Abstract
Protein expression of major hepatobiliary drug transporters (NTCP, OATPs, OCT1, BSEP, BCRP, MATE1, MRPs, and P-gp) in cancerous (C, n = 8) and adjacent noncancerous (NC, n = 33) liver tissues obtained from patients with chronic hepatitis C with hepatocellular carcinoma (HCV-HCC) were quantified by LC-MS/MS proteomics. Herein, we compare our results with our previous data from noninfected, noncirrhotic (control, n = 36) and HCV-cirrhotic (n = 30) livers. The amount of membrane protein yielded from NC and C HCV-HCC tissues decreased (31%, 67%) relative to control livers. In comparison with control livers, with the exception of NTCP, MRP2, and MATE1, transporter expression decreased in NC (38%–76%) and C (56%–96%) HCV-HCC tissues. In NC HCV-HCC tissues, NTCP expression increased (113%), MATE1 expression decreased (58%), and MRP2 expression was unchanged relative to control livers. In C HCV-HCC tissues, NTCP and MRP2 expression decreased (63%, 56%) and MATE1 expression was unchanged relative to control livers. Compared with HCV-cirrhotic livers, aside from NTCP, OCT1, BSEP, and MRP2, transporter expression decreased in NC (41%–71%) and C (54%–89%) HCV-HCC tissues. In NC HCV-HCC tissues, NTCP and MRP2 expression increased (362%, 142%), whereas OCT1 and BSEP expression was unchanged. In C HCV-HCC tissues, OCT1 and BSEP expression decreased (90%, 80%) relative to HCV-cirrhotic livers, whereas NTCP and MRP2 expression was unchanged. Expression of OATP2B1, BSEP, MRP2, and MRP3 decreased (56%–72%) in C HCV-HCC tissues in comparison with matched NC tissues (n = 8), but the expression of other transporters was unchanged. These data will be helpful in the future to predict transporter-mediated hepatocellular drug concentrations in patients with HCV-HCC.
Introduction
The World Health Organization estimated globally 71 million people had HCV, and over 10,0000 people with HCV died as a result of HCC in 2015 (World Health Organization, 2017). Over 90% of HCV patients treated with direct acting antiviral drug combinations achieve clearance of circulating HCV RNA or a sustained virological response, a result considered to be a functional cure (Bonaventura and Montecucco, 2016; Terrault et al., 2016). Despite this success, the incidence of diagnosis and treatment of HCV is low because up to 90% of people infected are unaware of their infection status (Institute of Medicine Committee on the Prevention and Control of Viral Hepatitis Infection, 2010; Hatzakis et al., 2011). The incidence of liver cirrhosis 25–30 years after HCV-infection ranges from 15% to 35% (Freeman et al., 2001). Once HCV-related cirrhosis is established, hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) typically develops at an annual rate of 1%–4% (Hassan et al., 2002; Blonski and Reddy, 2008), although rates of up to 8% have been reported in Japan (El-Serag, 2012).
Cross-sectional and case control studies have found a strong association between chronic HCV infection and HCC (Goodgame et al., 2003). However, the cause of carcinogenesis is unclear. An important clinical observation is that HCC in patients with HCV predominantly occurs in patients with advanced stages of hepatic fibrosis or cirrhosis (Blonski and Reddy, 2008; Lok et al., 2009; El-Serag, 2012; Morgan et al., 2013). Diagnosis of HCC is based upon imaging techniques and/or biopsy. The hepatocyte-specific magnetic resonance imaging contrast agent gadolinium ethoxybenzyl diethylenetriaminepentaacetic acid (Gd-EOB-DTPA) was developed to detect and characterize focal liver lesions (Schuhmann-Giampieri et al., 1992; Hamm et al., 1995). The hepatobiliary transport of Gd-EOB-DTPA is mediated by organic-anion transporting polypeptides 1B1 and 1B3 (OATP1B1, OATP1B3), Na-taurocholate cotransporting polypeptide (NTCP), and multidrug resistance-associated protein 3 (MRP3) located at the sinusoidal membrane and multidrug resistance-associated protein 2 (MRP2) situated at the canalicular membrane of hepatocytes (Leonhardt et al., 2010; Jia et al., 2014). During magnetic resonance imaging, hepatic focal lesions that have reduced uptake transporter expression are depicted as hypointense areas compared with the well-enhanced liver tissue with normal hepatobiliary function (Narita et al., 2009; Kitao et al., 2010; Tsuboyama et al., 2010; Vasuri et al., 2011).
Up to 90% of HCC patients are unable to undergo curative liver resection or receive a liver transplant (Colella et al., 1998; Fan et al., 1999; Fong et al., 1999). Drug resistance often hampers successful treatment of HCC with chemotherapeutic agents. Such resistance can be conferred by various mechanisms such as: 1) reduced uptake of the drug into the target cells; 2) alterations within the cells such as altered metabolism, an increased capacity to repair DNA or reduced apoptosis; and 3) an increased efflux of the drug from the target cells (Holohan et al., 2013). Drugs such as doxorubicin, cisplatin, or epirubicin used in transarterial chemoembolization therapy (i.e., arterial administration of chemotherapy followed by embolization of the arterial blood supply) and the oral kinase inhibitor sorafenib are known substrates of uptake and efflux transporters. Doxorubicin is a substrate of the efflux transporters P-glycoprotein (P-gp), breast cancer resistance protein (BRCP), and MRP1 (Fairchild et al., 1987; Wei et al., 2012; Saeed et al., 2015). Cisplatin is a substrate of hepatic organic cation transporters (OCT1, OCT2, and OCT3) and multidrug and toxin extrusion protein 1 (MATE1) (Yonezawa et al., 2006). Epirubicin is a substrate of P-gp (Tariq et al., 2016). Sorafenib is a substrate of OATP1B1, OATP1B3, OCT1, P-gp, and BCRP (Gnoth et al., 2010; Lagas et al., 2010; Swift et al., 2013; Zimmerman et al., 2013; Johnston et al., 2014).
Based on the above data, it is important to understand if transporter expression is down-regulated in HCV-HCC liver tissue to: 1) better design drugs to target HCC in HCV-infected patients and 2) predict transporter-mediated drug disposition (including hepatocellular concentrations) in patients with HCV-HCC. Current mRNA and immunohistochemical data on expression of plasma membrane transporters in cancerous (C) HCV-HCC and adjacent noncancerous (NC) and liver tissues is controversial. Therefore, for the first time, we quantified the protein expression of major hepatobiliary transporters in C and NC HCV-HCC liver resections by targeted proteomics and LC-MS/MS using the surrogate peptide approach. Here, we compare the results obtained with our previously published data on transporter expression in noninfected, noncirrhotic (control, 21–70 years) and HCV-cirrhotic livers (33–69 years) (Prasad et al., 2016; Wang et al., 2016).
Materials and Methods
Chemicals and Reagents.
The ProteoExtract Native Membrane Protein Extraction Kit was from Calbiochem (Temecula, CA). Iodoacetamide, dithiothreitol, trypsin, and the BCA assay kit were from Pierce Biotechnology (Rockford, IL). Sodium deoxycholate was from MP Biochemicals (Santa Ana, CA). Bespoke synthetic signature peptides were from New England Peptides (Boston, MA). Equivalent stable isotope-labeled internal standards (AQUA QuantPro, ±25% precision) and ammonium bicarbonate were from ThermoFisher Scientific (Rockford, IL). High-performance liquid chromatography-grade acetonitrile, methanol, and formic acid were from Fischer Scientific (FairLawn, NJ). Finally, deionized water was from a Q-Gard 2 purification cartridge water purifying system (Millipore, Bedford, MA). All reagents were analytical grade.
Procurement of Human Liver Samples.
Each liver sample was procured from patients undergoing liver transplant. The demographic and clinical characteristics of the liver donors are shown in Table 1. Gilead Sciences, Inc. (Foster City, CA) provided 25 frozen NC HCV-HCC liver resection samples (classified by a pathologist). Eight paired NC and C HCV-HCC liver resection samples were obtained from the Liver Tissue Cell Distribution System (LTCDS), University of Minnesota. All the HCV-HCC and HCV-cirrhotic liver samples were flash frozen in liquid nitrogen within <1 hour of collection. The control (noninfected, noncirrhotic) liver samples were frozen within <24 hours of collection. All the liver samples were then stored at −80°C until analysis. Demographics, acquisition, and storage of the control and HCV-cirrhotic livers have been published previously (Prasad et al., 2016; Wang et al., 2016).
TABLE 1.
Demographics of control, HCV-cirrhotic, and HCV-infected NC and C livers
Normal ranges for these covariates are the following; body mass index: 18.5–24.9; creatinine: 0.5–1.5 mg/dl; glomerular filtration rate: 90–120 ml/min; international normalized ratio: 0.8–1.2; alkaline phosphatase: 44–147 U/l; alanine aminotransferase: 7–40 U/l; aspartate aminotransferase: 10–34 U/l; albumin: 3.5–5.5 g/dl; total bilirubin: 0.3–1.9 mg/dl. Data represented as the mean ± S.D. LTCDS available as matched noncancerous and cancerous HCV-HCC liver samples.
| Control | HCV-Cirrhotic | HCV-HCC (Gilead) | HCV-HCC (LTCDS) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sample size | 36 | 30 | 25 | 8 |
| Age (years) | 47 ± 14 | 53 ± 8 | 59 ± 5 | 59 ± 6 |
| Sex | 18 male, 18 female | 18 male, 12 female | 20 male, 5 female | 7 male, 1 female |
| Race | 33 Caucasian, 2 African American, 1 Asian | 24 Caucasian, 4 African American, 1 Hispanic | 23 Caucasian, 1 African American, 1 Hispanic | 5 Caucasian, 2 African American, 1 Hispanic |
| BMI | NR | 31.7 ± 6.3 | 29.2 ± 7.6 | 30.4 ± 6.5 |
| Creatinine (mg/dl) | NR | NR | NR | 1.0 ± 0.5 |
| GFR (Cockcroft-Gault, ml/min) | NR | NR | 126 ± 30 | 88 ± 28 |
| INR | NR | 1.7 ± 0.5 | NR | 1.4 ± 0.7 |
| Alkaline phosphatase (U/l) | NR | 112 ± 54 | NR | 133 ± 49 |
| Alanine aminotransferase (U/l) | NR | 146 ± 243 | 77 ± 38 | 82 ± 104 |
| Aspartate aminotransferase (U/l) | NR | 223 ± 388 | NR | 87 ± 74 |
| Albumin (g/dl) | NR | 2.6 ± 0.6 | NR | 3.3 ± 0.5 |
| Total bilirubin (mg/dl) | NR | 3.6 ± 2.9 | NR | 1.2 ± 0.7 |
| Treatment regimen | NR | NR | 25 SOF + RBV | 3 SOF + RBV, 1 SOF + RBV+ PEG-IFN, 1 LDV, 3 NR |
INR, international normalized ratio; LDV, ledipasvir; NR, not recorded; PEG-IFN, peginterferon alpha-2a; RBV, ribavarin; SOF, sofosbuvir; U, units.
Membrane Extraction and Protein Trypsin Digestion.
Total membrane was isolated from approximately 100 mg of HCV-HCC human liver tissue as previously described using the ProteoExtract Native Membrane Protein Extraction Kit (Deo et al., 2012; Prasad et al., 2013, 2014, 2016; Wang et al., 2016). The isolated total membrane protein concentration of each sample was determined using the Pierce BCA protein assay kit. In triplicate, 2 µg/µl total membrane protein (80 µl) of each sample was reduced, denatured, alkylated, and digested according to our previously published protocol (Wang et al., 2015, 2016; Prasad et al., 2016). The peptide fragments generated by trypsin digestion were quantified by LC-MS/MS as described below.
Surrogate Peptide Selection and Quantification by LC-MS/MS.
Unique surrogate peptides were selected for quantification of each transporter (Supplemental Table 1) on the basis of previously reported selection criteria (Kamiie et al., 2008; Prasad and Unadkat, 2014) and used as calibrators. Corresponding labeled peptides, at [13C615N2]-lysine and [13C615N4]-arginine residues, were used as internal standards. The calibrators, ranging from approximately 0.3 to 110 fmol (on-column), were prepared by spiking 50 mM ammonium bicarbonate buffer (80 µl) with unlabeled surrogate peptide standards (10 µl) and labeled internal standards (20 µl). The quality control samples were prepared by spiking surrogate peptides into 50 mM ammonium bicarbonate buffer (at low, medium, and high concentrations). In addition, a biologic quality control sample, membrane protein from a collection of control livers, was included in each assay to ensure that the data matched previously published data (Prasad et al., 2016).
Surrogate peptides were quantified using an AB Sciex 6500 TQS tandem mass spectrometer (AB SCIEX, Framingham, MA) coupled with a Water’s Acquity UPLC system (Waters Corporation, Milford, MA) operated in electrospray positive ionization mode. The mass spectrometry conditions were: curtain gas: 20 psi; ion spray voltage: 5500 V; temperature: 350°C; gas 1: 50 psi; gas 2: 30 psi; and cell exit potential: 12 V.
Approximately, 8 µg of the trypsin digest (5 µl) was injected onto the column (Acquity UPLC HSS T3 1.8 µm 100A; 100 × 2.1 mm; Waters) fitted with a security guard column (C18, 4 × 2 mm; Phenomenex, Torrance, CA) and eluted at 0.3 ml/min with a gradient mobile phase consisting of water containing 0.1% formic acid (A) and acetonitrile containing 0.1% formic acid (B). The linear gradient was 0–3 minutes: 97% A 3% B; 3–10 minutes: 87% A 13% B; 10–20 minutes: 75% A 25% B; 20–22 minutes: 66.7% A 33.3% B; 22–23 minutes: 50% A 50% B; 23–24 minutes: 20% A 80% B; 24–28 minutes: 97% A 3% B. MS/MS analysis was performed by monitoring the surrogate peptides and the internal standards using instrument parameters listed in Supplemental Table 1.
LC-MS/MS data were processed by integrating the peak areas generated from the reconstructed ion chromatograms for the analyte peptides and respective heavy internal standards using Analyst Software 1.6.2 (Milford, MA). The peak response from two transitions of each peptide was averaged (after confirming that they were correlated) for quantification of samples, standards, and quality controls. The calibration curve for each surrogate peptides were linear (R2 > 0.99) with a lower limit of quantification ranging from 0.65 to 2.80 fmol (Supplemental Table 1). The accuracy (percentage error) and precision (coefficient of variation) of the assay, on the basis of the quality control samples, was 80%–120% and <20%, respectively.
Genotyping Methods and Genotype-Dependent Changes in OATP1B1 Protein Expression.
We previously showed correlation of some high frequency SLCO1B1 single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) with OATP1B1 protein expression in adult liver samples. Therefore, all HCV-HCC liver tissues were genotyped for SLCO1B1 SNPs [rs4149015, -11187G>A; rs2306283, 388A>G; rs4149056, 521T>C; rs4149057, 571T>C; and rs2291075 (597C>T)] as previously described (Wang et al., 2016).
Statistical Data Analyses.
Statistical difference (P < 0.05) in the expression of transporters between groups of livers was determined by the nonparametric Kruskal-Wallis and Dunn’s multiple comparisons statistical test. Transporter expression in matched NC and C HCV-HCC tissues were assessed by the nonparametric Wilcoxon signed-rank test. Correlation in transporter expression within NC and C HCV-HCC tissues were determined by the nonparametric Spearman test.
Results
Demographics.
In the HCV-infected liver groups there was a male sampling bias (Table 1). This is likely because HCV prevalence is greater in men than women (Armstrong et al., 2006; Rantala and van de Laar, 2008). Many of the HCV-positive donors exhibited abnormal international normalized ratio, alanine aminotransferase, aspartate aminotransferase, albumin, and bilirubin serum levels indicating liver damage. Consistent with previous reports of chronic hepatitis, serum alkaline phosphatase concentrations were much less elevated than alanine aminotransferase and aspartate aminotransferase serum levels (Desmet et al., 1994). LTCDS was able to provide a full list of medications taken by each HCV-HCC subject, but these data were not available for the Gilead samples (Supplemental Table 2).
Pooling of Samples.
Initially, total membrane protein yields and transporter expression levels (per microgram of membrane protein and per gram of liver) in NC HCV-HCC tissues from Gilead (n = 25) and LTCDS (n = 8) were assessed separately. No significant differences were observed between these two groups of livers (P > 0.05) for either total membrane protein yield or transporter expression level; therefore; the data from these two groups were pooled for all subsequent analyses detailed below.
Comparison of Total Membrane Protein Yield.
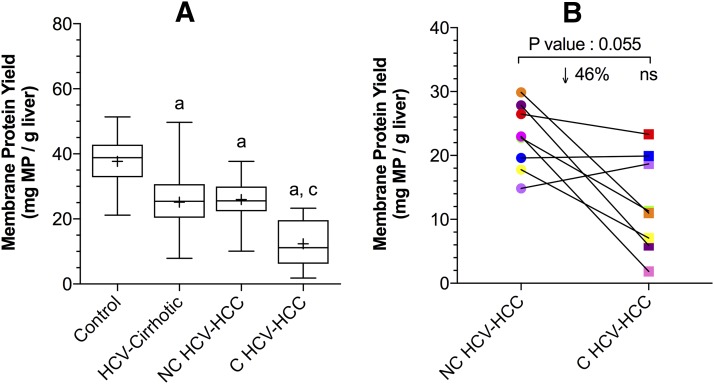
Compared with control livers, the total membrane protein yield (per gram of liver) from HCV-cirrhotic livers and NC or C HCV-HCC tissues was significantly lower by 33%, 31%, and 67%, respectively (Fig. 1A; P < 0.05). The total membrane protein yield from HCV-cirrhotic livers and NC HCV-HCC tissues was no different. The total protein yield from C HCV-HCC tissues was significantly lower than that from NC HCV-HCC tissues (52%; P < 0.05). In matched NC and C HCV-HCC tissues from the same person, the total membrane protein yield from C tissues was also lower than NC tissues (46%, Fig. 1B), but this did not reach significance, likely due to the small sample size (P = 0.055).
Fig. 1.
Total membrane protein yield from control livers, HCV-cirrhotic livers, NC HCV-HCC, and C HCV-HCC liver tissues (A) or matched NC HCV-HCC and C HCV-HCC liver tissues (B). (A) The membrane protein yield from HCV-cirrhotic livers, NC, and C HCV-HCC tissues was significantly lower than that from the control livers. The total membrane protein yield from C HCV-HCC tissues was also significantly lower than NC HCV-HCC tissues. Data on the total membrane protein yield of control and HCV-cirrhotic livers were taken from Prasad et al. (2016) and Wang et al. (2016), respectively. The data are represented as box-plots of the median (horizontal line), 75th (top of box), and 25th (bottom of box) quartiles, the smallest and largest values (whiskers) and mean (+) are shown. The symbols “a,” “b,” and “c” indicate a significant difference from control livers, HCV-cirrhotic livers, NC HCV-HCC tissues, respectively (P < 0.05, Kruskal-Wallis test). (B) In matched tissues, the yield of membrane protein from C HCV-HCC tissues was lower, but not significantly different (P = 0.055, Wilcoxon test) than that from NC-HCV-HCC tissues (n = 8). Each line connects data from the matched liver samples.
Hepatobiliary Transporter Protein Expression in Control, HCV-Cirrhotic, and C and NC HCV-HCC Human Livers.
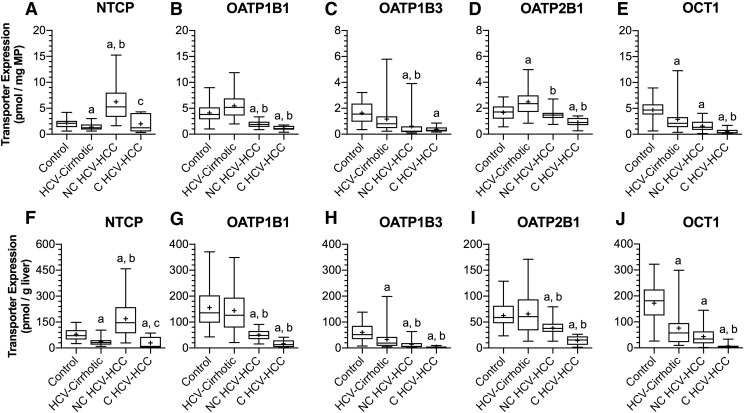
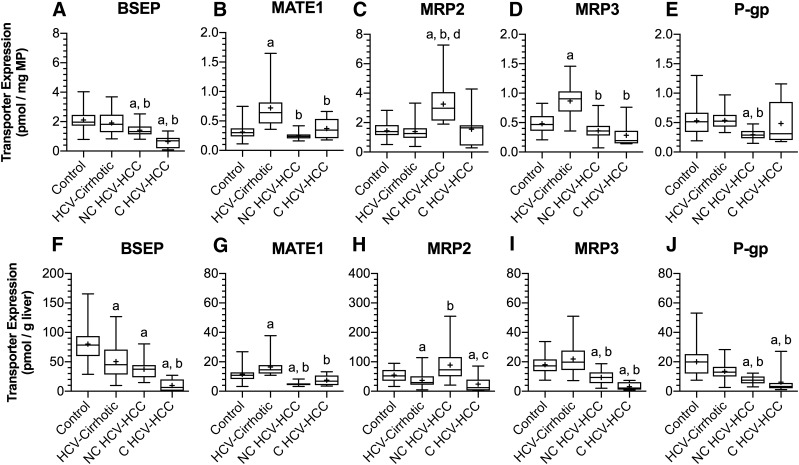
To predict human transporter-mediated drug disposition by physiologically based pharmacokinetic modeling, protein expression of relevant transporters must be calculated per gram of liver tissue and then scaled up to the weight of an adult liver. The hepatic transporters quantified included sinusoidal uptake transporters NTCP, OATP1B1, OATP1B3, OATP2B1, and OCT1; sinusoidal efflux transporters MRP3 and MRP4; and canalicular efflux transporters BSEP, BCRP, MATE1, MRP2, MRP3, and P-gp. When transport protein expression was below the lower limit of quantification, the lower limit of quantification was used in calculations as an estimate of changes in transporter expression. The data are presented normalized to milligram of membrane protein and gram of liver (Figs. 2 and 3).
Fig. 2.
Protein expression of NTCP, OATP1B1, OATP1B3, OATP2B1, and OCT1 in control livers, HCV-cirrhotic livers, NC HCV-HCC, and C HCV-HCC liver tissues normalized to milligram of membrane protein (A–E, respectively) or gram of liver (F and J, respectively). In comparison with control livers (per gram of liver), except for NTCP, transporter protein expression was reduced in both NC and C HCV-HCC tissues. NTCP expression was increased in NC HCV-HCC tissues and decreased in C HCV-HCC tissues relative to control livers. Similarly, compared with HCV-cirrhotic livers (per gram of liver), OATP1B1, OATP1B3, and OATP2B1 protein expression was decreased in both NC and C HCV-HCC tissues. NTCP protein expression in NC HCV-HCC tissues was greater than HCV-cirrhotic livers. OCT1 expression in C HCV-HCC tissues was lower than HCV-cirrhotic livers. Transporter expression data for control and HCV-cirrhotic livers were taken from Prasad et al. (2016) and Wang et al. (2016), respectively. The data are represented as box-plots the median (horizontal line), 75th (top of box) and 25th (bottom of box) quartiles, the smallest and largest values (whiskers) and mean (+) are shown. The symbols “a,” “b,” and “c” indicate a significant difference from control livers, HCV-cirrhotic livers, NC HCV-HCC liver tissues, respectively (P < 0.05, Kruskal-Wallis test).
Fig. 3.
The protein expression of BSEP, MATE1, MRP2, MRP3 and P-gp in control livers, HCV-cirrhotic livers, NC HCV-HCC and C HCV-HCC liver tissues normalized to milligram of membrane protein (A–E, respectively) or gram of liver (F and J, respectively). In comparison with control livers (per gram of liver), except for MATE1 and MRP2, transporter protein expression decreased in both NC and C HCV-HCC tissues. MATE1 expression in NC HCV-HCC tissues and MRP2 in C HCV-HCC tissues were lower than control livers. Likewise, generally transporter expression in both NC and C HCV-HCC tissues were lower than HCV-cirrhotic livers (per gram of liver). The exceptions being, BSEP expression was no different and MRP2 expression increased in NC HCV-HCC tissues, and MRP2 expression was no different in C HCV-HCC tissues from HCV-cirrhotic livers. Transporter expression data for control and HCV-cirrhotic livers were taken from Prasad et al. (2016) and Wang et al. (2016), respectively. The data are represented as box-plots of the median (horizontal line), 75th (top of box), and 25th (bottom of box) quartiles, the smallest and largest values (whiskers) and mean (+) are shown. The symbols “a,” “b,” and “c” indicate a significant difference from control livers, HCV-cirrhotic livers, NC HCV-HCC tissues, respectively (P < 0.05, Kruskal-Wallis test).
Differences in the protein expression of major hepatobiliary transporters in HCV-cirrhotic livers versus control livers have been previously described (Wang et al., 2016) and are not recapitulated here. In comparison with control livers (on a per gram of liver basis), with the exceptions of NTCP, MRP2, and MATE1, transporter expression decreased in both NC (38%–76%) and C (56%–96%) HCV-HCC tissues. In NC HCV-HCC tissues, NTCP expression increased (113%), MATE1 expression decreased (58%), and MRP2 expression was no different to control livers. In C HCV-HCC tissues, NTCP and MRP2 expression decreased (63%, 56%) compared with control livers, and MATE1 expression was unchanged relative to control livers.
In comparison with HCV-cirrhotic livers (on a per gram of liver basis), with the exceptions of NTCP, OCT1, BSEP, and MRP2, transporter expression also decreased in NC (41%–71%) and C (54%–89%) HCV-HCC tissues. In NC HCV-HCC tissues, expression of NTCP and MRP2 increased (362%, 142%) and expression of OCT1 and BSEP were unchanged relative to HCV-cirrhotic livers. In C HCV-HCC tissues, expression of OCT1 and BSEP decreased (90%, 80%), whereas NTCP and MRP2 expression was no different to HCV-cirrhotic livers. The only difference in transporter expression between NC and C HCV-HCC tissues (on a per gram of liver basis) was decreased expression of NTCP (83%) and MRP2 (73%) in C tissues. The outlined changes in transporter expression are summarized in Supplemental Table 3.
The impact of disease on transporter protein expression exhibited a transporter-dependent pattern, irrespective of whether it was normalized to milligrams of membrane protein or grams of liver. When transporter expression was normalized to milligram of membrane protein, expression of OATP1B1, OATP1B3, OCT1, BSEP, and P-gp were decreased (33%–66%); NTCP and MRP2 were increased (192%, 126%); and OATP2B1, MATE1, and MRP3 were unchanged in NC HCV-HCC tissues relative to control livers. In C HCV-HCC tissues, expression of OATPs OCT1 and BSEP were lower (46%–88%) than control, whereas expression of NTCP, MATE1, MRP2, MRP3, and P-gp were no different. In comparison with HCV-cirrhotic livers, expression of OATPs, BSEP, MATE1, MRP3, and P-gp decreased (26%–67%); NTCP and MRP2 increased (354%, 134%); and OCT1 expression was unchanged in NC HCV-HCC tissues. In C HCV-HCC tissues, expression of OATP1B1, OATP2B1, OCT1, BSEP, MATE1, and MRP3 were decreased (49%–81%), and NTCP, OATP1B3, MRP2, and P-gp were no different to HCV-cirrhotic livers. The outlined changes in transporter expression are summarized in Supplemental Table 4.
In all HCV-HCC tissues, expression of BCRP and MRP4 expression were below the lower limit of quantification (data not shown, LLOQ shown in Supplemental Table 1). In previous studies on control and HCV-cirrhotic livers, BCRP expression has been close to the LLOQ (control: 14/36 < LLOQ, HCV-cirrhotic: 22/30 < LLOQ) and MRP4 expression has been below the LLOQ. A different instrument was used in this study in which the LLOQ for BCRP was higher. Therefore we cannot draw any reliable conclusions about the difference in BCRP expression.
Expression of each of the hepatobiliary transporters did not correlate with clinical markers of liver function listed in Table 1 (r < 0.3). However, multiple hepatic transporters exhibited significant protein-protein expression correlation in NC and C HCV-HCC tissues [Supplemental Fig. 1; Spearman coefficient (r) ≥ 0.4, P < 0.05].
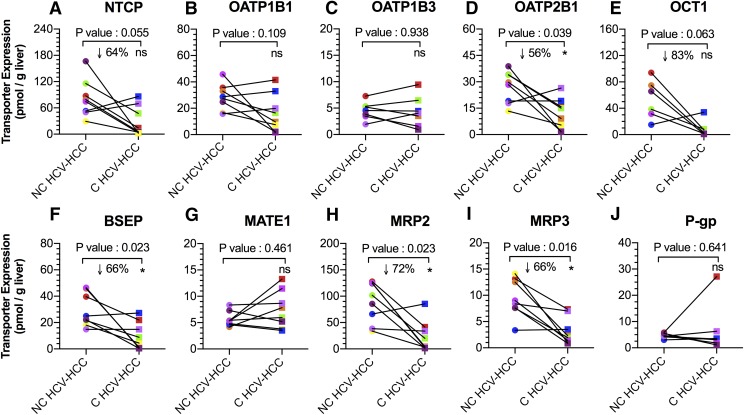
Comparison of Transporter Expression in Matched NC and C HCV-HCC Liver Tissues.
Expression of OATP2B1, BSEP, MRP2, and MRP3 (per gram of liver) in C HCV-HCC tissues was 56%, 66%, 72%, and 66% lower than NC HCV-HCC tissues (P < 0.05; Fig. 4). NTCP and OCT1 expression in C HCV-HCC tissues was also decreased (64% and 83%) relative to NC HCV-HCC tissues, but this difference was found not to be statistically significant (P = 0.06). Expression of the remaining transporters was no different. Transporter expression in some of the matched C HCV-HCC tissues was below the lower limit of quantification (LLOQ shown in Supplemental Table 1). In these circumstances, the lower limit of quantification was used as an estimate of changes in transporter expression.
Fig. 4.
Transport protein expression (per gram of liver) of NTCP, OATP1B1, OATP1B3, OATP2B1, OCT1, BSEP, MATE1, MRP2, MRP3, and P-gp in matched NC and C HCV-HCC liver tissues. Expression of OATP2B1, BSEP, MRP2 and MRP3 were significantly lower in C HCV-HCC tissues than NC HCV-HCC tissues. Expression of NTCP and OCT1 in C tissues also showed a tendency toward significance. *Statistical significance (P < 0.05, Wilcoxon test). Each line connects data from the matched liver samples.
Effect of SLCO1B1 Phenotype on Hepatic OATP1B1 Transport Protein Expression.
Previously we observed genotype-dependent expression of OATP1B1, therefore all HCV-HCC tissues were genotyped for three key nonsynonymous SLCO1B1 SNPs, c.388A>G, c.463C>A, and c.521T>C. HCV-HCC tissues heterozygous for c.463C>A had higher OATP1B1 expression than the reference allele HCV-HCC tissues (Supplemental Fig. 2A; P < 0.01). The remaining genotypes showed no significant difference in OATP1B1 expression; however, the frequency of each allelic variant was low. Individual SNPs of SLCO1B1 show significant linkage disequilibrium (Kalliokoski et al., 2008; Nies et al., 2013; Prasad et al., 2014). Therefore, the samples were grouped based upon SLCO1B1 haplotype (Supplemental Table 5). When normalized to gram of liver tissue, expression of OATP1B1 was significantly greater in heterozygotes with a *14 haplotype (Supplemental Fig. 2B; P < 0.05). The above interpretations of OATP1B1 protein expression were not affected by genotype. When the tissue samples with *14 haplotype were removed the trends remained the same (data not shown).
Discussion
This work, together with our previous reports on the protein expression of major hepatobiliary transporters in noninfected, noncirrhotic (control) and HCV-cirrhotic livers provide a comprehensive analysis of the impact of HCV-infection and HCV-HCC on hepatic drug transporter protein expression. HCV is a progressive fibrotic disease that results in a loss of hepatocyte microvilli (McGuire et al., 1992; Bataller and Brenner, 2005). Evidence for this is the decreased yield of membrane protein as the severity of disease increased (Fig. 1). Control livers yielded the greatest amount of membrane protein, followed by HCV-cirrhotic livers and NC HCV-HCC tissues and then C HCV-HCC tissues.
To compensate for the differences in disease severity and membrane protein yield, transporter expression was normalized to gram of liver. In some instances, this altered the pattern of transporter expression. OATP2B1, MATE1, and MRP3 expression in NC HCV-HCC tissues versus control livers was no different when normalized to milligram of membrane protein but significantly reduced when normalized to gram of liver (Figs. 2 and 3). Adjusting for the reduced membrane protein yield amplified the difference when transporter expression in HCV-HCC tissues was lower (but not significantly different) than control livers. Changes in transporter expression were not an artifact of variation in membrane protein yield because transporter expression in some matched NC versus C HCV-HCC tissues increased, whereas others decreased (Fig. 4).
Paracrine factors (e.g., hepatocyte nuclear factor 3β, interleukin-1β, interleukin-6, and tumor necrosis factor-α) modulate the expression of hepatobiliary drug transporters (Vavricka et al., 2004; Le Vee et al., 2008, 2009). Therefore, chronic inflammation associated with HCV-infection could be the cause of changes in transporter expression. Correspondingly, the broad interindividual variability in transporter expression could result from variability in tissue inflammation. However, the pathophysiological role of HCV-infection as another cause cannot be disregarded. Clinically, the severity of fibrosis in each of our HCV-HCC samples was equal (Ishak scores: 5–6). Liver biopsies from HCV patients have shown fibrosis-dependent increases in paracrine factors and downregulation of NTCP, OATP1B1, and OCT1 mRNA levels, with NTCP expression in the early stages of fibrosis being greater than noninfected, noncirrhotic livers (Nakai et al., 2008; Hanada et al., 2012).
Consistent with the above and our data, decreased OATP1B1, OATP1B3, OATP2B1, and OCT1 mRNA expression and OATP1B3 and OCT1 protein expression has been reported in HCV livers versus noninfected livers (Nakai et al., 2008; Ogasawara et al., 2010; Hanada et al., 2012; Wang et al., 2016). Decreased mRNA and protein expression of NTCP, OATP1B1, OATP1B3, OATP2B1, and OCT1 has also been reported in C HCV-HCC tissue versus surrounding NC HCV-HCC tissue and noninfected livers (Kinoshita and Miyata, 2002; Vavricka et al., 2004; Zollner et al., 2005; Schaeffeler et al., 2011; Heise et al., 2012). Due to an inverse relationship between OATP1B1/1B3 expression and markers of HCC progression (e.g., cytokeratin polypeptided 7 and 19); OATP1B1/1B3 expression and reoccurrence-related deaths in HCV-HCC subjects; and OCT1 expression and HCC patient survival and expression of OATP1B1/B3 and OCT1 have been proposed as biomarkers of HCV-HCC (Schaeffeler et al., 2011; Vasuri et al., 2011). Decreased OATP and NTCP expression in C HCV-HCC tissue relative to NC surrounding tissue correlates with in vivo data. In clinical screening, focal liver lesions are characterized by the appearance of hypointense areas created by decreased uptake of the OATP1B1, OATP1B3, and NTCP substrate Gd-EOB-DTPA (Narita et al., 2009; Tsuboyama et al., 2010).
For the expression of hepatic efflux transporters in HCV-cirrhotic versus noninfected livers, we and others have reported 1) decreased BSEP protein expression (Wang et al., 2016) and fibrosis-dependent decreased BSEP mRNA expression (Hanada et al., 2012), 2) increased MATE1 protein expression (Wang et al., 2016), 3) no change (Ros et al., 2003; Nakai et al., 2008; Kurzawski et al., 2012) or decreased (Ogasawara et al., 2010; Hanada et al., 2012) MRP2 mRNA expression, 4) no change in MRP3 mRNA expression (Ogasawara et al., 2010), and 5) increased P-gp mRNA expression (Ros et al., 2003; Ogasawara et al., 2010; Kurzawski et al., 2012). However, there was no change in BSEP, MRP2, MRP3, and P-gp mRNA and protein expression in C versus surrounding NC HCV-HCC tissue (Zollner et al., 2005; Tsuboyama et al., 2010).
In summary, the majority of our results are consistent with the aforementioned published literature, but there are some discrepancies (e.g., MRP3 protein expression in HCV versus noninfected tissue decreased rather than no change, protein expression of BSEP, MRP2, and MRP3 decreased in C versus surrounding NC HCV-HCC tissue rather than being no different). In the above published studies the noninfected and NC HCV-HCC liver tissues were collected from patients undergoing liver resection. The sampling procedures, disease severity and treatment regimen of patients varied and could account for the observed discrepancies. Additionally, changes in mRNA expression do not always correlate with changes in protein expression (Prasad et al., 2013).
Unlike noncirrhotic livers (r2 < 0.3), a moderate correlation in hepatobiliary transporter expression was observed in NC and C HCV-HCC tissues (r2 > 0.5; Supplemental Fig. 1) and HCV-cirrhotic livers, indicating HCV infection directly or indirectly causes downregulation of multiple transporters (Prasad et al., 2014; Wang et al., 2015, 2016). No correlation was observed between transporter expression and clinical markers of liver function. However, some of the medication taken by HCV-HCC subjects (Supplemental Table 2) have been shown to alter transporter expression in animal and cell models. Therefore, drug-induced changes in transporter expression cannot be discounted.
As there were multiple differences in transporter expression between HCV-cirrhotic and NC HCV-HCC livers, we recommend that NC HCV-HCC transporter expression data (pmol/g liver) should be used in future physiologically based pharmacokinetic modeling to predict systemic and hepatocellular drug concentrations in HCV-HCC patients. Since the volume of C in HCV-HCC is not consistent between HCV-HCC patients, it is much harder to individualize drug therapy based on expression of transporters in C HCV-HCC tissue. Our data suggest that there will be significant differences in local C HCV-HCC versus NC HCV-HCC hepatic tissue drug exposure [either local Cmax or AUC depending on the major route of elimination of the drug (Patilea-Vrana and Unadkat, 2016)]. For example, OCT1 expression in C HCV-HCC is approximately 20% of that in NC HCV-HCC and will therefore result in lower Cmax of an OCT1 substrate (for example cisplatin) in C versus NC HCV-HCC tissue. The difference, if any, in AUC in C versus NC HCV-HCC tissue will depend on whether the drug is cleared via nonhepatic clearance or not (Patilea-Vrana and Unadkat, 2016). Clinically, the volume of tumorous liver tissue in HCV-HCC subjects must be less 1% of the total liver volume for subjects to meet orthotopic liver transplantation criteria (Balogh et al., 2016).
There are some limitations to the above recommendation. First, although there were significant differences in the mean expression of many transporters between HCV cirrhotic and NC or C HCV-HCC livers, the interindividual variability was large. However, this is often the case in diseased population and therefore dosing recommendations are often based on the “average” patient. Unless biomarkers are available for all the quantified transporters, individualizing drug therapy in HCV-HCC patient will be difficult. Second, the total transporter expression in liver tissue quantified may not be functional because there may be differences in trafficking or posttranslational modification caused by the disease.
In conclusion, this is the first report to quantify the abundance of major hepatobiliary drug transporters in HCV-HCC patients using quantitative proteomics. The hepatic transporter protein expression data presented here will be useful in the development of diagnostic HCC imaging agents, drugs for the treatment of HCV-HCC, and prediction of transporter-mediated drug disposition in HCV-HCC patients.
Acknowledgments
We thank Tot Bui Nguyen for technical assistance. Liver resection samples from HCV-HCC subjects were kindly provided by Gilead Sciences, Inc. and Liver Tissue Cell Distribution System.
Abbreviations
- BCRP
breast cancer resistance protein
- BSEP
bile salt export pump
- C
cancerous
- Gd-EOB-DTPA
gadolinium ethoxybenzyl diethylenetriaminepentaacetic acid
- HCC
hepatocellular carcinoma
- HCV
chronic hepatitis C infection
- HCV-HCC
hepatitis C-infected subject with hepatocellular carcinoma
- LC-MS/MS
liquid chromatography tandem mass spectrometry
- LLOQ
lower limit of quantification
- LTCDS
liver tissue cell distribution system
- MATE
multidrug and toxin extrusion protein
- MRP
multidrug resistance-associated protein
- NC
noncancerous
- OATP
organic anion transporting polypeptide
- OCT
organic cation transporter
- P-gp
P-glycoprotein
- SNP
single nucleotide polymorphisms
Authorship Contributions
Participated in research design: Billington, Ray, Salphati, Xiao, Chu, Humphreys, Liao, Lee, Mathias, Hop, Rowbottom, Evers, Lai, Kelly, Prasad, Unadkat.
Conducted Experiments: Billington, Kelly.
Performed Data Analysis: Billington.
Wrote or contributed in the writing of the manuscript: Billington, Ray, Salphati, Xiao, Chu, Humphreys, Liao, Lee, Mathias, Hop, Rowbottom, Evers, Lai, Kelly, Prasad, Unadkat.
Footnotes
This work was supported by UWRAPT through funding from Ardea Biosciences, Biogen, Bristol-Myers Squibb, Genentech, Gilead Sciences, Merck & Co., and Takeda. Liver Tissue Cell Distribution System, who provided us with liver resection samples, is funded by the National Institutes of Health [Contract #HHSN276201200017C].
 This article has supplemental material available at dmd.aspetjournals.org.
This article has supplemental material available at dmd.aspetjournals.org.
References
- Armstrong GL, Wasley A, Simard EP, McQuillan GM, Kuhnert WL, Alter MJ. (2006) The prevalence of hepatitis C virus infection in the United States, 1999 through 2002. Ann Intern Med 144:705–714. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Balogh J, Victor D, III, Asham EH, Burroughs SG, Boktour M, Saharia A, Li X, Ghobrial RM, Monsour HP., Jr (2016) Hepatocellular carcinoma: a review. J Hepatocell Carcinoma 3:41–53. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bataller R, Brenner DA. (2005) Liver fibrosis. J Clin Invest 115:209–218. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blonski W, Reddy KR. (2008) Hepatitis C virus infection and hepatocellular carcinoma. Clin Liver Dis 12:661–674, x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bonaventura A, Montecucco F. (2016) Sofosbuvir/velpatasvir: a promising combination. World J Hepatol 8:785–789. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Colella G, Bottelli R, De Carlis L, Sansalone CV, Rondinara GF, Alberti A, Belli LS, Gelosa F, Iamoni GM, Rampoldi A, et al. (1998) Hepatocellular carcinoma: comparison between liver transplantation, resective surgery, ethanol injection, and chemoembolization. Transpl Int 11 (Suppl 1):S193–S196. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deo AK, Prasad B, Balogh L, Lai Y, Unadkat JD. (2012) Interindividual variability in hepatic expression of the multidrug resistance-associated protein 2 (MRP2/ABCC2): quantification by liquid chromatography/tandem mass spectrometry. Drug Metab Dispos 40:852–855. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Desmet VJ, Gerber M, Hoofnagle JH, Manns M, Scheuer PJ. (1994) Classification of chronic hepatitis: diagnosis, grading and staging. Hepatology 19:1513–1520. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- El-Serag HB. (2012) Epidemiology of viral hepatitis and hepatocellular carcinoma. Gastroenterology 142:1264–1273.e1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fairchild CR, Ivy SP, Kao-Shan CS, Whang-Peng J, Rosen N, Israel MA, Melera PW, Cowan KH, Goldsmith ME. (1987) Isolation of amplified and overexpressed DNA sequences from adriamycin-resistant human breast cancer cells. Cancer Res 47:5141–5148. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fan ST, Lo CM, Liu CL, Lam CM, Yuen WK, Yeung C, Wong J. (1999) Hepatectomy for hepatocellular carcinoma: toward zero hospital deaths. Ann Surg 229:322–330. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fong Y, Sun RL, Jarnagin W, and Blumgart LH (1999) An analysis of 412 cases of hepatocellular carcinoma at a Western center. Ann Surg 229:790–799, discussion 799–800. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- Freeman AJ, Dore GJ, Law MG, Thorpe M, Von Overbeck J, Lloyd AR, Marinos G, Kaldor JM. (2001) Estimating progression to cirrhosis in chronic hepatitis C virus infection. Hepatology 34:809–816. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gnoth MJ, Sandmann S, Engel K, Radtke M. (2010) In vitro to in vivo comparison of the substrate characteristics of sorafenib tosylate toward P-glycoprotein. Drug Metab Dispos 38:1341–1346. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goodgame B, Shaheen NJ, Galanko J, El-Serag HB. (2003) The risk of end stage liver disease and hepatocellular carcinoma among persons infected with hepatitis C virus: publication bias? Am J Gastroenterol 98:2535–2542. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamm B, Staks T, Mühler A, Bollow M, Taupitz M, Frenzel T, Wolf KJ, Weinmann HJ, Lange L. (1995) Phase I clinical evaluation of Gd-EOB-DTPA as a hepatobiliary MR contrast agent: safety, pharmacokinetics, and MR imaging. Radiology 195:785–792. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanada K, Nakai K, Tanaka H, Suzuki F, Kumada H, Ohno Y, Ozawa S, Ogata H. (2012) Effect of nuclear receptor downregulation on hepatic expression of cytochrome P450 and transporters in chronic hepatitis C in association with fibrosis development. Drug Metab Pharmacokinet 27:301–306. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hassan MM, Frome A, Patt YZ, El-Serag HB. (2002) Rising prevalence of hepatitis C virus infection among patients recently diagnosed with hepatocellular carcinoma in the United States. J Clin Gastroenterol 35:266–269. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hatzakis A, Wait S, Bruix J, Buti M, Carballo M, Cavaleri M, Colombo M, Delarocque-Astagneau E, Dusheiko G, Esmat G, et al. (2011) The state of hepatitis B and C in Europe: report from the hepatitis B and C summit conference*. J Viral Hepat 18 (Suppl 1):1–16. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heise M, Lautem A, Knapstein J, Schattenberg JM, Hoppe-Lotichius M, Foltys D, Weiler N, Zimmermann A, Schad A, Gründemann D, et al. (2012) Downregulation of organic cation transporters OCT1 (SLC22A1) and OCT3 (SLC22A3) in human hepatocellular carcinoma and their prognostic significance. BMC Cancer 12:109. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holohan C, Van Schaeybroeck S, Longley DB, Johnston PG. (2013) Cancer drug resistance: an evolving paradigm. Nat Rev Cancer 13:714–726. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Institute of Medicine Committee on the Prevention and Control of Viral Hepatitis Infection (2010) Hepatitis and Liver Cancer: A National Strategy for Prevention and Control of Hepatitis B and C (Colvin HM, Mitchell AE. eds) National Academies Press, US, Washington, DC. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jia J, Puls D, Oswald S, Jedlitschky G, Kühn JP, Weitschies W, Hosten N, Siegmund W, Keiser M. (2014) Characterization of the intestinal and hepatic uptake/efflux transport of the magnetic resonance imaging contrast agent gadolinium-ethoxylbenzyl-diethylenetriamine-pentaacetic acid. Invest Radiol 49:78–86. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnston RA, Rawling T, Chan T, Zhou F, Murray M. (2014) Selective inhibition of human solute carrier transporters by multikinase inhibitors. Drug Metab Dispos 42:1851–1857. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kalliokoski A, Backman JT, Neuvonen PJ, Niemi M. (2008) Effects of the SLCO1B1*1B haplotype on the pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of repaglinide and nateglinide. Pharmacogenet Genomics 18:937–942. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kamiie J, Ohtsuki S, Iwase R, Ohmine K, Katsukura Y, Yanai K, Sekine Y, Uchida Y, Ito S, Terasaki T. (2008) Quantitative atlas of membrane transporter proteins: development and application of a highly sensitive simultaneous LC/MS/MS method combined with novel in-silico peptide selection criteria. Pharm Res 25:1469–1483. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kinoshita M, Miyata M. (2002) Underexpression of mRNA in human hepatocellular carcinoma focusing on eight loci. Hepatology 36:433–438. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kitao A, Zen Y, Matsui O, Gabata T, Kobayashi S, Koda W, Kozaka K, Yoneda N, Yamashita T, Kaneko S, et al. (2010) Hepatocellular carcinoma: signal intensity at gadoxetic acid-enhanced MR Imaging--correlation with molecular transporters and histopathologic features. Radiology 256:817–826. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kurzawski M, Dziedziejko V, Post M, Wójcicki M, Urasińska E, Miętkiewski J, Droździk M. (2012) Expression of genes involved in xenobiotic metabolism and transport in end-stage liver disease: up-regulation of ABCC4 and CYP1B1. Pharmacol Rep 64:927–939. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lagas JS, van Waterschoot RA, Sparidans RW, Wagenaar E, Beijnen JH, Schinkel AH. (2010) Breast cancer resistance protein and P-glycoprotein limit sorafenib brain accumulation. Mol Cancer Ther 9:319–326. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Le Vee M, Gripon P, Stieger B, Fardel O. (2008) Down-regulation of organic anion transporter expression in human hepatocytes exposed to the proinflammatory cytokine interleukin 1beta. Drug Metab Dispos 36:217–222. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Le Vee M, Lecureur V, Stieger B, Fardel O. (2009) Regulation of drug transporter expression in human hepatocytes exposed to the proinflammatory cytokines tumor necrosis factor-alpha or interleukin-6. Drug Metab Dispos 37:685–693. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leonhardt M, Keiser M, Oswald S, Kühn J, Jia J, Grube M, Kroemer HK, Siegmund W, Weitschies W. (2010) Hepatic uptake of the magnetic resonance imaging contrast agent Gd-EOB-DTPA: role of human organic anion transporters. Drug Metab Dispos 38:1024–1028. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lok AS, Seeff LB, Morgan TR, di Bisceglie AM, Sterling RK, Curto TM, Everson GT, Lindsay KL, Lee WM, Bonkovsky HL, et al. HALT-C Trial Group (2009) Incidence of hepatocellular carcinoma and associated risk factors in hepatitis C-related advanced liver disease. Gastroenterology 136:138–148. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lozano R, Naghavi M, Foreman K, Lim S, Shibuya K, Aboyans V, Abraham J, Adair T, Aggarwal R, Ahn SY, et al. (2012) Global and regional mortality from 235 causes of death for 20 age groups in 1990 and 2010: a systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2010. Lancet 380:2095–2128. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McGuire RF, Bissell DM, Boyles J, Roll FJ. (1992) Role of extracellular matrix in regulating fenestrations of sinusoidal endothelial cells isolated from normal rat liver. Hepatology 15:989–997. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morgan RL, Baack B, Smith BD, Yartel A, Pitasi M, Falck-Ytter Y. (2013) Eradication of hepatitis C virus infection and the development of hepatocellular carcinoma: a meta-analysis of observational studies. Ann Intern Med 158:329–337. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakai K, Tanaka H, Hanada K, Ogata H, Suzuki F, Kumada H, Miyajima A, Ishida S, Sunouchi M, Habano W, et al. (2008) Decreased expression of cytochromes P450 1A2, 2E1, and 3A4 and drug transporters Na+-taurocholate-cotransporting polypeptide, organic cation transporter 1, and organic anion-transporting peptide-C correlates with the progression of liver fibrosis in chronic hepatitis C patients. Drug Metab Dispos 36:1786–1793. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Narita M, Hatano E, Arizono S, Miyagawa-Hayashino A, Isoda H, Kitamura K, Taura K, Yasuchika K, Nitta T, Ikai I, et al. (2009) Expression of OATP1B3 determines uptake of Gd-EOB-DTPA in hepatocellular carcinoma. J Gastroenterol 44:793–798. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nies AT, Niemi M, Burk O, Winter S, Zanger UM, Stieger B, Schwab M, Schaeffeler E. (2013) Genetics is a major determinant of expression of the human hepatic uptake transporter OATP1B1, but not of OATP1B3 and OATP2B1. Genome Med 5:1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ogasawara K, Terada T, Katsura T, Hatano E, Ikai I, Yamaoka Y, Inui K. (2010) Hepatitis C virus-related cirrhosis is a major determinant of the expression levels of hepatic drug transporters. Drug Metab Pharmacokinet 25:190–199. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Patilea-Vrana G, Unadkat JD. (2016) Transport vs. metabolism: what determines the pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of drugs? insights from the extended clearance model. Clin Pharmacol Ther 100:413–418. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prasad B, Evers R, Gupta A, Hop CE, Salphati L, Shukla S, Ambudkar SV, Unadkat JD. (2014) Interindividual variability in hepatic organic anion-transporting polypeptides and P-glycoprotein (ABCB1) protein expression: quantification by liquid chromatography tandem mass spectroscopy and influence of genotype, age, and sex. Drug Metab Dispos 42:78–88. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prasad B, Gaedigk A, Vrana M, Gaedigk R, Leeder JS, Salphati L, Chu X, Xiao G, Hop C, Evers R, et al. (2016) Ontogeny of hepatic drug transporters as quantified by LC-MS/MS proteomics. Clin Pharmacol Ther 100:362–370. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prasad B, Lai Y, Lin Y, Unadkat JD. (2013) Interindividual variability in the hepatic expression of the human breast cancer resistance protein (BCRP/ABCG2): effect of age, sex, and genotype. J Pharm Sci 102:787–793. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prasad B, Unadkat JD. (2014) Optimized approaches for quantification of drug transporters in tissues and cells by MRM proteomics. AAPS J 16:634–648. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rantala M, van de Laar MJ. (2008) Surveillance and epidemiology of hepatitis B and C in Europe - a review. Euro Surveill 13:18880. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ros JE, Libbrecht L, Geuken M, Jansen PL, Roskams TA. (2003) High expression of MDR1, MRP1, and MRP3 in the hepatic progenitor cell compartment and hepatocytes in severe human liver disease. J Pathol 200:553–560. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saeed M, Kadioglu O, Khalid H, Sugimoto Y, Efferth T. (2015) Activity of the dietary flavonoid, apigenin, against multidrug-resistant tumor cells as determined by pharmacogenomics and molecular docking. J Nutr Biochem 26:44–56. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schaeffeler E, Hellerbrand C, Nies AT, Winter S, Kruck S, Hofmann U, van der Kuip H, Zanger UM, Koepsell H, Schwab M. (2011) DNA methylation is associated with downregulation of the organic cation transporter OCT1 (SLC22A1) in human hepatocellular carcinoma. Genome Med 3:82. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schuhmann-Giampieri G, Schmitt-Willich H, Press WR, Negishi C, Weinmann HJ, Speck U. (1992) Preclinical evaluation of Gd-EOB-DTPA as a contrast agent in MR imaging of the hepatobiliary system. Radiology 183:59–64. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Swift B, Nebot N, Lee JK, Han T, Proctor WR, Thakker DR, Lang D, Radtke M, Gnoth MJ, Brouwer KL. (2013) Sorafenib hepatobiliary disposition: mechanisms of hepatic uptake and disposition of generated metabolites. Drug Metab Dispos 41:1179–1186. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tariq M, Alam MA, Singh AT, Panda AK, Talegaonkar S. (2016) Surface decorated nanoparticles as surrogate carriers for improved transport and absorption of epirubicin across the gastrointestinal tract: pharmacokinetic and pharmacodynamic investigations. Int J Pharm 501:18–31. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Terrault NA, Zeuzem S, Di Bisceglie AM, Lim JK, Pockros PJ, Frazier LM, Kuo A, Lok AS, Shiffman ML, Ben Ari Z, et al. HCV-TARGET Study Group (2016) Effectiveness of ledipasvir-sofosbuvir combination in patients with hepatitis C virus infection and factors associated with sustained virologic response. Gastroenterology 151:1131–1140.e5. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsuboyama T, Onishi H, Kim T, Akita H, Hori M, Tatsumi M, Nakamoto A, Nagano H, Matsuura N, Wakasa K, et al. (2010) Hepatocellular carcinoma: hepatocyte-selective enhancement at gadoxetic acid-enhanced MR imaging--correlation with expression of sinusoidal and canalicular transporters and bile accumulation. Radiology 255:824–833. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vasuri F, Golfieri R, Fiorentino M, Capizzi E, Renzulli M, Pinna AD, Grigioni WF, D’Errico-Grigioni A. (2011) OATP 1B1/1B3 expression in hepatocellular carcinomas treated with orthotopic liver transplantation. Virchows Arch 459:141–146. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vavricka SR, Jung D, Fried M, Grützner U, Meier PJ, Kullak-Ublick GA. (2004) The human organic anion transporting polypeptide 8 (SLCO1B3) gene is transcriptionally repressed by hepatocyte nuclear factor 3beta in hepatocellular carcinoma. J Hepatol 40:212–218. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang L, Collins C, Kelly EJ, Chu X, Ray AS, Salphati L, Xiao G, Lee C, Lai Y, Liao M, et al. (2016) Transporter expression in liver tissue from subjects with alcoholic or hepatitis C cirrhosis quantified by targeted quantitative proteomics. Drug Metab Dispos 44:1752–1758. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang L, Prasad B, Salphati L, Chu X, Gupta A, Hop CE, Evers R, Unadkat JD. (2015) Interspecies variability in expression of hepatobiliary transporters across human, dog, monkey, and rat as determined by quantitative proteomics. Drug Metab Dispos 43:367–374. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wei Y, Ma Y, Zhao Q, Ren Z, Li Y, Hou T, Peng H. (2012) New use for an old drug: inhibiting ABCG2 with sorafenib. Mol Cancer Ther 11:1693–1702. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- World Health Organization (2017) Global Hepatitis Report 2017, Geneva, Switzerland: World Health Organization. [Google Scholar]
- Yonezawa A, Masuda S, Yokoo S, Katsura T, Inui K. (2006) Cisplatin and oxaliplatin, but not carboplatin and nedaplatin, are substrates for human organic cation transporters (SLC22A1-3 and multidrug and toxin extrusion family). J Pharmacol Exp Ther 319:879–886. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zimmerman EI, Hu S, Roberts JL, Gibson AA, Orwick SJ, Li L, Sparreboom A, Baker SD. (2013) Contribution of OATP1B1 and OATP1B3 to the disposition of sorafenib and sorafenib-glucuronide. Clin Cancer Res 19:1458–1466. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zollner G, Wagner M, Fickert P, Silbert D, Fuchsbichler A, Zatloukal K, Denk H, Trauner M. (2005) Hepatobiliary transporter expression in human hepatocellular carcinoma. Liver Int 25:367–379. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]