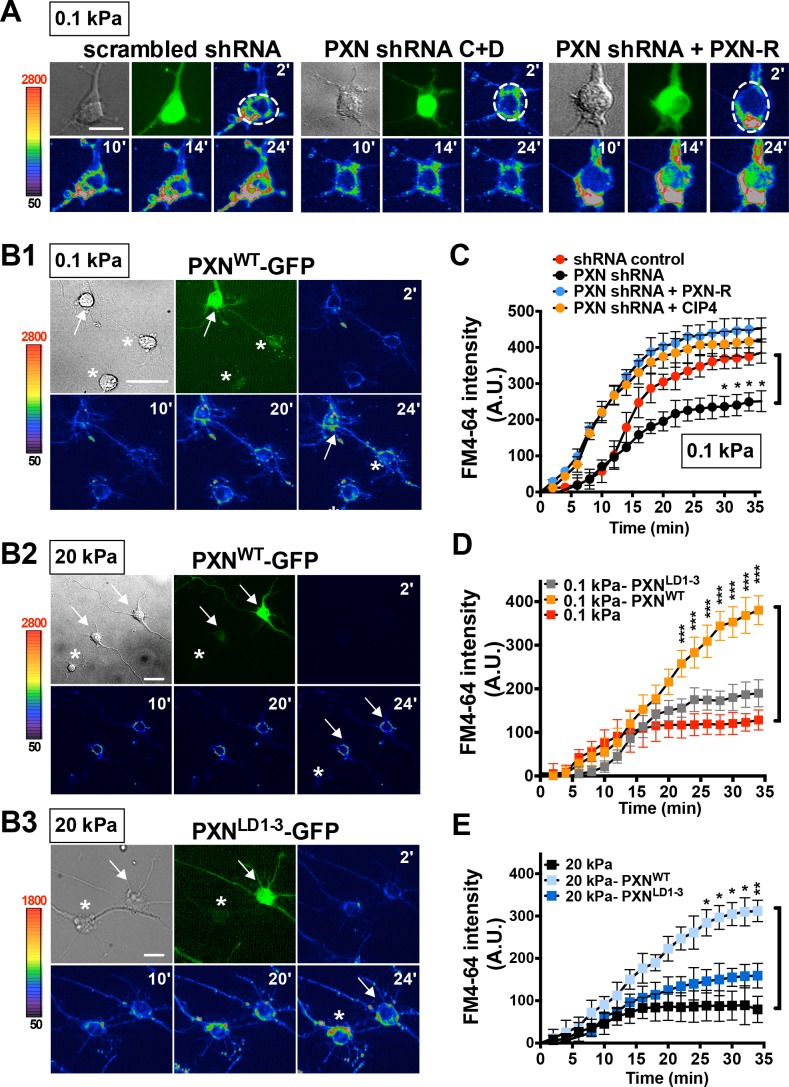
Figure 5. Paxillin is required for endocytosis promoted by a soft surface.
(A) Paxillin knockdown suppresses the endocytic activity of neurons grown on 0.1 kPa gels. Representative time-lapse images of FM4-64 uptake in 3-DIV neurons on substrates of varying elasticity. Hippocampal neurons on 0.1 kPa gels were transduced with lentiviral particles harboring an shRNA-resistant construct (‘PXN-R’) and/or constructs harboring scrambled control or paxillin (‘PXN shRNA C + D’) shRNA at 5 hr after cell plating. Dashed circles surround the region of interest (ROI) in quantitative FM4-64 measurements. Bar: 20 μm. (B) Similar to A, except constructs encoding GFP fusions of wild-type paxillin (‘PXNWT-GFP’; B1 and B2) or the corresponding LIM domain deletion mutant (‘PXNLD1-3-GFP’; B3) were used for lentiviral transduction. Asterisk: non-transduced neighboring cells. Arrows: neurons expressing GFP-tagged paxillin proteins. Bar: 20 μm. (C–E) Quantitative measurements of cumulative FM4-64 intensity (±SEM, n > 3 independent experiments, 7–12 cells for each set of experiments; *p<0.05; **p<0.001; ***p<0.0001; compared to control groups; multiple t tests), all from experiments similar to those described in A and B. Note that ectopic expression of wild-type paxillin, but not PXNLD1-3, restored rapid endocytic FM4-64 uptake on 20 kPa stiff gels.