Abstract
Recent innovations in peptide natural product biosynthesis reveal a surprising wealth of previously uncharacterized biochemical reactions that have potential applications in synthetic biology. Among these, the cyanobactins are noteworthy because these peptides are protected at their N- and C-termini by macrocyclization. Here, we use a novel bifunctional enzyme AgeMTPT to protect linear peptides by attaching prenyl and methyl groups at their free N- and C-termini. Using this peptide protectase in combination with other modular biosynthetic enzymes, we describe the total synthesis of the natural product aeruginosamide B and the biosynthesis of linear cyanobactin natural products. Our studies help to define the enzymatic mechanism of macrocyclization, providing evidence against the water exclusion hypothesis of transpeptidation and favoring the kinetic lability hypothesis.
Graphical Abstract
Ribosomally synthesized and posttranslationally modified peptide (RiPP) natural products are found in most organisms,1 revealing many new enzymatic reactions with new functionality.2 An area of increasing focus is the application of RiPP enzymes to problems in pharmaceutical discovery and development. One potential application is in improving the pharmacological properties of linear peptide drugs.3 RiPP biosynthetic enzymes offer solutions to rigidify peptide backbones and overcome limitations, including the creation of side-chain directed or head-to-tail macrocyclic peptides.1 As one of many examples,4–6 in the cyanobactin RiPPs,7 the PatG protease domain performs a N-C transamidation to yield a macrocyclic product.8
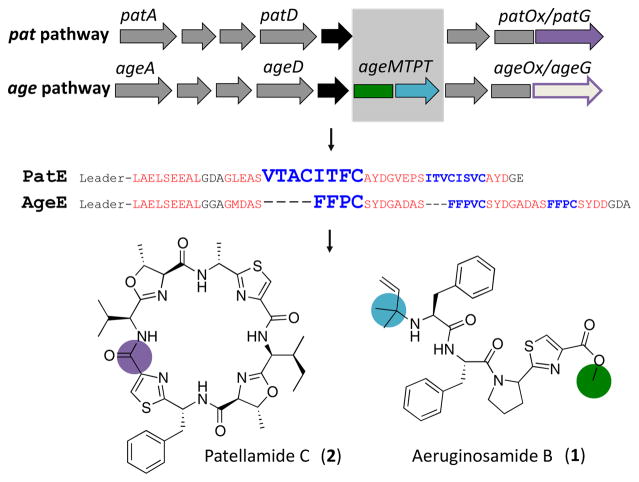
In contrast to macrocyclization, here we describe the biochemical basis of another peptide protection strategy, in which linear peptides are protected by chemical modifications at their N- and C-termini as found in aeruginosamide and relatives. Aeruginosamide B (1) belongs to a family of cyanobacterial natural products comprised of 3–4 amino acids, which contain thiazole rings and isoprene groups. The compounds are protected at the N- and C-termini by isoprenylation and methyl esterification, respectively.9–11 In a landmark paper, Leikoski et al. showed that aeruginosamide-like compounds are biosynthesized by a cyanobactin pathway age, which has several novel features in comparison to canonical cyanobactin pathways (Figures 1 and S1).11 Most notably, the cluster contains an ageMTPT gene (MT, methyltransferase; PT, prenyltransferase), which was annotated as a novel di-domain methyl/prenyltransferase. The ageMTPT gene product was proposed to carry out the dual methylation and prenylation reactions on the peptide termini observed in the natural product.11 By contrast, related prenyltransferases are known to prenylate the side-chains of amino acids within macrocyclic peptides.12–15 Likewise, enzymes that are known to exclusively methylate the α-carboxylate on peptides have not been characterized. Here, we provide biochemical characterization supporting these proposed functions of AgeMTPT.
Figure 1.
Biosynthesis of N- and C-protected cyanobactin peptides. Precursor peptides PatE and AgeE are modified by enzymes that are encoded on longer gene clusters. The well-characterized pat pathway leads to macrocycles, such as patellamide C (2). The age pathway encodes a novel enzyme AgeMTPT. The blue domain adds isoprene, while the green domain adds methyl. PatG performs macrocyclization (purple).
Additionally, the gene ageG was annotated as a homolog of PatG and related proteases, which produce N-C macrocycles such as 2. In contrast to PatG, AgeG would putatively synthesize short linear products via a hydrolytic, rather than transamidative mechanism. N-C cyclic RiPPs are widely found in nature, but the biochemical basis of circularization versus linearization is not known. One hypothesis is that exclusion of water from the active site promotes cyclization.16 Here, by comparing PatG and AgeG activity profiles we provide evidence that the specificity of cyclization over linearization is caused by the inherent chemistry of the cyclizing enzyme rather than by water exclusion.
A key feature of cyanobactin pathways is modularity, wherein enzymes from one pathway can be combined with enzymes and substrates from other pathways, to afford large numbers of derivatives via rational engineering.14 This led us to hypothesize that modular cyanobactin enzymes would be useful in making short peptides with blocked termini. Aeruginosamide A was chemically synthesized previously.17 Here, in lieu of chemical synthesis, we synthesize 1 using a modular set of biosynthetic enzymes.
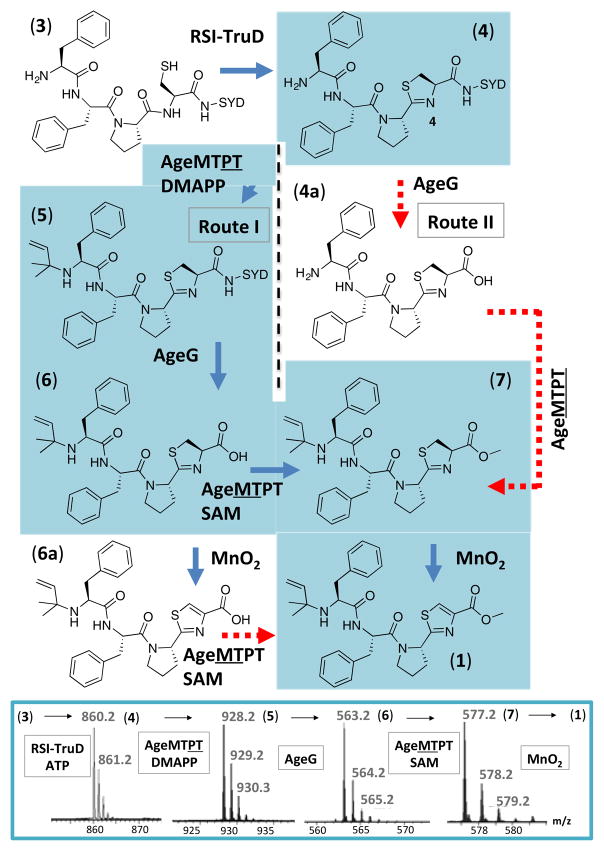
In characterized enzymes from circular cyanobactins, D proteins such as AgeD are heterocyclases that generate thiazoline on precursor peptides, such as AgeE. Subsequently, A proteases (e.g., AgeA) hydrolyze heterocyclized precursors to liberate free N-termini. Therefore, we used FFPCSYD (3), which mimics the AgeA-proteolyzed native substrate AgeE. We applied 3 to enzyme RSI-TruD, in which the heterocyclization recognition sequence RSI is appended to heterocyclase TruD from the tru pathway, allowing the reaction to proceed on short substrates without a long leader peptide.18–22 This led to formation of the thiazoline-containing FFPC*SYD (4, where C* indicates thiazoline; Figures 2 and S2A).
Figure 2.
Synthesis and biosynthesis of aeruginosamide B (1). Blue arrows indicate steps that worked using recombinant enzymes and pure chemicals. Red dashed arrows indicate minimal (or no) reactions. The metabolic pathway was determined on the basis of these reactions and previous knowledge of cyanobactin biosynthesis. At bottom are shown mass spectra [M+H]+ of species 4–7. Additional data in: Figures S2, S12, S13 and Tables S1–3.
Intermediate 4 is potentially a substrate for either the prenyltransferase AgeMTPT (route I) or the C-terminal protease AgeG (route II; Figures 2 and S3). A third possible route, oxidation first, is ruled out by the specificity of methylation (see below). To test route I, 4 was introduced to AgeMTPT and dimethylallyl pyrophosphate (DMAPP). This led to complete conversion of 4 to the singly prenylated product 5 (C5H9-FFPC*SYD, C5H9 = isoprene; Figures 2, S2-B and S4). AgeMTPT was relatively selective for 4, with a limited substrate scope (Figure S5-A); a preference for N-terminal Phe is likely given that 3 also acts as a substrate (Figure S5-B–D). Interestingly, AgeMTPT could also prenylate S-adenosylmethionine (SAM) and adenosine analogs to a minor degree (<5%; Figure S6). To test route II, 4 was introduced to AgeG, leading to very minor amounts of the expected proteolyzed product 4a (FFPC*) (Figure S7). In contrast, AgeG completely processed the route I-derived intermediate 5 to afford 6 (C5H9-FFPC*) (Figures 2 and S2-C). Competition reactions further supported route I (Figure S8). A limitation is that only the protease domain of AgeG was used; in previous studies of related enzymes PatG and TruG excised domains exhibited identical activity to full-length protein.
Subsequent reaction of 6 with AgeMTPT and SAM led to product 7 (C5H9-FFPC*-CH3; CH3, methyl; Figures 2 and S2-D). This reaction was slow (60% complete after 18 h). Using substrate 6a, in which the thiazoline was oxidized to thiazole, no methylation reaction was observed (Figure S9-A). Competition experiments containing both 6 and 6a confirmed this result, in that only 6 was methylated (Figure S9-B), indicating that oxidation occurs after methylation and is likely to be the last biosynthetic step.
With 7 in hand (Figure S10), a formal synthesis required oxidation to 1 (Figure S11). We used MnO223 (compounds 5 and 7), DDQ24 (compound 7) or K2CO3/O225 (compound 7) to produce aeruginosamide B (1). The structure of 7 was analyzed by NMR spectroscopy (Figure S12 and Table S3). Although 1 was clearly synthesized as seen by mass spectrometry (Figure S13), it was not stable, perhaps explaining why the natural product was not initially isolated.11
The above reactions demonstrate the enzymatic roles of AgeMTPT and AgeG protease and allow us to propose a biosynthetic route: 4 is the substrate for AgeMTPT prenylation, and AgeG hydrolyzes the C-terminus. AgeMTPT acts a second time, methylating the nascent C-terminus. Precedent suggests that AgeG oxidase synthesizes thiazole last (Figure S14).
Here, we show that AgeG hydrolyzes and linearizes AgeE. All other characterized AgeG homologs, such as PatG and TruG, do not naturally hydrolyze peptides, but instead catalyze a transpeptidation to produce N-C macrocycles.8, 16, 26 We therefore believed that comparing these enzymes would provide excellent insight into the enigmatic mechanism of macrocyclization.
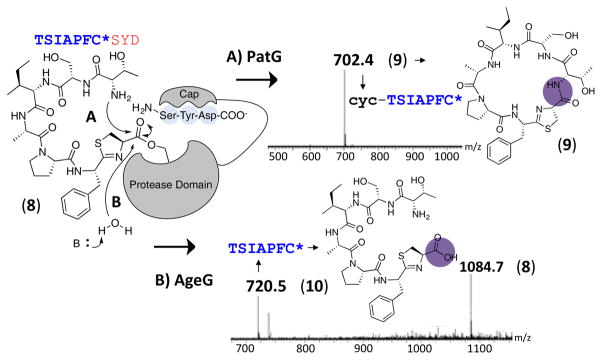
AgeG, PatG and relatives are subtilisin-like serine proteases. In comparison to canonical proteases, they contain an extra helical domain that interacts16, 26 with recognition sequence (RSIII, Ser-Tyr-Asp-COO−)8, 21 in the precursor peptide (Figure 3). Two models have been proposed to explain why PatG circularizes, rather than linearizes peptides and peptide analogs with many different sequences. In the first, the extra helical domain acts as a cap that excludes water.16 In the second, PatG favors transamidation because of a preference for amines as the nucleophile.8, 14, 26 A similar effect has long been proposed to explain transamidation in subtiligase, which was said to result from a greater “kinetic lability…toward amines as opposed to water.”27
Figure 3.
Model of circularization versus hydrolysis in cyanobactin proteases. As shown by mass spectrometry data (see Figure S18-A), while PatG macrocyclizes 8 to 9 (mechanism A), AgeG linearizes 8 to 10 (mechanism B).
In favor of the latter hypothesis, PatG was shown to hydrolyze and not macrocylize a peptide that terminates with glycolate (OH) rather than glycine (NH2).8 Moreover, in the presence of glycylglycine buffer, PatG performs transamidation between the normal substrate and the buffer, in addition to macrocyclization, indicating that the access to active site is not blocked.26
To further probe this issue, we compared the reactivity of PatG and AgeG protease domains. PatG was found to slowly proteolyze 5, which is the proposed native substrate of AgeG (Figure S15). This was expected, since PatG and AgeG are similar in sequence (Figure S16). Since the active site cap of the cyclizing PatG enzyme is also present in the linearizing AgeG enzyme, it raises the question of the role of the cap in cyclization (Figure 3). We found that PatG did not react with 4, whereas AgeG slowly proteolyzed 4 to linear product 4a (Figure S17). The lack of cyclization of 4 by AgeG could be due to either the small size of 4 or an inherent linearizing capability of AgeG. To differentiate between these possibilities, we compared reactivity of PatG/AgeG on substrate 8 (TSIAPFC*SYD) from the tru cyanobactin pathway that is normally macrocyclized by PatG to the natural product trunkamide.14 As expected, PatG cyclized 8 to product 9. In contrast, AgeG hydrolyzed 8 to the linear product 10 (Figures 3 and S18). This establishes AgeG as a cyanobactin C-terminal linearizing protease.
These results show that linearization versus macrocyclization is not cap-dependent. Instead, since the cap binds RSIII, as seen in elegant crystal structures,16 this binding may serve for substrate recognition. In cyanobactins, the N-terminal portion of the G-protein substrate is hypervariable, whereas the C-terminal portion is the recognition sequence. Therefore, the cap feature may be needed in order to recognize the hypervariable N-terminus via the conserved C-terminal recognition motif.16 Alternatively, since the order of proteolysis is critical to the fidelity of cyanobactin biosynthesis, this feature may help to recognize and position appropriate substrates. As shown here, different cyanobactin enzymes exhibit inherent substrate preferences for transamidation or hydrolysis. A similar phenomenon appears to be the case in subtiligases, wherein preference is controlled by the reactivity (“kinetic lability”) of the enzyme toward specific nucleophiles.27
This study reveals the biochemical basis of cyanobactin peptide protection. We characterize AgeMTPT, the first reported enzyme to block both termini of a linear peptide substrate. In other RiPPs, different enzymes block individual termini (examples include polytheonamide and plantazolicin).28,29 N-terminal prenylation is a rare modification that to our knowledge has not been previously examined biochemically. Furthermore, although C-terminal methylation is an observed posttranslational modification,30 the responsible enzymes are not characterized. Finally, several RiPP families are N-C macrocyclized,31–33 but the enzymatic basis of transamidation versus hydrolysis is not yet known. Here, with an AgeG/PatG comparison we provide evidence supporting the kinetic lability model as defined by Wells and co-workers.27
By determining substrate preferences of AgeMTPT and AgeG in vitro, here we define the proposed biosynthetic route to aeruginosamide and relatives. We also exploited the modularity of cyanobactin biosynthetic enzymes to combine pathways in the first total synthesis of 1.14,34 A related compound, aeruginosamide A was previously constructed via chemical synthesis through a 14-step reaction scheme.17 The enzymatic route presented here is concise while retaining the capacity to generate analogs. The rational use of enzymes from multiple pathways to create structurally unrelated natural products is a powerful tool for total synthesis. Additional advantages of enzymatic synthesis include independence from protecting groups, green reaction conditions, compatibility with aqueous solvents, and the potential for synthetic biology in living tissues. Here, we define methods to provide a roadmap for enzymatic synthesis of protected peptides.
Supplementary Material
Acknowledgments
Funding Sources
NIH GM102602
We thank Tom Smith and Krishna Parsawar for assistance with mass spectrometry.
Footnotes
Supporting Information. Experimental methods and additional data. This material is available free of charge via the Internet at http://pubs.acs.org
References
- 1.Arnison PG, Bibb MJ, Bierbaum G, Bowers AA, Bugni TS, Bulaj G, Camarero JA, Campopiano DJ, Challis GL, Clardy J, Cotter PD, Craik DJ, Dawson M, Dittmann E, Donadio S, Dorrestein PC, Entian KD, Fischbach MA, Garavelli JS, Göransson U, Gruber CW, Haft DH, Hemscheidt TK, Hertweck C, Hill C, Horswill AR, Jaspars M, Kelly WL, Klinman JP, Kuipers OP, Link AJ, Liu W, Marahiel MA, Mitchell DA, Moll GN, Moore BS, Müller R, Nair SK, Nes IF, Norris GE, Olivera BM, Onaka H, Patchett ML, Piel J, Reaney MJT, Ross RP, Sahl HG, Schmidt EW, Selsted ME, Severinov K, Shen B, Sivonen K, Smith L, Stein TH, Süssmuth RD, Tagg JR, Tang GL, Truman AW, Vederas JC, Walsh CT, Walton JD, Wenzel SC, Willey JM, van der Donk WA. Nat Prod Rep. 2013;30:108. doi: 10.1039/c2np20085f. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Skinnider MA, Johnston CW, Edgar RE, Dejong CA, Merwin NJ, Rees PN, Magarvey NA. Proc, Natl Acad USA. 2016;113:E6343. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1609014113. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Madala PK, Tyndall JDA, Nall T, Fairlie DP. Chem Rev. 2010;110:PR1. doi: 10.1021/cr900368a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Lohans CT, Vederas JC. J Antibiotics. 2014;67:23. doi: 10.1038/ja.2013.81. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Maksimov MO, Link AJ. Microbiol Biotechnol. 2014;41:333. doi: 10.1007/s10295-013-1357-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Ortega MA, van der Donk WA. Cell Chem Biol. 2016;23:31. doi: 10.1016/j.chembiol.2015.11.012. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Schmidt EW, Nelson JT, Rasko DA, Sudek S, Eisen JA, Haygood MG, Ravel J. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2005;102:7315. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0501424102. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.McIntosh JA, Robertson CR, Agarwal V, Nair SK, Bulaj G, Schmidt EW. J Am Chem Soc. 2010;132:15499. doi: 10.1021/ja1067806. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Carroll AR, Feng Y, Bowden BF. J Org Chem. 1996;61:4059. doi: 10.1021/jo951379o. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Lawton LA, Morris LA, Jaspars M. J Org Chem. 1999;64:5329. doi: 10.1021/jo990247i. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Leikoski N, Liu L, Jokela J, Wahlsten M, Gugger M, Calteau A, Permi P, Kerfeld CA, Sivonen K, Fewer DP. Cell Chem Biol. 2013;20:1033. doi: 10.1016/j.chembiol.2013.06.015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.McIntosh JA, Donia MS, Nair SK, Schmidt EW. J Am Chem Soc. 2011;133:13698. doi: 10.1021/ja205458h. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Donia MS, Schmidt EW. Cell Chem Biol. 2011;18:508. doi: 10.1016/j.chembiol.2011.01.019. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Sardar D, Lin Z, Schmidt EW. Cell Chem Biol. 2015;22:907. doi: 10.1016/j.chembiol.2015.06.014. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Parajuli A, Kwak DH, Dalponte L, Leikoski N, Galica T, Umeobika U, Trembleau L, Bent A, Sivonen K, Wahlsten M, Wang H, Rizzi E, De Bellis G, Naismith J, Jaspars M, Liu X, Houssen W, Fewer DP. Angew Chem. 2016;55:3596. doi: 10.1002/anie.201509920. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Koehnke J, Bent A, Houssen WE, Zollman D, Morawitz F, Shirran S, Vendome J, Nneoyiegbe AF, Trembleau L, Botting CH, Smith MM, Jaspars M, Naismith JH. Nat Struct Mol Biol. 2012;19:767–772. doi: 10.1038/nsmb.2340. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Chen Z, Ye T. New J of Chem. 2006;30:518. [Google Scholar]
- 18.Oman TJ, Knerr PJ, Bindman NA, Velasquez JE, van der Donk WA. J Am Chem Soc. 2012;134:6952. doi: 10.1021/ja3017297. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Koehnke J, Mann G, Bent A, Ludewig H, Shirran S, Botting CH, Lebl T, Houssen WE, Jaspars M, Naismith JH. Nat Chem Biol. 2015;11:558. doi: 10.1038/nchembio.1841. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Koehnke J, Bent AF, Zollman D, Smith K, Houssen WE, Zhu X, Mann G, Lebl T, Scharff R, Shirran S, Botting CH, Jaspars M, Schwarz-Linek U, Naismith JH. Angew Chem. 2013;52:13991. doi: 10.1002/anie.201306302. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Sardar D, Pierce E, McIntosh JA, Schmidt EW. ACS Synth Biol. 2015;4:167. doi: 10.1021/sb500019b. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Goto Y, Ito Y, Kato Y, Tsunoda S, Suga H. Cell Chem Biol. 2014;21:766. doi: 10.1016/j.chembiol.2014.04.008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Ishihara H, Shimura K. FEBS Lett. 1987;226:319. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(88)81447-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Li X, Li C, Yin B, Li C, Liu P, Li J, Shi Z. Chem Asian J. 2013;8:1408. doi: 10.1002/asia.201300267. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Huang Y, Gan H, Li S, Xu J, Wu X, Yao H. Tet Lett. 2010;51:1751. [Google Scholar]
- 26.Agarwal V, Pierce E, McIntosh J, Schmidt EW, Nair SK. Cell Chem Biol. 2012;19:1411. doi: 10.1016/j.chembiol.2012.09.012. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Abrahmsen L, Tom J, Burnier J, Butcher K, Kossiakoff A, Wells AJ. Biochemistry. 1991;30:4151. doi: 10.1021/bi00231a007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Freeman MF, Gurgui C, Helf MJ, Morinaka BI, Uria AR, Oldham NJ, Sahl HG, Matsunaga S, Piel J. Science. 2012;387 doi: 10.1126/science.1226121. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Lee J, Hao Y, Blair PM, Melby JO, Agarwal V, Burkhart BJ, Nair SK, Mitchell DA. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2013;110:122954. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1306101110. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Liu N, Song L, Liu M, Shang F, Anderson Z, Fox DJ, Challis GL, Huang Y. Chem Sci. 2016;7:482. doi: 10.1039/c5sc03021h. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Nguyen GK, Wang S, Qiu Y, Hemu X, Lian Y, Tam JP. Nat Chem Biol. 2014;10:732. doi: 10.1038/nchembio.1586. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Luo H, Hong SY, Sgambelluri RM, Angelos E, Li X, Walton JD. Chem Biol. 2014;21:1610. doi: 10.1016/j.chembiol.2014.10.015. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Harris KS, Durek T, Kaas Q, Poth AG, Gilding EK, Conlan BF, Saska I, Daly NL, van der Weerden NL, Craik DJ, Anderson MA. Nat Commun. 2015 doi: 10.1038/ncomms10199. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Sardar D, Schmidt EW. Curr Opin Chem Biol. 2016;31:15. doi: 10.1016/j.cbpa.2015.11.016. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.