Abstract
Background
Transfusion-transmitted malaria (TTM) is an accidental Plasmodium infection caused by whole blood or a blood component transfusion from a malaria infected donor to a recipient. Infected blood transfusions directly release malaria parasites in the recipient’s bloodstream triggering the development of high risk complications, and potentially leading to a fatal outcome especially in individuals with no previous exposure to malaria or in immuno-compromised patients. A systematic review was conducted on TTM case reports in non-endemic areas to describe the epidemiological characteristics of blood donors and recipients.
Methods
Relevant articles were retrieved from Pubmed, EMBASE, Scopus, and LILACS. From each selected study the following data were extracted: study area, gender and age of blood donor and recipient, blood component associated with TTM, Plasmodium species, malaria diagnostic method employed, blood donor screening method, incubation period between the infected transfusion and the onset of clinical symptoms in the recipient, time elapsed between the clinical symptoms and the diagnosis of malaria, infection outcome, country of origin of the blood donor and time of the last potential malaria exposure.
Results
Plasmodium species were detected in 100 TTM case reports with a different frequency: 45% Plasmodium falciparum, 30% Plasmodium malariae, 16% Plasmodium vivax, 4% Plasmodium ovale, 2% Plasmodium knowlesi, 1% mixed infection P. falciparum/P. malariae. The majority of fatal outcomes (11/45) was caused by P. falciparum whilst the other fatalities occurred in individuals infected by P. malariae (2/30) and P. ovale (1/4). However, non P. falciparum fatalities were not attributed directly to malaria. The incubation time for all Plasmodium species TTM case reports was longer than what expected in natural infections. This difference was statistically significant for P. malariae (p = 0.006). A longer incubation time in the recipient together with a chronic infection at low parasite density of the donor makes P. malariae a subtle but not negligible risk for blood safety aside from P. falciparum.
Conclusions
TTM risk needs to be taken into account in order to enhance the safety of the blood supply chain from donors to recipients by means of appropriate diagnostic tools.
Keywords: Blood transfusion, Malaria, Plasmodium, Blood component transfusion, Transfusion-transmitted malaria (TTM)
Background
Malaria is an infectious disease caused by intracellular protozoan parasites of the genus Plasmodium responsible for a potentially fatal acute febrile illness following invasion and multiplication in human red blood cells (RBCs) during their complex life cycle. Five species of Plasmodium are currently known to cause malaria in humans: the deadliest Plasmodium falciparum and Plasmodium vivax, Plasmodium malariae, Plasmodium ovale, Plasmodium knowlesi. Malaria parasites are naturally transmitted by the infective bites of female Anopheles mosquitoes during their blood meal. Malaria can manifest with severe symptoms leading to a fatal outcome in non-immune individuals, often young children and pregnant women in endemic areas or naïve adults in non-endemic settings, and remains asymptomatic in adults who have acquired a premunition maintained by repeated antigen exposure.
Transfusion-transmitted malaria (TTM) is an accidental Plasmodium infection caused by the transfusion of whole blood or a blood component from a malaria infected donor to a recipient, described for the first time by Woolsey in 1911 [1], that may cause severe clinical symptoms in the recipients, especially in those with no previous exposure to malaria or in immuno-compromised patients due to other coexisting diseases. Several systematic reviews have addressed the knowledge gap still existing in the epidemiology of TTM in the United States [2], Canada [3] and the Americas [4].
Plasmodium falciparum, P. vivax and P. malariae are the species most frequently detected in TTM [5]. Various aspects of the parasite biology make this accidental route of infection feasible such as the persistence of infection: P. falciparum can persist for at least 1 year before being cleared, P. vivax for 3 years whereas P. malariae is known to remain as a chronic infection at low density for decades [6]. All Plasmodium species are able to survive in stored blood, even if frozen, and retain their viability for at least 1 week, possibly well over 10 days depending on the conditions of storage; in fact, microscopically detectable malaria parasites were present even after 28 days of storage at 4 °C although a decrease of infectivity after 2 weeks was observed [6, 7]. An important difference between the natural infection and TTM is that the former undergoes an initial asymptomatic phase (pre-erythrocytic) which allows the activation of innate immunity cells against malaria parasites. This early phase has advantages on both sides of the host parasite arms race: the innate immunity gives the naïve host time to develop a more specific protective immunity; meanwhile the parasites manipulate the host’s immune system in order to escape. Infected blood transfusions directly release malaria parasites in the recipient’s bloodstream triggering the development of high risk complications and potentially leading to a fatal outcome [8]. Experimental evidence suggests that as few as 10 infected RBCs can be sufficient to transmit the infection; thus, even a small inoculum is potentially infectious. However, the mean incubation period for TTM is generally longer than the mean incubation period for the mosquito-transmitted malaria (MTM) for all Plasmodium species as reported by [9]: 16.0 (8–29) days for P. falciparum TTM compared to 13.1 (7–27) days in P. falciparum MTM; 57. 2 (6–106) days for P. malariae TTM compared to 34.8 (27–37) days for P. malariae MTM; 19.6 (8–30) days for P. vivax TTM compared to 13.4 (8–31) days for P. vivax MTM; 23 days for P. ovale TTM compared to 13.6 (11–16) days for P. ovale MTM [9]. Blood components such as RBCs, platelets and plasma, are commonly transfused to treat various conditions ranging from surgical procedures causing a temporary anaemia to a chronic one due to haematological disorders (haemoglobinopathies, glucose-6-phosphate-dehydrogenase (G6PD) deficiency, haemophilia). Blood banks require a preliminary screening of a potential blood donor to exclude the risk of current or previous infections which can be transmitted by a blood transfusion, including malaria. Criteria for haemovigilance are defined by the World Health Organization (WHO) and are adapted to each country according to national guidelines. Some countries such as USA rely on a pre-donation questionnaire for the screening of potential infected donors whereas some others, including France, UK and Australia, use antibody testing on donors who are considered at risk on the basis of the preliminary questionnaire [3]. Appropriate diagnostic tools need to be employed in order to enhance the safety of the blood supply chain from donors to recipients tailored to the local TTM risk. The sensitivity and specificity of the screening strategy of blood donors remains the crucial issue in order to ensure the safety of blood transfusions particularly in the case of malaria: in fact, serological tests currently employed do not indicate the actual parasitaemia because antibody levels can remain elevated for many years after infection of P. falciparum and P. vivax [10]. Also, the initial clinical symptoms are generally aspecific making the diagnosis more difficult and resulting in a further delay. Delayed or missed diagnosis of P. falciparum in particular increases the risk of severe disease which may be fatal especially in non-immune individuals.
Furthermore new technologies are available to selectively inactivate pathogens without damaging cells or plasma; a combination of riboflavin as a photosensitizer with a UV light illumination device (Mirasol System for Whole Blood; Terumo BCT, Lakewood, Colo.) proved to substantially reduce P. falciparum infectivity in whole blood samples without altering cell quality parameters [11]; this inactivation technology may well represent another layer of control to reduce the risk of TTM.
Lastly, infected recipients who do not develop any clinical illness may become asymptomatic carriers and thus a reservoir of malaria parasites if competent vectors were to be present; this event has serious implications especially in non-endemic countries where the majority of the population has never been exposed to malaria parasites.
The primary objective of this systematic review was to describe the epidemiological characteristics of TTM in non-endemic countries based on data available in the literature in order to evaluate the extent and dynamics of this particular risk of malaria transmission. The review specifically investigated: (i) which Plasmodium species are more often detected in TTM; (ii) if other Plasmodium species besides P. falciparum are likely to cause a lethal outcome of TTM; (iii) whether the incubation time in TTM is longer than in the natural infection; (iv) which blood component is more likely to be infective for the recipient (whole blood, red blood cells, platelets or plasma); (v) which diagnostic methods were used in donor screening and recipient diagnosis (microscopy, serological or molecular tests).
Methods
Literature search
A systematic review of all articles on TTM in non-endemic areas was carried out. Relevant articles were retrieved from Pubmed, EMBASE, Scopus, and LILACS databases using combinations of the following search terms: “malaria”, “blood transfusion”, “Plasmodium”, “transfusion”, adapted to each database without date or language restrictions until May 17th 2017. TTM cases in USA were retrieved from the annual Morbidity and Mortality Weekly Reports (MMWR) malaria surveillance reports. The following combination of MeSH and free string terms were used specifically in Pubmed:
((“Platelet Transfusion”[MeSH] OR “Transfusion Medicine”[MeSH] OR “Lymphocyte Transfusion”[MeSH] OR “Leukocyte Transfusion”[MeSH] OR “Erythrocyte Transfusion”[MeSH] OR “Blood Component Transfusion”[MeSH]) OR (Transfusion*)) AND ((malaria*) OR (Plasmodi*) OR (malaria [MeSH])). Original research papers were included and additional references retrieved from narrative reviews; restriction to case reports was deemed necessary as the main scope of this systematic review was to investigate in fine details the relevant characteristics of each reported case of TTM. Two independent investigators (FV, EM) screened titles and abstracts, selected articles for full text review, performed the final article selection; a third reviewer (AA) was consulted in case of disagreement in order to reach a consensus. Case reports were excluded if the Plasmodium species was described as “tertian” without further identification. Also, case reports occurred in malaria endemic countries were not considered unless the case report was ascertained to have happened in a non-endemic area of the country. Articles in Chinese, Russian, Arabic and Turkish languages without at least a summary in English were dropped. From each study the following data was extracted: study area, gender and age of blood donor and recipient, blood component transfused, Plasmodium species, malaria diagnostic method employed, blood donor screening method, incubation period (i.e. the time elapsed between the infected transfusion and the onset of clinical symptoms in the recipient), delayed diagnosis (i.e. time elapsed between the onset of clinical symptoms and the diagnosis of malaria), infection outcome, country of origin of the blood donor and time of the last potential malaria exposure. The protocol for this systematic review was published on PROSPERO database with the registration number CRD 42017062298.
Statistical analysis
The incubation time of each TTM case report was analysed through standard one sample two-tailed t-tests (level of significance α = 0.05) to evaluate the difference between incubation periods of TTM and MTM for each Plasmodium species. Reference mean values of MTM were drawn from the results shown by Dover and Schultz [9]. All statistical analyses were performed using R software, version 3.3.3 [12].
Results
The number of selected papers at each step of the screening and criteria for exclusion/inclusion are reported in the flow diagram (Fig. 1); 100 case reports of TTM were retrieved for the purpose of this review and the main epidemiological data is provided by Table 1. Fifty-four of these case reports occurred in the American continent, 38 in Europe, 3 in the Mediterranean area, 1 in India, 4 in South-East Asia.
Fig. 1.
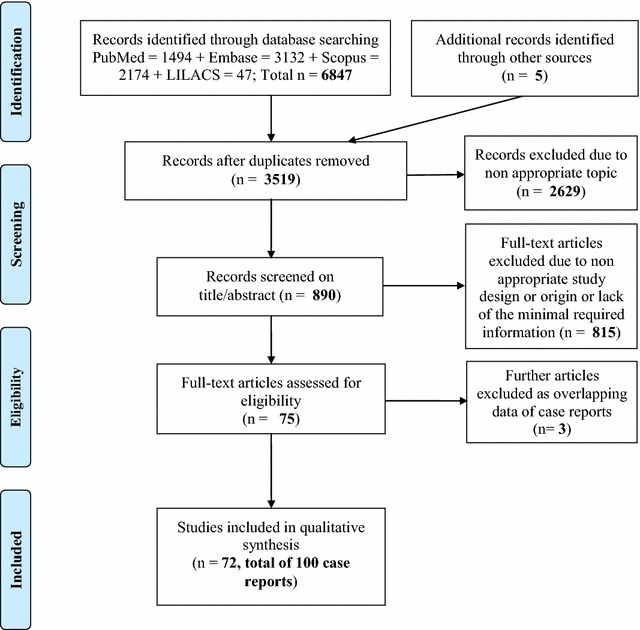
Flow diagram of the articles selection on transfusion transmitted- malaria in non-endemic areas
Table 1.
Reported cases of transfusion- transmitted malaria (TTM) in malaria non-endemic areas
| Countrya | Year | Donor gender and age | Donor origin and last exposure | Recipient gender and age | Recipient incubation (delayed diagnosis) | Recipient outcome | Blood component transfused | Plasmodium species | Diagnosis method recipient (donor) | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Canada | ||||||||||
| Western region | 1936 | M | Mediterranean area | F 13 years |
3 weeks (5 weeks) | Recovery | WB | P. malariae | LM (LM) | [17] |
| Ontario | 1936 | M | Romania 25 years |
F | 26 days (2 weeks) | Recovery | WB | P. malariae | LM (LM) | [18] |
| Alberta | 1977 | F 23 years |
Africa 2 years |
F 60 years |
29 days (29 days) | Recovery | WB | P. ovale | LM (IFAT) | [19] |
| Quebec | 1994 | N/A | Cameroon > 3 years |
M 63 years |
N/A (3 weeks) | Recovery | RBCs, PLTs, FFP | P. falciparum | LM (LM) | [20] |
| Ontario | 1995 | M | Mali 4 years |
F 24 years |
15 days (3 days) | Recovery | RBCs | P. falciparum | LM, PCR (PCR) | [20] |
| Ontario | 1997 | F 19 years |
Ghana 4 years |
F 62 years |
21 days (5 weeks) | Recovery | RBCs, FFP | P. falciparum | LM, PCR | [20] |
| USA | ||||||||||
| New York | 1911 | N/A | N/A | M 54 years |
11 days | “Pernicious anaemia” | WB | P. vivax | LM | [1] |
| Colorado | 1929 | M 32 years |
Greece 16 years |
F 2½ years |
19–25 days (on the day) | Recovery | WB | P. malariae | LM (LM) | [21] |
| New York | 1932 | M | Italy | F 1.5 years |
4 weeks (17 days) | Recovery | WB | P. malariae | LM | [22] |
| New York | 1932 | M | Italy 12 years |
M 9 months |
6 weeks | Recovery | WB | P. malariae | LM | [22] |
| New York | 1933 | F | Greece | F 8 years |
< 8 weeks | Death due to pneumonia | WB | P. malariae | LM | [22] |
| New York | 1936 | M | Greece 33 years |
F 1 year |
29 days | Recovery | WB | P. malariae | LM | [22] |
| New York | 1936 | M | Colombia 10 years |
M 3 years |
2 months | Recovery | WB | P. malariae | LM | [22] |
| New York | 1944 | M 40 years |
North Africa veteran 1 year |
F 32 years |
11–4 days (35 days) | Recovery | WB | P. malariae | LM (LM) | [23] |
| Rhode Island | 1946 | M or F | Italy or New England | F 40 years |
2 months (2 days) | Recovery | WB, FFP | P. malariae | LM (LM) | [24] |
| Pennsylvania | 1946 | N/A | Army returnee | F | 3 weeks (9 days) | Recovery | WB | P. vivax | LM | [25] |
| California | 1968 | M 19 years |
Vietnam veteran 7 months |
M 60 years |
4 days (on the day) | N/A | WB | P. falciparum | LM (LM) | [26] |
| Connecticut | 1968 | N/A | Mexico 5 years |
F 8 months |
6 ½ months | Recovery | WB | P. malariae | LM | [27] |
| Washington state | 1968 | M 22 years |
Vietnam veteran 1 year |
F 54 years |
13 days (9 days) | Recovery | WB | P. falciparum | LM (LM, IFAT) | [28] |
| Oklahoma | 1968 | M 21 years |
Vietnam veteran 5 months |
F 25 years |
16 days (7 days) | Recovery | WB | P. falciparum | LM (LM) | [28] |
| Washington D.C. | 1969 | M | Nigeria > 2 years |
M 56 years |
17 days (6 days) | Death | WB | P. falciparum | LM (LM, IFAT) | [29] |
| New York | 1970 | M | Ghana 1 year |
M 34 years |
6 days (2 days) | Recovery | WB | P. falciparum | LM (LM, IFAT) | [30] |
| Chicago | 1972 | N/A | N/A | M 5 months |
16 days (6 days) | Recovery | WB | P. vivax | LM | [31] |
| New York | 1971 | N/A | N/A | M 24 years |
Multiple transfusions (7 days) | Recovery | WB | P. vivax | LM (IFAT) | [32] |
| New York | 1974 | N/A | N/A | F 42 years |
9 weeks (on the day) | Recovery | RBCs, PLTs, FFP | P. malariae | LM (IFAT) | [32] |
| New York | 1974 | F 53 years |
Greece 22 years |
F 78 years |
Multiple transfusions (~ 30 days) | Recovery | WB, RBCs | P. malariae | LM, IFAT (IFAT) | [33] |
| New York | 1974 | M 38 years |
Cyprus 4 years |
F 42 years |
35 days (1 month) | Recovery | RBCs, PLTs, FFP | P. malariae | LM, IFAT (IFAT) | [33] |
| Tennessee | 1974 | M 28 years |
Nigeria 8 years |
F 15 years |
3 months (12 days) | Recovery | WB | P. malariae | LM (LM, IFAT) | [34] |
| Wisconsin | 1977 | N/A | Africa recent |
F 57 years |
Multiple transfusions (28 days) | Death due to refractory leukaemia | PLTs | P. falciparum | LM (LM) | [35] |
| New York state | 1978 | M | Ghana 10 months |
F 65 years |
16 days (1 day) | Recovery | WB, RBCs, FFP | P. falciparum | LM (IFAT) | [36] |
| California | 1980 | M | N/A | M 6 years |
15 days (2 days) | Recovery | RBCs | P. falciparum | LM (LM) | [37] |
| California | 1982 | M | Nigeria 7 years |
M premature |
6 weeks | Death due to pneumonia | WB | P. ovale | LM, IFAT (IFAT) | [38] |
| Boston | 1982 | N/A | N/A | M premature |
7 weeks (on the day) | Recovery | RBCs | P. malariae | LM (LM) | [39] |
| Boston | 1982 | N/A | N/A | M premature |
10 weeks (on the day) | Recovery | RBCs | P. malariae | LM (LM) | [39] |
| California | 1983 | M | Guatemala 6 months |
M premature |
5 weeks (on the day) | Recovery | WB | P. vivax | LM (LM) | [40] |
| California | 1983 | M | South America 6 months |
M infant |
14 days (on the day) | Recovery | WB | P. vivax | LM (IFAT) | [40] |
| Texas | 1992 | M 19 years |
Nigeria 7 months |
F 71 years |
7 days (on the day) | N/A | RBCs, PLTs | P. falciparum | LM (IFAT) | [41] |
| Texas | 1992 | M 19 years |
Nigeria 7 months |
M 65 years |
N/A | N/A | RBCs | P. falciparum | LM (IFAT) | [41] |
| California | 1992 | M 55 years |
China 44 years |
M 44 years |
7 months (3 months) | Recovery | RBCs | P. malariae | LM (IFAT) | [41] |
| Texas | 1994 | M | Nigeria recent | F 59 years |
20 days (on the day) | Recovery | RBCs | P. falciparum | LM (LM, IFAT) | [42] |
| Texas | 1994 | M | Ghana recent | M 46 years |
16 days (7 days) | Recovery | RBCs, FFP | P. falciparum | LM (LM, IFAT) | [42] |
| Pennsylvania | 1995 | M | Nigeria 3 years |
F 72 years |
Multiple transfusions | Recovery | RBCs | P. falciparum | LM (LM, IFAT) | [43] |
| Missouri | 1996 | M | West Africa 1 year |
M 70 years |
15 days (on the day) | Death | RBCs | P. falciparum | LM (LM, IFAT, PCR) | [44] |
| Missouri | 1997 | M | West Africa 2 years |
M 85 years |
21 days (on the day) | Death | RBCs | P. falciparum | LM (LM, IFAT, PCR) | [44] |
| Pennsylvania | 1998 | M | West Africa 2 years |
M 49 years |
35 days (on the day) | Recovery | RBCs | P. falciparum | LM (IFAT, PCR) | [44] |
| Texas | 2003 | M | Ghana 2 years |
69 years | 17 days (3 days) | Recovery | RBCs | P. falciparum | LM (LM, PCR, IFAT) | [45] |
| Texas | 2007 | M | Nigeria 6 years |
F 25 years |
Multiple transfusions | Recovery | RBCs | P. falciparum | LM (IFAT) | [46] |
| Washington D.C. | 2007 | M | West Africa | F | 15 days (on the day) | Recovery | RBCs | P. falciparum | LM, PCR (LM) | [47] |
| Washington D.C. | 2007 | M 27 years |
Nigeria 3 years |
M 27 years |
13–28 days (11 days) | Recovery | RBCs | P. falciparum | LM (IFAT, PCR) | [47] |
| New Jersey | 2007 | F 30 years |
Uganda > 1 year |
M 78 years |
1 year | Recovery | RBCs | P. falciparum | LM (IFAT, PCR) | [47] |
| N/A | 2007 | M 21 years |
Benin 4 years |
F 55 years |
1 month | Recovery | RBCs, PLTs, FFP | P. falciparum | LM, IFAT, PCR (IFAT, EIA) | [48] |
| Georgia | 2015 | M 20 years |
Liberia 15 years |
M 76 years |
6 months (2 days) | Recovery | RBCs, FFP | P. malariae | LM, PCR (LM, PCR, ELISA) | [49] |
| Colombia | ||||||||||
| Cali | 2011 | N/A | Rural area 9 months |
F Premature |
Multiple transfusions (on the day) | Recovery | RBCs | P. vivax | LM (PCR) | [50] |
| Brasil | ||||||||||
| Sao Paulo | 2008 | M | Atlantic forest 1 year |
N/A | 75 days (on the day) | Recovery | RBCs, PLTs, FFP | P. malariae | LM (LM, PCR, IFAT) | [51] |
| Spain | ||||||||||
| Valencia | 1987 | N/A | Congo | F 32years |
7 days (on the day) | N/A | WB | P. falciparum | LM (IFAT) | [52] |
| Madrid | 1997 | N/A | Central Africa | F 63 years |
3 weeks (4 weeks) | N/A | WB | P. falciparum | LM (IFAT) | [53] |
| Cordoba | 2002 | N/A | N/A | F 26 years |
Multiple transfusions (128 days) | Recovery | WB, RBCs | P. falciparum | LM IFAT |
[54] |
| UK | ||||||||||
| Midlands | 1935 | M | India 2 years |
M 26 years |
19 days (5 days) | Recovery | WB | P. vivax | LM (LM) | [55] |
| London | 1938 | M | Ceylon 12 years |
F 3 months |
10 weeks (on the day) | Death | WB | P. malariae | LM (LM) | [56] |
| Durham | 1946 | M | Yemen 7 years |
F 18 years |
7–8 weeks (10 days) | Recovery | WB | P. malariae | LM (LM) | [57] |
| N/A | 1959 | M 19 years |
Nigeria 1 year |
F 41 years |
16 days (6 days) | Recovery | WB | P. falciparum | LM (LM) | [58] |
| Oxford | 1966 | M | Far East 20 years |
M 33 years |
10 weeks (1 day) | Recovery | WB, FFP | P. malariae | LM (LM) | [59] |
| Buckingmanshire | 1967 | M | Army returnee | M 51 years |
N/A | Recovery | FFP | P. malariae | LM (LM) | [60] |
| Buckingmanshire | 1968 | M | Africa 18 months |
M 49 years |
11 days (12 days) | Recovery | WB | P. falciparum | LM (LM, IFAT) | [60] |
| London | 1986 | M | Africa | F 72 years |
13 days (12 days) | N/A | PLTs | P. falciparum | LM (LM, IFAT) | [61] |
| London | 1986 | M | Ghana | F 81 years |
14 days | N/A | WB | P. falciparum | LM (IFAT) | [61] |
| N/A | 1994 | F | Ghana 1 year |
M | 15 days (on the day) | N/A | WB | P. falciparum | LM (EIA, IFAT) | [5] |
| N/A | 1997 | F 19 years |
Ghana 3 years |
M 62 years |
4 days | Death | WB | P. falciparum | (EIA, IFAT) | [5] |
| N/A | 2003 | F 38 years |
Ghana 7 years |
M 51 years |
N/A | Death | WB | P. falciparum | LM (EIA, IFAT) | [5] |
| Netherlands | ||||||||||
| Leiden | 2011 | M 36 years |
Africa Costa Rica > 4 years |
F 59 years |
2 months (on the day) | Recovery | RBCs | P. malariae | LM, PCR (LM, IFAT, PCR) | [62] |
| Germany | ||||||||||
| Göttingen | 1998 | N/A | N/A | M 18 months |
14 days (9 days) | Recovery | RBCs | P. falciparum | LM | [63] |
| France | ||||||||||
| Poitiers | 1969 | M | Portugal 5 months |
F | 15 days (1 month) |
Recovery | WB | P. malariae | LM (IFAT) | [64] |
| Paris | 1957 | F | Tunisia 27 years |
F 32 years |
48 days (4 days) | Recovery | WB | P. vivax | LM | [65] |
| Paris | 1973 | M | Senegal 13 years |
M 30 years |
14 days (9 days) | Recovery | WB | P. falciparum | LM (IFAT) | [65] |
| Paris | 1975 | N/A | N/A | F 24 years |
15 days (18 days) | Recovery | WB | Plasmodium | LM (IFAT) | [66] |
| Tours | 1977 | N/A | N/A | F 47 years |
15 days (on the day) | Recovery | WB | P. vivax | LM | [67] |
| Rouen | 1976 | N/A | Senegal | N/A | 12 days (10 days) | Death | N/A | P. falciparum | (IFAT) | [68] |
| Rouen | 1976 | N/A | Ivory Coast | N/A | 13 days (6 days) | Death | N/A | P. falciparum | (IFAT) | [68] |
| Rouen | 1978 | N/A | N/A | N/A | 60 days (2 days) | Recovery | N/A | P. malariae | (IFAT) | [68] |
| Nancy | 1979 | M | Zaire 1 month |
F 29 years |
15 days (43 days) | Recovery | RBCs |
P. falciparum
P. malariae |
LM (IFAT) | [69] |
| Crèteil | 1980 | M | Central Africa | M infant |
2 months (3 days) | Recovery | RBCs, FFP | P. malariae | LM | [70] |
| Aulnay-sous-Bois | 1986 | N/A | N/A | F 64 years |
16 days (on the day) | Recovery | WB | P. ovale | LM | [71] |
| Libourne | 1990 | M | Comores < 6 months |
F 39 years |
1 month (on the day) | Recovery | WB | P. falciparum | LM | [72] |
| Le Chesnay | 2002 | F 19 years |
Africa 4 years |
M 81 years |
13 days (4 days) | Death | RBCs | P. falciparum | LM, IFAT, PCR (IFAT, PCR) | [73] |
| Tourcoing | 2013 | N/A | Endemic area 3 years |
F 75 years |
14 days (8 days) | Death | RBCs | P. falciparum | LM (IFAT, PCR) | [74] |
| Switzerland | ||||||||||
| Zurich | 1999 | M 30 years |
Cameroon 6 years |
M 70 years |
14 days (22 days) | Death | RBCs, FFP | P. falciparum | LM (IFAT, PCR) | [75] |
| Austria | ||||||||||
| Wien | 1929 | M | Endemic area 10 years |
N/A | 14 days | Recovery | WB | P. vivax | LM | [76] |
| Italy | ||||||||||
| Liguria | 1963 | N/A | N/A | M Premature |
28–40 days | Recovery | WB | P. malariae | LM | [77] |
| Liguria | 1963 | N/A | N/A | F 8 years |
1–13 days | Recovery | WB | P. vivax | LM | [78] |
| Liguria | 1964 | N/A | N/A | F 6 years |
Multiple transfusions (4 months) | Recovery | WB | P. vivax | LM | [78] |
| Sicily | 2005 | M | Philippine | F 35 years |
Multiple transfusions (4 months) | Recovery | WB | P. malariae | LM | [79] |
| Veneto | 2008 | N/A | N/A | F 29 years Morocco |
Multiple transfusions (2 weeks) | Recovery | RBCs | P. vivax | LM | [80] |
| Algeria | ||||||||||
| Algiers | 1918 | M | Greece 1 month |
F | 15 days (few days) | Recovery | WB | P. praecox b | LM (LM) | [13] |
| Lebanon | ||||||||||
| Beirut | 2007 | N/A | N/A | M 28 years |
1 ½ months (2 weeks) | Recovery | RBCs | P. falciparum | LM | [81] |
| Beirut | 2010 | N/A | N/A | F 46 years |
1 month (2 days) | Recovery | RBCs | P. ovale | LM | [82] |
| India | ||||||||||
| Shimla | 2006 | N/A | N/A | F 47 years |
12 days (on the day) | Recovery | WB | P. falciparum | LM | [83] |
| Korea | ||||||||||
| Taegu, South Corea | 2000 | M 21 years |
Endemic area | M 1 year |
15 days (5 days) | Recovery | RBCs, FFP | P. vivax | LM (LM, PCR) | [84] |
| Thailand | ||||||||||
| Bangkok | 2011 | M teenager |
Endemic area 3 weeks |
F 62 years |
15 days (on the day) | Recovery | RBCs | P. knowlesi | LM, PCR | [85] |
| Malaysia | ||||||||||
| Kuala Lumpur | 2012 | M 26 years |
Myanmar 9 months |
M 12 years |
1 week (on the day) | N/A | WB | P. vivax | LM, PCR (PCR) | [86] |
| Sabah | 2015 | M 51 years |
Endemic area | F 23 years |
16 days (on the day) | Recovery | WB | P. knowlesi | LM, PCR (LM, PCR) | [87] |
N/A data not available, WB whole blood, RBCs red blood cells, PLTs platelets, FFP fresh frozen plasma, LM light microscopy, ELISA enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay, IFAT indirect immunofluorescent antibody test, PCR polymerase chain reaction
aOnly non-endemic areas of the country if malaria endemic were included
bPossible misidentification of P. falciparum
The first report of TTM went back to 1911 and the most recent occurred in 2015, both in USA. The age of TTM case reports ranged from premature children to an 85 years old individual. The partitioning of cases in children and adults (≥ 18 years) when age was available resulted in 2 children and 39 adults for P. falciparum, 14 children and 12 adults for P. malariae, 8 children and 6 adults for P. vivax, 1 child and 3 adults for P. ovale, and 2 adults for P. knowlesi. Female versus male ratio was 1:1 for recipients and 1:6 for donors.
-
i.
Plasmodium species. The most common Plasmodium species detected in TTM resulted to be P. falciparum (45%) and P. malariae (30%); P. vivax, P. ovale were less frequently observed: 16 and 4% respectively; two TTM were caused by P. knowlesi (2%), and one by a mixed infection P. falciparum/P. malariae. Plasmodium praecox, an avian Plasmodium species, was described in a case report whose infection was acquired in Greece [13].
-
ii.
Species involved in fatal outcomes. The majority of fatal outcomes (11/45) was indeed caused by P. falciparum whilst all the other fatalities occurred in individuals infected by P. malariae (2/30) and P. ovale (1/4).
-
iii.
Incubation period (IP). Table 2 shows the differences in the mean incubation times for each Plasmodium species between TTM and MTM. For all species, the mean incubation time in TTM was longer, but the most relevant difference was observed for P. malariae (63.9 vs 34.6 days, p = 0.006).
-
iv.
Blood component causing TTM. The vast majority of TTM cases were caused by whole blood and/or RBCs transfusion; however, two TTM cases due to platelets and one TTM case due to plasma only were reported.
-
v.
Diagnostic method used for screening (if any) and diagnosis. They are also reported in detail in Table 1. Classical Light microscopy (LM) was the diagnostic method used in virtually all cases of TTM. Only in very few cases this was complemented by serology (IFAT: first time in 1974 for a case of P. malariae occurred in US, ex-Cyprus) and/or PCR (first time in 1995 for a case of P. falciparum occurred in Canada, ex-Mali). Donor “screening” was in fact in the earlier cases the diagnosis subsequently made on the donor, classically with microscopy. Serology (IFAT) was first reported on donors in 1968 (a case of P. falciparum occurred in UK, ex-Africa, and a case of the same species occurred in US, ex-Vietnam). When reported, serology (most often IFAT) appears to be by and large the most frequent method used for donor screening.
Table 2.
Mean values of transfusion-transmitted malaria (TTM) versus mosquito-transmitted malaria (MTM) incubation time in days
| Species | TTM (95% CI) | MTM (95% CI)a | p valueb |
|---|---|---|---|
| P. falciparum | 25.7 (7.4–43.9) | 13.1 (7–27) | 0.172 |
| P. malariae | 63.9 (43.5–84.4) | 34.8 (27–37) | 0.006 |
| P. ovale | 19.0 (11.7–26.3) | 13.6 (8–31) | 0.118 |
| P. vivax | 29.3 (12.3–46.2) | 13.4 (11–16) | 0.060 |
| P. knowlesi c | 15.5 (9.1–21.9) | 10.0 (/) | 0.058 |
CI confidence interval
Significance threshold p value <0.05 (in italic)
aAs reported by Dover and Schultz [9]
bObtained through one sample two-tailed Student’s t test, using the MTM mean value for the null hypothesis
cA range of the mean incubation time for this species in humans was not available in literature, so a direct comparison of CIs was not possible
Discussion
Transfusion-transmitted malaria is an alternative accidental Plasmodium infection which may cause morbidity and mortality especially in non-endemic areas where individuals have no premunition to malaria. Given the long-time span, over a century, of the case reports some countries which were endemic several decades ago are now malaria free such as the case of Greece and Italy. Therefore, it was not possible to infer any particular geographical pattern of TTM, whose occurrence may reflect people movements due to historical events as well as the proximity to a malaria endemic areas; an example is provided by the numerous army returnees from Vietnam to USA in the late 1960s who were not identified at the time as potential malaria infected blood donors, and caused an increase of TTM cases in the following years in USA [9]. Also, a limitation of this systematic review was due to the selection of exclusively case reports in order to describe the main characteristics of each episode; thus, prevalence studies were discarded as well as data on the occurrence of “transfusion outbreaks” such as the 54 cases of P. vivax TTM reported by the WHO to have taken place in Spain in 1971 due to a single blood bank in Barcelona [14]. Further limitations are due to the intrinsic nature of a systematic review based on different reports hampering the possibility to ascertain retrospectively how reliable were the clinical history and the timing of the diagnosis for each TTM case. The majority of fatal outcomes (11/45) was indeed caused by P. falciparum whilst all the other fatalities occurred in individuals infected by P. malariae (2/30) and P. ovale (1/4). However, these other fatalities were not attributable to malaria: two deaths were due to pneumonia and one was due to the complications of a premature newborn. Furthermore, all fatalities caused by P. falciparum were observed in adults and elderly people, which may reflect other co-morbidities or a more severe prognosis of malaria in adults compared to children within non-immune populations [15].
There are important differences between malaria natural infection and TTM with respect to the incubation time and delayed diagnosis: a longer incubation period was observed for all Plasmodium species as reported by Dover and Schultz [9] despite the absence of the pre-erythrocytic phase as the infected blood component directly transmits the erythrocytic stage of the parasite, namely the merozoite, to the recipient. This paradoxical phenomenon might be explained by the small inoculum of parasites from an asymptomatic donor which requires a longer period of time to develop the clinical symptoms [6]. The incubation period of TTM case reports was confirmed to be longer than the one described in natural infections as shown in Table 2: the difference reached statistical significance (p = 0.006) in P. malariae, which is arguably the species with the longest incubation time and lowest parasite density. No other statistically significant difference was observed possibly due to the limited number of case reports, thus any interpretation must be taken with caution. Moreover, particularly in some cases of P. falciparum, the IP was surprisingly and unusually long, and, although it might explained in theory by an exceedingly small number of parasites inoculated, a reporting error cannot be excluded. Nevertheless, such potential error is expected to have occurred across all TTM cases, thus making the observation still useful to reinforce the need to extend the window of time for a malaria diagnosis in blood transfusion recipients beyond the expected IP. Moreover, according to the reported data none of the TTM cases occurred in individuals with previous history of malaria, thus ruling out the possibility of recrudescence, circulating anti-malarial antibodies (as it would be the case in malaria endemic areas), or prophylaxis which might have delayed the onset of symptoms and diagnosis. Interestingly, the incubation time of the only mixed P. falciparum and P. malariae infection was of 15 days, a nearly typical incubation time for the dominant P. falciparum species compared to the milder P. malariae which employs 35 days on average to clinically develop.
Furthermore, the observation that almost half of the TTM cases reported in this systematic review are due to P. malariae (N = 30) and P. vivax (N = 16) reinforces the need to consider these other Plasmodium species as a not negligible cause of transfusion-transmitted malaria aside from P. falciparum.
Several layers of complexity underline the risk of TTM in non-endemic areas: on one hand, the limited proportion of potentially infective donors imposes a cost-effective strategy of blood donors screening, on the other hand the accuracy of such screening needs to be optimal for the serious outcomes of TTM in malaria naïve recipients.
In most non-endemic countries the first step in the blood supply chain is an epidemiological questionnaire to assess the potential donor’s risk to be infective which may result in a deferral for two groups of individuals: (i) those who were born and had lived for several years in malaria-endemic areas and (ii) those who were born and are resident in non-endemic areas but had visited an endemic area. According to the European guidelines individuals are acceptable as blood donors when an immunologic or molecular test for malaria is negative after at least 6 months since their last visit to an endemic area. When these donors have resided for more than 3 months in the endemic area, the deferral time may be longer. However long the deferral does not totally exclude infectious semi-immune individuals: in fact cases of TTM have been linked to donations given more than 5 years after the last potential exposure of the donor to P. falciparum and several decades in the case of P. malariae [3].
Conclusions
-
i.
The Plasmodium species most commonly involved in TTM were, expectedly, P. falciparum and P. malariae, but cases of P. vivax were not infrequent, either. This parasite is not known to remain so long in blood as the two other species, while it shares with P. ovale the phenomenon of hepatic hypnozoites (that, however, are not a possible source of transmission before they reach again the bloodstream).
-
ii.
Species involved in fatal outcomes. All fatal outcomes attributable to malaria were caused by P. falciparum and none by P. vivax, a parasite that has long been considered benign, although its potential to cause severe malaria has been repeatedly demonstrated in recent years [16].
-
iii.
The incubation period was longer than the average IP for mosquito-transmitted malaria, which may be a further reason for lack of suspicion and diagnostic delay.
-
iv.
Almost all TTM cases were caused by whole blood and/or RBCs transfusion, as expected, but for two cases by platelets and one by plasma only.
-
v.
Classical Light microscopy (LM) was used in all cases of TTM for diagnostic purposes. Only in very few cases this was complemented by serology and/or PCR in the more recent period. Serology (IFAT) was the most frequently used method for donor screening.
WHO regulations on blood donation needs to be reinforced as many of the TTM case reports observed even in the time span since blood safety guidelines were implemented could have been prevented if those guidelines had been applied with stringency. Thus, different strategies need to be combined in order to ensure the safety of blood transfusions i.e. blood donor screening by appropriate diagnostic tools, which should probably include molecular tests, and possibly parasite inactivation of the blood supply.
Authors’ contributions
FV and AA conceived the systematic review. FV and ZB wrote the manuscript after comments and discussion with AA, EM, GG, FP. GG performed the statistical analysis. EM was the second reviewer who double-checked the articles’ selection and data extraction. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Acknowledgements
We wish to thank Dr. Virginio Pietra and three anonymous reviewers for critical comments on the manuscript.
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Availability of data and materials
All data generated or analysed during this study are included in this published article.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Ethics approval and consent to participate
Not applicable.
Funding
This research received no specific funding from any agency, commercial or not-for-profit sectors.
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Abbreviations
- CI
confidence interval
- ELISA
enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay
- EMBASE
Excerpta Medica dataBASE
- FFP
fresh frozen plasma
- IFAT
indirect immunofluorescent antibody test
- LILACS
Latin America and the Caribbean Health Sciences Literature
- LM
light microscopy
- MeSH
medical subject heading
- MMWR
morbidity and mortality weekly report
- MTM
mosquito transmitted malaria
- PCR
polymerase chain reaction
- PLT
platelet
- RBC
red blood cell
- TTM
transfusion transmitted malaria
- USA
United States of America
- WB
whole blood
- WHO
World Health Organization
Footnotes
Federica Verra and Andrea Angheben contributed equally to this work
References
- 1.Woolsey G. Transfusion for pernicious anemia. Trans NY Surg Soci. 1911;132–3.
- 2.Mungai M, Tegtmeier G, Chamberland M, Parise M. Transfusion-transmitted malaria in the United States from 1963 through 1999. N Engl J Med. 2001;344:1973–1978. doi: 10.1056/NEJM200106283442603. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.O’Brien SF, Delage G, Seed CR, Pillonel J, Fabra CC, Davison K, et al. The epidemiology of imported malaria and transfusion policy in 5 nonendemic countries. Transfus Med Rev. 2015;29:162–171. doi: 10.1016/j.tmrv.2015.03.004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Alho RM, Machado KV, Val FF, Fraiji NA, Alexandre MA, Melo GC, et al. Alternative transmission routes in the malaria elimination era: an overview of transfusion-transmitted malaria in the Americas. Malar J. 2017;16:78. doi: 10.1186/s12936-017-1726-y. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Kitchen AD, Barbara JA, Hewitt PE. Documented cases of post-transfusion malaria occurring in England: a review in relation to current and proposed donor-selection guidelines. Vox Sang. 2005;89:77–80. doi: 10.1111/j.1423-0410.2005.00661.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Bruce-Chwatt LJ. Transfusion malaria. Bull World Health Organ. 1974;50:337–346. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Chattopadhyay R, Majam VF, Kumar S. Survival of Plasmodium falciparum in human blood during refrigeration. Transfusion. 2001;51:630–635. doi: 10.1111/j.1537-2995.2010.02872.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Garraud O. Mechanisms of transfusion-linked parasite infection. Transfus Clin Biol. 2006;13:290–297. doi: 10.1016/j.tracli.2006.11.005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Dover AS, Schultz MG. Transfusion-induced malaria. Transfusion. 1971;11:353–357. doi: 10.1111/j.1537-2995.1971.tb04429.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Wipasa J, Suphavilai C, Okell LC, Cook J, Corran PH, Thaikla K, et al. Long-lived antibody and B cell memory responses to the human malaria parasites, Plasmodium falciparum and Plasmodium vivax. PLoS Pathog. 2010;6:e1000770. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1000770. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Owusu-Ofori S, Kusi J, Owusu-Ofori A, Freimanis G, Olver C, Martinez CR, et al. Treatment of whole blood with riboflavin and UV light: impact on malaria parasite viability and whole blood storage. Shock. 2015;44(Suppl 1):33–38. doi: 10.1097/SHK.0000000000000280. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Team RC. R: a language and environment for statistical computing. Vienna: R Foundation for Statistical Computing; 2017. [Google Scholar]
- 13.Gubb AS. Accidental transference of the malarial parasite in the course of transfusion. Br Med J. 1919;2:74–75. doi: 10.1136/bmj.2.3055.74. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Velasco E, Gomez-Barroso D, Varela C, Diaz O, Cano R. Non-imported malaria in non-endemic countries: a review of cases in Spain. Malar J. 2017;16:260. doi: 10.1186/s12936-017-1915-8. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Baird JK, Masbar S, Basri H, Tirtokusumo S, Subianto B, Hoffman SL. Age-dependent susceptibility to severe disease with primary exposure to Plasmodium falciparum. J Infect Dis. 1998;178:592–595. doi: 10.1086/517482. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Naing C, Whittaker MA, Nyunt Wai V, Mak JW. Is Plasmodium vivax malaria a severe malaria? A systematic review and meta-analysis. PLoS Negl Trop Dis. 2014;8:e3071. doi: 10.1371/journal.pntd.0003071. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Cadham FT. Transmission of malaria by blood transfusion. Can Med Assoc J. 1936;34:428–430. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.McCulloch E. Quartan malaria transmitted by transfusion. Can Med Assoc J. 1937;7:26–29. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Sawyer DM, Wadsworth LD. Plasmodium ovale malaria in Canada following transfusion. Can Med Assoc J. 1977;117:923. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Slinger R, Giulivi A, Bodie-Collins M, Hindieh F, John RS, Sher G, et al. Transfusion-transmitted malaria in Canada. CMAJ. 2001;164:377–379. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Stein HB. Transmission of malaria by transfusion. Am J Dis Child. 1932;44:1048–1054. doi: 10.1001/archpedi.1932.01950120130010. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Wright FH. Accidental transmission of malaria through the injection of whole blood. J Pediatr. 1938;12:327–349. doi: 10.1016/S0022-3476(38)80042-1. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Sharnoff JG, Geiger J, Selzer I. Malaria transmitted by bank blood transfusion; report of two cases. Am J Clin Pathol. 1945;15:494. doi: 10.1093/ajcp/15.11.494. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Fischer WJ, Jr, York CL. Quartan malaria occurring subsequent to a blood transfusion. N Engl J Med. 1946;235:411–413. doi: 10.1056/NEJM194609192351203. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Schrack WD. Malaria infection acquired through blood transfusion. Public Health Rep. 1946;61:1630. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Chojnacki RE, Brazinsky JH, Barrett O., Jr Transfusion-introduced falciparum malaria. N Engl J Med. 1968;279:984–985. doi: 10.1056/NEJM196810312791808. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Czapek EE, Barry DW, Gryboski JD. Malaria in an infant transmitted by transfusion. JAMA. 1968;204:549–550. doi: 10.1001/jama.1968.03140190131020. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Fisher GU, Schultz MG. Unusual host-parasite relationship in blood-donors responsible for transfusion-induced falciparum malaria. Lancet. 1969;2:716–718. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(69)90428-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Brooks MH, Barry KG. Fatal transfusion malaria. Blood. 1969;34:806–810. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Seligman SJ, Choa MS. Transfusion-induced falciparum malaria. JAMA. 1971;217:479. doi: 10.1001/jama.1971.03190040071030. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Seeler RA, Miller RA, Lin CH, Lin SK. Transfusion-induced malaria. Plasmodium vivax in a 5-month-old child. Am J Dis Child. 1973;125:132–133. doi: 10.1001/archpedi.1973.04160010092023. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Tapper ML, Armstrong D. Malaria complicating neoplastic disease. Arch Intern Med. 1976;136:807–810. doi: 10.1001/archinte.1976.03630070051016. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Maulitz RM, Marr JS, Shookhoff HB. Transfusion malaria as a consequence of the 1974 war between Turkey and Greece—two cases. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 1976;25:1–4. doi: 10.4269/ajtmh.1976.25.1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Najem GRSJ. Transfusion-induced malaria from an asymptomatic carrier. Transfusion. 1976;16:473–476. doi: 10.1046/j.1537-2995.1976.16577039306.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Garfield MD, Ershler WB, Maki DG. Malaria transmission by platelet concentrate transfusion. JAMA. 1978;240:2285–2286. doi: 10.1001/jama.1978.03290210067033. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Yarrish RL, Janas JAS, Nosanchuk JS. Transfusion malaria. Treatment with exchange transfusion after delayed diagnosis. Arch Int Med. 1982;142:187–188. doi: 10.1001/archinte.1982.00340140189034. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Joishy SK, Lopez CG. Transfusion-induced malaria in a splenectomized β-thalassemia major patient and review of blood donor screening methods. Am J Hematol. 1980;8:221–229. doi: 10.1002/ajh.2830080214. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Rawlings JS, Beall SC. Transfusion malaria in a premature infant. Clin Pediatr. 1982;21:638–639. doi: 10.1177/000992288202101016. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Piccoli DA, Perlman S, Ephros M. Transfusion-acquired Plasmodium malariae infection in two premature infants. Pediatrics. 1983;72:560–562. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Shulman IA, Saxena S, Nelson JM, Furmanski M. Neonatal exchange transfusions complicated by transfusion-induced malaria. Pediatrics. 1984;73:330–332. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Transfusion malaria. MMWR. 1992;44.
- 42.Transfusion malaria. MMWR. 1994;46.
- 43.Transfusion malaria. MMWR. 1995;47.
- 44.Transfusion-transmitted malaria—Missouri and Pennsylvania, 1996–1998. MMWR. 1999;48:253–6. [PubMed]
- 45.Probable transfusion-transmitted malaria—Houston, Texas, 2003. MMWR. 2003;52:1075–6. [PubMed]
- 46.Transfusion malaria. MMWR. 2007;56.
- 47.Transfusion malaria. MMWR. 2009;58.
- 48.Gonzalez A, Nicolas JM, Munoz J, Castro P, Mas J, Valls ME, et al. Severe imported malaria in adults: retrospective study of 20 cases. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 2009;81:595–599. doi: 10.4269/ajtmh.2009.08-0637. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 49.Holtzclaw A, Mrsic Z, Managbanag J, Calvano T, Colombo C. Transfusion-transmitted malaria not preventable by current blood donor screening guidelines: a case report. Transfusion. 2016;56:2221–2224. doi: 10.1111/trf.13680. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 50.Echeverri D, Barreto DK, Osorio L, Cortés A, Martínez E. A case report of transfusion-transmitted Plasmodium vivax malaria from an asymptomatic donor to a premature newborn. Biomedica. 2012;32:8–12. doi: 10.7705/biomedica.v32i0.594. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 51.Scuracchio P, Vieira SD, Dourado DA, Bueno LM, Colella R, Ramos-Sanchez EM, et al. Transfusion-transmitted malaria: case report of asymptomatic donor harboring Plasmodium malariae. Rev Inst Med Trop São Paulo. 2011;53:55–59. doi: 10.1590/S0036-46652011000100010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 52.Notification de un caso de paludismo por transfusion. Boletin Epidemiologico Semanal. 1987.
- 53.Pizarro Portillo A, García Polo I, Fernández Dorado MT, Delgado Meliá T. Transfusion induced malaria. Revista Clínica Española. 1998;198:559–560. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 54.Tejero R, Gallego C, Lacasa MJ, Muñoz J. Nosocomial fever of unknown origin in a patient with polytrauma. Enferm Infecc Microbiol Clin. 2003;21:511–512. doi: 10.1016/S0213-005X(03)72997-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 55.Thomas WL, Keys S. Accidental transmission of malaria by blood transfusion. Lancet. 1936;227:536–537. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(01)36575-3. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 56.Nabarro D, Edward DG. Accidental transmission of malaria. Lancet. 1939;234:556–557. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(00)73942-0. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 57.Rogers KB. Quartan malaria transmitted by blood-transfusion; report of a case. Lancet. 1947;2:688. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(47)90717-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 58.Grant DB, Perinpanayagam MS, Shute PG, Zeitlin RA. A case of malignant tertian (Plasmodium falciparum) malaria after blood-transfusion. Lancet. 1960;2:469–470. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(60)91598-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 59.Vartan AE. Transfusion malaria in a man with Christmas disease. Br Med J. 1967;4:466. doi: 10.1136/bmj.4.5577.466. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 60.Dike AE. Two cases of transfusion malaria. Lancet. 1970;1:72–73. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(70)92641-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 61.DeSilva MCM, Barbara J. Two cases of transfusion-transmitted malaria (TTM) in the UK. Transfusion. 1988;28:86. doi: 10.1046/j.1537-2995.1988.28188127969.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 62.Brouwer EE, van Hellemond JJ, van Genderen PJJ, Slot E, van Lieshout L, Visser LG, Wismans PJ. A case report of transfusion-transmitted Plasmodium malariae from an asymptomatic non-immune traveller. Malar J. 2013;12:439. doi: 10.1186/1475-2875-12-439. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 63.Witt O, Iglauer A, Riggert J, Bommer W, Eber S. Transfusionsmalaria als Ursache von unklarem postoperativen Fieber. Monatsschr Kinderheilkd. 1998;146:1054–1056. doi: 10.1007/s001120050363. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 64.Payard J, Payard JM, de la Roy YDR, Giraud JR. Le paludisme transfusionnel. A propos d’un cas récent. Revue Francaise de Transfusion. 1970;13:181–187. doi: 10.1016/S0035-2977(70)80026-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 65.Besson P, Robert JF, Reviron J, Richard-Lenoble D, Gentilini M. A propos de deux observations de paludisme transfusionnel. essai de prevention associant un test d’immunofluorescence indirecte aux criteres de selection clinique. Rev Fr Transfus Immunohematol. 1976;19:369–373. doi: 10.1016/S0338-4535(76)80076-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 66.Andrianjafy M, Thuillier M, Gandrille MC. Case report. Presumption of transfusion malaria. Rev Fr Transfus Immunohematol. 1976;19:603–604. doi: 10.1016/S0338-4535(76)80036-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 67.Choutet P, Guilmot JL, Duong TH, Ginies G, Ravez G, Barrabes A, et al. Transfusional malaria. Another case. Semaine des Hopitaux. 1979;55:1539–1541. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 68.Brasseur P, Bonneau JC. Le paludisme transfusionnel: risque, prévention et coût. Expérience d’une année. Rev Fr Transfus Immunohematol. 1981;24:597–608. doi: 10.1016/S0338-4535(81)80055-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 69.Aymard JP, Vinet E, Lederlin P, Witz F, Colomb JN, Herbeuval R. Post-transfusional malaria: a case of double infection with Plasmodium falciparum and Plasmodium malariae. Rev Fr Transfus Immunohematol. 1980;23:491–493. doi: 10.1016/S0338-4535(80)80172-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 70.Richaud J, Canet J, Janaud JC. Paludisme post-transfusionnel chez un nourrisson de deux Mois. Archives Francaises de Pediatrie. 1982;39:161–163. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 71.Giacomini T, Baledent F, Hanania G. Transfusion malaria caused by Plasmodium ovale. A case. Presse Med. 1988;17:755–756. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 72.Nivet P, Capbern M. A case of transfusional Plasmodium falciparum malaria. Presse Med. 1991;20:1567. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 73.Bruneel F, Thellier M, Eloy O, Mazier D, Boulard G, Danis M, et al. Transfusion-transmitted malaria. Intensive Care Med. 2004;30:1851–1852. doi: 10.1007/s00134-004-2366-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 74.Joseph C, Meybeck A, Melliez H, Boyer T, Fortin-Lebraud L, Lovi V, et al. Tropical infection after a case of total hip arthroplasty. J Hosp Infect. 2014;87:179–181. doi: 10.1016/j.jhin.2014.04.009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 75.Frey-Wettstein M, Maier A, Markwalder K, Munch U. A case of transfusion transmitted malaria in Switzerland. Swiss Med Wkly. 2001;131:320. doi: 10.4414/smw.2001.09720. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 76.Flaum E. Wien Klin Wochenschr. 1929;42:589. [Google Scholar]
- 77.Sansone G, Centa A. Malaria caused by transfusion. I. Case in an infant. Pathologica. 1967;59:13–17. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 78.Sansone G, Centa A. Malaria caused by transfusion. II. Observations on 2 cases in patients splenectomized for Cooley’s disease. Pathologica. 1967;59:119–122. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 79.Neri SPD, Patamia I, Zoccolo A, Castellino P. Acute renal failure in Plasmodium malariae infection. J Med. 2008;66:166–168. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 80.Tagariello G, Sartori R, Inojosa WO, Candiotto L, Radossi P, Scarpa E, et al. Dramatic post-splenectomy onset of malaria caused by latent Plasmodium vivax in a female immigrant with severe immunological anaemia. Blood Transfus. 2014;12:428–430. doi: 10.2450/2014.0242-13. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 81.Maalouf N, Naja M, El Kinge AR, Zein-El-Dine S, Taher A. Transfusion-transmitted malaria: how vital is the need to screen in non-endemic countries? Transfus Med. 2007;17:415–416. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3148.2007.00780.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 82.Haydoura S, Mazboudi O, Charafeddine K, Bouakl I, Baban TA, Taher AT, et al. Transfusion-related Plasmodium ovale malaria complicated by acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS) in a non-endemic country. Parasitol Int. 2011;60:114–116. doi: 10.1016/j.parint.2010.10.005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 83.Chauhan V, Negi RC, Verma B, Thakur S. Transfusion transmitted malaria in a non-endemic area. J Assoc Physicians India. 2009;57:654–656. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 84.Lee YH, Lee HK, Choi KH, Hah JO, Lim SY. Transfusion-induced malaria in a child after open heart surgery in Korea. J Korean Med Sci. 2001;16:789–791. doi: 10.3346/jkms.2001.16.6.789. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 85.Traipattanakul J, Changpradub D, Trakulhun K, Phiboonbanakit D, Mungthin M. A first case of Plasmodium knowlesi malaria in Phramongkutklao Hospital. J Infect Dis Antimicrob Agents. 2014;31:91–100. [Google Scholar]
- 86.Anthony CN, Lau YL, Sum JS, Fong MY, Ariffin H, Zaw WL, et al. Malaysian child infected with Plasmodium vivax via blood transfusion: a case report. Malar J. 2013;12:308. doi: 10.1186/1475-2875-12-308. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 87.Bird EM, Parameswaran U, William T, Khoo TM, Grigg MJ, Aziz A, et al. Transfusion-transmitted severe Plasmodium knowlesi malaria in a splenectomized patient with beta-thalassaemia major in Sabah, Malaysia: a case report. Malar J. 2016;15:357. doi: 10.1186/s12936-016-1398-z. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Data Availability Statement
All data generated or analysed during this study are included in this published article.


