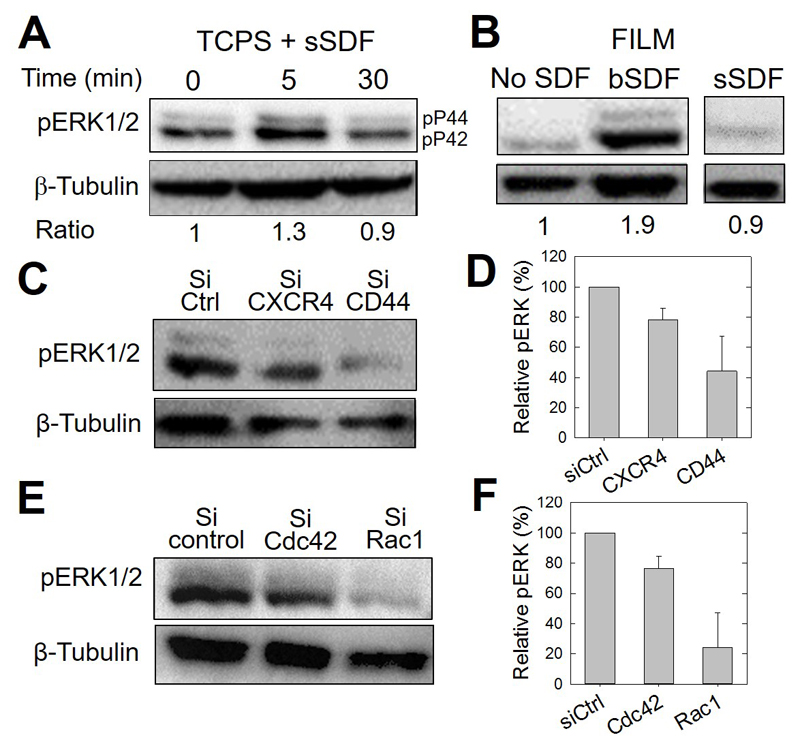
Figure 8.
CD44 involvement in CXCR4-medicated and bSDF-induced ERK1/2 phosphorylation in MDA-MB231 breast cancer cells. The different panels show representative western blots and their corresponding quantitative analysis using anti-phosphoERK1/2 antibodies (pERK) to reveal changes in the phosphorylation of ERK1/2. (A) Serum-starved MDA-MB-231 cells cultured on tissue culture polystyrene (TCPS) were used as a control to assess early ERK phosphorylation. The basal level was quantified after 5 min and 30 min of stimulation in a serum-containing medium. β-tubulin was taken as a control. The band intensity ratios (pERK1/2 / tubulin) are also given, the Time 0 being considered as a reference (arbitrarily set to 1). (B) pERK activation of cancer cells, cultured for 16 h on polyelectrolyte films in the absence (No SDF), with SDF-1α presented at the ventral side of the cells (bSDF), or with SDF-1α added in the growth medium (sSDF). The band intensity ratios are also given, the condition “No SDF” being set arbitrarily to 1. (C) pERK activation after selective CXCR4 and CD44 knock-down using siRNAs and (D) corresponding quantification of pERK/tubulin ratios, the control silencing being arbitrarily set to 100%. Two independent experiments were performed. (Data are mean ± SD). (E) pERK activation after selective Cdc42 and Rac1 knock-down using siRNAs and (F) corresponding quantification of pERK/tubulin ratios, the control silencing being arbitrarily set to 100%. Two independent experiments were performed. (Data are mean ± SD).