ABSTRACT
Shortly after cardiac Na+ channels activate and initiate the action potential, inactivation ensues within milliseconds, attenuating the peak Na+ current, INa, and allowing the cell membrane to repolarize. A very limited number of Na+ channels that do not inactivate carry a persistent INa, or late INa. While late INa is only a small fraction of peak magnitude, it significantly prolongs ventricular action potential duration, which predisposes patients to arrhythmia. Here, we review our current understanding of inactivation mechanisms, their regulation, and how they have been modeled computationally. Based on this body of work, we conclude that inactivation and its connection to late INa would be best modeled with a “feet-on-the-door” approach where multiple channel components participate in determining inactivation and late INa. This model reflects experimental findings showing that perturbation of many channel locations can destabilize inactivation and cause pathological late INa.
KEYWORDS: computational models, inherited arrhythmias, late sodium current, sodium channels
Introduction
In atrial and ventricular myocytes, the Na+ current (INa) initiates the action potential (AP) by depolarizing the membrane potential (Vm) from approximately −60 mV to +40 mV. The peak INa determines the maximum upstroke velocity (dVm/dtmax) and thus the conduction velocity.1 Within milliseconds (ms), most Na+ channels inactivate and allow outward K+ current to repolarize the membrane. The extent of Na+ channel inactivation and the time to begin recovery from inactivation determines the absolute or effective refractory period (ARP, ERP) where AP initiation is not possible (Fig. 1).2 Na+ channel inactivation, recovery from inactivation, and associated deactivation further dictate the relative refractory period (RRP). The RRP describes a time period when sufficient Na+ channels are available for reactivation and the Vm is further repolarized so that a stronger stimulus may initiate the next AP.2
Figure 1.
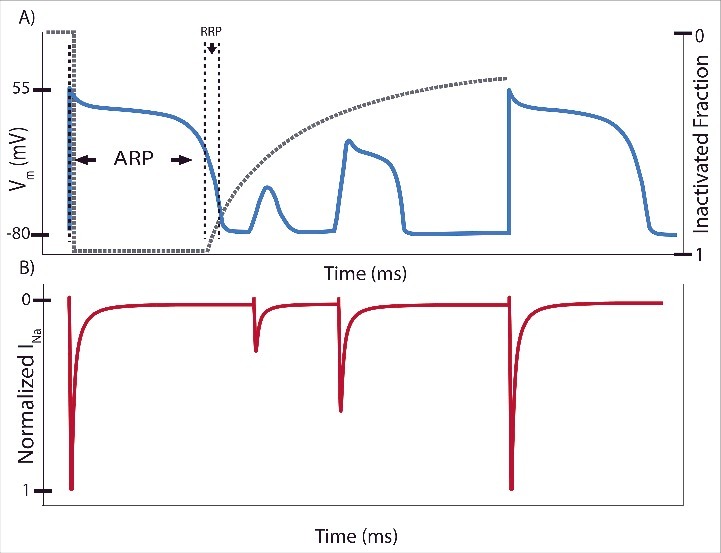
A representative action potential (AP) depicting the corresponding extent of Na+ channel inactivation (gray dashed line) with labeled absolute (ARP) and relative (RRP) refractory periods. Stimulation immediately after the initial AP results in shortened APs with reduced peak membrane potential (Vm) and peak Na+ current (INa). Once the Na+ channels have recovered sufficiently, they may be reactivated to elicit another full strength AP.
When Na+ channels do not inactivate completely, a measurable current of less than 0.5% of the peak current persists in the myocyte, known as late or persistent INa. This current is sustained because it travels through Na+ channels that do not inactivate completely, so they do not need go through recovery from inactivation. In large mammals, such as dogs and humans, late INa significantly modulates AP duration (APD) by providing a sustained influx of depolarizing Na+, which disrupts the “delicate balance” between the inward (primarily L-type Ca2+ current) and outward K+ currents of the AP plateau (Fig. 2).3,4 Due to the length of the AP plateau, this late component can contribute approximately twice the Na+ “load” over time compared with the peak current.5,6 Because the fraction of channels that carry late INa is small, minute changes to inactivation kinetics at normal heart rate will result in substantial changes to its magnitude, which will affect APD and facilitate (or prevent) anti-arrhythmic activity. APD prolongation based on altered Na+ channel inactivation and enhanced late INa is linked to arrhythmia in patients with inherited mutations,7 heart failure,8 and myocardial infarction.9 The purpose of this paper is to review recent and classical findings that shed light on the molecular mechanisms of inactivation and its regulation, how inactivation determines late INa, and how computational models may capture these mechanisms to connect them to arrhythmia mechanisms.
Figure 2.
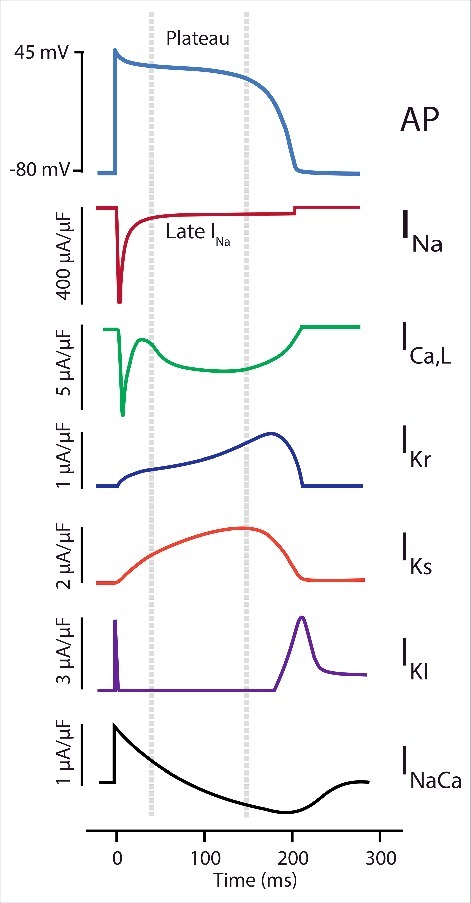
Major currents participating in the action potential (AP) plateau. Late INa is very effective at modulating the action potential duration (APD) because the other participating currents are relatively small and balance each other out, increasing membrane resistance and reducing the magnitude of dVm/dtmax.142 Representations of the cardiac Na+ current (INa), the L-type Ca2+ channel (ICa,L), the rapid and slow delayed rectifier K+ channels (IKr and IKs), the inward rectifier K+ channel (IK1), and current generated by the Na+-Ca2+ exchanger are shown during the AP.
Mechanisms of inactivation
Hodgkin and Huxley clearly recognized the concept of INa inactivation in 1952 during the first recordings of the axon INa and modeled it as a monoexponential time and voltage-dependent decay.10 Work with NaF perfused axons first identified late INa, which was especially pronounced during depolarizations to elevated potentials, suggesting two components of inactivation.11,12 Subsequent work identified additional components of inactivation that span many time domains, indicative of multiple relaxations. The fast component became known as fast inactivation (< 10 ms), while intermediate (∼100 ms), slow (1 s to 1 min), and ultra-slow (> 1 min) inactivation defined components of inactivation with longer time domains.13 During an AP, fast inactivation reduces the current to ∼0.5% of the peak within millseconds.6 Cardiac Na+ channels display reduced slow or ultraslow inactivation compared with neuronal channels, consistent with their essential role in initiating the heartbeat.14 Over the remainder of the AP, intermediate inactivation will continue to diminish late INa until Na+ channels begin to deactivate at negative potentials (below -60 mV).13 Sustained effort has been applied to measuring inactivation in these different time domains and connecting it to its molecular determinants within the Na+ channel.
Much of the work to elucidate effects on Na+ inactivation kinetics was conducted using voltage clamp techniques on Na+ channels in various expression systems. One must use caution when examining Na+ kinetic inactivation data because the voltage clamp measurements require adjustments for artifacts, and leak during recording may affect measurement of the late INa.
Measurement of tetrodotoxin (TTX) sensitive currents is commonly used to correct for membrane leak because it is particularly effective on the late INa compared with the peak INa.15 These experiments work by subtracting currents with TTX added from the control current to isolate the sensitive components. However, the cardiac Na+ channel (NaV1.5) is not particularly sensitive to TTX, so there are two possibilities to explain this enhanced sensitivity. First, the late INa may be carried by neuronal Na+ channels, which are highly TTX sensitive.16 Another possibility is that Na+ channels with altered inactivation may inherently be more sensitive to TTX. Further work is needed to distinguish between these two scenarios to precisely identify which channels are primarily carrying the late INa.
Further confounding the measurement of Na+ current, larger cells require a significant amount of time to charge the membrane to a certain potential. This slow charging is problematic when recording rapid Na+ channel activation kinetics, which are tightly coupled to inactivation kinetics. The cut-open Vaseline gap voltage clamp addresses this difficulty by isolating a patch of large oocytes for recording.17,18 In smaller cells, such as HEK cells, the patch clamp technique requires compensation for the resistance of the recording electrode and access to the cell, and even then, voltage artifacts are present when recording large currents, making peak current measurements unreliable.19 Whatever the expression system, it is always difficult to clamp the Vm when examining fast, large inward currents because during a depolarizing pulse the inward INa is moving the potential in the same direction as the amplifier, creating unstable positive feedback.20 These challenges in recording INa are likely responsible for significant variability in published results, particularly regarding the magnitude of the late INa, which relies on an accurate measure of the peak INa.
Functional voltage-gated Na+ channels (Nav) include nine isoforms that are formed by an α-subunit that comprises four homologous domains (DI-DIV) each with six helical membrane-spanning segments (S1-S6) (Fig. 3).21,22 In addition to Nav1.5 in cardiac tissue and Nav1.4 in the skeletal muscle, seven other isoforms are expressed in the nervous system.22 Within each domain, S1-S4 form the voltage sensing domain (VSD), which senses changes in Vm, and S5-S6 form the pore that allows for selective passage of Na+ ions. In the VSD, S4 contains positive charges, usually arginines, that are thrust outward upon membrane depolarization. These voltage-dependent conformational changes are tightly coupled to the activation, inactivation, deactivation, and recovery from inactivation of the Na+ channel. Intracellular linkers attach each domain to the next, connect the channel to the cytoskeleton and intracellular signaling pathways, and regulate channel gating. The C-terminus is composed of a structured proximal portion and unstructured distal portion.23,24 The structured portion has six α-helices that form an EF hand-like structure (α helices 1–5) and an IQ motif which surprisingly has higher calcium binding affinity than the EF-hand (α helix 6).24
Figure 3.
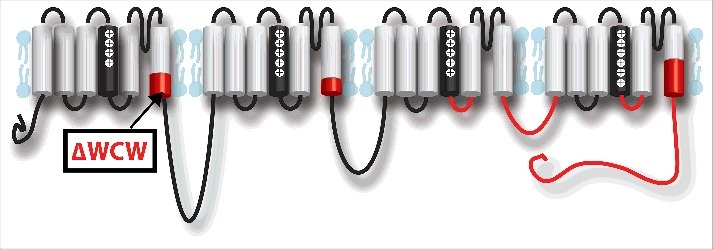
Structures involved in inactivation within the Nav1.5 α-subunit. Structures colored in red significantly affect fast inactivation. From N-terminal to C-terminal, the intracellular end of DI S6 segment (ΔWCW window),45,47 intracellular end of DII S6 segment,45 DIII S4-S5 linker,38,39,42 DIII-DIV linker,25-33 DIV S4-S5 linker,40-42 lower half of DIV S6 segment,44,47 and C-terminus.23,48-51,53
Clever experiments with intracellularly applied pronase, a non-specific protease, demonstrated that the fast inactivation gate is located on the intracellular face of the Na+ channel.25 Intracellular pronase perfusion removed inactivation while preserving INa activation and deactivation. After the Na+ channel was cloned, further work showed that antibodies,26 cleavage, 27 and additions28 to the intracellular DIII-DIV linker were sufficient to inhibit inactivation, and a primarily hydrophobic motif identified through site-directed mutagenesis on the linker is crucial for successful fast inactivation (IFMT): I-1488, F-1489, M-1490, and T-1491.29-31 Sulfhydryl accessibility studies showed that F1489 becomes inaccessible during fast inactivation,32 and the interaction between the channel and the motif is hydrophobic.30 Smaller residues containing glycine and proline provide the flexibility for a “hinged lid” or “chain” that allows IFMT to occlude the channel.33 How and where the DIII-DIV linker and these primarily hydrophobic residues interact with the rest of the channel has remained a key topic of research for many years.
Gating current recordings have yielded critical insights into the DIII-DIV linker interactions with the VSDs. The gating current arises from the rapid movement of the S4 charges within membrane, which enables their detection.34 Early gating current recordings showed that two-thirds of the gating charge, which is measured as the integral over time of the gating current, is immobilized when fast inactivation occurs, suggesting a connection between the VSDs and inactivation.35 The application of voltage clamp fluorometry (VCF) to NaV channels has allowed monitoring of each VSD individually, rather than the summation of their movement reported by the gating current.36,37 During VCF experiments, a fluorophore is attached to the S4 segment of a domain. When a potential is applied, S4 displacement results in a change of environment around the fluorophore, which is detected as a deflection in the fluorescence intensity with a high dynamic range amplifier. Using VCF, Cha et al. showed that the voltage-dependent kinetics of the DIII and DIV VSDs are modulated by inactivation.37
Site-directed mutagenesis has provided additional insights, showing inactivation can also be modulated by the S4-S5 linkers of DIII and DIV. A conserved alanine on the Nav1.2 DIII S4-S5 linker severely disrupted inactivation when it was mutated to glutamine and was proposed to serve as a hydrophobic “docking” site for the IFMT motif.38 Further work showed that some patients with long QT type 3 syndrome, which increases late INa, carry a mutation to a homologous conserved alanine within this linker in Nav1.5.39 The DIV S4-S5 has also been shown to significantly affect inactivation and suggested as a potential “docking” site for the inactivation gate.40,41 Confoundingly, accessibility studies with Nav1.4 showed that both the DIII S4-S5 and DIV S4-S5 linkers remain accessible when channels are inactivated.40,42
Mutagenesis work also aided in demonstrating that the S6 segments of DI, DII, and DIV modulate fast inactivation. An alanine-mutagenesis study showed that mutations in the center43 and in intracellular44 end of DIV S6 segment in Nav1.2 inhibited inactivation. Double mutations within the center and intracellular end of DIV S6 exhibit more inactivation inhibition, but the IFMT does not likely interact with the S6 segments as changing the hydrophobic characteristics of the mutations did not affect the phenotype. Mutations in the intracellular end of DIS6 and DIIS6 in Nav1.2 also inhibit fast inactivation45 while no mutations were found in DIIIS6.46 Finally, work with tryptophan scanning mutations in Nav1.4 in the DI and DIV S6 segments identified the “WCW” window located on the intracellular DI S6 segment that impairs fast inactivation.47
The C-terminus also plays an important role in modulating Na+ channel inactivation.48 Generally, each Na+ channel homolog has distinct fast inactivation kinetics. For example, Nav1.5 fast inactivation is slower than Nav1.4 due to differences in amino acid sequences in the C-terminal domains.49 In addition, swapping C-terminal domains between Nav1.5 and Nav1.2 causes a shift in voltage-dependent steady-state inactivation toward the potential of the original isoform.50 Mutations in the C-terminal domain have also been shown to disrupt fast inactivation and cause cardiac arrhythmias such as long QT syndrome.51,52
Work with truncated C-terminal mutants identified the importance of the sixth helix and the distal portion in inactivation regulation. When just the distal, unstructured portion of the C-terminus was removed, inactivation was not affected; however, when the distal portion along with the sixth helix were removed, inactivation was inhibited.23 Pull-down assays confirmed that the DIII-DIV linker interacts with the sixth helix and distal portion of the C-terminus, and mutagenesis showed that the interaction likely stabilizes the inactivated state.53
Toward the goal of understanding how various channel domains regulate NaV channel gating, recent VCF experiments have shown that DIV-VSD translocation serves as a rate limiting step to initiate fast inactivation.54 Later results also showed that the VSDs of DI-DIII are also likely involved with slower components of inactivation.55,56 Work with inactivation deficient mutations shows that the DIII-VSD also participates in fast inactivation but only after pulses with durations of 100s of ms.57,58 Together these results suggest a model where the hydrophobic IFM sequence of DIII-DIV linker quickly associates with DIV-VSD to initiate fast inactivation (Fig. 4). After about 100 ms, the DIII-DIV linker then associates with the DIII-VSD and supports its activated conformation. This late association will stabilize the inactivated state, causing a reduction in late INa.
Figure 4.
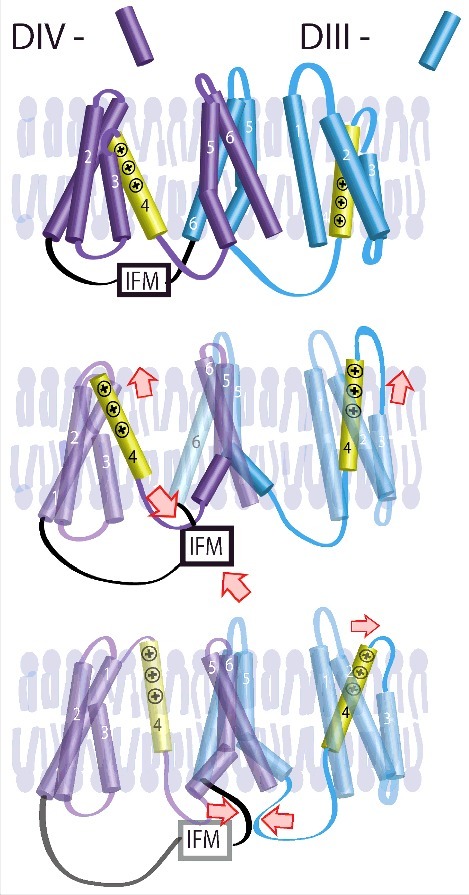
Inactivation is significantly determined by the DIII and DIV VSDs.57 After channel activation, IFM associates with the DIV-VSD to control inactivation onset. After ∼100 ms, the IFM also associates with the DIII-VSD, supporting its activated conformation. Only after the IFM dissociates from the DIII and DIV VSDs. © Hsu et al. Adapted by permission of the CC BY 4.0 license. Permission to reuse must be obtained from the rightsholder.57.
The above results show that Nav inactivation is a complex phenomenon that involves locations across the α-subunit. The various structures participating inactivation are highlighted in Fig. 3. The primary structure of fast inactivation is the DIII-DIV linker, which physically occludes the intracellular mouth of the channel. The linker's IFMT motif mediates successful occlusion through hydrophobic interactions between the linker and the channel. While the DIII-DIV linker occludes the pore, various structures across the α-subunit modulate the extent of inactivation and therefore late INa: the DIII and DIV VSDs, the DI and DIV S6 segments, and the C-terminal domain.
Regulation of inactivation by accessory subunits
Na+ channel inactivation is not only modulated by α-subunit structures, but also by external factors, such as accessory subunits and the external environment. These may regulate inactivation alone or in combination with the α-subunit.
The most studied interacting partners of the Nav α-subunit are the β-subunits, which are found in complex with the NaV channel α-subunit after purification. There are five types of voltage-gated Na+ channel β-subunits (β1–4 and β1b, a splice variant of β1).59-63 All β-subunits, with the exception of β1b, are composed of an extracellular immunoglobulin domain, a transmembrane segment, and an intracellular C-terminus.64 β1b is missing the transmembrane segment.65 The β1 and β3 subunits interact noncovalently with α-subunit62,66 while β2 and β4 covalently bind to α subunit through disulfide bonds.64,67 The expression level for each β-subunit is tissue and cell-specific with varying patterns over the course of development.68-70 While each β-subunit paralog causes an increase in channel expression, the regulation of biophysical properties including voltage-dependence of activation and inactivation, rate of inactivation, recovery from inactivation, and magnitude of persistent and resurgent INa are unique.63,64,71-74 Very recent structures of the Nav1.4-β1 complex in the electric eel show that the immunoglobulin domain of the β1 subunit interacts with the extracellular loops of the DI and DIV pore domain while the transmembrane domain interacts with the DIII-VSD.75 This structure serves as a basis for determining how β1-subunit interactions with the α-subunit mediate biophysical property regulation.75 However, the interactions revealed by this structure failed to elucidate how β1 regulates channel inactivation, suggesting that kinetic data are essential for fully understanding regulation of the channel by β subunits. Concurrently, we used the VCF technique to assess the modulation of Na+ channel VSD conformations by β1 and β3 during gating.76 The β1 subunit caused the DIV-VSD to activate at higher potentials. Because the DIV-VSD activation has been connected to fast inactivation onset, modulation of the DIV-VSD by β1 explains why it affects channel inactivation. Intriguingly, despite the sequence homology between the β1 and β3 subunit, the β3 subunit controls the DIII-VSD along with the DIV-VSD. This additional interaction with the DIII-VSD allows β3 to alter both current activation and inactivation kinetics.
The regulatory effects of β-subunits on Na+ channel inactivation are system and cell type specific. As a result, there are many conflicting results regarding the magnitude and direction of the inactivation shifts by different β-subunits.77 These discrepancies likely reflect the fact that α-subunits interact not only with β-subunits but also with many other modulating proteins that altogether form the macromolecular Na+ channel complex.78
Multiple Brugada syndrome-associated mutations have been identified in SCN1B (encoding for β1 subunit, E87Q, and β1b subunit H162P, W179X, R214Q), SCN2B (encoding for β2 subunit, D211G), and SCN3B (encoding for β3 subunit, L10P, V110I).65 Patients with the Brugada syndrome often have reduced INa, which can lead to arrhythmia through a variety of mechanisms.79 These mutations can cause INa reduction by lowering INa density, due to a hyperpolarizing shift in steady-state inactivation or altering inactivation onset and recovery rates.65 In contrast, mutations in β4 (L179F) and β1B (P213T) that are associated with long QT syndrome cause a depolarizing shift in steady-state inactivation.80 These mutations lead to increased channel availability and elevated late INa, which prolongs the ventricular AP and therefore the QT interval.
Work with various Nav β-subunit knockout mouse models have also revealed associated cardiac abnormalities. The Scn1b null mouse model exhibited increased APD and prolonged QT intervals with transient and persistent peak INa.81 Scn2b null mice showed reduced INa density with slower conduction velocity and repolarization in the right ventricular outflow tract, leading to ventricular arrhythmia.82 The Scn3b null mice also displayed cardiac abnormalities such as reduced peak INa and altered sinoatrial node recovery.83,84 Together, these findings demonstrate the physiologic relevance of β-subunits on the regulation of Na+ channel biophysical properties including inactivation, reactivation, and recovery.
Other than NaV β-subunits, the NaV α-subunit is associated with plethora of auxiliary subunits for additional regulatory effects. One prominent auxiliary subunit well known to bind the NaV α-subunit C-terminal domain is calmodulin (CaM).85 CaM is a bi-lobed, ∼17 kDa protein which functions as a ubiquitous Ca2+ sensing protein.86 Therefore, CaM association to NaV channels may endow the channels with Ca2+ regulation. The leading hypothesis concerning the nature of Ca2+ regulation of NaV channels involves shifts in the steady-state inactivation, thus tuning Na+ channel availability depending on levels of intracellular Ca2+.87 Despite extensive characterization, Ca2+ regulation of NaV channels appear to be idiosyncratic and isoform specific.88-91 Elevated intracellular Ca2+ has been reported to induce a depolarizing shift in the steady-state inactivation of NaV1.5,89,92-94 but other studies reported no shift in the steady-state inactivation of NaV1.5 in response to elevated intracellular Ca2+.88,91 Furthermore, elevated intracellular Ca2+ levels were reported to induce a hyperpolarizing shift in the steady-state inactivation in NaV1.4.88 Just as the functional effect of Ca2+ on NaV channel is controversial, the mechanism behind Ca2+ regulation of NaV channels is also debated. Ca2+ has been proposed to directly bind the C-terminal domain of NaV α-subunit to exert regulatory effect independent of CaM.92 Other models proposed that upon Ca2+ binding, Ca2+/CaM interacts with DIII-DIV linker to induce regulation of steady-state inactivation.95 Overall, the question of whether Ca2+ itself, or the ion in complex with CaM, regulates Na+ channel inactivation remains a controversial topic.
A group of four proteins, fibroblast growth factors (FGF 11–14), also referred to as fibroblast growth homologous factors (FHFs 1–4), interact with the C-terminal domain in the Ca2+-CaM complex.96,97 FHFs are differentially expressed in various tissues and lack the N-terminal signal sequence, causing them to remain in the cytoplasm and allowing them to regulate NaV and Ca2+ channels.78,96,98 Work with FHF1B demonstrated that its interaction with the C-terminal domain of Nav1.5 produces a hyperpolarizing shift in steady-state inactivation, and the mutation D1790G, which is already associated with the long QT type 3 syndrome, interrupts interaction between FHF1B and the C-terminus.99 In addition, a mutation in Nav1.5 that interrupts FHF binding to the C-terminal domain displayed slowed inactivation kinetics, resulting in increased late INa and prolonged APD.100
As can be appreciated from the results discussed above, many different accessory subunits can regulate NaV channel inactivation and disruption of this regulation leads to deadly arrhythmias. Fig. 5 presents a pictorial representation of accessory subunits involved in modulating inactivation. A precise understanding of how accessory subunits regulate inactivation will prove challenging because the channels are composed of subunits that interact with each other. However, this work will lead to an improved understanding of diseased states and potentially new therapeutic routes.
Figure 5.
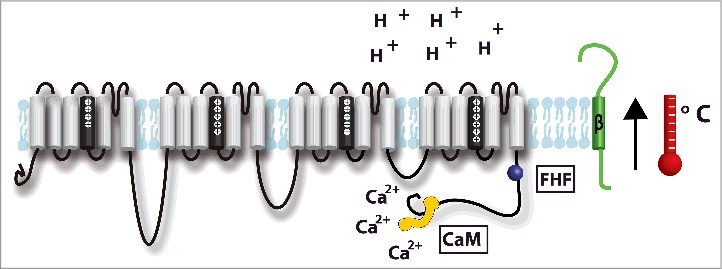
Accessory subunits involved in modulating Nav1.5 inactivation: β-subunit (green),59-74,80,81,83,84,143-145, fibroblast growth homologous factors (FHFs) (purple),96,97,99,121,122 and the CaM/Ca2+ complex (yellow).24,89,91,95-97,146-150 Environmental factors including extracellular pH,101,102,104,105,110 and temperature103,112-120,122 may also modulate Na+ channel inactivation.
Environmental regulation of inactivation
Acidosis and febrile states are both environmental factors that alter cardiac electrical activity by shifting Na+ channel inactivation properties. These effects are often exacerbated by underlying NaV1.5 mutations, which can lead to life-threatening phenotypes.101-103
In physiologic conditions, human arterial blood pH is maintained at approximately 7.4.101 If pH drops just 0.05 units, protein function may be altered,101 and pH below 6.95 results in deleterious effects on protein function in cardiomyocytes.101 During cardiac ischemia, myocytes experience pH as low as 5.9. Reduced extracellular pH due to arterial blood acidosis has been shown to reversibly destabilize the fast-inactivated state in wild-type NaV1.5 channels, leading to increased window current and increased late INa, and to destabilize the slow inactivated state.101,104 Specifically, proton block of wild-type channels accelerates the recovery from open state fast inactivation and delays its onset.101,102 In silico studies have demonstrated that these effects on wild-type channels can be sufficient to prolong the AP and decrease its maximum upstroke velocity, which affects conduction velocity.1,103,105 Both AP effects predispose patients to arrhythmia.103,106 The conclusions from these modeling studies have been strengthened by multiple reports of Brugada syndrome phenocopy induced by acidosis.107,108 When the patient's blood pH returned to physiologic conditions and electrolytes were balanced, the Brugada syndrome characteristic ECG was no longer present.108
Certain Nav1.5 mutations that cause long QT or Brugada syndromes result in APs that are more sensitive to acidosis.109,110 Studies have shown that a low pH environment in combination with these underlying mutations exacerbates the electrical abnormalities in individuals.103 For example, decreased extracellular pH paired with E1784K, the most common SCN5A (encoding for Nav1.5) mutant linked to both Brugada syndrome and LQT3, leads to significantly larger increases in late INa due to more severe alterations to the channel inactivation.109 Other groups have shown that certain long QT type 3 syndrome mutations are more sensitive to intracellular acidosis than others.111
Another environmental factor modulating the Na+ channel is body temperature. In healthy humans, without underlying mutations in Nav1.5 or other conditions, temperature-dependent cardiac abnormalities may occur in extreme hyperthermia but seldom when they experience a mild fever.112,113 In contrast, individuals with NaV channel mutations are more sensitive to core body temperature fluctuations with their susceptibility to arrhythmia being dependent on the mutation that they carry.110,114,115 Several studies have shown that hyperthermia has detrimental effects on asymptomatic Brugada syndrome patients causing Brugada syndrome ECG patterns to be unmasked under febrile conditions and remain unmasked when core body temperature is restored.116,117 Other clinical studies have presented in patients who only possessed a Brugada syndrome ECG pattern while in the febrile state.118,119 While the mechanisms responsible for this phenomenon are still under investigation, it is known that elevated temperature increases the rate of fast inactivation recovery and onset for wild-type Na+ channels, which leads to decreased late INa.114,116
The T1620M missense mutation found in SCN5A alters the temperature sensitivity of Na+ channel fast inactivation in patients with Brugada syndrome. As temperatures increase toward the physiologic range, these mutant cardiac Na+ channels demonstrate slower recovery from inactivation, leading to further loss of function of INa.115 Q10 extrapolation results suggest that febrile states would elicit worsening of this mutant's inactivation properties and become more arrhythmogenic.
However, studies of different SCN5A mutations suggest that febrile states do not worsen these mutation effects.116 Keller et al. demonstrated patients who had fever-induced type 1 Brugada syndrome and fever-induced arrhythmias also possessed mutations, such as R535X and L325R, which result in severe to absolute loss of INa at physiologic temperature. Thus, the study suggested that fever could not make the channel function any worse, and fever did not significantly worsen the biophysical changes to the channel. Therefore, the authors hypothesized that in heterozygous patients, possessing both wild-type and mutated Na+ channels, the effect of temperature accelerating the inactivation of the wild-type channels, not the effect on mutant channels, is responsible for altering the delicate balance of depolarization and repolarization currents and thus may lead to fever-induced arrhythmias. This hypothesis is supported by Gima and Rudy's modeling study which demonstrated that accelerated inactivation, a consequence of fever, of the T1620M NaV1.5 mutant channel causes a Brugada syndrome pseudo ECG phenotype through the resultant decrease in late INa combined with the already reduced peak INa from the mutant channel.116,120 Regardless of whether a SCN5A mutant makes a channel more sensitive to temperature effects, it is evident that febrile temperatures in combination with mutations increase the risk of fever-induced arrhythmias, particularly from asymptomatic Brugada syndrome patients.
Temperature-dependent cardiac electrical abnormalities are not limited to mutations in SCN5A. A recent study identified FHF2, a member of the FHF protein family known to modulate voltage-gated Na+ channel inactivation as previously discussed, as a key regulator of myocardial excitability that prevents conduction failure in mouse heart under hyperthermic conditions.121,122 Loss of FHF2, accelerates the rate of both open state and closed state inactivation of the Na+ channel. This change becomes functionally relevant under febrile temperatures when temperature dependence increases the inactivation rate, resulting in severely suppressed INa and ultimately conduction failure.
Environmental factors, such as acidosis and temperature, have significant effects on Na+ channel inactivation and are depicted in Fig. 5. Patients already harboring mutations for cardiac abnormalities, such as long QT or Brugada syndromes, often exhibit aggravated symptoms when subject to acidosis or hyperthermia. Understanding how environmental factors combine with channel structure to disrupt inactivation may lead to better clinical strategies for preventing these pathological situations.
Models of inactivation
Modeling of NaV channel inactivation began with Hodgkin and Huxley's work in 1952 with the squid giant axon.10 When analyzing the Na+ conductance curves, they inferred that Na+ conductance could be represented by a product of probabilistic gates, which required residence in a permissive conformation for conduction to occur. These gates could regulate either activation, with initial and maximum values of zero and one, respectively, or inactivation with hyperpolarized and depolarized values of one and zero, respectively. Hodgkin and Huxley found that the product of 3 activation gates and one inactivation gate adequately described the conductance curves. Under this model, 3 of 4 domains had an activation gate that must open for conduction to occur, and one domain had a gate that would close to mimic inactivation. Because conductance was represented as product of activation and inactivation, the activation and inactivation processes were assumed to be independent. While we now know that activation and inactivation are instead coupled, this idea that three domains primarily control activation and one primarily controls inactivation is still useful.123 Chandler and Meves' later work in 1970 suggested multiple components of Hodgkin and Huxley's inactivation gate.11,12 Their work with NaF perfused squid axons demonstrated that large depolarizations resulted in less steady-state inactivation and thus maintained late INa. They suggested amending Hodgkin and Huxley's single inactivation gate model to an inactivation gate with two components to account for transient peak in Na+ channel conductance upon activation followed by sustained late conductance. Further, they suggested that the Na+ channel may have two open states with a higher and lower probability of conductance.
As mentioned previously, the early pronase experiments, which localized inactivation to the intracellular part of the channel, suggested the use of a “inactivation particle” that would physically occlude the channel.25 Several years later, a study on gating charge movement suggested that inactivation immobilizes two thirds of the gating charge, but the inactivation process itself is not associated with any gating current.35,124 Because a voltage-dependent process produces an associated gating current, and inactivation lacks this associated gating current, Armstrong and Bezanilla concluded that inactivation must be a voltage-independent process, which is contrast to Hodgkin and Huxley's original theory.35 Additionally, because the fast time component of activation moves more than half of the total gating charge, and inactivation immobilizes two thirds of the total gating charge, Armstrong and Bezanilla deduced that inactivation must immobilize gating charge that was moved by channel activation. Thus, the processes of activation and inactivation are coupled. Combining these results led to the “ball and chain model” of inactivation. This model proposes that a “ball,” tethered to the intracellular channel by a polypeptide “chain,” occludes the mouth of the channel to bring about fast inactivation only after activation.35
The discovery of the IFMT motif on the DIII-DIV linker crucial for successful fast inactivation suggested that the “ball and chain” model of inactivation needed updating. First, the determination that a primarily hydrophobic IFM motif controls successful inactivation demonstrates that hydrophobic interactions occlude the pore rather than the proposed electrostatic attraction between the inactivation particle and channel.29 Second, structural studies determined that the middle of the DIII-DIV linker has an α-helical structure containing the IFMT motif, which is flanked by glycines N-terminally and prolines C-terminally.29,31 This structure and residue sequence suggests that the DIII-DIV linker functions as a “hinged lid” to occlude the pore instead of the “loosely tethered” blocking ball. In the “hinged lid” model of inactivation the DIII-DIV linker closes in on its “hinges,” composed of glycine or proline, to block the intracellular mouth of the channel.29 West further suggests that the IFM sequence serves as a hydrophobic “latch” to keep the lid closed.
Data collected from single-channel recordings in the giant squid axon in combination with the gating charge data required Markov type models that include state-dependent transitions to simulate their results.125,126 Experimental recordings kinetics confirm that transitions between hypothetical states can be made sufficiently fast for a valid state-dependent representation of Na+ channel processes such as inactivation.127 Markov models are also more generalizable and allow for activation and inactivation to be modeled as a coupled process and may be reduced to the Hodgkin-Huxley formalism if desired for simplicity.128 The earliest models incorporating inactivation included 3 states: an open, closed, and inactivated state.125,126
Vandenberg and Bezanilla in 1991 created a Markov-type model of INa with data from single-channel recordings in the giant squid axon.129 The recordings showed that channels not only inactivate from the open state but also from the closed state as well. In addition to adding transitions between inactivated, closed and open states, the models incorporated reversible inactivation along multiple closed states for better fits to recordings. Rate constants were obtained from the single-channel recordings using maximum likelihood analysis and scaled up to yield macroscopic gating and channel currents.
In the spirit of Chandler and Meves' observations of two types of Na+ channel conductance in 1970, Keynes detailed a “mode switching hypothesis” to explain inactivation.130 This hypothesis included two open states: one initial open state with a high probability of opening and a second open state with a lower probability of opening. He proposed that “modulation of energy wells” rather than movement of an inactivating particle to block the channel pore would theoretically explain the transition from the first open state to the second. Practically, he suggested that “voltage sensor S4d” drives the channel to a second open state through “lateral movement” or deionization of charge. This theory is in accordance with the finding that fluorescence signals near the DIV-VSD are associated with the slow component of gating and appear after signals associated with the faster component of gating (DI-DIII).131 Keynes defended his “mode switching” hypothesis based on new evidence suggesting Na+ channels maintain conductance even during inactivation.132 He also cited single channel recordings from Vandenberg and Bezanilla 1991 to support his theory.129 The recordings depict a channel with multiple openings initially after activation, but with time the number of openings would decrease. He thought this channel behavior would be best captured by a model with two open states. Later Keynes (1998) updated his model to include recent mutation studies suggesting that DIV S4 movement controls the onset of fast inactivation, or in other words, the initial transition from the first to the second open state.133 He further proposed that the hydration of the Na+ channel would control the transition from the second open state into an inactivated state. He finally suggested that the DIII-DIV linker controls the “hydration equilibrium” that eventually closes the channel.
Finally, the discovery of inherited long QT syndrome mutations that impair Na+ channel inactivation informed a new generation of models. In 1999, Clancy and Rudy simulated the ΔKPQ channel using a Markov type model.134 This mutation is in the DIII-DIV linker, and single channel recordings showed that the channel could enter a bursting state where inactivation fails to inactivate. To model this behavior, a six-state wild-type model was extended to include a “burst mode” that represents channel that fail to inactivate. Once a channel entered the “burst mode,” the channel lost its access to inactivation until it exited, producing late INa.. The model successfully recapitulated single channel data and reproduced the cell level behavior producing a prolonged APD, consistent with the long QT phenotype.
Toward molecularly detailed models of inactivation
While recent models are capable of recapitulating single channel behavior, they conflict with experimental evidence that shows that many different channel locales contribute to channel inactivation. Specifically, the models suggest that a specific, identifiable switch causes the channel to enter a mode where inactivation is impossible.
In contrast, the experimental findings detailed above suggest that several different channel domains contribute to inactivation during an AP. During the first few ms the DIV-VSD activates, enabling fast inactivation, which closes most of the channels. Subsequently, at least the DIII-VSD and C-terminal domain stabilize the inactivated conformation, causing more channels to occupy a non-conducting state. This mechanism is reminiscent of the “foot-on-the-door” mechanism used to explain Cd2+ ions promoting closure of the ultraslow inactivation gate in Nav1.4.135 However, instead of a single foot on the door, there are at least two feet, the C-terminal domain and the DIII-VSD that stabilize the inactivated state. Fig. 6 compares the traditional and the “feet-on-the-door” models of inactivation. The traditional model suggests that a switch induces the channel to enter a mode where inactivation is not possible while the “feet-on-the-door” model suggests that increased late INa is a consequence of one of the feet failing to stabilize the inactivated state. Because this model suggests that disruption of many different stabilizing events can cause increased late INa, it explains why mutations in various channel locations can augment late INa.
Figure 6.
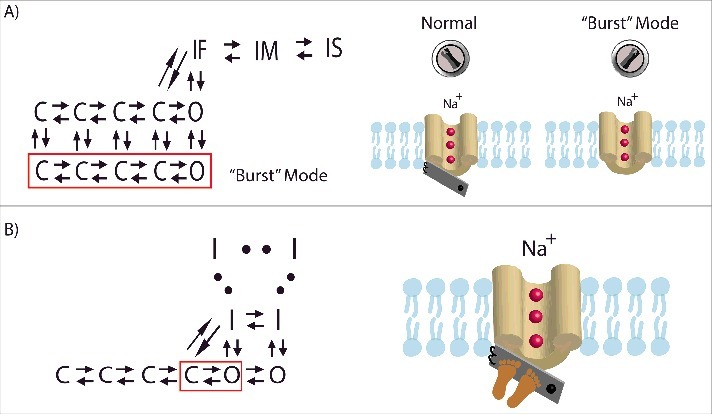
A comparison of the traditional and “feet-on-the-door” models. (A) In the traditional model, a switch induces the channel to enter a separate “burst” mode where inactivation is not possible. Once in the “burst” mode, the channel may not transition back to normal gating. The Markov type representation of this separate “bursting” mode is section of closed and open states (outlined in red) with rate parameters that prescribe periodic “bursting.”134 (B) The “feet-on-the-door” model of Na+ channel inactivation maintains that the IFM motif on the DIII-DIV linker is key for successful fast inactivation and that the C-terminal domain and the DIII-VSD keep the inactivation “door” closed. The corresponding Markov type representation includes a series of inactivated states with increasing stability. Higher stabilization allows the channel to occupy a deeper inactivated state where transitioning back to open and closed states is unlikely. Two open states are included where the rightmost open state has the higher open probability compared with left open state.130 Bursting behavior would be observed when channels occupy the left open and closed states (outlined in red). The extent of stabilization of inactivation determines the magnitude of late INa.
The creation of computational models that explicitly represent the molecular determinants of inactivation will not be trivial because each of these components cooperatively interact with each other, significantly increasing model complexity. Recent developments in channel optimization algorithms may be helpful in this effort.136,137 One potential approach to create a Markov type model with a large training set is to use state-mutating optimization routine. Instead of fixing the model topology which may overcomplicate the optimization, the routine identifies the optimal number of states along the corresponding rate parameters.136 Using the matrix exponential to compute cost saves time compared with using standard ODE solvers during the optimization.137 This expedited cost computation allows for larger sets of training data to be recapitulated in a reasonable amount of time.
While the challenge of creating molecularly based models of inactivation is not insignificant, there are many potential rewards. Because computational models of channels are readily incorporated into multi-scale cell and tissue models,136,138 this approach could be used to identify how inactivation should be targeted therapeutically to stabilize excitation at the tissue level to prevent arrhythmia. As additional structural data emerges, including the Cryo-EM structure of a mammalian NaV channel,139 conformational data from fluorescence experiments,140 and even NMR data showing channel dynamics,141 these models will only improve, provided that the computational approaches needed to incorporate this type of information into the models continue to be developed in parallel.
Disclosure of potential conflicts of interest
No potential conflicts of interest were disclosed.
Funding
This work was supported by National Institutes of Health under grant R01-HL136553 (JS) and grant T32-HL134635 (KM), and the American Heart Association under grant 15PRE25080073 (WZ).
References
- [1].Shaw RM, Rudy Y. Ionic Mechanisms of Propagation in Cardiac Tissue. Circ Res. 1997;81:727 LP-741. doi: 10.1161/01.RES.81.5.727. PMID:9351447 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [2].Jaye DA, Xiao Y-F, Sigg DC. Basic Cardiac Electrophysiology: Excitable Membranes BT – Cardiac Electrophysiology Methods and Models. In: Sigg DC, Iaizzo PA, Xiao Y-F, He B, editors Boston: (MA: ): Springer US; 2010. P. 41-51. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4419-6658-2_2 [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- [3].Hund TJ, Rudy Y. Rate dependence and regulation of action potential and calcium transient in a canine cardiac ventricular cell model. Circulation. 2004;110:3168-74. doi: 10.1161/01.CIR.0000147231.69595.D3. PMID:15505083 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [4].O'Hara T, Virág L, Varró A, Rudy Y. Simulation of the Undiseased Human Cardiac Ventricular Action Potential: Model Formulation and Experimental Validation. PLOS Comput Biol. 2011;7:e1002061. doi: 10.1371/journal.pcbi.1002061. PMID:21637795 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [5].Makielski JC. “Late sodium current: a mechanism for angina, heart failure, and arrhythmia.” J Cardiovasc Pharmacol. 2009;54:279-86. doi: 10.1097/FJC.0b013e3181a1b9e7. PMID:19333133 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [6].Makielski JC, Farley AL. Na+ Current in Human Ventricle: Implications for Sodium Loading and Homeostasis. J Cardiovasc Electrophysiol. 2006;17:S15−20. doi: 10.1111/j.1540-8167.2006.00380.x. PMID:16686671 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [7].Dumaine R, Wang Q, Keating MT, Hartmann HA, Schwartz PJ, Brown AM, Kirsch GE. Multiple mechanisms of Na+ channel–linked long-QT syndrome. Circ Res. 1996;78:916-24. doi: 10.1161/01.RES.78.5.916. PMID:8620612 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [8].Maltsev VA, Undrovinas A. Late sodium current in failing heart: Friend or foe? Prog Biophys Mol Biol. 2008;96:421-51. doi: 10.1016/j.pbiomolbio.2007.07.010. PMID:17854868 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [9].Huang B, El-Sherif T, Gidh-Jain M, Qin D, El-Sherif N. Alterations of sodium channel kinetics and gene expression in the postinfarction remodeled myocardium. J Cardiovasc Electrophysiol. 2001;12:218-25. doi: 10.1046/j.1540-8167.2001.00218.x. PMID:11232622 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [10].Hodgkin AL, Huxley AF. A quantitative description of membrane current and its application to conduction and excitation in nerve. J Physiol. 1952;117:500-44. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1952.sp004764. PMID:12991237 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [11].Chandler WK, Meves H. Sodium and potassium currents in squid axons perfused with fluoride solutions. J Physiol. 1970;211:623-52. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1970.sp009297. PMID:5501055 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [12].Chandler WK, Meves H. Rate constants associated with changes in sodium conductance in axons perfused with sodium fluoride. J Physiol. 1970;211:679-705. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1970.sp009299. PMID:5501057 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [13].Silva J. Slow Inactivation of Na+ Channels BT – Voltage Gated Sodium Channels. In: Ruben PC, editor Berlin: (Heidelberg: ): Springer Berlin Heidelberg; 2014. p. 33-49. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-41588-3_3 [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- [14].Richmond JE, Featherstone DE, a Hartmann H, Ruben PC. Slow inactivation in human cardiac sodium channels. Biophys J. 1998;74:2945-52. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(98)78001-4. PMID:9635748 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [15].Biet M, Barajas-Martinez H, Ton A-T, Delabre J-F, Morin N, Dumaine R. About half of the late sodium current in cardiac myocytes from dog ventricle is due to non-cardiac-type Na(+) channels. J Mol Cell Cardiol. 2012;53:593-8. doi: 10.1016/j.yjmcc.2012.06.012. PMID:22759452 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [16].Biet M, Morin N, Lessard-Beaudoin M, Graham RK, Duss S, Gagne J, Sanon NT, Carmant L, Dumaine R. Prolongation of action potential duration and QT interval during epilepsy linked to increased contribution of neuronal sodium channels to cardiac late Na+ current: potential mechanism for sudden death in epilepsy. Circ Arrhythm Electrophysiol. 2015;8:912-20. doi: 10.1161/CIRCEP.114.002693. PMID:26067667 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [17].Stefani E, Bezanilla F. Cut-open oocyte voltage-clamp technique. Methods Enzymol. 1998;293:300-18. doi: 10.1016/S0076-6879(98)93020-8. PMID:9711615 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [18].Rudokas MW, Varga Z, Schubert AR, Asaro AB, Silva JR. The Xenopus Oocyte Cut-open Vaseline Gap Voltage-clamp Technique With Fluorometry. J Vis Exp. 2014;:51040. doi: 10.3791/51040. PMID:24637712 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [19].Sakmann B, Neher E. (eds). Single-channel recording. Plenum Press, New York, 1995. doi: 10.1002/0471142301.ns0608s02. PMID:18428518. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [20].Williams SR, Wozny C. Errors in the measurement of voltage-activated ion channels in cell-attached patch-clamp recordings. Nat Comm. 2011;2:242. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [21].Catterall WA. Ion channel voltage sensors: structure, function, and pathophysiology. Neuron. 2010;67:915-28. doi: 10.1016/j.neuron.2010.08.021. PMID:20869590 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [22].Goldin AL, Barchi RL, Caldwell JH, Hofmann F, Howe JR, Hunter JC, Kallen RG, Mandel G, Meisler MH, Netter YB, et al.. Nomenclature of Voltage-Gated Sodium Channels. Neuron. 2000;28:365-8. doi: 10.1016/S0896-6273(00)00116-1. PMID:11144347 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [23].Cormier JW, Rivolta I, Tateyama M, Yang A-S, Kass RS. Secondary structure of the human cardiac Na+ channel C terminus: evidence for a role of helical structures in modulation of channel inactivation. J Biol Chem. 2002;277:9233-41. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M110204200. PMID:11741959 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [24].Chagot B, Potet F, Balser JR, Chazin WJ. Solution NMR structure of the C-terminal EF-hand domain of human cardiac sodium channel NaV1.5. J Biol Chem. 2009;284:6436-45. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M807747200. PMID:19074138 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [25].Armstrong CM, Bezanilla F, Rojas E. Destruction of Sodium Conductance Inactivation in Squid Axons Perfused with Pronase. J Gen Physiol. 1973;62:375 LP-391. doi: 10.1085/jgp.62.4.375. PMID:4755846 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [26].Vassilev PM, Scheuer T, Catterall WA. Identification of an intracellular peptide segment involved in sodium channel inactivation. Science. 1988;241:1658-61. doi: 10.1126/science.2458625. PMID:2458625 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [27].Stuhmer W, Conti F, Suzuki H, Wang X, Noda M, Yahagi N, Kubo H, Numa S. Structural parts involved in activation and inactivation of the sodium channel. Nature. 1989;339:597-603. doi: 10.1038/339597a0. PMID:2543931 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [28].Patton DE, Goldin AL. A voltage-dependent gating transition induces use-dependent block by tetrodotoxin of rat IIA sodium channels expressed in Xenopus oocytes. Neuron. 1991;7:637-47. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(91)90376-B. PMID:1657057 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [29].West JW, Patton DE, Scheuer T, Wang Y, Goldin AL, Catterall WA. A cluster of hydrophobic amino acid residues required for fast Na(+)-channel inactivation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992;89:10910-4. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.22.10910. PMID:1332060 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [30].Kellenberger S, West JW, Scheuer T, Catterall WA. Molecular Analysis of the Putative Inactivation Particle in the Inactivation Gate of Brain Type IIA Na+ Channels. J Gen Physiol. 1997;109:589-605. doi: 10.1085/jgp.109.5.589. PMID:9154906 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [31].Rohl CA, Boeckman FA, Baker C, Scheuer T, Catterall WA, Klevit RE. Solution structure of the sodium channel inactivation gate. Biochemistry. 1999;38:855-61. doi: 10.1021/bi9823380. PMID:9893979 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [32].Kellenberger S, Scheuer T, Catterall WA. Movement of the Na+ channel inactivation gate during inactivation. J Biol Chem. 1996;271:30971-9. doi: 10.1074/jbc.271.48.30971. PMID:8940085 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [33].Kellenberger S, West JW, Catterall WA, Scheuer T. Molecular analysis of potential hinge residues in the inactivation gate of brain type IIA Na+ channels. J Gen Physiol. 1997;109:607-17. doi: 10.1085/jgp.109.5.607. PMID:9154907 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [34].Bezanilla F. How membrane proteins sense voltage. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2008;9:323-32. doi: 10.1038/nrm2376. PMID:18354422 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [35].Armstrong CM, Bezanilla F. Inactivation of the sodium channel. II. Gating current experiments. J Gen Physiol. 1977;70:567-90. PMID:591912.doi: 10.1085/jgp.70.5.567 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [36].Mannuzzu LM, Moronne MM, Isacoff EY. Direct physical measure of conformational rearrangement underlying potassium channel gating. Science (80-). 1996;271:213. PMID:8539623.doi: 10.1126/science.271.5246.213 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [37].Cha A, Ruben PC, George ALJ, Fujimoto E, Bezanilla F. Voltage sensors in domains III and IV, but not I and II, are immobilized by Na+ channel fast inactivation. Neuron. 1999;22:73-87. doi: 10.1016/S0896-6273(00)80680-7. PMID:10027291 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [38].Smith MR, Goldin AL. Interaction between the sodium channel inactivation linker and domain III S4-S5. Biophys J. 1997;73:1885-95. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(97)78219-5. PMID:9336184 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [39].Smits JPP, Veldkamp MW, Bezzina CR, Bhuiyan ZA, Wedekind H, Schulze-Bahr E, Wilde AAM. Substitution of a conserved alanine in the domain IIIS4–S5 linker of the cardiac sodium channel causes long QT syndrome. Cardiovasc Res. 2005;67:459-66. doi: 10.1016/j.cardiores.2005.01.017. PMID:16039271 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [40].Lerche H, Peter W, Fleischhauer R, Pika-Hartlaub U, Malina T, Mitrovic N, Lehmann-Horn F. Role in fast inactivation of the IV/S4-S5 loop of the human muscle Na+ channel probed by cysteine mutagenesis. J Physiol. 1997;505:345-52. doi: 10.1111/j.1469-7793.1997.345bb.x. PMID:9423178 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [41].McPhee JC, Ragsdale DS, Scheuer T, Catterall WA. A critical role for the S4-S5 intracellular loop in domain IV of the sodium channel alpha-subunit in fast inactivation. J Biol Chem. 1998;273:1121-9. doi: 10.1074/jbc.273.2.1121. PMID:9422778 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [42].Popa MO, Alekov AK, Bail S, Lehmann-Horn F, Lerche H. Cooperative effect of S4-S5 loops in domains D3 and D4 on fast inactivation of the Na+ channel. J Physiol. 2004;561:39-51. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.2004.065912. PMID:15459238 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [43].McPhee JC, Ragsdale DS, Scheuer T, Catterall WA. A critical role for transmembrane segment IVS6 of the sodium channel alpha subunit in fast inactivation. J Biol Chem. 1995;270:12025-34. doi: 10.1074/jbc.270.20.12025. PMID:7744852 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [44].McPhee JC, Ragsdale DS, Scheuer T, Catterall WA. A mutation in segment IVS6 disrupts fast inactivation of sodium channels. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1994;91:12346-50. doi: 10.1073/pnas.91.25.12346. PMID:7991630 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [45].Yarov-Yarovoy V, McPhee JC, Idsvoog D, Pate C, Scheuer T, Catterall WA. Role of Amino Acid Residues in Transmembrane Segments IS6 and IIS6 of the Na+ Channel α Subunit in Voltage-dependent Gating and Drug Block. J Biol Chem. 2002;277:35393-401. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M206126200. PMID:12130650 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [46].Yarov-Yarovoy V, Brown J, Sharp EM, Clare JJ, Scheuer T, Catterall WA. Molecular determinants of voltage-dependent gating and binding of pore-blocking drugs in transmembrane segment IIIS6 of the Na(+) channel alpha subunit. J Biol Chem. 2001;276:20-7. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M006992200. PMID:11024055 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [47].Wang S-Y, Bonner K, Russell C, Wang GK. Tryptophan Scanning of D1S6 and D4S6 C-Termini in Voltage-Gated Sodium Channels. Biophys J. 2003;85:911-20. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(03)74530-5. PMID:12885638 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [48].Goldin AL. Mechanisms of sodium channel inactivation. Curr Opin Neurobiol. 2003;13:284-90. doi: 10.1016/S0959-4388(03)00065-5. PMID:12850212 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [49].Deschenes I, Trottier E, Chahine M. Implication of the C-terminal region of the alpha-subunit of voltage-gated sodium channels in fast inactivation. J Membr Biol. 2001;183:103-14. doi: 10.1007/s00232-001-0058-5. PMID:11562792 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [50].Mantegazza M, Yu FH, Catterall WA, Scheuer T. Role of the C-terminal domain in inactivation of brain and cardiac sodium channels. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2001;98:15348-53. doi: 10.1073/pnas.211563298. PMID:11742069 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [51].Wei J, Wang DW, Alings M, Fish F, Wathen M, Roden DM, George AL. Congenital Long-QT Syndrome Caused by a Novel Mutation in a Conserved Acidic Domain of the Cardiac Na+ Channel. Circulation. 1999;99:3165 LP-3171. doi: 10.1161/01.CIR.99.24.3165. PMID:10377081 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [52].Deschenes I, Baroudi G, Berthet M, Barde I, Chalvidan T, Denjoy I, Guicheney P, Chahine M. Electrophysiological characterization of SCN5A mutations causing long QT (E1784K) and Brugada (R1512W and R1432G) syndromes. Cardiovasc Res. 2000;46:55-65. doi: 10.1016/S0008-6363(00)00006-7. PMID:10727653 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [53].Motoike HK, Liu H, Glaaser IW, Yang A-S, Tateyama M, Kass RS. The Na+ channel inactivation gate is a molecular complex: a novel role of the COOH-terminal domain. J Gen Physiol. 2004;123:155-65. doi: 10.1085/jgp.200308929. PMID:14744988 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [54].Goldschen-Ohm MP, Capes DL, Oelstrom KM, Chanda B. Multiple pore conformations driven by asynchronous movements of voltage sensors in a eukaryotic sodium channel. Nat Commun. 2013;4:1350. doi: 10.1038/ncomms2356. PMID:23322038 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [55].Silva JR, Goldstein SAN. Voltage-sensor movements describe slow inactivation of voltage-gated sodium channels I: Wild-type skeletal muscle Na(V)1.4. J Gen Physiol. 2013;141:309-21. doi: 10.1085/jgp.201210909. PMID:23401571 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [56].Silva JR, Goldstein SAN. Voltage-sensor movements describe slow inactivation of voltage-gated sodium channels II: A periodic paralysis mutation in NaV1.4 (L689I). J Gen Physiol. 2013;141:323 LP-334. doi: 10.1085/jgp.201210910 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [57].Hsu EJ, Zhu W, Schubert AR, Voelker T, Varga Z, Silva JR. Regulation of Na+ channel inactivation by the DIII and DIV voltage-sensing domains. J Gen Physiol. 2017;14:389-403. doi: 10.1085/jgp.201611678. PMID:28232510. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [58].Varga Z, Zhu W, Schubert AR, Pardieck JL, Krumholz A, Hsu EJ, Zaydman MA, Cui J, Silva JR. Direct Measurement of Cardiac Na+ Channel Conformations Reveals Molecular Pathologies of Inherited Mutations. Circ Arrhythmia Electrophysiol. 2015;8:1228-39. doi: 10.1161/CIRCEP.115.003155 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [59].Hartshorne RP, Catterall WA. The sodium channel from rat brain. Purification and subunit composition. J Biol Chem. 1984;259:1667-75. PMID:6319405 [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [60].Kazen-Gillespie KA, Ragsdale DS, D'Andrea MR, Mattei LN, Rogers KE, Isom LL. Cloning, Localization, and Functional Expression of Sodium Channel β1A Subunits. J Biol Chem.. 2000;275:1079-88. doi: 10.1074/jbc.275.2.1079 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [61].Messner DJ, Catterall WA. The sodium channel from rat brain. Separation and characterization of subunits. J Biol Chem. 1985;260:10597-604. PMID:2411726 [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [62].Morgan K, Stevens EB, Shah B, Cox PJ, Dixon AK, Lee K, Pinnock RD, Hughes J, Richardson PJ, Mizuguchi K, et al.. beta 3: an additional auxiliary subunit of the voltage-sensitive sodium channel that modulates channel gating with distinct kinetics. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2000;97:2308-13. doi: 10.1073/pnas.030362197. PMID:10688874 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [63].Yu FH, Westenbroek RE, Silos-Santiago I, McCormick KA, Lawson D, Ge P, Ferriera H, Lilly J, DiStefano PS, Catterall WA, et al.. Sodium channel beta4, a new disulfide-linked auxiliary subunit with similarity to beta2. J Neurosci. 2003;23:7577-85. PMID:12930796 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [64].Calhoun JD, Isom LL. The role of non-pore-forming beta subunits in physiology and pathophysiology of voltage-gated sodium channels. Handb Exp Pharmacol. 2014;221:51-89. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-41588-3_4. PMID:24737232 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [65].Bao Y, Isom LL. NaV1.5 and Regulatory β Subunits in Cardiac Sodium Channelopathies. Card Electrophysiol Clin. 2014;6:679-94. doi: 10.1016/j.ccep.2014.07.002 [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- [66].Isom LL, De Jongh KS Patton DE, Reber BF, Offord J, Charbonneau H, Walsh K, Goldin AL, Catterall WA. Primary structure and functional expression of the beta 1 subunit of the rat brain sodium channel. Science. 1992;256:839-42. doi: 10.1126/science.1375395. PMID:1375395 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [67].Das S, Gilchrist J, Bosmans F, Van Petegem F. Binary architecture of the Nav1.2-beta2 signaling complex. Elife. 2016; 170 (470-482); e.11. doi: 10.7554/eLife.10960. PMID:26894959. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [68].O'Malley HA, Isom LL. Sodium channel beta subunits: emerging targets in channelopathies. Annu Rev Physiol. 2015;77:481-504. doi: 10.1146/annurev-physiol-021014-071846. PMID:25668026 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [69].Dominguez JN, Navarro F, Franco D, Thompson RP, Aranega AE. Temporal and spatial expression pattern of beta1 sodium channel subunit during heart development. Cardiovasc Res. 2005;65:842-50. doi: 10.1016/j.cardiores.2004.11.028. PMID:15721864 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [70].Okata S, Yuasa S, Suzuki T, Ito S, Makita N, Yoshida T, Li M, Kurokawa J, Seki T, Egashira T, et al.. Embryonic type Na+ channel β-subunit, SCN3B masks the disease phenotype of Brugada syndrome.. 2016;6:34198. PMID:27677334 doi: 10.1038/srep34198 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [71].Malhotra JD, Kazen-Gillespie K, Hortsch M, Isom LL. Sodium channel beta subunits mediate homophilic cell adhesion and recruit ankyrin to points of cell-cell contact. J Biol Chem. 2000;275:11383-8. doi: 10.1074/jbc.275.15.11383. PMID:10753953 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [72].Isom LL, Ragsdale DS, De Jongh KS Westenbroek RE, Reber BF, Scheuer T, Catterall WA. Structure and function of the beta 2 subunit of brain sodium channels, a transmembrane glycoprotein with a CAM motif. Cell. 1995;83:433-42. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(95)90121-3. PMID:8521473 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [73].Fahmi AI, Patel M, Stevens EB, Fowden AL, John JE, Lee K, Pinnock R, Morgan K, Jackson AP, Vandenberg JI. The sodium channel beta-subunit SCN3b modulates the kinetics of SCN5a and is expressed heterogeneously in sheep heart. J Physiol. 2001;537:693-700. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.2001.012691. PMID:11744748 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [74].Watanabe H, Darbar D, Kaiser DW, Jiramongkolchai K, Chopra S, Donahue BS, Kannankeril PJ, Roden DM. Mutations in sodium channel beta1- and beta2-subunits associated with atrial fibrillation. Circ Arrhythm Electrophysiol. 2009;2:268-75. doi: 10.1161/CIRCEP.108.779181. PMID:19808477 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [75].Yan Z, Zhou Q, Wang L, Wu J, Zhao Y, Huang G, Peng W, Shen H, Lei J, Yan N. Structure of the Nav1.4-β1 Complex from Electric Eel. Cell. 2017; doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2017.06.039. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [76].Zhu W, Voelker TL, Varga Z, Schubert AR, Nerbonne JM, Silva JR. Mechanisms of noncovalent β subunit regulation of Na+ channel gating. J Gen Physiol. 2017;doi: 10.1085/jgp.201711802 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [77].Wilde AAM, Brugada R. Phenotypical Manifestations of Mutations in the Genes Encoding Subunits of the Cardiac Sodium Channel. Circ Res. 2011;108:884 LP-897. doi: 10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.110.238469 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [78].Abriel H. Cardiac sodium channel Na(v)1.5 and interacting proteins: Physiology and pathophysiology. J Mol Cell Cardiol. 2010;48:2-11. doi: 10.1016/j.yjmcc.2009.08.025. PMID:19744495 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [79].Meregalli PG, Wilde AAM, Tan HL. Pathophysiological mechanisms of Brugada syndrome: Depolarization disorder, repolarization disorder, or more? Cardiovasc Res. 2005;67:367-78. doi: 10.1016/j.cardiores.2005.03.005. PMID:15913579 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [80].Giudicessi JR, Ackerman MJ. Genotype- and phenotype-guided management of congenital long QT syndrome. Curr Probl Cardiol. 2013;38:417-55. doi: 10.1016/j.cpcardiol.2013.08.001. PMID:24093767 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [81].Lopez-Santiago LF, Meadows LS, Ernst SJ, Chen C, Malhotra JD, McEwen DP, Speelman A, Noebels JL, Maier SKG, Lopatin AN, et al.. Sodium channel Scn1b null mice exhibit prolonged QT and RR intervals. J Mol Cell Cardiol. 2007;43:636-47. doi: 10.1016/j.yjmcc.2007.07.062. PMID:17884088 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [82].Bao Y, Willis BC, Frasier CR, Lopez-Santiago LF, Lin X, Ramos-Mondragón R, Auerbach DS, Chen C, Wang Z, Anumonwo J, et al.. Scn2b Deletion in Mice Results in Ventricular and Atrial Arrhythmias. Circ Arrhythmia Electrophysiol. 2016;9. doi: 10.1161/CIRCEP.116.003923 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [83].Hakim P, Gurung P, Pedersen P, Thresher P, Brice P, Lawrence P. Scn3b knockout mice exhibit abnormal ventricular electrophysiological properties. Prog Biophys Mol Biol. 2008;98:251-66. doi: 10.1016/j.pbiomolbio.2009.01.005. PMID:19351516 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [84].Hakim P., Thresher R., Grace A.A. HCL. Effects of flecainide and quinidine on action potential and ventricular arrhythmogenic properties in Scn3b knockout mice. Clin Exp Pharmacol Physiol. 2010;37:782-9. doi: 10.1111/j.1440-1681.2010.05369.x PMID:20132234 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [85].Mori M, Konno T, Ozawa T, Murata M, Imoto K, Nagayama K. Novel interaction of the voltage-dependent sodium channel (VDSC) with calmodulin: does VDSC acquire calmodulin-mediated Ca2+-sensitivity? Biochemistry. 2000;39:1316-23. doi: 10.1021/bi9912600. PMID:10684611 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [86].Klee CB, Crouch TH, Richman PG. Calmodulin. Annu Rev Biochem. 1980;49:489-515. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.49.070180.002421. PMID:6250447 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [87].Van Petegem F Lobo PA, Ahern CA. Seeing the forest through the trees: towards a unified view on physiological calcium regulation of voltage-gated sodium channels. Biophys J. 2012;103:2243-51. doi: 10.1016/j.bpj.2012.10.020. PMID:23283222 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [88].Deschenes I, Neyroud N, DiSilvestre D, Marban E, Yue DT, Tomaselli GF. Isoform-specific modulation of voltage-gated Na(+) channels by calmodulin. Circ Res. 2002;90:E49-57. doi: 10.1161/01.RES.0000012502.92751.E6. PMID:11884381 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [89].Tan HL, Kupershmidt S, Zhang R, Stepanovic S, Roden DM, Wilde AAM, Anderson ME, Balser JR. A calcium sensor in the sodium channel modulates cardiac excitability. Nature. 2002;415:442-7. doi: 10.1038/415442a. PMID:11807557 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [90].Casini S, Verkerk AO, van Borren MMGJ, van Ginneken ACG, Veldkamp MW, de Bakker JMT, Tan HL. Intracellular calcium modulation of voltage-gated sodium channels in ventricular myocytes. Cardiovasc Res. 2009;81:72-81. doi: 10.1093/cvr/cvn274. PMID:18829699 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [91].Ben-Johny M, Yang PS, Niu J, Yang W, Joshi-Mukherjee R, Yue DT. Conservation of Ca2+/calmodulin regulation across Na and Ca2+ channels. Cell. 2014;157:1657-70. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2014.04.035. PMID:24949975 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [92].Wingo TL, Shah VN, Anderson ME, Lybrand TP, Chazin WJ, Balser JR. An EF-hand in the sodium channel couples intracellular calcium to cardiac excitability. Nat Struct Mol Biol. 2004;11:219-25. doi: 10.1038/nsmb737. PMID:14981509 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [93].Biswas S, Deschenes I, Disilvestre D, Tian Y, Halperin VL, Tomaselli GF. Calmodulin regulation of Nav1.4 current: role of binding to the carboxyl terminus. J Gen Physiol. 2008;131:197-209. doi: 10.1085/jgp.200709863. PMID:18270170 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [94].Sarhan MF, Van Petegem F Ahern CA. A double tyrosine motif in the cardiac sodium channel domain III-IV linker couples calcium-dependent calmodulin binding to inactivation gating. J Biol Chem. 2009;284:33265-74. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M109.052910. PMID:19808664 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [95].Sarhan MF, Tung C-C, Van Petegem F Ahern CA. Crystallographic basis for calcium regulation of sodium channels. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2012;109:3558-63. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1114748109. PMID:22331908 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [96].Wang C, Chung BC, Yan H, Lee S-Y, Pitt GS. Crystal structure of the ternary complex of a NaV C-terminal domain, a fibroblast growth factor homologous factor, and calmodulin. Structure. 2012;20:1167-76. doi: 10.1016/j.str.2012.05.001. PMID:22705208 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [97].Wang C, Chung BC, Yan H, Wang H-G, Lee S-Y, Pitt GS. Structural analyses of Ca(2)(+)/CaM interaction with NaV channel C-termini reveal mechanisms of calcium-dependent regulation. Nat Commun. 2014;5:4896. doi: 10.1038/ncomms5896. PMID:25232683 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [98].Hennessey JA, Wei EQ, Pitt GS. Fibroblast Growth Factor Homologous Factors Modulate Cardiac Calcium Channels. Circ Res. 2013;113: doi: 10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.113.301215. PMID:23804213 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [99].Liu C, Dib-Hajj SD, Renganathan M, Cummins TR, Waxman SG. Modulation of the cardiac sodium channel Nav1.5 by fibroblast growth factor homologous factor 1B. J Biol Chem. 2003;278:1029-36. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M207074200. PMID:12401812 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [100].Musa H, Kline CF, Sturm AC, Murphy N, Adelman S, Wang C, Yan H, Johnson BL, Csepe TA, Kilic A, et al.. SCN5A variant that blocks fibroblast growth factor homologous factor regulation causes human arrhythmia. Proc Natl Acad Sci. 2015;112:12528-33. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1516430112. PMID:26392562 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [101].Jones DK, Peters CH, Tolhurst SA, Claydon TW, Ruben PC. Extracellular proton modulation of the cardiac voltage-gated sodium channel, NaV1.5. Biophys J. 2011;101:2147-56. doi: 10.1016/j.bpj.2011.08.056. PMID:22067152 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [102].Vilin YY, Peters CH, Ruben PC. Acidosis differentially modulates inactivation in Nav1.2, Nav1.4, and Nav1.5 channels. Front Pharmacol. 2012;3:109. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2012.00109. PMID:22701426 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [103].Peters CH, Abdelsayed M, Ruben PC. Triggers for arrhythmogenesis in the Brugada and long QT 3 syndromes. Prog Biophys Mol Biol. 2016;120:77-88. doi: 10.1016/j.pbiomolbio.2015.12.009. PMID:26713557 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [104].Jones DK, Claydon TW, Ruben PC. Extracellular protons inhibit charge immobilization in the cardiac voltage-gated sodium channel. Biophys J. 2013;105:101-7. doi: 10.1016/j.bpj.2013.04.022. PMID:23823228 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [105].Jones DK, Peters CH, Allard CR, Claydon TW, Ruben PC. Proton sensors in the pore domain of the cardiac voltage-gated sodium channel. J Biol Chem. 2013;288:4782-91. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M112.434266. PMID:23283979 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [106].Jones DK, Ruben PC. Proton modulation of cardiac I Na: A potential arrhythmogenic trigger. Handb Exp Pharmacol. 2014;221:169-81. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-41588-3_8. PMID:24737236 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [107].Omar HR, El-Khabiry E, Dalvi P, Mangar D, Camporesi EM. Brugada ECG pattern during hyperkalemic diabetic ketoacidosis. Ther Adv Endocrinol Metab. 2017;8:20-1. doi: 10.1177/2042018816680589. PMID:28203362 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [108].Anselm DD, Evans JM, Baranchuk A. Brugada phenocopy: A new electrocardiogram phenomenon. World J Cardiol. 2014;6:81-6. doi: 10.4330/wjc.v6.i3.81. PMID:24669289 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [109].Peters CH, Ruben PC. Acidosis: A Possible Trigger for Brugada Syndrome Associated Arrhythmia. Biophys J. 2014;106:327a. doi: 10.1016/j.bpj.2013.11.1880 [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- [110].Peters CH, Abdelsayed M, Ruben PC. Triggers for arrhythmogenesis in the Brugada and long QT 3 syndromes. Prog Biophys Mol Biol. 2016;120:77-88. doi: 10.1016/j.pbiomolbio.2015.12.009. PMID:26713557 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [111].Hu RM, Tan BH, Tester DJ, Song C, He Y, Dovat S, Peterson BZ, Ackerman MJ, Makielski JC. Arrhythmogenic biophysical phenotype for SCN5A mutation S1787N depends upon splice variant background and intracellular acidosis. PLoS One. 2015;10:e0124921. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0124921. PMID:25923670 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [112].Knowlton FP, Starling EH. The influence of variations in temperature and blood-pressure on the performance of the isolated mammalian heart. J Physiol. 1912;44:206-19. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1912.sp001511. PMID:16993122 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [113].Pasquié JL, Sanders P, Hocini M, Hsu LF, Scavée C, Jais P, Takahashi Y, Rotter M, Sacher F, Victor J, et al.. Fever as a precipitant of idiopathic ventricular fibrillation in patients with normal hearts. J Cardiovasc Electrophysiol. 2004;15:1271-6. doi: 10.1046/j.1540-8167.2004.04388.x. PMID:15574177 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [114].Abdelsayed M, Peters CH, Ruben PC. Differential thermosensitivity in mixed syndrome cardiac sodium channel mutants. J Physiol. 2015;593:4201-23. doi: 10.1113/JP270139. PMID:26131924 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [115].Dumaine R, Towbin JA, Brugada P, Vatta M, Nesterenko D V., Nesterenko V V., Brugada J, Brugada R, Antzelevitch C. Ionic Mechanisms Responsible for the Electrocardiographic Phenotype of the Brugada Syndrome Are Temperature Dependent. Circ Res. 1999;85:803-9. doi: 10.1161/01.RES.85.9.803. PMID:10532948 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [116].Keller DI, Rougier JS, Kucera JP, Benammar N, Fressart V, Guicheney P, Madle A, Fromer M, Schläpfer J, Abriel H. Brugada syndrome and fever: Genetic and molecular characterization of patients carrying SCN5A mutations. Cardiovasc Res. 2005;67:510-9. doi: 10.1016/j.cardiores.2005.03.024. PMID:15890323 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [117].Adler A, Topaz G, Heller K, Zeltser D, Ohayon T, Rozovski U, Halkin A, Rosso R, Ben-Shachar S, Antzelevitch C, et al.. Fever-induced Brugada pattern: How common is it and what does it mean? Hear Rhythm. 2013;10:1375-82. doi: 10.1016/j.hrthm.2013.07.030. PMID:23872691 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [118].De Marco S Giannini C, Chiavaroli V, De Leonibus C Chiarelli F, Mohn A. Brugada syndrome unmasked by febrile illness in an asymptomatic child. J. Pediatr. 2012;161:769-769.e1. doi: 10.1016/j.jpeds.2012.04.034. PMID:22608909 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [119].Rijal J, Giri S, Khanal S, Dahal K. A case of Brugada Syndrome unmasked by a postoperative febrile state. Casp J Intern Med. 2015;6:43-5. PMID:26221497 [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [120].Gima K, Rudy Y. Ionic current basis of electrocardiographic waveforms: A model study. Circ Res. 2002;90:889-96. doi: 10.1161/01.RES.0000016960.61087.86. PMID:11988490 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [121].Schoorlemmer J, Goldfarb M. Fibroblast growth factor homologous factors are intracellular signaling proteins. Curr Biol. 2001;11:793-7. doi: 10.1016/S0960-9822(01)00232-9. PMID:11378392 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [122].Park DS, Shekhar A, Marra C, Lin X, Vasquez C, Solinas S, Kelley K, Morley G, Goldfarb M, Fishman GI. Fhf2 gene deletion causes temperature-sensitive cardiac conduction failure. Nat Commun. 2016;7:12966. doi: 10.1038/ncomms12966. PMID:27701382 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [123].Ahern CA, Payandeh J, Bosmans F, Chanda B. The hitchhiker's guide to the voltage-gated sodium channel galaxy. J Gen Physiol. 2016;147:1-24. doi: 10.1085/jgp.201511492. PMID:26712848 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [124].Bezanilla F, Armstrong CM. Inactivation of the sodium channel. I. Sodium current experiments. J Gen Physiol. 1977;70:549-66. doi: 10.1085/jgp.70.5.549. PMID:591911 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [125].Colquhoun D, Hawkes AG. Relaxation and Fluctuations of Membrane Currents that Flow through Drug-Operated Channels. Proc R Soc London Ser B Biol Sci. 1977;199:231 LP-262. doi: 10.1098/rspb.1977.0137 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [126].Colquhoun D, Hawkes AG. On the stochastic properties of single ion channels. Proc R Soc London Ser B, Biol Sci. 1981;211:205-35. doi: 10.1098/rspb.1981.0003. PMID:6111797 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [127].Horn R, Lange K. Estimating kinetic constants from single channel data. Biophys J. 1983;43:207-23. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(83)84341-0. PMID:6311301 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [128].Rudy Y, Silva JR. Computational biology in the study of cardiac ion channels and cell electrophysiology. Q Rev Biophys. 2006;39:57-116. doi: 10.1017/S0033583506004227. PMID:16848931 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [129].Vandenberg CA, Bezanilla F. A sodium channel gating model based on single channel, macroscopic ionic, and gating currents in the squid giant axon. Biophys J. 1991;60:1511-33. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(91)82186-5. PMID:1663796 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [130].Keynes RD. A New Look at the Mechanism of Activation and Inactivation of Voltage-Gated Ion Channels. Proc R Soc London Ser B Biol Sci. 1992;249:107 LP-112. doi: 10.1098/rspb.1992.0091 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [131].Chanda B, Bezanilla F. Tracking Voltage-dependent Conformational Changes in Skeletal Muscle Sodium Channel during Activation. J Gen Physiol. 2002;120:629 LP-645. doi: 10.1085/jgp.20028679. PMID:12407076 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [132].Correa AM, Bezanilla F. Gating of the squid sodium channel at positive potentials: II. Single channels reveal two open states. Biophys J. 1994;66:1864-78. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(94)80979-8. PMID:8075323 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [133].Keynes RD, Elinder F. Modelling the activation, opening, inactivation and reopening of the voltage-gated sodium channel. Proc R Soc B Biol Sci. 1998;265:263-70. doi: 10.1098/rspb.1998.0291. PMID:9523428 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [134].Clancy CE, Rudy Y. Linking a genetic defect to its cellular phenotype in a cardiac arrhythmia. Nature. 1999;400:566-9. doi: 10.1038/23034. PMID:10448858 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [135].Szendroedi J, Sandtner W, Zarrabi T, Zebedin E, Hilber K, Dudley SCJ, Fozzard HA, Todt H. Speeding the recovery from ultraslow inactivation of voltage-gated Na+ channels by metal ion binding to the selectivity filter: a foot-on-the-door? Biophys J. 2007;93:4209-24. doi: 10.1529/biophysj.107.104794. PMID:17720727 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [136].Menon V, Spruston N, Kath WL. A state-mutating genetic algorithm to design ion-channel models. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2009;106:16829-34. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0903766106. PMID:19805381 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [137].Teed ZR, Silva JR. A computationally efficient algorithm for fitting ion channel parameters. MethodsX. 2016;3:577-88. doi: 10.1016/j.mex.2016.11.001. PMID:27924282 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [138].Silva JR, Pan H, Wu D, Nekouzadeh A, Decker KF, Cui J, Baker NA, Sept D, Rudy Y. A multiscale model linking ion-channel molecular dynamics and electrostatics to the cardiac action potential. Proc Natl Acad Sci. 2009;106:11102-6. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0904505106. PMID:19549851 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [139].Shen H, Zhou Q, Pan X, Li Z, Wu J, Yan N. Structure of a eukaryotic voltage-gated sodium channel at near-atomic resolution. Science. 2017;355. doi: 10.1126/science.aal4326. PMID:28183995 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [140].Zhu W, Varga Z, Silva JR. Molecular motions that shape the cardiac action potential: Insights from voltage clamp fluorometry. Prog Biophys Mol Biol. 2016;120:3-17. doi: 10.1016/j.pbiomolbio.2015.12.003. PMID:26724572 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [141].Brettmann JB, Urusova D, Tonelli M, Silva JR, Henzler-Wildman KA. Role of protein dynamics in ion selectivity and allosteric coupling in the NaK channel. Proc Natl Acad Sci. 2015;112:15366-71. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1515965112. PMID:26621745 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [142].Kleber AG, Rudy Y. Basic mechanisms of cardiac impulse propagation and associated arrhythmias. Physiol Rev. 2004;84:431-88. doi: 10.1152/physrev.00025.2003. PMID:15044680 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


