Figure 1.
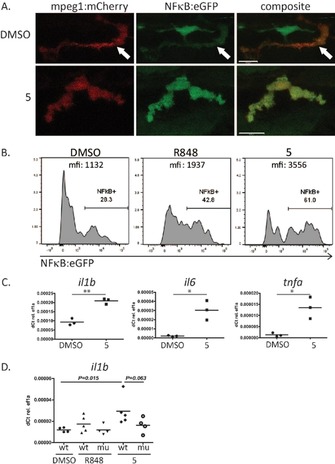
In vivo studies of the immune‐ activating functions of 5. (A) and (B) NFκB:eGFP induction by 5 in mpeg:mCherry positive macrophages in live zebrafish larvae. Zebrafish larvae (4 dpf) were stimulated with DMSO (control), R848 (positive control) or 5 for 6 h. A) Representative confocal images of macrophages in live NFκB:eGFP/mpeg:mCherry transgenic larvae. Upper panel: DMSO control (arrow demarcates macrophage). Lower panel: 5 (B) Flow cytometry analysis of NF‐κB induction in single‐cell suspensions of zebrafish larvae. Cells were pre‐gated on mpeg:mcherry macrophages and analysed for NFκB:eGFP expression. (C) Quantitative real‐ time PCR for RNA expression of the inflammatory cytokines il1b, il6, tnfa in wildtype zebrafish larvae after 6 h activation with 5. DMSO was used as negative control. (n=3) *P<0.05; ** P<0.01 (D) Il1b RNA expression in MyD88 mutant and wildtype zebrafish larvae after 6 h of stimulation with TLR ligands R848 and 5. DMSO was used as negative control. (n=4–5) Scale bars in A are 10 μm.
