Abstract
IMPORTANCE
The effects of position on retinal and choroidal structure are absent from the literature yet may provide insights into disease states such as age-related macular degeneration (AMD).
OBJECTIVE
To evaluate the effect of postural change on retinal and choroidal structures in healthy volunteers and patients with non-neovascular AMD.
DESIGN, SETTING, AND PARTICIPANTS
Prospective observational case series at an academic tertiary care retina service from September 2013 to April 2014 involving 4 unaffected volunteers (8 eyes) and 7 patients (8 eyes) with intermediate AMD. Healthy volunteers selected for the study had no evidence of ocular disease. Patients with AMD were required to have at least 10 intermediate-sized drusen.
EXPOSURES
Spectral-domain optical coherence tomography with enhanced depth imaging in upright (sitting) and supine positions. Stable imaging was achieved using a rotating adjustable mechanical arm that we constructed to allow the optical coherence tomography transducer to rotate 90°. The Iowa Reference Algorithms were used to quantify choroid and choriocapillaris thicknesses.
MAIN OUTCOMES AND MEASURES
Changes in sitting and supine position central macular thickness (in micrometers), total macular volume (in cubic millimeters), choroidal thickness (in micrometers), and choriocapillaris-equivalent thickness (CCET, in micrometers).
RESULTS
Choriocapillaris-equivalent thickness was thinner in healthy participants (9.89 μm; range, 7.15-12.5 μm) compared with patients with intermediate AMD (16.73 μm; range, 10.31-27.38 μm) (P = .02); there was no difference in overall choroidal thickness between the 2 groups (P = .38). There was a 15% CCET reduction among healthy participants when transitioning from a sitting (9.89 μm) to supine (8.4 μm; range, 6.92-10.7 μm) position (P = .02) vs a CCET reduction of 11.1% from sitting (16.73 μm) to supine (14.88 μm; range, 8.76-20.8 μm) positioning (P = .10) in patients with intermediate AMD.
CONCLUSIONS AND RELEVANCE
Intermediate AMD appears to be associated with an increase in CCET and with a lack of positional responses that are observed in the CCET of normal eyes. Our results suggest that although outer portions of the choroid do not appear to be responsive to modest positional or hydrostatic pressure, the choriocapillaris capacity is, and this is measurable in vivo. Whether this physiologic deviation that occurs in AMD is related to atrophy, inflammation, or changes in autoregulatory factors or growth factors remains to be determined.
Age-related macular degeneration (AMD) is the leading cause of irreversible blindness in industrialized nations. Etiologically, it is a multifactorial disease related to age, genetics, and environmental factors (eg, smoking and light exposure), with reduced function of the retinal pigment epithelium (RPE) and Bruch membrane (BM), resulting in retinal atrophy and/or choroidal neovascularization.1-3 The choroid also plays an important role in AMD pathogenesis, as significant changes in choroidal vascular dynamics and choriocapillaris (CC) structure have been observed in eyes with AMD.4-6 Some investigators have hypothesized that the choroid has a primary role in AMD and pathogenesis is related to localized choroidal ischemia underlying atrophic and inflammatory changes in the RPE-BM complex.7-9
In the normal physiologic state, the integrity of the retina and choroid relies on adequate blood perfusion from the central retinal artery and CC; the avascular region of the fovea relies entirely on blood flow in the subfoveal choroidal vasculature and CC. Understanding aspects of choroidal blood flow and CC structure, which may be central to understanding diseases such as AMD, may be investigated by assessing changes in retinal and choroidal structure in response to physiologic challenges such as increased intraocular pressure, lowered systemic supply, or by more subtle clinical interventions such as body positioning. Although the effects of position have been previously evaluated in vivo, we have been unable to identify another study examining the effects of postural changes on the choroid in AMD.10,11 Laser Doppler flowmetry had been used in studies assessing the effect of postural change on choroidal blood flow10,11 but these lack the ability to localize hemodynamic changes to specific choroidal strata. Postmortem anatomical histological studies provide information regarding vascular turnover and ghost vessels in AMD but cannot illuminate our understanding about perfusion. With advances in spectral-domain optical coherence tomography (OCT) and enhanced depth imaging,12,13 it is possible to image retinal and choroidal structures in vivo and in greater detail. Additionally, the development of robust, fully 3-dimensional algorithms, such as the Iowa Reference Algorithms, provide an objective measure of layer segmentation.14-16
The purpose of this study was to determine whether differences in the choroid and CC can be elicited by positional changes by evaluating a group of patients with intermediate AMD and healthy control participants under these conditions.
Methods
Patients
Patients with intermediate AMD were identified from our retina clinic, University of Iowa Retina Clinic (Clinic C). Inclusion criteria were AMD diagnosis after age 50 years, ability to provide informed consent, media clarity, and intermediate AMD based on the Age-Related Eye Disease Study grading system.17 Exclusion criteria included previous diagnosis of exudative neovascular AMD, retinal vascular disease, uveitis, high myopia (≥8.00 D), or other acquired macular disease; previous vitreoretinal surgery; previous ocular or orbital surgery other than uncomplicated cataract extraction; previous treatment with intravitreal injections; significant cataract-limiting image acquisition; current or former smoker; and inability to provide informed consent. Volunteer participants were screened for ocular or systemic disease. Patients with AMD had detailed medical and ophthalmic history recorded and complete examinations including best-corrected visual acuity, intraocular pressure, slitlamp biomicroscopy, and dilated fundus examination. All individuals provided signed informed consent. Prior to initiating the study, permission was obtained from the University of Iowa research ethics board. This study full adhered to the Declaration of Helsinki and all federal and state laws. The study was conducted from September 2013 to April 2014.
OCT Imaging, Segmentation, and Positioning Protocols
Optical coherence tomographic imaging was performed with the Spectralis Heidelberg spectral-domain OCT (Heidelberg Engineering). In the sitting position, OCT was acquired in the traditional manner. For supine positioning, a rotating adjustable mechanical arm was engineered and specifically constructed for this study to allow the Spectralis OCT to rotate 90° (perpendicular, rather than parallel, to the ground) and image individuals in the supine position (Figure 1). All images were reviewed in real time to ensure they were of adequate quality and all scans were performed by an experienced certified ophthalmic photographer (D.B.C.). Enhanced depth imaging was used to capture 30 × 30 volume scans, with the averaging set at 2 frames per scan line. These were 768 × 496 high-speed scans, with 61 A-scans per volume cube; all scans were centered on the fovea.
Figure 1. Custom-Built Optical Coherence Tomography for Sitting and Supine Measurements.
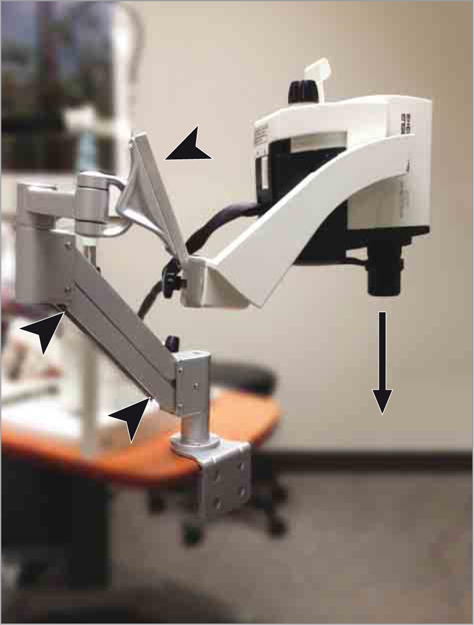
A rotating adjustable mechanical arm (arrowheads) was engineered and constructed to allow for the Spectralis optical coherence tomography to rotate 90° (perpendicular, rather than parallel, to the ground) and image a patient in the supine position (arrow).
The OCT volumes were automatically segmented using the Iowa Reference Algorithms. The first stage produces intraretinal surfaces including the BM (Figure 2).15,16 The choroid is then identified immediately beneath the BM, and a sufficiently large subvolume containing the choroid layer was selected as the target region to apply choroidal segmentation. A graph-based method was used to segment the choroidal surfaces (Figure 3) and a vertical intensity gradient was thus used to obtain the cost function, and smoothness constraints were adopted between neighboring A-scans.14 The choroidal boundaries were then segmented by graph optimization via solving the minimum s-t cut problem in the geometric graph used.14
Figure 2. Iowa Reference Algorithms.
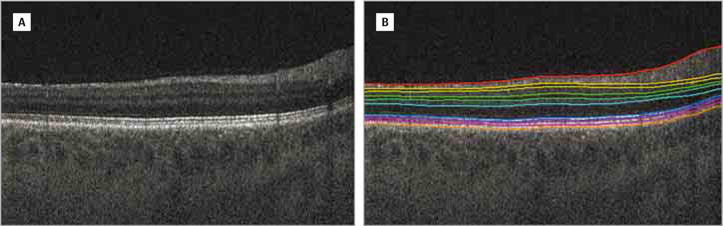
A, Original B-scan. B, Original B-scan with 11 intraretinal surfaces segmented.
Figure 3. Choroidal Layer Segmentation.
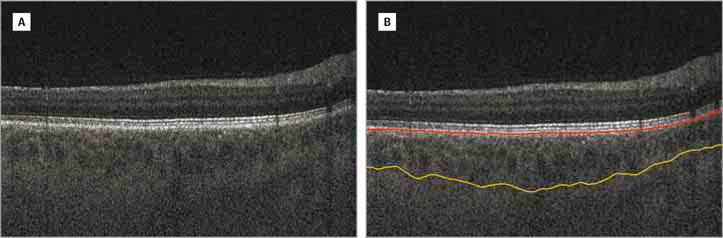
A, Original B-scan. B, Original B-scan with choroidal boundaries segmented. The red line indicates the Bruch membrane and yellow line, choroidal posterior boundary.
Next, the choroidal vascular segmentation was performed automatically, with a surface fitted over the superior edge of the choroidal vasculature. The CC cannot be resolved by standard clinical spectral-domain OCT; therefore, by using the BM as the top reference surface and the top of the vasculature as the bottom reference surface, the CC-equivalent thickness (CCET) was defined as the distance between these surfaces (Figure 4). We previously presented and validated this method with excellent reproducibility.14 Repeat scans with this method have previously shown an excellent coefficient of variation of 8.0% (calculated using the root mean square approach),14 making it ideal for assays with multiple testing such as our experimental design with both sitting and supine OCT imaging.
Figure 4. Choroid and Choriocapillaris Segmentation in a Patient With Intermediate Age-Related Macular Degeneration.
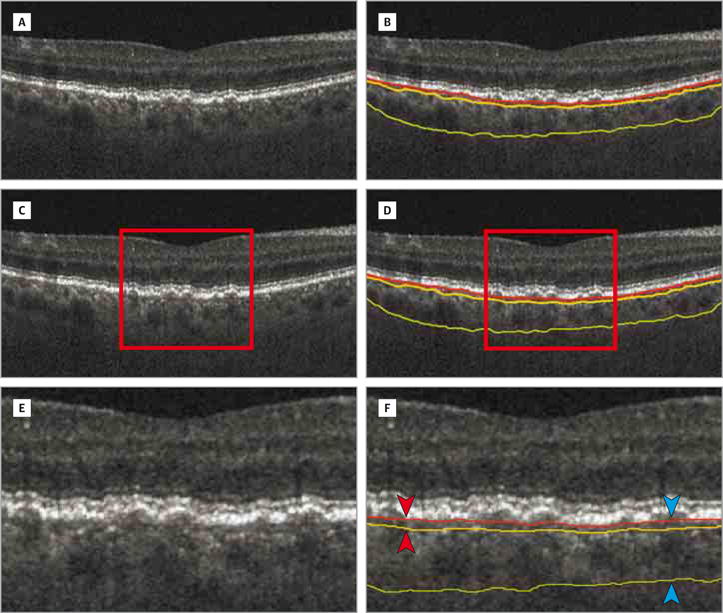
A, B-scan. B, B-scan with boundaries. B-scan with choriocapillaris-equivalent thickness (C and D). Enlarged views of parts C and D demonstrating choroidal vascular segmentation using the Bruch membrane as the top reference surface and the top of the choroidal vasculature as the bottom reference surface (E and F). F, The choriocapillaris-equivalent thickness is defined as the distance between the surfaces (red arrowheads). The choroidal thickness is defined as the distance between the Bruch membrane and choroidal posterior boundary (blue arrowheads). The red line indicates the Bruch membrane; yellow line, choroidal anterior boundary; and green line, choroidal posterior boundary.
Individuals were seated in the traditional upright position with their head stabilized for baseline enhanced depth imaging–OCT scans. Although blood pressure was not measured, individuals were then positioned supine for 10 minutes to allow for equilibration to hydrostatic pressure and any accommodation orthostatic regulatory mechanisms. The motion from the sitting to the supine position took approximately 30 seconds or less. During these 10 minutes of rest, the OCT adjustable arm was set to allow for supine OCT scanning. Supine OCT imaging was then performed in real time to ensure the capture of high-quality scans. No measurements were performed from the supine to sitting positions. Central macular thickness (CMT, in micrometers), total macular volume (TMV, in cubic millimeters), choroidal thickness (CT, in micrometers), and CCET (in micrometers) parameters were calculated as the average of the thickness for all A-scans in the macula.
Statistics
Mean and percentage changes in CMT, TMV, choroidal thickness, and CCET were assessed for significance using the t test; P < .05 was considered significant. No correction was made for multiple measures.
Results
A total of 16 eyes in 11 individuals were studied: 8 eyes in 4 healthy volunteers and 8 eyes in 7 patients with intermediate AMD. The mean (SD) age of volunteers was 54.0 (5.07) years (range, 46-58 years) while the mean (SD) age of patients with AMD was 74.3 (3.96) years (range, 69-81 years) (P = .01). Baseline sitting retinal and choroidal OCT characteristics for healthy participants and patients with AMD are summarized in the eTable in the Supplement. Across all measurements, healthy participants had thicker CMT (321 μm) compared with patients with intermediate AMD (290 μm) (P = .008) but there was no difference in TMV (P = .40) between the 2 groups. With respect to CCET, healthy participants had a thinner CCET measurement (9.89 μm; range, 7.15-12.5 μm) compared with patients with AMD (16.73 μm; range, 10.31-27.38 μm) (P = .02). There was no difference in CT between the 2 groups (P = .38).
On completing baseline (sitting) OCT imaging, all study participants were positioned in a supine manner as just described. Comparison between supine and sitting imaging is summarized in the Table and the eFigure in the Supplement. Overall, for both healthy participants and patients with AMD, there was no difference in CMT, TMV, and CT between the upright and supine positions. However, with respect to CCET, there was a 15% reduction in thickness from sitting (9.89 μm) to supine (8.4 μm; range, 6.92-10.7 μm) positions in healthy volunteers (P = .02). In patients with AMD, sitting (16.73 μm) to supine (14.88 μm; range, 8.76-20.8 μm) positioning produced a reduction in CCET of 11.1% (P = .10). No study participants experienced any adverse events or complications during the study and there were no mechanical or reliability issues with the adjustable arm during OCT imaging.
Table.
Retinal and Choroidal Optical Coherence Tomography Characteristics for Healthy Volunteers and Patients With Intermediate Dry AMD in Sitting and Supine Positions
| Characteristic | Mean (SD) [Range] | Difference, %a | P Value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sitting | Supine | |||
| Healthy (n = 8) | ||||
| CMT, μm | 321 (9) [309–334] |
325 (14) [311–353] |
+1.4 | .20 |
| TMV, mm3 | 8.64(0.4) [7.98–9.02] |
8.62 (0.3) [8.04–8.95] |
−0.2 | .50 |
| CT, μm | 205.97 (28.74) [161.75–251.38] |
203.21 (30.52) [153.37–249.63] |
−1.3 | .10 |
| CCET, μm | 9.89 (1.69) [7.15–12.5] |
8.4 (1.3) [6.92–10.7] |
−15.0 | .02 |
| AMD (n = 8) | ||||
| CMT, μm | 290 (27) [229–311] |
298 (27) [229–329] |
+2.6 | .20 |
| TMV,mm3 | 8.32 (0.77) [6.58–9.15] |
8.39 (0.79) [6.59–9.07] |
+0.8 | .50 |
| CT, μm | 180.38 (58.76) [124.28–306.78] |
182.24 (60.0) [126.56–314.51] |
+1.0 | .20 |
| CCET, μm | 16.73 (6.26) [10.31–27.38] |
14.88 (4.19) [8.76–20.8] |
−11.1 | .10 |
Abbreviations: AMD, age-related macular degeneration; CCET, choriocapillaris-equivalent thickness; CMT, central macular thickness; CT, choroidal thickness; TMV, total macular volume.
Percentage difference between sitting and supine positions; positive and negative indicate an increase and decrease, respectively.
Discussion
First, our results show that CCET is greater in patients with intermediate AMD compared with healthy volunteers. Second, the CC displays a greater degree of thinning in healthy participants when compared with patients with AMD in response to the positional change from sitting to supine.
Our findings are consistent with previous histological evidence showing that submacular CC thickness and the density of choroidal blood vessels are increased in eyes with early AMD compared with eyes without AMD.6 In addition, ex vivo capillary diameter in the macular CC area is larger in the eyes of patients with AMD compared with eyes without AMD.6 The Iowa Reference Algorithms do not distinguish sub-RPE deposits or BM thickening from the vascular CC, although they do exclude deposits or thickening internal to the BM hyperreflectivity, as the CCET is measured as the distance between BM to the upper surface of the choroidal vasculature.14-16 Bruch membrane thickness increases with aging5 and patients with AMD have increased thickness of the RPE-BM complex due to drusen and other sub-RPE deposits, which are key pathologic landmarks in AMD.9 This distinction is significant as incompressible deposits may reduce dynamic thickness changes resulting from vascular compliance.
Two prior studies have shown that CC thickness in patients is reduced in AMD compared with healthy individuals, which are in contradiction to our findings.5,18 However, these studies evaluated eyes with AMD much more severe than in our study, that is, eyes that contained geographic atrophy and disciform scarring that are characterized by extensive RPE loss.5 Retinal pigment epithelium loss and CC atrophy are known to be tightly coupled.19,20 Sohn and colleagues21 have shown that geographic atrophy is also associated with histological choroidal thinning. Therefore, we believe that the decrease in CC thickness, as observed in prior studies, is associated with more advanced AMD. Our entry criteria included the presence of intermediate AMD; based on the Age-Related Eye Disease Study, this category excludes geographic atrophy, choroidal neovascularization, or end-stage disciform scarring.17
We were particularly cautious when considering our results in comparison with ex vivo histological studies of AMD CC thickness because of potential vascular size or processing artifacts post mortem. However, one interpretation of our results is that lesser advanced forms of AMD may be associated with an increase in CC thickness due to the formation of new capillaries within the CC (ie, intrachoroidal neovascularization).6 Intrachoroidal neovascularization differs from the more clinically familiar (extra) choroidal neovascularization found in exudative AMD in which membranous new choroidal vessels extend beyond the choroid and into sub-RPE, subretinal, or intraretinal potential spaces. Intrachoroidal neovascularization is thought to occur parallel to, but subjacent to, the BM and occurs in response to anoxia.6
The dynamic response of the CCET to position is provocative and may be a potential clinical test of CC capacity or compliance. The apparent reduction of this response in patients with intermediate AMD compared with healthy participants supports our contention that this behavior may be related to vascular elasticity or compliance and is likely related to choroidal blood flow adjustments associated with postural changes.
Previous physiologic studies have shown that perturbations in body position initiate a passive response of the choroidal circulation.10 The aggregate choroidal vasculature (represented herein as CT) has not been shown to have an intrinsic ability to regulate thickness/blood flow during positional changes11; however, there may be situations by which a not-yet-identified mechanism increases choroidal blood flow when an eye is in a lower or supine position.10,22,23 These findings would be consistent with our hypothesis for the changes in CCET with positioning that we found in healthy individuals. In the presence of such a responsive or autoregulatory mechanism, a drop in perfusion and choroidal blood flow might be anticipated in the supine position; however, what is observed is an increase in choroidal blood flow, which is consistent with hydrostatic intravascular changes.10 The tilting of the body from standing to the supine position increases choroidal blood flow by an average of 11%; of which, this increase is mainly due to an 8% change in measured velocity.10 One way to increase blood flow would be to increase perfusion pressure, which may be mediated by CC constriction; this in turn would structurally manifest as a decrease in CCET.
Another possibility for the differences observed between healthy participants and patients with AMD is related to the presence of ghost vessels. We had previously shown that there are more ghost vessels in early AMD9; consequently, this may contribute to the increased thickness observed in our CCET segmentation measurements. These findings support the concept that microvascular changes are related to the pathogenesis of AMD and suggest that vascular endothelial cell loss occurs in association with sub-RPE deposit formation.9 This would cause an increase in CCET and a decrease in the intrinsic compliance of the CC, both of which we observed in our study. The increased density in ghost vessels would limit the ability of the CC to constrict and compress in the supine position and limit the overall perfusion in the choroid. Whether this is a global effect in the choroid or there exists regional differences related to areas of drusen accumulation or RPE atrophy remains to be seen.
An inability or incapacity to regulate choroidal blood flow may be related to AMD ischemic pathogenesis via loss of CC elasticity or compliance. Alternatively, the CC may already have reached its maximum carrying capacity and be unresponsive to thickness changes in intermediate AMD. Individuals who are homozygous for Y402H of complement factor H have been shown to develop abnormal choroidal blood flow decades before developing potential AMD; such changes have been hypothesized to be due to reduced vascular elasticity.24,25 Y402H (rs1061170) in complement factor H is a common polymorphism in the complement factor H gene, which is associated with a high risk for AMD.26 Age-related macular degeneration risk-associated complement factor H mutations are thought to be mediated via innate immunity pathways associated with complement system dysfunction, which may directly or indirectly affect choroidal vasculature. Indeed, donor eyes with the high-risk genotype have statistically increased levels of activated complement in the CC. Experimental in vivo human studies have shown that patients with AMD have a reduction in fluid-to-tissue ratio when compared with normal eyes, which may indicate choroidal ischemia early on in the disease pathogenesis.1
We showed changes in CCET in response of sitting to supine positioning, which may be related to reduced CC elasticity or compliance. Although this is a small difference, the value of documenting this observed effect warrants further meaningful investigation into this novel finding. In fact, several studies have identified blood flow as a predictor of visual loss, but the precise pathophysiological link between blood flow remains unclear.27-29 It has been shown that patients with diabetic retinopathy have a thicker subfoveal choroid, although this is not the case in diabetic macular edema.30,31 Other studies have shown increased CT in disease, such as central serous chorioretinopathy32,33 and polypoidal choroidal vasculopathy,34 and we wonder if these conditions, with intrinsic choroidal abnormalities, may in some way be related to CC elasticity or compliance. Our results showed a decrease in CMT in early AMD with no change in CT, which corroborates earlier evidence.35 The reduction in CMT in early AMD has been attributed to photoreceptor degeneration and outer retina loss, which may be possibly related to collections of drusen or sub-RPE deposits.36 We did not specifically target drusen in our study and did not observe any regional defects.
We are cognizant of the weaknesses and limitations of our pilot trial. First, there was a difference in age between healthy participants and patients with AMD. What portion of the CC or CCET changes may have been due to age and disease status cannot be fully understood from this pilot study. Although volunteers were on average above the age of earliest AMD diagnosis, they were also approximately 20 years younger than patients with AMD (54.0 vs 74.3 years; P = .01). Further evaluation of larger and more elderly populations (especially control volunteers) will be needed to confirm our findings. Second, our study was limited by a small sample size, which restricted our statistical power and increased the variability of outcome. We are currently undertaking larger studies to further explore the concepts elucidated herein. Nonetheless, the robust statistical significance in our pilot results is supportive of the notion that meaningful differences in response to posture exist and is encouraging for establishing the reproducibility of our findings. Third, although we are confident in our segmentation approach and its reproducibility,14 we acknowledge that errors may occur in segmentation that overestimated or underestimated CCET and CT, resulting in imprecise extrapolations. As previously mentioned, a larger validation study is needed to confirm our current observations.
Conclusions
In summary, we demonstrated that an increase in CCET in patients with AMD may be driven by the mechanism of increased vascular endothelial growth factor, intrachoroidal neo-vascularization, and ghost vessel accumulation. Moreover, we presented a novel finding that, in response to changes in CCET from the sitting to supine positions, there is compression of the CC that is blunted in patients with intermediate AMD. The latter findings may illustrate the concept of CC elasticity or compliance related to pathophysiological changes in choroidal blood flow.
Supplementary Material
Acknowledgments
Funding/Support: Dr Sonka has received grants from the National Institutes of Health. Dr Abràmoff has received grants from the National Institutes of Health and the Arnold and Mabel Beckman Initiative for Macular Research, as well as other support from the American Diabetes Association and the University of Iowa.
Role of the Funder/Sponsor: The funders had no role in the design and conduct of the study; collection, management, analysis, and interpretation of the data; preparation, review, or approval of the manuscript; and decision to submit the manuscript for publication.
Footnotes
Author Contributions: Dr Almeida had full access to all of the data in the study and takes responsibility for the integrity of the data and the accuracy of the data analysis.
Study concept and design: Almeida, Chin, Mullins, Folk, Abràmoff, Russell.
Acquisition, analysis, or interpretation of data: All authors.
Drafting of the manuscript: Almeida, Chin, Abràmoff.
Critical revision of the manuscript for important intellectual content: Almeida, Zhang, Mullins, Kucukevcilioglu, Critser, Sonka, Stone, Folk, Abràmoff, Russell.
Statistical analysis: Almeida, Zhang.
Obtained funding: Mullins, Sonka, Abràmoff, Russell.
Administrative, technical, or material support: Almeida, Zhang, Chin, Kucukevcilioglu, Critser, Sonka, Stone, Russell.
Study supervision: Almeida, Mullins, Sonka, Folk, Abràmoff, Russell.
Conflict of Interest Disclosures: All authors have completed and submitted the ICMJE Form for Disclosure of Potential Conflicts of Interest. Dr Mullins reported receiving honorarium from Imagen Bio outside of this study. Dr Sonka holds US patents related to image segmentation in N-dimensional space. Dr Abràmoff reported receiving support from IDx LLC. Dr Abràmoff also has patents for image segmentation in N-dimensional space and patents licensed to IDx LLC. No other disclosures were reported.
Supplemental content at jamaophthalmology.com
Contributor Information
David R. P. Almeida, Vitreoretinal Service, Department of Ophthalmology and Visual Sciences, University of Iowa Hospitals and Clinics, Iowa City.
Li Zhang, The Stephen A. Wynn Institute for Vision Research, University of Iowa, Iowa City.
Eric K. Chin, Vitreoretinal Service, Department of Ophthalmology and Visual Sciences, University of Iowa Hospitals and Clinics, Iowa City.
Robert F. Mullins, The Stephen A. Wynn Institute for Vision Research, University of Iowa, Iowa City.
Murat Kucukevcilioglu, The Stephen A. Wynn Institute for Vision Research, University of Iowa, Iowa City.
D. Brice Critser, Vitreoretinal Service, Department of Ophthalmology and Visual Sciences, University of Iowa Hospitals and Clinics, Iowa City.
Milan Sonka, The Stephen A. Wynn Institute for Vision Research, University of Iowa, Iowa City.
Edwin M. Stone, Vitreoretinal Service, Department of Ophthalmology and Visual Sciences, University of Iowa Hospitals and Clinics, Iowa City; The Stephen A. Wynn Institute for Vision Research, University of Iowa, Iowa City.
James C. Folk, Vitreoretinal Service, Department of Ophthalmology and Visual Sciences, University of Iowa Hospitals and Clinics, Iowa City.
Michael D. Abràmoff, Vitreoretinal Service, Department of Ophthalmology and Visual Sciences, University of Iowa Hospitals and Clinics, Iowa City; The Stephen A. Wynn Institute for Vision Research, University of Iowa, Iowa City; Iowa Institute for Biomedical Imaging, Iowa City; Veterns Affairs Medical Center, Iowa City, Iowa.
Stephen R. Russell, Vitreoretinal Service, Department of Ophthalmology and Visual Sciences, University of Iowa Hospitals and Clinics, Iowa City; The Stephen A. Wynn Institute for Vision Research, University of Iowa, Iowa City.
References
- 1.Coleman DJ, Silverman RH, Rondeau MJ, Lloyd HO, Khanifar AA, Chan RV. Age-related macular degeneration: choroidal ischaemia? Br J Ophthalmol. 2013;97(8):1020–1023. doi: 10.1136/bjophthalmol-2013-303143. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Zarbin MA. Current concepts in the pathogenesis of age-related macular degeneration. Arch Ophthalmol. 2004;122(4):598–614. doi: 10.1001/archopht.122.4.598. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Coleman AL, Yu F. Eye-related Medicare costs for patients with age-related macular degeneration from 1995 to 1999. Ophthalmology. 2008;115(1):18–25. doi: 10.1016/j.ophtha.2007.04.016. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.McLeod DS, Lutty GA. High-resolution histologic analysis of the human choroidal vasculature. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 1994;35(11):3799–3811. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Ramrattan RS, van der Schaft TL, Mooy CM, de Bruijn WC, Mulder PG, de Jong PT. Morphometric analysis of Bruch’s membrane, the choriocapillaris, and the choroid in aging. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 1994;35(6):2857–2864. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Spraul CW, Lang GE, Grossniklaus HE. Morphometric analysis of the choroid, Bruch’s membrane, and retinal pigment epithelium in eyes with age-related macular degeneration. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 1996;37(13):2724–2735. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Friedman E, Oak SM. Choroidal microcirculation in vivo. Bibl Anat. 1965;7:129–132. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Grunwald JE, Siu KK, Jacob SS, Dupont J. Effect of sildenafil citrate (Viagra) on the ocular circulation. Am J Ophthalmol. 2001;131(6):751–755. doi: 10.1016/s0002-9394(00)00944-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Mullins RF, Johnson MN, Faidley EA, Skeie JM, Huang J. Choriocapillaris vascular dropout related to density of drusen in human eyes with early age-related macular degeneration. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2011;52(3):1606–1612. doi: 10.1167/iovs.10-6476. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Longo A, Geiser MH, Riva CE. Posture changes and subfoveal choroidal blood flow. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2004;45(2):546–551. doi: 10.1167/iovs.03-0757. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Kaeser P, Orgül S, Zawinka C, Reinhard G, Flammer J. Influence of change in body position on choroidal blood flow in normal subjects. Br J Ophthalmol. 2005;89(10):1302–1305. doi: 10.1136/bjo.2005.067884. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Spaide RF, Koizumi H, Pozzoni MC. Enhanced depth imaging spectral-domain optical coherence tomography [published correction appears in Am J Ophthalmol. 2009;148(2):325] Am J Ophthalmol. 2008;146(4):496–500. doi: 10.1016/j.ajo.2008.05.032. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Margolis R, Spaide RF. A pilot study of enhanced depth imaging optical coherence tomography of the choroid in normal eyes. Am J Ophthalmol. 2009;147(5):811–815. doi: 10.1016/j.ajo.2008.12.008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Zhang L, Lee K, Niemeijer M, Mullins RF, Sonka M, Abràmoff MD. Automated segmentation of the choroid from clinical SD-OCT. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2012;53(12):7510–7519. doi: 10.1167/iovs.12-10311. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Abràmoff MD, Garvin MK, Sonka M. Retinal imaging and image analysis. IEEE Trans Med Imaging. 2010;3:169–208. doi: 10.1109/RBME.2010.2084567. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Garvin MK, Abràmoff MD, Wu X, Russell SR, Burns TL, Sonka M. Automated 3-D intraretinal layer segmentation of macular spectral-domain optical coherence tomography images. IEEE Trans Med Imaging. 2009;28(9):1436–1447. doi: 10.1109/TMI.2009.2016958. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Age-Related Eye Disease Study Research Group. The Age-Related Eye Disease Study system for classifying age-related macular degeneration from stereoscopic color fundus photographs: the Age-Related Eye Disease Study Report Number 6. Am J Ophthalmol. 2001;132(5):668–681. doi: 10.1016/s0002-9394(01)01218-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Sarks SH. Changes in the region of the choriocapillaris in ageing and degeneration. In: Shimizu K, editor. Acta XXIII Concilium Ophthalmologicum Kyoto 1978. I. Amsterdam, the Netherlands: Excerpta Medica; 1979. pp. 228–238. [Google Scholar]
- 19.Korte GE, Reppucci V, Henkind P. RPE destruction causes choriocapillary atrophy. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 1984;25(10):1135–1145. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Chen JC, Fitzke FW, Pauleikhoff D, Bird AC. Poor choroidal perfusion is a cause of visual impairment in age-related macular degeneration [ARVO abstract] Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 1984;30(3 suppl):153. [Google Scholar]
- 21.Sohn EH, Khanna A, Tucker BA, Abràmoff MD, Stone EM, Mullins RF. Structural and biochemical analyses of choroidal thickness in human donor eyes. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2014;55(3):1352–1360. doi: 10.1167/iovs.13-13754. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Sayegh FN, Weigelin E. Functional ophthalmodynamometry: comparison between brachial and ophthalmic blood pressure in sitting and supine position. Angiology. 1983;34(3):176–182. doi: 10.1177/000331978303400303. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Savin E, Bailliart O, Checoury A, Bonnin P, Grossin C, Martineaud JP. Influence of posture on middle cerebral artery mean flow velocity in humans. Eur J Appl Physiol Occup Physiol. 1995;71(2-3):161–165. doi: 10.1007/BF00854974. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Told R, Palkovits S, Haslacher H, et al. Alterations of choroidal blood flow regulation in young healthy subjects with complement factor H polymorphism. PLoS One. 2013;8(4):e60424. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0060424. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Jylhävä J, Eklund C, Pessi T, et al. Genetics of C-reactive protein and complement factor H have an epistatic effect on carotid artery compliance: the Cardiovascular Risk in Young Finns Study. Clin Exp Immunol. 2009;155(1):53–58. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2249.2008.03752.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Edwards AO, Ritter R, III, Abel KJ, Manning A, Panhuysen C, Farrer LA. Complement factor H polymorphism and age-related macular degeneration. Science. 2005;308(5720):421–424. doi: 10.1126/science.1110189. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Hwang JC, Konduru R, Zhang X, et al. Relationship among visual field, blood flow, and neural structure measurements in glaucoma. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2012;53(6):3020–3026. doi: 10.1167/iovs.11-8552. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Sato EA, Ohtake Y, Shinoda K, Mashima Y, Kimura I. Decreased blood flow at neuroretinal rim of optic nerve head corresponds with visual field deficit in eyes with normal tension glaucoma. Graefes Arch Clin Exp Ophthalmol. 2006;244(7):795–801. doi: 10.1007/s00417-005-0177-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Nicolela MT, Drance SM, Rankin SJ, Buckley AR, Walman BE. Color Doppler imaging in patients with asymmetric glaucoma and unilateral visual field loss. Am J Ophthalmol. 1996;121(5):502–510. doi: 10.1016/s0002-9394(14)75424-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Xu J, Xu L, Du KF, et al. Subfoveal choroidal thickness in diabetes and diabetic retinopathy. Ophthalmology. 2013;120(10):2023–2028. doi: 10.1016/j.ophtha.2013.03.009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Prager SG, Simader C, Deak GG, et al. Changes in macular perfusion during antiangiogenic treatment of diabetic macular edema [ARVO abstract 1761, poster A0198] 2014 http://www.arvo.org/Annual_Meeting/Past_Annual_Meetings/. Accessed September 4, 2014.
- 32.Fujiwara T, Imamura Y, Margolis R, Slakter JS, Spaide RF. Enhanced depth imaging optical coherence tomography of the choroid in highly myopic eyes. Am J Ophthalmol. 2009;148(3):445–450. doi: 10.1016/j.ajo.2009.04.029. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Kim SW, Oh J, Kwon SS, Yoo J, Huh K. Comparison of choroidal thickness among patients with healthy eyes, early age-related maculopathy, neovascular age-related macular degeneration, central serous chorioretinopathy, and polypoidal choroidal vasculopathy. Retina. 2011;31(9):1904–1911. doi: 10.1097/IAE.0b013e31821801c5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Manjunath V, Fujimoto JG, Duker JS. Cirrus HD-OCT high definition imaging is another tool available for visualization of the choroid and provides agreement with the finding that the choroidal thickness is increased in central serous chorioretinopathy in comparison to normal eyes. Retina. 2010;30(8):1320–1321. doi: 10.1097/IAE.0b013e3181e798b1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Wood A, Binns A, Margrain T, et al. Retinal and choroidal thickness in early age-related macular degeneration. Am J Ophthalmol. 2011;152(6):1030–1038.e2. doi: 10.1016/j.ajo.2011.05.021. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Schuman SG, Koreishi AF, Farsiu S, Jung SH, Izatt JA, Toth CA. Photoreceptor layer thinning over drusen in eyes with age-related macular degeneration imaged in vivo with spectral-domain optical coherence tomography. Ophthalmology. 2009;116(3):488–496.e2. doi: 10.1016/j.ophtha.2008.10.006. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.


