Abstract
We evaluated whether metabolic factors were associated with cognitive decline, compared to baseline cognitive function, among geriatric population. The present study evaluated data from an ongoing prospective community-based Korean cohort study. Among 1,387 participants who were >65 years old, 422 participants were evaluated using the Korean mini-mental status examination (K-MMSE) at the baseline and follow-up examinations. The mean age at the baseline was 69.3 ± 2.9 years, and 222 participants (52.6%) were men. The mean duration of education was 7.1 ± 3.6 years. During a mean follow-up of 5.9 ± 0.1 years, the K-MMSE score significantly decreased (−1.1 ± 2.7 scores), although no significant change was observed in the homeostasis model assessment of insulin resistance (HOMA-IR) value. Participants with more decreased percent changes in K-MMSE scores had a shorter duration of education (p = 0.001), older age (p = 0.022), higher baseline K-MMSE score (p < 0.001), and increased insulin resistance (∆HOMA-IR, p = 0.002). The correlation between the percent changes in K-MMSE and ∆HOMA-IR values remained significant after multivariable adjustment (B = −0.201, p = 0.002). During a 6-year follow-up of older Koreans with normal baseline cognitive function, increased insulin resistance was significantly correlated with decreased cognitive function.
Introduction
The increasing geriatric population is associated with increasing prevalence of dementia and cognitive dysfunction in many countries, including Korea1–3. The World Health Organization has reported that 47.5 million people had dementia in 2016, with global totals projected to reach 75.6 million people in 2030 and 135.5 million people in 20504. Dementia in geriatric populations affects the individuals’ and their families’ quality of life, which creates a societal burden, and the global estimated economic burden was approximately 604 billion US dollars in 20104. Therefore, it would be helpful to identify and address modifiable factors that can help to reduce the global burden of dementia.
Epidemiological studies have revealed associations of cognitive impairment and/or dementia with type 2 diabetes mellitus5,6. Insulin resistance, hyperglycemia, and obesity are probable mechanistic links in this association. Few longitudinal studies have evaluated this issue, although many cross-sectional studies have confirmed the relationship between insulin resistance and cognitive decline7–10. One longitudinal study evaluated middle-aged adults (45–64 years old at baseline in the Atherosclerosis Risk in Communities cohort), and revealed that baseline hyperinsulinemia was associated with a rapid decline in cognitive function7. Another longitudinal nationwide population-based survey revealed that higher baseline HOMA-IR and fasting insulin levels were associated with a greater decline in verbal fluency8. However, to the best of our knowledge, no studies have evaluated the effects of longitudinal changes in insulin resistance on cognitive function.
Although clinical studies of patients with diabetes have demonstrated that hyperglycemia is associated with cognitive dysfunction, it remains controversial whether hyperglycemia is associated with cognitive dysfunction among older individuals or among individuals with normal glucose tolerance or prediabetes9–12. Among patients with impaired glucose tolerance, there is very little evidence regarding a relationship between impaired glucose tolerance and cognitive impairment12,13. However, among participants with normal glucose tolerance, poor glucose tolerance was associated with cognitive impairment12,13. The Leiden 85-plus Study prospectively evaluated 599 individuals from the age of 85 years and revealed that HbA1c concentrations were not associated with cognitive dysfunction9.
It has also been suggested that obesity is a risk factor for cognitive dysfunction, although this relationship remains unclear, as the few longitudinal studies have provided conflicting results14–16.
As geriatric populations are consistently growing, it is important to determine whether metabolic factors are related to cognitive dysfunction among older individuals, and whether addressing these metabolic factors can help prevent cognitive dysfunction. In the present prospective community-based cohort study, we aimed to identify metabolic factors that were associated with cognitive decline among older individuals with normal baseline cognitive function.
Methods
Study population
The present study evaluated data from the Ansung cohort study, which is a prospective community-based study that began in 2001 and is supported by National Genome Research Institute (Korean Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, Cheongju, Korea). That study is a part of the Korean Genome Epidemiology Study, which is a community-based epidemiological survey of Korean individuals who are 40–69 years old. The Ansung study recruited residents of Ansung who had lived in the surveyed region for ≥6 months. According to the 2000 census, Ansung is a rural community with 132,906 residents. Detailed information regarding the Ansung study’s selection criteria and sampling plan has been published previously17,18, and the study’s protocol was approved by the institutional review board of the Korean Centers for Disease Control and Prevention and the study was carried out in accordance with the protocol. Informed consent was obtained from all participants and/or their legal guardians. All methods were performed in accordance with the relevant guidelines and regulations.
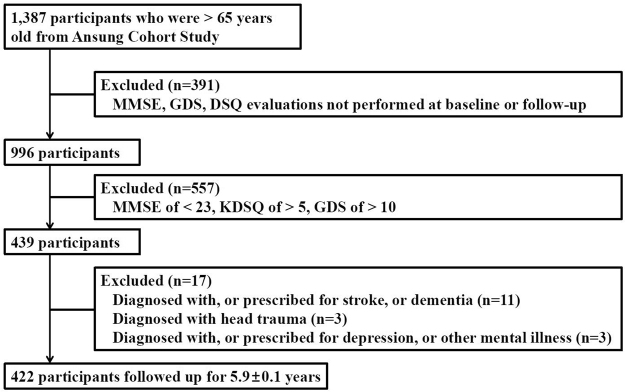
The Ansung cohort study evaluated 1,387 participants who were >65 years old, completed a baseline examination in 2001, and were surveyed biennially until 2014. Data from these participants were considered for inclusion in the present study. However, we excluded 391 participants because they did not complete the baseline or follow-up Korean mini-mental status examination (K-MMSE), the Korean geriatric depression score tool (GDS-K), or the Korean dementia screening questionnaire (KDSQ). In addition, we excluded 557 participants with a K-MMSE score of <23, a KDSQ score of >5, or a GDS-K score of >10. Participants with impaired baseline cognitive function (low K-MMSE score or high KDSQ score) were excluded because we only intended to evaluate individuals with normal baseline cognitive function. Participants with high GDS scores were excluded to minimize the influence of depressiveness on the MMSE results, as depression can be associated with low MMSE scores19. Furthermore, we excluded 17 participants who had been diagnosed with stroke, dementia, depression, or head trauma. Thus, data from 422 eligible participants were included in the final analyses (Fig. 1). The mean follow-up duration was 5.9 ± 0.1 years.
Figure 1.
Flow chart showing selection of the study population from Ansung cohort study.
Assessing cognitive impairment and depression
Cognitive impairment and depression were measured at the baseline and follow-up examinations. Cognitive impairment was evaluated using the K-MMSE and KDSQ tools. The 30-item K-MMSE was specifically developed and validated for assessing the general cognitive function of older Korean individuals20. The results are scored from 0 to 30 points, with scores of ≥23 points indicating normal cognition, scores of 17–22 points indicating mild cognitive impairment, and scores of <17 points indicating moderate-to-severe impairment. The 15-item KDSQ is a sensitive test for early dementia screening, and the results are not influenced by age or educational level21. The results are scored from 0 to 15 points, with scores of >5 points considered suggestive of cognitive impairment. Depressive symptoms were assessed using the 15-item GDS-K22. The results are scored from 0 to 15 points, with scores of >10 points considered suggestive of depressive mood. Changes in the K-MMSE, GDS-K, and KDSQ scores were calculated as:
| 1 |
| 2 |
| 3 |
| 4 |
Measuring anthropometric parameters
Face-to-face or telephone interviews were used to obtain data regarding the participants’ age, sex, duration of education, medical history, alcohol consumption, and smoking status. Former smokers were defined as individuals who had smoked >5 packs of cigarettes during their lifetime, and participants were defined as having quit smoking if they had stopped smoking ≥6 months before the baseline examination. Former drinkers were defined as individuals who had consumed 5 g of ethanol/day, and participants were defined as having quit drinking if they had stopped consuming alcohol ≥6 months before the baseline examination. Medical histories of diabetes, hypertension, stroke, dementia, head trauma, depression, and other mental illness were identified based on self-reported diagnoses.
The participants’ height and body weight were measured using the standard methods (scale and wall-mounted extensometer) while the participants were wearing light-weight clothes. Body mass index (BMI) was calculated as weight divided by height squared (kg/m2). Changes in BMI (∆BMI) were calculated as:
| 5 |
Laboratory testing and homeostasis model assessment of insulin resistance calculation
All participants fasted for at least 14 h before undergoing the blood sampling. Plasma specimens were separated using centrifugation (2,000 rpm for 20 min at 4 °C) and tested immediately. Plasma glucose concentrations were measured using the hexokinase method (ADVIA 1650 Auto Analyzer; Bayer, Leverkusen, Germany), and plasma insulin concentrations were measured using the IRMA test kit (bioSource Europe S.A., Niverlles, Belgium). Fasting concentrations of total cholesterol, high-density lipoprotein cholesterol (HDL-C), low-density lipoprotein cholesterol (LDL-C), and triglycerides were measured enzymatically using the Hitachi 747 chemistry analyzer (Hitachi, Tokyo, Japan). Concentrations of HbA1c were evaluated using high-performance liquid chromatography with a Bio-Rad Variant II HbA1c analyzer (Bio-Rad, Montreal, Quebec, Canada). Consenting participants underwent apolipoprotein E genotyping using the methods of Hixson and Vernier23, and the results were categorized based on the presence or absence of the ε4 allele. HOMA-IR24, ∆HOMA-IR, ∆HbA1c, and ∆fasting insulin were calculated as:
| 6 |
| 7 |
| 8 |
| 9 |
Statistical analysis
Normally distributed data were presented as mean ± standard deviation, non-normally distributed data were reported as median (interquartile range [IQR]), and categorical data were reported as number (%). The participants’ characteristics at the baseline and 6-year follow-up examinations were compared using the paired t-test, Wilcoxon signed-rank test, and Mann-Whitney U test, as appropriate. Pearson’s correlation coefficient was used to estimate the relationship between cognitive function and the related parameters. B refers to standardized beta value. Associations of cognitive function with the other factors were analyzed using multivariable linear regression models. Model 1 was adjusted for age, sex, baseline K-MMSE score, education duration, and baseline GDS-K score. Model 2 was adjusted for the factors in model 1 plus smoking status, history of diabetes, history of hypertension, and BMI. Model 3 was adjusted for the factors in model 2 plus the apolipoprotein E ε4 genotype status. Differences were considered statistically significant at p-values of <0.05, and all analyses were performed using IBM SPSS software (version 22.0; IBM Corp., Armonk, NY, USA).
Data Availability
The datasets generated during and/or analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
Results
Baseline characteristics
The participants’ characteristics at the baseline and follow-up examinations are shown in Table 1. The mean follow-up duration was 5.9 ± 0.1 years, the mean age at baseline was 69.3 ± 2.9 years, and 222 participants (52.6%) were men. The mean education duration was 7.1 ± 3.6 years. At baseline, 115 participants (27.3%) had hypertension, compared to 207 participants (49.1%) at the follow-up. At baseline, 89 participants (21.1%) had diabetes, compared to 113 participants (26.8%) at the follow-up. The K-MMSE scores decreased significantly from 26.5 ± 1.9 at baseline to 25.4 ± 2.9 at the follow-up (∆K-MMSE, −1.1 ± 2.7, percent changes in K-MMSE, −4.1 ± 10.3%). The KDSQ scores increased significantly (median increase: 1.0, IQR: –1.0 to 4.0). The GDS-K scores also increased significantly at the follow-up. The laboratory test results from the follow-up revealed a significant decrease in the LDL-C concentration and significant increases in the HDL-C and creatinine concentrations. The laboratory results for lipid profile, including LDL-C, HDL-C, and triglycerides, were only analyzed for 371 participants who were not receiving dyslipidemia treatment. No significant differences were observed in the values for HOMA-IR, fasting insulin, and HbA1c. Seventy-two participants (17.1%) were found to have the apolipoprotein E ε4 genotype (Table 1).
Table 1.
Characteristics of the participants at baseline and follow-up.
| Baseline (n = 422) | Follow-up (n = 422) | p -value | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Age, years | 69.3 ± 2.9 | 75.3 ± 2.9 | <0.001 |
| Male sex, n (%) | 222 (52.6) | ||
| Education duration, years | 7.1 ± 3.6 | ||
| Hypertension, n (%) | 115 (27.3) | 207 (49.1) | |
| Diabetes, n (%) | 89 (21.1) | 113 (26.8) | |
| Ever smoker, n (%) | 151 (35.8) | 167 (39.6) | |
| Current alcohol intake, n (%) | 198 (46.9) | 194 (46.0) | |
| BMI, kg/m2 | 23.9 ± 3.1 | 23.7 ± 3.3 | 0.015 |
| ∆BMI, kg/m2 | −0.17 ± 1.38 | ||
| K-MMSE baseline, score | 26.5 ± 1.9 | 25.4 ± 2.9 | <0.001 |
| ∆K-MMSE, score | −1.1 ± 2.7 | ||
| Percent changes in K-MMSE | −4.1 ± 10.3 | ||
| HOMA-IR baseline | 1.78 (1.34, 2.56) | 1.79 (1.31, 2.56) | 0.970 |
| ∆HOMA-IR | −0.02 (−0.56, 0.56) | ||
| KDSQ, score | 2.0 (1.0, 4.0) | 3.0 (1.0, 6.0) | <0.001 |
| ∆KDSQ, score | 1.0 (−1.0, 4.0) | ||
| GDS-K score | 2.0 (1.0, 4.0) | 2.0 (0, 5.0) | <0.001 |
| ∆GDS-K score | 0.6 ± 3.5 | ||
| Fasting insulin, μIU/L | 8.8 ± 5.4 | 8.8 ± 4.2 | 0.845 |
| ∆fasting insulin, μIU/L | −0.1 ± 5.9 | ||
| HbA1c, % (mmol/mol) | 5.8 ± 0.8 (40 ± 3) | 5.8 ± 0.7 (40 ± 3) | 0.616 |
| ∆HbA1c, % (mmol/mol) | 0 ± 0.6 (2.2 ± 2.2) | ||
| LDL-C, mg/dLa | 120.0 ± 28.7 | 109.5 ± 29.1 | <0.001 |
| HDL-C, mg/dLa | 43.1 ± 10.5 | 44.3 ± 11.8 | 0.041 |
| Triglycerides, mg/dLa | 128.4 ± 62.6 | 121.8 ± 58.2 | 0.055 |
| Creatinine, mg/dL | 0.9 ± 0.2 | 1.1 ± 0.3 | <0.001 |
| APOE ε4 genotype, % | 72 (17.1) |
K-MMSE, Korean mini mental status examination; KDSQ, Korean dementia screening questionnaire; GDS-K, Korean geriatric depression scale; APOE ε4, apolipoprotein ε4; LDL-C, low-density lipoprotein cholesterol; HDL-C, high-density lipoprotein cholesterol.
Continuous variables are reported as mean ± standard deviation for normally distributed variables, while median (interquartile range) is used for HOMA-IR, ∆HOMA-IR, KDSQ, and GDS-K (non-normally distributed variables), and n (%) is used for categorical variables. The ∆ values refer to the change between baseline and follow-up.
aLipid profile was only evaluated among participants who were not receiving dyslipidemia treatment (n = 371).
Correlations of K-MMSE with factors at baseline
Pearson’s correlation analyses revealed that lower K-MMSE values were correlated with shorter education durations (r = 0.393, p < 0.001), higher KDSQ scores (r = −0.129, p = 0.008), and higher GDS-K scores (r = −0.128, p = 0.008). Baseline K-MMSE values were not significantly correlated with age, baseline BMI, ∆BMI, ∆KDSQ score, ∆GDS-K score, baseline HOMA-IR, ∆HOMA-IR, baseline fasting insulin, ∆fasting insulin, baseline HbA1c, ∆HbA1c, baseline lipid profiles, or creatinine (Table 2).
Table 2.
Correlations between baseline K-MMSE and related factors.
| Correlation coefficient ( r ) | p -value | |
|---|---|---|
| Age, years | −0.016 | 0.746 |
| Education, years | 0.393 | <0.001 |
| Baseline BMI, kg/m2 | −0.058 | 0.240 |
| ∆BMI, kg/m2 | 0.005 | 0.927 |
| Baseline KDSQ, score | −0.129 | 0.008 |
| ∆KDSQ, score | 0.031 | 0.523 |
| Baseline GDS-K, score | −0.128 | 0.008 |
| ∆GDS-K, score | 0.028 | 0.569 |
| Baseline HOMA-IR | 0.006 | 0.902 |
| ∆HOMA-IR | −0.027 | 0.586 |
| Baseline fasting insulin, μIU/L | −0.019 | 0.703 |
| ∆fasting insulin, μIU/L | −0.028 | 0.566 |
| Baseline HbA1c, % (mmol/mol) | 0.034 | 0.481 |
| ∆HbA1c, % (mmol/mol) | −0.048 | 0.326 |
| Baseline LDL-C, mg/dLa | −0.002 | 0.961 |
| Baseline HDL-C, mg/dLa | −0.031 | 0.526 |
| Baseline triglycerides, mg/dLa | −0.020 | 0.974 |
| Baseline creatinine, mg/dL | 0.021 | 0.840 |
K-MMSE, Korean mini mental status examination; KDSQ, Korean dementia screening questionnaire; GDS-K, Korean geriatric depression scale; LDL-C, low-density lipoprotein cholesterol; HDL-C, high-density lipoprotein cholesterol. The ∆ values refer to the change between baseline and follow-up.
aLipid profile was only evaluated among participants who were not receiving dyslipidemia treatment (n = 371).
Correlations of percent changes in K-MMSE with related factors
Pearson’s correlation analyses revealed that a greater decrease in K-MMSE between baseline and follow-up was correlated with older age (r = –0.102, p = 0.037), shorter education duration (r = 0.168, p = 0.001), higher baseline K-MMSE score (r = –0.187, p < 0.001), and increases in HOMA-IR values (r = –0.155, p = 0.001) and fasting insulin levels between baseline and follow-up (r = –0.160, p = 0.001). The percent changes in K-MMSE values were not significantly correlated with the values for baseline BMI, ∆BMI, baseline KDSQ score, ∆KDSQ score, GDS-K score, ∆GDS-K score, baseline HOMA-IR, baseline fasting insulin, baseline HbA1c, ∆HbA1c, lipid profiles, or creatinine (Table 3).
Table 3.
Correlations of percent changes in K-MMSE between baseline and follow-up and related factors.
| Correlation coefficient ( r ) | p -value | |
|---|---|---|
| Age, years | −0.102 | 0.037 |
| Education, years | 0.168 | 0.001 |
| K-MMSE baseline, score | −0.187 | <0.001 |
| BMI, kg/m2 | −0.012 | 0.810 |
| ∆BMI, kg/m2 | 0.044 | 0.370 |
| KDSQ, score | 0.042 | 0.388 |
| ∆KDSQ, score | −0.082 | 0.093 |
| GDS-K, score | 0.006 | 0.909 |
| ∆GDS-K, score | −0.081 | 0.096 |
| HOMA-IR baseline | 0.057 | 0.247 |
| ∆HOMA-IR | −0.155 | 0.001 |
| Fasting insulin, μIU/L | 0.073 | 0.133 |
| ∆fasting insulin, μIU/L | −0.160 | 0.001 |
| HbA1c, % (mmol/mol) | −0.052 | 0.289 |
| ∆HbA1c, % (mmol/mol) | 0.040 | 0.412 |
| LDL-C, mg/dLa | 0.044 | 0.366 |
| HDL-C, mg/dLa | −0.020 | 0.687 |
| Triglyceride, mg/dLa | 0.037 | 0.447 |
| Creatinine, mg/dL | 0.050 | 0.308 |
K-MMSE, Korean mini mental status examination; KDSQ, Korean dementia screening questionnaire; GDS-K, Korean geriatric depression scale; LDL-C, low-density lipoprotein cholesterol; HDL-C, high-density lipoprotein cholesterol. The ∆ values refer to the change between baseline and follow-up.
aLipid profile was only evaluated among participants who were not receiving dyslipidemia treatment (n = 371).
Multivariable linear regression models for percent changes in K-MMSE and the hyperinsulinemia variables
After adjusting model 1 for age, sex, baseline K-MMSE score, education duration, and baseline GDS-K score, we observed that an increase in HOMA-IR was correlated with a reduction in K-MMSE between baseline and follow-up (B = −0.139, p = 0.003). After adjusting for the variables in model 2 (model 1 plus smoking status, distort of diabetes, history of hypertension, and BMI), we observed that the negative correlation between change of HOMA-IR and K-MMSE remained significant (standardized beta [B] = −0.137, p = 0.004). After adjusting for the variables in model 3 (model 2 plus apolipoprotein E ε4 genotype status), the correlation between change of HOMA-IR and K-MMSE remained significant (B = −0.138, p = 0.004). Percent changes in K-MMSE values were not correlated with ∆BMI, ∆GDS-K scores, and ∆HbA1c before and after adjusting covariates before and after adjusting covariates (Table 4).
Table 4.
Multivariable linear regression models of percent changes in K-MMSE between baseline and follow-up and their correlations with metabolic factors.
| B of ∆HOMA-IR | 95% confidence interval | p-value | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Unadjusted | −0.155 | −1.444, −0.349 | 0.001 |
| Model 1 | −0.139 | −1.326, −0.281 | 0.003 |
| Model 2 | −0.137 | −1.304, −0.257 | 0.004 |
| Model 3 | −0.138 | −1.307, −0.256 | 0.004 |
| B of ∆BMI | 95% confidence interval | p-value | |
| Unadjusted | 0.044 | −0.389, 1.044 | 0.370 |
| Model 1 | 0.009 | −0.630, 0.758 | 0.856 |
| Model 2 | 0.015 | −0.597, 0.822 | 0.755 |
| Model 3 | 0.018 | −0.586, 0.850 | 0.717 |
| B of ∆GDS-K | 95% confidence interval | p-value | |
| Unadjusted | −0.081 | −0.517, 0.043 | 0.096 |
| Model 1 | −0.079 | −0.516, 0.051 | 0.107 |
| Model 2 | −0.073 | −0.494, 0.074 | 0.146 |
| Model 3 | −0.074 | −0.501, 0.073 | 0.143 |
| B of ∆HbA1c | 95% confidence interval | p-value | |
| Unadjusted | 0.040 | −0.959, 2.334 | 0.412 |
| Model 1 | 0.009 | −1.422, 1.729 | 0.849 |
| Model 2 | 0.016 | −1.324, 1.875 | 0.735 |
| Model 3 | 0.016 | −1.341, 1.869 | 0.746 |
K-MMSE, Korean mini mental status examination; BMI, body mass index; GDS-K, Korean geriatric depression scale.
Multivariable linear regression analysis was done. B refers to standardized beta value. Model 1 adjusts for age, sex, baseline K-MMSE, education duration, baseline GDS-K. Model 2 adjusts for model 1 factors and additionally adjusts for smoking status, history of diabetes and hypertension, and BMI. Model 3 adjusts for model 2 factors and additionally adjusts for APOE ε4 genotype status.
Discussion
This community-based prospective cohort study of older individuals with normal cognitive function revealed that cognitive decline was associated with a 6-year increase in insulin resistance, after adjusting for age, sex, baseline K-MMSE, education duration, baseline GDS-K, smoking status, history of diabetes, history of hypertension, BMI, and apolipoprotein E ε4 genotype status. Among the various metabolic factors, cognitive dysfunction was associated with changes in insulin resistance, but not with existing or changing hyperglycemia or obesity. Furthermore, greater cognitive declines were observed for participants with greater increases in insulin resistance.
Most previous studies investigating the association of insulin resistance with cognitive dysfunction have used a cross-sectional design, and few longitudinal studies have been performed7–10. During a 6-year follow-up, baseline hyperinsulinemia among middle-aged adults (45–64 years old at baseline) in the Atherosclerosis Risk in Communities cohort was associated with greater cognitive decline7. In addition, a recent 11-year Finnish nation-wide population-based survey revealed that higher baseline HOMA-IR and fasting insulin values independently predicted a greater decline in verbal fluency8. Furthermore, our findings are consistent with previous findings that insulin resistance is related to cognitive decline7,10,25–28. Moreover, we evaluated the relationship between changes in insulin resistance and cognitive decline, and the results suggest that controlling insulin resistance could help prevent cognitive decline in the older population.
Insulin receptors are widely distributed throughout the brain, which suggests that the brain is a major insulin target29. Furthermore, insulin resistance is observed in the neuronal cells of patients with Alzheimer’s disease (AD), which suggests that insulin resistance may cause neuronal cell dysfunction and lead to cognitive dysfunction and dementia30,31. Interestingly, mice receiving a high-fat diet exhibited impaired binding to brain insulin receptors32, which agrees with the findings from the brains of patients with early-stage AD. Therefore, neurons in the brain might be damaged by insulin receptor dysfunction. Moreover, peripheral insulin resistance could induce neuronal damage though amyloid beta and cytokines, as peripheral hyperinsulinemia can increase amyloid beta concentrations33 and plasma and cerebrospinal fluid concentrations of interleukin-6 and tumor necrosis factor alpha34. The increased concentrations of amyloid beta and inflammatory cytokines could induce neuronal loss, amyloid beta plaques, and neurofibrillary tangles35.
The present study did not detect any significant relationship between the baseline HOMA-IR and K-MMSE values. Although many previous studies have identified a positive association between insulin resistance and cognitive dysfunction7,25,27,28, other studies did not detect any significant association36,37. These discrepancies may be related to differences in the study populations and cognitive function assessment methods. For example, studies with positive results generally evaluated individuals who did not have baseline cognitive dysfunction28, were relatively young7 or were women38,39. In addition, insulin resistance may mainly affect executive dysfunction, which is best evaluated using the Trail Making Test39,40 and/or verbal fluency38,41, rather than tools that consider all brain function domains. However, the present study did not detect any significant correlation between cognitive function and insulin resistance when we only analyzed women. Therefore, it appears that methodology differences are more important, rather than sex-based differences.
It is suggested that hyperglycemia is associated with poor cognitive outcomes. It has been shown in both cross-sectional studies42 and prospective studies43, although there are conflicting results. The present study failed to detect a significant correlation between hyperglycemia and cognitive function or change in cognitive function. This may be because the HbA1c range was relatively narrow (caused by the community-based design), while most studies with positive results evaluated patients with diabetes. Moreover, hyperglycemia mainly affects processing speed, attention, and visual-spatial processing44, which may not be accurately assessed using only the MMSE tool.
Although many studies have revealed an association between obesity and the risk of dementia12,14–16,43,44, the association appears to be complex. For example, some reports have indicated that higher BMI was associated with less cognitive decline in a cognitively unimpaired community-dwelling population, and there are reports of increased dementia risk for both obese and underweight people12,15,45. In addition, studies have demonstrated that midlife obesity is more strongly related to dementia, compared to obesity among older people12,14. We did not detect any significant association between BMI and K-MMSE or the change in K-MMSE. This may be related to the participants’ relatively normal BMI (mean 23.9 kg/m2), or midlife BMI having a greater effect on the cognitive function of older individuals, compared to current BMI.
The present study evaluated the participants’ serum cholesterol concentrations after excluding individuals who were receiving dyslipidemia medication. However, the follow-up examinations revealed lower concentrations of triglycerides and LDL-C, and higher concentrations of HDL-C. These changes may be partially explained by aging-related changes46, and enrollment in the cohort may also have improved the participants’ lifestyle, as it was accompanied by an increase in HDL-C concentrations. Furthermore, there is the possibility of recall bias regarding medication histories, as these data were obtained using questionnaire responses, rather than prescription records.
The present study has several strengths. First, to the best of our knowledge, ours is the first study to evaluate the association between changes in insulin resistance and cognitive function. Thus, our findings may help elucidate the importance of controlling insulin resistance to prevent cognitive decline among older individuals. Second, we analyzed data from the Ansung cohort study, which provides a large study sample, a community-based prospective design, and long-term follow-up data with information regarding potential confounding factors. Third, we adjusted for important covariates, including GDS-K score, education duration, history of diabetes, history of hypertension, and apolipoprotein E ε4 genotype status. Fourth, we excluded patients with high GDS scores to minimize the influence of depressiveness on the MMSE results, as depression can be associated with low MMSE scores18. Fifth, we excluded participants with conditions that could influence cognitive function, such as stroke, dementia, depression, and head trauma.
The study also has potential limitations. First, although the current study used data from a large-scale prospective community-based cohort study, only 422 subjects were assessed for cognitive function, which may have limited the assessment of metabolic factors’ effect on cognitive change. Second, the follow-up period may not be sufficient to detect a decrease in cognitive function among individuals with normal baseline cognitive function, and the 6-year change in the MMSE value was relatively small. Third, cognitive function was only evaluated using MMSE, although insulin resistance and hyperglycemia are reportedly more related to verbal performance or executive function. Fourth, increased insulin resistance was associated with a decrease in MMSE during the study, although we did not evaluate whether improvements in insulin resistance prevented cognitive decline. In addition, although the MMSE is a widely used tool for cognitive dysfunction screening, it cannot identify small changes in cognitive function (e.g., cognitive aging) because of a ceiling effect. Therefore, more accurate evaluation of cognitive function must be performed using detailed neurocognitive assessments without ceiling effects.
In conclusion, increased insulin resistance was associated with decreased cognitive function during a 6-year follow-up of older individuals with normal baseline cognitive function. However, baseline HbA1c, baseline BMI, ∆HbA1c, and ∆BMI values were not associated with changes in cognitive function. These relationships were independent of apolipoprotein E ε4 genotype status. Based on our results, further interventional studies are needed to evaluate the effect of controlling insulin resistance on cognitive dysfunction among older individuals.
Author Contributions
S.H.K. and M.K.M researched data and wrote the manuscript. M.K.M., Y.J.P., and J.Y.L. contributed to the discussion and reviewed/edited the manuscript. N.H.C. contributed to the data research and discussion.
Competing Interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Footnotes
Publisher's note: Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Contributor Information
Nam H. Cho, Email: chnaha@ajou.ac.kr
Min Kyong Moon, Email: mkmoon@snu.ac.kr.
References
- 1.Danaei G, et al. National, regional, and global trends in fasting plasma glucose and diabetes prevalence since 1980: systematic analysis of health examination surveys and epidemiological studies with 370 country-years and 2 • 7 million participants. Lancet. 2011;378:31–40. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(11)60679-X. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Ferri CP, et al. Global prevalence of dementia: a Delphi consensus study. Lancet. 2006;366:2112–2117. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(05)67889-0. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Korean Diabetes Association, Korean diabetes fact sheet 2015. http://www.diabetes.or.kr/temp/KDA_fact_sheet%202015.pdf (2015).
- 4.World Health Organization Dementia Fact Sheet. http://www.who.int/mediacentre/factsheets/fs362/en/ (2016).
- 5.Ott A, et al. Association of diabetes mellitus and dementia: the Rotterdam Study. Diabetologia. 1996;39:1392–1397. doi: 10.1007/s001250050588. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Peila R, Rodriguez BL, Launer LJ. Type 2 diabetes, APOE gene, and the risk for dementia and related pathologies. Diabetes. 2002;51:1256–1262. doi: 10.2337/diabetes.51.4.1256. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Young SE, Mainous AG, Carnemolla M. Hyperinsulinemia and cognitive decline in a middle-aged cohort. Diabetes Care. 2006;29:2688–2693. doi: 10.2337/dc06-0915. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Ekblad L. L. et al. Insulin Resistance Predicts Cognitive Decline: An 11-Year Follow-up of a Nationally Representative Adult Population Sample. Diabetes Care dc162001 (2017) [DOI] [PubMed]
- 9.Van den Berg E, De Craen A, Biessels G, Gussekloo J, Westendorp R. The impact of diabetes mellitus on cognitive decline in the oldest of the old: a prospective population-based study. Diabetologia. 2006;49:2015–2023. doi: 10.1007/s00125-006-0333-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Xu WL, von Strauss E, Qiu CX, Winblad B, Fratiglioni L. Uncontrolled diabetes increases the risk of Alzheimer’s disease: a population-based cohort study. Diabetologia. 2009;52:1031–1039. doi: 10.1007/s00125-009-1323-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Bruce DG, et al. Predictors of cognitive decline in older individuals with diabetes. Diabetes Care. 2008;31:2103–2107. doi: 10.2337/dc08-0562. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Whitmer RA, Gunderson EP, Barrett-Connor E, Quesenberry CP, Yaffe K. Obesity in middle age and future risk of dementia: a 27 year longitudinal population based study. BMJ. 2005;330(7054):1360. doi: 10.1136/bmj.38446.466238.E0. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Lamport DJ, Lawton CL, Michael WM, Louise D. Impairments in glucose tolerance can have a negative impact on cognitive function: a systematic research review. Neurosci Biobehavior Rev. 2009;33(3):394–413. doi: 10.1016/j.neubiorev.2008.10.008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Kivipelto M, et al. Obesity and vascular risk factors at midlife and the risk of dementia and Alzheimer disease. Arch. Neurology. 2005;62:1556–1560. doi: 10.1001/archneur.62.10.1556. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Yaffe K, et al. Predictors of maintaining cognitive function in older adults The Health ABC Study. Neurology. 2009;72(23):2029–2035. doi: 10.1212/WNL.0b013e3181a92c36. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Buchman A, Schneider J, Wilson R, Bienias J, Bennett D. Body mass index in older persons is associated with Alzheimer disease pathology. Neurology. 2006;67:1949–1954. doi: 10.1212/01.wnl.0000247046.90574.0f. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Baik I, et al. Association of snoring with chronic bronchitis. Arch Int Med. 2008;168:167–173. doi: 10.1001/archinternmed.2007.8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Cho YS, et al. A large-scale genome-wide association study of Asian populations uncovers genetic factors influencing eight quantitative traits. Nat Genet. 2009;41:527–534. doi: 10.1038/ng.357. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Xu W, Qiu CX, Wahlin Å, Winblad B, Fratiglioni L. Diabetes mellitus and risk of dementia in the Kungsholmen project A 6-year follow-up study. Neurology. 2004;63:1181–1186. doi: 10.1212/01.WNL.0000140291.86406.D1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Kang Y, Na DL, Hahn S. A validity study on the Korean Mini-Mental State Examination (K-MMSE) in dementia patients. J Korean Neurol Assoc. 1997;15:300–308. [Google Scholar]
- 21.Yang DW, Chey JY, Kim SY, Kim BS. The development and validation of Korean dementia Screening questionnaire (KDSQ) J Korean Neurol Assoc. 2002;20:135–141. [Google Scholar]
- 22.Bae JN, Cho MJ. Development of the Korean version of the Geriatric Depression Scale and its short form among elderly psychiatric patients. J Psychosomat Res. 2004;57:297–305. doi: 10.1016/j.jpsychores.2004.01.004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Hixson JE, Vernier DT. Restriction isotyping of human apolipoprotein E by gene amplification and cleavage with HhaI. J Lipid Res. 1990;31:545–548. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Matthews DR, et al. Homeostasis model assessment: insulin resistance and beta-cell function from fasting plasma glucose and insulin concentrations in man. Diabetologia. 1985;28:412–419. doi: 10.1007/BF00280883. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Razay G, Wilcock GK. Hyperinsulinaemia and Alzheimer’s disease. Age Ageing. 1994;23:396–399. doi: 10.1093/ageing/23.5.396. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Matsuzaki T, et al. Insulin resistance is associated with the pathology of Alzheimer disease The Hisayama Study. Neurology. 2010;75:764–770. doi: 10.1212/WNL.0b013e3181eee25f. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Luchsinger JA, Tang M-X, Shea S, Mayeux R. Hyperinsulinemia and risk of Alzheimer disease. Neurology. 2004;63:1187–1192. doi: 10.1212/01.WNL.0000140292.04932.87. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Kuusisto J, et al. Association between features of the insulin resistance syndrome and Alzheimer’s disease independently of apolipoprotein E4 phenotype: cross sectional population based study. BMJ. 1997;315:1045–1049. doi: 10.1136/bmj.315.7115.1045. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Werther GA, et al. Localization and characterization of insulin receptors in rat brain and pituitary gland using in vitro autoradiography and computerized densitometry. Endocrinology. 1987;121:1562–1570. doi: 10.1210/endo-121-4-1562. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Steen E, et al. Impaired insulin and insulin-like growth factor expression and signaling mechanisms in Alzheimer’s disease–is this type 3 diabetes? J Alzheimer Dis. 2005;7:63–80. doi: 10.3233/JAD-2005-7107. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Moloney AM, et al. Defects in IGF-1 receptor, insulin receptor and IRS-1/2 in Alzheimer’s disease indicate possible resistance to IGF-1 and insulin signalling. Neurobiol Aging. 2010;31:224–243. doi: 10.1016/j.neurobiolaging.2008.04.002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Moroz N, Tong M, Longato L, Xu H, de la Monte SM. Limited Alzheimer-type neurodegeneration in experimental obesity and type 2 diabetes mellitus. J Alzheimer Dis. 2008;15:29–44. doi: 10.3233/JAD-2008-15103. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Watson GS, Craft S. The role of insulin resistance in the pathogenesis of Alzheimer’s disease: implications for treatment. CNS Drugs. 2003;17:27–45. doi: 10.2165/00023210-200317010-00003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Craft S. Insulin resistance syndrome and Alzheimer’s disease: age-and obesity-related effects on memory, amyloid, and inflammation. Neurobiol Aging. 2005;26:65–69. doi: 10.1016/j.neurobiolaging.2005.08.021. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Fishel MA, et al. Hyperinsulinemia provokes synchronous increases in central inflammation and β-amyloid in normal adults. Arch Neurol. 2005;62:1539–1544. doi: 10.1001/archneur.62.10.noc50112. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Isik AT, et al. Is there any relation between insulin resistance and cognitive function in the elderly? Int Psychogeriatr. 2007;19:745–756. doi: 10.1017/S1041610207005406. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Stolk RP, et al. Insulin and cognitive function in an elderly population. The Rotterdam Study. Diabetes Care. 1997;20:792–795. doi: 10.2337/diacare.20.5.792. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Ekblad LL, et al. Insulin resistance is associated with poorer verbal fluency performance in women. Diabetologia. 2015;58:2545–2553. doi: 10.1007/s00125-015-3715-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Schuur M, et al. Insulin-resistance and metabolic syndrome are related to executive function in women in a large family-based study. Eur J Epidemiol. 2010;25:561–568. doi: 10.1007/s10654-010-9476-y. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Abbatecola AM, et al. Insulin resistance and executive dysfunction in older persons. J Am Geriatr Soc. 2004;52:1713–1718. doi: 10.1111/j.1532-5415.2004.52466.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Benedict C, et al. Impaired insulin sensitivity as indexed by the HOMA score is associated with deficits in verbal fluency and temporal lobe gray matter volume in the elderly. Diabetes Care. 2012;35:488–494. doi: 10.2337/dc11-2075. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Yaffe K, et al. Diabetes, glucose control, and 9-year cognitive decline among older adults without dementia. Arch Neurol. 2012;69:1170–1175. doi: 10.1001/archneurol.2012.1117. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Prickett C, Brennan L, Stolwyk R. Examining the relationship between obesity and cognitive function: A systematic literature review. Obes Res Clin Pract. 2015;9:93–113. doi: 10.1016/j.orcp.2014.05.001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44.Dahl AK, Hassing LB. Obesity and cognitive aging. Epidemiol Rev. 2013;35:22–32. doi: 10.1093/epirev/mxs002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45.Sturman M, et al. Body mass index and cognitive decline in a biracial community population. Neurology. 2008;70:360–367. doi: 10.1212/01.wnl.0000285081.04409.bb. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46.Ettinger WH, et al. Lipoprotein lipids in older people. Results from the Cardiovascular Health Study. The CHS Collaborative Research Group. Circulation. 1992;86:858–869. doi: 10.1161/01.CIR.86.3.858. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Data Availability Statement
The datasets generated during and/or analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.