Abstract
Background
Late embryogenesis abundant (LEA) proteins are large groups of hydrophilic proteins with major role in drought and other abiotic stresses tolerance in plants. In-depth study and characterization of LEA protein families have been carried out in other plants, but not in upland cotton. The main aim of this research work was to characterize the late embryogenesis abundant (LEA) protein families and to carry out gene expression analysis to determine their potential role in drought stress tolerance in upland cotton. Increased cotton production in the face of declining precipitation and availability of fresh water for agriculture use is the focus for breeders, cotton being the backbone of textile industries and a cash crop for many countries globally.
Results
In this work, a total of 242, 136 and 142 LEA genes were identified in G. hirsutum, G. arboreum and G. raimondii respectively. The identified genes were classified into eight groups based on their conserved domain and phylogenetic tree analysis. LEA 2 were the most abundant, this could be attributed to their hydrophobic character. Upland cotton LEA genes have fewer introns and are distributed in all chromosomes. Majority of the duplicated LEA genes were segmental. Syntenic analysis showed that greater percentages of LEA genes are conserved. Segmental gene duplication played a key role in the expansion of LEA genes. Sixty three miRNAs were found to target 89 genes, such as miR164, ghr-miR394 among others. Gene ontology analysis revealed that LEA genes are involved in desiccation and defense responses. Almost all the LEA genes in their promoters contained ABRE, MBS, W-Box and TAC-elements, functionally known to be involved in drought stress and other stress responses. Majority of the LEA genes were involved in secretory pathways. Expression profile analysis indicated that most of the LEA genes were highly expressed in drought tolerant cultivars Gossypium tomentosum as opposed to drought susceptible, G. hirsutum. The tolerant genotypes have a greater ability to modulate genes under drought stress than the more susceptible upland cotton cultivars.
Conclusion
The finding provides comprehensive information on LEA genes in upland cotton, G. hirsutum and possible function in plants under drought stress.
Electronic supplementary material
The online version of this article (10.1186/s12863-017-0596-1) contains supplementary material, which is available to authorized users.
Keywords: Cotton (Gossypium spp), Identification, LEA proteins, miRNAs, Gene ontology, Gene expression, Genome, Drought
Background
Drought stress has resulted in to massive losses in crop production and also has altered the natural equilibrium of the environment [1]. To save the ecosystem and enhance production, advanced molecular breeding is the recipe for activation and regulation of specific stress-related genes [2]. Water deficit stress do led to a series of changes including biochemical alterations like accumulation of osmolytes and specific proteins involved in stress tolerance [3]. One of the proteins that play a role in the mechanism of drought resistance is the LEA types of protein known as dehydrin [4]. In cotton production, drought is the main abiotic stress responsible for plant growth compromise and severe yield loss. Even though cotton is considered to be relatively tolerant to water deficit, its optimal growth and yield negatively affected when water supply is limited or interrupted [5]. Water is an essential element for biotic component of the biosphere, such that various responses have evolved to withstand water deficit in all plants and animals, to enable them withstand long periods of water deprivation by adopting a type of life condition known as anhydrobiosis [6].
There is great agronomic significance to understand cotton plant responses to water deficit due to the huge economic losses that results from drought [7]. Cotton metabolism and yield are negatively affected under water deficit conditions, especially at flowering stage [8]. Plants have acquired an evolutionary response to withstand the effect of low water availability, a condition that can disadvantage their growth and development. As immobile organisms, plants possess diverse strategies of responses to drought. Among the molecules highly associated with plant responses to water limitation are the late embryogenesis abundant (LEA) proteins [9]. These proteins are widespread in the plant kingdom and highly enriched during the late stages of embryogenesis and in vegetative tissues in response to water deficit [10].
LEA proteins were first discovered more than 30 years ago and were observed to accumulate at late stages of plant seed development [11]. The LEA proteins have been found in various tissues of abiotic stressed plants and non-plant organisms known to be tolerant to desiccation, such as bacteria and some invertebrates [12]. LEA proteins are members of a large group of hydrophilic, glycine-rich proteins present in a wide range of plant species [13]. This class of proteins are known to be intrinsically disordered in their structures and are mainly expressed under water deprivation condition [14]. The LEA genes are highly diverse, with wide distribution in the plant kingdom and has pivotal role in various stress tolerance responses [15].
Scientific investigations on LEA protein families have been on-going for more than two decades [16]. Although there has been a strong association of LEA protein families with environmental stress tolerance of significance drought and cold stress [17], LEA protein families for most of that time, their function has been entirely obscure [18]. Considerable evidence gives an indication that LEA genes are involved in desiccation, though their precise function is unknown [19]. The bacterial group 1 LEA proteins have the ability to block enzyme inactivation upon freeze–thaw treatments in vitro and it has analogous functions to plant LEA proteins [10]. Therefore, there is need to conduct a genome wide characterization of LEA protein families in cotton. The recent upland cotton genome publications, G. hirsutum [20], G. arboreum [21] and Gossypium raimondii [22], enabled us to carry out the identification and characterization of all cotton LEA genes. In this study, we identified 242, 136 and 142 candidate LEA proteins in G. hirsutum, G. arboreum and G. raimondii respectively, analysed their phylogenetic tree relationships, chromosomal positions, duplicated gene events, gene structure, conserved motif compositions and profiling analysis of gene expression from different cotton plant organs. Our results provides a strong platform for better understanding of the roles and evolutionary history of LEA genes, and will help in future studies of the molecular and biological functions of LEA protein families in cotton.
Methods
Identification of LEA gene families
The conserved LEA protein domains were downloaded from Hidden Markov Model (HMM) (PF 03760, PF03168, PF03242, PF02987, PF0477, PF10714, PF04927 and PF00257. In order to identify the LEA proteins in cotton, the HHM profile of LEA protein was subsequently employed as a query to perform a HMMER search (http://hmmer.janelia.org/) [23] against the G. hirsutum and G. arboreum, which were obtained from cotton genome project (http://www.cgp.genomics.org.cn) and G. raimondii genome downloaded from Phytozome (http://www.Phytozome.net/), with E-value <0.01. All redundant sequences were discarded from further analysis based on cluster W17 alignment results. SMART and PFAM database were used to verify the presence of the LEA gene domains. The isoelectric points and molecular mass of LEA proteins were estimated by ExPASy Server tool (http://web.expasy.org/compute_pi/). In addition, subcellular location prediction of upland cotton, Gossypium hirsutum LEA proteins was conducted using the TargetP1.1 (http://www.cbs.dtu.dk/services/TargetP/) server [24] and Protein Prowler Subcellular Localisation Predictor version 1.2 (http://bioinf.scmb.uq.edu.au/pprowler_webapp_1-2/) [25]. Validation and determination of the possible cell compartmentalization of the LEA protein was done by WoLFPSORT (https://wolfpsort.hgc.jp/) [26].
Chromosomal locations and syntenic analysis
The chromosomal distribution of LEA genes were mapped on cotton chromosomes based on gene position, from up down by Circos-0.69 (http://circos.ca/) [27]. Homologous genes of G. hirsutum, G. raimondii and G. arboreum were identified by BLASTP with threshold >80% in similarity and at least in 80% alignment ratio to their protein total lengths. Default parameters were maintained in all of the steps. Tandem duplications were designated as multiple genes of one family located within the same or neighbouring intergenic region [28]. The Ks/Ka value is an important tool in determining selection pressure acting on the protein coding genes. The genes paralogous pair, which has Ka/Ks, ratio greater than 1, denotes activating evolution under beneficial selection, indicating that at least some of the mutations were advantageous. When the ratio is equal to 1, then the mutation is neutral but if the ratio is less than 1, it implies that the mutation is disadvantageous or under purifying selection [29]. In the estimation of Ks and Ka substitution rate, we used an alignment of multiple nucleotide sequences of homologous genes which code for LEA proteins. In this research, paralogous pairs were aligned using MEGA 6.0. synonymous substitution (Ks) and non-synonymous substitution (Ka) rate were obtained by Dnasp [30].
Phylogenetic analyses, gene structure organization and motif composition of the LEA proteins in cotton
Full-length sequences of G. hirsutum, G. arboreum, G. raimondii, P. tabuliformis and A. thaliana LEA proteins were first aligned using ClustalW on MEGA 6 software [31] then conducted phylogenetic analyses based on protein sequences, with neighbour joining (NJ) method. Support for each node was tested with 1000 bootstrap replicates. The analysis of phylogenetic tree was carried out on upland cotton, G. hirsutum. The gene structures were obtained through comparing the genomic sequences and their predicted coding sequences from the cotton genome project. In addition, MEME (Multiple Expectation Maximization for Motif EliCitation) online program (http:// meme.nbcr.net/meme/cgi-bin/meme.cgi) [32], was used to identify the conserved protein motifs, with maximum number of different motif at 20; the minimum and largest base sequence width of 6 and 50 respectively.
Prediction of miRNAs targeted LEA genes
The miRNA sequences were obtained from miRBase (http://www.mirbase.org/) [33], the Plant miRNA database (http://bioinformatics.cau.edu.cn/PMRD/) [34] and EST database (http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/ nucest) LEA genes targeted by miRNAs were predicted by searching 5′ and 3´ UTRs and the CDS of all LEA genes for complementary sequences of the cotton miRNAs using the psRNATarget server with default parameters (http://plantgrn.noble.org/psRNATarget/?function=3) [35].
Promoter cis-element analysis
Promoter sequences (2 kb upstream of the translation start site) of all LEA genes were obtained from the cotton genome project (http://cgp.genomics.org.cn/page/species/index.jsp).Transcriptional response elements of LEA genes promoters were predicted using using the PLACE database (http://www.dna.affrc.go.jp/PLACE/signals can.html) [36].
Gene ontology (GO) annotation
The functional grouping of LEA proteins sequences and the analysis of annotation data were executed using Blast2GO PRO software version 4.1.1 (https://www.blast2go.com). Blast2GO annotation associates genes or transcripts with GO terms using hierarchical terms, cellular component (CC), biological process (BP) and molecular function (MF). Genes were described in three categories of the GO classification terms: molecular function, biological processes and cellular components.
Plant materials and treatment
One-month-old cotton seedlings of G. tomentosum-AD3–00 (P0601211), G. hirsutum-CRI-12 (G09091801–2) and their BC2F1 genotypes, with G. tomentosum as the donor and G. hirsutum as the recurrent parent were used to examine the expression patterns of the LEA genes under drought condition. G. tomentosum is drought tolerant genotype while G. hirsutum is drought susceptible genotype. The two upland cotton accessions are perennially grown and maintained by our research group, in Sanya Island, Hainan province, China. Plants were grown in boxes, with dimension of 41 × 41 cm, with a depth of 30 cm and with three biological replications in the greenhouse located at the cotton research institute, Chinese Academy of Agricultural Sciences (CAAS), Anyang, Henan province, China. The greenhouse conditions were set with temperature at 23 ± 1 °C and a 14-h light/10-h dark photoperiod. After one month of growth, watering was totally withdrawn from drought treated seedlings but not in control. The samples for RNA extraction were collected at 0, 7 and 14th day of drought stress exposure, for plants under drought and control. Root, stem and leaf were the main organs of target in this study.
RNA isolation and qRT-PCR verification
RNA extraction kit, EASYspin plus plant RNA kit, obtained from Aid Lab, China was used to extract total RNA from roots, stems and leaves. The quality and concentration of each RNA sample was determined using gel electrophoresis and a NanoDrop 2000 spectrophotometer. Only RNAs which met the criterion 260/280 ratio of 1.8–2.1, 260/230 ratio ≥ 2.0, were used for further analyses and stored at −80 °C. The cotton constitutive Ghactin7 gene, forward “ATCCTCCGTCTTGACCTTG” and reverse sequence “TGTCCGTCAGGCAACTCAT” was used as a reference gene and specific LEA genes primers were used for qRT-PCR validation. The first-strand cDNA synthesis was carried out with TranScript-All-in-One First-Strand cDNA Synthesis SuperMix for qPCR, obtained from TRAN, it was used in accordance with the manufacturer’s instructions. Primer Premier 5 was used to design 43 LEA primers with melting temperatures of 55–60 °C, primer lengths of 18–25 bp, and amplicon lengths of 101–221 bp. Details of the primers are shown in (Additional file 1: Table S1). Fast Start Universal SYBRgreen Master (Rox) (Roche, Mannheim, Germany) was used to perform qRT-PCR in accordance with the manufacturer’s instructions. Reactions were prepared in a total volume of 20 μL, containing 10 μL of SYBR green master mix, 2 μL of cDNA template, 6 μL of ddH2O, and 2 μL of each primer to make a final concentration of 10 μM.
Results
Identification of LEA genes in cotton
The HMM profile of the Pfam LEA domains (PF3760, PF03168, PF03242, PF02987, PF00477, PF10714, PF00257 and PF 04927) were used as the query to identify LEA genes in the cotton genomes. Two hundred and eighty LEA genes were identified in upland cotton, Gossypium hirsutum, one hundred-seventy LEA genes in G. raimondii and one hundred-fifty LEA genes in G. arboreum. All the LEA genes were analyzed manually using the SMART and PFAM database (http://pfam.xfam.org/) to verify the presence of the LEA gene domain. Finally, 242, 136 and 142 candidate LEA proteins were identified in G. hirsutum, G. arboreum and G. raimondii respectively. All identified LEA genes were grouped into eight groups, ranging from LEA 1 to LEA 6, dehydrin and seed maturation protein (SMP). To validate our classification of upland cotton LEA genes, we compared the LEA genes nomenclature with previous identification adopted by Hundertmark and Hincha [12] and Bies-Etheve et al. [37] (Table 1).
Table 1.
LEA proteins distribution in upland cotton compared with other plants
| LEA genes grouping in this study | Pfam | Hundertmark et al. (2008) | Bies-Etheve et al. (2008) | Arabidopsis | G. hirsutum (AD) | G. arboreum (A) | G. raimondii (D) | Pinus tabuliformis | TOTALS |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| LEA 1 | PF03760 | LEA1 | LEA4 | 7 | 9 | 4 | 4 | 3 | 27 |
| LEA 2 | PF03168 | LEA2 | LEA7 | 3 | 157 | 85 | 89 | 1 | 335 |
| LEA 3 | PF03242 | LEA3 | LEA6 | 4 | 16 | 6 | 7 | 6 | 39 |
| LEA 4 | PF02987 | LEA4 | LEA3 | 12 | 13 | 8 | 7 | 16 | 56 |
| LEA 5 | PF00477 | LEA5 | LEA1 | 6 | 9 | 7 | 6 | 3 | 31 |
| LEA 6 | PF10714 | PvLEA18 | LEA8 | 3 | 4 | 2 | 4 | 0 | 13 |
| SMP | PF04927 | SMP | LEA5 | 6 | 10 | 16 | 17 | 0 | 49 |
| DEHYDRIN | PF00257 | Dehydrin | LEA2 | 10 | 24 | 8 | 8 | 1 | 51 |
| TOTALS | 51 | 242 | 136 | 142 | 30 | 601 | |||
The physicochemical parameters of each LEA gene were calculated by using ExPASy, an online tool [38]. Most of the LEA proteins in the same family had similar physicochemical parameters. Cotton LEAs of the LEA 4 contained a greater number of amino acid residues as depicted by their protein lengths (aa), followed closely by the dehydrins (Table 2). Dehydrins have been found to contain high number of amino acid residues from the structural analysis of LEA genes in Brassica napus [39]. Cotton LEA_6 family members all had relatively low molecular masses, ranging from 10.177 to 11.9634 kDa, similar findings was also reported in the analysis of B. napus LEA genes, in which all the LEA 6 genes had lower molecular masses [39]. Approximately two- thirds of the cotton LEA proteins had high isoelectric points Pl ≥ 7.0, including majority of LEA 2 family.
Table 2.
LEA gene in upland cotton, Gossypium hirsutum and their sequence characteristics and subcellular location prediction and chromosome position
| GENE ID | PROTEIN TYPE | GENE ANNOTATION | LENGTH (aa) | Pl | MM(aa) | Chr NO | Start | End | Position | Sub cellular localization | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Wolfpsort | Pprowler | TargetP | ||||||||||
| CotAD_ 04417 | DEHYDRIN | DEHYDRIN-4 | 98 | 6.33 | 10,753.6 | At_chr08 | 2,270,863 | 2,271,159 | 296 | nucl | other | _ |
| CotAD_ 07367 | DEHYDRIN | DEHYDRIN-24 | 1431 | 6.31 | 160,755.92 | scaffold72.1 | 2,201,874 | 2,209,455 | 7581 | plas | other | _ |
| CotAD_ 08352 | DEHYDRIN | DEHYDRIN-23 | 160 | 5.45 | 17,797.83 | scaffold190.1 | 910,057 | 911,647 | 1590 | nucl | other | _ |
| CotAD_ 10,502 | DEHYDRIN | DEHYDRIN-8 | 235 | 8.18 | 26,216.65 | Dt01_chr15 | 2,276,230 | 2,277,176 | 946 | nucl | other | _ |
| CotAD_ 11,398 | DEHYDRIN | DEHYDRIN-13 | 51 | 6.52 | 5513.09 | Dt06_chr25 | 776,882 | 777,140 | 258 | nucl | other | S |
| CotAD_ 13,947 | DEHYDRIN | DEHYDRIN-19 | 449 | 4.92 | 49,643.3 | Dt13_chr18 | 1,193,127 | 1,196,473 | 3346 | nucl | other | _ |
| CotAD_ 15,928 | DEHYDRIN | DEHYDRIN-18 | 180 | 7.98 | 19,341.26 | Dt12_chr26 | 638,305 | 639,445 | 1140 | nucl | other | _ |
| CotAD_ 16,331 | DEHYDRIN | DEHYDRIN-15 | 128 | 5.46 | 14,436.09 | Dt08_chr24 | 877,320 | 877,836 | 516 | mito | other | _ |
| CotAD_ 19,173 | DEHYDRIN | DEHYDRIN-5 | 180 | 7.98 | 19,330.23 | At_chr12 | 883,350 | 884,512 | 1162 | cyto | other | _ |
| CotAD_ 22,357 | DEHYDRIN | DEHYDRIN-2 | 197 | 5.48 | 22,224.51 | At_chr02 | 824,855 | 825,544 | 689 | chlo | other | _ |
| CotAD_ 27,143 | DEHYDRIN | DEHYDRIN-14 | 135 | 9.49 | 14,720.04 | Dt07_chr16 | 115,939 | 116,435 | 496 | chlo | other | _ |
| CotAD_ 29,610 | DEHYDRIN | DEHYDRIN-16 | 172 | 5.89 | 19,224.36 | Dt08_chr24 | 936,161 | 936,813 | 652 | cyto | other | _ |
| CotAD_ 31,255 | DEHYDRIN | DEHYDRIN-10 | 199 | 5.5 | 22,423.72 | Dt02_chr14 | 711,572 | 712,266 | 694 | chlo | other | _ |
| CotAD_ 35,513 | DEHYDRIN | DEHYDRIN-12 | 161 | 4.79 | 17,827.6 | Dt05_chr19 | 393,056 | 394,685 | 1629 | chlo | other | _ |
| CotAD_ 42,408 | DEHYDRIN | DEHYDRIN-20 | 344 | 9.01 | 37,987.42 | Dt13_ch18 | 453,295 | 454,329 | 1034 | chlo | other | _ |
| CotAD_ 46,550 | DEHYDRIN | DEHYDRIN-1 | 135 | 9.33 | 14,717.04 | At_chr01 | 69,396 | 69,892 | 496 | cyto | other | _ |
| CotAD_ 50,983 | DEHYDRIN | DEHYDRIN-9 | 243 | 8.82 | 26,199.73 | Dt02_chr14 | 297,459 | 298,432 | 973 | cyto | other | _ |
| CotAD_ 53,264 | DEHYDRIN | DEHYDRIN-22 | 211 | 5.04 | 23,789.31 | scaffold1899.1 | 95,851 | 96,576 | 725 | cyto | other | _ |
| CotAD_ 57,587 | DEHYDRIN | DEHYDRIN-17 | 211 | 5.22 | 23,654.28 | Dt09_chr23 | 187,778 | 188,503 | 725 | cyto | other | _ |
| CotAD_ 64,203 | DEHYDRIN | DEHYDRIN-6 | 178 | 6.48 | 19,521.14 | At_chr13 | 125,424 | 126,358 | 934 | chlo | other | _ |
| CotAD_ 65,889 | DEHYDRIN | DEHYDRIN-11 | 608 | 5.62 | 67,130.02 | Dt03_chr17 | 396,530 | 401,988 | 5458 | cyto | other | _ |
| CotAD_ 70,948 | DEHYDRIN | DEHYDRIN-21 | 332 | 8.46 | 37,102.53 | Dt13_chr18 | 41,714 | 42,880 | 1166 | chlo | other | _ |
| CotAD_ 75,267 | DEHYDRIN | DEHYDRIN-7 | 332 | 8.22 | 37,096.42 | At_chr13 | 210,365 | 211,531 | 1166 | nucl | other | _ |
| CotAD_ 75,537 | DEHYDRIN | DEHYDRIN-3 | 533 | 5.39 | 58,793.08 | At_chr03 | 254,566 | 259,519 | 4953 | plas | other | _ |
| CotAD_ 16,594 | LEA1 | LEA 1–7 | 115 | 6.9 | 13,315.99 | Dt13_chr18 | 1,203,659 | 1,204,098 | 439 | mito | other | _ |
| CotAD_ 16,595 | LEA1 | LEA 1–8 | 115 | 6.9 | 13,315.99 | Dt13_chr18 | 1,204,716 | 1,205,155 | 439 | cyto | other | _ |
| CotAD_ 17,186 | LEA1 | LEA 1–1 | 165 | 5.81 | 17,459.58 | At_chr06 | 1,273,709 | 1,274,303 | 594 | plas | other | _ |
| CotAD_ 20,491 | LEA1 | LEA 1–6 | 165 | 6.08 | 17,343.5 | Dt06_chr25 | 298,147 | 298,732 | 585 | cyto | other | _ |
| CotAD_ 30,219 | LEA1 | LEA 1–2 | 113 | 6.3 | 12,106.42 | Dt02_chr14 | 23,536 | 24,035 | 499 | chlo | other | _ |
| CotAD_ 31,140 | LEA1 | LEA 1–3 | 164 | 9.3 | 16,871.44 | Dt02_chr14 | 28,053 | 28,616 | 563 | cyto | other | _ |
| CotAD_ 48,976 | LEA1 | LEA 1–9 | 116 | 8.01 | 13,437.07 | scaffold842.1 | 284,300 | 284,742 | 442 | chlo | other | _ |
| CotAD_ 51,667 | LEA1 | LEA 1–4 | 164 | 9.33 | 16,897.52 | Dt02_chr14 | 443,597 | 444,162 | 565 | nucl | other | _ |
| CotAD_ 52,203 | LEA1 | LEA 1–5 | 420 | 9.1 | 45,990.36 | Dt02_chr14 | 444,540 | 450,345 | 5805 | cyto | other | _ |
| CotAD_ 00275 | LEA2 | LEA 2–98 | 274 | 10.09 | 29,834.66 | Dt09_chr23 | 2,049,164 | 2,049,988 | 824 | chlo | other | M |
| CotAD_ 00465 | LEA2 | LEA 2–101 | 304 | 9.59 | 33,689.28 | Dt09_chr23 | 3,367,709 | 3,368,936 | 1227 | chlo | other | M |
| CotAD_ 00799 | LEA2 | LEA 2–154 | 337 | 8.96 | 38,982.02 | scaffold26.1 | 2,048,605 | 2,051,804 | 3199 | golg | other | M |
| CotAD_ 00808 | LEA2 | LEA 2–155 | 226 | 10.08 | 26,011.22 | scaffold26.1 | 2,100,130 | 2,100,810 | 680 | cyto | other | M |
| CotAD_ 01033 | LEA2 | LEA 2–105 | 202 | 9.06 | 22,587.14 | Dt10_chr20 | 1,010,984 | 1,011,592 | 608 | chlo | other | M |
| CotAD_ 01298 | LEA2 | LEA 2–107 | 218 | 10.22 | 24,021.4 | Dt10_chr20 | 5,288,414 | 5,289,070 | 656 | cyto | other | _ |
| CotAD_ 01321 | LEA2 | LEA 2–108 | 238 | 9.54 | 26,020.28 | Dt10_chr20 | 5,756,514 | 5,757,230 | 716 | cyto | SP | M |
| CotAD_ 01385 | LEA2 | LEA 2–89 | 247 | 7 | 27,497.03 | Dt09_chr23 | 159,994 | 161,690 | 1696 | cyto | other | _ |
| CotAD_ 01700 | LEA2 | LEA 2–100 | 260 | 9.36 | 28,399.83 | Dt09_chr23 | 2,815,779 | 2,816,561 | 782 | cyto | other | _ |
| CotAD_ 02652 | LEA2 | LEA 2–97 | 212 | 10.05 | 23,764.43 | Dt09_chr23 | 2,032,508 | 2,033,146 | 638 | mito | other | _ |
| CotAD_ 03037 | LEA2 | LEA 2–63 | 262 | 9.05 | 28,472.57 | Dt05_chr19 | 1,838,069 | 1,841,145 | 3076 | cyto | other | _ |
| CotAD_ 03649 | LEA2 | LEA 2–34 | 320 | 9.82 | 35,345.6 | At_chr09 | 1,775,719 | 1,776,844 | 1125 | cyto | other | _ |
| CotAD_ 03784 | LEA2 | LEA 2–75 | 116 | 6.82 | 13,537.66 | Dt07_chr16 | 548,573 | 548,923 | 350 | chlo | other | _ |
| CotAD_ 05724 | LEA2 | LEA 2–32 | 197 | 10.05 | 22,442.51 | At_chr09 | 1,755,547 | 1,756,140 | 593 | chlo | other/SP | _ |
| CotAD_ 05725 | LEA2 | LEA 2–33 | 238 | 9.73 | 27,552.78 | At_chr09 | 1,759,512 | 1,760,228 | 716 | nucl | SP | _ |
| CotAD_ 06037 | LEA2 | LEA 2–115 | 205 | 10.07 | 22,125.81 | Dt13_ch18 | 90,455 | 91,072 | 617 | chlo | SP | _ |
| CotAD_ 07087 | LEA2 | LEA2–3 | 206 | 9.75 | 22,853.64 | At_chr02 | 2,101,730 | 2,102,350 | 620 | plas | other | _ |
| CotAD_ 08181 | LEA2 | LEA 2–99 | 202 | 8.61 | 22,460.02 | Dt09_chr23 | 2,228,567 | 2,229,175 | 608 | cyto | SP | _ |
| CotAD_ 08350 | LEA2 | LEA 2–152 | 198 | 5.02 | 22,266.98 | scaffold190.1 | 904,483 | 905,252 | 769 | chlo | SP | _ |
| CotAD_ 08837 | LEA2 | LEA 2–125 | 245 | 8.77 | 26,376.34 | scaffold280.1 | 51,952 | 53,959 | 2007 | golg | other | _ |
| CotAD_ 09578 | LEA2 | LEA 2–30 | 260 | 9.39 | 28,406.84 | At_chr09 | 1,173,118 | 1,173,900 | 782 | chlo | other | _ |
| CotAD_ 09685 | LEA2 | LEA 2–93 | 251 | 10.07 | 27,153.8 | Dt09_chr23 | 686,730 | 687,485 | 755 | chlo | SP | C |
| CotAD_ 09732 | LEA2 | LEA 2–96 | 232 | 9.44 | 25,906.5 | Dt09_chr23 | 1,174,994 | 1,175,943 | 949 | chlo | other | _ |
| CotAD_ 10,376 | LEA2 | LEA 2–48 | 277 | 9.92 | 30,152.74 | Dt01_chr15 | 100,033 | 100,866 | 833 | chlo | SP | M |
| CotAD_ 11,658 | LEA2 | LEA 2–84 | 263 | 9.82 | 29,835.19 | Dt08_chr24 | 199,067 | 199,858 | 791 | cyto | SP | M |
| CotAD_ 11,875 | LEA2 | LEA 2–147 | 175 | 6.95 | 20,070.28 | scaffold42.1 | 647,003 | 647,530 | 527 | chlo | SP | M |
| CotAD_ 11,876 | LEA2 | LEA 2–148 | 209 | 10.01 | 23,563.32 | scaffold42.1 | 677,153 | 677,782 | 629 | chlo | SP | _ |
| CotAD_ 11,878 | LEA2 | LEA 2–149 | 226 | 9.49 | 25,841.73 | scaffold42.1 | 688,643 | 689,323 | 680 | chlo | SP | _ |
| CotAD_ 11,879 | LEA2 | LEA 2–150 | 129 | 9.45 | 15,037.05 | scaffold42.1 | 690,007 | 690,396 | 389 | chlo | SP | _ |
| CotAD_ 12,375 | LEA2 | LEA 2–25 | 190 | 8.59 | 21,328.78 | At_chr09 | 106,696 | 107,358 | 662 | chlo | SP | _ |
| CotAD_ 13,115 | LEA2 | LEA 2–86 | 192 | 9.42 | 20,770.35 | Dt08_chr24 | 1,183,052 | 1,183,630 | 578 | extr | SP | _ |
| CotAD_ 13,584 | LEA2 | LEA 2–67 | 250 | 9.96 | 28,048.83 | Dt06_chr25 | 364,402 | 365,154 | 752 | golg | SP | _ |
| CotAD_ 13,827 | LEA2 | LEA 2–114 | 360 | 7.87 | 40,945.87 | Dt12_chr26 | 971,427 | 972,748 | 1321 | E.R. | mTP | C |
| CotAD_ 14,147 | LEA2 | LEA 2–16 | 212 | 9.94 | 23,855.54 | At_chr07 | 774,151 | 774,789 | 638 | mito | SP | S |
| CotAD_ 15,892 | LEA2 | LEA 2–112 | 307 | 7.7 | 34,741.21 | Dt12_chr26 | 406,661 | 409,153 | 2492 | chlo | mTP | _ |
| CotAD_ 16,731 | LEA2 | LEA 2–94 | 258 | 10.01 | 28,519.44 | Dt09_chr23 | 724,944 | 725,720 | 776 | chlo | other | _ |
| CotAD_ 17,044 | LEA2 | LEA 2–17 | 151 | 4.84 | 16,422.87 | At_chr07 | 972,098 | 972,634 | 536 | cyto | SP | S |
| CotAD_ 17,045 | LEA2 | LEA 2–18 | 219 | 9.79 | 23,930.18 | At_chr07 | 992,750 | 993,409 | 659 | cyto | SP | _ |
| CotAD_ 17,062 | LEA2 | LEA 2–19 | 244 | 9.78 | 27,393.16 | At_chr07 | 1,176,161 | 1,176,895 | 734 | chlo | mTP | C |
| CotAD_ 17,101 | LEA2 | LEA 2–9 | 222 | 9.26 | 25,294.09 | At_chr06 | 94,601 | 95,269 | 668 | mito | SP | S |
| CotAD_ 17,102 | LEA2 | LEA 2–10 | 209 | 10.35 | 23,661.48 | At_chr06 | 122,145 | 122,774 | 629 | nucl | SP | _ |
| CotAD_ 17,103 | LEA2 | LEA 2–11 | 265 | 6.7 | 30,299.29 | At_chr06 | 134,827 | 135,702 | 875 | mito | SP | C |
| CotAD_ 17,649 | LEA2 | LEA 2–37 | 235 | 8.5 | 26,726.9 | At_chr10 | 359,189 | 361,440 | 2251 | chlo | SP | _ |
| CotAD_ 18,210 | LEA2 | LEA 2–141 | 203 | 10.17 | 22,501.33 | scaffold377.1 | 414,366 | 414,977 | 611 | cyto | SP | C |
| CotAD_ 18,233 | LEA2 | LEA 2–145 | 203 | 10.08 | 22,406.26 | scaffold377.1 | 560,351 | 560,962 | 611 | chlo | SP | _ |
| CotAD_ 18,546 | LEA2 | LEA 2–95 | 173 | 9.91 | 19,695.85 | Dt09_chr23 | 893,109 | 893,715 | 606 | chlo | mTP | M |
| CotAD_ 18,729 | LEA2 | LEA 2–142 | 277 | 9.92 | 30,227.97 | scaffold336.1 | 433,013 | 433,846 | 833 | chlo | SP | _ |
| CotAD_ 19,078 | LEA2 | LEA 2–42 | 216 | 9.83 | 24,007.7 | At_chr12 | 18,103 | 18,753 | 650 | nucl | other | _ |
| CotAD_ 19,107 | LEA2 | LEA 2–43 | 183 | 9.04 | 20,031.24 | At_chr12 | 312,977 | 313,528 | 551 | chlo | SP | C |
| CotAD_ 19,205 | LEA2 | LEA 2–46 | 297 | 6.83 | 33,395.7 | At_chr12 | 1,142,954 | 1,145,475 | 2521 | chlo | SP | S |
| CotAD_ 19,213 | LEA2 | LEA 2–38 | 100 | 9.64 | 11,538.35 | At_chr10 | 410,401 | 410,703 | 302 | chlo | mTP | _ |
| CotAD_ 19,214 | LEA2 | LEA 2–39 | 181 | 9.32 | 20,628.72 | At_chr10 | 411,491 | 412,036 | 545 | nucl | SP | S |
| CotAD_ 19,375 | LEA2 | LEA 2–111 | 225 | 8.57 | 25,956.2 | Dt11_chr21 | 1,023,165 | 1,023,842 | 677 | golg | mTP | C |
| CotAD_ 20,020 | LEA2 | LEA 2–13 | 250 | 9.89 | 27,947.68 | At_chr06 | 997,148 | 997,900 | 752 | mito | SP | _ |
| CotAD_ 20,308 | LEA2 | LEA 2–72 | 191 | 9.56 | 21,054.44 | Dt06_chr25 | 1,390,037 | 1,390,612 | 575 | chlo | cTP | C |
| CotAD_ 21,731 | LEA2 | LEA 2–62 | 244 | 9.83 | 27,381.21 | Dt05_chr19 | 1,524,633 | 1,525,367 | 734 | nucl | other | _ |
| CotAD_ 21,924 | LEA2 | LEA 2–110 | 262 | 10.16 | 28,411.4 | Dt11_chr21 | 855,130 | 855,918 | 788 | nucl | SP | S |
| CotAD_ 23,646 | LEA2 | LEA 2–74 | 204 | 9.81 | 21,921.93 | Dt07_chr16 | 34,227 | 34,841 | 614 | nucl | SP | _ |
| CotAD_ 24,019 | LEA2 | LEA 2–71 | 203 | 10.04 | 22,391.06 | Dt06_chr25 | 652,496 | 653,107 | 611 | mito | SP | S |
| CotAD_ 24,497 | LEA2 | LEA 2–106 | 263 | 8.64 | 29,247.79 | Dt10_chr20 | 1,715,959 | 1,719,093 | 3134 | chlo | other | _ |
| CotAD_ 24,499 | LEA2 | LEA 2–138 | 175 | 7.66 | 20,026.25 | scaffold238.1 | 343,833 | 344,360 | 527 | chlo | SP | _ |
| CotAD_ 25,271 | LEA2 | LEA 2–139 | 209 | 10.01 | 23,559.33 | scaffold238.1 | 356,524 | 357,153 | 629 | nucl | SP | _ |
| CotAD_ 26,038 | LEA2 | LEA 2–140 | 226 | 9.43 | 25,852.71 | scaffold238.1 | 383,318 | 383,998 | 680 | chlo | SP | S |
| CotAD_ 26,981 | LEA2 | LEA 2–26 | 274 | 10.09 | 29,936.66 | At_chr09 | 239,371 | 240,195 | 824 | chlo | other | _ |
| CotAD_ 27,453 | LEA2 | LEA 2–131 | 239 | 9.76 | 26,994.13 | scaffold477.1 | 176,874 | 179,526 | 2652 | mito | SP | _ |
| CotAD_ 27,789 | LEA2 | LEA 2–151 | 184 | 9.41 | 20,135.39 | scaffold699.1 | 759,396 | 759,950 | 554 | E.R. | SP | M |
| CotAD_ 28,249 | LEA2 | LEA 2–27 | 150 | 9.24 | 16,764.6 | At_chr09 | 274,309 | 275,011 | 702 | nucl | SP | _ |
| CotAD_ 28,252 | LEA2 | LEA 2–13 | 222 | 8.65 | 24,982.77 | At_chr07 | 296,696 | 299,063 | 2367 | mito | other | _ |
| CotAD_ 28,872 | LEA2 | LEA 2–57 | 257 | 9.1 | 26,949.97 | Dt03_chr17 | 1,936,828 | 1,937,663 | 835 | nucl | SP | _ |
| CotAD_ 29,279 | LEA2 | LEA 2–116 | 305 | 9.66 | 34,588.47 | Dt13_chr18 | 639,522 | 641,549 | 2027 | chlo | SP | _ |
| CotAD_ 31,344 | LEA2 | LEA 2–132 | 101 | 5.51 | 11,711.01 | scaffold1346.1 | 193,028 | 193,333 | 305 | chlo | other | _ |
| CotAD_ 31,535 | LEA2 | LEA 2–8 | 240 | 7.89 | 27,649.86 | At_chr05 | 790,866 | 791,588 | 722 | vacu | other | _ |
| CotAD_ 31,536 | LEA2 | LEA 2–136 | 210 | 9.19 | 23,875.63 | scaffold1346.1 | 213,521 | 214,153 | 632 | plas | SP | _ |
| CotAD_ 31,537 | LEA2 | LEA 2–133 | 254 | 10.22 | 27,558.52 | scaffold1841.1 | 200,526 | 201,290 | 764 | nucl | cTP | C |
| CotAD_ 31,780 | LEA2 | LEA 2–87 | 310 | 9.93 | 34,525.38 | Dt08_chr24 | 1,487,296 | 1,488,516 | 1220 | chlo | other | _ |
| CotAD_ 31,782 | LEA2 | LEA 2–90 | 210 | 7.72 | 23,638.39 | Dt09_chr23 | 194,606 | 195,238 | 632 | chlo | SP | _ |
| CotAD_ 31,860 | LEA2 | LEA 2–153 | 206 | 9.82 | 22,839.69 | scaffold257.1 | 1,162,406 | 1,163,026 | 620 | cyto | SP | _ |
| CotAD_ 31,906 | LEA2 | LEA 2–137 | 232 | 9.66 | 26,256.38 | scaffold769.1 | 292,760 | 295,431 | 2671 | cyto | mTP | M |
| CotAD_ 31,936 | LEA2 | LEA 2–53 | 152 | 4.74 | 16,462.97 | Dt01_chr15 | 598,039 | 598,839 | 800 | mito | SP | _ |
| CotAD_ 32,487 | LEA2 | LEA 2–36 | 305 | 9.97 | 33,718.76 | At_chr11 | 169,902 | 171,217 | 1315 | mito | other | _ |
| CotAD_ 32,645 | LEA2 | LEA 2–66 | 199 | 9.3 | 22,785.41 | Dt06_chr25 | 246,850 | 247,449 | 599 | chlo | SP | C |
| CotAD_ 32,847 | LEA2 | LEA 2–24 | 249 | 9.79 | 27,707.74 | At_chr09 | 61,155 | 61,904 | 749 | extr | cTP | C |
| CotAD_ 33,143 | LEA2 | LEA 2–54 | 305 | 9.63 | 34,544.43 | Dt02_chr14 | 1,894,174 | 1,896,197 | 2023 | chlo | SP | _ |
| CotAD_ 33,144 | LEA2 | LEA 2–60 | 240 | 8.49 | 27,655.92 | Dt05_chr19 | 151,373 | 152,095 | 722 | chlo | SP | S |
| CotAD_ 34,476 | LEA2 | LEA 2–92 | 320 | 9.92 | 35,579.84 | Dt09_chr23 | 448,827 | 449,952 | 1125 | cyto | SP | _ |
| CotAD_ 34,798 | LEA2 | LEA 2–68 | 222 | 9.23 | 25,253.03 | Dt06_chr25 | 385,794 | 386,462 | 668 | nucl | SP | _ |
| CotAD_ 35,069 | LEA2 | LEA 2–69 | 209 | 10.25 | 23,628.4 | Dt06_chr25 | 396,513 | 397,142 | 629 | chlo | SP | _ |
| CotAD_ 35,091 | LEA2 | LEA 2–70 | 288 | 7.1 | 32,755.52 | Dt06_chr25 | 403,729 | 404,595 | 866 | extr | SP | _ |
| CotAD_ 35,514 | LEA2 | LEA 2–61 | 206 | 5.9 | 23,420.27 | Dt05_chr19 | 399,904 | 400,524 | 620 | mito | SP | C |
| CotAD_ 36,328 | LEA2 | LEA 2–144 | 450 | 4.92 | 49,131.5 | scaffold821.1 | 548,888 | 550,240 | 1352 | chlo | other | _ |
| CotAD_ 36,446 | LEA2 | LEA 2–78 | 231 | 9.47 | 24,949.39 | Dt08_chr24 | 58,782 | 59,477 | 695 | chlo | other | _ |
| CotAD_ 36,583 | LEA2 | LEA 2–146 | 206 | 8.88 | 22,761.2 | scaffold821.1 | 625,818 | 626,438 | 620 | chlo | other | _ |
| CotAD_ 37,776 | LEA2 | LEA 2–91 | 202 | 9.02 | 22,357.93 | Dt09_chr23 | 337,931 | 338,539 | 608 | chlo | SP | S |
| CotAD_ 37,888 | LEA2 | LEA 2–21 | 283 | 10.15 | 31,410.18 | At_chr08 | 2,313,418 | 2,314,578 | 1160 | chlo | other | _ |
| CotAD_ 38,978 | LEA2 | LEA 2–85 | 210 | 9.76 | 22,644.27 | Dt08_chr24 | 376,609 | 377,241 | 632 | nucl | SP | S |
| CotAD_ 39,064 | LEA2 | LEA 2–50 | 210 | 9.48 | 23,699.74 | Dt01_chr15 | 220,837 | 221,469 | 632 | chlo | other | _ |
| CotAD_ 39,719 | LEA2 | LEA 2–52 | 191 | 6.29 | 20,961.07 | Dt01_chr15 | 397,156 | 397,731 | 575 | nucl | mTP | _ |
| CotAD_ 40,324 | LEA2 | LEA 2–15 | 204 | 9.81 | 21,780.76 | At_chr07 | 720,430 | 721,044 | 614 | plas | SP | _ |
| CotAD_ 41,569 | LEA2 | LEA 2–47 | 208 | 10.19 | 22,559.45 | At_chr13 | 343,514 | 344,140 | 626 | chlo | other | _ |
| CotAD_ 41,571 | LEA2 | LEA 2–88 | 270 | 9.56 | 30,627.54 | Dt09_chr23 | 64,512 | 65,324 | 812 | chlo | SP | _ |
| CotAD_ 41,925 | LEA2 | LEA 2–128 | 188 | 9.22 | 21,941.4 | scaffold1231.1 | 94,270 | 94,836 | 566 | nucl | other | _ |
| CotAD_ 42,599 | LEA2 | LEA 2–129 | 373 | 9.9 | 43,118.75 | scaffold1231.1 | 96,297 | 98,517 | 2220 | cyto | Other | M |
| CotAD_ 44,357 | LEA2 | LEA 2–143 | 210 | 9.34 | 23,874.6 | scaffold1088.1 | 451,853 | 452,485 | 632 | cyto | other | C |
| CotAD_ 45,324 | LEA2 | LEA 2–109 | 256 | 9.99 | 28,431.93 | Dt11_chr21 | 55,317 | 61,829 | 6512 | chlo | other | _ |
| CotAD_ 46,873 | LEA2 | LEA 2–29 | 259 | 10 | 28,603.52 | At_chr09 | 355,476 | 356,255 | 779 | vacu | other | _ |
| CotAD_ 47,322 | LEA2 | LEA2–5 | 220 | 9.85 | 24,666.72 | At_chr03 | 430,461 | 431,123 | 662 | chlo | SP | _ |
| CotAD_ 47,454 | LEA2 | LEA 2–130 | 661 | 6.14 | 73,583.12 | scaffold1851.1 | 116,914 | 132,924 | 16,010 | cysk | SP | C |
| CotAD_ 47,495 | LEA2 | LEA 2–76 | 318 | 10.09 | 35,234.15 | Dt07_chr16 | 1,185,327 | 1,186,479 | 1152 | chlo | SP | S |
| CotAD_ 47,749 | LEA2 | LEA 2–77 | 251 | 9.41 | 27,769.63 | Dt07_chr16 | 1,400,323 | 1,401,078 | 755 | chlo | mTP | M |
| CotAD_ 48,050 | LEA2 | LEA 2–103 | 217 | 9.28 | 24,968.87 | Dt10_chr20 | 968,935 | 969,588 | 653 | mito | other | _ |
| CotAD_ 48,069 | LEA2 | LEA 2–104 | 181 | 9.57 | 20,577.73 | Dt10_chr20 | 970,347 | 970,892 | 545 | extr | SP | S |
| CotAD_ 48,336 | LEA2 | LEA 2–58 | 211 | 9.12 | 23,479.93 | Dt04_chr22 | 552,418 | 553,053 | 635 | nucl | SP | _ |
| CotAD_ 48,753 | LEA2 | LEA 2–12 | 210 | 9.28 | 23,676.69 | At_chr06 | 482,445 | 483,077 | 632 | mito | SP | _ |
| CotAD_ 48,769 | LEA2 | LEA 2–28 | 304 | 9.56 | 33,675.21 | At_chr09 | 334,020 | 335,245 | 1225 | nucl | SP | _ |
| CotAD_ 49,818 | LEA2 | LEA 2–119 | 317 | 4.63 | 35,274.16 | scaffold2616.1 | 21,219 | 22,172 | 953 | cyto | SP | _ |
| CotAD_ 53,045 | LEA2 | LEA 2–102 | 206 | 7.58 | 22,650.27 | Dt10_chr20 | 363,682 | 364,302 | 620 | cyto | cTP | C |
| CotAD_ 53,263 | LEA2 | LEA 2–23 | 251 | 10.11 | 27,168.81 | At_chr09 | 24,397 | 25,152 | 755 | chlo | SP | _ |
| CotAD_ 53,981 | LEA2 | LEA 2–123 | 247 | 6.59 | 27,715.29 | scaffold3326.1 | 42,209 | 43,944 | 1735 | mito | cTP | C |
| CotAD_ 54,337 | LEA2 | LEA 2–14 | 152 | 4.84 | 16,453.02 | At_chr07 | 366,521 | 367,321 | 800 | chlo | SP | S |
| CotAD_ 55,224 | LEA2 | LEA 2–55 | 210 | 9.66 | 23,769.83 | Dt03_chr17 | 607,531 | 608,163 | 632 | mito | SP | M |
| CotAD_ 56,356 | LEA2 | LEA 2–22 | 173 | 9.96 | 19,737.98 | At_chr09 | 18,712 | 19,318 | 606 | chlo | SP | S |
| CotAD_ 56,696 | LEA2 | LEA 2–56 | 213 | 9.51 | 23,750.48 | Dt03_chr17 | 634,717 | 635,358 | 641 | nucl | SP | _ |
| CotAD_ 58,358 | LEA2 | LEA 2–113 | 209 | 10.19 | 23,626.51 | Dt12_ch26 | 897,133 | 897,762 | 629 | chlo | SP | S |
| CotAD_ 59,405 | LEA2 | LEA 2–61 | 320 | 9.9 | 35,457.72 | Dt05_chr19 | 251,378 | 252,501 | 1123 | chlo | SP | S |
| CotAD_ 60,279 | LEA2 | LEA 2–124 | 247 | 8.76 | 26,619.63 | scaffold2414.1 | 50,037 | 52,048 | 2011 | chlo | SP | _ |
| CotAD_ 60,435 | LEA2 | LEA2–1 | 251 | 9.57 | 27,952.81 | At_chr01 | 137,428 | 138,183 | 755 | chlo | cTP | C |
| CotAD_ 60,617 | LEA2 | LEA 2–49 | 210 | 9.51 | 23,780.9 | Dt01_chr15 | 198,189 | 198,821 | 632 | mito | SP | _ |
| CotAD_ 61,173 | LEA2 | LEA2–7 | 215 | 9.84 | 24,043 | At_chr04 | 59,864 | 60,511 | 647 | chlo | cTP | _ |
| CotAD_ 61,391 | LEA2 | LEA 2–51 | 191 | 6.29 | 20,884.97 | Dt01_chr15 | 284,374 | 284,949 | 575 | chlo | SP | C |
| CotAD_ 62,996 | LEA2 | LEA2–2 | 318 | 9.95 | 35,356.25 | At_chr01 | 176,895 | 178,045 | 1150 | nucl | SP | _ |
| CotAD_ 63,174 | LEA2 | LEA 2–117 | 377 | 9.77 | 41,228.93 | scaffold3177.1 | 19,137 | 21,221 | 2084 | E.R. | SP | C |
| CotAD_ 64,004 | LEA2 | LEA 2–73 | 219 | 9.65 | 23,825.02 | Dt07_chr16 | 34,198 | 34,857 | 659 | chlo | other | _ |
| CotAD_ 64,120 | LEA2 | LEA 2–41 | 218 | 10.14 | 24,050.43 | At_chr12 | 951 | 1607 | 656 | chlo | SP | _ |
| CotAD_ 64,346 | LEA2 | LEA 2–64 | 210 | 8.99 | 23,572.5 | Dt06_chr25 | 59,643 | 60,275 | 632 | chlo | SP | _ |
| CotAD_ 64,347 | LEA2 | LEA 2–65 | 235 | 9.44 | 26,111.93 | Dt06_chr25 | 62,524 | 63,231 | 707 | plas | cTP | C |
| CotAD_ 64,657 | LEA2 | LEA 2–40 | 262 | 10.22 | 28,516.58 | At_chr11 | 144,295 | 145,083 | 788 | vacu | SP | _ |
| CotAD_ 65,119 | LEA2 | LEA 2–79 | 206 | 8.88 | 22,733.19 | Dt08_chr24 | 59,660 | 60,280 | 620 | golg | SP | _ |
| CotAD_ 65,370 | LEA2 | LEA 2–126 | 326 | 9.99 | 36,098.18 | scaffold3528.1 | 84,696 | 86,784 | 2088 | chlo | other | _ |
| CotAD_ 66,245 | LEA2 | LEA 2–82 | 450 | 4.94 | 48,836.2 | Dt08_chr24 | 121,249 | 122,601 | 1352 | chlo | other | _ |
| CotAD_ 66,538 | LEA2 | LEA2–6 | 211 | 9.47 | 23,424.96 | At_chr04 | 59,282 | 59,917 | 635 | chlo | SP | _ |
| CotAD_ 66,551 | LEA2 | LEA 2–118 | 225 | 9.28 | 25,226.24 | scaffold3976.1 | 20,354 | 21,031 | 677 | cyto | other | _ |
| CotAD_ 66,774 | LEA2 | LEA 2–80 | 216 | 9.92 | 24,090.84 | Dt08_chr24 | 68,424 | 69,074 | 650 | chlo | SP | _ |
| CotAD_ 66,775 | LEA2 | LEA 2–81 | 225 | 9.61 | 25,078.29 | Dt08_chr24 | 72,945 | 73,622 | 677 | chlo | SP | S |
| CotAD_ 67,823 | LEA2 | LEA 2–20 | 222 | 9.49 | 23,928.26 | At_chr08 | 132,953 | 133,621 | 668 | cyto | SP | S |
| CotAD_ 68,063 | LEA2 | LEA2–4 | 218 | 9.3 | 23,245.72 | At_chr03 | 191,498 | 192,154 | 656 | cyto | SP | _ |
| CotAD_ 68,189 | LEA2 | LEA 2–35 | 206 | 6.71 | 22,579.21 | At_chr10 | 67,607 | 68,227 | 620 | chlo | cTP | C |
| CotAD_ 69,737 | LEA2 | LEA 2–134 | 213 | 9.75 | 23,867.69 | scaffold2095.1 | 202,243 | 202,884 | 641 | chlo | SP | S |
| CotAD_ 69,738 | LEA2 | LEA 2–135 | 210 | 9.88 | 23,893.04 | scaffold2095.1 | 208,893 | 209,525 | 632 | chlo | SP | _ |
| CotAD_ 70,003 | LEA2 | LEA 2–42 | 191 | 9.63 | 20,942.44 | At_chr12 | 171,793 | 172,368 | 575 | cyto | cTP | C |
| CotAD_ 70,190 | LEA2 | LEA 2–120 | 430 | 4.81 | 48,185.02 | scaffold4817.1 | 31,921 | 37,140 | 5219 | cyto | other | _ |
| CotAD_ 70,192 | LEA2 | LEA 2–122 | 130 | 4.74 | 14,420.49 | scaffold4817.1 | 38,397 | 38,789 | 392 | nucl | SP | M |
| CotAD_ 71,431 | LEA2 | LEA 2–59 | 186 | 9.58 | 20,579.98 | Dt05_chr19 | 65,530 | 66,090 | 560 | extr | other | _ |
| CotAD_ 72,458 | LEA2 | LEA 2–127 | 192 | 9.54 | 20,613.31 | scaffold3083.1 | 91,828 | 92,406 | 578 | cysk | SP | _ |
| CotAD_ 72,913 | LEA2 | LEA 2–121 | 315 | 4.63 | 35,071.89 | scaffold4398.1 | 34,689 | 36,390 | 1701 | cysk | SP | _ |
| CotAD_ 73,966 | LEA2 | LEA 2–45 | 320 | 9.96 | 35,484.73 | At_chr12 | 365,460 | 366,583 | 1123 | chlo | other | _ |
| CotAD_ 74,713 | LEA2 | LEA 2–83 | 211 | 9.12 | 23,479.93 | Dt08_chr24 | 158,342 | 158,977 | 635 | golg | other | _ |
| CotAD_ 76,129 | LEA2 | LEA 2–44 | 209 | 10.19 | 23,626.51 | At_chr12 | 317,009 | 317,638 | 629 | chlo | other | _ |
| CotAD_ 01504 | LEA3 | LEA 3–13 | 93 | 8.82 | 10,469.06 | Dt09_chr23 | 1,171,108 | 1,171,516 | 408 | chlo | other | C |
| CotAD_ 04558 | LEA3 | LEA 3–1 | 100 | 9.75 | 10,627.15 | At_chr04 | 288,394 | 288,796 | 402 | chlo | mTP | S |
| CotAD_ 04559 | LEA3 | LEA 3–2 | 100 | 9.34 | 10,419.9 | At_chr04 | 291,007 | 291,400 | 393 | chlo | SP | S |
| CotAD_ 21,416 | LEA3 | LEA 3–9 | 92 | 9.83 | 9667.02 | Dt04_chr22 | 127,037 | 127,390 | 353 | chlo | mTP | C |
| CotAD_ 22,634 | LEA3 | LEA 3–11 | 100 | 9.18 | 10,503.02 | Dt04_chr22 | 853,079 | 853,496 | 417 | mito | SP | S |
| CotAD_ 23,118 | LEA3 | LEA 3–12 | 99 | 9.56 | 10,350.8 | Dt04_chr22 | 855,441 | 855,830 | 389 | cyto | mTP | S |
| CotAD_ 24,498 | LEA3 | LEA 3–8 | 126 | 6.27 | 13,502.83 | Dt03_chr17 | 1,079,773 | 1,082,222 | 2449 | chlo | mTP | M |
| CotAD_ 26,668 | LEA3 | LEA 3–16 | 98 | 9.34 | 10,595.99 | scaffold141.1 | 891,415 | 891,795 | 380 | chlo | mTP | M |
| CotAD_ 33,003 | LEA3 | LEA 3–15 | 120 | 7.02 | 13,729.35 | scaffold944.1 | 428,674 | 429,107 | 433 | chlo | mTP | M |
| CotAD_ 35,021 | LEA3 | LEA 3–5 | 85 | 9.77 | 9781.28 | At_chr11 | 537,390 | 537,732 | 342 | chlo | mTP | M |
| CotAD_ 36,999 | LEA3 | LEA 3–4 | 126 | 6.27 | 13,484.86 | At_chr08 | 1,181,217 | 1,183,629 | 2412 | cyto | mTP | M |
| CotAD_ 40,972 | LEA3 | LEA 3–7 | 124 | 9.51 | 14,155.5 | At_chr13 | 122,903 | 123,887 | 984 | chlo | mTP | M |
| CotAD_ 41,714 | LEA3 | LEA 3–14 | 105 | 9.3 | 11,363.76 | Dt11_chr21 | 445,383 | 445,797 | 414 | chlo | mTP | M |
| CotAD_ 43,605 | LEA3 | LEA 3–3 | 92 | 9.75 | 9709.1 | At_chr04 | 475,252 | 475,623 | 371 | nucl | mTP | C |
| CotAD_ 46,270 | LEA3 | LEA 3–6 | 105 | 9.51 | 11,449.87 | At_chr11 | 673,169 | 673,590 | 421 | golg | mTP | S |
| CotAD_ 56,728 | LEA3 | LEA 3–10 | 98 | 9.66 | 10,549.99 | Dt04_chr22 | 520,431 | 520,811 | 380 | golg | mTP | S |
| CotAD_ 00667 | LEA4 | LEA 4–12 | 239 | 9.03 | 26,335.09 | scaffold26.1 | 961,112 | 961,910 | 798 | chlo | cTP | C |
| CotAD_ 02872 | LEA4 | LEA 4–4 | 569 | 5.89 | 62,916.57 | Dt05_chr19 | 496,264 | 498,058 | 1794 | mito | other | _ |
| CotAD_ 05963 | LEA4 | LEA 4–5 | 266 | 5.2 | 29,264.99 | Dt05_chr19 | 2,777,842 | 2,778,935 | 1093 | extr | SP | S |
| CotAD_ 09404 | LEA4 | LEA 4–7 | 127 | 9.21 | 13,553.37 | Dt07_chr16 | 2,927,050 | 2,928,024 | 974 | chlo | cTP | C |
| CotAD_ 09405 | LEA4 | LEA 4–8 | 109 | 9.96 | 12,066.81 | Dt07_chr16 | 2,946,007 | 2,947,047 | 1040 | chlo | mTP | M |
| CotAD_ 10,044 | LEA4 | LEA 4–3 | 634 | 5.78 | 68,352.06 | At_chr07 | 513,343 | 515,454 | 2111 | nucl | mTP | _ |
| CotAD_ 13,989 | LEA4 | LEA 4–10 | 109 | 10.04 | 12,094.87 | Dt13_chr18 | 1,907,725 | 1,908,766 | 1041 | chlo | mTP | M |
| CotAD_ 22,633 | LEA4 | LEA 4–6 | 136 | 6.93 | 14,614.04 | Dt06_chr25 | 240,527 | 241,024 | 497 | chlo | other | _ |
| CotAD_ 23,824 | LEA4 | LEA 4–9 | 405 | 5.88 | 44,549.64 | Dt12_chr26 | 2,459,614 | 2,460,913 | 1299 | chlo | other | _ |
| CotAD_ 50,359 | LEA4 | LEA4–1 | 284 | 5.13 | 31,311.17 | At_chr03 | 809,118 | 810,165 | 1047 | cyto | SP | S |
| CotAD_ 62,314 | LEA4 | LEA 4–11 | 239 | 9.03 | 26,258.97 | scaffold3310.1 | 9965 | 10,763 | 798 | cyto | cTP | C |
| CotAD_ 62,659 | LEA4 | LEA4–2 | 568 | 5.96 | 62,738.55 | At_chr06 | 14,807 | 16,597 | 1790 | cyto | other | _ |
| CotAD_ 74,061 | LEA4 | LEA 4–4 | 405 | 5.69 | 44,521.59 | At_chr12 | 408,138 | 409,436 | 1298 | nucl | other | _ |
| CotAD_ 03264 | LEA5 | LEA 5–4 | 110 | 5.55 | 11,915.92 | Dt06_chr25 | 1,093,153 | 1,093,598 | 445 | nucl | other | _ |
| CotAD_ 07516 | LEA5 | LEA 5–2 | 123 | 5.78 | 13,999.94 | At_chr09 | 1,687,267 | 1,687,988 | 721 | cyto | other | _ |
| CotAD_ 22,539 | LEA5 | LEA 5–9 | 102 | 5.49 | 11,072.09 | scaffold613.1 | 610,955 | 611,364 | 409 | chlo | other | _ |
| CotAD_ 31,869 | LEA5 | LEA 5–8 | 102 | 5.49 | 11,072.09 | scaffold1551.1 | 323,034 | 323,444 | 410 | nucl | other | _ |
| CotAD_ 33,321 | LEA5 | LEA 5–7 | 110 | 5.55 | 11,972.03 | scaffold1788.1 | 214,115 | 214,558 | 443 | chlo | other | _ |
| CotAD_ 46,888 | LEA5 | LEA 5–1 | 144 | 7.76 | 16,526.85 | At_chr08 | 563,572 | 564,774 | 1202 | chlo | other | _ |
| CotAD_ 48,469 | LEA5 | LEA 5–5 | 171 | 8.39 | 19,503.27 | Dt08_chr24 | 159,604 | 160,805 | 1201 | nucl | other | _ |
| CotAD_ 56,699 | LEA5 | LEA 5–6 | 94 | 8.1 | 10,073.96 | Dt10_chr20 | 81,020 | 81,398 | 378 | chlo | other | _ |
| CotAD_ 57,519 | LEA5 | LEA 5–3 | 94 | 8.1 | 10,073.96 | At_chr12 | 153,745 | 154,123 | 378 | vacu | other | _ |
| CotAD_ 13,789 | LEA6 | LEA 6–3 | 86 | 7.8 | 9580.48 | Dt12_chr26 | 651,517 | 651,777 | 260 | nucl | other | _ |
| CotAD_ 19,623 | LEA6 | LEA6–1 | 94 | 4.76 | 10,176.98 | At_chr01 | 1,336,340 | 1,336,624 | 284 | extr | other | _ |
| CotAD_ 44,941 | LEA6 | LEA 6–4 | 114 | 11.83 | 11,963.43 | scaffold3339.1 | 62,119 | 62,571 | 452 | cyto | other | _ |
| CotAD_ 53,438 | LEA6 | LEA 6–2 | 94 | 4.75 | 10,257.11 | Dt07_chr16 | 78,654 | 78,938 | 284 | chlo | SP | M |
| CotAD_ 11,594 | SMP | SMP-10 | 264 | 4.85 | 26,898.86 | scaffold189.1 | 992,496 | 993,467 | 971 | cyto | other | _ |
| CotAD_ 12,680 | SMP | SMP-3 | 169 | 4.63 | 17,180.76 | At_chr07 | 1,633,754 | 1,634,391 | 637 | cyto | other | _ |
| CotAD_ 12,681 | SMP | SMP-4 | 144 | 4.61 | 14,950.53 | At_chr07 | 1,636,123 | 1,636,635 | 512 | chlo | other | _ |
| CotAD_ 12,682 | SMP | SMP-5 | 258 | 4.56 | 26,168.03 | At_chr07 | 1,639,467 | 1,640,458 | 991 | cyto | other | _ |
| CotAD_ 39,233 | SMP | SMP-7 | 171 | 4.49 | 17,755.88 | Dt13_chr18 | 1,963,715 | 1,964,463 | 748 | chlo | other | _ |
| CotAD_ 43,455 | SMP | SMP-6 | 261 | 4.79 | 26,971.01 | Dt12_chr26 | 1,316,599 | 1,317,706 | 1107 | chlo | other | _ |
| CotAD_ 45,390 | SMP | SMP-1 | 252 | 6.35 | 26,222.21 | At_chr01 | 335,790 | 337,578 | 1788 | chlo | other | _ |
| CotAD_ 51,205 | SMP | SMP-9 | 253 | 6.46 | 26,151.04 | scaffold1984.1 | 277,433 | 279,262 | 1829 | chlo | other | _ |
| CotAD_ 66,708 | SMP | SMP-2 | 258 | 6.44 | 27,923.82 | At_chr04 | 123,169 | 126,337 | 3168 | cyto | other | _ |
| CotAD_ 67,721 | SMP | SMP-8 | 264 | 4.93 | 26,885.82 | scaffold4155.1 | 34,277 | 35,248 | 971 | cyto | other | _ |
LEA: late embryogenesis abundant protein; LEA1, 2, 3, 4, 5 and 6 indicates the sub families of LEA proteins while the −1, −2,-3…. Represents the protein annotation number i.e. LEA1–1, the first member of LEA1 sub family; SMP: seed maturation protein; chlo: chloroplast; cyto: cytoplasm; extr: extracellular part of the cell; nucl: nucleus; mito: mitochondrion; cysk: cytoskeleton; golg: golgi body; vacu: vacuole; plas: plasma membrane; E.R: endoplasmic reticulum; SP: Secretory pathway (presence of a signal peptide); mTP: mitochondrial targeting peptide; cTP: chloroplast transit peptide; Other (nucleus, cytoplasmic, or otherwise). C: cytoplasm; S: secretory pathway; M: mitochondrion and -: others/other cell organelles; chr: chromosome; Dt: sub genome D and At: sub-genome A
The only LEA proteins with all its members having Pl < 7, were the SMPs, this results is in agreement to Pl values obtained for SMPs in Brassica napus, all had Pl < 7.0 [39]. The grand average of hydropathy (GRAVY) results as obtained from ExPASy indicated that cotton LEA 2 proteins are the most hydrophobic, with all except three with GRAVY values <0. The rest of the LEA proteins were highly hydrophilic, with almost all of the groups had gravy value of less than 0, these results are consistent with those of the LEA proteins in Arabidopsis thaliana [40]. Low hydrophobicity and high net charge are the main characteristics of other LEA proteins [38] which enables them to be totally or partially disordered, this unique features is an attribute which gives the LEA proteins the ability to form flexible structural elements such as molecular chaperones which are integral for the protection of plants from desiccation effects [41]. TargetP1.1 (http://www.cbs.dtu.dk/services/TargetP/) server [24] and Protein Pprowler Subcellular Localisation Predictor version 1.2 (http://bioinf.scmb.uq.edu.au/Pprowler_webapp_1–2/) [25], were used to predict the subcellular location of 242 Gossypium hirsutum LEA proteins, most of the LEA proteins were predicted to participate in the secretory pathway, same as the Brassica napus LEA proteins [39] (Table 2 and Additional file 2: Table S2).
We further used WoLFPSORT [26] to investigate the particular cell compartments in which the LEA proteins were embedded in, 148 LEA genes were predicted to be chloroplasts proteins, 47 as cytoplasm proteins, 20 as mitochondrion proteins, 35 as nucleus proteins, 11 as Golgi body proteins, 7 as extracellular proteins, 7 as plasma proteins, 4 as vacuole proteins and 3 as endoplasmic reticulum proteins. The details of other characteristics of the nucleic acid and protein sequences are provided in (Table 2). LEA genes have ubiquitous distribution across cell compartments with unique subcellular localization [42]. LEA 4 gene families were found to be widely distributed in cell structures such as cytosol, mitochondria, plastid, ER, and pexophagosome [42]. The unique and wide distribution of LEA genes within the various cell structures is to establish interactions with various cellular membranes under stress conditions. The broad subcellular distribution of LEA proteins highlights the requirement for each cellular compartment to be provided with protective mechanisms to cope with drought stress [17]. In Summary, both experimental and prediction data indicates that LEA proteins have wide distribution in subcellular compartments [42].
Phylogenetic analyses, gene structure and protein motifs of LEA genes in upland cotton
To examine the evolutionary history and relationships of LEA protein families, an unrooted phylogenetic tree was constructed from alignments of the full lengths of LEA gene sequences with Neighbor-joining method based on similarities of the LEA genes in upland cotton, G. hirsutum. We constructed phylogenetic tree of all the groups of LEA genes separately, which we further combined with intron-exon and motifs to unearth more information about phylogenetic tree and LEA genes similarities (Fig. 1). Gene structural diversity and conserved motif divergence are possible mechanisms for the evolution of multigene families [43]. To gain further information into the structural diversity of cotton LEA genes, we analyzed the exon / intron organization in the full-length cDNAs with their corresponding genomic DNA sequences of individual LEA genes in cotton (Fig. 1). Most closely related LEA gene members within the same groups shared similar gene structures in terms of either intron numbers or exon lengths. For example, LEA 1,3,4,5, SMP and dehydrins genes had one to four introns with exception of LEA 2 and 6, which had zero to five introns. This result is in agreement with earlier finding in which dehydrin were found to have introns [44]. By contrast, the gene structure appeared to be more variable in LEA 2 which had the largest number of genes, with sizes of exon/intron structure variants with striking distinctions (Additional file 3: Figure S1). The result suggest the divergence functions of this group of protein family in upland cotton.
Fig. 1.
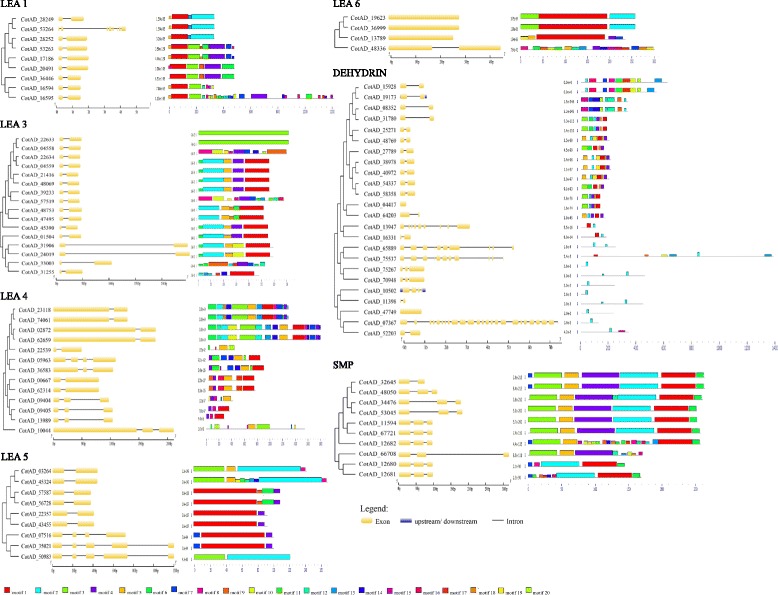
Phylogenetic tree, gene structure and motif compositions of LEA genes in upland cotton. The phylogenetic tree was constructed using MEGA 6.0. Exon/intron structures of LEA genes in upland cotton, exons introns and up / down-stream were represented by yellow boxes, black lines and blue boxes, respectively. Protein motif analysis represented by different colours, and each motif represented by number
Twenty-five distinct motifs were identified. Motifs 1, 2, 3, 4, 5 and 6 were common among all the different groups of LEA genes, similar motifs have been previously identified in other plant species, including maize [45], Arabidopsis thaliana [40], tomato [46] among other plants. Motif analysis of the cotton LEA proteins showed that members of each LEA group possess several group-specific conserved motifs (Table 3). Similar features have been reported for LEA proteins in Solanum lycopersicum [46], Arabidopsis [40], Prunus [47] and poplar [48]. For example, a distinctive and conserved motif in the dehydrin group is the repeated motif, EKKGIMDKIKEKLPG (motif K, richness in lysine residues), in this study, we identified a unique motif among the dehydrin families, GEGREKKGFLEKIKEKLPGHHKKTEEAS, which we named as K1, because of the close similarity with the K- motif. In addition, the commonly known motifs such as EHHEKKGIMDKIKEKLPGHH (K motif) and HSLLEKLHRSNSSSSSSSSDE (S- motif) were also observed. K motif is rich in lysine (K) residues and it is known for protective role of enzymatic activities from the drought effects [49]. The motif pattern formation indicates that cotton LEA proteins are actively involved in various biological processes and are group specific in terms of their activities. The distinct nature of the conserved motifs observed in all the LEA protein families, gives an indication that, the LEA proteins evolved from the gene expansion within their specific gene families. In addition, LEA 4 gene families were found to contain repeats of conserved motif 3, in which in some cases, the repeats were 5, the same attribute was also noted in which they were found to have tendencies of harboring repeat motifs, more so motif 8 [37]. We further did comparison of the common motifs with already identified motif, by the use of Tomtom motif comparison tool, adopting the distance measure of Sandelin-Wasserman function [50]. Motif 1 had 23 matches, with 5 jolma2013, 3 JASPERCORE2014 vertebrates and 15-uniprobe mouse. In motif 2, had 35 matches, 5 jolma2013, 5JASPERCORE2014 vertebrates and 25-uniprobe mouse. With MEME functional tool, we were able to affirm the similarities of our motifs to already published motif in the motif database.
Table 3.
A consensus amino acid sequence of the different motifs features of each upland cotton LEA protein families
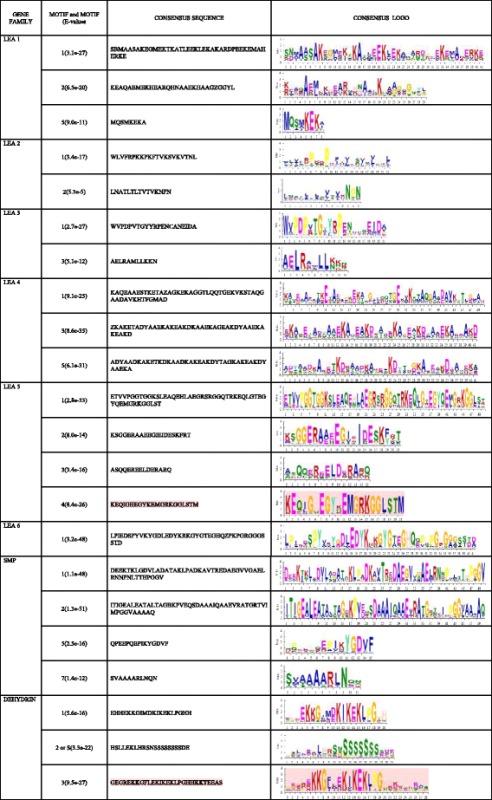
The colour scheme of the logo indicates amino acid types. Polar: green = uncharged; blue = +vely charged; red = -vely charged; Non-polar: violet/purple = aliphatic. As described by Dure, 2001
Phylogenetic analyses of the LEA -proteins in cotton with other plants
To get a better understanding of the evolutionary history and relationships of LEA gene families in cotton to other plants, multiple sequence alignment of 242 genes for G. hirsutum, 136 genes for G. arboreum, 146 genes for G. raimondii, 30 genes for Pinus tabuliformis and 51 genes for Arabidopsis LEA protein sequences (Fig. 2) were done. The boot strap values for some nodes of the NJ tree were low due to long sequence similarities. The reliability of the phylogenetic tree was done by reconstructing the phylogenetic tree with minimal evolution method. The trees produced by the two methods were identical thus the results were consistent. Based on the Phylogenetic tree analysis, LEA genes in cotton were further classified into eight (8) groups. LEA 2 was the largest group with 334 genes from G. hirsutum (157), G. raimondii (89), G. arboreum (85), A. thaliana (3) and P. tabuliformis (1). All the ortholog genes in LEA 2 were found in upland cotton, G. hirsutum, G. arboreum and G. raimondii genome while no ortholog genes were observed between upland cotton, G. hirsutum to either Arabidopsis thaliana and or P. tabuliformis. The second largest group were LEA 4, with highest number of genes 13 and 16 in P. tabuliformis and upland cotton respectively. Upland cotton, G. hirsutum contained the highest numbers of LEA genes of the following groups, LEA 1, LEA 2, LEA 3, LEA 5, LEA 6, SMP and dehydrin with the exception of LEA 4. Among all the LEA gene groups, only LEA 6 had fewer genes, 10 and 3 gene in cotton genome and Arabidopsis respectively (Table 1). The total number of ortholog genes between upland cotton, G. hirsutum, G. arboreum and G. raimondii were 201 out of 601 genes mapped on the Phylogenetic tree, which translates to 33%.
Fig. 2.
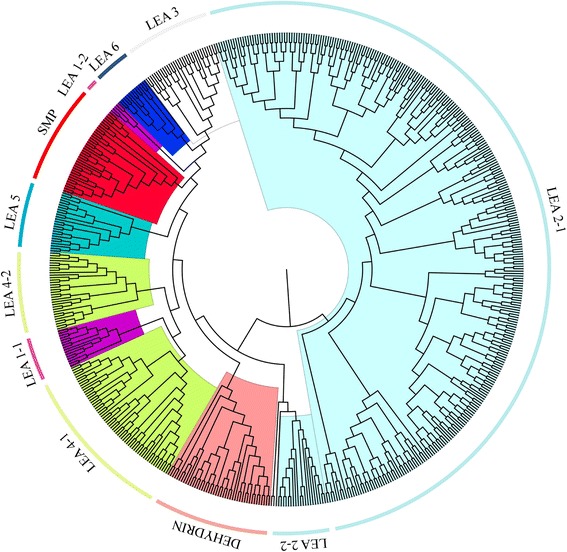
Phylogenetic relationship of LEA genes in three cotton species with Arabidopsis and Pinus tabuliformis. Neighbor-joining phylogeny of 242 genes for G. hirsutum, 136 genes for G. arboreum, 146 genes for G. raimondii, 30 genes for Pinus tabuliformis and 51 Arabidopsis LEA protein sequences, as constructed by MEGA 6.0. The difference colours mark the various LEA gene types
In this study, no ortholog genes were detected between upland cotton, G. hirsutum, P. tabuliformis and Arabidopsis. All the ortholog genes were detected only among the cotton species; this could be due to their evolution. Upland cotton, G. hirsutum emerged through hybridization mechanism between A and D genome [51]. Based on the results, there was close relationship between Arabidopsis and cotton species as compared to P. tabuliformis. The LEA genes seems to have a common evolutionary history [37], the aggregation pattern of the genes within the tree showed that LEA 1, LEA3, LEA 4, LEA5, LEA 6 and SMP had a common origin, similar results have also been obtained in the analysis of LEA genes in potato, in which SMP, LEA 1, LEA4 and LEA 5 shared a common point of origin [52]. A unique feature on the abundance of cotton LEA genes and their distribution was observed in which LEA 2 formed the majority of the cotton LEA gene families (Table 1 and Fig. 2). Analysis of the LEA genes in monocots and dicots, nearly half of the species containing LEA genes, the majority of the genes belong to the LEA 4 and dehydrin families [39]. The analysis of cotton LEA genes with other plants revealed that main differences occur in the LEA 2 genes (Fig. 2). The abundance of LEA 2 genes was lowest in Pinus tabuliformis (1) and Arabidopsis (3) and higher in G. hirsutum (157), G. arboreum (85) and G. raimondii (89). Similar results were also been observed in which lower proportions of other LEA gene families were observed in grapevine but significantly higher number of LEA 2 genes were observed in rice and poplar [53]. It is important to note that, such large number of LEA 2 families have not been described in the previously investigated genomes of poplar [48], rice [11] and Arabidopsis [40]. This result may be explained in part by the improved annotation of the higher plant genomes available at Phytozome (v10.2) and also by the fact that LEA 2 is an unusual group composed of ‘a typical’ proteins of hydrophobic nature. This finding suggests that the LEA protein families in higher plants may be larger and much more complex than previously described. On the other hand, minor variations were observed in the other upland cotton LEA gene families. Based on this result, the entire LEA 2 gene families probably were the last to evolve among the LEA gene families in higher plants.
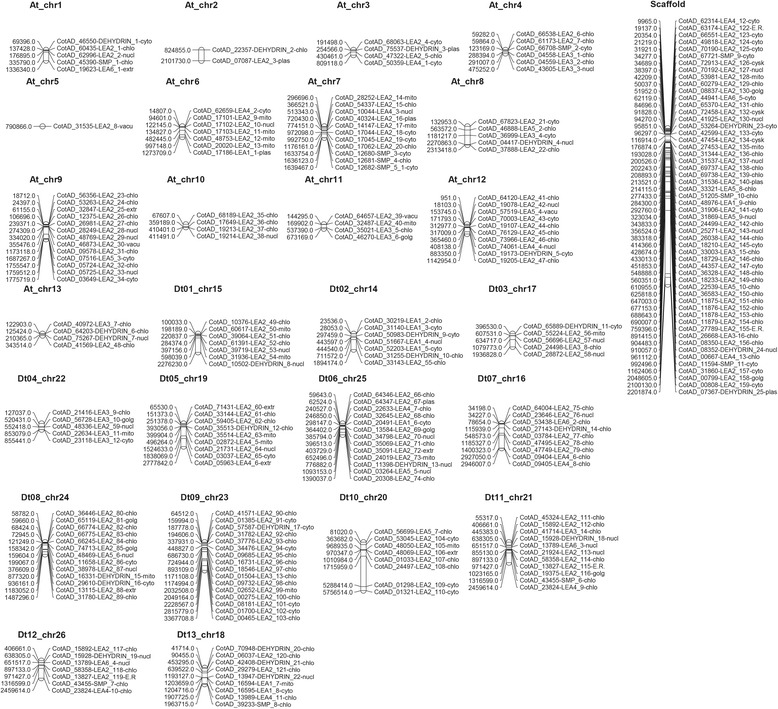
Chromosomal distribution of cotton genes encoding LEA proteins
To determine the chromosomal locations of cotton LEA genes based on their positions, data retrieved from the whole cotton genome sequences were used. Chromosome distribution was done by BLASTN search against G. hirsutum and G. arboreum in cotton genome project and G.raimondii genome database in Phytozome (http://www.phytozome.net/cotton.php). One hundred and eighty six (186) upland cotton LEA genes were mapped in all chromosomes by Map chart and 56 upland LEA genes into unknown chromosomes (scaffold). A plot of LEA genes on the cotton genome shows that LEA loci are found on every chromosome (Fig. 3). The distribution of the mapped LEA genes were more in Dt with 110 (59%) compared to At, with only 76 (41%) genes. However, the densities of these loci were high on Dt_chr 09, with 9% of all the LEA genes. Gene loss was observed on At_chr 05, with a single gene compared to its homolog chromosome Dt_chr 05, which had 9 genes. Similar case was also noted on chromosome At_chr02 and Dt_chr02 with 2 and 7genes respectively. This result indicates an element of gene loss during the hybridization period, as result of crossing over or other internal or external chromosomal phenomenon.
Fig. 3.
LEA genes distribution in tetraploid upland cotton, Gossypium hirsutum chromosomes. Chromosomal position of each LEA genes was mapped according to the upland cotton genome. The chromosome number is indicated at the top of each chromosome
In the A genome of, G. arboreum 136 LEA genes were mapped across all the 13 chromosomes, high density of these loci were observed on chromosome 10, which contained 21 genes, translating to 15% of all the LEA genes in the genome. The mapping of the gene loci were generally uniform, the lowest loci density was observed on chromosome 9, with 5 genes (4%), followed by chr 2, chr5 and chr 8, with 6 genes each (Fig. 3). In D genome, (G. raimondii), 143 LEA genes were distributed across all the chromosomes. The highest gene loci density was in chromosome 9 with 18 genes (13%) and the lowest density was in chromosome 12, with only 5 genes (3%). The mapping of the LEA genes in both diploid and tetraploid cotton chromosomes, tend to have a unique clustering pattern, high density LEA gene clusters were observed in specific chromosomal regions, either at the upper arm, lower arm or the middle region of the chromosomes as shown on chromosomes At_ch01, Dt01_chr15, Dt02_chr14, Dt05_chr19 and Dt10_chr20 within the AD genome, chr02, chr05, chr06 and chr07 in A genome and in D genome, ch07 and chr11 (Fig. 4). The clustering pattern of the LEA gene and chromosomal location could be attributed to LEA gene duplication patterns [37].
Fig. 4.
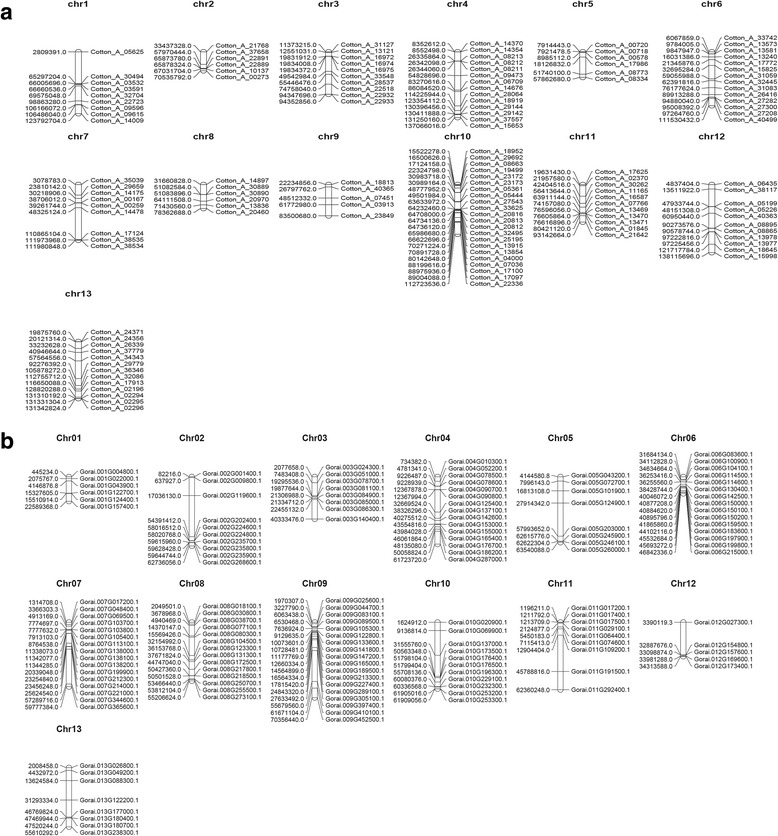
LEA genes distribution in A and D cotton chromosomes: Chromosomal position of each LEA genes was mapped according to the upland cotton genome. The chromosome number is indicated at the top of each chromosome. a: chromosomes of the diploid cotton of A genome, G. arboreum; b: chromosomes of the diploid cotton of D genome, G. raimondii
In general, genes which belong to the same family are distributed across the entire chromosomes in order to ensure their maximum functionalization [54]; this was evident in LEA 2 genes, which was distributed across the entire chromosomes of both tetraploid and diploid cotton (Figs. 3 and 4). It was unique to find some members of LEA gene families with restricted distribution, mainly found in some chromosomes but not all like dehydrin despite of their numbers, this implies that dehydrin like genes have the tendency to duplicate and evolve more conservatively within a particular chromosome.
Gene duplication and syntenic analysis
Expansion of gene families occurs through three processes namely, segmental duplication, tandem duplication and whole genome duplication [55]. Homologous and orthologous genes are the products of gene duplication events. Duplicated genes function in stress response and development processes in plants [56]. To analyse the relationships between the LEA genes and gene duplication events, syntenic blocks of LEA genes were combined among G. hirsutum, G. raimondii and G. arboreum (Fig. 5). A total of 241 LEA genes were duplicated across the three cotton genome. The most duplicated genes were detected between G. hirsutum and its ancestors, G. arboreum and G. raimondii, this could be due the origin of G. hirsutum, as a result of polyploidization of A and D genome (Table 4). Two types of duplication, tandem and segmental duplication event were identified. Majority of the duplicated LEA genes, were segmental, this implied that, segmental gene duplication, had a major contributing factor during the evolution time [57]. The Ka/Ks ratio is a pointer to selective pressure acting on a protein-coding gene. It has been observed that some systematic bias in some species do occur more easily in the process of nucleotides substitutions because of species diversity and high mutation rate do accelerates the changes in amino acid proportions [58]. The analysis of the Ka /Ks ratios of the 156 paralogous pairs, were less than 1 and only 20 had ratios of more than 1. Majority of LEA 2, LEA 4 and SMP had very low Ka/Ks ratios; the highest Ka/Ks ratio of 2.59265 was noted in LEA 6. This result is consistent to the previous findings of Brassica napus LEA genes, LEA 3 and LEA 6, families recorded higher Ka/Ks ratios, whereas LEA 5 and LEA 2 gene families recorded lowest Ka/Ks ratios [39]. In general Ka/Ks for paralogous gene pair of LEA genes had a range of 0 to 2.593 with mean of 0.4717. This result gives an indication that the LEA genes have been influenced extensively by purifying selection during the process of their evolution. LEA 2 gene families preferentially do have conserved structure and functions under selective pressure [59].
Fig. 5.
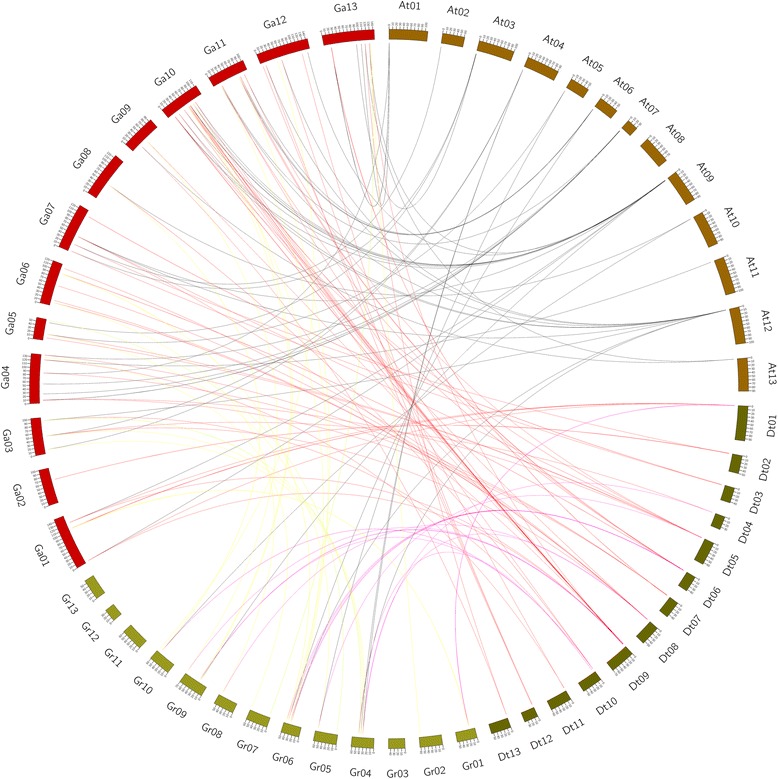
Syntenic relationships among LEA genes from G. hirsutum, G. raimondii and G. arboretum. G. hirsutum, G. raimondii and G. arboretum chromosomes are indicated in different colours. The putative orthologous LEA genes between G. hirsutum and G. raimondii, G. hirsutum and G. arboretum, and G. raimondii and G. arboretum by different colours
Table 4.
Gene duplication, Ks, Ka and Ka/Ks values calculated for paralogous LEA gene pairs in cotton genome
| GENE FAMILY | Paralogous gene pairs | Length (aa) | Ka | Ks | Ka/Ks | Negative/purifying selection | P-Value (Fisher) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| A | B | |||||||
| DEHYDRIN | CotAD_66,538 | CotAD_74,713 | 633 | 0.01677 | 0.04094 | 0.409579 | YES | 0.0891624 |
| DEHYDRIN | CotAD_70,948 | CotAD_75,267 | 996 | 0.33429 | 0.42203 | 0.792098 | YES | 0.122937 |
| DEHYDRIN | CotAD_53,981 | Cotton_A_05444 | 753 | 0.00533 | 0.01072 | 0.49715 | YES | 0.365412 |
| DEHYDRIN | CotAD_65,119 | Cotton_A_13573 | 618 | 0.01516 | 0.04762 | 0.318478 | YES | 0.0332022 |
| DEHYDRIN | CotAD_66,245 | Cotton_A_13581 | 1350 | 0.01615 | 0.03716 | 0.434571 | YES | 0.0218162 |
| DEHYDRIN | CotAD_64,004 | Cotton_A_14354 | 657 | 0.02039 | 0.07908 | 0.257869 | YES | 0.00188419 |
| DEHYDRIN | CotAD_66,774 | Cotton_A_23172 | 648 | 0.0101 | 0.05547 | 0.182079 | YES | 0.0030156 |
| DEHYDRIN | CotAD_66,775 | Cotton_A_23173 | 675 | 0.02652 | 0.06314 | 0.419977 | YES | 0.0380326 |
| DEHYDRIN | CotAD_60,435 | Cotton_A_24371 | 699 | 2.87675 | 2.00242 | 1.43664 | NO | 0.319287 |
| DEHYDRIN | CotAD_58,358 | Cotton_A_29692 | 633 | 0.01197 | 0.05683 | 0.210713 | YES | 0.00684175 |
| DEHYDRIN | CotAD_66,538 | Cotton_A_33548 | 633 | 0.00417 | 0.00659 | 0.63267 | YES | 0.549017 |
| DEHYDRIN | CotAD_70,948 | Cotton_A_40365 | 996 | 0.33435 | 0.4385 | 0.762473 | YES | 0.0864744 |
| DEHYDRIN | CotAD_75,267 | Cotton_A_40365 | 996 | 0.00385 | 0.0094 | 0.409167 | YES | 0.292983 |
| DEHYDRIN | CotAD_65,119 | Gorai.008G218500.1 | 618 | 0.00214 | 0.00666 | 0.321634 | YES | 0.36944 |
| DEHYDRIN | Cotton_A_13573 | Gorai.008G218500.1 | 618 | 0.01297 | 0.0548 | 0.236675 | YES | 0.00834018 |
| LEA1 | CotAD_01033 | CotAD_08181 | 606 | 0.05146 | 0.15416 | 0.3338 | YES | 0.000633352 |
| LEA1 | CotAD_00275 | CotAD_39,719 | 822 | 0.01476 | 0.03476 | 0.424567 | YES | 0.130131 |
| LEA1 | CotAD_01033 | CotAD_46,550 | 606 | 0.0493 | 0.18716 | 0.263397 | YES | 1.42E-05 |
| LEA1 | CotAD_01298 | CotAD_64,120 | 654 | 0.0404 | 0.13464 | 0.300053 | YES | 0.000332152 |
| LEA1 | CotAD_00275 | Cotton_A_14009 | 822 | 0.01475 | 0.04503 | 0.327622 | YES | 0.0184625 |
| LEA1 | CotAD_01298 | Cotton_A_22932 | 654 | 0.03303 | 0.12281 | 0.268983 | YES | 0.000202033 |
| LEA1 | CotAD_01033 | Cotton_A_27543 | 606 | 0.05146 | 0.1456 | 0.353443 | YES | 0.00202823 |
| LEA1 | CotAD_01298 | Gorai.004G155000.1 | 630 | 2.63603 | 3.65804 | 0.720612 | YES | 0.753791 |
| LEA1 | CotAD_01033 | Gorai.009G305100.1 | 606 | 0.05153 | 0.14499 | 0.355394 | YES | 0.00205763 |
| LEA2 | CotAD_11,658 | _Cotton_A_40499 | 789 | 0.02309 | 0.01751 | 1.3191 | NO | 0.985982 |
| LEA2 | CotAD_01700 | CotAD_09578 | 780 | 0.01202 | 0.02634 | 0.456421 | YES | 0.151105 |
| LEA2 | CotAD_02652 | CotAD_14,147 | 636 | 0.00835 | 0.01974 | 0.422805 | YES | 0.226532 |
| LEA2 | Cotton_A_13471 | CotAD_17,103 | 180.94 | 2.32397 | 1.11323 | 0.778217 | YES | 837 |
| LEA2 | CotAD_13,584 | CotAD_20,020 | 750 | 0.00878 | 0.01711 | 0.513478 | YES | 0.287642 |
| LEA2 | CotAD_17,062 | CotAD_21,731 | 732 | 0.00719 | 0.04161 | 0.17276 | YES | 0.00506705 |
| LEA2 | CotAD_03649 | CotAD_31,344 | 960 | 0.01103 | 0.02214 | 0.497982 | YES | 0.177084 |
| LEA2 | CotAD_17,101 | CotAD_31,535 | 666 | 0.01576 | 0.04026 | 0.391498 | YES | 0.077316 |
| LEA2 | CotAD_17,102 | CotAD_31,536 | 627 | 0.00422 | 0.03365 | 0.125467 | YES | 0.0107355 |
| LEA2 | Cotton_A_31083 | CotAD_35,069 | 939 | 2.2748 | 1.83858 | 1.23726 | NO | 0.447623 |
| LEA2 | CotAD_19,214 | CotAD_35,514 | 543 | 0.00955 | 0.02509 | 0.380645 | YES | 0.19023 |
| LEA2 | CotAD_19,623 | CotAD_36,999 | 282 | 0.03296 | 0.04771 | 0.69081 | YES | 0.631725 |
| LEA2 | CotAD_18,546 | CotAD_37,776 | 519 | 0.01016 | 0.04195 | 0.242116 | YES | 0.0375368 |
| LEA2 | CotAD_03649 | CotAD_37,888 | 960 | 0.04522 | 0.54142 | 0.08352 | YES | 9.32E-36 |
| LEA2 | CotAD_40,972 | CotAD_38,978 | 591 | 0.96025 | 2.04193 | 0.470264 | YES | 0.00125135 |
| LEA2 | CotAD_32,847 | CotAD_39,064 | 612 | 0.01106 | 0.0461 | 0.239936 | YES | 0.0153075 |
| LEA2 | CotAD_12,375 | CotAD_42,408 | 597 | 2.42062 | 1.68288 | 1.43838 | NO | 0.288342 |
| LEA2 | CotAD_28,872 | CotAD_44,941 | 720 | 0.0141 | 0.01369 | 1.03042 | NO | 0.900519 |
| LEA2 | CotAD_08181 | CotAD_46,550 | 606 | 0.00654 | 0.04975 | 0.131503 | YES | 0.00250188 |
| LEA2 | CotAD_25,271 | CotAD_48,769 | 405 | 0.00647 | 0.01063 | 0.609395 | YES | 0.539117 |
| LEA2 | CotAD_28,252 | CotAD_53,263 | 492 | 0.01356 | 0.04285 | 0.31656 | YES | 0.069282 |
| LEA2 | CotAD_09685 | CotAD_53,981 | 753 | 0.00711 | 0.04386 | 0.162112 | YES | 0.00252472 |
| LEA2 | CotAD_35,091 | CotAD_60,435 | 753 | 0.03016 | 0.07689 | 0.392211 | YES | 0.0144267 |
| LEA2 | CotAD_46,873 | CotAD_60,617 | 630 | 0.00835 | 0.03452 | 0.241852 | YES | 0.0372109 |
| LEA2 | CotAD_46,888 | CotAD_61,391 | 573 | 0.01387 | 0.05313 | 0.261111 | YES | 0.0175133 |
| LEA2 | CotAD_35,069 | CotAD_62,996 | 954 | 0.00551 | 0.03643 | 0.151164 | YES | 0.0017334 |
| LEA2 | CotAD_17,045 | CotAD_64,004 | 657 | 0.02247 | 0.06523 | 0.344452 | YES | 0.0157104 |
| LEA2 | CotAD_36,328 | CotAD_64,346 | 630 | 0.01777 | 0.07564 | 0.23489 | YES | 0.000973496 |
| LEA2 | CotAD_21,924 | CotAD_64,657 | 786 | 0.01373 | 0.04693 | 0.292471 | YES | 0.0120925 |
| LEA2 | CotAD_50,359 | CotAD_66,538 | 633 | 0.01677 | 0.04094 | 0.409579 | YES | 0.0891624 |
| LEA2 | CotAD_19,078 | CotAD_66,774 | 648 | 0.01009 | 0.04842 | 0.208435 | YES | 0.00834864 |
| LEA2 | CotAD_53,438 | CotAD_68,189 | 618 | 0.02341 | 0.02898 | 0.80786 | YES | 0.519399 |
| LEA2 | CotAD_20,308 | CotAD_70,003 | 573 | 0.00915 | 0.02291 | 0.399181 | YES | 0.206152 |
| LEA2 | CotAD_03649 | CotAD_73,966 | 960 | 0.04597 | 0.527 | 0.087231 | YES | 4.70E-35 |
| LEA2 | CotAD_37,888 | CotAD_73,966 | 960 | 0.01528 | 0.0442 | 0.345761 | YES | 0.0157353 |
| LEA2 | CotAD_23,118 | CotAD_74,061 | 1215 | 0.01611 | 0.06882 | 0.234049 | YES | 5.00E-05 |
| LEA2 | CotAD_59,405 | CotAD_76,129 | 627 | 0 | 0.00654 | 0 | YES | 0 |
| LEA2 | CotAD_13,584 | Cotton_A_01845 | 750 | 0.00878 | 0.02294 | 0.382644 | YES | 0.139381 |
| LEA2 | CotAD_20,020 | Cotton_A_01845 | 750 | 0 | 0.00568 | 0 | YES | 0 |
| LEA2 | CotAD_01700 | Cotton_A_02196 | 780 | 0.09992 | 0.58986 | 0.169389 | YES | 8.68E-22 |
| LEA2 | CotAD_09578 | Cotton_A_02196 | 780 | 0.0903 | 0.59944 | 0.150635 | YES | 7.07E-24 |
| LEA2 | Gorai.007G048400.1 | Cotton_A_02294 | 576 | 2.54671 | 1.77281 | 1.43654 | NO | 0.3084 |
| LEA2 | CotAD_02652 | Cotton_A_02370 | 636 | 0.01256 | 0.03311 | 0.379343 | YES | 0.101339 |
| LEA2 | CotAD_14,147 | Cotton_A_02370 | 636 | 0.00416 | 0.01312 | 0.316903 | YES | 0.244174 |
| LEA2 | CotAD_09685 | Cotton_A_05444 | 753 | 0.0089 | 0.04387 | 0.202818 | YES | 0.00516244 |
| LEA2 | CotAD_10,376 | Cotton_A_05625 | 831 | 0.00645 | 0.03444 | 0.187227 | YES | 0.00723285 |
| LEA2 | CotAD_19,375 | Cotton_A_06435 | 675 | 0.01345 | 0.05541 | 0.242679 | YES | 0.00759106 |
| LEA2 | CotAD_01700 | Cotton_A_07036 | 780 | 0.01551 | 0.03701 | 0.419158 | YES | 0.0752732 |
| LEA2 | CotAD_09578 | Cotton_A_07036 | 780 | 0.00342 | 0.01037 | 0.33004 | YES | 0.256013 |
| LEA2 | Cotton_A_02196 | Cotton_A_07036 | 780 | 0.09428 | 0.60765 | 0.155148 | YES | 1.27E-23 |
| LEA2 | CotAD_12,681 | Cotton_A_08212 | 432 | 0.03121 | 0.04928 | 0.633189 | YES | 0.35887 |
| LEA2 | Gorai.005G043200.1 | Cotton_A_08334 | 792 | 0.00507 | 0.01526 | 0.332323 | YES | 0.16956 |
| LEA2 | CotAD_03649 | Cotton_A_08663 | 960 | 0.00549 | 0.00437 | 1.25606 | NO | 0.744588 |
| LEA2 | CotAD_37,888 | Cotton_A_08663 | 960 | 0.04378 | 0.55839 | 0.07841 | YES | 1.73E-37 |
| LEA2 | CotAD_10,044 | Cotton_A_09473 | 1902 | 0.00274 | 0.00228 | 1.20458 | NO | 0.731531 |
| LEA2 | CotAD_46,888 | Cotton_A_09596 | 573 | 0.00922 | 0.0453 | 0.203506 | YES | 0.0147038 |
| LEA2 | CotAD_46,873 | Cotton_A_09615 | 630 | 0.00835 | 0.03452 | 0.241852 | YES | 0.0372109 |
| LEA2 | CotAD_32,487 | Cotton_A_13240 | 630 | 0.00425 | 0.01917 | 0.221854 | YES | 0.103356 |
| LEA2 | CotAD_17,101 | Cotton_A_13469 | 666 | 0.00195 | 0.01318 | 0.148053 | YES | 0.121749 |
| LEA2 | CotAD_31,535 | Cotton_A_13469 | 666 | 0.01377 | 0.04718 | 0.291898 | YES | 0.0234164 |
| LEA2 | CotAD_31,536 | Cotton_A_13470 | 627 | 0.00211 | 0.03373 | 0.062455 | YES | 0.00360292 |
| LEA2 | CotAD_17,103 | Cotton_A_13471 | 837 | 2.58712 | 2.32397 | 1.11323 | NO | 0.778217 |
| LEA2 | CotAD_17,045 | Cotton_A_14354 | 657 | 0.00201 | 0.01262 | 0.159578 | YES | 0.13409 |
| LEA2 | CotAD_17,062 | Cotton_A_14370 | 732 | 0.0099 | 0.02648 | 0.374024 | YES | 0.0618224 |
| LEA2 | CotAD_21,731 | Cotton_A_14370 | 732 | 0.00899 | 0.02354 | 0.381916 | YES | 0.138838 |
| LEA2 | CotAD_03649 | Cotton_A_14478 | 960 | 0.04592 | 0.52972 | 0.086683 | YES | 3.29E-35 |
| LEA2 | CotAD_37,888 | Cotton_A_14478 | 960 | 0.01247 | 0.03528 | 0.353401 | YES | 0.0321315 |
| LEA2 | CotAD_25,271 | Cotton_A_14676 | 405 | 0.00647 | 0.03234 | 0.200226 | YES | 0.085476 |
| LEA2 | CotAD_31,140 | Cotton_A_15998 | 747 | 0.00174 | 0.0058 | 0.300994 | YES | 0.356655 |
| LEA2 | CotAD_20,308 | Cotton_A_17625 | 573 | 0.01375 | 0.02296 | 0.59881 | YES | 0.347235 |
| LEA2 | CotAD_44,941 | Cotton_A_17986 | 720 | 0.01233 | 0.01369 | 0.900555 | YES | 0.874489 |
| LEA2 | CotAD_13,827 | Cotton_A_18645 | 1104 | 2.12092 | 1.89653 | 1.11832 | NO | 0.642563 |
| LEA2 | CotAD_21,924 | Cotton_A_18919 | 786 | 0.01028 | 0.05219 | 0.196967 | YES | 0.00026749 |
| LEA2 | CotAD_19,078 | Cotton_A_23172 | 648 | 0 | 0.00672 | 0 | YES | 0 |
| LEA2 | CotAD_35,069 | Cotton_A_24356 | 954 | 0.00551 | 0.03178 | 0.173291 | YES | 0.00508945 |
| LEA2 | CotAD_35,091 | Cotton_A_24371 | 699 | 3.50309 | 1.61186 | 2.17333 | NO | 0.036477 |
| LEA2 | CotAD_22,539 | Cotton_A_25195 | 408 | 1.23265 | 1.24112 | 0.993172 | YES | 1 |
| LEA2 | CotAD_23,646 | Cotton_A_27282 | 609 | 0.02587 | 0.03738 | 0.692044 | YES | 0.542393 |
| LEA2 | CotAD_23,646 | Cotton_A_27300 | 609 | 0.04249 | 0.13135 | 0.323481 | YES | 0.000630664 |
| LEA2 | Cotton_A_27282 | Cotton_A_27300 | 609 | 0.04363 | 0.11818 | 0.369227 | YES | 0.00568388 |
| LEA2 | CotAD_08181 | Cotton_A_27543 | 606 | 0 | 0.00697 | 0 | YES | 0 |
| LEA2 | CotAD_40,972 | Cotton_A_29659 | 591 | 0.96659 | 2.0709 | 0.466747 | YES | 0.00123143 |
| LEA2 | CotAD_48,976 | Cotton_A_29779 | 660 | 0 | 0.00642 | 0 | YES | 0 |
| LEA2 | CotAD_19,214 | Cotton_A_30889 | 543 | 0.00237 | 0.0083 | 0.285978 | YES | 0.347253 |
| LEA2 | CotAD_35,514 | Cotton_A_30889 | 543 | 0.00716 | 0.01659 | 0.431351 | YES | 0.312651 |
| LEA2 | CotAD_35,513 | Cotton_A_30890 | 651 | 0.02193 | 0.05102 | 0.429783 | YES | 0.0738291 |
| LEA2 | CotAD_13,115 | Cotton_A_31059 | 576 | 0.0207 | 0.0379 | 0.546252 | YES | 0.312514 |
| LEA2 | CotAD_30,219 | Cotton_A_32495 | 597 | 0.01105 | 0.03626 | 0.304817 | YES | 0.0618481 |
| LEA2 | CotAD_50,359 | Cotton_A_33548 | 633 | 0.01678 | 0.03388 | 0.495283 | YES | 0.175709 |
| LEA2 | CotAD_74,713 | Cotton_A_33548 | 633 | 0.01678 | 0.03388 | 0.495283 | YES | 0.175709 |
| LEA2 | CotAD_23,118 | Cotton_A_38117 | 1215 | 0.01611 | 0.06077 | 0.265138 | YES | 0.000321992 |
| LEA2 | CotAD_56,699 | Cotton_A_38534 | 639 | 0.02021 | 0.04493 | 0.449883 | YES | 0.106618 |
| LEA2 | CotAD_56,696 | Cotton_A_38535 | 630 | 0.01838 | 0.02269 | 0.809786 | YES | 0.670475 |
| LEA2 | CotAD_59,405 | Cotton_A_40363 | 627 | 0.00636 | 0.04016 | 0.158424 | YES | 0.00848415 |
| LEA2 | CotAD_46,888 | Gorai.001G122700.1 | 573 | 0.0046 | 0.0148 | 0.310385 | YES | 0.238274 |
| LEA2 | CotAD_46,873 | Gorai.001G124400.1 | 630 | 0.00208 | 0.00674 | 0.30909 | YES | 0.361889 |
| LEA2 | CotAD_28,872 | Gorai.005G203000.1 | 720 | 0.01233 | 0.02762 | 0.446407 | YES | 0.170613 |
| LEA2 | CotAD_44,941 | Gorai.005G203000.1 | 720 | 0.00175 | 0.01368 | 0.127787 | YES | 0.0998325 |
| LEA2 | Cotton_A_17986 | Gorai.005G203000.1 | 720 | 0.01055 | 0.02762 | 0.382183 | YES | 0.12817 |
| LEA2 | CotAD_30,219 | Gorai.006G104100.1 | 597 | 0.00884 | 0.00707 | 1.25015 | NO | 0.743557 |
| LEA2 | Cotton_A_32495 | Gorai.006G104100.1 | 597 | 0.01106 | 0.04362 | 0.25359 | YES | 0.0255988 |
| LEA2 | CotAD_17,101 | Gorai.006G150200.1 | 666 | 0.01977 | 0.04018 | 0.491966 | YES | 0.209339 |
| LEA2 | CotAD_31,535 | Gorai.006G150200.1 | 666 | 0.00391 | 0.01981 | 0.197433 | YES | 0.082505 |
| LEA2 | Cotton_A_13469 | Gorai.006G150200.1 | 666 | 0.01777 | 0.04018 | 0.442182 | YES | 0.10598 |
| LEA2 | CotAD_23,646 | Gorai.006G199800.1 | 609 | 0.04249 | 0.11411 | 0.372373 | YES | 0.00460089 |
| LEA2 | Cotton_A_27282 | Gorai.006G199800.1 | 609 | 0.04364 | 0.10127 | 0.4309 | YES | 0.0292702 |
| LEA2 | Cotton_A_27300 | Gorai.006G199800.1 | 609 | 0.00852 | 0.01474 | 0.578415 | YES | 0.130872 |
| LEA2 | Cotton_A_02294 | Gorai.007G048400.1 | 576 | 2.54671 | 1.77281 | 1.43654 | NO | 0.3084 |
| LEA2 | Gorai.002G235700.1 | Gorai.007G048400.1 | 576 | 2.49387 | 1.6786 | 1.48568 | NO | 0.261229 |
| LEA2 | Cotton_A_29142 | Gorai.007G365600.1 | 630 | 0.02641 | 0.05237 | 0.504231 | YES | 0.0996897 |
| LEA2 | CotAD_08181 | Gorai.009G305100.1 | 606 | 0.00435 | 0.02103 | 0.206723 | YES | 0.090366 |
| LEA2 | CotAD_19,214 | Gorai.010G176400.1 | 543 | 0.00955 | 0.01664 | 0.574182 | YES | 0.403293 |
| LEA2 | CotAD_35,514 | Gorai.010G176400.1 | 543 | 0 | 0.00822 | 0 | YES | 0 |
| LEA2 | Cotton_A_30889 | Gorai.010G176400.1 | 543 | 0.00716 | 0.00825 | 0.8675 | YES | 0.63691 |
| LEA3 | CotAD_31,344 | CotAD_37,888 | 960 | 0.0445 | 0.58201 | 0.076463 | YES | 1.76E-39 |
| LEA3 | CotAD_31,344 | CotAD_73,966 | 960 | 0.04525 | 0.56675 | 0.079847 | YES | 1.38E-37 |
| LEA3 | CotAD_31,344 | Cotton_A_08663 | 960 | 0.01103 | 0.02662 | 0.414477 | YES | 0.0917464 |
| LEA3 | CotAD_31,344 | Cotton_A_14478 | 960 | 0.0452 | 0.56976 | 0.079332 | YES | 9.48E-38 |
| LEA3 | CotAD_68,063 | Cotton_A_35039 | 654 | 0.0041 | 0.00611 | 0.670634 | YES | 0.565408 |
| LEA3 | CotAD_76,129 | Cotton_A_40363 | 627 | 0.00636 | 0.03331 | 0.190971 | YES | 0.0241426 |
| LEA4 | CotAD_73,966 | Cotton_A_08663 | 960 | 0.04453 | 0.54363 | 0.081917 | YES | 8.99E-37 |
| LEA4 | CotAD_73,966 | Cotton_A_14478 | 960 | 0.00552 | 0.00865 | 0.63778 | YES | 0.447461 |
| LEA4 | Cotton_A_08663 | Cotton_A_14478 | 960 | 0.04448 | 0.54647 | 0.081397 | YES | 6.22E-37 |
| LEA4 | CotAD_48,769 | Cotton_A_14676 | 405 | 0 | 0.02141 | 0 | YES | 0 |
| LEA4 | CotAD_64,120 | Cotton_A_22932 | 654 | 0.00607 | 0.01278 | 0.475195 | YES | 0.348209 |
| LEA4 | Gorai.004G155000.1 | Cotton_A_22932 | 630 | 2.64206 | 3.59311 | 0.735312 | YES | 0.675748 |
| LEA4 | CotAD_46,550 | Cotton_A_27543 | 606 | 0.00654 | 0.04242 | 0.154221 | YES | 0.00764013 |
| LEA4 | CotAD_64,120 | Gorai.004G155000.1 | 630 | 2.60195 | 2.91277 | 0.893293 | YES | 0.834736 |
| LEA4 | Cotton_A_22932 | Gorai.004G155000.1 | 630 | 2.64206 | 3.59311 | 0.735312 | YES | 0.675748 |
| LEA4 | CotAD_70,003 | Gorai.006G083600.1 | 573 | 0.01378 | 0.02282 | 0.603673 | YES | 0.351221 |
| LEA4 | Cotton_A_17625 | Gorai.006G083600.1 | 573 | 0.01841 | 0.02287 | 0.804972 | YES | 0.670413 |
| LEA4 | CotAD_46,550 | Gorai.009G305100.1 | 606 | 0.00655 | 0.02791 | 0.234738 | YES | 0.0613694 |
| LEA4 | Cotton_A_27543 | Gorai.009G305100.1 | 606 | 0.00435 | 0.01395 | 0.311662 | YES | 0.239375 |
| LEA5 | CotAD_39,719 | Cotton_A_14009 | 822 | 0.00325 | 0.00976 | 0.333365 | YES | 0.258994 |
| LEA5 | CotAD_53,263 | Cotton_A_22889 | 492 | 0.01631 | 0.04279 | 0.38131 | YES | 0.103316 |
| LEA5 | CotAD_74,061 | Cotton_A_38117 | 1215 | 0.00426 | 0.01476 | 0.28873 | YES | 0.0817353 |
| LEA6 | CotAD_42,408 | Cotton_A_13854 | 642 | 3.29524 | 1.27099 | 2.59265 | NO | 0.00291028 |
| LEA6 | CotAD_60,617 | Gorai.001G124400.1 | 630 | 0.01046 | 0.04152 | 0.251878 | YES | 0.00495557 |
| LEA6 | Cotton_A_09615 | Gorai.001G124400.1 | 630 | 0.01046 | 0.04152 | 0.251878 | YES | 0.00495557 |
| SMP | Cotton_A_31083 | CotAD_62,996 | 939 | 2.26658 | 1.80077 | 1.25867 | NO | 0.353457 |
| SMP | CotAD_47,454 | Cotton_A_07451 | 810 | 0.01141 | 0.05967 | 0.191218 | YES | 0.000658403 |
| SMP | CotAD_61,391 | Cotton_A_09596 | 573 | 0.0046 | 0.00736 | 0.624435 | YES | 0.545436 |
| SMP | CotAD_64,657 | Cotton_A_18919 | 786 | 0.00683 | 0.00508 | 1.345 | NO | 0.764969 |
| SMP | CotAD_62,996 | Cotton_A_24356 | 954 | 0 | 0.01351 | 0 | YES | 0 |
| SMP | Cotton_A_31083 | Cotton_A_24356 | 939 | 2.26658 | 1.8524 | 1.22359 | NO | 0.3981 |
| SMP | CotAD_61,391 | Gorai.001G122700.1 | 573 | 0.01855 | 0.05313 | 0.349233 | YES | 0.0424313 |
| SMP | Cotton_A_09596 | Gorai.001G122700.1 | 573 | 0.01387 | 0.0453 | 0.306205 | YES | 0.042074 |
| SMP | Cotton_A_02294 | Gorai.002G235700.1 | 627 | 0.00614 | 0.0377 | 0.162756 | YES | 0.0142575 |
| SMP | CotAD_61,173 | Gorai.004G137100.1 | 645 | 0.01861 | 0.04646 | 0.400532 | YES | 0.0204369 |
| SMP | Cotton_A_31127 | Gorai.004G137100.1 | 645 | 0.01965 | 0.0431 | 0.45597 | YES | 0.124339 |
| SMP | CotAD_47,454 | Gorai.009G452500.1 | 810 | 1.79916 | 1.14125 | 1.57648 | NO | 0.0145321 |
| SMP | Cotton_A_07451 | Gorai.009G452500.1 | 810 | 1.85045 | 1.14684 | 1.61353 | NO | 0.0110846 |
A B: paralogous gene pair; aa amino acids, Ka non-synonymous substitutions per non-synonymous site, Ks synonymous substitutions per synonymous site); Ka/Ks the ratio, SMP seed maturation protein, LEA Late embryogenesis abundance, Yes presence of purifying selection while NO absence of purifying selection
Prediction of LEA genes (mRNA) targeted by miRNAs in upland cotton
Large groups of small RNAs, known as microRNAs (miRNAs) are reported as the regulators in plant adaptation to abiotic stresses [60]. In transgenic creeping bent grass, Agrostis stolonifera, over expression of rice miR319a showed enhanced salt and drought tolerance [61]; over expression of miR396c and miR394 in plants was due to hypersensitive to salinity stress [62]. In cotton, Gossypium hirsutum, a group of miRNAs and their targets have been identified, and some of them respond to salt and drought stresses [60]. To get more information on LEA genes functions, we carried out the prediction of miRNAs targets on LEA transcripts (mRNA) by the use of psRNATarget, the same as been used for other functional genes in cotton [63]. Out of 242 upland cotton LEA genes, 89 genes were found to be targeted by 63 miRNAs, representing 37% of all the LEA genes (Additional file 4: Table S3). The highest levels of target were detected on the following genes with more than 6 miRNAs; CotAD_00799 (6 miRNAs), CotAD_06037 (9 miRNAs), CotAD_13,827 (6 miRNAs), CotAD_19,205 (6 miRNAs), CotAD_31,936 (6 miRNAs) CotAD_33,143 (6miRNAs), CotAD_41,925 (8miRNAs) and CotAD_69,738 (7miRNAs) as highlighted in (Additional file 4: Table S3). The rest of the genes were either targeted by one or not more than 5 miRNAs. The high number of miRNAs targeting LEA genes could possibly had direct or indirect correlation to their stress tolerance levels to abiotic stress more so drought. Some specific miRNAs had high level of target to various genes such as ghr-miR164 (5 genes), ghr-miR2949a-3p (7 genes), ghr-miR2950 (10 genes), ghr-miR7492a (10 genes), ghr-miR7492b (10 genes), ghr-miR7492c (10 genes), ghr-miR7495a (10 genes), ghr-miR7495b (10 genes), ghr-miR7504a (5 genes), ghr-miR7507 (5 genes), ghr-miR7510a (6 genes), ghr-miR7510b (10 genes), ghr-miR827b (4 genes) and lastly ghr-miR827c (4 genes). It has been found that miRNAs might be playing a role in response to drought and salinity stresses through targeting a series of stress-related genes [60]. Cotton ghr-miR7510b not only involved in drought stress but also highly up regulated in ovule and fibre, thus has an integral role in fibre formation [64]. Deep sequencing of miRNA under drought and salinity, ghr-miR408a, ghr-miR2911, ghr-miR156a/c/d and ghr-miR3954a/b were found to have differential expression in either of the stress factors, drought and salt stress [60].
Gene ontology (GO) annotation
The biological processes, molecular functions and cellular components of cotton LEA genes were examined according Gene Ontology (GO) data base. Blast2GO v4.0 was used to carry out the analysis (Fig. 6 and Additional file 5: Table S4). The results showed that the 242 LEA genes were putatively involved in a range of biological processes. Of the 5 terms of biological processes defined by Blast2Go terms, most LEA genes were predicted to function in the response to desiccation (~29%), followed by response to stress and response to defense. Molecular function prediction indicated that all 242 LEA genes, majority were involved in signal transducer activity, transferase activity and DNA binding. In cellular component prediction of LEA genes exhibited to be involved in membrane were 117, membrane parts (113), cell (13) and cell part (13). Higher numbers of upland cotton, G. hirsutum LEA genes were mainly involved in cellular component and molecular functions and few were found to be involved in biological processes. In all the LEA groups, molecular functions, biological process and cellular components were noted except in LEA 1 in which only two GO functions, biological process and cellular components were observed.
Fig. 6.
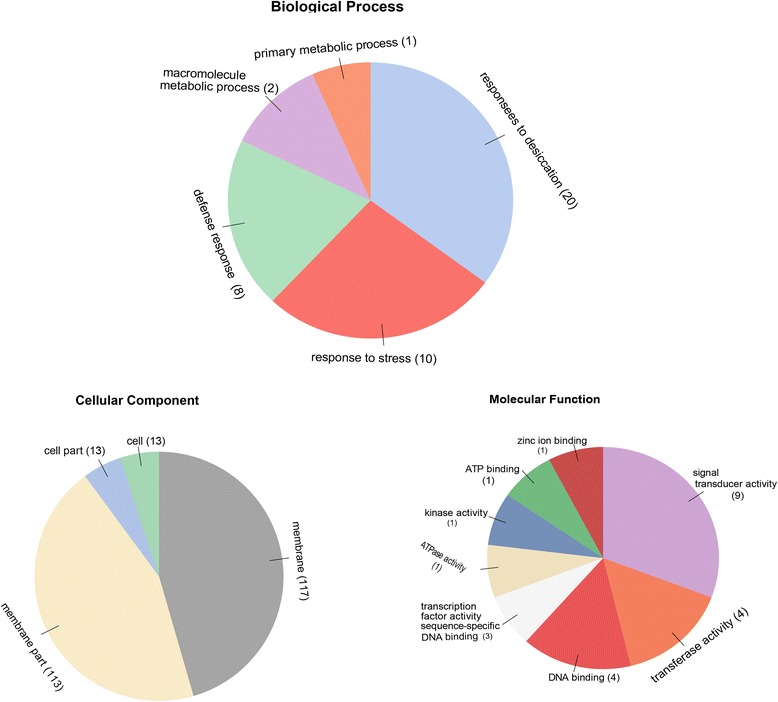
Gene Ontology (GO) annotation results for upland cotton LEA genes. GO analysis of 242 LEA protein sequences predicted for their involvement in biological processes (BP), molecular functions (MF) and cellular components (CC). For the results presented as detailed bar diagrams, as illustrated in Additional file 5: Table S4
Promoter cis-element analysis
Promoter sequences, 2 kb upstream and downstream of the translation start and stop site of all the LEA genes were obtained from the cotton genome project. Transcriptional response elements of LEA genes promoters were analyzed using the PLACE database (http://www.dna.affrc.go.jp/PLACE/signalscan.html) [36]. In order to determine cis –acting regulator element, we queried a section of the sequence of each gene, but only the start and end codon were used for the selection of cis–promoter elements. Analysis of the promoter region of all upland cotton LEA genes identified the presence of various stress responsive cis-acting regulatory elements, including DRE/CRT, ABRE, LTRE and MYBS. These stress-responsive elements were relatively abundant in the promoters of the upland cotton LEA genes, more specifically ABREs (Fig. 7 and Additional file 6: Table S5), indicating that LEA proteins may have an important functional role in drought stress response and tolerance in upland cotton, G. hirsutum. There were significant differences in the average proportions of the promoter elements detected within the different LEA gene families (Fig. 7).
Fig. 7.
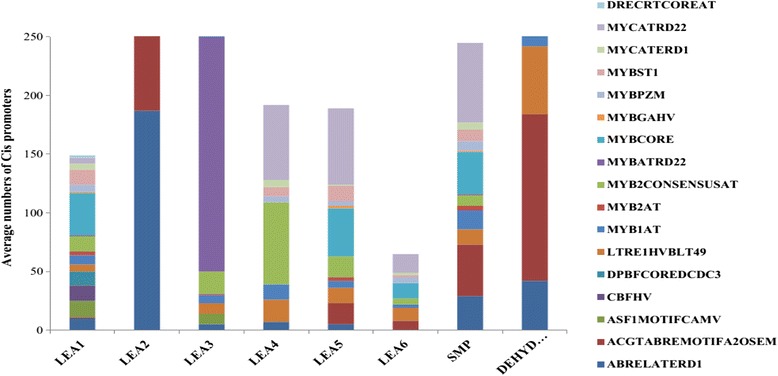
Average number of the cis-promoters ABRELATERD1 (ACGTG), DRECRTCOREAT (G/ACCGAC), MYBCORE (TAACTG), LTRE1HVBLT49 (CCGAC) and others in promoter region of Gossypium hirsutum LEA genes from each LEA families. The promoter regions were analyzed in the 1 kb upstream promoter region of translation start site using the PLACE database
The upland cotton LEA genes from LEA 2, LEA3, SMP and dehydrins gene families contained the highest average proportions of stress-responsive elements, while those from LEA 1 and LEA 6 contained the lowest proportions. ABRELATERD1 (ACGTG) was the dominant cis promoter elements, similar findings, with the predominance of ABRE cis-element, have been reported for LEA genes in tomato [46], Arabidopsis [40] and Chinese plum [47]. ABRE is a cis-acting element majorly involved in abscisic acid signaling in response to abiotic stresses, while DRE/CRT and LTRE are major cis-acting regulatory elements involved in the ABA-independent gene expression in response to water deficit (DRE/CRT) and cold (DRE/CRT and LTRE) [65]. MYBS is well-studied cis-acting promoter element with key role in the abscisic acid-dependent signaling pathway in response to drought, salt and cold [66].
Upland cotton LEA genes expression analysis under drought stress
To examine the expression profile of LEA proteins family in various tissues under drought stress treatments, we selected 42 LEA genes based on phylogenetic tree analysis, intron–exon and protein motif features, for each LEA group. Three cotton genotypes, G. tomentosum, a wild type known to be drought resistant, G. hirsutum, an elite cultivar, though drought susceptible cultivar and their backcross type BC2F1 generation were cultivated in the greenhouse under drought simulated and well watered condition. The qRT-PCR analysis was done on the three sets of accessions on different plant organs, roots, stems, and leaves. The results showed that LEA genes were differentially expressed under drought treatment across different tissues tested. Based on the cluster analysis, gene expression profiling were categorized into 2 groups, sub group 1, included 15 genes; the majority in this cluster of genes were up regulated in G. tomentosum in all tissues after 14 days of stress exposure and down regulation after 7 days of stress except in root, which showed partial expression. In G. hirsutum, majority of the genes were up regulated after treatment except in leave tissues in which the genes showed down regulation. In BC2F1, majority of the genes were down regulated after one week of exposure but expression was high after two weeks under drought stress. This result showed that these genes might be involved either directly or indirectly in drought stress, and their role was majorly concentrated in roots and stem. The second cluster, with 28 genes, the majority of the genes showed down regulation after one week of stress in all the tissues across the three genotypes. Some genes were up regulated across the three genotypes after 2 weeks of drought treatment. The results exhibited differential expression pattern in the 3 genotypes tested (Fig. 8). Some of the LEA genes were differentially expressed in the three plant organs and genotypes tested while others showed same expression pattern in different tissues, this could be due to functional divergence of LEA genes during plant development, for instance, CotAD_16,595 and CotAD_40,972 were highly expressed in the roots in all the three genotypes (Fig. 1), implying that they could be responsible for enhancing roots traits to drought tolerance. CotAD_13,827 and CotAD_31,906 were highly expressed in the leaves while others such as CotAD_10,044 and CotAD_03264 were highly up regulated in the stem. Further analysis of the expression showed that more than a half the upland cotton LEA genes were increased in roots and leaves at 7th and 14th day of stress as opposed to the stem. Roots and leaves tissues are highly sensitive to drought, the roots is the first organ to be affected by water deficit [67]. The leaves wilt or become chlorotic in stress conditions and affects photosynthesis process [68].
Fig. 8.
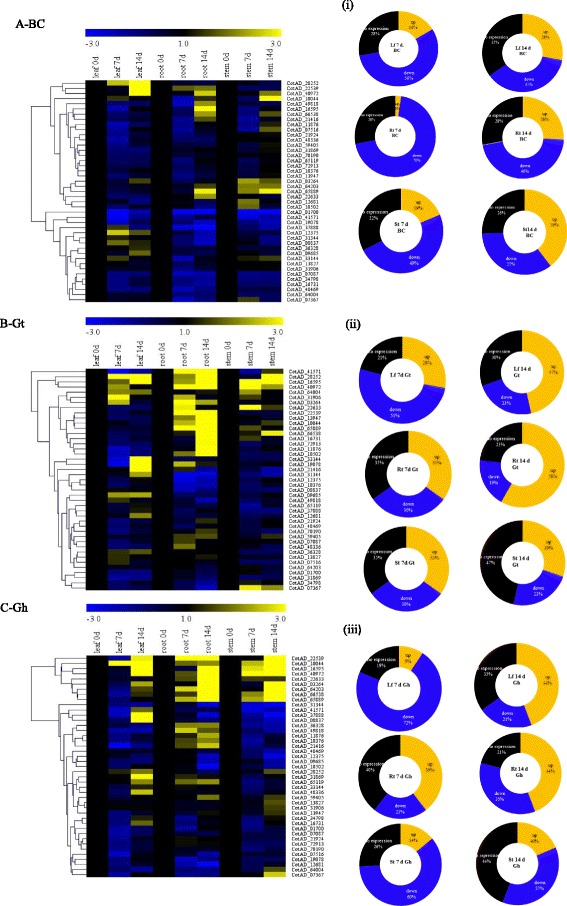
Differential expression of upland cotton LEA genes under drought stress. The heat map was visualized using Mev.exe program. (Showed by log2 values) in control, and in treated samples 7 and 14 days after drought treatment. a – BC2F1 (offspring), b – Gossypium tomentosum and c – Gossypium hirsutum. (i) Yellow – up regulated, blue – down regulated and black- no expression. (i). Percentage of genes exhibiting different responses to dehydration in leaf, root and stem of BC2F1; (ii). Percentage of genes exhibiting different responses to dehydration in leaf, root and stem of Gossypium tomentosum (iii). Percentage of genes exhibiting different responses to dehydration in leaf, root and stem of Gossypium hirsutum
Discussion
LEA proteins family is a large and widely diversified across plant kingdom [15]. The LEA gene family has been identified in several crops, such as rice and maize [69], in other organisms such as invertebrates and microorganisms [70]. However, characterization of the LEA protein family and their role in drought stress tolerance in upland cotton has never been reported. In this study, we identified different numbers of LEA genes in G. hirsutum (242), G. arboreum (136), G. raimondii (142), A. thaliana (51) and P. tabuliformis (30). The number of LEA genes in cotton genome AD (G. hirsutum) were higher than A (G. arboreum) and D (G. raimondii). The number of LEA genes in AD is approximately 1.78 and 1.70 times that in A and D respectively. The high number of LEA genes in G. hirsutum were more likely caused by gene duplication and the conservation of the LEA genes during the polyploidization process, signifying the important role played by these groups of gene families in the process of plant growth and development [40].
Gene duplication, is a major feature of genomic architecture, with cardinal role in the process of plant genomic and organismal evolution, resulting into new raw genetic materials for genetic drift, mutation and selection, which ultimately results into emergence of new gene functions and evolution of gene networks [71]. Gene duplication mechanism not only lead to the expansion of genome content but aids in the diversification of gene function to ensure adequate adaptability and evolution of plants [55]. The tetraploid cotton have undergone whole genome duplication events during their evolution period [72] and G. hirsutum emerged through allopolyploidy [73]. In this study, only 46 (17%) tandemly duplicated genes were detected, similarly only 6 genes were found to be tandemly duplicated in Brassica napus, perhaps because the evolution of upland cotton and Brassica napus are due to whole genome duplication [74, 75]. Majority of the upland LEA genes showed a close relationship with respect to the block locations of G. arboreum and G. raimondii LEA genes.
A phylogenetic analysis provided evidence of the contribution of whole genome duplication contribution to Upland cotton LEA genes abundance. LEA gene expansion through whole genome duplication have been observed in Arabidopsis [37] and Brassica napus [86]. The Gossypium arboreum genome contained 136 LEA genes and G. raimondii genome had 142 LEA genes; therefore, a WGD process would be expected to produce more than 242 LEA genes in Gossypium hirsutum. The LEA genes numbers proportions in G. hirsutum (tetraploid) implied that a larger number of the duplicated LEA genes were lost or became functionless after whole genome duplication. The loss of Upland cotton LEA genes could have been due to chromosomes rearrangement, the same mechanism was also observed in the case of Brassica [76]. The expansion of LEA genes in upland cotton was majorly through segmental duplication, 44% (130/242) of the upland cotton LEA genes emerged through segmental duplication. This finding is concurrent to observation made in Brassica 72 out of 108 genes occurred through segmental duplication [39] and in Arabidopsis in which 24% of its LEA genes arose through segmental type of gene duplication [40]. In synteny analysis, we identified 241 pairs with high similarity, implying that most LEA gene family members are embedded in highly-conserved syntenic regions, and some genes were either lost or recovered. The loss or gain of genes within the syntenic region have been observed in a number of gene families not only in LEA genes [77].
Characterization and structural analysis of genes with major functions on abiotic and biotic stress factors have been found to have fewer introns [48]. The analysis of the upland cotton LEA genes, LEA 1, 3, 4, 5, SMP and dehydrins genes had one to four intron with exception of LEA 2 and 6, which had zero to five introns. The reduced intron numbers in stress responsive genes have been recorded, such as trehalose-6-phosphate synthase gene family which plays an important role in abiotic stress and metabolic regulation [78]. The existence of introns in a genome is argued to cause enormous burden on the host [79]. The burden is because the introns requires a spliceosome, which is among the largest molecular complexes in the cell, comprising 5 small nuclear RNAs and more than 150 proteins [79]. It has also been found that intron transcription is costly in terms of time and energy [80]. Moreover, introns can extend the length of the nascent transcript, resulting into an additional expense for transcription [81].
The motif protein analysis and composition of each LEA gene family largely varied, although some amino acid-rich regions were detected, similar to previous studies done on Arabidopsis [40] and legumes [82]. We found that that genes belonging to the same families exhibited similar gene structure and motif composition. This results is consistent to previous studies which recorded similar exon - intron and protein motif within the same group of the LEA genes [23]. LEA proteins have disordered structure along their sequences due to their amino acid compositions [83]. LEA proteins play key roles in the plant cell despite of their disordered structure [41], they have the ability to form chaperons with other elements [84].The structural flexibility of the LEA proteins facilitate interactions with other macromolecules, such as membrane proteins, hence cell membrane stability during drought stress [85]. These results demonstrate that LEA proteins have intrinsic characteristics which enables them to functions as flexible integrators in protecting other molecules under drought stress and other forms of abiotic stress factors [86].
In relation to gene ontology (GO) analysis, biological processes, molecular functions and cellular components are features of genes or gene products that enable us to understand the diverse molecular functions of proteins. Cellular component and molecular activities were highest among the upland cotton LEA proteins, this could be in line with their functions of protecting the membranes and enzymes to maintain cellular activities under drought stress conditions [87]. The finding in this study is concurrent to previous studies which reported that LEA proteins are mainly located in subcellular regions such as chloroplast, nucleus, cytoplasm and mitochondria in Arabidopsis [40] and tomato [46]. The subcellular localization and the role of the LEA protein in the cell are positively correlated. Binding to different molecules such as ATP binding (GO: 0005524), sequence-specific DNA binding (GO: 0003700) and zinc ion binding (GO: 0008270) were the major activities for the action of upland LEA proteins as molecular function. Binding of LEA proteins to nucleic acids in order to protect cellular structures by constructing hydrogen network was reported, which is related to the roles of LEA proteins in drought stress tolerance [88]. In addition, LEA protein family groups have been found to enhance membrane stabilization through chaperons formation with phospholipids and other sugar molecules as described in model membranes under drought condition [87]. The molecular function of LEA proteins in drought stress may be through the binding activity.
In addition, biological processes in response to stress factors were dominant, response to desiccation (GO: 0009269); abscisic acid transport (GO: 0080168); response to stress (GO: 0006950); response to water (GO: 0009415); auxin-activated signalling pathway (GO: 0009734); response to water deprivation (GO: 0009414); response to cytokinin (GO: 0009735) and phosphorylation (GO: 0016310). These biological roles detected in cotton LEA proteins were consistent with earlier findings of biological functions of the LEA proteins such as oxidant scavenging activity, enzyme and nucleic acid preservation and membrane maintenance, these biological functions protect cell structures from the deleterious effects of drought and other abiotic stress factors [89]. Our findings is further supported by the highly up regulation of LEA proteins in various studies done in transgenic modal plant, Arabidopsis [90] and bacteria [91].
The small RNAs are a diverse class of non-coding regulatory with important function in gene regulation under drought stress conditions by destroying the target gene transcripts in plants [92]. The analysis of upland cotton miRNAs showed that 89 LEA transcripts were targeted by 63 different miRNAs. The NAC gene family are plant-specific transcriptional factors known to play diverse roles in various plant developmental processes, MYB is a transcriptional factor family mainly involved in controlling various processes like responses to biotic and abiotic stresses, development, differentiation, metabolism, defense among other biological processes while mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) gene families also do play an important roles in plant growth, development and defense response. The three plant transcriptional factors, MYB, NAC and MAPK are ranked top under the context of drought and salinity indicating their important roles for the plant to combat drought and salinity stress. Through target prediction, a series of cotton miRNAs were found to be associated with MYB, NAC and MAPK genes including miR164 [60, 93]. In this research work miR164 was found to target four (5) LEA genes, CotAD_03784, CotAD_07516, CotAD_19,375, CotAD_24497and CotAD_63,174. The association of these 5 LEA genes with miR164, which have been found to be linked to highly ranked plants transcription factors under drought and salt stress, provides a strong evidence of a major role played by LEA genes in drought stress. A small RNA like miR827 have been found to confer drought tolerance in transgenic Arabidopsis, homologous form of the same miRNA, denoted as Hv-miR827, have been proved to confer drought tolerance in barley [94]. The same miRNA, ghr-miR827a/b/c/d, was found to target 12 different LEA genes, this implied that these genes targeted by the miRNA had a direct functional role in enhancing drought tolerance in upland cotton.
Gene promoters, also termed as cis-element, play various key roles in the transcriptional regulation of genes controlling a number of abiotic stress and plant hormones responses. Phyto-hormones enhance the ability of plants to adapt to changing environments. Many abiotic stress-related and plant hormones-related cis-elements, including W-Box, MBS, HSE, ABRE and TCA-elements, have been identified [95]. All of these and other cis-elements were detected in our investigation. Therefore, the results obtained is in agreement to the various cis-acting element detected in the analysis of LEA genes in various plants such as tomato [46], Chinese plum [47], in brassica [39] and poplar [48]. In each LEA gene, contained more than four cis-elements related to abiotic stress signal responsiveness, which provides strong evidence, that these genes might have important functions under different drought stresses.
A number of studies have shown that LEA genes do have a significant contribution in drought stress [69]. From the heatmap and expression pattern of cotton LEA gene families, high number of LEA genes showed higher expression levels across all the plant organs tested. The high expression levels of these genes under drought condition, indicates the maintenance functions during stress conditions, leading to drought tolerance of the plants. A unique observation was made, in which high percentage of the LEA 2 genes, used in the expression analysis, almost all showed high expression, and it would be of interest to characterize this group of LEA gene family in upland cotton. High expression pattern of the LEA genes have been observed in Brassica napus [39], Prunus meme [47], Arabidopsis [40] and sweet orange [53]. LEA genes have been found to have wide distribution and abundance among the terrestrial plants as opposed to aquatic plants, the abundance of these gene families could be pegged on to their conservative role, aquatic plants do not suffer from drought stress, thus the shrinking number of LEA genes. Therefore, the finding of this work and previous publication on function of LEA genes may explain why the LEA gene family have a wider distribution in terrestrial plants but not moss plants [96]. LEA families with close taxonomic relationships generally exhibited similar scales and distributions. However, the scales of the LEA gene family differ in upland cotton Gossypium hirsutum and other higher plants such as Theobroma cacao L, sweet orange, Arabidopsis among others; this could be due to changes in the environmental conditions. The high number of LEA genes in upland cotton, suggested that stress adaptation might have initiated the evolution of protein coding sequences which are LEA specific. Similar observation have been reported in maize in which adaptation to abiotic stress led to evolution of protein coding sequences, leading to the variation of LEA genes in maize compared to rice [97]. We carried out the expression profiling of the LEA genes in drought susceptible upland cotton, Gossypium hirsutum, drought tolerant cultivar Gossypium tomentosum and their BC2F1 offspring. High numbers of genes were found to be highly up regulated in G. tomentosum than in G. hirsutum (Figs. 8 and 9). The results obtained is concurrent to similar findings which have been reported in maize landraces with varying drought stress tolerance levels when compared at the transcriptional level [98]. This result implied that more tolerant cotton genotypes had a greater ability to rapidly adjust more genes under drought stress than the more susceptible cotton cultivars. Moreover, rapid adjustments of greater number of differentially expressed genes and of different transcriptome factor families is considered an important trait of the drought tolerant genotypes [99].
Fig. 9.
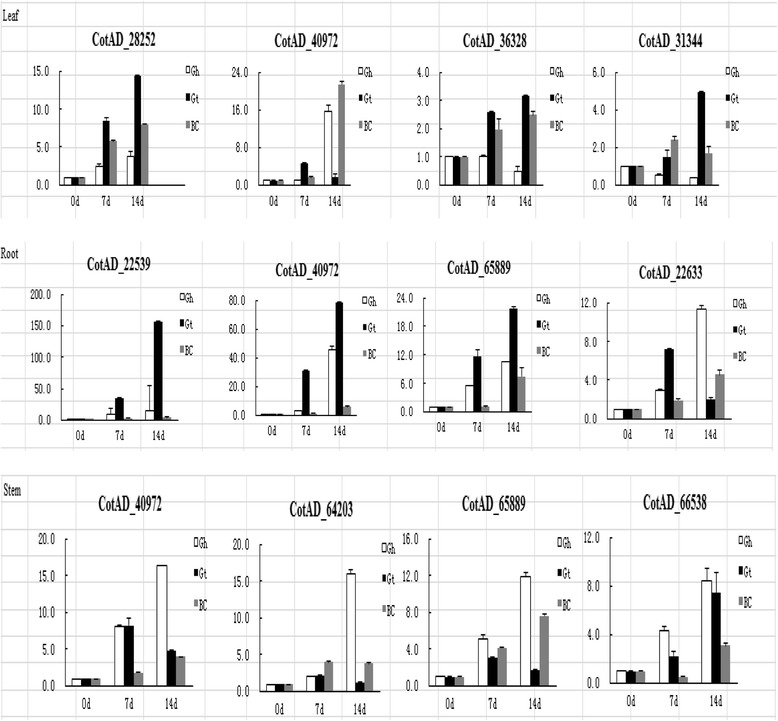
Quantitative PCR analysis of the selected LEA genes. Abbreviations: Rt (root), Sm (stem) and Lf (leaf). 0, 7 and 14 days of stress. Gh - Gossypium hirsutum, Gt - Gossypium tomentosum and BC-BC2F1 offspring. Y-axis: relative expression (2−ΔΔCT)
Conclusions
This research work provides the very first detailed analysis, characterization and expression profile of upland LEA genes under drought condition. A total of 242 LEA genes were identified in upland cotton and divided into eight groups. Chromosomal mapping and syntenic analysis showed that all the LEA genes were distributed in all the cotton chromosomes with some genes clustering either on the upper arm or the middle region of the chromosomes. Segmental gene duplication was found to have played a major role in the expansion of upland cotton LEA genes coupled with whole genome duplication. High numbers of cotton LEA genes had few introns. Genes belonging to the same family exhibited similar gene structures and protein motif composition. Expression profiling of the selected LEA genes showed differential expression under drought treatment across different plant organs. The outcome of this research provides the most current information thus will increases our understanding of LEA genes in cotton and the general role in drought stress tolerance. This work lays the very first foundation for further investigations of the very specific functions of these LEA proteins in cotton in reference to drought stress and other abiotic stress factors.
Additional files
List of primers used for upland cotton, Gossypium hirsutum LEA genes expression analysis under drought stress. (DOCX 19 kb)
LEA gene in upland cotton, Gossypium hirsutum and their subcellular location prediction. The colour scheme indicates where the genes are sub-localized. (DOCX 90 kb)
Phylogenetic tree, gene structure and motif compositions of LEA 2 genes in upland cotton. The phylogenetic tree was constructed using MEGA 6.0. Exon/intron structures of LEA genes in upland cotton, exons introns and up / down-stream were represented by yellow boxes, black lines and blue boxes, respectively. Protein motif analysis represented by different colours, and each motif represented by number. (PDF 3609 kb)
LEA genes and mRNA targets. (DOCX 53 kb)
Gene ontology (GO) terms annotation of LEA genes in upland cotton. (DOCX 66 kb)
Cis element analysis of putative LEA promoters related to drought stress. (DOCX 719 kb)
Data. Newick format for the phylogenetic tree. (NWK 19 kb)
Acknowledgements
We are sincerely grateful to Prof Dr. Wang Kunbo, Dr. Liu and all the teachers in our research team for their valuable guidance in the course of this research work. To all the members of the research team, we do appreciate the moral support and the immense support we received during the period of this research work.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Funding
This research program was financially sponsored by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (31671745, 31530053) and the National key research and development plan (2016YFD0100306).
Availability of data and materials
All the relevant data and Additional file 7 are all availed including the primers sequences used in the LEA genes expression profiling.
Abbreviations
- GO
Gene ontology
- GolS
Galactinol synthase
- LEA
Late embryogenesis abundance
- miRNA
Micro ribonucleic acid
- SMP
Seed maturation proteins
Authors’ contributions
ROM and WK designed the experiment, LP, JNK, LH, HS implemented and collected the data. ROM analyzed the results and prepared the manuscript. JNK, LH, LP, FL, WXX, CX, ZZ, ZZM and WK revised the manuscript. All authors reviewed and approved the final manuscript.
Ethics approval and consent to participate
No ethical nor consent to participate in this research was sought, this not application in this research work.
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Footnotes
Electronic supplementary material
The online version of this article (10.1186/s12863-017-0596-1) contains supplementary material, which is available to authorized users.
Contributor Information
Richard Odongo Magwanga, Email: magwangarichard@yahoo.com.
Pu Lu, Email: lupu1992@163.com.
Joy Nyangasi Kirungu, Email: nyangasijoy@yahoo.com.
Hejun Lu, Email: luhejunicr@163.com.
Xingxing Wang, Email: wxx1991@126.com.
Xiaoyan Cai, Email: cxycri@163.com.
Zhongli Zhou, Email: zhonglizhou@163.com.
Zhenmei Zhang, Email: xyxuezhihua@163.com.
Haron Salih, Email: salih234@yahoo.com.
Kunbo Wang, Email: wkbcri@163.com.
Fang Liu, Phone: +8613949507902, Email: liufcri@163.com.
References
- 1.Cramer GR, Urano K, Delrot S, Pezzotti M, Shinozaki K. Effects of abiotic stress on plants: a systems biology perspective. BMC Plant Biol. 2011;11:163. doi: 10.1186/1471-2229-11-163. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Lawlor DW. Genetic engineering to improve plant performance under drought: physiological evaluation of achievements, limitations, and possibilities. J Exp Bot. 2013:83–108. [DOI] [PubMed]
- 3.Shinozaki K, Yamaguchi-Shinozaki K. Gene networks involved in drought stress response and tolerance. J Exp Bot. 2007:221–7. [DOI] [PubMed]
- 4.Arumingtyas EL, Savitri ES, Purwoningrahayu RD. Protein profiles and Dehydrin accumulation in some soybean varieties (Glycine max L. Merr) in drought stress conditions. Am. J. Plant Sci. 2013;4:134–141. [Google Scholar]
- 5.Information B. Effect of Water-Deficit Stress on Reproductive Development in the Cotton Pistil 1984;37–43.
- 6.Hoekstra FA, Golovina EA, Buitink J. Mechanisms of plant desiccation tolerance. Trends Plant Sci. 2001;6:431–438. doi: 10.1016/S1360-1385(01)02052-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Cammarano D, Payero J, Basso B, Wilkens P, Grace P. Agronomic and economic evaluation of irrigation strategies on cotton lint yield in Australia. Crop Pasture Sci. 2012;63:647–655. doi: 10.1071/CP12024. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Pilon C, Oosterhuis DM, Ritchie G, Oliveira EADP. Effect of drought in the osmotic adjustment of cotton Plants 2002;60–65.
- 9.Olvera-Carrillo Y, Luis Reyes J, Covarrubias AA. Late embryogenesis abundant proteins. Plant Signal Behav. 2011;6:586–589. doi: 10.4161/psb.6.4.15042. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Campos F, Cuevas-Velazquez C, Fares MA, Reyes JL, Covarrubias AA. Group 1 LEA proteins, an ancestral plant protein group, are also present in other eukaryotes, and in the archeae and bacteria domains. Mol Gen Genomics. 2013;288:503–517. doi: 10.1007/s00438-013-0768-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Wang X-S, Zhu H-B, Jin G-L, Liu H-L, W-R W, Zhu J. Genome-scale identification and analysis of LEA genes in rice (Oryza Sativa L.) Plant Sci. 2007;172:414–420. doi: 10.1016/j.plantsci.2006.10.004. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Hundertmark M, Hincha DK. LEA ( Late Embryogenesis Abundant ) proteins and their encoding genes in Arabidopsis thaliana. 2008;22:1–22. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- 13.Amara I, Zaidi I, Masmoudi K, Dolors Ludevid M, Pagès M, Goday A, et al. Insights into late embryogenesis abundant (LEA) proteins in plants: from structure to the functions. Am. J. Plant Sci. 2014;5:3440–3455. [Google Scholar]
- 14.Mouillon J, Gustafsson P, Harryson P. Structural investigation of disordered stress proteins. Comparison of full-length dehydrins with isolated peptides of their conserved segments. Plant Physiol. 2006;141:638–650. doi: 10.1104/pp.106.079848. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Gao J, Lan T. Functional characterization of the late embryogenesis abundant ( LEA ) protein gene family from Pinus Tabuliformis ( Pinaceae ) in Escherichia Coli. Nat. Publ. Gr. Nat Publ Group. 2016:1–10. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- 16.Iturriaga G. The LEA proteins and trehalose loving couple: a step forward in anhydrobiotic engineering. Biochem J. 2008;410:1–2. doi: 10.1042/BJ20071633. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Hand SC, Menze MA, Toner M, Boswell L, Moore DLEA. Proteins during water stress: not just for plants anymore. Annu Rev Physiol. 2011;73:115–134. doi: 10.1146/annurev-physiol-012110-142203. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Tunnacliffe A, Wise MJ. The continuing conundrum of the LEA. Proteins. 2007:791–812. [DOI] [PubMed]
- 19.Wise MJ. LEAping to conclusions : A computational reanalysis of late embryogenesis abundant proteins and their possible roles. 2003;19:1–19. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- 20.Zhang T, Hu Y, Jiang W, Fang L, Guan X, Chen J, et al. Sequencing of allotetraploid cotton (Gossypium hirsutum L. acc. TM-1) provides a resource for fiber improvement. Nat Biotechnol. 2015;33:531–537. doi: 10.1038/nbt.3207. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Li F, Fan G, Wang K, Sun F, Yuan Y, Song G, et al. Genome sequence of the cultivated cotton Gossypium arboreum. Nat Genet. 2014;46:567–572. doi: 10.1038/ng.2987. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Paterson AH, Wendel JF, Gundlach H, Guo H, Jenkins J, Jin D, et al. And the evolution of spinnable cotton fibres. Nature. Nat Publ Group. 2012;492:423–427. doi: 10.1038/nature11798. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Finn RD, Clements J, Eddy SRHMMER. Web server: interactive sequence similarity searching. Nucleic Acids Res. 2011;39 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- 24.Emanuelsson O, Brunak S, von Heijne G, Nielsen H. Locating proteins in the cell using TargetP, SignalP and related tools. Nat Protoc. 2007;2:953–971. doi: 10.1038/nprot.2007.131. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Bodén M, Hawkins J. Prediction of subcellular localization using sequence-biased recurrent networks. Bioinformatics. 2005;21:2279–2286. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/bti372. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Horton P, Park KJ, Obayashi T, Fujita N, Harada H, Adams-Collier CJ, et al. WoLF PSORT: protein localization predictor. Nucleic Acids Res. 2007;35 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- 27.Krzywinski M, et al. Circos: an information aesthetic for comparative genomics. Genome Res. 2009;19:1639–1645. doi: 10.1101/gr.092759.109. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Du D, Hao R, Cheng T, Pan H, Yang W, Wang J, et al. Genome-wide analysis of the AP2/ERF gene family in Prunus Mume. Plant Mol Biol Report. 2013;31:741–750. doi: 10.1007/s11105-012-0531-6. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Wang Y, Pan F, Chen D, Chu W, Liu H, Xiang Y. Genome-wide identification and analysis of the Populus Trichocarpa TIFY gene family. Plant Physiol Biochem Elsevier Masson SAS. 2017;115:360–371. doi: 10.1016/j.plaphy.2017.04.015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Librado P, Rozas J. DnaSP v5: a software for comprehensive analysis of DNA polymorphism data. Bioinformatics. 2009;25:1451–1452. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/btp187. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Li K-B. ClustalW-MPI: ClustalW analysis using distributed and parallel computing. Bioinformatics. 2003;19:1585–1586. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/btg192. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Bailey TL, Boden M, Buske FA, Frith M, Grant CE, Clementi L, et al. MEME suite: tools for motif discovery and searching. Nucleic Acids Res. 2009;37 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- 33.Kozomara A, Griffiths-Jones S. MiRBase: annotating high confidence microRNAs using deep sequencing data. Nucleic Acids Res. 2014;42 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- 34.Zhang Z, Yu J, Li D, Zhang Z, Liu F, Zhou X, et al. PMRD: plant microRNA database. Nucleic Acids Res. 2009;38 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- 35.Dai X, Zhao PX. PsRNATarget: a plant small RNA target analysis server. Nucleic Acids Res. 2011;39 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- 36.Higo K, Ugawa Y, Iwamoto M, Korenaga T. Plant cis-acting regulatory DNA elements (PLACE) database: 1999. Nucleic Acids Res. 1999:297–300. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- 37.Bies-Ethève N, Gaubier-Comella P, Debures A, Lasserre E, Jobet E, Raynal M, et al. Inventory, evolution and expression profiling diversity of the LEA (late embryogenesis abundant) protein gene family in Arabidopsis thaliana. Plant Mol Biol. 2008;67:107–124. doi: 10.1007/s11103-008-9304-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Artimo P, Jonnalagedda M, Arnold K, Baratin D, Csardi G, De Castro E, et al. ExPASy: SIB bioinformatics resource portal. Nucleic Acids Res. 2012;40 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- 39.Liang Y, Xiong Z, Zheng J, Xu D, Zhu Z, Xiang J, et al. Genome-wide identification, structural analysis and new insights into late embryogenesis abundant (LEA) gene family formation pattern in Brassica napus. Sci Rep. 2016;6:24265. doi: 10.1038/srep24265. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Hundertmark M, Hincha DKLEA. (Late embryogenesis abundant) proteins and their encoding genes in Arabidopsis thaliana. BMC Genomics. 2008;9:118. doi: 10.1186/1471-2164-9-118. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Fuxreiter M, Simon I, Friedrich P, Tompa P. Preformed structural elements feature in partner recognition by intrinsically unstructured proteins. J Mol Biol. 2004;338:1015–1026. doi: 10.1016/j.jmb.2004.03.017. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Candat A, Paszkiewicz G, Neveu M, Gautier R, Logan DC, Avelange-Macherel M-H, et al. The ubiquitous distribution of late embryogenesis abundant proteins across cell compartments in Arabidopsis offers tailored protection against abiotic stress. Plant Cell. 2014;26:3148–3166. doi: 10.1105/tpc.114.127316. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Hu R, Qi G, Kong Y, Kong D, Gao Q, Zhou G. Comprehensive analysis of NAC domain transcription factor gene family in Populus trichocarpa. BMC Plant Biol. 2010;10:145. doi: 10.1186/1471-2229-10-145. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44.Jiménez-bremont JF, Maruri-lópez I, Ochoa-alfaro AE, Delgado-sánchez P, Bravo J, Rodríguez-kessler M. LEA Gene Introns : is the Intron of Dehydrin Genes a Characteristic of the Serine-Segment? 2013;128–40.
- 45.Li X, Cao J. Late embryogenesis abundant ( LEA ) gene family in maize : identification. Evolution, and Expression Profiles. 2016:15–28.
- 46.Cao J, Li X. Identification and phylogenetic analysis of late embryogenesis abundant proteins family in tomato (Solanum lycopersicum) Planta. 2014;241:757–772. doi: 10.1007/s00425-014-2215-y. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47.Du D, Zhang Q, Cheng T, Pan H, Yang W, Sun L. Genome-wide identification and analysis of late embryogenesis abundant (LEA) genes in Prunus mume. Mol Biol Rep. 2013;40:1937–1946. doi: 10.1007/s11033-012-2250-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 48.Lan T, Gao J, Zeng QY. Genome-wide analysis of the LEA (late embryogenesis abundant) protein gene family in Populus trichocarpa. Tree Genet Genomes. 2013;9:253–264. doi: 10.1007/s11295-012-0551-2. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 49.Reyes JL, Rodrigo MJ, Colmenero-Flores JM, Gil JV, Garay-Arroyo A, Campos F, et al. Hydrophilins from distant organisms can protect enzymatic activities from water limitation effects in vitro. Plant. Cell Environ. 2005;28:709–718. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3040.2005.01317.x. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 50.Gupta S, Stamatoyannopoulos JA, Bailey TL. Noble WS. Quantifying similarity between motifs. 2007;8 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- 51.Lee M-K, Zhang Y, Zhang M, Goebel M, Kim HJ, Triplett BA, et al. Construction of a plant-transformation-competent BIBAC library and genome sequence analysis of polyploid upland cotton (Gossypium hirsutum L.) BMC Genomics. 2013;14:208. doi: 10.1186/1471-2164-14-208. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 52.Charfeddine S, Saïdi MN, Charfeddine M, Gargouri-Bouzid R. Genome-wide identification and expression profiling of the late embryogenesis abundant genes in potato with emphasis on dehydrins. Mol Biol Rep. 2015;42:1163–1174. doi: 10.1007/s11033-015-3853-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 53.Muniz Pedrosa A, Martins CDPS, Gonçalves LP, Costa MGC. Late embryogenesis abundant (LEA) constitutes a large and diverse family of proteins involved in development and abiotic stress responses in sweet orange (Citrus sinensis L. Osb.). PLoS One. 2015;10 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- 54.Philippe R, Courtois B, McNally KL, Mournet P, El-Malki R, Le Paslier MC, et al. Structure, allelic diversity and selection of Asr genes, candidate for drought tolerance, in Oryza sativa L. and wild relatives. Theor Appl Genet. 2010;121:769–787. doi: 10.1007/s00122-010-1348-z. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 55.Xu G, Guo C, Shan H, Kong H. Divergence of duplicate genes in exon-intron structure. Proc Natl Acad Sci. 2012;109:1187–1192. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1109047109. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 56.Liu Z, Adams KL. Expression partitioning between genes duplicated by polyploidy under abiotic stress and during organ development. Curr Biol. 2007;17:1669–1674. doi: 10.1016/j.cub.2007.08.030. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 57.Salih H, Gong W, He S, Sun G, Sun J, Genome-wide DX. Characterization and expression analysis of MYB transcription factors in Gossypium hirsutum. BMC genet BMC Genet. 2016:1–12. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- 58.Ng PC, Henikoff SSIFT. Predicting amino acid changes that affect protein function. Nucleic Acids Res. 2003;31:3812–3814. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkg509. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 59.Gao J, Lan T. Functional characterization of the late embryogenesis abundant (LEA) protein gene family from Pinus tabuliformis (Pinaceae) in Escherichia Coli. Sci Rep. 2016;6:19467. doi: 10.1038/srep19467. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 60.Xie F, Wang Q, Sun R, Zhang B. Deep sequencing reveals important roles of microRNAs in response to drought and salinity stress in cotton. 2015;66:789–804. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- 61.Zhou M, Li D, Li Z, Hu Q, Yang C, Zhu L, et al. Constitutive expression of a miR319 gene alters plant development and enhances salt and drought tolerance in transgenic creeping Bentgrass. Plant Physiol. 2013;161:1375–1391. doi: 10.1104/pp.112.208702. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 62.Gao S, Yang L, Zeng HQ, Zhou ZS, Yang ZM, Li H, et al. A cotton miRNA is involved in regulation of plant response to salt stress. Sci Rep. 2016;6:19736. doi: 10.1038/srep19736. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 63.Wang Z, Hobson N, Galindo L, Zhu S, Shi D, McDill J, et al. The genome of flax (Linum usitatissimum) assembled de novo from short shotgun sequence reads. Plant J. 2012;72:461–473. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-313X.2012.05093.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 64.Xie F, Jones DC, Wang Q, Sun R, Zhang B. Small RNA sequencing identifies miRNA roles in ovule and fibre development. Plant Biotechnol J. 2015;13:355–369. doi: 10.1111/pbi.12296. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 65.Yamaguchi-Shinozaki K, Shinozaki K. Organization of cis-acting regulatory elements in osmotic- and cold-stress-responsive promoters. Trends Plant Sci. 2005;10:88–94. doi: 10.1016/j.tplants.2004.12.012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 66.Li C, Ng CKY, Fan LM. MYB Transcription factors, active players in abiotic stress signaling. Environ Exp Bot. 2014;114:80–91. doi: 10.1016/j.envexpbot.2014.06.014. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 67.Opitz N, Marcon C, Paschold A, Malik WA, Lithio A, Brandt R, et al. Extensive tissue-specific transcriptomic plasticity in maize primary roots upon water deficit. J Exp Bot. 2016;67:1095–1107. doi: 10.1093/jxb/erv453. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 68.Flexas J, Bota J, Loreto F, Cornic G, Sharkey TD. Diffusive and metabolic limitations to photosynthesis under drought and salinity in C3 plants. Plant Biol. 2004:269–79. [DOI] [PubMed]
- 69.Hong-bo S, Zong-suo L, Ming-an S. LEA proteins in higher plants : Structure, function, gene expression and regulation. 2005;45:131–5. [DOI] [PubMed]
- 70.Sasaki K, Christov NK, Tsuda S, Imai R. Identification of a novel LEA protein involved in freezing tolerance in wheat. Plant Cell Physiol. 2014;55:136–147. doi: 10.1093/pcp/pct164. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 71.Flagel LE, Wendel JE. Gene duplication and evolutionaary novelty in plants. New Phytol. 2009;183:557–564. doi: 10.1111/j.1469-8137.2009.02923.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 72.Li F, Fan G, Lu C, Xiao G, Zou C, Kohel RJ, et al. Genome sequence of cultivated upland cotton (Gossypium hirsutum TM-1) provides insights into genome evolution. Nat Biotechnol. 2015;33:524–530. doi: 10.1038/nbt.3208. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 73.Nekrutenko A, Baker RJ. Subgenome-specific markers in allopolyploid cotton Gossypium hirsutum: implications for evolutionary analysis of polyploids. Gene. 2003;306:99–103. doi: 10.1016/S0378-1119(03)00427-X. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 74.Chalhoub B, Denoeud F, Liu S, Parkin IAP, Tang H, Wang X, et al. Early allopolyploid evolution in the post-Neolithic Brassica napus oilseed genome. Science (80-. ) 2014;345:950–953. doi: 10.1126/science.1253435. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 75.Hasan M, Seyis F, Badani AG, Pons-Kühnemann J, Friedt W, Lühs W, et al. Analysis of genetic diversity in the Brassica napus L. gene pool using SSR markers. Genet Resour Crop Evol. 2006;53:793–802. doi: 10.1007/s10722-004-5541-2. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 76.Cheng F, Wu J, Liang J, Wang X. Genome triplication drove the diversification of brassica plants. Brassica rapa. Genome. 2015:115–20. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- 77.Yu J, Tehrim S, Zhang F, Tong C, Huang J, Cheng X, et al. Genome-wide comparative analysis of NBS-encoding genes between brassica species and Arabidopsis thaliana. BMC Genomics. 2014;15:3. doi: 10.1186/1471-2164-15-3. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 78.Xie DW, Wang XN, LS F, Sun J, Zheng W, Li ZF. Identification of the trehalose-6-phosphate synthase gene family in winter wheat and expression analysis under conditions of freezing stress. J Genet. 2015;94:55–65. doi: 10.1007/s12041-015-0495-z. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 79.Wahl MC, Will CL, Lührmann R. The spliceosome: design principles of a dynamic RNP machine. Cell. 2009:701–18. [DOI] [PubMed]
- 80.Lane N, Martin W. The energetics of genome complexity. Nature. 2010;467:929–934. doi: 10.1038/nature09486. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 81.Jeffares DC, Penkett CJ, Bähler J. Rapidly regulated genes are intron poor. Trends Genet. 2008:375–8. [DOI] [PubMed]
- 82.Battaglia M, Covarrubias AA. Late embryogenesis abundant (LEA) proteins in legumes. Front Plant Sci. 2013;4:190. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2013.00190. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 83.Dure L, Crouch M, Harada J, Ho THD, Mundy J, Quatrano R, et al. Common amino acid sequence domains among the LEA proteins of higher plants. Plant Mol Biol. 1989;12:475–486. doi: 10.1007/BF00036962. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 84.Goyal K, Walton Lj, Tunnacliffe A. LEA proteins prevent protein aggregation due to water stress. Biochem J [Internet] 2005;388:151–157. Available from: http://biochemj.org/lookup/doi/10.1042/BJ20041931 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- 85.Olvera-Carrillo Y, Luis RJ, Covarrubias AA. Late embryogenesis abundant proteins: versatile players in the plant adaptation to water limiting environments. Plant SignalBehav. 2011;6 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- 86.Patil A, Nakamura H. Disordered domains and high surface charge confer hubs with the ability to interact with multiple proteins in interaction networks. FEBS Lett. 2006;580:2041–2045. doi: 10.1016/j.febslet.2006.03.003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 87.Tolleter D, Hincha DK, Macherel D. A mitochondrial late embryogenesis abundant protein stabilizes model membranes in the dry state. Biochim Biophys Acta Biomembr. 1798;2010:1926–1933. doi: 10.1016/j.bbamem.2010.06.029. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 88.Shih MD, Lin SD, Hsieh JS, Tsou CH, Chow TY, Lin TP, et al. Gene cloning and characterization of a soybean (Glycine max L.) LEA protein, GmPM16. Plant Mol Biol. 2004;56:689–703. doi: 10.1007/s11103-004-4680-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 89.Reyes JL, Campos F, Wei H, Arora R, Yang Y, Karlson DT, et al. Functional dissection of Hydrophilins during in vitro freeze protection. Plant Cell Environ. 2008;31:1781–1790. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3040.2008.01879.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 90.Puhakainen T, Hess MW, Mäkelä P, Svensson J, Heino P, Palva ET. Overexpression of multiple dehydrin genes enhances tolerance to freezing stress in Arabidopsis. Plant Mol Biol. 2004;54:743–753. doi: 10.1023/B:PLAN.0000040903.66496.a4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 91.Liu Y, Zheng Y. PM2, a group 3 LEA protein from soybean, and its 22-mer repeating region confer salt tolerance in Escherichia Coli. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2005;331:325–332. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2005.03.165. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 92.Ambros V, Chen X. The regulation of genes and genomes by small RNAs. Development. 2007;134:1635–1641. doi: 10.1242/dev.002006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 93.Mallory AC, Dugas DV, Bartel DP, Bartel B. MicroRNA regulation of NAC-domain targets is required for proper formation and separation of adjacent embryonic, vegetative, and floral organs. Curr Biol. 2004;14:1035–1046. doi: 10.1016/j.cub.2004.06.022. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 94.Ferdous J, Whitford R, Nguyen M, Brien C, Langridge P, Tricker PJ. Drought-inducible expression of Hv-miR827 enhances drought tolerance in transgenic barley. Funct Integr Genomics. 2017;17:279–292. doi: 10.1007/s10142-016-0526-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 95.Kim JS, Mizoi J, Yoshida T, Fujita Y, Nakajima J, Ohori T, et al. An ABRE promoter sequence is involved in osmotic stress-responsive expression of the DREB2A gene, which encodes a transcription factor regulating drought-inducible genes in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell Physiol. 2011;52:2136–2146. doi: 10.1093/pcp/pcr143. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 96.Kamisugi Y, Cuming AC. The evolution of the abscisic acid-response in land plants: comparative analysis of group 1 LEA gene expression in moss and cereals. Plant Mol Biol. 2005;59:723–737. doi: 10.1007/s11103-005-0909-z. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 97.Liu H, Wang X, Warburton ML, Wen W, Jin M, Deng M, et al. Genomic, transcriptomic, and phenomic variation reveals the complex adaptation of modern maize breeding. Mol Plant. 2015;8:871–884. doi: 10.1016/j.molp.2015.01.016. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 98.Rabbani MA. Monitoring expression profiles of Rice genes under cold, drought, and high-salinity stresses and abscisic acid application using cDNA microarray and RNA gel-blot analyses. Plant Physiol. 2003;133:1755–1767. doi: 10.1104/pp.103.025742. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 99.Peng Z, He S, Gong W, Sun J, Pan Z, Xu F, et al. Comprehensive analysis of differentially expressed genes and transcriptional regulation induced by salt stress in two contrasting cotton genotypes. BMC Genomics. 2014;15:760. doi: 10.1186/1471-2164-15-760. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
List of primers used for upland cotton, Gossypium hirsutum LEA genes expression analysis under drought stress. (DOCX 19 kb)
LEA gene in upland cotton, Gossypium hirsutum and their subcellular location prediction. The colour scheme indicates where the genes are sub-localized. (DOCX 90 kb)
Phylogenetic tree, gene structure and motif compositions of LEA 2 genes in upland cotton. The phylogenetic tree was constructed using MEGA 6.0. Exon/intron structures of LEA genes in upland cotton, exons introns and up / down-stream were represented by yellow boxes, black lines and blue boxes, respectively. Protein motif analysis represented by different colours, and each motif represented by number. (PDF 3609 kb)
LEA genes and mRNA targets. (DOCX 53 kb)
Gene ontology (GO) terms annotation of LEA genes in upland cotton. (DOCX 66 kb)
Cis element analysis of putative LEA promoters related to drought stress. (DOCX 719 kb)
Data. Newick format for the phylogenetic tree. (NWK 19 kb)
Data Availability Statement
All the relevant data and Additional file 7 are all availed including the primers sequences used in the LEA genes expression profiling.


