Abstract
Genetic and archaeological findings hint that wildcats became house cats earlier—and in a different place—than previously thought
The aloof and elusive nature of cats is perhaps their most distinctive feature, endearing to some and exasperating to others. Despite its mercurial tendencies, the house cat is the most popular pet in the world. A third of American households have feline members, and more than 600 million cats live among humans worldwide. Yet as familiar as these animals are, a complete understanding of their origins has proved elusive. Whereas other once wild animals were domesticated for their milk, meat, wool or labor, cats contribute virtually nothing in the way of sustenance or work. How, then, did they become fixtures in our homes?
Scholars long believed that the ancient Egyptians were the first to keep cats as pets, starting around 3,600 years ago. But genetic and archaeological discoveries made over the past 10 years have revised this scenario—and have generated fresh insights into both the ancestry of the domestic cat and how its relationship with humans evolved.
IN BRIEF.
Unlike other domesticated creatures, the house cat contributes little to human survival. Researchers have therefore wondered how and why cats came to live among people.
Experts traditionally thought that the Egyptians were the first to domesticate the cat, some 3,600 years ago.
But recent genetic and archaeological discoveries indicate that cat domestication began in the Fertile Crescent, perhaps around 10,000 years ago, when agriculture was getting under way.
The findings suggest that cats started making themselves at home around people to take advantage of the mice and food scraps found in their settlements.
CAT’S CRADLE
The question of where domestic cats first arose has been challenging to resolve for several reasons. Although a number of investigators suspected that all varieties descend from just one cat species— Felis silvestris, the wildcat—they could not be certain. In addition, that species is represented by populations living throughout the Old World—from Scotland to South Africa and from Spain to Mongolia—and until recently scientists had no way of determining unequivocally which of these wildcat populations gave rise to the tamer, domestic kind. Indeed, as an alternative to the Egyptian origins hypothesis, some researchers had even proposed that cat domestication occurred in a number of different locations, with each domestication spawning a different breed. Confounding the issue was the fact that members of these wildcat groups are hard to tell apart from one another and from feral domesticated cats with so-called mackerel- tabby coats because all of them have the same pelage pattern of curved stripes and they interbreed freely with one another, further blurring population boundaries.
FINDINGS: The House Cat’s Ancestor.
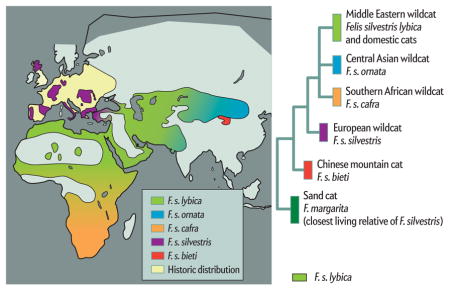
Researchers examined DNA belonging to nearly 1,000 wildcats and domestic cats from across the Old World to determine which subspecies of the wildcat, Felis silvestris, gave rise to the house cat. They found that the DNA clustered into five groups, based on similarity of sequence, and noted that the wildcats within each group came from the same region of the world (map). The domestic cats, however, grouped only with F. silvestris lybica, the Middle Eastern wildcat (photograph). This result established that all domestic cats are descended from F. s. lybica alone (family tree).
In 2000 one of us (Driscoll) set out to tackle the question by assembling DNA samples from some 979 wildcats and domestic cats in southern Africa, Azerbaijan, Kazakhstan, Mongolia and the Middle East. Because wildcats typically defend a single territory for life, he expected that the genetic composition of wildcat groups would vary across their geographical ranges but remain stable over time, as is observed in many other felid species. If regional indigenous groups of these animals could be distinguished from one another on the basis of their DNA, and if the DNA of domestic cats more closely resembled that of one of the wildcat populations, then he would have clear evidence for where domestication began.
In the genetic analysis, published in 2007, Driscoll, another of us (O’Brien) and their colleagues focused on two kinds of DNA that molecular biologists traditionally examine to differentiate subgroups of mammal species: DNA from mitochondria, which is inherited exclusively from the mother, and short, repetitive sequences of nuclear DNA known as microsatellites. Using established computer routines, they assessed the ancestry of each of the 979 individuals sampled based on their genetic signatures. Specifically, they measured how similar each cat’s DNA was to that of all the other cats and grouped the animals having similar DNA together. They then asked whether most of the animals in a group lived in the same region.
SIDE TITLE: Early Domestication.
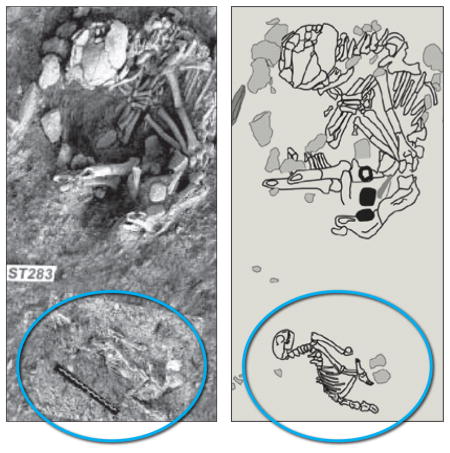
Traditionally the ancient Egyptians have been credited with domesticating the cat by roughly 3,600 years ago. But in 2004 archaeologists working on the Mediterranean island of Cyprus discovered a 9,500-year-old burial of an adult human and a cat (circled in photograph, left, and map, right). Because cats are not native to Cyprus, people must have brought them over by boat, probably from the nearby Levantine coast. The find thus suggests that people in the Middle East began keeping cats as pets long before the Egyptians did.
The results revealed five genetic clusters, or lineages, of wildcats. Four of these lineages corresponded neatly with four of the known subspecies of wildcat and dwelled in specific places: F. silvestris silvestris in Europe, F. s. bieti in China, F. s. ornata in Central Asia and F. s. cafra in southern Africa. The fifth lineage, however, included not only the fifth known subspecies of wildcat— F. s. lybica in the Middle East—but also the hundreds of domestic cats that were sampled, including purebred and mixed-breed felines from the U.S., the U.K. and Japan. In fact, genetically, F. s. lybica wildcats collected in remote deserts of Israel, the United Arab Emirates and Saudi Arabia were virtually indistinguishable from domestic cats. That the domestic cats grouped with F. s. lybica alone among wildcats meant that domestic cats arose in a single broad locale, the Middle East, and not in other places where wildcats are native.
Once we had figured out where domestic cats came from, the next step was to ascertain when they had become domesticated. Geneticists can often estimate when a particular evolutionary event occurred by studying the quantity of random genetic mutations that accumulate at a steady rate over time. But this so-called molecular clock ticks a mite too slowly to precisely date events as recent as the past 10,000 years, the likely interval for cat domestication. To get a bead on when the taming of the cat began, we turned to the archaeological record. One recent find has proved especially informative in this regard.
In 2004 Jean-Denis Vigne of the National Museum of Natural History in Paris and his colleagues reported unearthing the earliest evidence suggestive of humans keeping cats as pets. The discovery comes from the Mediterranean island of Cyprus, where 9,500 years ago an adult human of unknown gender was laid to rest in a shallow grave. An assortment of items accompanied the body— stone tools, a lump of iron oxide, a handful of seashells and, in its own tiny grave just 40 centimeters away, an eight-month- old cat, its body oriented in the same westward direction as the human’s.
Because wildcats are not native to Mediterranean islands other than Sicily, we know that people must have brought them over by boat, probably from the adjacent Levantine coast. Together the transport of cats to the island and the burial of the human with a cat indicate that people had a special, intentional relationship with cats nearly 10,000 years ago in some parts of the Middle East. This locale is consistent with the geographic origin we arrived at through our genetic analyses. It appears, then, that cats were being tamed just as humankind was establishing the first settlements in a part of the Middle East known as the Fertile Crescent—the Cradle of Civilization.
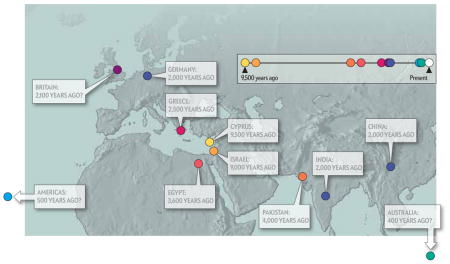
DISPERSAL: Have Cats, Will Travel.
As agriculture and permanent human settlements spread from the Fertile Crescent to the rest of the world, so, too, did domestic cats. The map below shows the earliest putative occurrences of domestic cats in regions around the globe.
A CAT AND MOUSE GAME?
With the geography and an approximate age of the initial phases of cat domestication established, we could begin to revisit the old question of why cats and humans ever developed a special relationship. Felids in general are unlikely candidates for domestication. The ancestors of most domesticated animals lived in herds or packs with clear dominance hierarchies. (Humans unwittingly took advantage of this structure by supplanting the alpha individual, thus facilitating control of entire cohesive groups.) These herd animals were already accustomed to living cheek by jowl, so provided that food and shelter were plentiful, they adapted easily to confinement.
Felids, in contrast, are solitary hunters that defend their home ranges fiercely from others of the same sex (the pride-living lions are the exception to this rule). Moreover, whereas most domesticates feed on widely available plant foods, felids are obligate carnivores, meaning they have a limited ability to digest anything but meat—a far rarer menu item. In fact, they have lost the ability to taste sweet carbohydrates altogether. And as to utility to humans, let us just say that our cats do not take instruction well. Such attributes suggest that whereas other domesticates were recruited from the wild by humans who bred them for specific tasks, ancestors of domestic cats most likely chose to live among humans because of opportunities they found for themselves.
Early settlements in the Fertile Crescent between 9,000 and 10,000 years ago, during the Neolithic period, created a completely new environment for any wild animals that were sufficiently flexible and inquisitive (or scared and hungry) to exploit it. The house mouse, Mus musculus domesticus, was one such creature. Archaeologists have found remains of this rodent, which originated in the Indian subcontinent, among the first human stores of wild grain from Israel, which date to around 10,000 years ago. The house mice could not compete well with the local wild mice outside, but by moving into people’s homes and silos, they thrived.
It is almost certainly the case that these house mice attracted cats. But the trash heaps on the outskirts of town were probably just as great a draw, providing year-round pickings for those felines resourceful enough to seek them out. Both these food sources would have encouraged wildcats to adapt to living with people; in the lingo of evolutionary biology, natural selection favored those wildcats that were able to cohabit with humans and thereby gain access to the trash and mice.
Over time, wildcats more tolerant of living in human-dominated environments began to proliferate in villages throughout the Fertile Crescent. Natural selection in this new niche would have been principally for tameness, but competition among cats would also have continued to influence their evolution and limit how pliant they became. Because these proto–domestic cats were undoubtedly mostly left to fend for themselves, their hunting and scavenging skills remained sharp. Even today most domesticated cats are free agents that can easily survive independently of humans, as evinced by the plethora of feral cats around the world.
Considering that small cats do little obvious harm, people probably did not mind their company. They might have even encouraged the cats to stick around when they saw them dispatching mice and snakes. Cats may have held other appeal, too. Some experts speculate that wildcats just so happened to possess features that might have preadapted them to developing a relationship with people. In particular, these cats have “cute” features— large eyes, a snub face and a high, round forehead, among others—that are known to elicit nurturing from humans. In all likelihood, then, some people took kittens home simply because they found them adorable, giving cats a singular foothold at the human hearth.
TIMELINE: From Wild to Mild.
Researchers believe, based on archaeological and historic records, that the transformation of the Middle Eastern wildcat into a ubiquitous pet transpired over thousands of years.
10,500–9,500 years ago House mouse remains preserved with human stores of grain in Israel; origin of agriculture and of permanent human settlements creates opportunities for cats willing to get close enough to humans to hunt house mice
9,500 years ago Human and cat double burial on Mediterranean island of Cyprus; earliest evidence of special relationship between people and cats
3,700 years ago Ivory cat statuette sculpted in Israel; suggests cats were a common sight around human settlements in the Fertile Crescent
3,600 years ago Artists paint domesticated cats from Thebes, Egypt; oldest clear evidence of fully domesticated cat
2,900 years ago Cats become “official deity” of Egypt in the form of the goddess Bastet; huge number of cats sacrificed and mummified in her sacred city indicates that Egyptians were breeding domestic cats
2,300 years ago The height of cat worship in Egypt; the Ptolemeic rulers maintain strict bans on the export of cats
2,000 years ago Cat remains preserved at the German site of Tofting in Schleswig and increasing references to cats in art and literature show that domestic cats were common throughout Europe
1350–1767 The Tamara Maew (or “Cat-Book Poems”), composed by Buddhist monks in Thailand, describes indigenous natural breeds, such as the Siamese, which arose largely through genetic drift, as opposed to human intervention
1800s Most of the modern breeds developed in the British Isles, according to writings of English natural history artist Harrison Weir
1871 Cat show at the Crystal Palace in London is first to include human-created breeds
2001 First cloned pet, a kitten named “cc,” is born at Texas A&M University’s College of Veterinary Medicine




Why was F. s. lybica the only subspecies of wildcat to be domesticated? Anecdotal evidence suggests that certain other subspecies, such as the European wildcat and the Chinese mountain cat, are less tolerant of people. If so, this trait alone could have precluded their adoption into homes. The friendlier southern African and Central Asian wildcats, on the other hand, might very well have become domesticated under the right conditions. But F. s. lybica had the good luck of proximity to the first human settlements. As agriculture spread out from the Fertile Crescent, so, too, did the tame scions of F. s. lybica, filling the same niche in each region they entered—and effectively shutting the door on local wildcat populations. Had domestic cats from the Fertile Crescent never arrived in Africa or Asia, perhaps the indigenous wildcats in those regions would have been drawn to homes and villages as urban civilizations developed there.
RISE OF THE GODDESS
We do not know how long it took to transform the Middle Eastern wildcat into an affectionate home companion. Animals can be domesticated rapidly under controlled conditions. But without doors or windowpanes, Neolithic farmers would have been hard-pressed to control the breeding of cats even if they wanted to. It seems reasonable to suggest that the lack of human influence on breeding and the probable intermixing of proto-domestic cats and wildcats militated against rapid taming, causing the metamorphosis to occur over thousands of years.
Although the exact timeline of cat domestication remains uncertain, long-known archaeological evidence affords some insight into the process. After the Cypriot find, the next oldest hints of an association between humans and cats are a feline molar tooth from an archaeological deposit in Israel dating to roughly 9,000 years ago and another tooth from Pakistan dating to around 4,000 years ago.
Testament to full domestication comes from a much later period. A nearly 3,700-year-old ivory cat statuette from Israel suggests the cat was a common sight around homes and villages in the Fertile Crescent before its introduction to Egypt. This scenario makes sense, given that all the other domestic animals (except the donkey) and plants were introduced to the Nile Valley from the Fertile Crescent. But it is Egyptian paintings from the so-called New Kingdom period— Egypt’s golden era, which began nearly 3,600 years ago—that provide the oldest known unmistakable depictions of full domestication. These paintings typically show cats poised under chairs, sometimes collared or tethered, and often eating from bowls or feeding on scraps. The abundance of these illustrations signifies that cats had become common members of Egyptian households by this time.
It is in large part as a result of evocative images such as these that scholars traditionally perceived ancient Egypt as the locus of cat domestication. However, even the oldest Egyptian representations of wildcats are 5,000 to 6,000 years younger than the 9,500-year-old Cypriot burial. Although ancient Egyptian culture cannot claim initial domestication of the cat among its many achievements, it surely played a pivotal role in subsequently molding the dynamic of domestication and the spread of cats throughout the world. Indeed, the Egyptians took the love of cats to a whole new level. By 2,900 years ago the domestic cat had become the official deity of Egypt in the form of the goddess Bastet, and such cats were sacrificed, mummified and buried in great numbers at Bastet’s sacred city, Bubastis. The sheer number of cat mummies found there, measured by the ton, indicates that Egyptians were not just harvesting feral or wild populations but, for the first time in history, were actively breeding domestic cats.
Egypt officially prohibited the export of its venerated cats for centuries. Nevertheless, by 2,500 years ago the animals had made their way to Greece, proving the inefficacy of export bans. By 2,000 years ago, grain ships sailed directly from Alexandria to destinations throughout the Roman Empire, and cats are certain to have been onboard to keep the rats in check. Thus introduced, cats would have established colonies in port cities and then fanned out from there. Later, when the Romans expanded their empire, domestic cats traveled with them and became common throughout Europe. Evidence for their spread comes from the German site of Tofting in Schleswig, which dates to between the 4th and 10th centuries, as well as increasing references to cats in art and literature from that period. (Oddly, domestic cats seem to have reached the British Isles before the Romans brought them over—a dispersal that researchers cannot yet explain.)
Meanwhile, on the opposite side of the globe, domestic cats had presumably spread to the Orient almost 2,000 years ago, along well-established trade routes between Greece and Rome and the Far East, reaching China by way of Mesopotamia and arriving in India via land and sea. Then something interesting happened. Because no native wildcats with which the newcomers could interbreed lived in the Far East, the Oriental domestic cats soon began evolving along their own trajectory. Small, isolated groups of Oriental domestics gradually acquired distinctive coat colors and other mutations through a process known as genetic drift, in which traits that are neither beneficial nor maladaptive become fixed in a population.
This drift led to the emergence of the Korat, the Siamese, the Birman and other “natural breeds,” which were described by Thai Buddhist monks in a book called the Tamara Maew (meaning “Cat-Book Poems”) that may date back to 1350. The putative antiquity of these breeds received support from the results of genetic studies announced in 2008, in which Marilyn Menotti-Raymond of the National Cancer Institute and Leslie Lyons of the University of California, Davis, found DNA differences between today’s European and Oriental domestic cat breeds indicative of more than 700 years of independent cat breeding in Asia and Europe.
BREEDING: The Truth about Cats and Dogs.
Unlike dogs, which exhibit a huge range of sizes, shapes and temperaments, house cats are relatively homogeneous, differing mostly in the characteristics of their coats. The reason for the relative lack of variability in cats is simple: humans have long bred dogs to assist with particular tasks, such as hunting or sled pulling, but cats, which lack any inclination for performing most tasks that would be useful to humans, experienced no such selective breeding pressures.

As to when domestic cats reached the Americas, little is known. Christopher Columbus and other seafarers of his day reportedly carried cats with them on transatlantic voyages. And voyagers onboard the Mayflower and residents of Jamestown are said to have brought cats with them to control vermin and to bring good luck. How house cats got to Australia is even murkier, although recent DNA analysis by our team affirms that the Australian cats are of a European type (rather than Oriental) and likely arrived with European explorers in the 1600s, 40,000 years after the aboriginal Australians settled the continent.
BREEDING FOR BEAUTY
Although humans might have played some minor role in the development of the natural breeds in the Orient, concerted efforts to produce novel breeds did not begin until relatively recently. Even the Egyptians, who we know were breeding cats extensively, do not seem to have been selecting for visible traits, probably because distinctive variants had not yet arisen: in their paintings, both wildcats and house cats are depicted as having the same mackerel-tabby coat. Experts believe that most of the modern breeds were developed in the British Isles in the 19th century, based on the writings of English natural history artist Harrison Weir. And in 1871 the first proper fancy cat breeds—breeds created by humans to achieve a particular appearance—were displayed at a cat show held at the Crystal Palace in London (a Persian won, although the Siamese was a sensation).
GENETICS: Saving the Scottish Wildcat.
As the northernmost representative of the European wildcat, the Scottish wildcat lives under environmental and climatic conditions unlike those experienced by any other wildcat. It is also critically endangered, thanks to interbreeding with feral domestic cats. According to the latest rough estimate, perhaps only 400 pure Scottish wildcats survive. But sorting the Scottish feline from hybrids and domestic cats is challenging because they all look so similar. To that end, the authors recently discovered a unique genetic signature of the Scottish wildcat that permits precise identification. This development will facilitate implementation of legal protection of this animal.
Today the Cat Fancier’s Association and the International Cat Association recognize nearly 60 breeds of domestic cat. Just a dozen or so genes account for the differences in coat color, fur length and texture, as well as other, subtler coat characteristics, such as shading and shimmer, among these breeds.
Thanks to the sequencing of the entire genome of an Abyssinian cat named Cinnamon in 2007, geneticists have identified the mutations that produce such traits as tabby patterning, black, white and orange coloring, long hair and many others. Beyond differences in the pelage-related genes, however, the genetic variation between domestic cat breeds is very slight—comparable to that seen between adjacent human populations, such as the French and the Italians.
The wide range of sizes, shapes and temperaments seen in dogs—consider the Chihuahua and Great Dane—is absent in cats. Felines show much less variety because, unlike dogs—which were bred from prehistoric times for such tasks as guarding, hunting and herding— early cats were under no such selective breeding pressures. To enter our homes, they had only to evolve a people-friendly disposition.
So are today’s house cats truly domesticated? Well, yes, certainly they are—but perhaps only just. Although they satisfy the criterion of tolerating people, most domestic cats are feral and do not rely on people to feed them or to find them mates. And whereas other domesticates, like dogs, look quite distinct from their wild ancestors, the average domestic cat largely retains the wild body plan. It does exhibit a few morphological differences, however—namely, slightly shorter legs, a smaller brain and, as Charles Darwin noted, a longer intestine, which may have been an adaptation to scavenging kitchen scraps.
The house cat has not stopped evolving, though—far from it. Armed with artificial insemination and in vitro fertilization technology, cat breeders today are pushing domestic cat genetics into uncharted territory: they are hybridizing house cats with other felid species to create exotic new breeds. The Bengal and the Caracat, for example, resulted from crossing the house cat with the Asian leopard cat and the caracal, respectively. The domestic cat may thus be on the verge of an unprecedented and radical evolution into a multispecies composite whose future can only be imagined.
MORE TO EXPLORE.
The Natural History of the Wild Cats. Andrew Kitchener. Cornell University Press, Comstock Publishing Associates, 1997.
A Natural History of Domesticated Mammals. Second edition. Juliet Clutton-Brock. Cambridge University Press, Natural History Museum, 1999.
The Near Eastern Origin of Cat Domestication. Carlos A. Driscoll et al. in Science, Vol. 317, pages 519–523; 2007.
Patterns of Molecular Genetic Variation among Cat Breeds. Marilyn Menotti-Raymond et al. in Genomics, Vol. 91, No. 1, pages 1–11; 2008.
The British Museum Book of Cats. Juliet Clutton-Brock. The British Museum Press, Natural History Museum, 2012.
Biography
Carlos A. Driscoll is WWF Chair of Conservation Genetics at the Wildlife Institute of India. In 2007 he published the first DNA-based family tree of Felis silvestris, the species to which the domestic cat belongs. He is currently hunting for the individual genes that determine domestic behavior. Juliet Clutton-Brock, a founding member of the International Council for Archaeozoology, is a pioneer in the study of domestication and the early interface between the wild and the domestic. Andrew C. Kitchener is principal curator of vertebrates at National Museums Scotland, where he studies geographical variation and hybridization in mammals and birds. Stephen J. O’Brien is retired chief of the NCI’s Laboratory of Genomic Diversity. He has studied the genetics of cheetahs, lions, orangutans, pandas, humpback whales and HIV.


