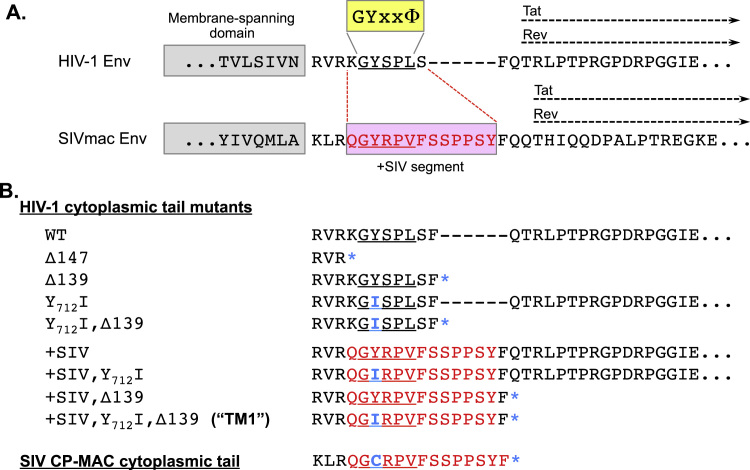
Fig. 1.
Schematic of HIV-1 Env cytoplasmic tail mutants. (A) Partial amino acid sequences of HIV-1 R3A and SIVmac239 Envs are shown, including part of the membrane-spanning domain and the highly conserved Tyr-dependent endocytosis motif (GYxxΦ). For both viruses, the positions overlapping the second exons of Tat and Rev in alternative reading frames are shown. The indicated segment from SIVmac (+SIV) was substituted into the HIV-1 Env CT to create Env constructs shown in Panel B. (B) HIV-1 Env CT mutants created to evaluate effects on Env surface expression. Substitutions included a Y712I substitution (HXB2 numbering) and/or a premature termination codon (*). Mutations were also made in the same positions in the Envs of HIV-1 89.6, 89.6 N7 (N197Q), and JRFL. Dashes (–) are used to facilitate alignment and highlight SIV residues with no homology in HIV-1 (SSPPSY). The sequence of SIV CP-MAC, which exhibits high levels of Env surface expression (LaBranche et al., 1994, LaBranche et al., 1995, Sauter et al., 1996), is shown for reference.