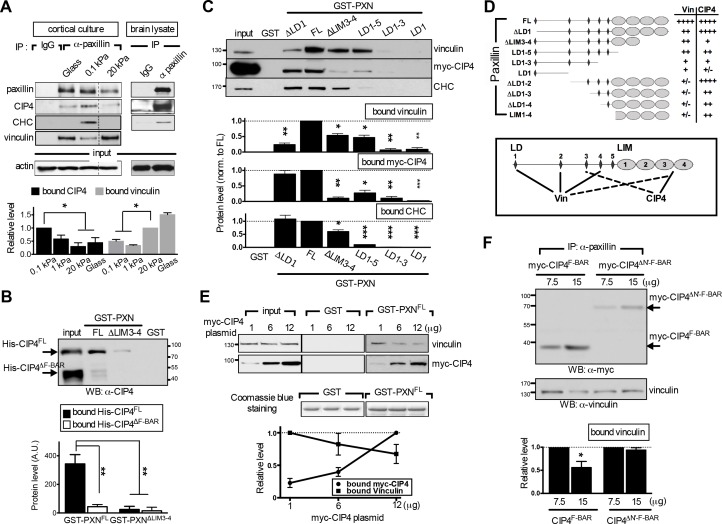
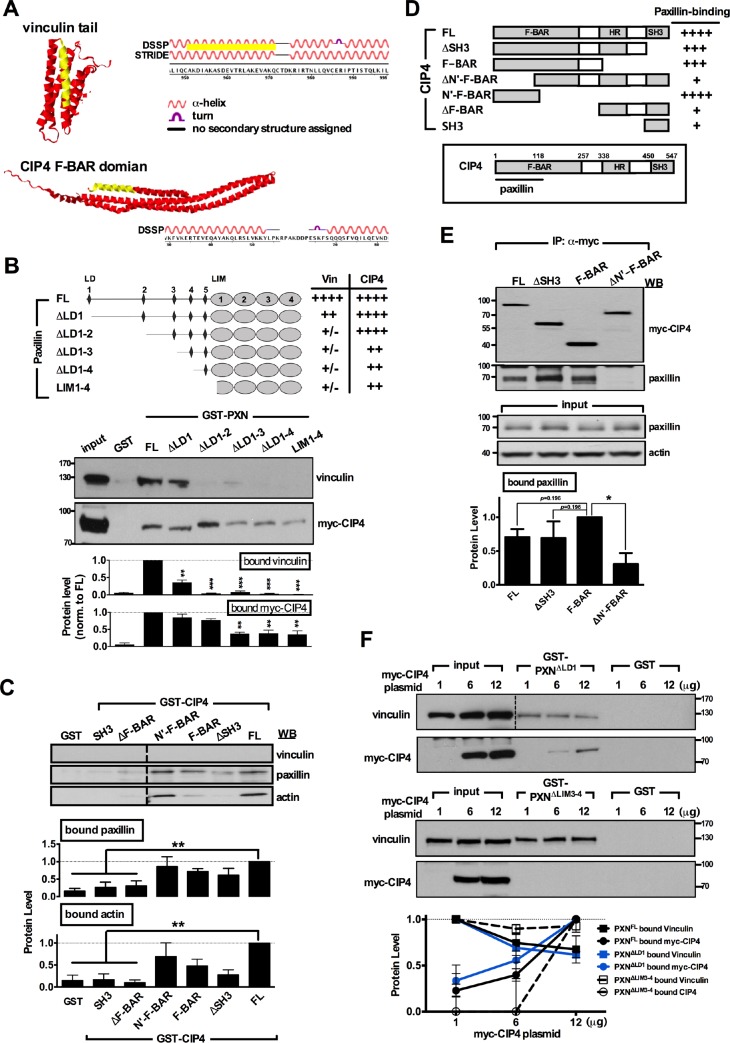
Figure 4. The endocytic F-BAR protein CIP4 directly associates with paxillin and competes with vinculin for paxillin binding.
(A) Paxillin preferentially binds endocytic factors in neurons grown on soft substrates. Paxillin-associated complexes were immunoprecipitated (IP) in lysates made from E17.5 rat brain or from cortical neuronal cultures grown on different substrates using a specific paxillin antibody and were then detected by western blot analysis. Normal rabbit IgG (‘IgG’) served as a negative control. Histograms show the opposing binding preference of paxillin toward CIP4/CHC or vinculin when grown on soft (0.1 kPa or 1 kPa) versus rigid (20 kPa or glass) substrates. Data represent mean intensity ±SEM (n = 3 independent experiments; *p<0.05; t-test). (B) Western blot showing direct interaction of paxillin with CIP4. Bacterially expressed His-CIP4 was purified by fast protein liquid chromatography and subjected to a GST pull-down assay using GST-PXNFL, GST-PXN∆LIM3-4 or GST alone. Precipitants were analyzed by western blotting with antibodies specific to CIP4. Histograms summarize protein levels as determined by immunoblotting of full-length (His-CIP4) or F-BAR domain-deleted (His-ΔF-BAR) CIP4 pulled-down by GST-paxillin variants (±SEM, n = 3; normalized to the corresponding GST-PXNFL or GST-PXN∆LIM3-4 inputs; **p<0.01, t test). (C and D). Mapping of paxillin domains interacting with CIP4 or vinculin. (C) GST pull-down and immunoblotting of vinculin, myc-CIP4, and CHC in lysates of myc-CIP4-expressing HEK293T cells. Histograms reflect quantification of levels of proteins pulled-down by GST fusions of full-length (“FL“) or LIM domain- and/or LD motif-deleted forms of paxillin, all from experiments similar to those shown in top panels (±SEM, n ≥ 3 independent experiments; *p<0.05; **p<0.01; ***p<0.001; t test). (D) Schematic of GST fusion proteins used in c. Table summarizing relative CIP4 or vinculin (‘Vin’) binding by paxillin deletion mutants or full-length protein. Solid lines mark primary sites of interaction, and dashed lines mark accessory interaction motifs for strong binding to vinculin or CIP4. Binding strength relative to full-length paxillin indicated as: ‘++++' >75% > ‘+++' >50% > ‘++' >25% > '+' >5% > '+/-'. (E) In vitro protein interaction and competitive binding assays in HEK293T cells transfected with various amounts (1, 6, and 12 µg) of plasmids encoding myc-tagged CIP4 protein (myc-CIP4) and/or control vectors, as indicated. Cell lysates were subjected to a GST pull-down assay with GST-PXNFL or GST alone, and immunoblotted with vinculin and myc antibodies. Line chart depicts averaged protein levels as determined by immunoblotting of CIP4 or vinculin pulled-down by GST-PXNFL (±SEM, n = 4; normalized to band intensity of corresponding GST-paxillin variant). (F) In vivo protein interaction and competitive binding assays in HEK293T cells transfected with various amounts (7.5 μg and 15 μg) of plasmids encoding the F-BAR domain (‘F-BAR’) alone or F-BAR-domain-deleted (‘ΔN’-F-BAR’) CIP4 and/or control vectors, as indicated. Cell lysates were immunoprecipitated by paxillin antibodies and blotted with myc or vinculin antibodies. Histograms show relative protein levels as determined by immunoblotting of vinculin co-immunoprecipitated by paxillin antibodies (±SEM, n = 3; *p<0.05, t test).