In the crystal, intermolecular weak C—H⋯O hydrogen bonds link the molecules into the supramolecular chains propagating along the a axis.
Keywords: crystal structure, nitrophenyl, methylacetamide, benzamide, dimethoxybenzene, Hirshfeld surface
Abstract
In the title compound, C15H14N2O5, the benzene rings are nearly coplanar, making a dihedral angle of 4.89 (8)°. An intramolecular N—H⋯O hydrogen bond occurs between the imino and methoxy groups. In the crystal, weak C—H⋯O hydrogen bonds link the molecules into supramolecular chains propagating along the a-axis direction. π–π stacking is observed between parallel benzene rings of neighbouring chains, the centroid-to-centroid distance being 3.6491 (10) Å. Three-dimensional Hirshfeld surface analyses and two-dimensional fingerprint plots have been used to analyse the intermolecular interactions present in the crystal.
Chemical context
Amides have a very important place in both organic and biological chemistry. They are used as building blocks for natural products such as proteins and peptides. However, amides are not restricted to biological systems, but also have a wide range of uses in pharmaceutical chemistry (Khalafi-Nezhad et al., 2005 ▸; Valeur & Bradley, 2009 ▸). Many amide derivatives have been found to possess antitumor, antimicrobial, anti-HIV, anti-inflammatory, anticonvulsant, antibacterial, antifungal, analgesic and anticancer properties (Kushwaha et al., 2011 ▸; Fu et al., 2010 ▸; Carbonnelle et al., 2005 ▸; Siddiqui et al., 2008 ▸). Benzamides and their derivatives are compounds of biological and pharmaceutical importance. A variety of benzamide derivatives have been synthesized by the interaction of aniline derivatives that carry electron-donating groups (anisidines, toluidines) and acyl chlorides (2,3-dimethoxybenzoyl chloride and 3-acetoxy-2-methylbenzoyl chloride) in a slightly basic medium (Cakmak et al., 2016 ▸; Demir et al., 2015 ▸).
Structural commentary
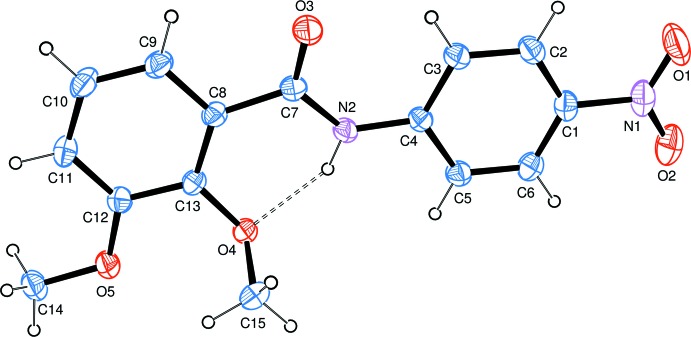
The molecular structure of the title compound is shown in Fig. 1 ▸. The bond distances and angles are found to be in good agreement with those in analogous structures (Demir et al., 2015 ▸; Tahir et al., 2011 ▸). In the molecule, the benzene rings are nearly coplanar, with a dihedral angle of 4.89 (8)°. An intramolecular N—H⋯O hydrogen bond (Table 1 ▸) occurs between the imino and methoxy groups.
Figure 1.
The molecular structure of the title compound, with displacement ellipsoids drawn at the 50% probability level. The intramolecular N—HċO (Table 1 ▸) hydrogen bond is shown as a double dashed line.
Table 1. Hydrogen-bond geometry (Å, °).
| D—H⋯A | D—H | H⋯A | D⋯A | D—H⋯A |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| N2—H2⋯O4 | 0.87 (2) | 1.924 (19) | 2.6805 (16) | 144.6 (17) |
| C5—H5⋯O3i | 0.93 | 2.48 | 3.2597 (19) | 141 |
Symmetry code: (i) 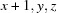 .
.
Supramolecular features
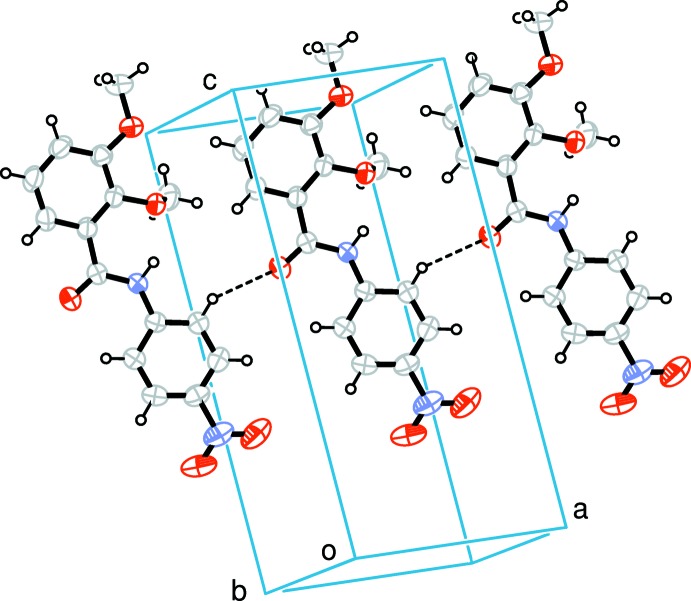
In the crystal, adjacent molecules are linked by weak C—H⋯O hydrogen bonds, forming supramolecular chains propagating along the a-axis direction (Table 1 ▸, Fig. 2 ▸). π–π stacking is observed between parallel benzene rings of adjacent chains, the centroid-to-centroid distance being 3.6491 (10) Å.
Figure 2.
Packing of the title compound in the unit cell. Dashed lines indicate the C—H⋯O hydrogen bonds (see Table 1 ▸).
Hirshfeld surface analysis
Three-dimensional Hirshfeld surfaces (HS) were generated using Crystal Explorer 3.1 (Wolff et al., 2013 ▸) based on the results of the single crystal X-ray diffraction studies. Two-dimensional fingerprint plots (FPs) provide a visual representation of crystal-packing interactions in the structure. The HS is a useful tool for describing the surface characteristics and gaining additional insight into the intermolecular interactions of the molecules.
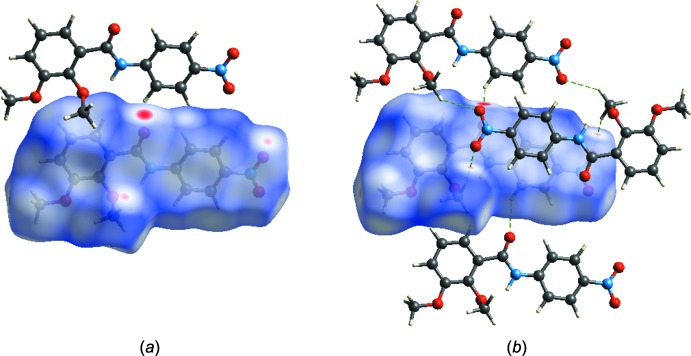
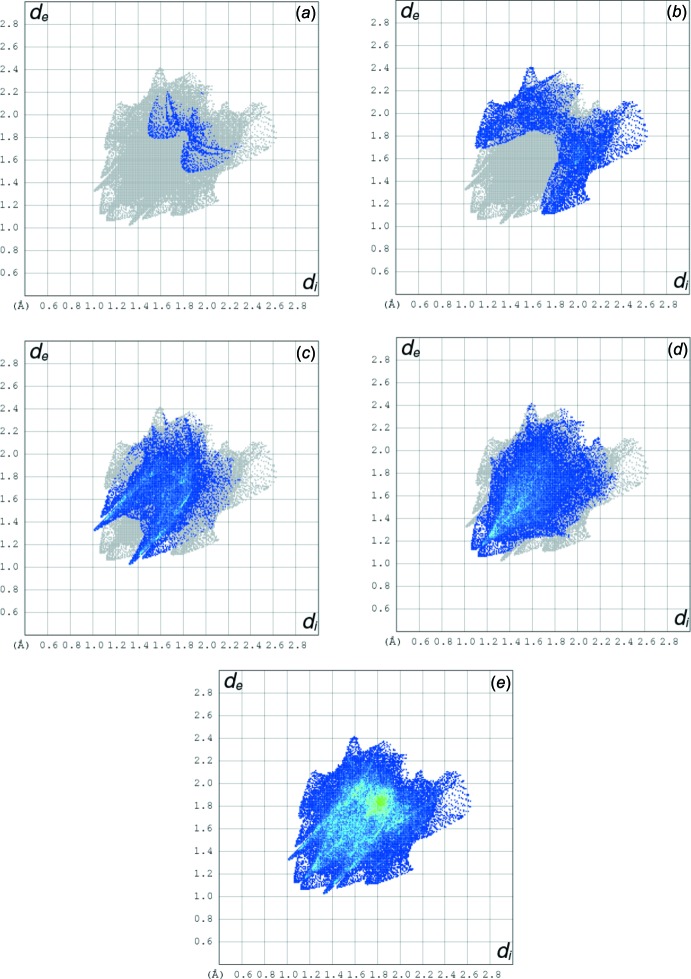
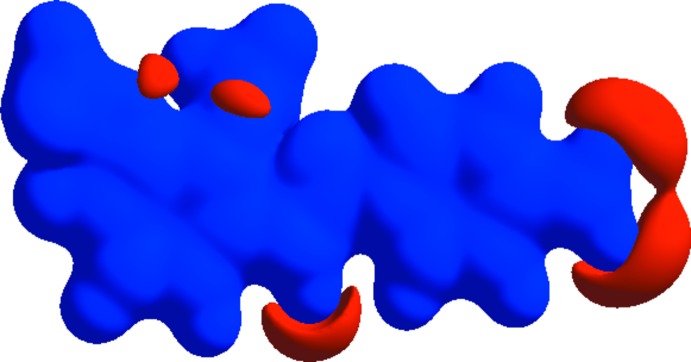
The molecular Hirshfeld surface, d norm, is depicted in Fig. 3 ▸ and mapped over the range −0.1763 to 1.2643 Å. Strong hydrogen-bond interactions, such as C—H⋯O, are seen as a bright-red area on the Hirshfeld surfaces (Şen et al., 2017 ▸). The fingerprint plots over the Hirshfeld surfaces illustrate the significant differences between the intermolecular interaction patterns. In Fig. 4 ▸, it is observed Ninside⋯Houtside = 2.3%, Cinside⋯Houtside = 15.7%, Oinside⋯Houtside = 29.7%, Hinside⋯Houtside = 38% and all atomsinside⋯all atomsoutside = 100% of the total interactions. Fig. 4 ▸ shows that the major contributions are from H⋯H (38%) and O⋯H (30%) interactions. Fig. 5 ▸ illustrates the distribution of positive and negative potential over the Hirshfeld surfaces. Blue regions correspond to positive electrostatic potential (indicating hydrogen-bond donors) and the red regions to negative electrostatic potential (indicating hydrogen-bond acceptors) (Kumar et al., 2013 ▸).
Figure 3.
Hirshfeld d norm (a) for 2,3-dimethoxy-N-(4-nitrophenyl)benzamide and (b) showing the hydrogen bonding.
Figure 4.
Hirshfeld surface fingerprint of the title compound, (a) Ninside⋯Houtside (2.3%), (b) Cinside⋯Houtside (15.7%), (c) Oinside⋯Houtside (29.7%), (d) Hinside⋯Houtside (38%), (e) all atomsinside⋯all atomsoutside (100% of total interactions).
Figure 5.
Electrostatic potential mapped on the Hirshfeld surface with ±0.25 au
IR spectroscopic analyses
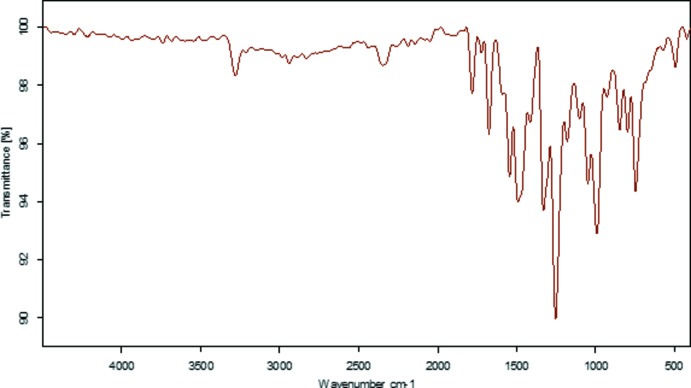
The FT–IR spectrum of 2,3-dimethoxy-N-(4-nitrophenyl)benzamide, shown in Fig. 6 ▸, has several characterization bands. The first characteristic absorption band is at 3311 cm−1 and was assigned to the N—H stretching vibration. The second remarkable very strong vibrational band is located at 1689 cm−1 and can be attributed to the C=O stretching vibration. Another group wavenumber is the C—N stretching vibration that appears at 862 cm−1. This vibration frequency belongs to the nitro group attached to the phenyl ring at the 4-position. The asymmetrical and symmetrical stretching vibrations of the nitro group are observed at 1549 and 1327 cm−1, respectively. In the IR spectrum, peaks corresponding to –C=O– stretching and –NH– stretching indicate the presence of an amide linkage. These values are in agreement with those previously reported for similar compounds (Cakmak et al., 2016 ▸; Demir et al., 2015 ▸).
Figure 6.
The FT–IR spectrum of the title compound.
Database survey
A search of the Cambridge Structural Database (CSD, Version 5.38, last update May 2017; Groom et al., 2016 ▸) for the 2,3-dimethyl-N-(phenyl)benzamide skeleton gave 17 hits. One of these compounds, viz. 2,3-dimethoxy-N-(4-methylphenyl)benzamide, also named as 2,3-dimethoxy-N-(p-tolyl)benzamide (UYALEN; Cakmak et al., 2016 ▸) is similar to the title compound. However, here the two aryl rings are inclined to one another by ca 34.16°, despite the presence of an intramolecular N—H⋯Omethoxy hydrogen bond. A search for the 4-nitrophenylbenzamide skeleton gave 16 hits. They include 4-nitrophenylbenzamide itself, also called benz-p-nitroanilide (BUTDID; Du Plessis et al., 1983 ▸) and two polymorphs (orthorhombic and monoclinic) of 4′-nitrosalicylanilide (respectively, KADZEU and KADZIY; Etter et al., 1988 ▸). Here, the aryl rings are inclined to one another by ca 62.30° in BUTDID, 11.24 (10)° in KADZEU, and 3.02 (12) and 2.69 (12)° in the two independent molecules of the monoclinic polymorph of 4′-nitrosalicylanilide, i.e. KADZIY. The same dihedral angle in the title compound is 4.89 (9)°. Only in BUTDID, with a dihedral angle of ca 62.30°, is there no intramolecular N—H⋯O hydrogen present.
Synthesis and crystallization
To a solution of 4-nitroaniline (10 mmol) and triethylamine (10 mmol) in THF (10 ml) was added dropwise a THF (10 ml) solution of 2,3-dimethoxybenzoyl chloride (11 mmol) at room temperature. The reaction mixture was stirred at room temperature for 15 h and then the resulting white salt precipitate was filtered off and then 150 ml water was added dropwise to the filtrate. The precipitate was filtered off and washed several times with water to remove excessive aniline derivative and trimethylamine hydrochloride salt. The crude product was crystallized from acetonitrile (yield 2.09 g 63%; m.p. 448–451 K; Demir et al., 2015 ▸; Cakmak et al., 2016 ▸).
Refinement
Crystal data, data collection and structure refinement details are summarized in Table 2 ▸. The imino-H atom was located in a difference-Fourier map. All C-bound H atoms were positioned geometrically and refined using a riding model with C—H = 0.93–0.97 Å and U iso(H) = 1.2–1.5U eq(C).
Table 2. Experimental details.
| Crystal data | |
| Chemical formula | C15H14N2O5 |
| M r | 302.28 |
| Crystal system, space group | Triclinic, P
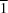
|
| Temperature (K) | 296 |
| a, b, c (Å) | 6.9293 (5), 7.3270 (5), 15.7411 (11) |
| α, β, γ (°) | 94.198 (6), 96.189 (6), 116.053 (5) |
| V (Å3) | 707.27 (9) |
| Z | 2 |
| Radiation type | Mo Kα |
| μ (mm−1) | 0.11 |
| Crystal size (mm) | 0.74 × 0.49 × 0.28 |
| Data collection | |
| Diffractometer | Stoe IPDS 2 |
| Absorption correction | Integration (X-RED32; Stoe & Cie, 2002 ▸) |
| T min, T max | 0.947, 0.972 |
| No. of measured, independent and observed [I > 2σ(I)] reflections | 10204, 2776, 2011 |
| R int | 0.109 |
| (sin θ/λ)max (Å−1) | 0.617 |
| Refinement | |
| R[F 2 > 2σ(F 2)], wR(F 2), S | 0.039, 0.114, 1.09 |
| No. of reflections | 2776 |
| No. of parameters | 203 |
| H-atom treatment | H atoms treated by a mixture of independent and constrained refinement |
| Δρmax, Δρmin (e Å−3) | 0.16, −0.15 |
Supplementary Material
Crystal structure: contains datablock(s) I, global. DOI: 10.1107/S2056989017017741/xu5912sup1.cif
Structure factors: contains datablock(s) I. DOI: 10.1107/S2056989017017741/xu5912Isup2.hkl
Supporting information file. DOI: 10.1107/S2056989017017741/xu5912Isup3.cml
CCDC reference: 1580287
Additional supporting information: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report
Acknowledgments
The authors acknowledge the Faculty of Arts and Sciences, Ondokuz Mayıs University, Turkey, for the use of the Stoe IPDS 2 diffractometer (purchased under grant F.279 of the University Research Fund).
supplementary crystallographic information
Crystal data
| C15H14N2O5 | Z = 2 |
| Mr = 302.28 | F(000) = 316 |
| Triclinic, P1 | Dx = 1.419 Mg m−3 |
| a = 6.9293 (5) Å | Mo Kα radiation, λ = 0.71073 Å |
| b = 7.3270 (5) Å | Cell parameters from 12957 reflections |
| c = 15.7411 (11) Å | θ = 2.6–27.5° |
| α = 94.198 (6)° | µ = 0.11 mm−1 |
| β = 96.189 (6)° | T = 296 K |
| γ = 116.053 (5)° | Prism, colorless |
| V = 707.27 (9) Å3 | 0.74 × 0.49 × 0.28 mm |
Data collection
| Stoe IPDS 2 diffractometer | 2776 independent reflections |
| Radiation source: sealed X-ray tube, 12 x 0.4 mm long-fine focus | 2011 reflections with I > 2σ(I) |
| Plane graphite monochromator | Rint = 0.109 |
| Detector resolution: 6.67 pixels mm-1 | θmax = 26.0°, θmin = 2.6° |
| rotation method scans | h = −8→8 |
| Absorption correction: integration (X-RED32; Stoe & Cie, 2002) | k = −9→9 |
| Tmin = 0.947, Tmax = 0.972 | l = −19→19 |
| 10204 measured reflections |
Refinement
| Refinement on F2 | 0 restraints |
| Least-squares matrix: full | Hydrogen site location: mixed |
| R[F2 > 2σ(F2)] = 0.039 | H atoms treated by a mixture of independent and constrained refinement |
| wR(F2) = 0.114 | w = 1/[σ2(Fo2) + (0.0593P)2 + 0.0364P] where P = (Fo2 + 2Fc2)/3 |
| S = 1.09 | (Δ/σ)max < 0.001 |
| 2776 reflections | Δρmax = 0.16 e Å−3 |
| 203 parameters | Δρmin = −0.15 e Å−3 |
Special details
| Geometry. All esds (except the esd in the dihedral angle between two l.s. planes) are estimated using the full covariance matrix. The cell esds are taken into account individually in the estimation of esds in distances, angles and torsion angles; correlations between esds in cell parameters are only used when they are defined by crystal symmetry. An approximate (isotropic) treatment of cell esds is used for estimating esds involving l.s. planes. |
Fractional atomic coordinates and isotropic or equivalent isotropic displacement parameters (Å2)
| x | y | z | Uiso*/Ueq | ||
| O4 | 0.64070 (15) | 0.29058 (17) | 0.80665 (6) | 0.0545 (3) | |
| O5 | 0.60933 (17) | 0.26544 (19) | 0.97197 (7) | 0.0616 (3) | |
| N2 | 0.4382 (2) | 0.2366 (2) | 0.64515 (8) | 0.0511 (3) | |
| O3 | 0.10391 (19) | 0.2209 (2) | 0.63299 (8) | 0.0808 (4) | |
| C13 | 0.4424 (2) | 0.2492 (2) | 0.83248 (9) | 0.0471 (3) | |
| C4 | 0.4797 (2) | 0.2459 (2) | 0.56018 (9) | 0.0459 (3) | |
| C8 | 0.2622 (2) | 0.2150 (2) | 0.77272 (10) | 0.0488 (4) | |
| O2 | 0.8200 (3) | 0.2760 (3) | 0.30063 (10) | 0.1064 (5) | |
| N1 | 0.6417 (3) | 0.2623 (2) | 0.30988 (11) | 0.0768 (5) | |
| C7 | 0.2601 (2) | 0.2247 (2) | 0.67740 (10) | 0.0517 (4) | |
| C12 | 0.4247 (2) | 0.2346 (2) | 0.91990 (10) | 0.0507 (4) | |
| C1 | 0.5861 (3) | 0.2588 (2) | 0.39713 (10) | 0.0570 (4) | |
| C3 | 0.3267 (3) | 0.2228 (3) | 0.49000 (10) | 0.0549 (4) | |
| H3 | 0.188086 | 0.202409 | 0.498155 | 0.066* | |
| O1 | 0.5080 (3) | 0.2514 (3) | 0.25036 (9) | 0.1153 (6) | |
| C5 | 0.6860 (2) | 0.2752 (2) | 0.54688 (10) | 0.0540 (4) | |
| H5 | 0.788868 | 0.291175 | 0.593672 | 0.065* | |
| C9 | 0.0660 (2) | 0.1701 (3) | 0.80232 (11) | 0.0598 (4) | |
| H9 | −0.055930 | 0.146485 | 0.763333 | 0.072* | |
| C6 | 0.7391 (3) | 0.2808 (3) | 0.46522 (11) | 0.0597 (4) | |
| H6 | 0.876591 | 0.299130 | 0.456262 | 0.072* | |
| C11 | 0.2278 (3) | 0.1919 (3) | 0.94704 (10) | 0.0610 (4) | |
| H11 | 0.215193 | 0.184597 | 1.005063 | 0.073* | |
| C2 | 0.3818 (3) | 0.2305 (3) | 0.40828 (10) | 0.0594 (4) | |
| H2B | 0.281017 | 0.216468 | 0.361048 | 0.071* | |
| C10 | 0.0500 (3) | 0.1603 (3) | 0.88803 (12) | 0.0667 (5) | |
| H10 | −0.081928 | 0.131915 | 0.906628 | 0.080* | |
| C14 | 0.6008 (3) | 0.2573 (3) | 1.06211 (10) | 0.0672 (5) | |
| H14A | 0.740231 | 0.281308 | 1.091532 | 0.101* | |
| H14B | 0.563274 | 0.360514 | 1.084938 | 0.101* | |
| H14C | 0.493006 | 0.124535 | 1.070342 | 0.101* | |
| C15 | 0.8027 (3) | 0.5006 (3) | 0.83037 (13) | 0.0752 (5) | |
| H15A | 0.935274 | 0.518241 | 0.810544 | 0.113* | |
| H15B | 0.751827 | 0.589244 | 0.804407 | 0.113* | |
| H15C | 0.828921 | 0.534368 | 0.891963 | 0.113* | |
| H2 | 0.540 (3) | 0.244 (3) | 0.6846 (12) | 0.072 (5)* |
Atomic displacement parameters (Å2)
| U11 | U22 | U33 | U12 | U13 | U23 | |
| O4 | 0.0428 (5) | 0.0755 (8) | 0.0474 (6) | 0.0287 (5) | 0.0087 (4) | 0.0056 (5) |
| O5 | 0.0594 (6) | 0.0816 (8) | 0.0443 (6) | 0.0319 (6) | 0.0082 (5) | 0.0108 (5) |
| N2 | 0.0453 (7) | 0.0696 (9) | 0.0424 (7) | 0.0301 (6) | 0.0038 (5) | 0.0075 (6) |
| O3 | 0.0560 (7) | 0.1396 (13) | 0.0604 (7) | 0.0554 (8) | 0.0078 (5) | 0.0211 (7) |
| C13 | 0.0438 (7) | 0.0507 (9) | 0.0508 (8) | 0.0236 (6) | 0.0127 (6) | 0.0076 (6) |
| C4 | 0.0485 (8) | 0.0452 (8) | 0.0443 (7) | 0.0217 (6) | 0.0051 (6) | 0.0057 (6) |
| C8 | 0.0440 (7) | 0.0521 (9) | 0.0522 (8) | 0.0228 (6) | 0.0102 (6) | 0.0078 (7) |
| O2 | 0.1207 (13) | 0.1259 (14) | 0.0872 (11) | 0.0572 (11) | 0.0587 (10) | 0.0277 (9) |
| N1 | 0.1039 (13) | 0.0702 (10) | 0.0590 (9) | 0.0362 (9) | 0.0319 (9) | 0.0164 (7) |
| C7 | 0.0443 (8) | 0.0595 (10) | 0.0522 (8) | 0.0245 (7) | 0.0057 (6) | 0.0076 (7) |
| C12 | 0.0531 (8) | 0.0515 (9) | 0.0494 (8) | 0.0245 (7) | 0.0104 (6) | 0.0094 (7) |
| C1 | 0.0736 (10) | 0.0493 (9) | 0.0486 (8) | 0.0258 (8) | 0.0177 (7) | 0.0102 (7) |
| C3 | 0.0518 (8) | 0.0631 (10) | 0.0505 (9) | 0.0272 (7) | 0.0043 (6) | 0.0090 (7) |
| O1 | 0.1461 (15) | 0.1591 (17) | 0.0487 (8) | 0.0731 (13) | 0.0207 (9) | 0.0256 (9) |
| C5 | 0.0496 (8) | 0.0629 (10) | 0.0515 (8) | 0.0278 (7) | 0.0061 (6) | 0.0063 (7) |
| C9 | 0.0451 (8) | 0.0729 (11) | 0.0647 (10) | 0.0278 (8) | 0.0127 (7) | 0.0157 (8) |
| C6 | 0.0586 (9) | 0.0623 (11) | 0.0634 (10) | 0.0293 (8) | 0.0201 (8) | 0.0107 (8) |
| C11 | 0.0670 (10) | 0.0690 (11) | 0.0549 (9) | 0.0325 (8) | 0.0256 (8) | 0.0196 (8) |
| C2 | 0.0682 (10) | 0.0594 (10) | 0.0472 (8) | 0.0273 (8) | 0.0010 (7) | 0.0092 (7) |
| C10 | 0.0523 (9) | 0.0820 (13) | 0.0743 (11) | 0.0318 (9) | 0.0277 (8) | 0.0247 (9) |
| C14 | 0.0816 (12) | 0.0716 (12) | 0.0448 (9) | 0.0317 (9) | 0.0075 (8) | 0.0086 (8) |
| C15 | 0.0497 (9) | 0.0840 (14) | 0.0778 (12) | 0.0158 (9) | 0.0176 (8) | 0.0110 (10) |
Geometric parameters (Å, º)
| O4—C13 | 1.3849 (16) | C1—C6 | 1.371 (2) |
| O4—C15 | 1.441 (2) | C3—C2 | 1.379 (2) |
| O5—C12 | 1.3612 (18) | C3—H3 | 0.9300 |
| O5—C14 | 1.4311 (19) | C5—C6 | 1.373 (2) |
| N2—C7 | 1.3547 (19) | C5—H5 | 0.9300 |
| N2—C4 | 1.3983 (19) | C9—C10 | 1.370 (2) |
| N2—H2 | 0.870 (19) | C9—H9 | 0.9300 |
| O3—C7 | 1.2115 (18) | C6—H6 | 0.9300 |
| C13—C8 | 1.394 (2) | C11—C10 | 1.380 (2) |
| C13—C12 | 1.402 (2) | C11—H11 | 0.9300 |
| C4—C3 | 1.391 (2) | C2—H2B | 0.9300 |
| C4—C5 | 1.392 (2) | C10—H10 | 0.9300 |
| C8—C9 | 1.393 (2) | C14—H14A | 0.9600 |
| C8—C7 | 1.506 (2) | C14—H14B | 0.9600 |
| O2—N1 | 1.221 (2) | C14—H14C | 0.9600 |
| N1—O1 | 1.216 (2) | C15—H15A | 0.9600 |
| N1—C1 | 1.465 (2) | C15—H15B | 0.9600 |
| C12—C11 | 1.383 (2) | C15—H15C | 0.9600 |
| C1—C2 | 1.370 (2) | ||
| C13—O4—C15 | 113.96 (12) | C6—C5—H5 | 119.7 |
| C12—O5—C14 | 117.60 (13) | C4—C5—H5 | 119.7 |
| C7—N2—C4 | 129.19 (13) | C10—C9—C8 | 120.98 (15) |
| C7—N2—H2 | 113.0 (12) | C10—C9—H9 | 119.5 |
| C4—N2—H2 | 117.7 (12) | C8—C9—H9 | 119.5 |
| O4—C13—C8 | 120.97 (12) | C1—C6—C5 | 118.91 (15) |
| O4—C13—C12 | 118.37 (12) | C1—C6—H6 | 120.5 |
| C8—C13—C12 | 120.61 (13) | C5—C6—H6 | 120.5 |
| C3—C4—C5 | 119.50 (14) | C10—C11—C12 | 119.99 (14) |
| C3—C4—N2 | 123.89 (13) | C10—C11—H11 | 120.0 |
| C5—C4—N2 | 116.58 (13) | C12—C11—H11 | 120.0 |
| C9—C8—C13 | 118.36 (14) | C1—C2—C3 | 119.54 (15) |
| C9—C8—C7 | 116.01 (13) | C1—C2—H2B | 120.2 |
| C13—C8—C7 | 125.63 (13) | C3—C2—H2B | 120.2 |
| O1—N1—O2 | 123.34 (17) | C9—C10—C11 | 120.66 (14) |
| O1—N1—C1 | 118.39 (18) | C9—C10—H10 | 119.7 |
| O2—N1—C1 | 118.27 (18) | C11—C10—H10 | 119.7 |
| O3—C7—N2 | 122.79 (14) | O5—C14—H14A | 109.5 |
| O3—C7—C8 | 120.31 (13) | O5—C14—H14B | 109.5 |
| N2—C7—C8 | 116.90 (12) | H14A—C14—H14B | 109.5 |
| O5—C12—C11 | 125.07 (14) | O5—C14—H14C | 109.5 |
| O5—C12—C13 | 115.56 (13) | H14A—C14—H14C | 109.5 |
| C11—C12—C13 | 119.37 (14) | H14B—C14—H14C | 109.5 |
| C2—C1—C6 | 121.87 (15) | O4—C15—H15A | 109.5 |
| C2—C1—N1 | 119.17 (16) | O4—C15—H15B | 109.5 |
| C6—C1—N1 | 118.95 (16) | H15A—C15—H15B | 109.5 |
| C2—C3—C4 | 119.64 (15) | O4—C15—H15C | 109.5 |
| C2—C3—H3 | 120.2 | H15A—C15—H15C | 109.5 |
| C4—C3—H3 | 120.2 | H15B—C15—H15C | 109.5 |
| C6—C5—C4 | 120.53 (14) | ||
| C15—O4—C13—C8 | 107.52 (16) | O1—N1—C1—C2 | 4.1 (3) |
| C15—O4—C13—C12 | −74.91 (17) | O2—N1—C1—C2 | −175.90 (16) |
| C7—N2—C4—C3 | −6.9 (3) | O1—N1—C1—C6 | −176.93 (17) |
| C7—N2—C4—C5 | 174.65 (15) | O2—N1—C1—C6 | 3.1 (2) |
| O4—C13—C8—C9 | 178.74 (14) | C5—C4—C3—C2 | −0.4 (2) |
| C12—C13—C8—C9 | 1.2 (2) | N2—C4—C3—C2 | −178.75 (15) |
| O4—C13—C8—C7 | −2.0 (2) | C3—C4—C5—C6 | −0.2 (2) |
| C12—C13—C8—C7 | −179.54 (15) | N2—C4—C5—C6 | 178.27 (14) |
| C4—N2—C7—O3 | −0.2 (3) | C13—C8—C9—C10 | 0.2 (2) |
| C4—N2—C7—C8 | 179.49 (14) | C7—C8—C9—C10 | −179.11 (16) |
| C9—C8—C7—O3 | 9.6 (2) | C2—C1—C6—C5 | −0.3 (3) |
| C13—C8—C7—O3 | −169.65 (16) | N1—C1—C6—C5 | −179.30 (15) |
| C9—C8—C7—N2 | −170.15 (14) | C4—C5—C6—C1 | 0.6 (2) |
| C13—C8—C7—N2 | 10.6 (2) | O5—C12—C11—C10 | −178.99 (15) |
| C14—O5—C12—C11 | −1.3 (2) | C13—C12—C11—C10 | 1.3 (2) |
| C14—O5—C12—C13 | 178.43 (14) | C6—C1—C2—C3 | −0.2 (3) |
| O4—C13—C12—O5 | 0.7 (2) | N1—C1—C2—C3 | 178.71 (15) |
| C8—C13—C12—O5 | 178.26 (14) | C4—C3—C2—C1 | 0.6 (2) |
| O4—C13—C12—C11 | −179.54 (14) | C8—C9—C10—C11 | −0.9 (3) |
| C8—C13—C12—C11 | −2.0 (2) | C12—C11—C10—C9 | 0.1 (3) |
Hydrogen-bond geometry (Å, º)
| D—H···A | D—H | H···A | D···A | D—H···A |
| N2—H2···O4 | 0.870 (19) | 1.924 (19) | 2.6805 (16) | 144.6 (17) |
| C5—H5···O3i | 0.93 | 2.48 | 3.2597 (19) | 141 |
Symmetry code: (i) x+1, y, z.
References
- Cakmak, S., Kutuk, H., Odabasoglu, M., Yakan, H. & Buyukgungor, O. (2016). Lett. Org. Chem. 13, 181–194.
- Carbonnelle, D., Ebstein, F., Rabu, C., Petit, J. Y., Gregoire, M. & Lang, F. (2005). Eur. J. Immunol. 35, 546–556. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Demir, S., Cakmak, S., Dege, N., Kutuk, H., Odabasoglu, M. & Kepekci, R. A. (2015). J. Mol. Struct. 1100, 582–591.
- Du Plessis, M. P., Modro, T. A. & Nassimbeni, L. R. (1983). J. Crystallogr. Spectrosc. Res. 13, 179–189.
- Etter, M. C., Urbańczyk-Lipkowska, Z., Ameli, T. M. & Panunto, T. W. (1988). J. Crystallogr. Spectrosc. Res. 18, 491–507.
- Farrugia, L. J. (2012). J. Appl. Cryst. 45, 849–854.
- Fu, J., Cheng, K., Zhang, Z.-M., Fang, R.-Q. & Zhu, H.-L. (2010). Eur. J. Med. Chem. 45, 2638–2643. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Groom, C. R., Bruno, I. J., Lightfoot, M. P. & Ward, S. C. (2016). Acta Cryst B72, 171–179. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- Khalafi-Nezhad, A., Parhami, A., Soltani Rad, M. N. & Zarea, A. (2005). Tetrahedron Lett. 46, 6879–6882.
- Kumar, S. M., Manjunath, B., Lingaraju, G., Abdoh, M., Sadashiva, M. & Lokanath, N. (2013). Cryst. Struct. Theory Appl. 02, 124–131.
- Kushwaha, N., Saini, R. K. & Kushwaha, S. K. (2011). Int. J. Chem. Tech. Res. (USA), 3, 203–209.
- Şen, F., Kansiz, S. & Uçar, İ. (2017). Acta Cryst. C73, 517–524. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Sheldrick, G. M. (2015a). Acta Cryst. A71, 3–8.
- Sheldrick, G. M. (2015b). Acta Cryst. C71, 3–8.
- Siddiqui, N., Alam, M. S. & Ahsan, W. (2008). Acta Pharm. 58, 445–454. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Spek, A. L. (2009). Acta Cryst. D65, 148–155. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- Stoe & Cie (2002). Stoe & Cie, Darmstadt, Germany.
- Valeur, E. & Bradley, M. (2009). Chem. Soc. Rev. 38, 606–631. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Wolff, S., Grimwood, D., McKinnon, J., Turner, M., Jayatilaka, D. & Spackman, M. (2013). Crystal Explorer. University of Western Australia, Perth, Australia.
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Crystal structure: contains datablock(s) I, global. DOI: 10.1107/S2056989017017741/xu5912sup1.cif
Structure factors: contains datablock(s) I. DOI: 10.1107/S2056989017017741/xu5912Isup2.hkl
Supporting information file. DOI: 10.1107/S2056989017017741/xu5912Isup3.cml
CCDC reference: 1580287
Additional supporting information: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report