings: pulse1 175v/5 ms/50 ms/2 × /10%/+ -pulse2 20v/50 ms/50 ms/5 × /40%/+-. Genomic DNA was recovered 5 days later and was analyzed using PCR-RE (Supplementary Figure S1C).
Generation of mutant mice
PAXX mutant mice were generated using CRISPR/Cas9 according to the protocol developed by Masahito Ikawa’s laboratory.16 Briefly, the pX330-derived plasmid coding for Cas9 and the guide RNA were microinjected into mouse zygotes that were isolated from the ampullae of superovulated mice. For superovulation, 5 IU PMS and, 48 h later, 5 IU HCG was injected intraperitoneally into female B6/CBA F1 mice of ~6 weeks. Subsequently, they were mated with male B6/CBA F1 mice (C57Bl6NCr and CBA mice: Charles River Laboratories, Saint-Germain-Nuelles, France). The day after, embryos were isolated and placed into M2 medium (Sigma, St. Louis, CA, USA) and the plasmid was injected at a concentration of 5 ng/μl into the pronucleus using a microscope (Nikon, Tokyo, Japan) with micromanipulators (Narishige, London, UK), Vacutip holding pipettes (Eppendorf, Hamburg, Germany), and homemade injection pipettes prepared from borosilicate capillary glass (Harvard Apparatus, Holliston, MA, USA) as well as a Femtojet apparatus (Eppendorf). Pseudopregnant mice received ~20 zygotes. The procedure was approved by the local ethical committee and the French Ministry of Education and Research (#01501.03).
PAXX1 and PAXX2 mice were genotyped by PCR-RE (MuPAXX_F1, MuPAXX_R1, 500 bp) followed by BsrBI or SacI RE digestion, respectively (Supplementary Figures S1C and D). Xlf KO mice were genotyped as previously described.17 PAXX1 and PAXX2 mice were backcrossed up to six times on C57Bl/6 to segregate away any putative off-target mutation. PAXX/Xlf double KO mice were generated by intercrossing PAXX−/−/Xlf+/− or PAXX+/−/Xlf−/− mice. All mice were sacrificed humanely.
Phleomycin and IR sensitivity assay
T lymphocytes were isolated from 6- to 10-week-old spleens and enriched for CD3+ cells using magnetic sorting (Dynabeads Untouched mouse T cells, Invitrogen). Purified T cells were stained with CellTrace BV421 fluorescent dye (Thermo-Fisher Scientific, Villebon sur Yvette, France). Overall, 3 × 105 T cells were plated in 48-well plates in triplicate in DMEN-Glutamax, FCS 10%, β-Me 0.1%, sodium pyruvate 1%, penicillin and streptomycin 1%, and NEAA 1%. Culture plates were irradiated (0–4 Gy) and let for 4 h in incubator at 37 °C to allow for DNAdsb repair. T cells were then activated by the addition of CD3/CD28-coated dynabeads (Thermo-Fisher Scientific) and 1000 u/ml IL2. After 4 days of culture, cells were stained with anti-TCRβ−PE (Sony, Weybridge, Surrey, UK) and analyzed by FACS (LSR-Fortessa, Becton Dickinson, Rungis, France) to score the number of T-cell divisions through the dilution of the CellTrace dye (Figure 2a). The index of proliferation (EI) was calculated according to the following formula:
where N represents the number of cells in each (0–i) divided cell population.26 For each sample, the relative proliferative index after IR was calculated relative to the proliferation without IR and dose–response curves were drawn to compare samples.
MEFs were obtained and transformed with SV40 Large T antigen (MEF-SV) as previously described.17 Phleomycin sensitivity assays were performed on MEF-SV using the IncuCyte Live Cell Analysis System (Essen BioScience, Ann Harbor, MI, USA). Briefly, MEF-SV of various genotypes were plated in triplicates at 3500 cells/well in 48-well plates and incubated with increasing doses (0, 50, 100, and 200 ng/ml) of Phleomycin. Real-time images of the wells were recorded (× 4 lens) every 12 h over 7 days to monitor cell proliferation. A mask, which identifies visible objects in each image, was applied to quantify the occupied area (% confluence) of every well at each time points (Supplementary Figure S2A). The final score of cell viability/proliferation was determined by integrating the area under the % confluence curves over time by using rectangular approximation as depicted in Supplementary Figure S2B). Given i, the various time points used for recording (from 1 to n), the growth index (GI), represented by the area under the curve, is calculated by the formula:
For each experimental condition, cell viability is calculated relative to the GI in the absence of drug (set as 100% growth) and plotted according to Phleomycin concentrations.
Immunoblotting, histology, and immunohistochemistry
Expression of PAXX was analyzed by western blotting on thymic protein extracts using rabbit polyclonal anti-C9orf142 antibody (ab126353, Abcam, Paris, France). Embryonic heads were fixed overnight at 4 °C by immersion in 4% paraformaldehyde and embedded in paraffin with a Tissu-tek processor (VIP, Leica, Wetzlar, Germany). Five μm coronal sections were then obtained using a microtome (Leica RM2125RT) and mounted onto glass slides for histologic analyses. After paraffin removal and citrate treatment, the brain sections were permeabilized with 0.5% Triton X-100 in phosphate-buffered saline (PBS) for 15 min and incubated for 2 h with 7.5% fetal bovine serum and 7.5% goat serum in PBS. The sections were incubated with rabbit anti-CC3 (Cell Signaling, Leiden, The Netherlands, 9661, 1 : 200) overnight at 4 °C. After washing, the sections were incubated with goat anti-rabbit Alexa Fluor 488 or 594 conjugated secondary antibody (Thermo-Fisher Scientific, 1 : 400) for 1 h. After washing, nuclear staining was achieved by incubation with 4’-6-Diamidino-2-phenylindole to quantify apoptosis induction by the detection of pyknotic nuclei. Slides were mounted under Fluoromount (Southern Biotechnologies Associates, Birmingham, AL, USA). Tissues were examined under a fluorescence microscope (Pathfinder, Nikon) with a × 10 or × 20 objective in three channels (appearing red, green, and blue in all figures) as separate files. These images were then stacked with Photoshop software (Adobe, San Jose, CA, USA). All statistical analyses were performed on Prism (GraphPad, La Jolla, CA, USA, Version 7.00).
Immunophenotyping
Immunophenotyping of PAXX mice was performed as described.17 T-cell populations from the thymus and spleen were identified with anti-CD8 (clone 5.3–6.7), anti-CD4 (GK1.5), and anti-CD3 (145-2C11). Splenic B cells were analyzed using anti-B220 (R6-60.2) and anti-IgM (II/41) and anti-CD19 (6D5). All antibodies were from BD Biosciences. Flow cytometry was performed on the BD LSR-Fortessa (Becton Dickinson, Rungis, France) and analyzed with FlowJo (Ashland, OR, USA). For immunophenotyping of PAXX/Xlf DKO embryos, FLs and thymuses were microdissected under a binocular magnifying lens and passed through a 26-gauge needle of 1-ml syringe and filtered. For thymocytes, cell suspensions were stained with fluorescent-labeled antibodies from BD Biosciences (Becton Dickinson, Rungis, France) Anti-CD25 (clone PC61) and Anti-CD3ε (145-2C11) and from Sony anti-CD4 (GK1.5), anti-CD8β (YTS156.7.7), anti-CD44 (IM7), anti-CD117 (2B8), and anti-CD28 (E18). For B-lineage, cell suspensions were stained with fluorescent-labeled antibodies from Biolegend (San Diego, CA, USA): anti-IgM (clone RMM-1) and anti-CD43 (S11), and from the Sony: anti-CD19-APCCy7 (6D5) and anti-B220 (RA3-6B2). For intracellular IgM staining, cell suspensions were first labeled as above, fixed with the fixation buffer from eBioscience (ThermiFischer Scientific, Villebon sur Yvette, France) intracellular staining kit, and incubated 30 min with anti- IgM from Sony (clone RMM-1).
TCRα repertoire study
TCRα repertoire analyses were performed by SMARTer 5’ RACE cDNA amplification as previously described on thymocytes.17 CDR3 sequences were identified using LymAnalyzer27 and represented by circos-plot using VDJtools.28 Each TRAV–TRAJ association was recorded in a FlowJo-based file to calculate frequencies of TRAV and TRAJ proximal and distal gene usage. Statistical analyses were performed using Mann–Whitney non-parametric t-test under Prism v6.
TCRβ and IgH V(D)J rearrangement analysis
TCRβ rearrangements (D-Jβ2 and Vβ10-D-Jβ2) were analyzed by PCR on genomic DNA from E18.5 fetal thymuses of various genotypes according to Gartner et al.29 Briefly, 1ng of thymic gDNA were amplified using primers TCRB-D2U-S 5′-GTAGGCACCTGTGGGGAAGAAACT-3′, TCRB-J2D-A 5′-TGAGAGCTGTCTCCTACTATCGATT-3′, TCRB-V10-S 5′-GCGCTTCTCACCTCAGTCTTCAG-3′, blotted, and hybridized using a PCR-derived TCR-Jβ2 DNA probe (Jbeta2F-5′-GAATTCTTGGTAGCCCTTTTCTGC-3′ and Jbeta2 R-5′-GGGTGGAAGCGAGAGATGT-3′) as depicted on Figure 3b. For IgH rearrangements (VH–DJH) studies, FL CD19+ B-lineage cells were sorted on FACSAriaIII and analyzed by PCR on 1ng genomic DNA according to Schlissel et al.30 Input DNA was analyzed using a GAPDH PCR.
Acknowledgments
We thank Catherine Cailleau (SEAT) for exceptional care of our mouse lines, Sophie Berissi for help in immunohistochemistry and Olivier Alibeu, Aurore Pouliet, and Christine Bole-Feyssot (Genomic facility, Imagine Institute) for their assistance in NGS. This work was supported by institutional grants from INSERM, the Institut National du Cancer (PLBIO16-280), the Agence Nationale de la Recherche ('Investissement d’Avenir' program ANR-10-IAHU-01), and by grants from La Ligue Nationale contre le Cancer (Equipe Labellisée LA LIGUE), Pasteur Institute, ANR (Program REVIVE and grant Twothyme) to AC.
Footnotes
Supplementary Information accompanies this paper on Cell Death and Differentiation website (http://www.nature.com/cdd)
Edited by H-U Simon
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Supplementary Material
References
- Sancar A, Lindsey-Boltz LA, Unsal-Kacmaz K, Linn S. Molecular mechanisms of mammalian DNA repair and the DNA damage checkpoints. Annu Rev Biochem 2004; 73: 39–85. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jung D, Giallourakis C, Mostoslavsky R, Alt FW. Mechanism and control of V(D)J recombination at the immunoglobulin heavy chain locus. Annu Rev Immunol 2006; 24: 541–570. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lieber MR. The mechanism of double-strand DNA break repair by the nonhomologous DNA end-joining pathway. Annu Rev Biochem 2010; 79: 181–211. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gao Y, Sun Y, Frank KM, Dikkes P, Fujiwara Y, Seidl KJ et al. A critical role for DNA end-joining proteins in both lymphogenesis and neurogenesis. Cell 1998; 95: 891–902. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frank KM, Sekiguchi JM, Seidl KJ, Swat W, Rathbun GA, Cheng HL et al. Late embryonic lethality and impaired V(D)J recombination in mice lacking DNA ligase IV. Nature 1998; 396: 173–177. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Villartay JP, Fischer A, Durandy A. The mechanisms of immune diversification and their disorders. Nat Rev Immunol 2003; 3: 962–972. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Alt FW, Zhang Y, Meng FL, Guo C, Schwer B. Mechanisms of programmed DNA lesions and genomic instability in the immune system. Cell 2013; 152: 417–429. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Xing M, Yang M, Huo W, Feng F, Wei L, Jiang W et al. Interactome analysis identifies a new paralogue of XRCC4 in non-homologous end joining DNA repair pathway. Nat Commun 2015; 6: 6233. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ochi T, Blackford AN, Coates J, Jhujh S, Mehmood S, Tamura N et al. DNA repair. PAXX, a paralog of XRCC4 and XLF, interacts with Ku to promote DNA double-strand break repair. Science 2015; 347: 185–188. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Craxton A, Somers J, Munnur D, Jukes-Jones R, Cain K, Malewicz M. XLS (c9orf142) is a new component of mammalian DNA double-stranded break repair. Cell Death Differ 2015; 22: 890–897. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tadi SK, Tellier-Lebegue C, Nemoz C, Drevet P, Audebert S, Roy S et al. PAXX is an accessory c-NHEJ factor that associates with Ku70 and has overlapping functions with XLF. Cell Rep 2016; 17: 541–555. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Balmus G, Barros AC, Wijnhoven PW, Lescale C, Hasse HL, Boroviak K et al. Synthetic lethality between PAXX and XLF in mammalian development. Genes dev 2016; 30: 2152–2157. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kumar V, Alt FW, Frock RL. PAXX and XLF DNA repair factors are functionally redundant in joining DNA breaks in a G1-arrested progenitor B-cell line. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2016; 113: 10619–10624. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lescale C, Abramowski V, Bedora-Faure M, Murigneux V, Vera G, Roth DB et al. RAG2 and XLF/Cernunnos interplay reveals a novel role for the RAG complex in DNA repair. Nat Commun 2016; 7: 10529. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liu X, Shao Z, Jiang W, Lee BJ, Zha S. PAXX promotes KU accumulation at DNA breaks and is essential for end-joining in XLF-deficient mice. Nat Commun 2017; 8: 13816. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mashiko D, Fujihara Y, Satouh Y, Miyata H, Isotani A, Ikawa M. Generation of mutant mice by pronuclear injection of circular plasmid expressing Cas9 and single guided RNA. Sci Rep 2013; 3: 3355. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vera G, Rivera-Munoz P, Abramowski V, Malivert L, Lim A, Bole-Feysot C et al. Cernunnos deficiency reduces thymocyte life span and alters the T cell repertoire in mice and humans. Mol Cell Biol 2013; 33: 701–711. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li G, Alt FW, Cheng HL, Brush JW, Goff PH, Murphy MM et al. Lymphocyte-specific compensation for XLF/cernunnos end-joining functions in V(D)J recombination. Mol Cell 2008; 31: 631–640. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roque T, Haton C, Etienne O, Chicheportiche A, Rousseau L, Martin L et al. Lack of a p21waf1/cip -dependent G1/S checkpoint in neural stem and progenitor cells after DNA damage in vivo. Stem cells 2012; 30: 537–547. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Teague TK, Tan C, Marino JH, Davis BK, Taylor AA, Huey RW et al. CD2 expression redefines thymocyte development during the pre-T to DP transition. Int Immunol 2010; 22: 387–397. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kajikhina K, Tsuneto M, Melchers F. B-lymphopoiesis in fetal liver, guided by chemokines. Adv Immunol 2016; 132: 71–89. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hung PJ, Chen BR, George R, Liberman C, Morales AJ, Colon-Ortiz P et al. Deficiency of XLF and PAXX prevents DNA double-strand break repair by non-homologous end joining in lymphocytes. Cell Cycle 2017; 16: 286–295. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zha S, Guo C, Boboila C, Oksenych V, Cheng HL, Zhang Y et al. ATM damage response and XLF repair factor are functionally redundant in joining DNA breaks. Nature 2011; 469: 250–254. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haeussler M, Schonig K, Eckert H, Eschstruth A, Mianne J, Renaud JB et al. Evaluation of off-target and on-target scoring algorithms and integration into the guide RNA selection tool CRISPOR. Genome Biol 2016; 17: 148. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cong L, Ran FA, Cox D, Lin S, Barretto R, Habib N et al. Multiplex genome engineering using CRISPR/Cas systems. Science 2013; 339: 819–823. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roederer M. Interpretation of cellular proliferation data: avoid the panglossian. Cytometry A 2011; 79: 95–101. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yu Y, Ceredig R, Seoighe C. LymAnalyzer: a tool for comprehensive analysis of next generation sequencing data of T cell receptors and immunoglobulins. Nucleic Acids Res 2016; 44: e31. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shugay M, Bagaev DV, Turchaninova MA, Bolotin DA, Britanova OV, Putintseva EV et al. VDJtools: Unifying Post-analysis of T Cell Receptor Repertoires. PLoS Comput Biol 2015; 11: e1004503. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gartner F, Alt FW, Monroe R, Chu M, Sleckman BP, Davidson L et al. Immature thymocytes employ distinct signaling pathways for allelic exclusion versus differentiation and expansion. Immunity 1999; 10: 537–546. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schlissel MS, Corcoran LM, Baltimore D. Virus-transformed pre-B cells show ordered activation but not inactivation of immunoglobulin gene rearrangement and transcription. J Exp Med 1991; 173: 711–720. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.