Summary
Human breast cancer cells are known to activate adjacent “normal-like” cells to enhance their own growth, but the cellular and molecular mechanisms involved are poorly understood. We now show by both phenotypic and functional measurements that normal human mammary progenitor cells are significantly under-represented in the mammary epithelium of patients' tumor-adjacent tissue (TAT). Interestingly, fibroblasts isolated from TAT samples showed a reduced ability to support normal EGF-stimulated mammary progenitor cell proliferation in vitro via their increased secretion of transforming growth factor β. In contrast, TAT fibroblasts promoted the proliferation of human breast cancer cells when these were co-transplanted in immunodeficient mice. The discovery of a common stromal cell-mediated mechanism that has opposing growth-suppressive and promoting effects on normal and malignant human breast cells and also extends well beyond currently examined surgical margins has important implications for disease recurrence and its prevention.
Keywords: breast cancer, activated stromal fibroblasts, TGF-β, tumor-adjacent tissue, suppression of normal breast tissue progenitors
Graphical Abstract
Highlights
-
•
Alterations to the breast tissue extend as far as 6 cm away from the primary tumors
-
•
The matching contralateral non-tumor-bearing breast tissue remains unaltered
-
•
Tumor-adjacent breast tissue contained significantly diminished progenitor pool
-
•
Extending surgical margins may not be effective in reducing risk of tumor recurrence
Because breast-conserving surgeries are popular among breast cancer patients, studying the “normal” tissue remaining after the surgery is important for understanding how this tissue is primed to promote the growth of residual tumor cells. In this article, Raouf and colleagues show that tumor-adjacent breast tissue contains altered fibroblasts that diminish normal progenitor proliferation while augmenting breast cancer cell growth.
Introduction
Breast-conserving surgeries are now widely used for women with small invasive breast cancers as well as ductal carcinoma in situ (Morrow et al., 2009). However, up to 10% of the women with small invasive cancers experience local tumor recurrence within 10 years (Early Breast Cancer Trialists' Collaborative Group et al., 2011, Fisher et al., 2002, Mamounas et al., 2012, Silverstein et al., 1999, Veronesi et al., 2002) and, in the absence of supplementary radiation treatment, this risk is increased 4-fold. These findings have suggested the possibility that the “normal” tissue remaining after the surgery is primed to promote the growth of residual tumor cells (Fisher et al., 2002, Kunkler et al., 2015, Vinh-Hung and Verschraegen, 2004). This concept in turn, has raised unanswered questions as to the optimal distance to adopt in extending the surgical margin beyond the apparent limit of the primary tumor mass (McCahill et al., 2012, Morrow et al., 2012, Taghian et al., 2005, Young et al., 2007).
Historically, the histologically normal-appearing mammary tissue adjacent to breast tumors has long been used as a comparator to identify tumor-specific mutations and gene expression signatures in the adjacent malignant cells (Banerji et al., 2012, Curtis et al., 2012, Pereira et al., 2016, Shah et al., 2012). However, this tumor-adjacent tissue (TAT) obtained from as far away as 2 cm from the primary tumor has been found to contain shorter telomeric DNA and increased prevalence of loss of heterozygosity loci similar to the primary tumor cells (Deng et al., 1996, Forsti et al., 2001, Teschendorff et al., 2016, Zhou et al., 2012). In addition, the transcriptomes of TAT samples often approximate a gene expression signature of invasive breast cancer, and can be predictive of disease progression in early premalignant lesions (Allinen et al., 2004, Finak et al., 2008, Graham et al., 2011). TAT transcriptomes that include features of wound healing and transforming growth factor β (TGF-β) signaling have also been found to correlate with reduced patient overall survival (Finak et al., 2006, Roman-Perez et al., 2012, Sun et al., 2013). Similarly, DNA methylation profiling of matched breast tumors and TAT samples has revealed common patterns, some of which appear inversely related to the altered gene expression profiles in these cells (Fleischer et al., 2014). Overall, TAT samples have been reported to show increased DNA methylation compared with unrelated samples of healthy breast tissue, but to a lesser extent than that seen in malignant breast cells (Teschendorff et al., 2016). Interestingly, fibroblasts isolated from TAT samples obtained up to 1 cm away from primary breast tumors were found to induce epithelial to mesenchymal transition (EMT) in normal mammary cells and promote the migration of malignant mammary cells (Gao et al., 2010, Hsu et al., 2017). However, measurements of the frequency or functional property of the mammary progenitors present in TAT regions has not been previously examined.
To address this gap, we isolated and characterized the progenitor cells in TAT samples obtained up to 6 cm from primary estrogen receptor-positive (ER+) as well as the ER− primary tumors. The results show the progenitor compartments to be significantly reduced compared with similarly analyzed cells from healthy reduction mammoplasty tissue. We further show that the TAT samples, but not the matching contralateral non-tumor-bearing breast tissue, contain TGF-β-secreting fibroblasts that replicate this effect on normal progenitors by decreasing expression of α6-integrin (CD49f) and the epithelial cell adhesion molecule (EpCAM). In addition, these cells promote breast cancer cell proliferation. These findings provide evidence of breast cancer-activated production of TGF-β that acts simultaneously as a promoter of tumor cell growth and a localized suppressor of progenitor activity in immediate adjacent “normal” tissue.
Results
Tumor-Adjacent Breast Tissue Contains Decreased Expression of CD49f and EpCAM and Has a Diminished Progenitor Pool
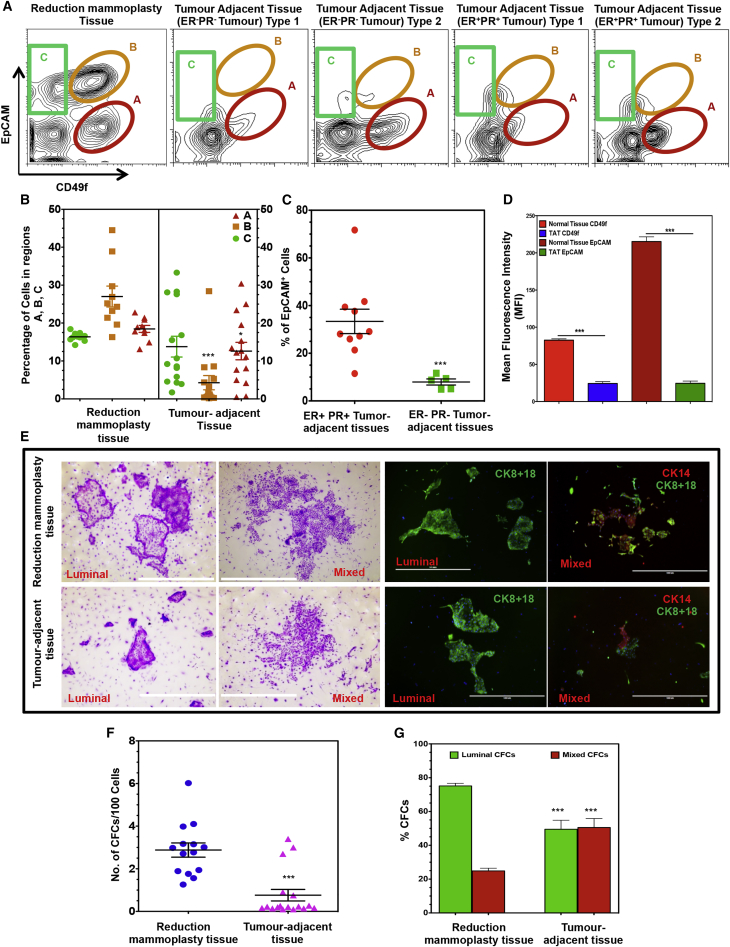
Figure 1 illustrates the sorting strategy used to separate the Lin−EpCAMlowCD49fhigh (bipotent progenitor-enriched) fraction, the Lin−EpCAMhighCD49flow (luminal progenitor-enriched) fraction, and the Lin−EpCAMhighCD49f− (mature luminal cell) fraction (regions A, B, and C, respectively) (Eirew et al., 2008, Eirew et al., 2012). Comparison of these phenotype distributions obtained from 15 different TAT-far and 10 normal reduction mammoplasty samples showed the TAT samples contained significantly reduced proportions of the luminal progenitor-enriched (27% ± 8.6% versus 4.2% ± 7.2%) and bipotent-enriched (18.4% ± 2.9% versus 12.6% ± 8.8%) subsets (Figure 1B). EpCAM+ cells were also found to be more prevalent in the TAT samples obtained from patients with ER+PR+ compared with ER−PR− tumors (29.1% ± 9.5% compared with 7.9% ± 2.9%; Figure 1C). Total CD49f and EpCAM protein expression was also significantly decreased in the TAT samples compared with the healthy breast cells (3.8- ± 0.6-fold and 11- ± 2-fold, respectively; Figure 1D).
Figure 1.
Decreased CD49f and EpCAM Expression and Progenitor Content of TAT Samples
(A) Representative FACS plots showing population A, a bipotent progenitor-enriched EpCAMlowCD49fhigh fraction; population B, a luminal progenitor-enriched EpCAMhighCD49flow fraction; and population C, a CD49f−EpCAMhigh fraction that lacks progenitor activity in the different types of tissues analyzed. TAT samples were divided into those where population A comprised either <15% or >15% of the Lin− cells and are shown separately for patients whose tumors were ER−PR− or ER+PR+.
(B) Comparison of the relative numbers of different populations shown in (A) obtained from 15 different TAT-far (patient nos. 1–15; Table S1) and 10 normal reduction mammoplasty samples were analyzed. Both populations A (p < 0.05) and B (p < 0.001) were reduced relative to their counterparts in normal breast tissue. Values shown are the mean ± SEM.
(C) TAT samples from 5 ER− tumors (patient nos. 1, 2, 3, 7, and 10; Table S1) contained a smaller proportion of EpCAM+ Lin− cells (p < 0.001) compared with those next to 10 ER+ tumors (patient nos. 4–6, 8, 9, and 11–15; Table S1). Values shown are the means ± SEM.
(D) Comparison of average mean fluorescent intensities (MFI) of CD49f and EpCAM in 10 normal and 15 different TAT samples (patient nos. 1–15; Table S1). Values shown are the means ± SEM.
(E) Representative photographs of colonies obtained from freshly isolated CFCs from normal breast and TAT samples. Luminal colonies were identified based on their exclusive content of cytokeratin 8/18+ cells and mixed colonies based on their content of both cytokeratin 8/18+ and cytokeratin 14+ cells in the same colony. Scale bars represent 400 μm.
(F) Comparison of the CFC frequencies in Lin− cells obtained from 14 different normal breasts and 15 different TAT samples (patient nos. 1–15; Table S1). Values shown are the means ± SEM.
(G) Comparison of the frequencies of the separate CFC subtypes in the Lin− cells from 14 different normal breast tissue and 15 different TAT samples (patient nos. 1–15; Table S1) assessed in (F). Values shown were derived from counting stained colonies and are means ± SEM from 15 experiments (∗∗∗p < 0.0001).
Colony-forming cell (CFC) assays performed on these samples showed the expected mixed, luminal-only and myoepithelial-only progenitor differentiation activity of each phenotype in both TAT and normal tissue samples (Figure 1E). However, the TAT samples contained significantly fewer progenitor cells compared with the reduction mammoplasty samples (7.05- ± 1.0-fold lower; Figure 1F). The TAT samples also showed a selective reduction in luminal-restricted progenitors compared with their counterparts in normal tissue, consistent with the changes seen in their expected phenotypes (Figure 1G). Interestingly, the TAT-far samples showed a similar decrease in relative progenitor content as the TAT-near samples (Figure S1B), which was independent of the age of the donor whether normal (Figure S1C; median age = 42, r = 0.476) or TAT samples (Figures S1D and S1E; median age = 45, r = 0.093). In addition, we found that the organoids including some branching acinar structures generated in 3-week Matrigel cultures of normal breast cells were not obtained from the TAT samples although minimal branching from these was observed in cultures when the frequency of EpCAM+ cells was high (>40%) (Figure S1F).
TAT Fibroblasts Suppress Normal CFC Production In Vitro
Stromal fibroblasts play essential roles in regulating stem and progenitor cell functions in the mammary gland (Kuperwasser et al., 2004, Makarem et al., 2013). To determine whether fibroblasts in TAT regions contribute to the altered progenitor prevalence in the mammary populations contained therein, we tested their ability to support the clonogenic activity of normal breast epithelial progenitor cells compared with that of fibroblasts isolated from normal reduction mammoplasty samples. Initial characterization of the cells in the early passage cultures from which the fibroblasts were obtained confirmed their consistent expression of fibroblast-specific protein 1 and absence of EpCAM+, CD45+, and CD31+ cells, indicating a consistent absence of mammary epithelial cells, hematopoietic cells, and vascular endothelial cells (Figures S2A and S2B). Fibroblasts derived from both TAT and tumor samples showed strong expression of markers for activated fibroblasts (αSMA and FAP proteins) while the fibroblasts obtained from the mammoplasty tissue showed very little or no expression of these markers (Figures S2B and S2C). These results suggest that the fibroblasts resident in the TATs have an activated phenotype similar to the fibroblasts obtained from within the tumor mass.
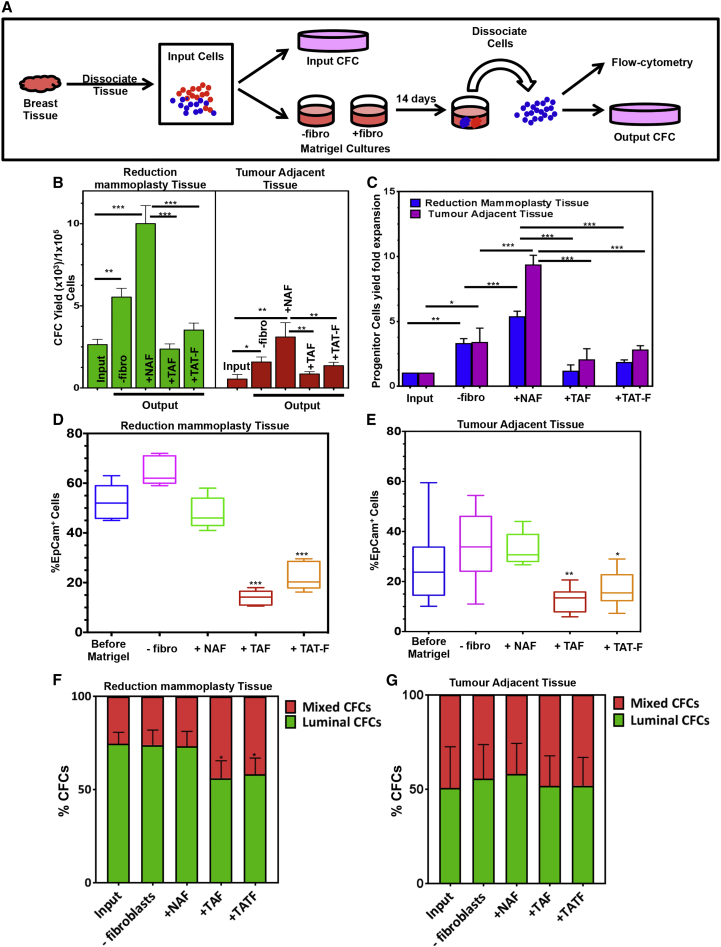
We next compared the ability of fibroblasts obtained from TAT and normal mammoplasty sources to support normal mammary CFC expansion in 3D Matrigel cultures. Addition of irradiated mouse NIH3T3 fibroblasts supported a nearly 1,000-fold increase in the number of mammary CFCs present after 3 weeks in vitro (Figure 2A), as reported previously (Makarem et al., 2013). Here, we found that a 2.6- ± 0.3-fold increase in CFCs was obtained from Lin− cells from healthy breast tissue when no fibroblasts were added and this doubled (to a 4.9- ± 0.4-fold increase over input) when normal fibroblasts from the normal breast reduction tissue samples were included (Figures 2B, 2C, and S3A). Under the latter conditions, the frequency of CD49f+ (Figure 2D) and EpCAM+ cells (Figure 2E) in the harvested cells was preserved. Parallel examination of the yield of CFCs in both 2D and mammosphere cultures initiated with the same cells showed that, within three to four passages, respectively, the CFC yields were substantially reduced below input levels (Figures S3B and S3C). Accordingly, all subsequent studies of CFC generation in vitro were undertaken using the Matrigel culture system.
Figure 2.
TAT-Derived Fibroblasts Show a Decreased Ability to Support Progenitor Cell Expansion in Matrigel Cultures
(A) Experimental design.
(B) Effect of including fibroblasts from 5 different normal and 5 different TAT (patient nos. 3, 4, 6, 9, and 10; Table S1) breast tissues on CFC yields from 14-day Matrigel cultures initiated with normal breast (11 different samples) or TAT (10 different samples, patient nos. 2, 3, 4–9, 11, and 12) Lin− cells. Values shown are the means ± SEM from experiments.
(C–E) Same data as in (B) expressed as fold changes relative to the corresponding input values. Parallel comparison of FACS-determined frequencies of EpCAM+ cells obtained in cultures initiated with Lin− normal (D) or Lin− TAT (E) cells. Box and Whisker plots are used to show the median and the min to max range of the values.
(F) Effect of different sources of fibroblasts, same as described in (B), on the relative yields of luminal and bipotent CFCs compared with the input ratio of these cells in cultures initiated with normal mammary cells.
(G) Parallel data as in (F) but for cultures initiated with Lin− TAT cells.
Values shown are the means ± SEM. ∗p < 0.05, ∗∗p < 0.005, ∗∗∗p < 0.0005.
Parallel investigation of the effects of fibroblasts from both normal (reduction mammoplasty) breast tissue, from TAT samples, and from breast tumors on the generation of CFCs from normal and TAT-derived Lin− cells showed that, in the absence of added fibroblasts, the percentages of EpCAM+ cells and yield of CFCs from Lin− TAT cells were both increased above the input values, although the results were highly variable (Figures 2B–2E). When the same cells or normal Lin− cells were co-cultured with TAT fibroblasts, the proportion of EpCAM+ cells decreased. However, when the Lin− TAT cells were co-cultured with normal fibroblasts, there was a consistent increase in EpCAM+ cells and a 9.1- ± 1.8-fold increase in CFC numbers over the input values. Interestingly, this was not achieved when Lin− TAT or normal breast cells were co-cultured with fibroblasts isolated from tumor tissue. In this latter case, the initial low frequency of EpCAM+ cells did not change and there was no increase in the yield of CFCs (Figures 2B, 2C, and 2E). We also noted that the addition of fibroblasts from either TAT or tumor sources to cultures of normal Lin− breast cells reduced the proportion of luminal CFCs recovered more markedly than the number of bipotent CFC (as indicated by the ratios of these), thus mimicking the reduced proportion of luminal CFCs present in the fresh TAT samples (Figure 2F). However, this ratio was not further eroded in the Lin− TAT cultures regardless of the source of fibroblasts added (Figure 2G).
As a further control, we compared the effect of fibroblasts isolated from breast tissue contralateral to the tumor-bearing breast (CNTB) from three patients on the CFC yield in co-cultures with Lin− cells from normal breast tissue (Figure S4A). The results were similar to those obtained with fibroblasts isolated from normal donors (Figures S4B–S4D).
TAT Fibroblasts Produce an Abnormal TGF-β-Enriched Environment
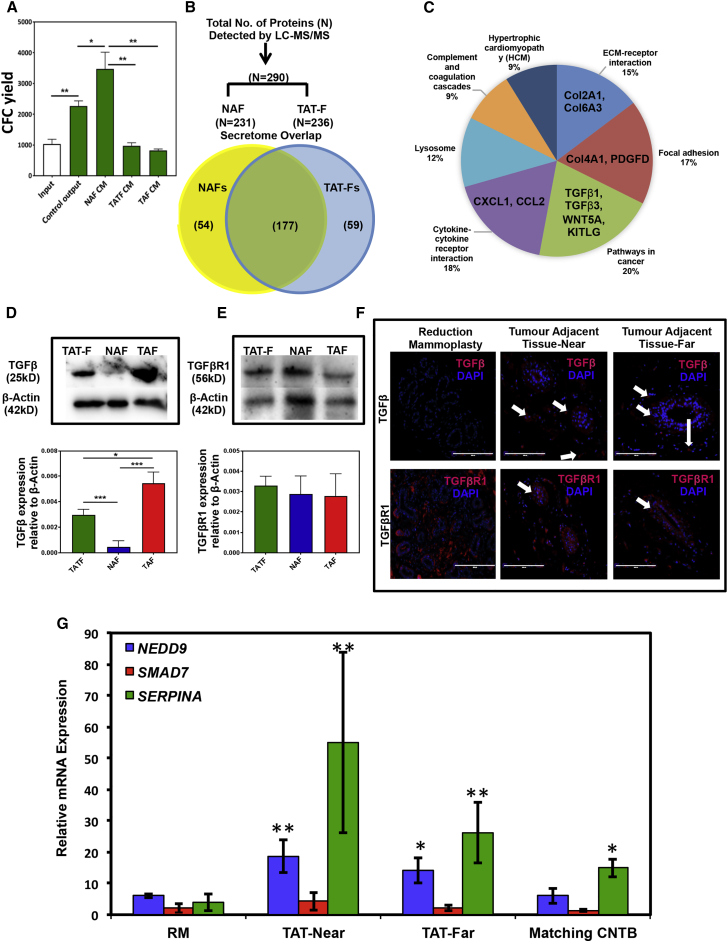
To investigate the possibility that the negative effects displayed by fibroblasts isolated from within breast cancers on mammary CFCs in vitro are mediated by differentially secreted factors, we cultured Lin− cells from normal breast tissue in 3D Matrigel with conditioned media (CM) collected from different sources of fibroblasts for 14 days. CM from normal breast tissue-derived fibroblasts (NAF) significantly increased the progenitor cell proliferation compared with the control, whereas CM from TAT and tumor tissue-derived fibroblasts (TATF and tumor-associated fibroblasts [TAFs], respectively) inhibited the progenitor cell proliferation (Figure 3A). To identify the secreted factors responsible for this negative effect displayed by TAT-Fs, we used 2D liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry (LC-MS/MS) to compare CM prepared from normal or TAT-derived fibroblasts. An unbiased analysis of these results revealed that the normal breast and TAT-derived fibroblasts shared a similar secretome profile (i.e., 177 proteins out of 290 were shared; Figure 3B; Tables S2 and S3). However, we also identified 59 and 54 proteins that were unique to the secretome profiles of the TAT and normal fibroblasts, respectively (Figure 3B). Interestingly, among the former, pathways in cancer and cytokine-cytokine receptor interaction were highlighted (Figure 3C), whereas the unique elements of the normal fibroblast secretome were restricted to lysosome signaling based on the KEGG database (data not shown). Among the proteins in cancer pathways, TGF-β signaling was strongly represented (Figure 3C; Table S3).
Figure 3.
TAT Fibroblasts Exhibit a TGF-β-Enriched Secretome Signature and Abnormal Presence of TGF-β in Histologically Normal TAT Samples
(A) Effect of conditioned medium collected from 3 different normal and 3 different TAT-derived (patient nos. 3, 4, and 6; Table S1) fibroblasts on CFC yields from 14-day Matrigel cultures initiated with normal breast (3 different samples) Lin− cells. Values shown are the means ± SEM from experiments.
(B) Comparison of differentially expressed proteins in the secretome of fibroblasts derived from 3 different normal breast and 3 different TAT samples (patient nos. 3, 4, and 6; Table S1) determined by unbiased, high content comparison of mass spectrometric analysis (MS) of liquid chromatographically (LC) purified proteins in 48-hr conditioned medium.
(C) Display of relative numbers of uniquely secreted proteins analyzed using the KEGG Pathway Database (Table S3). Western blot analysis of TGF-β (D) and TGF-βR1 (E) in fibroblasts obtained from 3 different TAT samples (patient nos. 3, 4, and 6; Table S1), 3 different normal breast tissues and 3 different TAT sample matched tumor tissues (patient nos. 3, 4, and 6; Table S1). The upper panels show representative blots and the lower panels show the average expression values obtained from analyses of 3 different fibroblast lines using Actin as the loading control. Values shown are the means ± SEM.
(F) Representative histological sections prepared from normal breast and TAT samples stained with anti-TGF-β and anti-TGF-βR1 antibodies (in red) with DAPI used to visualize cell nuclei (blue color). Photomicrographs shown are representative of 3 experiments. Arrows in the pictures show the presence of TGF-β (upper panel) or TGF-βR1 (lower panel) in the tumour adjacent “near” or “far” tissue sections. Scale bars represent 200 μm.
(G) Transcript levels of known TGF-β target genes (SERPIN-A, SMAD7, and NEDD9) determined by qPCR in the different tissue samples shown. Results are from 3 different normal and 3 matched TAT-near, TAT-far and contralateral non-tumor containing breast (CNTB) samples (patient nos. 4, 6, and 12; Table S1) after being normalized against GAPDH transcript levels.
Values shown are the means ± SEM. ∗p < 0.05, ∗∗p < 0.005, ∗∗∗p < 0.0005.
To evaluate whether TGF-β might be responsible for the negative effects of TAT-derived fibroblasts on mammary CFC generation in vitro, we examined TGF-β and the TGF-βR1 expression in these fibroblasts and compared it with the fibroblasts obtained from the matching tumor samples and to those from normal breast tissue. The levels of TGF-β in the normal fibroblasts were undetectable, whereas those obtained from both the tumors and TAT samples showed strong TGF-β protein expression (Figure 3D), but this was higher in the fibroblasts from the tumors. Among the TAT-derived fibroblasts, no significant difference in TGF-β expression was observed. In contrast, TGF-βR1 protein was ubiquitously expressed in all three sources of fibroblasts (Figure 3E), although TGF-βR1 transcripts where present at a lower level in the normal fibroblasts (Figure S5A). Immunofluorescence staining revealed strong TGF-β protein expression in the TAT-near and -far tissues, whereas TGF-β protein was not detectable in healthy breast tissue (Figure 3F). Strong TGF-βR1 expression was detected in all tissues examined. However, in the normal tissue, TGF-βR1 expression was predominantly confined to the fibroblasts and basal mammary (myoepithelial) cells, but was also seen in the luminal cells in the TAT samples (Figure 3F). TGF-β target genes such as SERPIN-A and NEDD9 were also significantly upregulated in TAT-near and -far samples compared with the healthy breast tissues or to the matched CNBT breast tissue samples (Figure 3G) These observations suggest that while TGF-β is not normally present in healthy breast tissue, it is nevertheless responsive to TGF-β, and the tissue adjacent to breast tumors is commonly a TGF-β-enriched environment in which TGF-β signaling becomes activated.
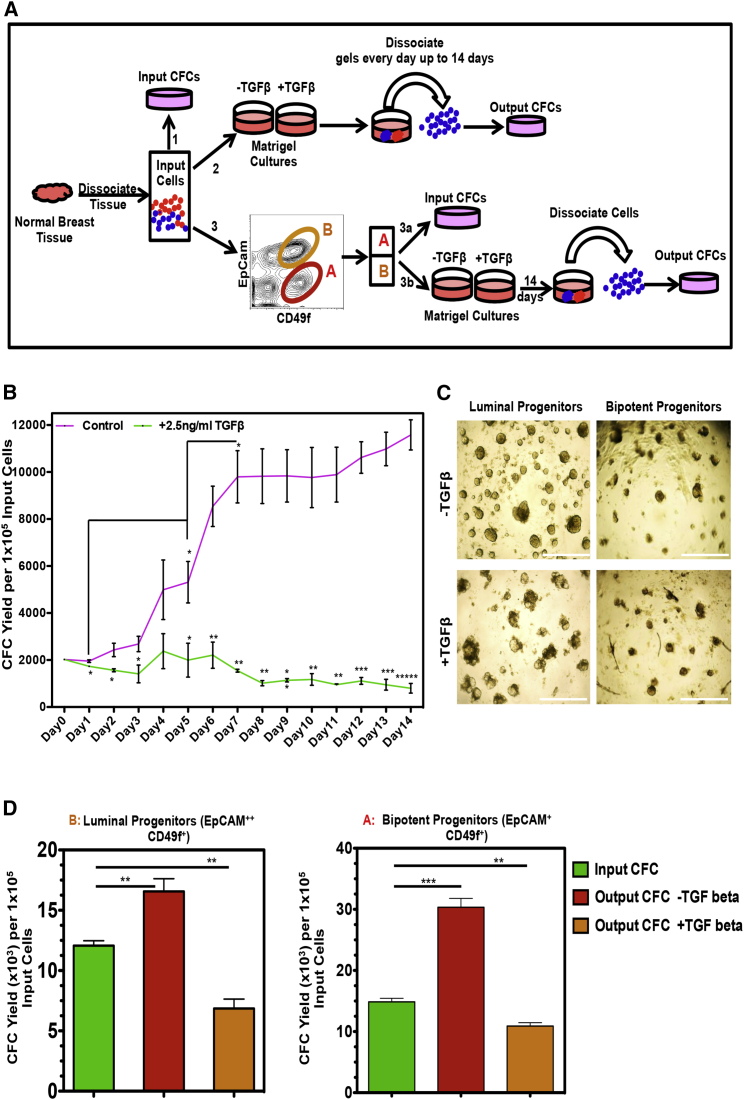
The Reduced Frequency of Mammary CFCs in TAT Samples Is Mediated by TGF-β-Activated SMAD4
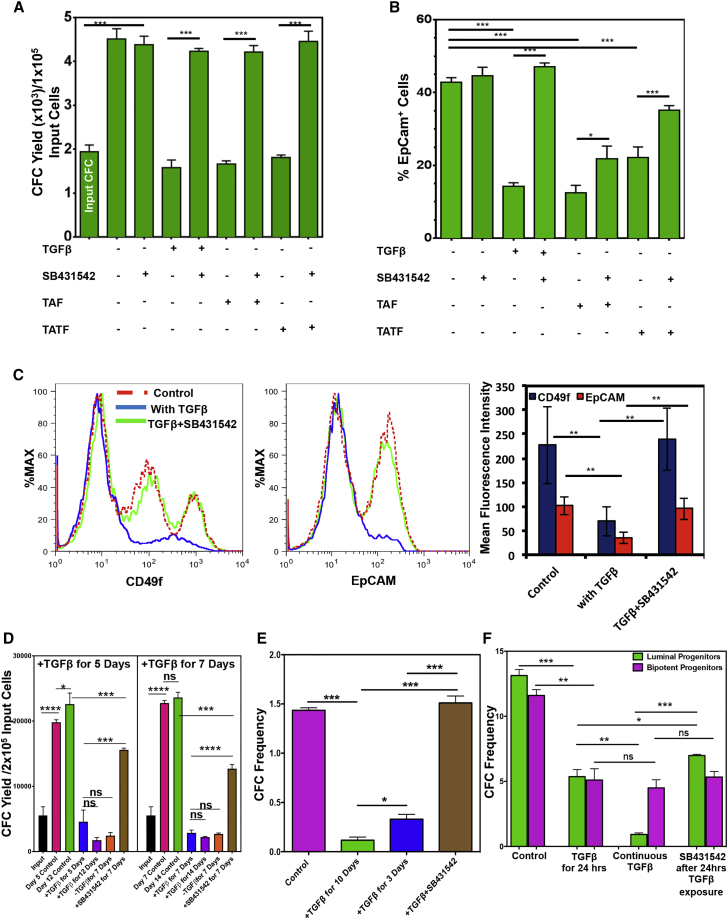
To determine whether TAT-secreted TGF-β is responsible for the diminished progenitor pool in these samples, Lin− cells from normal breast tissue were co-cultured in Matrigel for 3, 5, and 14 days in the presence of increasing doses of recombinant TGF-β (rTGF-β) and the number of CFCs present at these times was then measured (Figure S5B). As little as 0.5 ng/mL of rTGF-β was sufficient to significantly reduce CFC yields, but 2.5 ng/mL showed the most consistent and sustained decrease. The changes in CFC numbers tracked daily over 14 days in Matrigel cultures initiated with total Lin− cells showed a biphasic expansion, in which the first significant increase was seen on day 5 and then again on day 7, after which no significant further expansion occurred (Figures 4A and 4B). Addition of 2.5 ng/mL rTGF-β significantly diminished this output and prevented any net increase (Figure 4B). The rTGF-β also prevented the formation of multi-branched organoid structures in these cultures (data not shown). In Matrigel cultures initiated with the fluorescence-activated cell sorting (FACS)-purified luminal and bipotent progenitor-enriched populations rTGF-β also significantly decreased CFC yields, but did not inhibit the formation of organized (mainly spherical) structures (Figures 4C and 4D). Moreover, exposure to rTGF-β significantly increased propidium iodide retention in the luminal (CD49f+EpCAM+) and the bipotent (CD49f+EpCAMlow/−) progenitors, suggesting that TGF-β causes cell death in these progenitors (Figure S5C). The rTGF-β-induced decrease in CFC yield was completely reversed by SB431542, a SMAD4/TGF-β signaling inhibitor (Figures S5D and S5E), which also reversed the negative effects of added fibroblasts from TAT or tumor samples (Figure 5A). The addition of rTGF-β or TAT or tumor-derived fibroblasts also significantly reduced the yield of EpCAM+ cells in the same cultures (Figure 5B), and decreased CD49f and EpCAM expression on the CFCs present, and these effects were also reversed in the presence of SB431542 (Figures 5B and 5C). However, delayed addition of SB43142 after 5 days of exposure to TGF-β in Matrigel cultures failed to completely rescue CFC generation, even after another 7 days in the absence of TGF-β (Figure 5D).
Figure 4.
TGF-β Inhibits Normal Progenitor Cell Outputs In Vitro
(A) Experimental design.
(B) Time course analysis of changing CFC numbers in Matrigel cultures initiated with three different Lin− reduction samples in the presence or absence of added TGF-β. Values shown are the means ± SEM from three experiments.
(C) Representative photomicrographs of the structures seen in the Matrigel cultures initiated with FACS-purified luminal or bipotent progenitor-enriched fractions with or without TGF-β. Scale bars represent 1000 μm.
(D) Comparison of the average input and 14-day yields of CFCs in the cultures initiated with three different normal FACS-purified luminal or bipotent progenitor-enriched fractions with or without TGF-β (∗p < 0.05, ∗∗p < 0.005, ∗∗∗p < 0.0005, ∗∗∗∗p < 0.00005). Values shown are the means ± SEM from three experiments.
Figure 5.
TAT-Derived Fibroblasts Do Not Support the Generation of CFCs, and This Is Mediated by TGF-β-Induced SMAD4 Signaling in the Target Cells
Matrigel cultures were initiated with Lin− breast reduction cells and different sources of fibroblasts (3 different normal and 3 different TAT samples from patient nos. 3, 4, and 6; Table S1) and treated with the SMAD4 inhibitor (SB31542) or TGF-β ± SB431542 or vehicle controls. Some cells were used to obtain input CFCs. Matrigels were dissolved after 14 days, output CFCs were obtained, and average per each condition is depicted in a bar graph (A). Values shown are the means ± SEM from three experiments.
(B) EpCAM+ cell frequency values for the same cultures analyzed in (A).
(C) Representative FACS profiles of CD49f (left panel) and EpCAM (right panel) stained cells from the same cultures analyzed in (A). Mean ± SEM assessments of the MFIs of cells from three experiments are depicted in the lower panel.
(D) Yields of CFCs in 14-day Matrigel cultures initiated with three different normal breast Lin− cells that were subjected to TGF-β for varying initial periods followed by normal medium ± SB431542. Values shown are the means ± SEM from three experiments.
(E) Effect of TGF-β added after 24 hr for 3 or 10 days on the CFC frequency of normal Lin− cells. Values shown are the means ± SEM from three experiments.
(F) Effect on colony formation by FACS-purified populations of luminal or bipotent CFC-enriched populations plated in 2D assays of the addition of TGF-β for 24 hr starting 24 hr after plating ± SB431542 for an additional 9 days. Some cultures were also exposed to TGF-β continuously. Values shown are the means ± SEM from three experiments (∗p < 0.05; ∗∗p < 0.005; ∗∗∗p < 0.0005; ∗∗∗∗p < 0.00005; ns, p > 0.05).
Addition of rTGF-β to 2D assays of Lin− cells also reduced colony formation within 3 days, and had an even more pronounced inhibitory effect after 7 days. These effects were prevented due to the addition of an SMAD4 blocker SB431542 (Figure 5E). Interestingly, even a 24-hr exposure to rTGF-β was sufficient to reduce colony formation, by both luminal and the bipotent progenitors, by approximately 2-fold; but, after 10 days of rTGF-β exposure, luminal colony formation was further reduced another by 5- to 10-fold, whereas colony formation by the bipotent CFCs remained unchanged (Figure 5F). Similarly, blocking TGF-β signaling after a 24-hr exposure to rTGF-β reversed some of the luminal clonogenic activity, but did not affect the clonogenic potential of the bipotent progenitors. These results were consistent with the finding that the fraction of luminal-enriched progenitors showed higher levels of TGF-βR1 protein expression compared with the bipotent progenitor-enriched cells (Figure S5F).
TGF-β Hinders Progenitor Cell Expansion by Decreasing CD49f and EpCAM Expression
To examine the possibility that the inhibitory effects of TGF-β exposure might be via an induced EMT mechanism, we measured transcripts of candidate target genes and EMT markers in the FACS-purified bipotent and the luminal progenitor-enriched cell fractions isolated from Matrigel cultures containing no or 2.5 ng/mL added TGF-β. In presence of rTGF-β, these transcripts were significantly upregulated in the bipotent progenitors but not in the luminal progenitors (Figures S5G–S5I), despite the finding that the luminal progenitors showed higher expression of TGF-βR1 (Figure S5F). These observations suggest that the TGF-β-induced block in progenitor cell expansion, at least in luminal progenitors, is not mediated by an EMT mechanism.
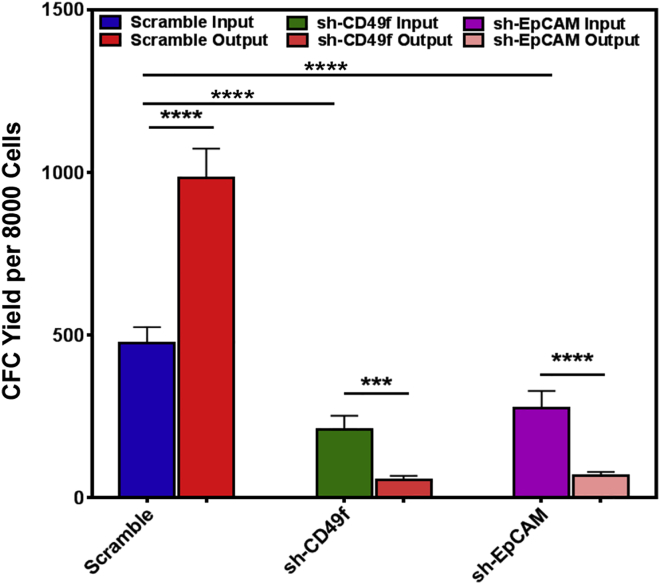
Because rTGF-β treatment of normal breast cells produced a significant decrease in their expression of EpCAM and CD49f (Figure 5C), which closely mimics the low expression of these proteins in the cells in the TAT samples (Figure 1D), we next asked whether this effect might be related to the reduced yield of CFCs. The CD49f and EpCAM proximal promoter regions contain SMAD4 consensus DNA binding sites (Figure S6A), consistent with their expression being regulated by TGF-β/SMAD4 signaling. To investigate this possibility, we first generated lentiviral vectors containing short hairpin RNAs to EpCAM and CD49f transcripts (or scrambled controls), and then examined the expression of CD49f and EpCAM in transduced progenitor populations. The results showed effective and specific knock down of both genes by 80% ± 3% and 75% ± 4%, respectively (Figures S6B–S6D). CFC assays of transduced GFP+ (FACS-purified) cells, before and after being cultured in Matrigel, showed that the decreased expression of CD49f or EpCAM was associated with a decreased CFC activity both before and after the cells were cultured in Matrigel (Figure 6).
Figure 6.
Forced Decreased Expression of CD49f or EpCAM Reduces Normal Progenitor Cell Detection and Generation In Vitro
Effects of lentiviral-mediated decreased expression of CD49f and EpCAM (using lentiviral GFP vectors encoding specific sh-cDNAs) on colony formation by transduced (GFP+) normal Lin− breast cells before and after 14 days of incubation in Matrigel cultures. Values shown are the mean ± SEM from three experiments (∗∗∗p < 0.001, ∗∗∗∗p < 0.00005).
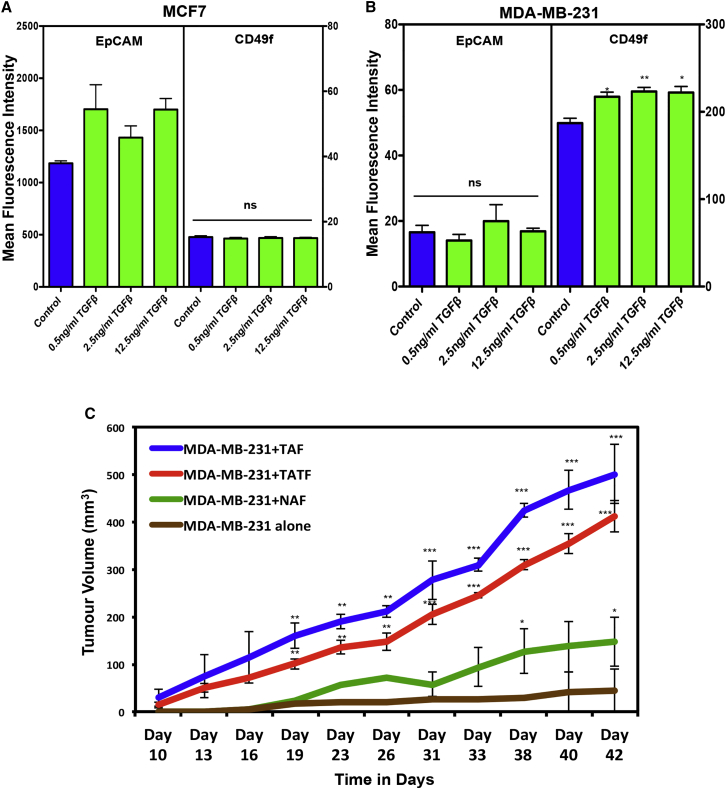
To determine whether TGF-β exerts similar effects on breast cancer cells as it does on normal breast epithelial cells, we examined CD49f and EpCAM protein expression MCF7 and MDA-MB-231 cells exposed (or not) to rTGF-β (Figures 7A and 7B). Interestingly, rTGF-β failed to decrease CD49f or EpCAM expression in these cells, suggesting that malignant breast cancer cells acquire altered responses to TGF-β. In addition, we examined the ability of different sources of fibroblasts to support the proliferation of MDA-MB231 cells in vivo. For this purpose, the MDA-MB231 cells were co-injected with fibroblasts derived from normal breast, TAT, or tumor tissue into immune-deficient mice and tumor growth was measured. The results showed that all sources of fibroblasts enhanced the growth of the tumors generated (Figure 7C). However, the fibroblasts from the TAT and tumor samples had the greatest effect in this regard. The presence of fibroblasts in the xenografts was confirmed by examining the expression of αSMA and S100A4 proteins in the tumors (Figure S7A). Of note, the presence of fibroblasts did not increase angiogenesis in the xenografts (Figure S7A, CD31 expression). A similar pattern of enhanced growth of the MCF7 and MDA-MB-231 cells in co-cultures containing these different sources of fibroblasts was also obtained (Figure S7B).
Figure 7.
Tumor-Adjacent Breast Tissue Fibroblasts Enhance Breast Cancer Tumor Growth
(A and B) Effect of TGF-β on CD49f and EpCAM expression on MCF7 and MD-MB-231 cells assessed after 2 days of exposure in vitro. Values shown are the means ± SEM MFIs measured in three experiments (∗p < 0.05, ∗∗p < 0.005).
(C) Effect of co-injected fibroblasts from different tissue sources (3 normal and 3 matched TAT and tumor samples from patient nos. 3, 4, and 6; Table S1) on the tumor growth rates of MDA-MB-231 cells transplanted subcutaneously into immunodeficient mice. Co-injected fibroblasts from tumors (TAFs) or TAT (TAT-Fs) significantly (∗∗p < 0.005; ∗∗∗p < 0.001) enhanced tumor growth compared with MD-MB-231 cells alone.
Discussion
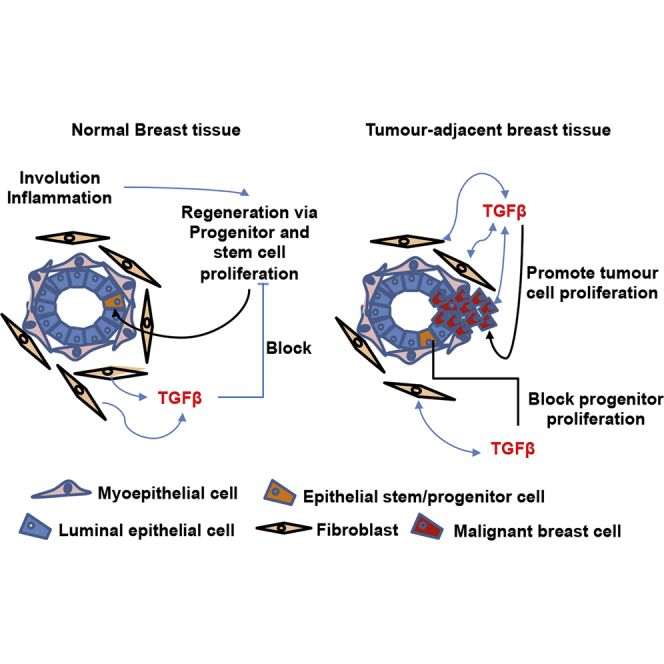
Normal-like tissue adjacent to breast cancer tumors has been the focus of much research efforts to understand the contributions of this cellular environment to tumor cell development, growth, and recurrence. Studies to date have focused on identifying changes in the promoter methylation status and altered gene expression in bulk samples of very proximal TAT samples, but more detailed analysis of the biological changes in different cell types present in these has been lacking. Here, we show that the numbers of cells with normal mammary luminal-restricted and bipotent clonogenic activity in the histologically normal tumor-adjacent mammary epithelium are significantly reduced. We also present strong evidence that the underlying mechanism is an abnormal, tumor-activated secretion of TGF-β by the stromal fibroblasts in the TAT locale (niche) that suppresses normal mammary progenitor expansion by causing a decrease in CD49f and EpCAM expression. In addition, we show that the same process can have an opposite effect on malignant human mammary cells exemplified by an ability of the same fibroblasts (and TGF-β) to promote their growth both in vitro and in vivo (in xenografted immunodeficient mice). CD49f and EpCAM, through interaction with the extracellular matrix proteins, activate cell survival and cell proliferation signals in epithelial cells (Lambert et al., 2012, Maetzel et al., 2009, Martowicz et al., 2013, Schwartz and Assoian, 2001) and, therefore, the TGF-β-induced suppression of their expression in progenitor cells could result in cell death. In breast cancer cells, however, we show that exposure to TGF-β has no effect on the expression of these genes. TGF-β has also been shown to induce proliferation and survival of breast cancer cells (Seoane and Gomis, 2017). These findings establish the biological origin and in situ consequences in TAT regions of human breast tissue of the disparate effects of TGF-β on normal and malignant mammary cells (Bhola et al., 2013, Dumont and Arteaga, 2000, Gong et al., 2015). However, our findings revealed a detectable, albeit reduced, sensitivity of normal bipotent progenitors as well as luminal progenitors to inhibition by TGF-β and a consequent effect in situ in TAT regions on both cell types. The apparent discrepancy between our findings and the previously reported data (Bruna et al., 2012) can be explained by the fact that we measured bipotent progenitor yields in the systems used to test the effects of TGF-β not predicted by their frequency due to a relative decrease in total cells. We also added TGF-β to our CFC assays after 24 hr to avoid potential effects of TGF-β on progenitor or fibroblast attachment to the culture dish. Interestingly, in another recent study TGF-β was shown to decrease the colony-forming activity of mouse mammary epithelial progenitors (Prater et al., 2014), suggesting that the effects herein reported are common to both species.
The current role of TGF-β in breast carcinogenesis is postulated to switch from acting initially as a tumor suppressor on premalignant cells to a tumor promoting growth factor during the later stages of tumor progression (Derynck et al., 2001, Ikushima and Miyazono, 2010, Pickup et al., 2013). The results presented here provide further support for this model by showing that TGF-β acts as a tumor suppressor in situ in histologically normal human mammary epithelial tissue adjacent to breast tumors, while also confirming its ability to augment the growth of established malignant human breast cancer cells (Figure S8).
In this study, we analyzed the ability of early passage fibroblasts obtained from breast tumors, matching TAT-near and -far samples, matching CNTB tissue from the same patients and from normal breast tissue from reduction mammoplasty samples. Comparison of their activities in Matrigel co-cultures with normal mammary epithelial cells showed the TGF-β-mediated inhibitory effects of fibroblasts obtained from within, or very close to tumor tissue was shared by fibroblasts obtained from tissue as far away as 6 cm from the tumor margin. The consistency of these findings in fibroblasts passaged several times in vitro to ensure their purity at >90% strongly suggests that their altered state and secretome profile persisted in the absence of continued proximity to tumor cells. This possibility, in turn, suggests additional TGF-β-mediated mechanisms involving suppression of local immune cell activity that would also enhance the selective regrowth of residual tumor cells (Donatelli et al., 2014, Nam et al., 2008, Teicher, 2007).
Breast-conserving surgeries, including lumpectomy, are often effective in treating small invasive breast cancer tumors (Fisher et al., 2002, Singletary et al., 2005), but approximately 10%–15% of these women develop local tumor recurrence, often with metastasis (Bijker et al., 2001). Moreover, younger age (<40 years) and tumor stage both increase the risk of local breast tumor recurrence (Arvold et al., 2011, Pirone et al., 2012, Voduc et al., 2010). Our observation that breast tissue alterations can extend well beyond the 1-cm surgical margin currently used could therefore have translational implications. For example, it is inviting to speculate that there could be increased benefit from reverting more frequently to radical mastectomies, or the use of TGF-β signaling blockers to reduce the risk of local tumor recurrence. The present studies also suggest more extensive analysis of the clinical generality of our findings could be helpful in improving prognostication.
Experimental Procedures
Tissue Sample Collection
Breast tumor tissue and TAT samples were obtained from patients undergoing mastectomy procedures who had not received any neoadjuvant chemotherapy and/or radiation treatment (Table S1). Contralateral tumor-free breast tissues were obtained from patients undergoing prophylactic bilateral mastectomies. Healthy breast tissues were obtained from patients undergoing reduction mammoplasties. All samples were obtained with written informed patient consent according to protocols approved by the University of Manitoba's Research Ethics Board.
Tissue Dissociation and Cell Separation
Tumor samples were minced and dissociated for 16 hr in Ham's F12 and DMEM dissociation medium (1:1 vol/vol) F12 to DMEM supplemented with 2% wt/vol BSA, 300 U/mL collagenase, 100 U/mL hyaluronidase, 10 ng/mL epidermal growth factor (EGF), 1 mg/mL insulin, and 0.5 mg/mL hydrocortisone. The cell pellets were treated with red blood cell lysis buffer as per the manufacturer's protocol prior to being resuspended and cryopreserved in 6% dimethylsulfoxide-containing fetal bovine serum (FBS)-supplemented medium and stored in liquid nitrogen. Reduction mammoplasty tissue, TAT, and matched contralateral tumor-free tissue were processed as described previously (Raouf and Sun, 2013, Stingl et al., 2005).
Primary Fibroblasts Cultures
TAFs were obtained from cryopreserved breast tumor samples. In brief, cell pellets were thawed and made into single cells. Up to 3 × 106 cells placed in 10-cm tissue culture plates in DMEM/F12 medium supplemented with 10% FBS. After 4 hr at 37°C the medium and non-adherent cells were removed and fresh medium added. Fibroblasts from either normal (NAFs) or TAT (TAT-Fs) samples were cultured to 70%–75% confluence in DMEM/F12 medium supplemented with 10% FBS, and passaged at least twice before being used in any experiments.
Matrigel Cultures
A total of 2 × 105 bulk cells or 5 × 104 luminal or bipotent progenitors were placed on top of Matrigels, and plates were then incubated for up to 21 days with SF7 medium supplemented with 70 μg/mL bovine pituitary extract. In some experiments, the medium was supplemented with 2.5 ng/mL TGF-β (Sigma, catalog no. T7039) or 10 μM of the SB431542 SMAD4 blocker (Sigma, catalog no. S4317), or vehicle control (PBS or DMSO, accordingly). For some experiments 105 single cells were mixed with 105 fibroblasts and placed in Matrigel cultures as described previously (Basak et al., 2015, Makarem et al., 2013). On the indicated days, gels were dissolved with dispase and cells were recovered.
Secretome Analysis of the Primary Fibroblast Cells
CM was collected from low passaged primary fibroblasts (NAFs and TAT-Fs) concentrated, digested, and analyzed via 2D LC-MS. A total of 95,229 peptide sequences were selected and were merged to identify 881 individual proteins. Of these, 290 proteins were identified as secreted proteins using the gene ontology cellular component filter class (DAVID Bioinformatics Database and the Secreted Protein Database; spd.cbi.pku.edu).
Mouse Xenograft Assays
MDA-MB-231 cells were either alone or co-injected with different fibroblasts into the flank of 6 to 8-week-old female BALB/c (H-2d) RAG2−/− IL-2Rγc−/− immunodeficient mice. Animal maintenance was performed in accordance with the animal care guidelines of the University of Manitoba, Canada. All the animal experiments were approved by the Animal Care and ethical Committee of the University of Manitoba, Canada.
For full details of the experimental procedures, please refer to the Supplemental Information.
Author Contributions
S.C. conducted the experiments and co-wrote the manuscript. P.B. and P.E. conducted some of the experiments. J.S. provided pathological evaluation of the tumor-adjacent breast tissue samples. E.B. contributed to data interpretation. S.K.K. and M.M. provided the BALB/c (H-2d) RAG2−/− IL-2Rγc−/− immunodeficient mice and helped design the xenograft experiments. M.M. and L.C.M. provided critical review of the manuscript. S.C. and A.R. designed the experiments and analyzed data. C.J.E. and A.R. analyzed data and co-wrote the manuscript.
Acknowledgments
We thank H. Chapko, S. Blellock, and A. Berdnikov for collection of tumor-adjacent breast tissue and breast tumors and the Manitoba Breast Tumor Bank for collection of breast reduction samples. This work was made possible by postdoctoral fellowships from Research Manitoba and the Canadian Breast Cancer Foundation- Prairie/NWT region to S.C., grants from the Canadian Breast Cancer Foundation – Prairie/NWT region to A.R., M.M., and L.C.M., the Canadian Cancer Society Research Institute grants to S.K.K. and C.J.E., Natural Sciences and Engineering Research Council grant to S.K.K., and Keeping Abreast Foundation grant to A.R.
Published: December 7, 2017
Footnotes
Supplemental Information includes Supplemental Experimental Procedures, seven figures, and three tables and can be found with this article online at https://doi.org/10.1016/j.stemcr.2017.11.002.
Supplemental Information
References
- Allinen M., Beroukhim R., Cai L., Brennan C., Lahti-Domenici J., Huang H., Porter D., Hu M., Chin L., Richardson A. Molecular characterization of the tumor microenvironment in breast cancer. Cancer Cell. 2004;6:17–32. doi: 10.1016/j.ccr.2004.06.010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arvold N.D., Taghian A.G., Niemierko A., Abi Raad R.F., Sreedhara M., Nguyen P.L., Bellon J.R., Wong J.S., Smith B.L., Harris J.R. Age, breast cancer subtype approximation, and local recurrence after breast-conserving therapy. J. Clin. Oncol. 2011;29:3885–3891. doi: 10.1200/JCO.2011.36.1105. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Banerji S., Cibulskis K., Rangel-Escareno C., Brown K.K., Carter S.L., Frederick A.M., Lawrence M.S., Sivachenko A.Y., Sougnez C., Zou L. Sequence analysis of mutations and translocations across breast cancer subtypes. Nature. 2012;486:405–409. doi: 10.1038/nature11154. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Basak P., Chatterjee S., Weger S., Bruce M.C., Murphy L.C., Raouf A. Estrogen regulates luminal progenitor cell differentiation through H19 gene expression. Endocr. Relat. Cancer. 2015;22:505–517. doi: 10.1530/ERC-15-0105. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bhola N.E., Balko J.M., Dugger T.C., Kuba M.G., Sanchez V., Sanders M., Stanford J., Cook R.S., Arteaga C.L. TGF-beta inhibition enhances chemotherapy action against triple-negative breast cancer. J. Clin. Invest. 2013;123:1348–1358. doi: 10.1172/JCI65416. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bijker N., Peterse J.L., Duchateau L., Julien J.P., Fentiman I.S., Duval C., Di Palma S., Simony-Lafontaine J., de Mascarel I., van de Vijver M.J. Risk factors for recurrence and metastasis after breast-conserving therapy for ductal carcinoma in-situ: analysis of European Organization for Research and Treatment of Cancer Trial 10853. J. Clin. Oncol. 2001;19:2263–2271. doi: 10.1200/JCO.2001.19.8.2263. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bruna A., Greenwood W., Le Quesne J., Teschendorff A., Miranda-Saavedra D., Rueda O.M., Sandoval J.L., Vidakovic A.T., Saadi A., Pharoah P. TGFbeta induces the formation of tumour-initiating cells in claudinlow breast cancer. Nat. Commun. 2012;3:1055. doi: 10.1038/ncomms2039. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Curtis C., Shah S.P., Chin S.F., Turashvili G., Rueda O.M., Dunning M.J., Speed D., Lynch A.G., Samarajiwa S., Yuan Y. The genomic and transcriptomic architecture of 2,000 breast tumours reveals novel subgroups. Nature. 2012;486:346–352. doi: 10.1038/nature10983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deng G., Lu Y., Zlotnikov G., Thor A.D., Smith H.S. Loss of heterozygosity in normal tissue adjacent to breast carcinomas. Science. 1996;274:2057–2059. doi: 10.1126/science.274.5295.2057. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Derynck R., Akhurst R.J., Balmain A. TGF-beta signaling in tumor suppression and cancer progression. Nat. Genet. 2001;29:117–129. doi: 10.1038/ng1001-117. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Donatelli S.S., Zhou J.M., Gilvary D.L., Eksioglu E.A., Chen X., Cress W.D., Haura E.B., Schabath M.B., Coppola D., Wei S. TGF-beta-inducible microRNA-183 silences tumor-associated natural killer cells. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA. 2014;111:4203–4208. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1319269111. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dumont N., Arteaga C.L. Transforming growth factor-beta and breast cancer: tumor promoting effects of transforming growth factor-beta. Breast Cancer Res. 2000;2:125–132. doi: 10.1186/bcr44. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Early Breast Cancer Trialists' Collaborative Group. Darby S., McGale P., Correa C., Taylor C., Arriagada R., Clarke M., Cutter D., Davies C., Ewertz M. Effect of radiotherapy after breast-conserving surgery on 10-year recurrence and 15-year breast cancer death: meta-analysis of individual patient data for 10,801 women in 17 randomised trials. Lancet. 2011;378:1707–1716. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(11)61629-2. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eirew P., Kannan N., Knapp D.J., Vaillant F., Emerman J.T., Lindeman G.J., Visvader J.E., Eaves C.J. Aldehyde dehydrogenase activity is a biomarker of primitive normal human mammary luminal cells. Stem Cells. 2012;30:344–348. doi: 10.1002/stem.1001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eirew P., Stingl J., Raouf A., Turashvili G., Aparicio S., Emerman J.T., Eaves C.J. A method for quantifying normal human mammary epithelial stem cells with in vivo regenerative ability. Nat. Med. 2008;14:1384–1389. doi: 10.1038/nm.1791. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Finak G., Bertos N., Pepin F., Sadekova S., Souleimanova M., Zhao H., Chen H., Omeroglu G., Meterissian S., Omeroglu A. Stromal gene expression predicts clinical outcome in breast cancer. Nat. Med. 2008;14:518–527. doi: 10.1038/nm1764. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Finak G., Sadekova S., Pepin F., Hallett M., Meterissian S., Halwani F., Khetani K., Souleimanova M., Zabolotny B., Omeroglu A. Gene expression signatures of morphologically normal breast tissue identify basal-like tumors. Breast Cancer Res. 2006;8:R58. doi: 10.1186/bcr1608. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fisher B., Anderson S., Bryant J., Margolese R.G., Deutsch M., Fisher E.R., Jeong J.H., Wolmark N. Twenty-year follow-up of a randomized trial comparing total mastectomy, lumpectomy, and lumpectomy plus irradiation for the treatment of invasive breast cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2002;347:1233–1241. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa022152. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fleischer T., Frigessi A., Johnson K.C., Edvardsen H., Touleimat N., Klajic J., Riis M.L., Haakensen V.D., Warnberg F., Naume B. Genome-wide DNA methylation profiles in progression to in situ and invasive carcinoma of the breast with impact on gene transcription and prognosis. Genome Biol. 2014;15:435. doi: 10.1186/s13059-014-0435-x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Forsti A., Louhelainen J., Soderberg M., Wijkstrom H., Hemminki K. Loss of heterozygosity in tumour-adjacent normal tissue of breast and bladder cancer. Eur. J. Cancer. 2001;37:1372–1380. doi: 10.1016/s0959-8049(01)00118-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gao M.Q., Kim B.G., Kang S., Choi Y.P., Park H., Kang K.S., Cho N.H. Stromal fibroblasts from the interface zone of human breast carcinomas induce an epithelial mesenchymal transition-like state in breast cancer cells in vitro. J. Cell Sci. 2010;123:3507–3514. doi: 10.1242/jcs.072900. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gong C., Qu S., Liu B., Pan S., Jiao Y., Nie Y., Su F., Liu Q., Song E. MiR-106b expression determines the proliferation paradox of TGF-beta in breast cancer cells. Oncogene. 2015;34:84–93. doi: 10.1038/onc.2013.525. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graham K., Ge X., de Las Morenas A., Tripathi A., Rosenberg C.L. Gene expression profiles of estrogen receptor-positive and estrogen receptor-negative breast cancers are detectable in histologically normal breast epithelium. Clin. Cancer Res. 2011;17:236–246. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-10-1369. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hsu H.C., Liu L.C., Wang H.Y., Hung C.M., Lin Y.C., Ho C.T., Way T.D. Stromal fibroblasts from the interface zone of triple negative breast carcinomas induced epithelial-mesenchymal transition and its inhibition by emodin. PLoS One. 2017;12:e0164661. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0164661. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ikushima H., Miyazono K. TGFbeta signalling: a complex web in cancer progression. Nat. Rev. Cancer. 2010;10:415–424. doi: 10.1038/nrc2853. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kunkler I.H., Williams L.J., Jack W.J., Cameron D.A., Dixon J.M., investigators P.I. Breast-conserving surgery with or without irradiation in women aged 65 years or older with early breast cancer (PRIME II): a randomised controlled trial. Lancet Oncol. 2015;16:266–273. doi: 10.1016/S1470-2045(14)71221-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuperwasser C., Chavarria T., Wu M., Magrane G., Gray J.W., Carey L., Richardson A., Weinberg R.A. Reconstruction of functionally normal and malignant human breast tissues in mice. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA. 2004;101:4966–4971. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0401064101. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lambert A.W., Ozturk S., Thiagalingam S. Integrin signaling in mammary epithelial cells and breast cancer. ISRN Oncol. 2012;2012:493283. doi: 10.5402/2012/493283. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maetzel D., Denzel S., Mack B., Canis M., Went P., Benk M., Kieu C., Papior P., Baeuerle P.A., Munz M. Nuclear signalling by tumour-associated antigen EpCAM. Nat. Cell Biol. 2009;11:162–171. doi: 10.1038/ncb1824. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Makarem M., Kannan N., Nguyen L.V., Knapp D.J., Balani S., Prater M.D., Stingl J., Raouf A., Nemirovsky O., Eirew P. Developmental changes in the in vitro activated regenerative activity of primitive mammary epithelial cells. PLoS Biol. 2013;11:e1001630. doi: 10.1371/journal.pbio.1001630. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mamounas E.P., Anderson S.J., Dignam J.J., Bear H.D., Julian T.B., Geyer C.E., Jr., Taghian A., Wickerham D.L., Wolmark N. Predictors of locoregional recurrence after neoadjuvant chemotherapy: results from combined analysis of National Surgical Adjuvant Breast and Bowel Project B-18 and B-27. J. Clin. Oncol. 2012;30:3960–3966. doi: 10.1200/JCO.2011.40.8369. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martowicz A., Rainer J., Lelong J., Spizzo G., Gastl G., Untergasser G. EpCAM overexpression prolongs proliferative capacity of primary human breast epithelial cells and supports hyperplastic growth. Mol. Cancer. 2013;12:56. doi: 10.1186/1476-4598-12-56. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCahill L.E., Single R.M., Aiello Bowles E.J., Feigelson H.S., James T.A., Barney T., Engel J.M., Onitilo A.A. Variability in reexcision following breast conservation surgery. JAMA. 2012;307:467–475. doi: 10.1001/jama.2012.43. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morrow M., Harris J.R., Schnitt S.J. Surgical margins in lumpectomy for breast cancer – bigger is not better. N. Engl. J. Med. 2012;367:79–82. doi: 10.1056/NEJMsb1202521. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morrow M., Jagsi R., Alderman A.K., Griggs J.J., Hawley S.T., Hamilton A.S., Graff J.J., Katz S.J. Surgeon recommendations and receipt of mastectomy for treatment of breast cancer. JAMA. 2009;302:1551–1556. doi: 10.1001/jama.2009.1450. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nam J.S., Terabe M., Kang M.J., Chae H., Voong N., Yang Y.A., Laurence A., Michalowska A., Mamura M., Lonning S. Transforming growth factor beta subverts the immune system into directly promoting tumor growth through interleukin-17. Cancer Res. 2008;68:3915–3923. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-08-0206. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pereira B., Chin S.F., Rueda O.M., Vollan H.K., Provenzano E., Bardwell H.A., Pugh M., Jones L., Russell R., Sammut S.J. The somatic mutation profiles of 2,433 breast cancers refines their genomic and transcriptomic landscapes. Nat. Commun. 2016;7:11479. doi: 10.1038/ncomms11479. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pickup M., Novitskiy S., Moses H.L. The roles of TGFbeta in the tumour microenvironment. Nat. Rev. Cancer. 2013;13:788–799. doi: 10.1038/nrc3603. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pirone J.R., D'Arcy M., Stewart D.A., Hines W.C., Johnson M., Gould M.N., Yaswen P., Jerry D.J., Smith Schneider S., Troester M.A. Age-associated gene expression in normal breast tissue mirrors qualitative age-at-incidence patterns for breast cancer. Cancer Epidemiol. Biomarkers Prev. 2012;21:1735–1744. doi: 10.1158/1055-9965.EPI-12-0451. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prater M.D., Petit V., Alasdair Russell I., Giraddi R.R., Shehata M., Menon S., Schulte R., Kalajzic I., Rath N., Olson M.F. Mammary stem cells have myoepithelial cell properties. Nat. Cell Biol. 2014;16:942–950. doi: 10.1038/ncb3025. 941–947. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raouf A., Sun Y.J. In vitro methods to culture primary human breast epithelial cells. Methods Mol. Biol. 2013;946:363–381. doi: 10.1007/978-1-62703-128-8_23. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roman-Perez E., Casbas-Hernandez P., Pirone J.R., Rein J., Carey L.A., Lubet R.A., Mani S.A., Amos K.D., Troester M.A. Gene expression in extratumoral microenvironment predicts clinical outcome in breast cancer patients. Breast Cancer Res. 2012;14:R51. doi: 10.1186/bcr3152. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwartz M.A., Assoian R.K. Integrins and cell proliferation: regulation of cyclin-dependent kinases via cytoplasmic signaling pathways. J. Cell Sci. 2001;114:2553–2560. doi: 10.1242/jcs.114.14.2553. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seoane J., Gomis R.R. TGF-beta family signaling in tumor suppression and cancer progression. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Biol. 2017 doi: 10.1101/cshperspect.a022277. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shah S.P., Roth A., Goya R., Oloumi A., Ha G., Zhao Y., Turashvili G., Ding J., Tse K., Haffari G. The clonal and mutational evolution spectrum of primary triple-negative breast cancers. Nature. 2012;486:395–399. doi: 10.1038/nature10933. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Silverstein M.J., Lagios M.D., Groshen S., Waisman J.R., Lewinsky B.S., Martino S., Gamagami P., Colburn W.J. The influence of margin width on local control of ductal carcinoma in situ of the breast. N. Engl. J. Med. 1999;340:1455–1461. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199905133401902. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Singletary S.E., Patel-Parekh L., Bland K.I. Treatment trends in early-stage invasive lobular carcinoma: a report from the National Cancer Data Base. Ann. Surg. 2005;242:281–289. doi: 10.1097/01.sla.0000171306.74366.22. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stingl J., Raouf A., Emerman J.T., Eaves C.J. Epithelial progenitors in the normal human mammary gland. J. Mammary Gland Biol. Neoplasia. 2005;10:49–59. doi: 10.1007/s10911-005-2540-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sun X., Gierach G.L., Sandhu R., Williams T., Midkiff B.R., Lissowska J., Wesolowska E., Boyd N.F., Johnson N.B., Figueroa J.D. Relationship of mammographic density and gene expression: analysis of normal breast tissue surrounding breast cancer. Clin. Cancer Res. 2013;19:4972–4982. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-13-0029. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taghian A., Mohiuddin M., Jagsi R., Goldberg S., Ceilley E., Powell S. Current perceptions regarding surgical margin status after breast-conserving therapy: results of a survey. Ann. Surg. 2005;241:629–639. doi: 10.1097/01.sla.0000157272.04803.1b. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Teicher B.A. Transforming growth factor-beta and the immune response to malignant disease. Clin. Cancer Res. 2007;13:6247–6251. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-07-1654. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Teschendorff A.E., Gao Y., Jones A., Ruebner M., Beckmann M.W., Wachter D.L., Fasching P.A., Widschwendter M. DNA methylation outliers in normal breast tissue identify field defects that are enriched in cancer. Nat. Commun. 2016;7:10478. doi: 10.1038/ncomms10478. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Veronesi U., Cascinelli N., Mariani L., Greco M., Saccozzi R., Luini A., Aguilar M., Marubini E. Twenty-year follow-up of a randomized study comparing breast-conserving surgery with radical mastectomy for early breast cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2002;347:1227–1232. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa020989. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vinh-Hung V., Verschraegen C. Breast-conserving surgery with or without radiotherapy: pooled-analysis for risks of ipsilateral breast tumor recurrence and mortality. J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 2004;96:115–121. doi: 10.1093/jnci/djh013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Voduc K.D., Cheang M.C., Tyldesley S., Gelmon K., Nielsen T.O., Kennecke H. Breast cancer subtypes and the risk of local and regional relapse. J. Clin. Oncol. 2010;28:1684–1691. doi: 10.1200/JCO.2009.24.9284. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Young O.E., Valassiadou K., Dixon M. A review of current practices in breast conservation surgery in the UK. Ann. R. Coll. Surg. Engl. 2007;89:118–123. doi: 10.1308/003588407X155473. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhou X., Meeker A.K., Makambi K.H., Kosti O., Kallakury B.V., Sidawy M.K., Loffredo C.A., Zheng Y.L. Telomere length variation in normal epithelial cells adjacent to tumor: potential biomarker for breast cancer local recurrence. Carcinogenesis. 2012;33:113–118. doi: 10.1093/carcin/bgr248. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.