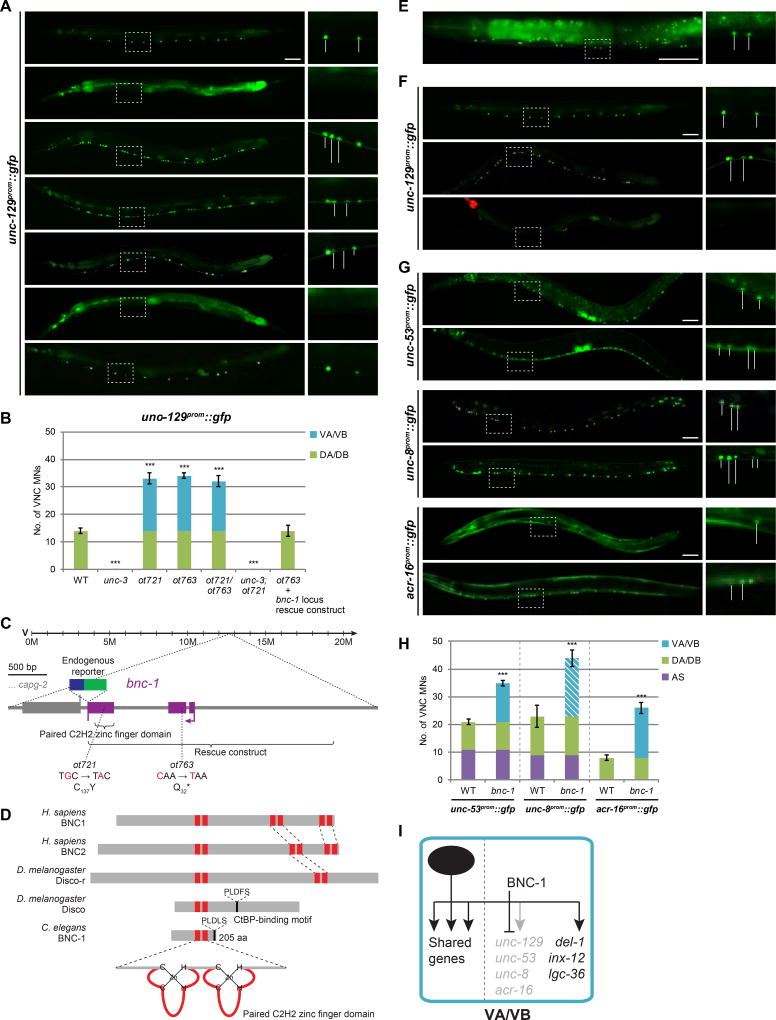
Figure 2. bnc-1 is a class-specific regulator of motor neuron identity.
A: unc-129 is expressed in DA/DB MNs (class member neurons within white bounding rectangle is magnified in inset on the right) and is regulated by unc-3. In ot721 and ot763 animals (which do not complement each other), unc-129 is derepressed in VA/VB MNs in an unc-3-dependent manner. This phenotype is rescued by the genomic locus of a novel C. elegans gene, bnc-1 (basonuclin 1). Wildtype (WT); all scale bars = 50 µm.
B. Quantification for A; error bars show standard deviation (SD). Unpaired t-tests were performed for all mutants compared to WT; ***p < 0.001; n ≥ 13.
C: bnc-1 gene locus.
D: BNC-1 protein and its orthologs.
E: Endogenous bnc-1 locus tagged with mNG shows remarkably specific expression in VA/VB MNs (except for VB1) in the VNC (see Fig.S4A for additional expression elsewhere). Gut auto-fluorescence (*); stitched together from two images of the same worm; showing anterior half of worm.
F: bnc-1 cDNA driven by an unc-3 promoter in DA/DB/VA/VB MNs in bnc-1 mutants rescues the unc-129 derepression phenotype in VA/VB, and is sufficient to ectopically repress unc-129 in DA/DB MNs. WT image repeated from A; red pharyngeal expression marks unc-3prom::bnc-1 transgene.
G: Expression of the unc-3-dependent class-specific effector genes unc-53 (DA/AS), unc-8 (DA/DB/AS) and acr-16 (DB) are derepressed in VA/VB MNs of bnc-1 mutants.
H: Quantification for G; error bars show SD. Superimposed diagonal stripes indicate dim expression. Unpaired t-tests were performed for all mutants compared to WT; ***p < 0.001; n ≥ 13.
I: Genetic model depicting BNC-1 repressing DA/DB-specific effector genes in VA/VB MNs.