Abstract
Imperatorin (IMT) is a furanocoumarin from the root of Phlomis younghusbandii (Lamiaceae) with various activities. In the present study, the anti-inflammatory effects of IMT were evaluated by examining dimethylbenzene-induced ear edema, acetic acid-induced vascular permeability and by performing cotton pellet granuloma assessments in mice. In addition, the expression of pro-inflammatory cytokines, including tumor necrosis factor (TNF)-α, interleukin (IL)-6 and IL-1β, were detected using enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay kits in mice and using reverse transcription polymerase chain reaction analysis in RAW 264.7 cells. The expression levels of inducible nitric oxide synthase (iNOS), cyclooxygenase-2 (COX-2), nuclear p65, cytosolic p65 and inhibitor of nuclear factor (NF)-κB (IκB) in RAW 264.7 cells were determined using western blot analysis. The results showed that the oral administration of IMT significantly inhibited the inflammatory reactions and reduced the release of TNF-α, IL-6 and IL-1β reactions and reduced and suppressed the mRNA expression of TNF-A expressionact1o, and the protein expression of iNOS and COX-2 in the RAW 264.7 cells. The results also indicated that IMT suppressed the activity of NF-κB via upregulating p65 and IκB in the cytoplasm and downregulating p65 in the nucleus. In conclusion, IMT possessed notable anti-inflammatory activities in vitro and in vivo through inhibiting the NF-κB pathway.
Keywords: Phlomis younghusbandii, inflammatory cytokines, cyclooxygenase-2, inducible nitric oxide synthase, RAW 264.7
Introduction
Inflammation (Latin, inflammatio) represents a complex biological response, which occurs in reaction to any type of injury to the body, including damage to cells and from irritants or pathogens (1). Inflammation is a protective response, and immune cells, blood vessels and molecular mediators are involved in this process. The acute stage of inflammation is the initial response of the body to harmful stimuli and persists for a short-term in which it mediates the host defense against infections (2,3). The inflammatory response requires active termination when it is no longer required to prevent unnecessary ‘bystander’ damage to tissues. Failure to do so results in chronic inflammation and cellular destruction. Chronic inflammation is present in the long term and can predispose the host to various chronic illnesses, including cancer (4,5). For example, individuals who have chronic inflammatory bowel diseases are at high risk of developing colon cancer (4). Therefore, inhibiting inflammatory activity may be a target in the treatment of cancer and other diseases.
Imperatorin (IMT) is a bioactive furanocoumarin, the structure of which is shown in Fig. 1. IMT is an effective component extracted from traditional Chinese medicines and is widely distributed in the plant kingdom, particularly in Angelica dahurica, A. archangelica, Peucedani, Notopterygium and Radix Glehniae (6,7). It has been reported that IMT has a wide range of potent pharmacological activities, including antibacterial, antitumor, anticonvulsant, acute neurotoxic effects and abirritation (8–11). Of note, previous investigations have demonstrated that IMT possesses notable anti-inflammatory activity by inhibiting the production of nitric oxide (NO) and prostaglandin E2 (PGE2), and decreasing the expression of inducible nitric oxide synthase (iNOS), cyclooxygenase (COX)-2 and microsomal prostaglandin E synthase (12–14). However, few systemic investigations of the molecular mechanisms underlying the anti-inflammatory effects of IMT have been performed, which limits the clinical uses of this compound for treating inflammatory diseases. Therefore, due to the anti-inflammatory activity of IMT, the present study further evaluated the inhibitory effects of IMT against inflammation in vitro and in vivo, to understand the mechanism underlying its effects.
Figure 1.
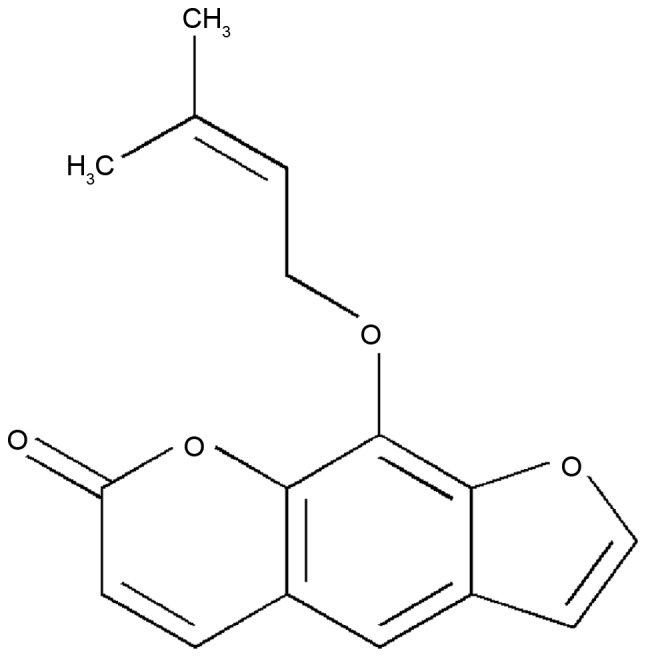
Chemical structure of imperatorin.
The present study detected the anti-inflammatory effects of IMT on dimethylbenzene-induced ear edema in mice, acetic acid-induced vascular permeability in mice and cotton pellet-induced granuloma in rats, and in LPS-induced RAW264.7 cells. In addition, the levels of tumor necrosis factor (TNF)-α, interleukin (IL)-6 and IL-1β in LPS-induced endotoxemic mice and LPS-induced RAW264.7 cells were measured. The protein expression levels of iNOS, COX-2, nuclear p65 [p65 (N)], cytosolic p65 [p65 (C)] and IκB (C) in LPS-induced RAW264.7 were also investigated to elucidate the anti-inflammatory mechanism of IMT.
Materials and methods
Chemicals
IMT was purchased from Shanghai Bomaide Biotech. Co., Ltd. (Shanghai, China); TNF-α, IL-6, and IL-1β enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) kits were purchased from Invitrogen; Thermo Fisher Scientific, Inc. (Waltham, MA, USA); dimethyl benzene was purchased from the Sino Pharm. (Chengdu, China); Dulbecco's modified Eagle's medium (DMEM), fetal bovine serum (FBS) and trypsinase were from Gibco; Thermo Fisher Scientific, Inc.; the Cell Counting Kit-8, bicinchoninic acid (BCA) protein assay reagent and goat-anti-rabbit/rat horseradish-peroxidase (HRP)-conjugated secondary antibodies (cat. nos. A0208 and A0192) were purchased from Beyotime Institute of Biotechnology (Haimen, China); lipopolysaccharide (LPS), dimethyl sulfoxide (DMSO) and Evans blue were purchased from Sigma; Merck Millipore (Darmstadt, Germany); COX-2 (cat. no. sc-19999), p65 (cat. no. sc-56735), IκB (cat. no. sc-945) and Histone H1 (cat. no. sc-8030) antibodies were purchased from Santa Cruz Biotechnology, Inc. (Santa Cruz, CA, USA); anti-β-actin antibody (cat. no. ab8226) and anti-iNOS antibody (cat. no. ab15323) were purchased from Abcam (Cambridge, MA, USA).
Animals and IMT treatment
A total of 150 Institute of Cancer Research (ICR) mice (weight, 20±2 g; n=75 female; n=75 male) and 50 Sprague-Dawley rats (weight, 220±20 g; n=25 female; n=25 male) were purchased from the Shanghai Laboratory Animal Centre (Shanghai, China). Each animal was housed under standard conditions (21±1°C, 50–10% relative humidity, 12 h light/dark cycle) and had free access to food and water. The experimental protocols were approved by the Animal Care and Use Committee of The First Affiliated Hospital of Xinjiang Medical University (Urumuqi, China).
The anti-inflammatory activity of IMT in vivo was determined against dimethylbenzene-induced ear edema in mice, acetic acid-induced vascular permeability in mice and cotton pellet-induced granuloma in rats. A total of 50 mice or rats were randomly divided into five groups of 10 animals, including a control, positive control and three graded IMT treatments groups. IMT was administered orally at doses of 15, 30 or 60 mg/kg. The positive control group received indometacin (10 mg/kg/day) by intraperitoneal (i.p.) injection and the control group received an equal volume of vehicle (0.5% CMC-Na, 10 ml/kg/day), which had been used to dilute IMT. For the assessment of dimethylbenzene-induced ear edema and acetic acid-induced vascular permeability in mice, mice received one dose of the treatment (1 dose of 15, 30 or 60 mg/kg for IMT, 10 mg/kg for indometacin). To assess the cotton pellet-induced granuloma in rats, treatments were administered once daily for 7 consecutive days (15, 30 or 60 mg/kg/day for IMT, 10 mg/kg/day for indometacin).
Assessment of dimethylbenzene-induced ear edema in mice
The assessment of dimethylbenzene-induced ear edema in mice was performed according to the method described in a previous report (15). In brief, dimethyl benzene was applied locally to the right ear 1 h following final drug administration. The mice were sacrificed under anesthesia via sodium pentobarbital injection (40 mg/kg i.p.) 1 h following dimethylbenzene application. The right ear and left ear were then amputated at the same location. Finally, the ear edema was calculated by subtracting the weight of the left ear from that of the right ear.
Assessment of acetic acid-induced vascular permeability in mice
The acetic acid-induced vascular permeability assessment in mice was performed according to a previously reported method with modification (15). At 1 h following final drug administration, each mouse was injected intravenously with Evans blue (2% in normal saline; 10 ml/kg) and was injected abdominally with acetic acid (0.7% in saline; 10 ml/kg). Following injection of acetic acid for 20 min, all the mice were sacrificed by cervical dislocation. The abdominal cavity was then washed several times with 5 ml of saline solution per mouse. The rinsed solution was collected and centrifuged for 15 min (780 × g at 4°C). Finally, the absorbance of Evans blue in the supernatant was determined at 630 nm with a spectrophotometer (Model 721; Shanghai Optical Instrument Factory Co., Ltd., Shanghai, China).
Assessment of cotton pellet-induced granuloma in rats
The assessment of cotton pellet-induced granuloma in rats was performed to evaluate the chronic anti-inflammatory activity of IMT and was performed as described previously (16). In brief, a small section of sterile cotton pellet (50±1 mg) was applied subcutaneously to the dorsolateral skin of the anesthetized rats (one on either side), and drugs were administered once daily for 7 days consecutively. On day 8, all rats were sacrificed and the pellets with granuloma were excised. The increments of the wet and dry weights of the pellets were used to evaluate granuloma formation.
Measurement of levels of TNF-α, IL-6 and IL-1β in LPS-induced endotoxemic mice
The mice were injected with IMT (15, 30 and 60 mg/kg) for 24 h in the presence of LPS (2 mg/kg). Subsequently, the mice were sacrificed and serum was collected to measure blood levels of TNF-α, IL-6 and IL-1β using ELISA kits, according to the manufacturer's protocols.
Cell culture
The murine macrophage RAW264.7 cell line was purchased from the Shanghai Cell Bank of the Chinese Academy of Sciences (Shanghai, China), and the cells were cultured in DMEM with 10% FBS, 1% penicillin and 1% streptomycin in a 5% CO2 humidified atmosphere at 37°C.
Analysis of cell viability using a Cell Counting kit-8 (CCK-8 assay)
The effects of IMT on cellular viability were evaluated using a CCK-8 assay according to the manufacturer's protocol. The RAW264.7 cells (5×103 cells/well) were seeded into 96-well plates and incubated with either increasing concentrations of IMT (18.5, 37, 74, 148, 296 and 592 µM) or vehicle (DMSO) in the presence of LPS (100 ng/ml). Following treatment for 72 h, CCK-8 solution was added to each well and incubated for another 1 h in the incubator. The absorbance at 450 nm was then read using a 96-well plate reader (Bio-Rad Laboratories, Inc., Hercules, CA, USA). The results were determined as a percentage of the DMSO control cells.
Quantitative analysis of the mRNA expression levels of TNF-α, IL-6 and IL-1β in RAW 264.7 cells
The effects of IMT on the mRNA expression levels of TNF-α, IL-6 and IL-1β were determined using reverse transcription-quantitative polymerase chain reaction (RT-qPCR) analysis. The RAW264.7 cells at a density of 3×105 cells/well were seeded into 6-well plates and incubated with either increasing concentrations of IMT (55.5, 111 and 222 µM) or vehicle (DMSO) in the presence of 100 ng/ml LPS for 72 h at 37°C. Subsequently, the cells were collected and total RNA was extracted using an RNAiso Plus kit (Takara Biotechnology Co., Ltd., Dalian, Japan). The total RNA was then used to synthesize cDNA of TNF-α, IL-6, IL-1β and β-actin using PrimeScript™ RT reagent kits (Takara Biotechnology Co., Ltd.). The reverse transcription temperature protocol was as follows: 37°C for 15 min and 85°C for 5 sec. The synthesized cDNAs were amplified using SYBR Green mix on a CFX96 Touch Real-Time PCR detection system (Bio-Rad Laboratories, Inc.). Each 10-µl reaction mixture contained 5 µl of SYBR Premix (Bio-Rad Laboratories, Inc.), 1 µl of 2 µM forward and reverse primer mix, 1 µl of cDNA, and 3 µl of ddH2O. The PCR thermocycling conditions were as follows: 95°C for 10 min, followed by 39 cycles of 95°C for 15 sec and 60°C for 60 sec. All primers used for RT-qPCR analysis are shown in Table I. The relative mRNA expression levels of TNF-α, IL-6 and IL-1β were assessed via 2−ΔΔCq relative quantitative analysis (17) and all samples were analyzed in triplicate.
Table I.
Primers used for reverse transcription-quantitative polymerase chain reaction analysis.
| Gene | Primer sequence (5′-3′) |
|---|---|
| TNF-α | Forward: CAGGTTCTGTCCCTTTCACTCACT |
| Reverse: GTTCAGTAGACAGAAGAGCGTGGT | |
| IL-6 | Forward: TGGAGTACCATAGCTACCTGGAGT |
| Reverse: TCCT-TAGCCACTCCTTCTGTGACT | |
| IL-1β | Forward: ATGGCAACTGTTCCTGAACTC |
| Reverse: TTAGGAAGACACGGATTCCAT | |
| β-actin | Forward: GGGAAATCGTGCGTGACATCAAAG |
| Reverse: CATACCCAAGAAGGAAGGCTGGAA |
TNF-α, tumor necrosis factor-α; IL, interleukin.
Western blot analysis
The effects of IMT on the protein expression levels of iNOS, COX-2, p65 (N), p65 (C) and IκB (C) were measured in the LPS-induced RAW264.7 cells using western blot analysis. Following treatment with either graded concentrations of IMT (55.5, 111 and 222 µM) or vehicle (DMSO) in the presence of 100 ng/ml LPS for 72 h, the cells were collected and total protein was extracted using western blot and IP cell lysis buffer (Sangon Biotech Co., Ltd.). Subsequently, the concentration of total protein was determined using BCA protein assay reagent (Sangon Biotech Co., Ltd.). The total protein (40 µg) in each sample was separated by 12% sodium dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide electrophoresis (SDS-PAGE) and blotted onto polyvinylidene difluoride (PVDF) filter membranes. The proteins on the PVDF membrane were then probed with anti-iNOS (1:1,000), anti-COX-2 (1:200), anti- p65 (1:200), anti-cytosolic IκB (1:200), anti-β-actin (1:5,000) and anti-Histone H1 (1:500) antibodies at 4°C for 12 h, followed by incubation with corresponding HRP-conjugated secondary antibodies (1:7,000) for 2 h at 37°C. Finally, the immunoreactive bands were visualized using ECL-detecting reagents and optical density (OD) values were analyzed using Image J 2X software. To normalize for protein loading, the expression levels of iNOS, COX-2, p65 (C) and IκB (C) were expressed as a relative value to that of β-actin, and the expression level of p65 (N) was expressed as a relative value to that of Histone H1.
Statistical analysis
All results are expressed as the mean ± standard deviation of three independent experiments performed in triplicate. Statistical analyses were performed using the SPSS 19.0 software package (IBM SPSS, Armonk, NY, USA). One-way analysis of variance with Dunnett's test was used to compare the means between two groups. P<0.05 was considered to indicate a statistically significance difference.
Results
Assessment of dimethylbenzene-induced ear edema
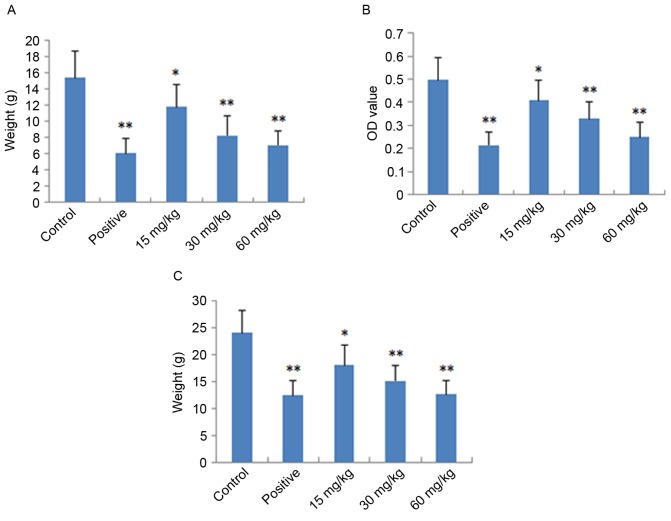
The local and acute anti-inflammatory activities of IMT were evaluated by measuring its inhibition of dimethylbenzene-induced ear edema in mice. As shown in Fig. 2A, IMT had significant and dose-dependent inhibitory effects on ear edema at concentrations of 15, 30 and 60 mg/kg, compared with the control group (P<0.05, P<0.01 and P<0.01, respectively). At a dose of 60 mg/kg, the anti-inflammatory activity of IMT was comparable with that of indometacin at a dose of 10 mg/kg.
Figure 2.
Anti-inflammatory effects of imperatorin on mice/rats. Indometacin (10 mg/kg) was used as the positive control drug. (A) Results of dimethylbenzene-induced ear edema assessment in mice; (B) results of acetic acid-induced vascular permeability assessment in mice; (C) results of cotton pellet-induced granuloma assessment in rats. Data are expressed as the mean ± standard deviation (n=10). *P<0.05 and **P<0.01, compared with the control group. OD, optical density.
Assessment of acetic acid-induced vascular permeability
The acute anti-inflammatory activity of IMT was also detected by measuring its inhibition of acetic acid-induced vascular permeability in mice. As shown in Fig. 2B, IMT at doses of 15, 30 and 60 mg/kg significantly inhibited the increased vascular permeability induced by acetic acid in mice, which also occurred in a dose-dependent manner (P<0.05, P<0.01 and P<0.01, respectively), compared with the control group. The inhibitory effect of IMT on dye leakage at a dose of 60 mg/kg was comparable with that of indometacin at the dose of 10 mg/kg.
Cotton granuloma assessment
The chronic anti-inflammatory activity of IMT was performed by measuring its inhibition of cotton pellet-induced granuloma in rats, the results of which are shown in Fig. 2C. The anti-inflammatory effect of IMT was observed at the doses of 15, 30 and 60 mg/kg. Compared with the control group, IMT significantly reduced ball fralunoma weight at doses of 15, 30 and 60 mg/kg (P<0.05, P<0.01 and P<0.01, respectively). The positive control drug, indometacin (10 mg/kg), also manifested significant anti-inflammatory activity (P<0.01).
Effects of IMT on LPS-induced cell viability
The effects of IMT on LPS-induced cell viability were evaluated using CCK-8. As shown in Fig. 3, no significant effect was observed when the RAW 264.7 cells were treated with graded concentrations of IMT (18.5–592 µM) in the presence of 100 ng/ml LPS for 72 h, compared with the control group (P>0.05). This indicated that IMT had no inhibitory effect on RAW 264.7 cell growth.
Figure 3.
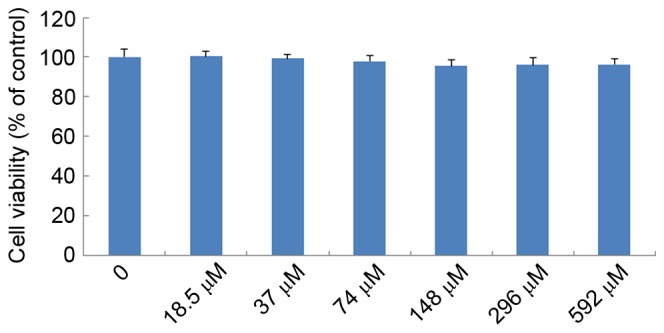
Effects of IMT on cell viability of RAW 264.7 cells. Following treatment with either increasing concentrations of IMT (18.5, 37, 74, 148, 296 and 592 µM) or vehicle (DMSO, negative control) for 72 h, cell viability was determined using a Cell Counting Kit-8 assay. Data are expressed as the mean ± standard deviation (n=6). IMT, imperatorin.
Effects of IMT on TNF-α, IL-6 and IL-1β in vitro and in vivo
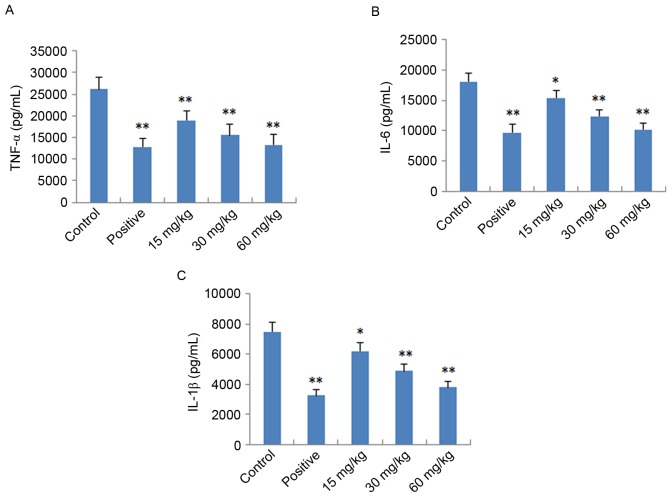
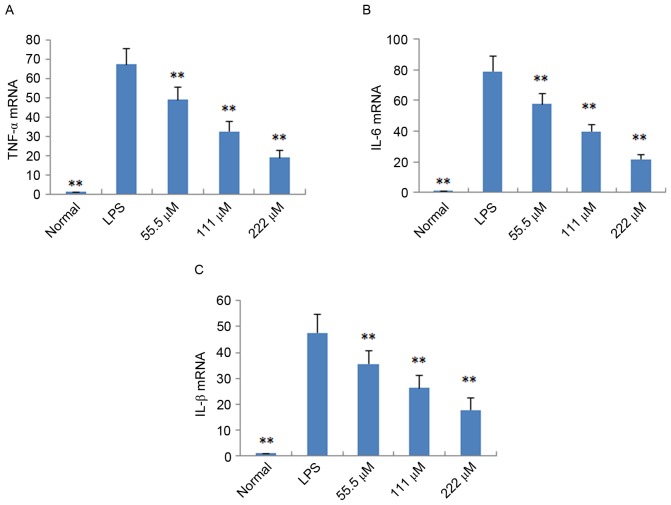
To further verify the anti-inflammatory effects of IMT in vitro and in vivo, the expression levels of pro-inflammatory cytokines (TNF-α, IL-6 and IL-1β) were determined in LPS-induced endotoxemic mice and RAW 264.7 cells using ELISA and RT-qPCR analysis, respectively. As shown in Fig. 4, following treatment with IMT (55.5, 111 and 222 µM), the levels of TNF-α, IL-6 and IL-1β induced by LPS were significantly reduced, compared with those in the LPS group (P<0.05) in the LPS-induced endotoxemic mice. In the LPS-induced RAW 264.7 cells, the mRNA expression levels of these pro-inflammatory cytokines were also significantly downregulated, compared with those in the LPS group (P<0.01; Fig. 5).
Figure 4.
Effect of imperatorin on plasma levels of (A) TNF-α, (B) IL-6 and (C) IL-1β in lipopolysaccharide-induced endotoxemic mice. Indometacin (10 mg/kg) was used as the positive control drug. Data are expressed as the mean ± standard deviation (n=10). *P<0.05 and **P<0.01, compared with the control group. TNF-α, tumor necrosis factor-α; IL, interleukin.
Figure 5.
Effect of imperatorin on (A) TNF-α, (B) IL-6 and (C) IL-1β in RAW 264.7 cells induced by LPS. Data are expressed as the mean ± standard deviation (n=10). **P<0.01, compared with the control group. LPS, lipopolysaccharide, TNF-α, tumor necrosis factor-α; IL, interleukin.
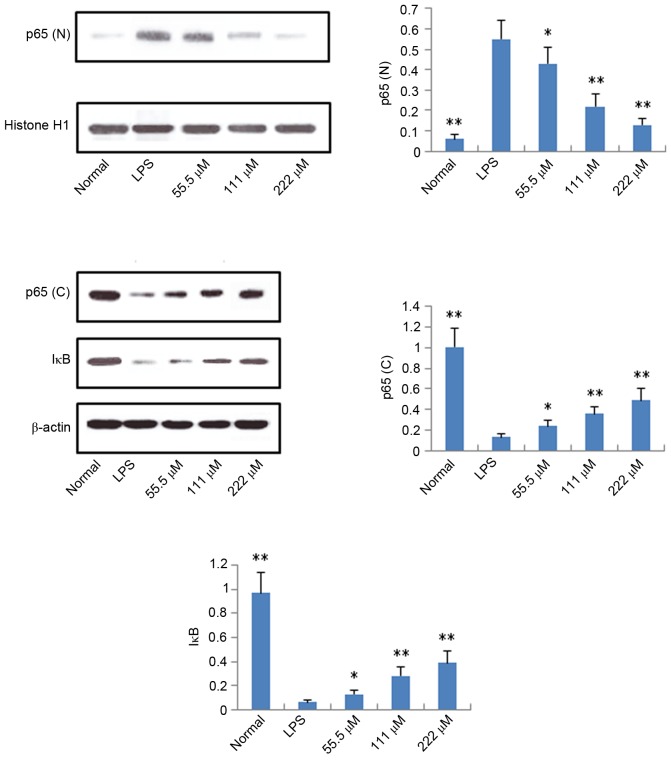
Protein expression levels of iNOS, COX-2, p65 and IκB
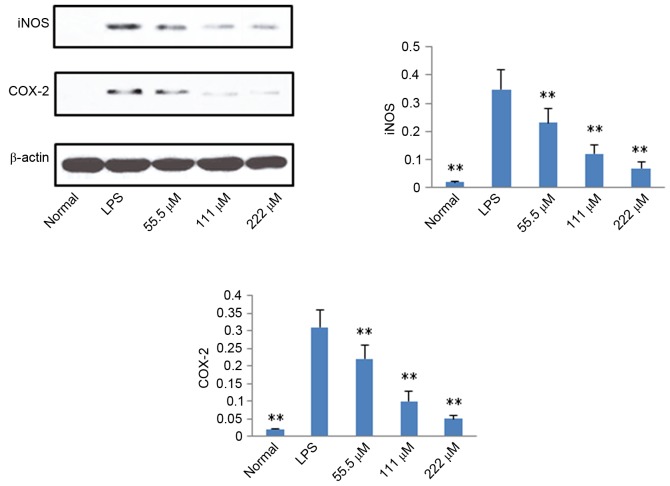
According to the results described above, IMT not only inhibited topical ear edema, vascular permeability and granuloma in vivo, but also suppressed the expression levels of pro-inflammatory cytokines TNF-α, IL-6 and IL-1β in vitro and in vivo. To further investigate the possible mechanisms underlying these changes, the protein expression levels of iNOS, COX-2, p65 (N), p65 (C) and IκB (C) were measured using western blot analysis. As shown in Figs. 6 and 7, compared with the LPS group, the protein expression levels of iNOS, COX-2 and p65 (N) were markedly downregulated in the IMT groups, whereas the protein expression of p65 (C) and IκB (C) were significantly upregulated in the LPS-induced RAW 264.7 cells.
Figure 6.
Effects of imperatorin on expression levels of iNOS and COX-2 in RAW 264.7 cells induced by LPS. Data are expressed as the mean ± standard deviation (n=10). **P<0.01, compared with the control group. LPS, lipopolysaccharide; iNOS, inducible nitric oxide synthase; COX-2, cyclooxygenase-2.
Figure 7.
Effects of imperatorin on expression levels of p65 (N), p65 (C) and IκB (C) in RAW 264.7 cells induced by LPS. Data are expressed as the mean ± standard deviation (n=10). *P<0.05 and **P<0.01, compared with the control group. LPS, lipopolysaccharide; p65 (N), nuclear p65; p65 (C), cytosolic p65; IκB, inhibitor of nuclear factor-κB.
Discussion
In the present study, comprehensive analyses of the acute and chronic anti-inflammatory activities of IMT were performed using mouse and rat models of inflammation. In addition, the in vitro anti-inflammatory effect of IMT was demonstrated using LPS-stimulated RAW264.7 macrophages. IMT significantly inhibited the levels of pro-inflammatory cytokines TNF-α, IL-6 and IL-1β in vitro and in vivo. The expression levels of pro-inflammatory enzymes COX-2 and iNOS were downregulated in the LPS-stimulated RAW264.7 macrophages treated with IMT.
The anti-inflammatory effect of IMT was evaluated using three popular in vivo models: Dimethylbenzene-induced ear edema, acetic acid-induced vascular permeability, and cotton pellet-induced granuloma (18,19). The assessment of dimethylbenzene-induced ear edema in mice is a useful model for preliminary experiments of acute anti-inflammatory activity. In the inflammatory response, there is increased vascular permeability; therefore, vascular permeability was assessed to further demonstrate the anti-inflammatory effects of IMT. In addition, cotton pellet-induced granuloma was assessed to evaluate the chronic anti-inflammatory activity. The results of the present study showed that IMT at doses of 15, 30 and 60 mg/kg led to topic inhibition of dimethylbenzene-induced ear edema in mice in a dose-dependent manner. At the same doses, IMT exhibited similar inhibitory effects on the increased vascular permeability of mice. IMT also significantly and dose-dependently reduced the weights of the cotton pellet granuloma in the cotton pellet-induced model of chronic inflammation in rats. These data suggested that IMT had potential anti-inflammatory activity, therefore; the effect of IMT on the release of inflammatory cytokines and mediators was also examined to elucidate its anti-inflammatory mechanism.
Inflammation is a local response to irritants, tissue injury and infection. During inflammation, circulating macrophages, mast cells and neutrophils produce cytokines, including TNF-α, IL-6 and IL-1β, which further exaggerate inflammatory responses (20). TNF-α, IL-6 and IL-1β are important in mediating acute inflammatory reactions. IL-1β can induce fever through enhancing the synthesis of PGE2. As with IL-1, TNF-α can trigger fever, either directly by inducing PGE2 synthesis or indirectly by stimulating the release of IL-1. Subsequently, TNF-α and IL-1 trigger secondary inflammatory effects by inducing the synthesis of IL-6 (21). Therefore, inhibition of these pro-inflammatory cytokines is an important treatment strategy for inflammatory diseases. In the present study, IMT suppressed the production of TNF-α, IL-6 and IL-1β in Raw264.7 cells and LPS-induced endotoxemic mice in a dose-dependent manner. These results indicated that IMT in LPS-stimulated macrophages and LPS-stimulated mice exerted anti-inflammatory effects by inhibiting the expression and secretion of pro-inflammatory cytokines.
In addition to cytokines, the inflammatory response induced by inflammatory mediators is generated through the upregulation of several inducible genes, including iNOS and COX-2. iNOS is expressed in macrophages under normal and pathological conditions. In infectious and with pro-inflammatory stimuli, a high protein expression level of iNOS is induced to produce NO, which is an important messenger molecule with a critical function in the host immune defence (22). COX is also a molecular target for anti-inflammatory treatments, which have been used for hundreds of years; for example, aspirin, a selective COX-2 inhibitor and nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug, has been used globally since 1899 (23). It is well known that the COX enzyme consists of at least two isoforms, COX-1 and COX-2. In humans, COX-1 protein is expressed at relatively stable levels in several normal tissues, whereas the protein expression of COX-2 is low in the majority of normal mammalian tissues in response to stimuli, including LPS insult. In macrophages, the LPS-induced induction and activation of signal transduction pathways results in activation of the gene expression of the COX-2 (22). In the present study, LPS significantly elevated the protein expression levels of iNOS and COX-2 in macrophages, and these levels were markedly suppressed by IMT in a dose-dependent manner. These results further supported the ability of IMT to inhibit inflammation, and this inhibitory effect may be associated with suppressing the production of inflammatory mediators iNOS and COX-2.
It is well known that NF-κB is a major regulator of pathogen- and inflammatory cytokine-inducible gene regulation (24). Several stimuli, including pro-inflammatory cytokines, can activate NF-κB, and activated NF-κB can induce the protein expression of pro-inflammatory cytokines, COX-2 and iNOS (25). NF-κB is a family of inducible dimeric transcription factors, which includes five members: Rel (c-Rel), RelA (p65), RelB, NF-κB1 (p50/p105) and NF-κB2 (p52/p100) (26). In unstimulated cells, the NF-κB family members (homodimers or heterodimers) are bound to ankyrin rich regions of IκB, an inhibitor of NF-κB protein, which serves to retain NF-κB dimers in the cytoplasm and thus inhibiting initiation of target gene transcription (26). As IκB dissociates from NF-κB, activated NF-κB is translocated to the nucleus and exerts its function as a transcription factor. In the present study, it was found that, following LPS stimulation of RAW 264.7 cells, the protein expression of p65 (N) was higher, compared with that of the control group, whereas the protein expression levels of p65 (C) and IκB (C) were significantly downregulated, which indicated that LPS led to the activation of NF-κB. IMT significantly increased the protein expression levels of p65 and IκB in the cytoplasm of LPS-triggered RAW 264.7 cells, and decreased the protein expression of p65 (N). These data indicated that IMT inhibited the LPS-induced activity of NF-κB in macrophages, and then suppressed the production of pro-inflammatory cytokines and mediators.
In conclusion, IMT exhibited significant anti-inflammatory effects in vitro and in vivo. IMT reduced the release of proinflammatory cytokines (TNF-α, IL-6 and IL-1β), inhibited the expression of inducible enzymes (iNOS and COX-2), and suppressed the activity of NF-κB via upregulation of the expression of p65 (C) and IκB (C), and downregulation of the expression of p65 (N).
References
- 1.Ferrero-Miliani L, Nielsen OH, Andersen PS, Girardin SE. Chronic inflammation: Importance of NOD2 and NALP3 in interleukin-1beta generation. Clin Exp Immunol. 2007;147:227–235. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2249.2006.03261.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Ryan GB, Majno G. Acute inflammation. A review. Am J Pathol. 1977;86:183–276. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Ward PA. Fundamentals of Inflammation. Cambridge University Press; Cambridge: 2010. Acute and Chronic Inflammation; pp. 1–16. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Shacter E, Weitzman SA. Chronic inflammation and cancer. Oncology (Williston Park) 2002;16:217–226. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Aggarwal BB, Vijayalekshmi RV, Sung B. Targeting inflammatory pathways for prevention and therapy of cancer: Short-term friend, long-term foe. Clin Cancer Res. 2009;15:425–430. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-08-0149. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Baek NI, Ahn EM, Kim HY, Park YD. Furanocoumarins from the root of Angelica dahurica. Arch Pharm Res. 2000;23:467–470. doi: 10.1007/BF02976574. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Yang XH, Hu X. Advance in pharmacology of imperatorin and isoimperatorin pharmacology. J Nanchang Uni Med Sic. 2012;52:95–97. [Google Scholar]
- 8.García-Argáez AN, Ramírez Apan TO, Delgado H Parra, Velázquez G, Martínez-Vázquez M. Anti-inflammatory activity of coumarins from Decatropis bicolor on TPA ear mice model. Plant Med. 2000;66:279–281. doi: 10.1055/s-2000-14894. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Kawaii S, Tomono Y, Ogawa K, Sugiura M, Yano M, Yoshizawa Y, Ito C, Furukawa H. Antiproliferative effect of isopentenylated coumarins on several cancer cell lines. Anticancer Res. 2001;21:1905–1911. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Luszczki JJ, Wojda E, Andres-Mach M, Cisowski W, Glensk M, Glowniak K, Czuczwar SJ. Anticonvulsant and acute neurotoxic effects of imperatorin, osthole and valproate in the maximal electroshock seizure and chimney tests in mice: A comparative study. Epilepsy Res. 2009;85:293–299. doi: 10.1016/j.eplepsyres.2009.03.027. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Wang MY, Ma YY, Li XB. Pharmcological effect of four linear furocomarins in Radix Angelicae dahuricae. Nat Prod Res Dev. 2010;22:485–489. [Google Scholar]
- 12.Abad MJ, de las Heras B, Silván AM, Pascual R, Bermejo P, Rodriguez B, Villar AM. Effects of furocoumarins from Cachrys trifida on some macrophage functions. J Pharm Pharmacol. 2001;53:1163–1168. doi: 10.1211/0022357011776432. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Ban HS, Lim SS, Suzuki K, Jung SH, Lee S, Lee YS, Shin KH, Ohuchi K. Inhibitory effects of furanocoumarins isolated from the roots of Angelica dahurica on prostaglandin E2 production. Planta Med. 2003;69:408–412. doi: 10.1055/s-2003-39702. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Huang GJ, Deng JS, Liao JC, Hou WC, Wang SY, Sung PJ, Kuo YH. Inducible nitric oxide synthase and cyclooxygenase-2 participate in anti-inflammatory activity of imperatorin from Glehnia littoralis. J Agric Food Chem. 2012;60:1673–1681. doi: 10.1021/jf204297e. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Li Q, Yang S, Yang S, Xin F, Wang M. Anti-inflammatory activity of phlomisoside F isolated from Phlomis younghusbandii Mukerjee. Int Immunopharmacol. 2015;28:724–730. doi: 10.1016/j.intimp.2015.07.035. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Santos F, Rao VS. Antiinflammatory and antinociceptive effects of 1,8-cineole a terpenoid oxide present in many plant essential oils. Phytother Res. 2000;14:240–244. doi: 10.1002/1099-1573(200006)14:4<240::AID-PTR573>3.0.CO;2-X. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Livak KJ, Schmittgen TD. Analysis of relative gene expression data using real time quantitative PCR and the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 2001;25:402–408. doi: 10.1006/meth.2001.1262. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Winter CA, Porter CC. Effect of alterations in side chain upon anti-inflammatory and liver glycogen activities of hydrocortisone esters. J Am Pharm Assoc Am Pharm Assoc. 1957;46:515–519. doi: 10.1002/jps.3030460902. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Wang QS, Yang L, Cui WY, Chen L, Jiang YH. Anti-inflammatory and anti-nociceptive activities of methanol extract from aerial part of Phlomis younghusbandii Mukerjee. PLoS One. 2014;9:e89149. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0089149. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Watkins LR, Maier SF, Goehler LE. Immune activation: The role of pro-inflammatory cytokines in inflammation, illness responses and pathological pain states. Pain. 1995;63:289–302. doi: 10.1016/0304-3959(95)00186-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Feghali CA, Wright TM. Cytokines in acute and chronic inflammation. Front Biosci. 1997;2:d12–d26. doi: 10.2741/A171. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Murakami A, Ohigashi H. Targeting NOX, INOS and COX-2 in inflammatory cells: Chemoprevention using food phytochemicals. Int J Cancer. 2007;121:2357–2363. doi: 10.1002/ijc.23161. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Vane JR, Botting RM. Mechanism of Action of Nonsteroidal Anti-inflammatory Drugs. Am J Med. 1998;104:2S–8S; 21S-22S. doi: 10.1016/S0002-9343(97)00203-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Baeuerle PA, Baichwal VR. NF-kappaB as a frequent target for immunosuppressive and anti-inflammatory molecules. Adv Immunol. 1997;65:111–137. doi: 10.1016/S0065-2776(08)60742-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Lee KM, Kang BS, Lee HL, Son SJ, Hwang SH, Kim DS, Park JS, Cho HJ. Spinal NF-kB activation induces COX-2 upregulation and contributes to inflammatory pain hypersensitivity. Eur J Neurosci. 2004;19:3375–3381. doi: 10.1111/j.0953-816X.2004.03441.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Brown KD, Claudio E, Siebenlist U. The roles of the classical and alternative nuclear factor-kappaB pathways: Potential implications for autoimmunity and rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Res Ther. 2008;10:212. doi: 10.1186/ar2457. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]