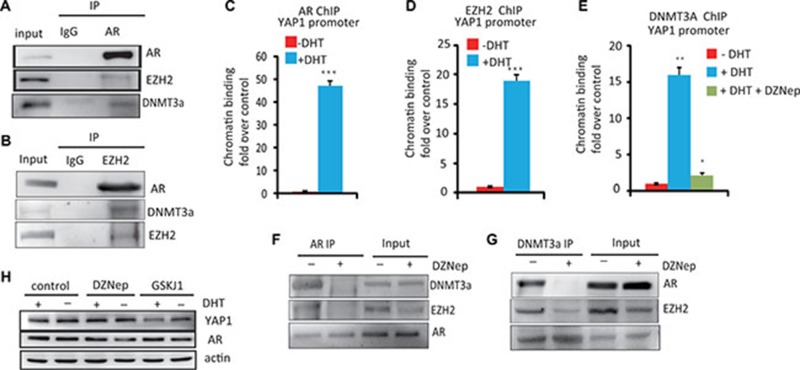
Figure 3. The essential role of the AR–DNMT3a and EZH2 complex in the regulation of YAP1 expression.
(A) Immunoprecipitation of AR in LNCaP cells followed by immunoblot analysis of EZH2, DNMT3a. IgG represents a control antibody used for IPs. (B) Co-IP of EZH2 and AR, DNMT3a in LNCaP cells (C) ChIP–PCR analysis of AR on YAP1 promoter. LNCaP cells were hormone starved for 12 h and then treated with ethanol, R1881 (10 nM) or DZNep (10 μM) for 6 h. Cells were then harvested for ChIP and analyzed by qPCR using. (D) ChIP–PCR analysis of EZH2 binding to the YAP1 gene promoter. (E) ChIP–PCR analysis of DNMT3a binding to the YAP1 gene promoter. LNCaP cells were treated with ethanol, R1881 or DZNep as indicated (F) Immunoprecipitation of AR in LNCaP cells treated with DZNep followed by immunoblot analysis of AR, EZH2 and DNMT3a. (G) IP with DNMT3a Ab in LNCaP cell treated with DZNep (10 μM) followed by immunoblot analysis of EZH2 AR and DNMT3a. (H) LNCaP cells were hormone starved for 12 h and then treated with ethanol or R1881 (10 nM), DZNep (10 μM) and GSKJ1(10 μM) for 8 h, WB analysis of YAP1 and AR protein expression.