Abstract
Coxiella burnetii, the causative agent of Q fever, is a zoonotic pathogen associated with sylvatic or domestic transmission cycles, with rodents being suspected to link the two transmission cycles. Infection and subsequent disease in humans has historically been associated with contact with infected livestock, especially sheep. However, recently there have been reports of Q fever outbreaks associated with contact with infected rodents and dogs. Studies exploring the potential role of these animal hosts in the epidemiology of Q fever in many developing countries in Africa are very limited. This study aimed to determine the potential role of rodents and dogs in the epidemiological cycle of C. burnetti in Zambia. Using pathogen-specific polymerase chain reaction assays targeting the 16S rRNA gene, C. burnetii was detected for the first time in 45% of rodents (9/20), in one shrew and in 10% of domestic dogs (15/150) screened in Zambia. Phylogenetic characterization of six samples based on the isocitrate synthase gene revealed that the strains were similar to a group of isolates from chronic human Q fever patients, goats and rodents reported in multiple continents. Considering the close proximity of domestic dogs and rodents to humans, especially in resource-limited communities, the presence of C. burnetii in these animals could be of significant public health importance. It is thus important to determine the burden of Q fever in humans in such resource-limited communities where there is close contact between humans, rodents and dogs.
Keywords: Coxiella burnetii, Domestic dogs, Rodents, Phylogenetic analysis, Zambia
Letter to the Editor
Coxiella burnetii, the causative agent of the zoonotic disease Q fever, is assumed to have a sylvatic and a domestic transmission cycle in which livestock play the most important role, with rodents suspected to act as a link between the two cycles [1]. Human infection is characterized by febrile illness and community-acquired pneumonia that may become chronic, resulting in mortalities in few cases [2]. In livestock, the disease is mainly asymptomatic, but has been associated with abortions and decreased livestock productivity, with consequent negative socioeconomic effects on livestock farmers [2].
Whilst there have been no reported cases of Q fever in humans in Zambia, serologic evidence in humans has been reported in areas where they co-exist with livestock [3]. Moreover, the presence of C. burnetii in Zambian livestock has been genetically confirmed [4]. However, the potential role of rodents and domestic dogs in the epidemiology of Q fever in Zambia has not been explored, despite the observed association between these hosts and disease outbreaks in humans in other countries [1, 5]. This study aimed to detect and characterize C. burnetii in rodents and semi-confined domestic dogs from rural and peri-urban settings, respectively, to ascertain the potential role of these animal hosts in the epidemiological cycle of this pathogen.
In 2012–2013, blood and internal organs (spleen, lungs, heart and liver) were sampled from 20 rodents (Mastomys natalensis: n = 11; Gerbillinae sp.: n = 7; Saccostomus campestris: n = 2) and one shrew trapped from Nyimba (n = 9) and Namwala (n = 12) Districts in Zambia. The blood and internal organs from each rodent were pooled and homogenized. One-hundred-and-fifty blood samples were collected from dogs from 2016 to 2017 in Chilanga District [Mwembeshi (n = 86) and Mapepe (n = 64)]. Nyimba and Namwala Districts are plague-endemic rural areas [6] whereas Chilanga District is mostly peri-urban.
DNA was extracted from canine blood and homogenates of blood and internal organs of rodents. For molecular detection, the primers QR-FO (5′-ATT GAA GAG TTT GAT TCT GG-3′) and QR-RO (5’-CGG CCT CCC GAA GGT TAG-3′), which amplify a 1450 bp fragment of the 16S rRNA gene of C. burnetii, were used [7]. Coxiella-positive samples were further characterized by amplification of a 738 bp fragment of the C. burnetii-specific isocitrate dehydrogenase (icd) gene using the primer pair icdtrg_f (5′-CGG AGT TAA CCG GAG TAT CCA-3′) and icdtrg_r (5′-CCG TGA ATT TCA TGA TGT TAC CTT T-3′) [8]. Purified polymerase chain reaction products of the icd gene were sequenced directly by the Sanger method using a 3130 genetic analyzer. The sequences obtained (four from rodents and two from dogs) were deposited in the GenBank database (accession numbers LC319605–LC319610) and utilized in the phylogenetic analyses.
Overall, the shrew, 45% of rodents (9/20) and 10% of dogs (15/150) screened were positive for C. burnetii. Nyimba District had a prevalence of 11.1% (1/9) whilst for Namwala, the prevalence was 75% (9/12) in rodents. The detection among the rodents was as follows: Saccostomus campestris (2/2), Gerbillinae sp. (4/7) and Mastomys natalensis (3/11). The prevalence in dogs by sampling sites was 10.9% for Mwembeshi and 9.3% for Mapepe.
Nucleotide BLAST comparison (https://blast.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/Blast.cgi) revealed that all the Zambian C. burnetii icd gene sequences showed highest similarity (99%) to that of C. burnetii strain MAN (GenBank: AF146293), which was isolated from a chronic human case of Q fever in France [9]. Phylogenetic analysis of the icd gene sequences revealed that C. burnetii isolates separated into three main groups (Fig. 1). Group I consisted of isolates from acute human Q fever patients, ticks and cows. Group II included isolates from chronic human Q fever patients, goats, rodents and dogs (Fig. 1). The Zambian strains of C. burnetii belonged to “chronic” group II, intimating possible long-term circulation of the pathogen in these hosts. Group III consisted of chronic human Q fever isolates found in Canada and the USA.
Fig. 1.
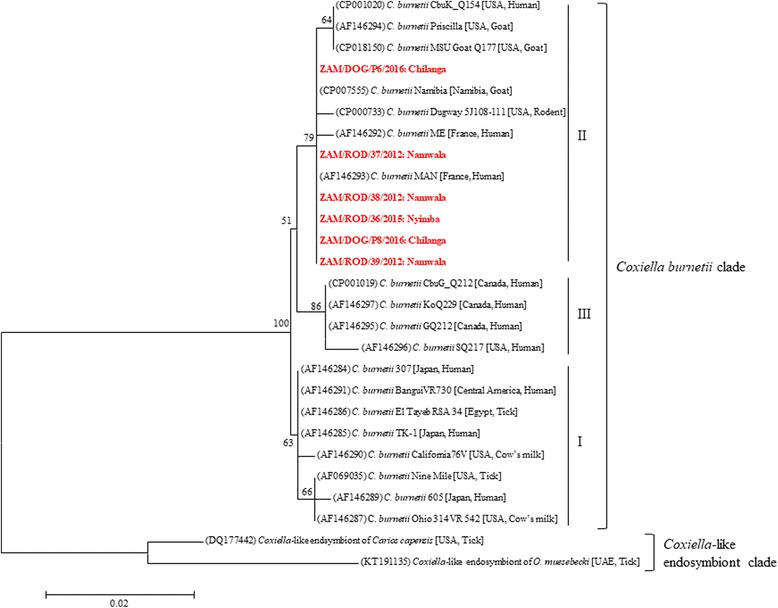
Evolutionary relationships of Coxiella strains based on isocitrate dehydrogenase (icd) gene sequences. The neighbor-joining tree was constructed using Kimura 2-parameter model in MEGA software. The GenBank accession numbers are in parentheses while the host and country of origin are in square brackets. The Coxiella strains characterized in this study are in bold and red text, with the district of origin indicated after the colon. Bootstrap values ≥ 50% are shown at branch nodes. The scale-bar indicates the number of substitutions per site
To the best of our knowledge, this is the first report of molecular detection and characterization of C. burnetii in rodents and semi-confined domestic dogs in Zambia. Moreover, studies in these animal hosts are very limited in many developing countries in sub-Saharan Africa. In most rural and peri-urban communities of Zambia, humans, especially children, are in contact with the environment co-shared with rodents and dogs, a factor which could predispose them to infection through inhalation of contaminated environmental dust [10]. Since the dogs sampled were semi-confined, the risk of infection potentially extends to a wider community. Furthermore, as the rodents sampled were trapped in plague-endemic areas [6], there is a possibility that individuals living in these communities could be co-infected by both pathogens. Along with the fact that Plasmodium falciparum malaria is endemic in Zambia and presents with similar clinical signs, these scenarios could pose serious challenges with regards to diagnosis and patient management in resource-limited settings.
Our findings demonstrated the circulation of C. burnetii in rodents and domestic dogs, highlighting the potential threat this pathogen poses to humans. This emphasizes the need for more extensive studies to determine the burden of Q fever in humans in communities where rodents and dogs have tested positive and in other regions of the country to determine the reservoir role of these animals.
Acknowledgements
Not applicable.
Funding
This work was partly supported by the Japan Initiative for Global Research Network on Infectious Diseases (J-GRID) and the Japan Agency for Medical Research and Development (AMED)/Japan International Cooperation Agency (JICA) within the framework of the Science and Technology Research Partnership for Sustainable Development (SATREPS).
Availability of data and materials
All data generated and/or analysed during the current study are included in this published article. Sequences are deposited in the GenBank database under the accession numbers LC319605–LC319610.
Abbreviations
- Icd
Isocitrate dehydrogenase
- rRNA
Ribosomal ribonucleic acid
Authors’ contributions
SC and ES conceived and designed the study; SC, ES, MCS, KC and BMH were involved in sample collection and processing; SC and ES conducted most of the experiments; MS, AT, ASM, SM and BMH were project leaders and made conceptual contributions; All authors were involved in data analysis, interpretation of results, writing, revising. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Ethics approval and consent to participate
Ethical approval to conduct the study was granted by the University of Zambia Biomedical and Research Ethics Committee (009-09-15).
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Contributor Information
Simbarashe Chitanga, Email: schitanga@gmail.com.
Edgar Simulundu, Email: esikabala@yahoo.com.
Martin C. Simuunza, Email: martin.simuunza@unza.zm
Katendi Changula, Email: katendic@yahoo.com.
Yongjin Qiu, Email: yong_qiu@czc.hokudai.ac.jp.
Masahiro Kajihara, Email: kajihara@czc.hokudai.ac.jp.
Ryo Nakao, Email: ryo.nakao@vetmed.hokudai.ac.jp.
Michelo Syakalima, Email: michsan65@gmail.com.
Ayato Takada, Email: atakada@czc.hokudai.ac.jp.
Aaron S. Mweene, Email: asmweene04@yahoo.com
Samson Mukaratirwa, Email: Mukaratirwa@ukzn.ac.za.
Bernard M. Hang’ombe, Email: mudenda68@yahoo.com
References
- 1.Meerburg BG, Reusken CBEM. The role of wild rodents in spread and transmission of Coxiella burnetii needs further elucidation. Wildl Res. 2011;38:617–625. doi: 10.1071/WR10129. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Vanderburg S, Rubach MP, Halliday JE, Cleaveland S, Reddy EA, Crump JA. Epidemiology of Coxiella burnetii infection in Africa: a OneHealth systematic review. PLoS Negl Trop Dis. 2014;8:e2787. doi: 10.1371/journal.pntd.0002787. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Okabayashi T, Hasebe F, Samui KL, Mweene AS, Pandey SG, Yanase T, et al. Short report: prevalence of antibodies against spotted fever, murine typhus, and Q fever rickettsiae in humans living in Zambia. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 1999;61:70–72. doi: 10.4269/ajtmh.1999.61.70. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Qiu Y, Nakao R, Namangala B, Sugimoto C. First genetic detection of Coxiella burnetii in Zambian livestock. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 2013;89:518–519. doi: 10.4269/ajtmh.13-0162. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Buhariwalla F, Cann B, Marrie TJ. A dog-related outbreak of Q fever. Clin Infect Dis. 1996;23:753–755. doi: 10.1093/clinids/23.4.753. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Hang'ombe BM, Nakamura I, Samui KL, Kaile D, Mweene AS, Kilonzo BS, et al. Evidence of Yersinia pestis DNA from fleas in an endemic plague area of Zambia. BMC Res Notes. 2012;5:72. doi: 10.1186/1756-0500-5-72. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Masuzawa T, Sawaki K, Nagaoka H, Akiyama M, Hirai K, Yanagihara Y. Identification of rickettsiae isolated in Japan as Coxiella burnetii by 16S rRNA sequencing. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol. 1997;47:883–884. doi: 10.1099/00207713-47-3-883. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.de Bruin A, de Groot A, de Heer L, Bok J, Wielinga PR, Hamans M, et al. Detection of Coxiella burnetii in complex matrices by using multiplex quantitative PCR during a major Q fever outbreak in The Netherlands. Appl Environ Microbiol. 2011;77:6516–6523. doi: 10.1128/AEM.05097-11. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Van Nguyen S, To H. Yamaguchi T, Fukushi H, Hirai K. Molecular cloning of an immunogenic and acid-induced isocitrate dehydrogenase gene from Coxiella burnetii. FEMS Microbiol Lett. 1999;175:101–106. doi: 10.1111/j.1574-6968.1999.tb13607.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.de Rooij MM, Borlee F, Smit LA, de Bruin A, Janse I, Heederik DJ, et al. Detection of Coxiella burnetii in ambient air after a large Q fever outbreak. PLoS One. 2016;11:e0151281. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0151281. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Data Availability Statement
All data generated and/or analysed during the current study are included in this published article. Sequences are deposited in the GenBank database under the accession numbers LC319605–LC319610.


