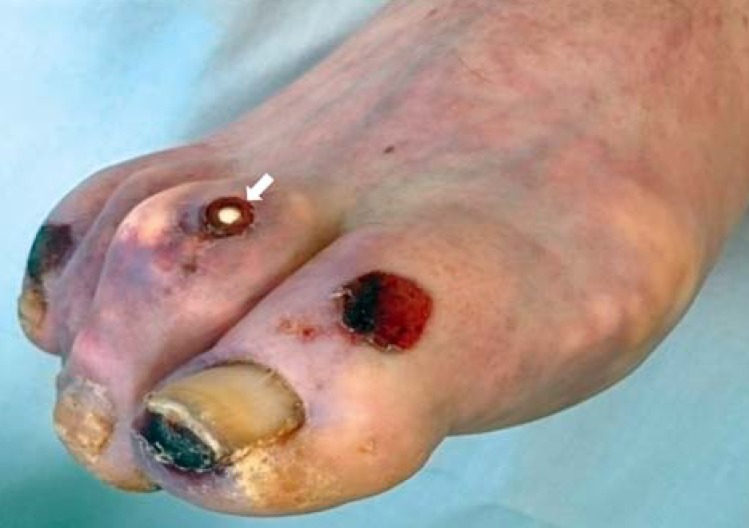
A 73-year-old man was admitted to the intensive care unit after suffering a myocardial infarction without ST elevation and undergoing successful cardiopulmonary resuscitation. He had a prior history of coronary heart disease, high-grade ischemic cardiomyopathy, chronic renal failure, and chronic gouty arthritis with multiple gouty tophi. He had also had hyperuricemia for many years, with uric acid concentrations of up to 9.8 mg/dl. Initial treatment with febuxostat 80 mg bid had failed to lower the uric acid level adequately and was switched to allopurinol 300 mg po qd. This resulted in normalization of the uric acid level, as documented in the current admission (4.7 mg/dl). The already formed gouty tophi on the tips and joints of the fingers and toes nevertheless persisted. Skin ulcerations caused by gouty tophi were found on the left third toe and the right second toe (Figure). This case can serve as a reminder that patients with hyperuricemia should be treated with allopurinol as first-line treatment and with febuxostat only as second-line treatment.
Gouty tophi on the right metatarsophalangeal joint and on the interphalangeal joints of the toes of the right foot. The white arrow points to an ulcerated tophus.
Cite this as: Jud P, Verheyen N, Fruhwald F: Multiple chronic gouty tophi.
Translated from the original German by Ethan Taub, M.D.
Footnotes
Conflict of interest statement:
The authors state that they have no conflict of interest.