Abstract
Human adenovirus type 4 (HAdV-4) is most commonly isolated in military settings. We conducted detailed molecular characterization on 36 HAdV-4 isolates recovered from civilian adults with acute respiratory disease (ARD) in the northeastern United States during 2011–2015. Specimens came from college students, residents of long-term care facilities or nursing homes, a cancer patient, and young adults without co-morbidities. HAdV-4 genome types 4a1 and 4a2, the variants most frequently detected among US military recruits in basic training before the restoration of vaccination protocols, were isolated in most cases. Two novel a-like variants were recovered from students enrolled at a college in Tompkins County, New York, USA, and a prototype-like variant distinguishable from the vaccine strain was isolated from an 18-year-old woman visiting a physician’s office in Ulster County, New York, USA, with symptoms of influenza-like illness. Our data suggest that HAdV-4 might be an underestimated causative agent of ARD among civilian adults.
Keywords: adenovirus type 4, ARD, acute respiratory disease, ILI, influenza-like illness, next-generation sequencing, genome typing, viruses, respiratory infections, United States, adenovirus, HAdV-4, outbreak, civilians
Human adenovirus type 4 (HAdV-4), the only human adenovirus classified within species E, was first identified in the early 1950s in association with military outbreaks of febrile respiratory illness and is well-recognized worldwide as a prevalent causative agent of acute respiratory disease (ARD) and ocular disease (1–6). Surveillance studies conducted in the United States and other countries have demonstrated a leading role for this particular adenovirus type in the etiology of outbreaks of febrile respiratory illness in military recruit training facilities (7–11), where crowding and environmental contamination appear to facilitate transmission among nonvaccinated trainees (12,13). By using restriction enzyme analyses of viral DNA, several studies have reported extensive intratypic genetic variability for HAdV-4 (14–16). Two major clusters of genetic homology have been identified among circulating genomic variants: prototype (p)–like viruses, which are closely related to prototype strain RI-67, and a-like viruses, which exhibit, among other characteristics, distinct BamHI restriction profiles (15), a distinct inverted terminal repeat (17,18), and a different genetic make-up in the E3 region (A.E. Kajon, unpub. data).
HAdV-4 respiratory infections are preventable by vaccination with the live oral formulation of the nonattenuated p-like strain exclusively licensed for military use (19,20). After 15 years of discontinuation of HAdV-4 vaccination protocols with the consequent resurgence of continuous outbreaks of HAdV-4–associated illness in US recruit training facilities nationwide, US Department of Defense reinstated the vaccine in November 2011, dramatically reducing the number of cases of HAdV infection in basic training camps (21,22).
The absence of a sentinel system for HAdV surveillance outside of the military has made assessing the burden of disease attributable to HAdV-4 infection among civilians difficult. The limited epidemiologic data available in the published literature suggest that respiratory disease associated with HAdV-4 infection is detected at a significantly lower frequency than disease associated with species C or B HAdV types among children and that HAdV-4 infection occurs rarely among civilian adults (23–27).
Consequently, the apparent increased frequency of detection of cases and case clusters of HAdV-4 respiratory infection in the northeastern United States, documented by the New York State Department of Health (NYSDOH) or the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) (data not shown), caught our attention. In this article, we report the molecular characterization of 36 select HAdV-4 isolates from a selection of retrospectively evaluated cases among civilians.
Methods
Source of Specimens
We obtained HAdV-4–positive specimens from patients with ARD/influenza-like illness (ILI) characterized by fever >37.8°C and cough, sore throat, or other respiratory symptoms. We selected cases that were originally identified by the NYSDOH as part of its activities for the US Sentinel Physician ILI Surveillance Network (https://www.cdc.gov/flu/weekly/pdf/flu-surveillance-overview) or that represented special HAdV cases referred to the CDC for investigation because of their clinical disease severity or occurrence during an outbreak. Institutional review board review was not required for the processing of clinical samples or for the evaluation of patient information, which were obtained during routine diagnostic workups at the Clinical Virology Laboratory, Yale–New Haven Hospital (New Haven, Connecticut, USA), and the University of Rochester Medical Center (Rochester, New York, USA). Review board approval was also not required for the typing protocol used on deidentified HAdV isolates at the Lovelace Respiratory Research Institute (Albuquerque, New Mexico, USA).
Virus Isolation and Initial Identification
Virus isolation from respiratory specimens and typing was performed at CDC (Atlanta, Georgia, USA) or the Virology Laboratory, Wadsworth Center NYSDOH (Albany, New York, USA). The virus isolates were initially identified as HAdV-4 by molecular procedures as previously described (28,29).
Genome Typing by Restriction Enzyme Analysis
Cultured isolates were shipped to Lovelace Respiratory Research Institute for propagation and extraction of intracellular viral DNA from infected A549 cell monolayers as previously reported (30). We digested viral DNA samples with a panel of 6 endonucleases to identify genomic variants following the initial guidelines of Li and Wadell (15) and as previously applied to the genomic characterization of US military strains (16) to facilitate comparisons. In brief, we digested 1 μg of purified viral DNA with BamHI, DraI, EcoRI, EcoRV, SmaI, and XhoI (New England Biolabs, Ipswich, MA, USA) in a 20-μL reaction following the manufacturer’s recommended conditions. For the isolates selected for complete genomic sequencing, we performed genome typing by in silico digestion of their viral DNA with the same panel of enzymes using Geneious Pro 9 (Biomatters Ltd, Auckland, New Zealand) (31).
Genome Sequencing and Analysis
We then carried out next-generation sequencing reactions at the Wadsworth Center’s Applied Genomics Technology Core with the purified viral genomic DNA prepared at Lovelace Respiratory Research Institute. The 12 isolates that were selected for next-generation sequencing were representative of the set of identified variants on the basis of restriction enzyme analysis, location, and date of detection. We prepared libraries with the NexteraXT kit (Illumina, San Diego, CA, USA) and performed paired-end sequencing on the Illumina MiSeq using the NextSeq 500 cycle v2 kit (Illumina). We assembled all genomic sequences de novo using the Illumina BaseSpace cloud application for SPAdes 3.5 (http://spades.bioinf.spbau.ru/release3.5.0/manual.html); we then remapped the sample sequences to the consensus sequence using Geneious Pro 9 (https://www.geneious.com/). Confirmation of sequence accuracy for specific regions of the genome was carried out by Sanger sequencing of PCR amplicons as needed. We annotated the HAdV-4 genomes using curated reference sequences available for the prototype RI-67 strain (GenBank accession no. AY594253), the vaccine strain CL68578 (GenBank accession no. AY487947), and several military isolates representing previously described genomic variants (GenBank accession nos. EF371058, AY599837, and AY599835).
For phylogenetic analysis, we aligned the genomic sequences generated in this study with reference strains (Table 1) using MAFFT in Geneious Pro 9. We constructed a maximum-likelihood tree on the basis of the Kimura 2-parameter model (32) with 500 bootstrap replicates using MEGA6 (33).
Table 1. Clinical isolates and reference strains used in the phylogenetic analysis of HAdV-4 strains recovered from cases of acute respiratory infection detected in northeastern United States, 2011–2015*.
| Virus name | Place and year of isolation | Genome type | GenBank accession no. |
|---|---|---|---|
| Isolates from this study | |||
| TB071911 | Yale, CT, 2011 | 4a2 | KY996453 |
| 12-12752 (NY7) | NY, 2012 | 4a2 | KY996450 |
| 12-27440 (NY8) | NY, 2012 | 4a1 | KY996451 |
| 13-5497 (NY11) | NY, 2013 | 4a SmaI v | KY996449 |
| 14-4876 (NY16) | NY, 2014 | 4a2 | KY996448 |
| 14-9111 (NY17) | NY, 2014 | 4a1 | KY996442 |
| 14-33430 (NY20) | NY, 2014 | 4a1 | KY996445 |
| 14-38662 (NY21) | NY, 2014 | 4a1 | KY996443 |
| 14-38813 (NY22) | NY, 2014 | 4a1 | KY996444 |
| 15-418 (NY23) | NY, 2015 | 4a1 | MF002042 |
| 15-3477 (NY24) | NY, 2015 | 4a SmaI/XhoI v | KY996446 |
| 15-4054 (NY25) |
NY, 2015 |
4p |
KY996447 |
| Reference strains | |||
| RI-67 | Fort Leonard Wood, MO, 1952 | 4p | AY594253 |
| CL68578† | Camp Lejeune, NC, 1965 | 4p | AY487947 |
| RU-2533 | Cape May, NJ, 1966 | 4p | MF002043 |
| NHRC90339 | Cape May, NJ, 2001 | 4p4 | EF371058 |
| NHRC42606 | Fort Jackson, SC, 2002 | 4a2 | AY599835 |
| NHRC3 | Brooks Air Force Base, TX, 2003 | 4a1 | AY599837 |
*HAdV-4, human adenovirus type 4; NHRC, Naval Health Research Center; v, variant. †Vaccine strain.
Results
Case Descriptions
The HAdV-4–positive ARD/ILI cases we evaluated occurred in otherwise healthy teenagers, young adults in college, and older adult patients who were residing in long-term care facilities, with 1 older adult patient hospitalized in a cancer center. Some cases required prolonged hospitalization or had fatal outcomes.
Nosocomial Outbreak of HAdV-4 Respiratory Infection in Long-Term Care Facility for Elderly—Boston, Massachusetts, April–May 2006
A detailed description of this outbreak was published by Kandel et al. in 2010 (34). In brief, the outbreak occurred in a unit with 40 residents of mean age 88 (range 66–99) years. During April–May 2006, fifteen residents had symptoms of ARD. HAdV-4 infection was confirmed for 4 residents who had positive virus culture results through PCR amplification and sequencing of the hexon hypervariable regions 1–6 as described by Lu and Erdman (28). The nasopharyngeal aspirates from 3 symptomatic residents gave negative virus culture results, and the remaining 8 residents were not sampled. Three of the 4 patients with confirmed HAdV-4 infections died of complications from ARD. Isolates from 2 of the confirmed cases of HAdV-4–associated pneumonia identified during this outbreak were processed for viral DNA extraction and detailed characterization. The 2 respiratory isolates were genome typed as variant 4a1 by restriction enzyme analysis at Lovelace Respiratory Research Institute.
Adult Case of Severe Pneumonia—Connecticut, July 2011
One author (M.L.L.) was involved in testing, consulting, and advising on this case as the clinical laboratory director and as an infectious disease specialist. A 26-year-old man with an unremarkable medical history sought treatment at an emergency department for a 3-day illness involving severe headache, photophobia, nausea, vomiting, and chills. He had seen his doctor 2 days earlier and was treated with azithromycin without improvement. His lumbar puncture results were normal, but a chest radiograph showed a left upper lobe infiltrate. Blood work showed a normal white blood cell count with 27% band cells, anemia, thrombocytopenia, and elevated creatinine. The patient was admitted and treated with ceftriaxone and azithromycin. On the following day, he experienced severe respiratory distress, so he was intubated and transferred to intensive care. His nasopharyngeal swab tested positive by panadenovirus PCR at the Clinical Virology Laboratory, Yale New Haven Hospital. On the 5th day after hospital admission, the patient remained febrile, and his chest radiograph showed diffuse bilateral infiltrates; dialysis was initiated for a creatinine of 4.9 mg/dL (or 430 µmol/L, reference range 53–106 µmol/L). By using the pan-adenovirus PCR, the plasma viral load was determined to be 1.16 × 104 copies/mL. Molecular typing conducted at CDC confirmed the presence of HAdV-4 in both the nasopharyngeal swab and plasma specimens. By using a HAdV-4–specific PCR (35), the plasma viral load was determined to be 5.00 × 105 copies/mL. The patient eventually recovered with supportive therapy. The HAdV-4 isolate obtained from the nasopharyngeal swab was genome typed at Lovelace Respiratory Research Institute as variant 4a2 by restriction enzyme analysis.
Cases of ILI among College Students—New York, 2011–2015
During December 2011–October 2015, several HAdV-4–positive cases were identified at the Wadsworth Center Virology Laboratory among students enrolled at 7 colleges in 6 New York counties (Table 2; Figure 1). Persons arrived at their corresponding student health clinics with symptoms of ILI but tested negative for influenza by the CDC human influenza virus real-time reverse transcriptase PCR diagnostic panel. Four different HAdV-4 genomic variants were isolated from this group of patients 18–25 years of age (Table 2).
Table 2. Basic demographics, clinical characteristics, and virology findings of 33 cases of HAdV-4 acute respiratory infection detected by New York State Department of Health surveillance, New York, USA, 2011–2015*.
| Case ID | Specimen collection date | Specimen | Patient age, y/sex | Setting | County | Diagnosis | Genome type† |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NY1 | 2011 Dec | NPS, OPS | 19/M | College 1 | Albany | ILI | 4a1 |
| NY2 | 2011 Dec | NSW | 18/M | College 2 | Tompkins | ILI | 4a2 |
| NY3 | 2012 Jan | NPS, OPS | 29/M | Outpatient visit | Broome | ILI | 4a2 |
| NY4 | 2012 Jan | NPS, OPS | 21/F | College 1 | Albany | ILI | 4a2 |
| NY5 | 2012 Jan | NPS, OPS | 21/M | College 1 | Albany | ILI | 4a2 |
| NY6 | 2012 Jan | NPS, OPS | 22/M | College 1 | Albany | ILI | 4a2 |
| NY7 | 2012 Apr | NPS | 22/F | College 3 | Clinton | ILI | 4a2‡ |
| NY8 | 2012 Aug | NPS/TA | 43/F | ICU | Ontario | Pneumonia, acute respiratory distress syndrome | 4a1‡ |
| NY9 | 2012 Sep | NPS | 98/F | Nursing home | Dutchess | Pneumonia | 4a1 |
| NY10 | 2012 Oct | TS | 43/M | Cancer center | New York | Fatal outcome | 4a2 |
| NY11 | 2013 Feb | NPS | 21/M | College 4 | Tompkins | ILI | 4a SmaI v‡ |
| NY12 | 2013 Feb | NPS, OPS | 20/F | College 4 | Tompkins | ILI | 4a SmaI v |
| NY13 | 2013 Mar | NPS | 19/M | College 4 | Tompkins | ILI | 4a SmaI v |
| NY14 | 2013 Apr | NPS, OPS | 18/M | College 4 | Tompkins | ILI | 4a SmaI v |
| NY15 | 2013 Dec | NPS | 21/F | College 4 | Tompkins | ILI | 4a1 |
| NY16 | 2014 Feb | NPS | 19/M | College 5 | Cortland | ILI | 4a2‡ |
| NY17 | 2014 Mar | NPS | 20/F | College 6 | Nassau | ILI | 4a2‡ |
| NY18 | 2014 Mar | NPS | 18/F | College 7 | Broome | ILI | 4a2 |
| NY19 | 2014 May | NPS, OPS | 19/F | College 4 | Tompkins | ILI | 4a2 |
| NY20 | 2014 Oct | NPS | 18/M | College 2 | Tompkins | ILI | 4a1‡ |
| NY21 | 2014 Dec | NPS, OPS | 25/F | College 4 | Tompkins | ILI | 4a1‡ |
| NY22 | 2014 Dec | NPS | 18/M | College 2 | Tompkins | ILI | 4a1‡ |
| NY23 | 2015 Jan | NPS | 13/M | Outpatient visit | Schenectady | ILI | 4a1‡ |
| NY24 | 2015 Feb | NPS, OPS | 20/M | College 4 | Tompkins | ILI | 4a SmaI/XhoI v‡ |
| NY25 | 2015 Feb | NPS, OPS | 18/F | Outpatient visit | Ulster | ILI | 4p‡ |
| NY26 | 2015 Oct | NPS | 21/M | College 2 | Tompkins | ILI | 4a1 |
| NY27 | 2015 Oct | NPS | 20/M | College 2 | Tompkins | ILI | 4a1 |
| NY28 | 2015 Oct | NPS | 18/F | College 2 | Tompkins | ILI | 4a1 |
| NY29 | 2015 Oct | NPS | 20/M | College 2 | Tompkins | ILI | 4a1 |
| NY30 | 2015 Oct | NPS | 18/F | College 2 | Tompkins | ILI | 4a1 |
| NY31 | 2015 Oct | NPS | 18/M | College 2 | Tompkins | ILI | 4a1 |
| NY32 | 2015 Oct | NPS | 19/F | College 2 | Tompkins | ILI | 4a1 |
| NY33 | 2015 Oct | NPS | 22/M | College 2 | Tompkins | ILI | 4a1 |
*HAdV-4, human adenovirus type 4; ICU, intensive care unit; ID, identification; ILI, influenza-like illness; NPS, nasopharyngeal swab; OPS, oropharyngeal swab; TA, tracheal aspirate; TS, throat swab; v, variant exhibiting unpublished profiles for the specified endonucleases. †Determined by restriction enzyme analysis of viral genomic DNA performed in vitro, in silico, or both with BamHI, DraI, EcoRI, EcoRV, SmaI, and XhoI and designated according to Li and Waddell (15). ‡Restriction enzyme analysis by in silico digestion.
Figure 1.
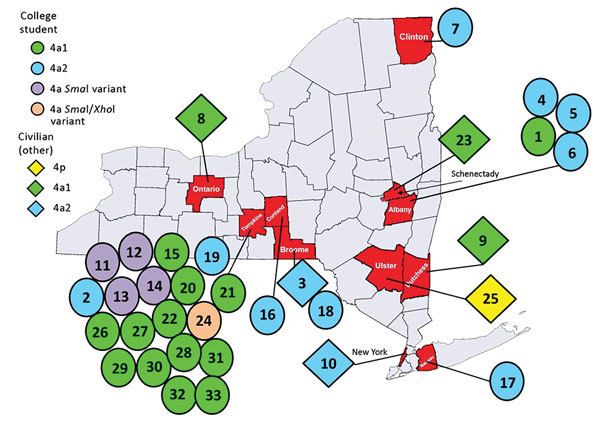
Geographic distribution of cases of human adenovirus type 4 (HAdV-4) infection identified by the New York State Department of Health through sentinel surveillance efforts targeting influenza-like illness (ILI), by HAdV-4 type, by type of civilian, by county, New York, USA, 2011–2015. Respiratory specimens were collected from patients with ILI at physicians’ offices, long-term care facilities, hospitals, and colleges and submitted to the Clinical Virology Laboratory at Wadsworth Center (Albany, New York, USA) to identify the causative agent.
Additional Cases of HAdV-4 Infection Identified by ILI Surveillance—New York, 2011–2015
During 2011–2015, ILI surveillance efforts identified 5 additional cases of acute HAdV-4 respiratory infection of variable severity (Table 2; Figure 1). These cases included infections in 2 adult patients (NY3 and NY25) sampled in physicians’ offices, a case of pneumonia reported in a nursing home (NY9), a fatal case involving respiratory complications in a patient at a cancer center (NY10), and a case of ARD detected in a teenager at a pediatric clinic (NY23).
Adult Case of Severe Pneumonia—Ontario County, New York, August 2012
One author (M.M.) was involved in testing, consulting, and advising on this case as the director of the Virology Laboratory at the Strong Memorial Hospital, University of Rochester Medical Center. A 43-year-old woman with cough and an unremarkable medical history sought treatment at the emergency department of University of Rochester Medical Center, Monroe County (NY8; Table 2; Figure 1). She was prescribed levofloxacin for presumed community-acquired pneumonia and sent home. Four days later, she was admitted with worsening cough, shortness of breath, and rigors and was found to have bilateral infiltrates on chest radiograph, anemia, and leukocytosis. She subsequently required intubation for declining respiratory status. Despite treatment with multiple broad-spectrum antimicrobial drugs, she experienced severe hypoxic hypercarbic respiratory failure requiring venous-venous extracorporeal mechanical oxygenation. Her nasopharyngeal swab was positive for HAdV by FilmArray (BioFire Diagnostics, bioMérieux, Marcy l’Etoile, France). She was treated with 3 doses of cidofovir. Her hospital course was complicated by severe acute kidney injury, acute tubular necrosis, and anuria requiring continuous veno-venous hemofiltration. Additional complications included cerebral edema, intracranial hemorrhage, and persistent hypertension. She was weaned from the ventilator after 40 days and was discharged to in-patient rehabilitation on day 53 of hospitalization. A year after discharge, she continued to experience bronchiectasis and dyspnea on exertion but had otherwise returned to her previous level of function. HAdV was isolated from cultures of the patient’s tracheal aspirate and nasopharyngeal swab, and a PCR of her peripheral blood demonstrated a virus load of 3.47 × 105 copies/mL. Molecular typing at the Wadsworth Center identified the virus as HAdV-4. The HAdV-4 isolate was genome typed as variant 4a1 by both in vitro and in silico restriction enzyme analyses (Table 2).
Virology Findings
Among these 36 select cases (some associated with outbreaks and some epidemiologically unlinked ARD cases) that occurred during 2009–2015 in the northeastern United States, 5 different genomic variants of HAdV-4 were identified by gel-based or in silico restriction enzyme analysis (Figure 2). Isolate NY25 (GenBank accession no. KY996447) was identified as 4p-like (Figure 3) and was indistinguishable from the prototype strain RI-67 or the vaccine strain CL68578 by restriction enzyme analysis (Figure 2). Of the 35 a-like isolates, 18 were classified as genome type 4a1, 12 as genome type 4a2, 4 as genome type 4a SmaI v (having a 4a-like genome with a novel SmaI profile), and 1 as genome type 4a SmaI/XhoI v (having a 4a-like genome with novel SmaI and XhoI profiles) (Table 2).
Figure 2.
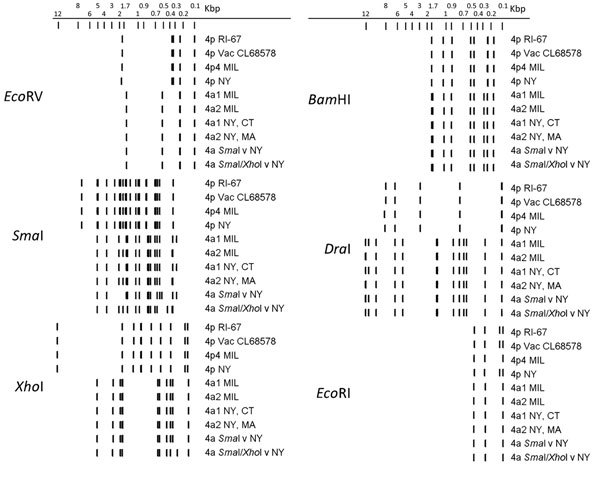
In silico restriction enzyme analysis of human adenovirus type 4 genomes representing the spectrum of genetic variability of the 36 isolates characterized in study of acute respiratory infection detected in the northeastern United States, 2011–2015. We generated restriction enzyme profiles for the completely sequenced genomes obtained in this study and from reference sequences available in GenBank using Geneious Pro (31). 4p4 MIL is isolate NHR90339, 4a1 MIL is isolate NHRC3, and 4a2 MIL is isolate 42606; 4a SmaI v is isolate NY11 (GenBank accession no. KY996449) and 4a SmaI/XhoI v is isolate NY24 (GenBank accession no. KY996446). MIL, military isolate; v, variant; Vac, vaccine strain.
Figure 3.
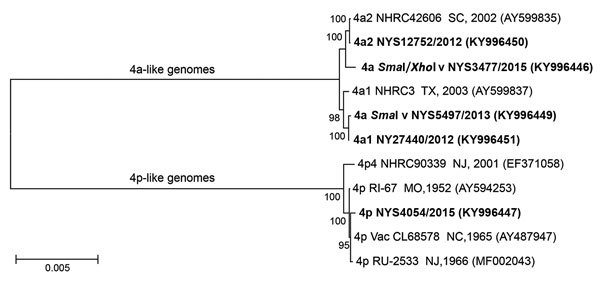
Phylogenetic analysis of complete genomic sequences of human adenovirus type 4 reference strains and clinical isolates representative of those examined in study of cases of acute respiratory infection detected in northeastern United States, 2011–2015. We inferred the phylogenetic tree using the maximum-likelihood method on the basis of the Kimura 2-parameter model (32). Evolutionary analyses were conducted in MEGA6 (33). Isolates sequenced in this study are in bold. GenBank accession numbers are in parentheses. Scale bar indicates substitutions per site.
To investigate a possible transmission event of the vaccine strain administered orally to US military recruits since October 2011 (22), we further characterized the 4p-like strain isolated from case NY25 by whole-genome sequencing. We identified 10 point mutations scattered throughout the genome (6 nonsynonymous and a 3-nt [CAG] in-frame insertion at position 23402 within the L4 coding region and open reading frame of the 100-kDa protein), distinguishing the 2015 isolate from the vaccine strain, CL68578. Phylogenetic analysis of HAdV-4 genomic sequences (Figure 3) also showed this isolate to be more closely related to strains RI-67 and CL68578 than to strain NHRC 90339 (GenBank accession no. EF371058), which was isolated at the Coast Guard Recruit Training Center (Cape May, New Jersey, USA) in 2001 and is representative of genome type 4p4, the only p-like variant detected at military training facilities through 2011 (16) (A.E. Kajon, unpub. data). The phylogenetic analysis revealed 2 major clades, recapitulating the original observations and genomic clustering of variants by Li and Wadell (15). The analysis also showed the SmaI variant to be closely related to genome type 4a1 and the SmaI/XhoI variant to be closely related to genome type 4a2.
Discussion
Enhanced influenza surveillance by public health laboratories initiated after the emergence of pandemic influenza A(H1N1) in 2009, as well as the wider availability of molecular diagnostic assays for multiple viral pathogens, have resulted in increased diagnostic efforts to determine the etiology of influenza-negative ILI, with consequent increased detection of HAdV-associated ARD. As part of our ongoing collaborative efforts to describe the molecular epidemiology and determine the prevalence of HAdV-associated respiratory disease, we examined HAdV-4 isolates recovered from college students with acute febrile respiratory illness in New York and several adults with severe respiratory disease in other locations in the northeastern United States. Restriction enzyme analysis with enzymes previously used to characterize HAdV strains from military recruits (16) and complete genomic sequencing identified 5 different genomic variants among the characterized clinical HAdV-4 isolates. Two of these variants, 4a1 and 4a2, had been previously identified in association with outbreaks of febrile respiratory illness in military recruit training facilities in the United States and found to be highly prevalent in the basic training environment nationwide before reinstatement of recruit vaccination protocols in 2011 (16) (A.E. Kajon, unpub. data). The genomic variant 4a1 was isolated from the respiratory specimens of 18 of 36 civilians and 4a2 from the respiratory specimens of 12 of 36 civilians retrospectively examined in this study. Two previously unreported variants closely related to 4a1 (SmaI v, n = 4) and 4a2 (SmaI/XhoI v, n = 1) were identified among the 8 examined cases detected at college 4 in Tompkins County, New York. Surprisingly, a p-like, vaccine-like strain was isolated from a respiratory specimen obtained from an 18-year-old woman (case NY25) at a physician’s office in Ulster County, New York, in February 2015. The genome of this clinical isolate (15–4054; Table 1) had a close similarity to the vaccine strain CL68578, and the NYSDOH epidemiology team confirmed contact between this patient and an active member of the military. However, the mutations distinguishing the genome of this isolate from that of the vaccine strain exclude possible transmission from this source. Evolution of this p-like virus from the vaccine strain is highly likely, considering the ability of HAdV-4 to establish persistent infections in gut lymphoid tissue (36) and that vaccinated persons shed the infectious-nonattenuated vaccine strain in their stool (37).
Our molecular epidemiology study of HAdV-4 infections in nonvaccinated military recruits in training during 1997–2011 demonstrated the lack of circulation of vaccine-like strains in the military environment during the 15 years of clear dominance of this re-emerging type as a causative agent of febrile respiratory illness in US recruit training camps (16). Unfortunately, no studies have reported genome typing data for civilian isolates obtained during the same period. A p-like variant designated 4p4 was identified as the only HAdV-4 genomic variant detected among military trainees at the US Coast Guard Training Center in Cape May through 2011 and, albeit with relatively low prevalence, as the only p-like variant circulating at the other 7 military training sites under surveillance (16) (A.E. Kajon, unpub. data).
Conceivably, exposure of the general population to the nonattenuated vaccine strain could have continued through fecal shedding from persons vaccinated during 1971–1997. Another possibility is that the p-like variants could have been circulating among civilian communities at low prevalence since the 1950s, when they were first identified (2). This topic warrants additional research and continued surveillance to further our understanding of the dynamics and routes of transmission of respiratory HAdVs that have the ability to establish persistent infection in the gut lymphoid tissue.
On the basis of the severity of the clinical presentation of some cases in this study, the HAdV-4 vaccine currently licensed for military use should be considered a potentially valuable resource to prevent disease in susceptible populations living in closed communities, such as college settings, summer camps, and long-term care facilities. Our data and reports of cases of severe ARD associated with HAdV-4 infection in Italy and Singapore (38,39) suggest that the role of this HAdV type in the etiology of adult civilian ARD might have been underestimated in the absence of access to molecular (or other) typing resources. Further, in view of the results of this study and previous research documenting the contribution of HAdV infection to influenza-negative ILI (29), the inclusion of HAdV in differential diagnostic test panels would be invaluable to better assess the role of HAdVs as causative agents of severe respiratory illness and to prevent unnecessary treatment of patients with influenza-negative ILI with anti-influenza agents. In addition, while the failure to detect influenza virus does not guarantee the virus was never present, the detection of HAdV in these cases assists in alleviating concerns regarding influenza vaccine failure. Finally, the potential differences in pathogenicity, transmissibility, and fitness between p-like and a-like genomic variants of HAdV-4 that would explain the marked predominance of a-like variants in the examined collections of HAdV-4–positive respiratory specimens representing sampling of ARD in civilian and military populations in the United States over the past 5 decades (16,40) deserve further investigation.
Acknowledgments
We dedicate this work in memoriam to our co-author Marilyn Menegus in celebration of her passion for clinical virology.
The authors thank Mathew Shudt for providing technical support with genomic sequencing.
This work was partially supported by the CDC (cooperative agreement no. 5U50CK000423). C.R.B. is supported by the University of New Mexico Infectious Diseases and Inflammation National Institutes of Health Training Grant T32-AI007538.
About the Author
Biography
Dr. Kajon is a scientist in the Infectious Disease Program at Lovelace Respiratory Research Institute in Albuquerque, New Mexico, and adjunct faculty at the Department of Molecular Genetics and Microbiology and a member of the Center for Infectious Disease and Immunity at the University of New Mexico. Her primary research interests include molecular epidemiology of adenovirus respiratory infections, natural history of adenovirus infections in transplant recipients, and viral pathogenesis.
Footnotes
Suggested citation for this article: Kajon AE, Lamson DM, Bair CR, Lu X, Landry ML, Menegus M, et al. Adenovirus type 4 respiratory infections among civilian adults, northeastern United States, 2011–2015. Emerg Infect Dis. 2018 Feb [date cited]. https://doi.org/10.3201/eid2402.171407
Preliminary results from this study were presented at the 12th International Adenovirus Meeting, August 16–20, 2016; Barsinghausen, Germany.
Deceased.
References
- 1.Hilleman MR, Werner JH. Recovery of new agent from patients with acute respiratory illness. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1954;85:183–8. 10.3181/00379727-85-20825 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Hilleman MR, Werner JH, Dascomb HE, Butler RL, Stewart MT. Epidemiology of RI(RI-67) group respiratory virus infections in recruit populations. Am J Hyg. 1955;62:29–42. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Van Der Veen J, Van Der Ploeg G. An outbreak of pharyngoconjunctival fever caused by types 3 and 4 adenovirus at Waalwijk, The Netherlands. Am J Hyg. 1958;68:95–105. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Aoki K, Kato M, Ohtsuka H, Ishii K, Nakazono N, Sawada H. Clinical and aetiological study of adenoviral conjunctivitis, with special reference to adenovirus types 4 and 19 infections. Br J Ophthalmol. 1982;66:776–80. 10.1136/bjo.66.12.776 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Gomes SA, Gabbay YB, Nascimento JP, Niel C. Genome analysis of adenovirus 4a, a causative agent of pharyngoconjunctival fever and respiratory diseases in Brazil. J Med Virol. 1988;26:453–9. 10.1002/jmv.1890260413 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Ariga T, Shimada Y, Ohgami K, Tagawa Y, Ishiko H, Aoki K, et al. New genome type of adenovirus serotype 4 caused nosocomial infections associated with epidemic conjunctivitis in Japan. J Clin Microbiol. 2004;42:3644–8. 10.1128/JCM.42.8.3644-3648.2004 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Hendrix RM, Lindner JL, Benton FR, Monteith SC, Tuchscherer MA, Gray GC, et al. Large, persistent epidemic of adenovirus type 4-associated acute respiratory disease in U.S. army trainees. Emerg Infect Dis. 1999;5:798–801. 10.3201/eid0506.990609 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Gray GC, Goswami PR, Malasig MD, Hawksworth AW, Trump DH, Ryan MA, et al. ; Adenovirus Surveillance Group. Adult adenovirus infections: loss of orphaned vaccines precipitates military respiratory disease epidemics. Clin Infect Dis. 2000;31:663–70. 10.1086/313999 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Kolavic-Gray SA, Binn LN, Sanchez JL, Cersovsky SB, Polyak CS, Mitchell-Raymundo F, et al. Large epidemic of adenovirus type 4 infection among military trainees: epidemiological, clinical, and laboratory studies. Clin Infect Dis. 2002;35:808–18. 10.1086/342573 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Russell KL, Hawksworth AW, Ryan MA, Strickler J, Irvine M, Hansen CJ, et al. Vaccine-preventable adenoviral respiratory illness in US military recruits, 1999-2004. Vaccine. 2006;24:2835–42. 10.1016/j.vaccine.2005.12.062 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Mölsä M, Hemmilä H, Rönkkö E, Virkki M, Nikkari S, Ziegler T. Molecular characterization of adenoviruses among finnish military conscripts. J Med Virol. 2016;88:571–7. 10.1002/jmv.24364 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Broderick MP, Hansen CJ, Russell KL. Exploration of the effectiveness of social distancing on respiratory pathogen transmission implicates environmental contributions. J Infect Dis. 2008;198:1420–6. 10.1086/592711 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Russell KL, Broderick MP, Franklin SE, Blyn LB, Freed NE, Moradi E, et al. Transmission dynamics and prospective environmental sampling of adenovirus in a military recruit setting. J Infect Dis. 2006;194:877–85. 10.1086/507426 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Adrian T. Genome type analysis of adenovirus type 4. Intervirology. 1992;34:180–3. 10.1159/000150280 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Li QG, Wadell G. The degree of genetic variability among adenovirus type 4 strains isolated from man and chimpanzee. Arch Virol. 1988;101:65–77. 10.1007/BF01314652 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Kajon AE, Moseley JM, Metzgar D, Huong HS, Wadleigh A, Ryan MA, et al. Molecular epidemiology of adenovirus type 4 infections in US military recruits in the postvaccination era (1997-2003). J Infect Dis. 2007;196:67–75. 10.1086/518442 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Houng HS, Clavio S, Graham K, Kuschner R, Sun W, Russell KL, et al. Emergence of a new human adenovirus type 4 (Ad4) genotype: identification of a novel inverted terminal repeated (ITR) sequence from majority of Ad4 isolates from US military recruits. J Clin Virol. 2006;35:381–7. 10.1016/j.jcv.2005.11.008 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Dehghan S, Seto J, Liu EB, Walsh MP, Dyer DW, Chodosh J, et al. Computational analysis of four human adenovirus type 4 genomes reveals molecular evolution through two interspecies recombination events. Virology. 2013;443:197–207. 10.1016/j.virol.2013.05.014 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Gutekunst RR, White RJ, Edmondson WP, Chanock RM. Immunization with live type 4 adenovirus: determination of infectious virus dose and protective effect of enteric infection. Am J Epidemiol. 1967;86:341–9. 10.1093/oxfordjournals.aje.a120744 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.van der Veen J, Abarbanel MF, Oei KG. Vaccination with live type 4 adenovirus: evaluation of antibody response and protective efficacy. J Hyg (Lond). 1968;66:499–511. 10.1017/S0022172400028242 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Hoke CH Jr, Hawksworth A, Snyder CE Jr. Initial assessment of impact of adenovirus type 4 and type 7 vaccine on febrile respiratory illness and virus transmission in military basic trainees, March 2012. MSMR. 2012;19:2–4. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Radin JM, Hawksworth AW, Blair PJ, Faix DJ, Raman R, Russell KL, et al. Dramatic decline of respiratory illness among US military recruits after the renewed use of adenovirus vaccines. Clin Infect Dis. 2014;59:962–8. 10.1093/cid/ciu507 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Brandt CD, Kim HW, Vargosko AJ, Jeffries BC, Arrobio JO, Rindge B, et al. Infections in 18,000 infants and children in a controlled study of respiratory tract disease. I. Adenovirus pathogenicity in relation to serologic type and illness syndrome. Am J Epidemiol. 1969;90:484–500. 10.1093/oxfordjournals.aje.a121094 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Fox JP, Brandt CD, Wassermann FE, Hall CE, Spigland I, Kogon A, et al. The virus watch program: a continuing surveillance of viral infections in metropolitan New York families. VI. Observations of adenovirus infections: virus excretion patterns, antibody response, efficiency of surveillance, patterns of infections, and relation to illness. Am J Epidemiol. 1969;89:25–50. 10.1093/oxfordjournals.aje.a120913 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Schmitz H, Wigand R, Heinrich W. Worldwide epidemiology of human adenovirus infections. Am J Epidemiol. 1983;117:455–66. 10.1093/oxfordjournals.aje.a113563 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Kajon AE, Suarez MV. Molecular epidemiology of adenoviruses isolated from hospitalized children with severe lower acute respiratory infection in Santiago, Chile. J Med Virol. 1990;30:294–7. 10.1002/jmv.1890300412 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Kajon AE, Mistchenko AS, Videla C, Hortal M, Wadell G, Avendaño LF. Molecular epidemiology of adenovirus acute lower respiratory infections of children in the south cone of South America (1991-1994). J Med Virol. 1996;48:151–6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Lu X, Erdman DD. Molecular typing of human adenoviruses by PCR and sequencing of a partial region of the hexon gene. Arch Virol. 2006;151:1587–602. 10.1007/s00705-005-0722-7 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Lamson DM, Kajon A, Shudt M, Girouard G, St George K. Detection and genetic characterization of adenovirus type 14 strain in students with influenza-like illness, New York, USA, 2014–2015. Emerg Infect Dis. 2017;23:1194–7. 10.3201/eid2307.161730 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Kajon AE, Erdman DD. Assessment of genetic variability among subspecies b1 human adenoviruses for molecular epidemiology studies. Methods Mol Med. 2007;131:335–55. 10.1007/978-1-59745-277-9_23 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Kearse M, Moir R, Wilson A, Stones-Havas S, Cheung M, Sturrock S, et al. Geneious Basic: an integrated and extendable desktop software platform for the organization and analysis of sequence data. Bioinformatics. 2012;28:1647–9. 10.1093/bioinformatics/bts199 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Kimura M. A simple method for estimating evolutionary rates of base substitutions through comparative studies of nucleotide sequences. J Mol Evol. 1980;16:111–20. 10.1007/BF01731581 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Tamura K, Stecher G, Peterson D, Filipski A, Kumar S. MEGA6: Molecular Evolutionary Genetics Analysis version 6.0. Mol Biol Evol. 2013;30:2725–9. 10.1093/molbev/mst197 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Kandel R, Srinivasan A, D’Agata EM, Lu X, Erdman D, Jhung M. Outbreak of adenovirus type 4 infection in a long-term care facility for the elderly. Infect Control Hosp Epidemiol. 2010;31:755–7. 10.1086/653612 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Lu X, Trujillo-Lopez E, Lott L, Erdman DD. Quantitative real-time PCR assay panel for detection and type-specific identification of epidemic respiratory human adenoviruses. J Clin Microbiol. 2013;51:1089–93. 10.1128/JCM.03297-12 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Roy S, Calcedo R, Medina-Jaszek A, Keough M, Peng H, Wilson JM. Adenoviruses in lymphocytes of the human gastro-intestinal tract. PLoS One. 2011;6:e24859. 10.1371/journal.pone.0024859 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Stanley ED, Jackson GG. Spread of enteric live adenovirus type 4 vaccine in married couples. J Infect Dis. 1969;119:51–9. 10.1093/infdis/119.1.51 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Narra R, Bono P, Zoccoli A, Orlandi A, Piconi S, Grasselli G, et al. Acute respiratory distress syndrome in adenovirus type 4 pneumonia: A case report. J Clin Virol. 2016;81:78–81. 10.1016/j.jcv.2016.06.005 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Kalimuddin S, Chan YFZ, Wu IQ, Tan QL, Murthee KG, Tan BH, et al. A report of adult human adenovirus infections in a tertiary hospital. Open Forum Infect Dis. 2017;4:ofx053. 10.1093/ofid/ofx053 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Hang J, Vento TJ, Norby EA, Jarman RG, Keiser PB, Kuschner RA, et al. Adenovirus type 4 respiratory infections with a concurrent outbreak of coxsackievirus A21 among United States Army Basic Trainees, a retrospective viral etiology study using next-generation sequencing. J Med Virol. 2017;89:1387–94. 10.1002/jmv.24792 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


