Figure 4.
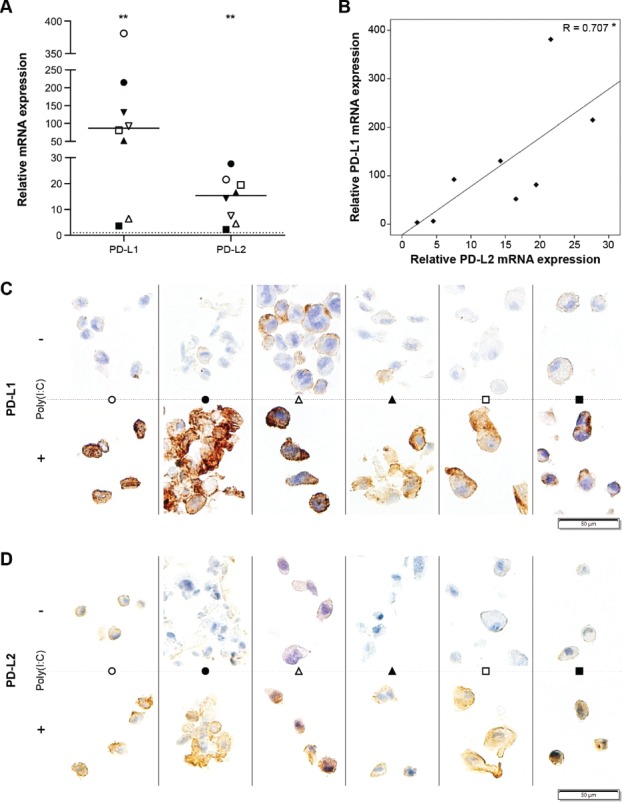
Poly(I:C) stimulates PD-L1 and PD-L2 expression on primary human glioblastoma cells via enhanced protein production. (A) Poly(I:C) upregulates mRNA transcription of PD-L1 and PD-L2 in primary human glioblastoma cells. mRNA expression following poly(I:C) treatment is shown relative to the basal, naïve condition (dashed line at 1); n = 8; Wilcoxon Signed Ranks test. (B) Plot showing the correlation between PD-L1 and PD-L2 mRNA expression following poly(I:C) treatment relative to naïve cells; Pearson's correlation coefficient. (C-D) Poly(I:C) increases both membrane and intracellular expression of PD-L1 (C) and PD-L2 (D) on primary human glioblastoma cells; n = 6; representative areas per specimen are shown. Bar represents median. Symbols depict primary glioblastoma cells derived from different glioblastoma patients. -, no poly(I:C); +, 10µg/ml poly(I:C); *, p < 0.05; **, p < 0.01.
