Abstract
Vitiligo is a disorder causing skin depigmentation, in which several factors have been proposed for its pathogenesis: Environmental, genetic and biological aspects of melanocytes, even those of the surrounding keratinocytes. However, the lack of understanding of the mechanisms has complicated the task of predicting the development and progression. The present study used microarray analysis to characterize the transcriptional profile of skin from Vitiligo Vulgaris (VV) patients and the identified transcripts were validated using targeted high-throughput RNA sequencing in a broader set of patients. For microarrays, mRNA was taken from 20 skin biopsies of 10 patients with VV (pigmented and depigmented skin biopsy of each), and 5 biopsies of healthy subjects matched for age and sex were used as a control. A signature was identified that contains the expression pattern of 722 genes between depigmented vitiligo skin vs. healthy control, 1,108 between the pigmented skin of vitiligo vs. healthy controls and 1,927 between pigmented skin, depigmented vitiligo and healthy controls (P<0.05; false discovery rate, <0.1). When comparing the pigmented and depigmented skin of patients with vitiligo, which reflects the real difference between both skin types, 5 differentially expressed genes were identified and further validated in 45 additional VV patients by RNA sequencing. This analysis showed significantly higher RNA levels of calpain-3, dopachrome tautomerase, melan-A and tyrosinase-related protein-1 genes. The data revealed that the pigmented skin of vitiligo is already affected at the level of gene expression and that the main differences between pigmented and non-pigmented skin are explained by the expression of genes associated with pigment metabolism.
Keywords: gene expression, vitiligo vulgaris, skin, mexican population
Introduction
Vitiligo is a skin disease characterized by the lack of pigmentation in the skin, it affects approximately 0.1 to 2% of the world population. However, its prevalence varies considerably among populations and ethnic groups: 0.14% in Russia, 1% in USA, and 2.5% in Japan (1), although the highest incidence has been described in Mexico (4%) and India (8.8%) (1,2). The most common clinical variant of vitiligo is vitiligo vulgaris (VV), in which the patient presents asymptomatic, well-circumscribed, milky-white macules involving one or multiple body regions or segments (3). The lack of pigmentation could be attributed to two main causes: a) the absence of melanocytes, which are dendritic cells derived from the neural crest that migrates to the epidermis and then to the hair follicle during embryogenesis, or b) the inability of these cells to produce and store melanin in melanosomes in the process of melanogenesis (4). In this context, the pathological origin of vitiligo has not yet been fully understood. Several hypotheses and theories have been developed to explain these depigmentation processes (5–8).
Although melanocyte is responsible for the pigmentation process in vertebrates (9), the significance of the surrounding environment has been neglected, e.g., keratinocytes (8,10). Currently, it is known that the signaling mechanism that activates the route of melanogenesis is controlled by genes, whose products act as enzymes, structural proteins, transcriptional regulators, transporters, receptors and growth factors related to the melanogenesis process (11). Some of the hormones and products from the hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal axis, and their respective receptors and negative regulators, trigger a nuclear signaling cascade that leads to the activation or repression of tyrosinase, a key enzyme in the pigmentation process, including the final amount of melanin produced (12,13). A major hormone regulator in melanin synthesis is the α-melanocyte-stimulating hormone (α-MSH), produced by pituitary gland, which interacts with a specific cell surface receptor [Melanocortin 1 Receptor (MC1R)] to stimulate melanin synthesis and other differentiated melanocyte functions (11).
Today, knowledge about genes and signaling pathways potentially involved in the development of vitiligo is increasing (14–17); for example, the expression profile of approximately sixteen thousand genes, in an in vitro culture of melanocytes obtained from five subjects with vitiligo, was analyzed using microarrays (17), describing five routes involved in the development of this disease: i) Development of melanocytes; ii) intracellular processing and vesicular trafficking of tyrosinase gene family protein; iii) packaging and transport of melanosomes; iv) cell adhesion; and v) processing and presentation of antigens (17).
In addition, previous reports of gene expression involved in the melanocortin system (14) and melanogenesis signaling pathways (15) showed modified expression levels of proopiomelanocortin (POMC), melanocortin 1 receptor (MC1R), melanocortin 4 receptor (MC4R), tyrosinase-related protein 1 (TYRP1) and dopachrome tautomerase (DCT), among other genes, in tissue affected by vitiligo when compared with healthy tissue samples from patients with vitiligo and normal skin from controls.
To date, there are few studies that involve the complete tissue analysis of patients with vitiligo. The identification of the expression profile of genes potentially involved in the development of the disease will be useful in understanding the molecular mechanism of its development to select potential therapeutic targets for its specific treatment.
In this study, we used microarray analysis to characterize the transcriptional profile of the skin of patients with VV and the identified transcripts were validated by the use of high-throughput RNA sequencing in a larger set of patients to determine the expression pattern that could play a role in the pathogenesis of vitiligo and the clinical types of this disease.
Materials and methods
Selection of participants
Fifty-five Northeastern Mexican patients from the states of Coahuila, Nuevo Leon, San Luis Potosi, Tamaulipas, and Zacatecas were recruited between November 2009 and May 2015 at the Dermatology Department of the University Hospital-UANL, in Monterrey, Nuevo Leon, Mexico. The Ethics and Research Committee of the Faculty of Medicine-UANL approved and registered the protocol and forms of informed consent under the code DE08-008 and DE13-001. After signing their informed consent, the patients were interviewed and evaluated to confirm the diagnosis of VV. Five healthy controls were also included for the Microarray analysis. None of VV patients had received any specific treatment in the previous six months to recruitment. The stage of VV (active AVV/stable SVV) was determined by intervals of time in the manifestation of new depigmented areas (stable vitiligo with lesional stability of >1 year), or enlargement of the already existing ones.
Sample collection and processing
Two skin biopsies of 4 mm were obtained from each patient with vitiligo. The first biopsy was obtained from the central part of the affected skin (called depigmented vitiligo skin) and the second from the healthy areas of the skin of patients with vitiligo (called pigmented vitiligo skin), generally 3 cm from the affected skin. Only a skin biopsy was taken from healthy control subjects (called control skin).
The skin tissue from the biopsies was immediately suspended in 5 volumes of RNA Later Solution (Ambion; Thermo Fisher Scientific, Inc., Waltham, MA, USA) after collection, and stored at 4°C overnight. The next day, the supernatant was remove, and the samples were stored at −80°C until the time for analysis.
Total RNA was isolated from the samples using the RNeasy fibrous tissue mini kit (Qiagen, Inc., Valencia, CA, USA) according to the manufacturer's instructions and quantified using a NanoDrop® ND-8000 spectrophotometer (Thermo Fisher Scientific, Inc., Wilmington, DE, USA) and Qubit® RNA BR Assay kit (Thermo Fisher Scientific, Inc., Waltham, MA, USA). The quality/integrity of the extracted RNA was evaluated by an Experion Automated electrophoresis System (Bio-Rad Laboratories, Inc., Hercules, CA, USA).
Microarray assays
The biopsies taken from depigmented and pigmented skin from ten vitiligo patients (5 AVV and 5 SVV) and a skin biopsy of each of the five healthy controls were analyzed. For each sample, 100 ng of total RNA was amplified, purified, fragmented and labeled using the GeneChip® IVT Express kit, (Affymetrix; Thermo Fisher Scientific, Inc.) according to the manufacturer's instructions. 12.5 µg of fragmented and labeled target were hybridized with Affymetrix GeneChip® Human Gene u133 plus Array (Affymetrix; Thermo Fisher Scientific, Inc.), at 45°C for 16 h, on a GeneChip® Hybridization Oven 640 (Affymetrix; Thermo Fisher Scientific, Inc.), according to the manufacturer's recommendation. The hybridized arrays were washed and stained on a GeneChip® Fluidics Station 450, scanned on a GeneChip® Scanner 3000 7G (Affymetrix; Thermo Fisher Scientific, Inc.), and then CEL image data files were generated for each matrix.
Data analysis
CEL files were processed using the affy package in R (https://cran.r-project.org). Data were pre-processed using RMA and normalized using quantile-normalization (18). t-test and F-tests were used to determine a P-value for differentially expressed genes between groups. P-values were adjusted for multiple tests using the False Discovery Rate (FDR) approach (19). Principal component analysis (PCA) was performed in R.
Annotation and functional analysis
Further information about the genes was obtained from NetAffx™ Analysis Center (http://www.affymetrix.com) and NCBI databases (http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov).
Functional annotation was performed by uploading the resulting gene list onto DAVID (20,21) (Database for Annotation, Visualization and Integrated Discovery, https://david.ncifcrf.gov/tools.jsp). Genes were mapped to KEGG-pathways and scored according to P-values (EASE Score, modified Fisher's exact test) and corrected for multiple testing according to the Benjamini-Hochberg False Discovery Rate correction provided by the DAVID tool.
TruSeq Targeted RNA Expression analysis
Skin biopsies from 45 vitiligo patients (23 AVV and 22 SVV) were analyzed by TruSeq Targeted RNA Expression (Illumina, Inc., San Diego, CA, USA). RNA was obtained and cDNA was prepared with ProtoScript® Reverse Transcriptase (New England Biolabs, Ipswich, MA, USA) according to the manufacturer's instructions. RNA expression analysis was performed on an Illumina MiSeq with MiSeq® Reagent Kit v3 (150 cycle) and TruSeq® Targeted RNA Custom Panel Kit designed to detect the expression profile of the calpain 3 (CAPN3), dopachrome tautomerase (DCT), glycerol-3-phosphate dehydrogenase 1 (GPD1), melan-A (MLANA) and tyrosinase-related protein 1 (TYRP1). RNA-Seq data were analyzed within Base Space (https://basespace.illumina.com) using the tool TruSeq Targeted RNA. Count data were exported and normalized per sample by equalizing the total number of counts (multiplying by the average of the total counts per sample then dividing by the accumulated counts per sample).
Results
Microarray analysis
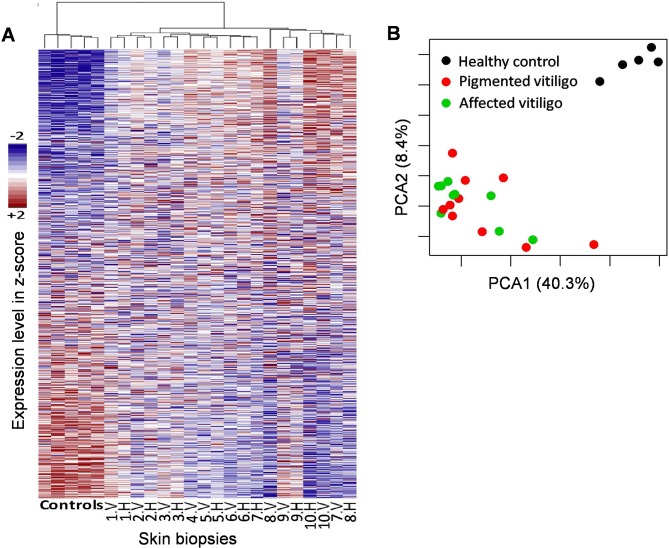
In the analysis performed on vitiligo samples using microarray analysis, we first compared whether the unaffected skin holds a higher similarity to healthy controls than to the affected skin of the patients; one of the pigmented skin samples from a vitiligo patient was discarded from the microarray analyses as it lacked sufficient quality to be used. A PCA and hierarchical clustering shows that the unaffected skin is more similar to vitiligo samples than to healthy controls (Fig. 1), suggesting that pigmented skin in vitiligo patients is already affected regardless of its clinical evidence.
Figure 1.
Overall variability of gene expression profiles. (A) Randomly selected 5,000 genes (rows) ranked by average expression, and samples (columns) grouped by hierarchical clustering. The vitiligo depigmented skin samples are indicated as ‘V’, and ‘P’ corresponding pigmented vitiligo skin from vitiligo patients. (B) First two principal components coordinate. The variability explained by each component is shown in labels. PCA, principal component analysis.
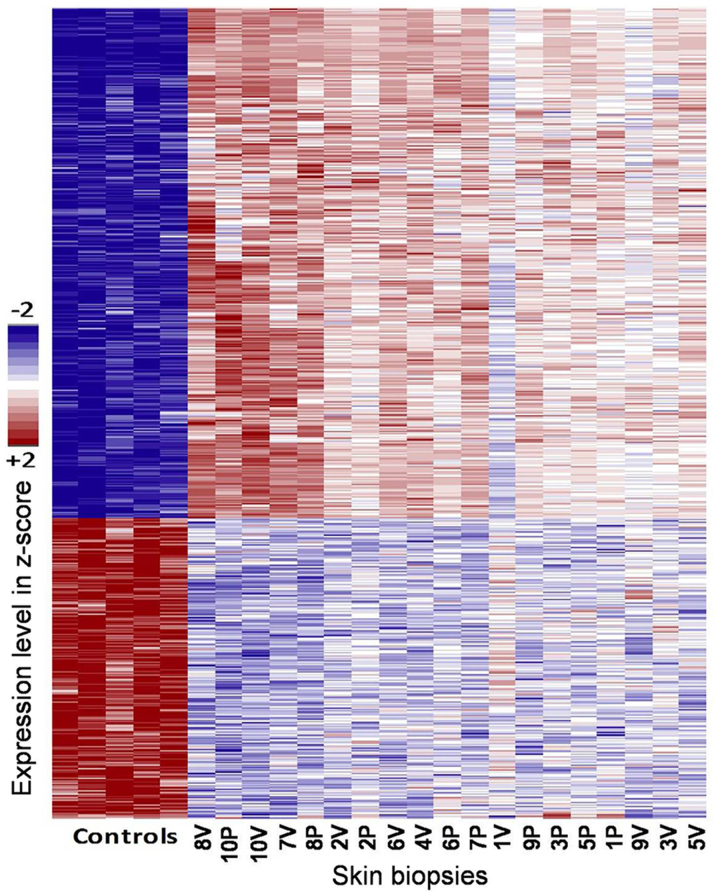
Further analysis comparing the healthy controls vs. skin samples from vitiligo patients (de/pigmented tissue) confirmed the existence of a large number of hits (1,927 probes at FDR <0.1) (Fig. 2).
Figure 2.
Comparison between controls and vitiligo lesions + asymptomatic tissue from vitiligo patients. The differential expressed genes are shown in rows and samples in columns. Blue and red color shows down regulated⁄upregulated genes respectively in Z-score scale. V and P labels denote ‘vitiligo depigmented skin’ and ‘pigmented vitiligo skin’ from vitiligo patients samples respectively. Only genes with FDR <0.1 are shown.
Then we compared different combinations of groups at FDR <0.1, showing that there are differences between the three groups, with altered expression patterns (over and under expressed) when analyzing the more than 25,000 genetic targets present in Affymetrix Gene Chip® Human Gene u133 plus Array. Further, we observed several changes when comparing the healthy controls and patients independent of sample type (pigmented or depigmented skin of patients with vitiligo) that reached the 1,927 probes (Table I). When comparing the pigmented tissue of vitiligo patients against healthy controls, the difference decreases to 1,108 (Table I). Surprisingly, the number decreases further to 722 when comparing the depigmented vitiligo samples to healthy controls (Table I). Finally, the differences are modest when comparing the vitiligo depigmented samples against pigmented asymptomatic tissue, consistent with the initial observation that the asymptomatic tissue is already compromised. Therefore, we focused on these minor differences between vitiligo samples and their healthy counterparts, observing the differences in the important components of pigmentation (Fig. 3). Moreover, we noted that the expression profile of these genes were similar to those from healthy controls. On the other hand, no relationship was found between expression pattern variations, gender, age, or type of vitiligo.
Table I.
Inference of pathways involved in vitiligo, according to the probes that presented altered expression patterns (over and sub expressed).
| Comparison/N | Biological altered pathways |
|---|---|
| Vitiligo depigmented skin vs. vitiligo pigmented skin vs. controls (N=1,927) | Alternative splicing/Splice variant DNA-binding/Nucleic acid binding/Zinc-finger/Transcription factor and transcription regulation/Krueppel-associated box |
| Metal-binding | |
| Phosphoprotein | |
| Krueppel-associated box | |
| Coiled coil | |
| Vitiligo pigmented skin vs. controls (N=1,108) | Alternative splicing/Splice variant |
| Intracellular | |
| Krueppel-associated box | |
| Coiled coil | |
| Vitiligo depigmented skin vs. controls (N=722) | Keratin filament |
| High sulphur keratin-associated protein | |
| Splice variant | |
| Krueppel-associated box | |
| Vitiligo depigmented skin vs. vitiligo pigmented skin (N=6) | Melanosome/melanosome membrane |
| Uncharacterised domain, di-copper centre | |
| Tyrosinase/Tyrosine metabolism | |
| Topological domain: Lumenal, melanosome | |
| Melanin biosynthesis/Melanogenesis |
(N) Altered genetic target from of 25,000 targets present in Affymetrix GeneChip® Human Gene u133 plus Array.
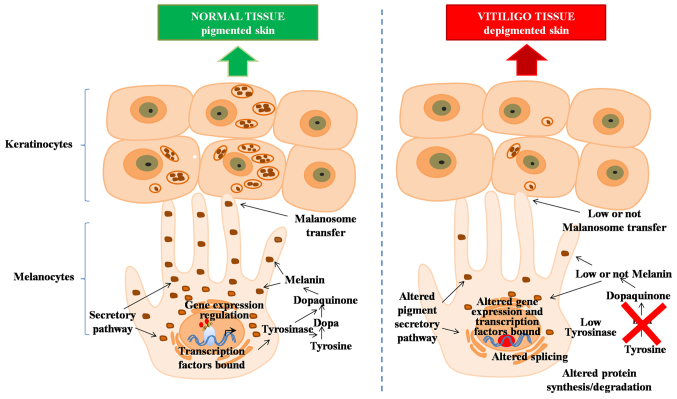
Figure 3.
Biological processes involved in skin pigmentation and development of vitiligo. On the left are presented routes in normal skin pigmentation process; on the right are represented the major routes detected as altered in skin of vitiligo subjects.
Functional Annotation of observed differences
Using the DAVID functional annotation tool, the genes identified in each comparison were grouped into functional categories such as alternative splicing processes, splice variants, DNA and RNA binding domains, transcription, and expression regulation, amongs others (Table I). However, by focusing on the comparisons made between the pigmented and depigmented skin of vitiligo patients it becomes apparent that the mainly compromised genes are involved in the pigmentation process, finding groups of genes responsible for pigment production, granule and melanosome, melanogenesis, tyrosine metabolism, melanin biosynthesis and metabolic process, all of these involved in the development of this disease (Fig. 3).
TruSeq targeted RNA Expression analysis expression validation patterns
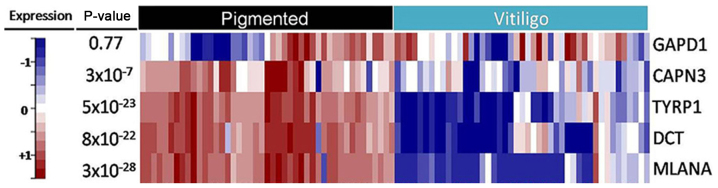
Surprisingly, the main differences between asymptomatic and depigmented skin from vitiligo patients were narrowed to only six probes (Fig. 4), five of which correspond to undrexpressed genes in vitiligo tissue samples, i.e., dopachrome tautomerase (id. 205338_s_at, 205337_at DCT;), melan-A (id. 206427_s_at MLANA), tyrosinase-related protein 1 (id. 205694_at TYRP1), calpain 3 (id. 211890_x_at CAPN3), and glycerol-3-phosphate dehydrogenase 1 (id. 204997_at: GPD1). These genes have been mostly related to melanogenesis, tyrosine metabolism, and glycerophospholipid metabolism. Therefore, these genes were selected for validation by targeted RNA-Sequencing.
Figure 4.
Comparison of six probes of healthy tissue and vitiligo lesion biopsies at FDR <0.1. Blue and red color represent down⁄upregulated genes, respectively.
The expression analysis performed on skin biopsies from 45 additional VV patients confirmed the existence of significant differences in the expression pattern of three genes involved in skin pigmentation: DCT, MLANA and TYRP1. In addition, CAPN3 was also significant, although at a lower level. In addition to microarray analysis, no relationship was identified between the variants in the patterns of expression, gender, age, or type of vitiligo. Moreover, in the case of the GAPD1 gene, no significant difference in the expression pattern between asymptomatic skin and vitiligo lesions was found by NGS when compared to previous observations using microarray analysis (Fig. 5).
Figure 5.
Comparison of asymptomatic and vitiligo lesion biopsies from RNA-Seq analysis for CAPN3, DCT, GAPD1, MLANA and TYRP1 gene. Data show expression profiles obtained from the validation of the 5 genes selected by microarray. Black and light blue color of the top corresponds to pigmented and depigmented vitiligo skin samples from vitiligo patients. Blue and red color is the down regulated⁄upregulated genes.
Discussion
Most vitiligo studies conducted in the Mexican population are focused in demographics and clinical characteristics. To date, the molecular etiology and genetic factors interacting in the development of vitiligo within this population have not been considered.
Up to date, there has been only two expression studies of vitiligo using microarray technology. In the first study, melanocyte culture in vitro from 5 samples of VV patients were analyzed (17); in addition to the small number of samples, it did not reflect the contribution of the skin's environment as it only represents the alterations of a single cellular type (melanocytes); further, the expression pattern could be modified under cell culture conditions. This report found altered an expression pattern of genes involved in the development and function of melanocytes, proposing an autoimmune response as a secondary event caused by the abnormal function of melanocytes (17). In our study, we also observed some similarities in the expression pattern of genes involved in pigment synthesis, melanosome, granule pigment, cytoplasmic vesicles (possibly melanosomas), plus redox reaction processes related to diverse functions, including cell-cell recognition, cell-surface receptors, muscle structure, and the immune system. However, our results reflect the expression profile of the whole skin.
In a second report, an expression study using the Smyth line from chicken, an avian model for human autoimmune vitiligo, the microarray analysis results support the multifactorial etiology of vitiligo, where inflammatory/innate immune activity and oxidative stress, and the adaptive immune response play a predominant role in melanocyte loss. The microarray analysis results provided comprehensive information at transcriptome level, supporting the multifactorial etiology of vitiligo, where, along with the apparent inflammatory/innate immune activity and oxidative stress, the adaptive immune response plays a predominant role in melanocyte loss (22).
In the biological context of the skin, the melanocyte represents less than ten percent of epidermal cells (23,24). The functional clustering analysis made using the DAVID database points towards the involvement of an altered functional group composed by genes involved in diverse biological processes, such as transcription and transcription regulation, transcriptional repression, alternative splicing, and keratin filament. The observation that melanocytes are the main cell type affected in vitiligo does not rule out the participation of other cellular components of the skin in the development of this disease, as supported by the major affected pathways of pigment synthesis, packaging and transport of pigment, when the depigmented vitiligo tissue was compared with the pigmented skin of vitiligo. For this reason, and considering that keratinocytes are the predominant cell type in this tissue (25), their role could involve an important function in skin pigmentation (10,26). Even when the differences in expression patterns between a) pigmented skin and b) affected skin vs. control skin the same metabolic routes are affected, in the first case a greater number of genes are involved (Table I), these could be explained by compensatory mechanisms (14,27) in which the skin of the vitiligo patient tends to stimulate pigmentation by regulating the expression factors involved in pigmentation, increasing or decreasing their expression to maintain skin homeostasis.
After analyzing the genes showing a different expression pattern, a group of 5 genes, involved in the melanogenic routes, intracellular cysteine proteases, and oxidative stress, were selected for validation by TruSeq Targeted RNA Expression analysis. The validation assays showed a differential expression tendency in four genes: CAPN3, DCT, MLANA and TYRP1. However, GPD1 was not found differentially expressed by NGS. These results are consistent with Regazzetti et al (28), whom validated a group of genes in skin biopsies from patients with vitiligo, finding low expression levels of MLANA, DCT, and TYRP1 in vitiligo skin lesions when compared to skin around the injured and uninjured (pigmented/asymptomatic) tissue.
The CAPN3 gene was under expressed in the skin of patients with vitiligo; previously, Stromberg et al reported that this gene was up regulated in melanocyte cultures obtained from vitiligo lesions (17). This gene encodes a large subunit of neutral calpain of protease 3 activated by muscle calcium, a heterodimer consisting of a large subunit and a small subunit is a major intracellular protease that is ubiquitously expressed in human tissues and other and other tissue-specific isoforms. Its function on the skin is not clear, but it has been observed that CAPN3 variants can play a pro-apoptotic role in melanoma cells and its down regulation, as observed in highly aggressive melanomas, could contribute to their progression (29). In melanocytic cells, CAPN3 expression may be regulated by MITF (30) which regulates a broad variety of genes whose functions range from pigment production (such as DCT, MC1R, MLANA, TYR and TYP1) to the cell-cycle regulation, migration and survival; moreover, MITF-mediated up regulation of CAPN3 has been reported in melanoma (30).
The GPD1 gene encodes a member of the NAD-dependent glycerol-3-phosphate dehydrogenase protein family, playing a critical role in carbohydrate and lipid metabolism (31). Along with GPD2, the mitochondrial isoform, it constitutes a glycerol phosphate shuttle that facilitates the transfer of reducing equivalents from the cytosol to the mitochondria, playing a crucial role in osmoregulation and redox balance (32). In our study, the microarray analysis showed the under expression of this gene in tissue from patients with vitiligo lesions. As a result of expression profile validation, made by RNA-Seq in a number of samples, no significant differences were observed between the expression profiles of affected pigmented skin in vitiligo patients. However, we observed a higher expression in some of the samples that possibly participate in the oxidative stress response experienced by the skin cells of these patients, a mechanism that has been described in this disease. So far, the participation of this gene in vitiligo has not been explored.
In addition, NGS provides a better approach to gene expression profile analysis, as this technology enables high resolution research for all of the RNA present in a sample, including mRNA sequence and abundance (33). Its usefulness has been compared with microarray technology and Real-Time PCR in the analysis of expression profiles (34–36); therefore, it has been used in transcriptome analysis in clinical research (36–39).
The analysis of expression by directed sequencing of RNA (RNAseq) has been helpful in the efficient evaluation of expression profiles of multiple genes in human pathological and non-pathological conditions (40–43). In particular, RNAseq using NGS, not only shows the expression levels of a transcript, but the presence of isoforms in the samples analyzed (44). In patients affected by dermatological diseases such as psoriasis, systemic lupus erythematosus (45–47), and vitiligo, these tools are an excellent alternative inidentifying modified gene expression patterns in key routes of skin homeostasis, pigmentation, and cell survival at a low cost and reduced time in comparison to RT-qPCR.
In conclusion, we found alterations in the expression pattern of depigmented vitiligo lesions when compared to pigmented asymptomatic skin of vitiligo patients and against healthy control samples. These results reflect that even the clinically unaffected (pigmented) skin shows an impaired melanogesis process in a patient with vitiligo; the observed changes are related to processes regulating gene expression and splicing that eventually will end up in skin depigmentation by altering the levels of proteins involved in this process. Up regulated expression profiles detected by microarray analysis for CAPN3, DCT, MLAN-A and TYRP1 in VV patients was validated using NGS TruSeq Targeted RNA Expression analysis, and whose altered functions on pigment production, and possibly in melanocyte cell survival, affect skin pigmentation, thus suggesting that these tools are an excellent alternative in identifying the expression pattern of genes involved in the development of this disease. On the other hand, we did not find any differences in the gene expression profiles of active or stable VV.
Acknowledgements
Thanks to all participants and collaborators in this study. Thanks, also, to the personnel of the Department of Dermatology of the University's Hospital and the Molecular Biology, Genomics and Sequencing Unit Center for Research and Development in Health Sciences, UANL. We appreciate the kindness and help of the personnel in the Unit of Molecular Diagnosis-Department of Molecular Medicine, Faculty of Medicine-UANL, for their support during the development of this study. The participating students were supported by the CONACyT (grant no. 220719). The authors also wish to thank Dr Daniel Díaz, Ph.D. for his kind assistance in proofreading this manuscript.
References
- 1.Steiner D, Bedin V, Moraes MB, Tadeu R, Steiner VT. Vitiligo. An Bras Dermatol. 2004;79:335–351. doi: 10.1590/S0365-05962004000300010. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Parsad D, Dogra S, Kanwar AJ. Quality of life in patients with vitiligo. Health Qual Life Outcomes. 2003;1:58. doi: 10.1186/1477-7525-1-58. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Ezzedine K, Lim HW, Suzuki T, Katayama I, Hamzavi I, Lan CC, Goh BK, Anbar T, Silva de Castro C, Lee AY, et al. Revised classification/nomenclature of vitiligo and related issues: The vitiligo global issues consensus conference. Pigment Cell Melanoma Res. 2012;25:E1–E13. doi: 10.1111/j.1755-148X.2012.00997.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Sehgal VN, Srivastava G. Vitiligo: Compendium of clinico-epidemiological features. Indian J Dermatol Venereol Leprol. 2007;73:149–156. doi: 10.4103/0378-6323.32708. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Spritz RA. The genetics of generalized vitiligo and associated autoimmune diseases. J Dermatol Sci. 2006;41:3–10. doi: 10.1016/j.jdermsci.2005.10.001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Spritz RA. The genetics of generalized vitiligo and associated autoimmune diseases. Pigment Cell Res. 2007;20:271–278. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0749.2007.00384.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Tazi-Ahnini R, McDonagh AJ, Wengraf DA, Lovewell TR, Vasilopoulos Y, Messenger AG, Cork MJ, Gawkrodger DJ. The autoimmune regulator gene (AIRE) is strongly associated with vitiligo. Br J Dermatol. 2008;159:591–596. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2133.2008.08718.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Mohammed GF, Gomaa AH, Al-Dhubaibi MS. Highlights in pathogenesis of vitiligo. World J Clin Cases. 2015;3:221–230. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v3.i3.221. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.McCurdy HM. Enzyme localization during melanogenesis. J Cell Biol. 1969;43:220–228. doi: 10.1083/jcb.43.2.220. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Lee AY. Role of keratinocytes in the development of vitiligo. Ann Dermatol. 2012;24:115–125. doi: 10.5021/ad.2012.24.2.115. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Slominski A, Ermak G, Wortsman J. Modification of melanogenesis in cultured human melanoma cells. In Vitro Cell Dev Biol Anim. 1999;35:564–565. doi: 10.1007/s11626-999-0093-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Gillbro JM, Marles LK, Hibberts NA, Schallreuter KU. Autocrine catecholamine biosynthesis and the beta-adrenoceptor signal promote pigmentation in human epidermal melanocytes. J Invest Dermatol. 2004;123:346–353. doi: 10.1111/j.0022-202X.2004.23210.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Rousseau K, Kauser S, Pritchard LE, Warhurst A, Oliver RL, Slominski A, Wei ET, Thody AJ, Tobin DJ, White A. Proopiomelanocortin (POMC), the ACTH/melanocortin precursor, is secreted by human epidermal keratinocytes and melanocytes and stimulates melanogenesis. FASEB J. 2007;21:1844–1856. doi: 10.1096/fj.06-7398com. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Kingo K, Aunin E, Karelson M, Philips MA, Rätsep R, Silm H, Vasar E, Soomets U, Kõks S. Gene expression analysis of melanocortin system in vitiligo. J Dermatol Sci. 2007;48:113–122. doi: 10.1016/j.jdermsci.2007.06.004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Kingo K, Aunin E, Karelson M, Rätsep R, Silm H, Vasar E, Kõks S. Expressional changes in the intracellular melanogenesis pathways and their possible role in the pathogenesis of vitiligo. J Dermatol Sci. 2008;52:39–46. doi: 10.1016/j.jdermsci.2008.03.013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Nagui NA, Mahmoud SB, Abdel Hay RM, Hassieb MM, Rashed LA. Assessment of gene expression levels of proopiomelanocortin (POMC) and melanocortin-1 receptor (MC1R) in vitiligo. Australas J Dermatol. 2017;58:e36–e39. doi: 10.1111/ajd.12408. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Stromberg S, Bjorklund MG, Asplund A, Rimini R, Lundeberg J, Nilsson P, Pontén F, Olsson MJ. Transcriptional profiling of melanocytes from patients with vitiligo vulgaris. Pigment Cell Melanoma Res. 2008;21:162–171. doi: 10.1111/j.1755-148X.2007.00429.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Irizarry RA, Hobbs B, Collin F, Beazer-Barclay YD, Antonellis KJ, Scherf U, Speed TP. Exploration, normalization and summaries of high density oligonucleotide array probe level data. Biostatistics. 2003;4:249–264. doi: 10.1093/biostatistics/4.2.249. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Benjamini Y, Hochberg Y. Controlling the false discovery rate: A practical and powerful approach to multiple testing. J Royal Stat Soc. 1995;57:289–300. [Google Scholar]
- 20.Huang da W, Sherman BT, Lempicki RA. Systematic and integrative analysis of large gene lists using DAVID bioinformatics resources. Nat Protoc. 2009;4:44–57. doi: 10.1038/nprot.2008.211. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Huang da W, Sherman BT, Lempicki RA. Bioinformatics enrichment tools: Paths toward the comprehensive functional analysis of large gene lists. Nucleic Acids Res. 2009;37:1–13. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkn923. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Shi F, Kong BW, Song JJ, Lee JY, Dienglewicz RL, Erf GF. Understanding mechanisms of vitiligo development in Smyth line of chickens by transcriptomic microarray analysis of evolving autoimmune lesions. BMC Immunol. 2012;13:18. doi: 10.1186/1471-2172-13-18. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Jimbow K, Quevedo WC, Jr, Fitzpatrick TB, Szabo G. Some aspects of melanin biology: 1950–1975. J Invest Dermatol. 1976;67:72–89. doi: 10.1111/1523-1747.ep12512500. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Feinmesser M, Tsabari C, Fichman S, Hodak E, Sulkes J, Okon E. Differential expression of proliferation- and apoptosis-related markers in lentigo maligna and solar keratosis keratinocytes. Am J Dermatopathol. 2003;25:300–307. doi: 10.1097/00000372-200308000-00004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Baroni A, Buommino E, De Gregorio V, Ruocco E, Ruocco V, Wolf R. Structure and function of the epidermis related to barrier properties. Clin Dermatol. 2012;30:257–262. doi: 10.1016/j.clindermatol.2011.08.007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Yoshida Y, Hachiya A, Sriwiriyanont P, Ohuchi A, Kitahara T, Takema Y, Visscher MO, Boissy RE. Functional analysis of keratinocytes in skin color using a human skin substitute model composed of cells derived from different skin pigmentation types. FASEB J. 2007;21:2829–2839. doi: 10.1096/fj.06-6845com. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Moretti S, Fabbri P, Baroni G, Berti S, Bani D, Berti E, Nassini R, Lotti T, Massi D. Keratinocyte dysfunction in vitiligo epidermis: Cytokine microenvironment and correlation to keratinocyte apoptosis. Histol Histopathol. 2009;24:849–857. doi: 10.14670/HH-24.849. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Regazzetti C, Joly F, Marty C, Rivier M, Mehul B, Reiniche P, Mounier C, Rival Y, Piwnica D, Cavalié M, et al. Transcriptional analysis of vitiligo skin reveals the alteration of wnt pathway: A promising target for repigmenting vitiligo patients. J Invest Dermatol. 2015;135:3105–3114. doi: 10.1038/jid.2015.335. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Moretti D, Del Bello B, Cosci E, Biagioli M, Miracco C, Maellaro E. Novel variants of muscle calpain 3 identified in human melanoma cells: Cisplatin-induced changes in vitro and differential expression in melanocytic lesions. Carcinogenesis. 2009;30:960–967. doi: 10.1093/carcin/bgp098. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Hoek KS, Schlegel NC, Eichhoff OM, Widmer DS, Praetorius C, Einarsson SO, Valgeirsdottir S, Bergsteinsdottir K, Schepsky A, Dummer R, Steingrimsson E. Novel MITF targets identified using a two-step DNA microarray strategy. Pigment Cell Melanoma Res. 2008;21:665–676. doi: 10.1111/j.1755-148X.2008.00505.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Guindalini C, Lee KS, Andersen ML, Santos-Silva R, Bittencourt LR, Tufik S. The influence of obstructive sleep apnea on the expression of glycerol-3-phosphate dehydrogenase 1 gene. Exp Biol Med (Maywood) 2010;235:52–56. doi: 10.1258/ebm.2009.009150. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Hubmann G, Guillouet S, Nevoigt E. Gpd1 and Gpd2 fine-tuning for sustainable reduction of glycerol formation in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Appl Environ Microbiol. 2011;77:5857–5867. doi: 10.1128/AEM.05338-11. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Finotello F, Di Camillo B. Measuring differential gene expression with RNA-seq: Challenges and strategies for data analysis. Brief Funct Genomics. 2015;14:130–142. doi: 10.1093/bfgp/elu035. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Hurd PJ, Nelson CJ. Advantages of next-generation sequencing versus the microarray in epigenetic research. Brief Funct Genomic Proteomic. 2009;8:174–183. doi: 10.1093/bfgp/elp013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Git A, Dvinge H, Salmon-Divon M, Osborne M, Kutter C, Hadfield J, Bertone P, Caldas C. Systematic comparison of microarray profiling, real-time PCR and next-generation sequencing technologies for measuring differential microRNA expression. RNA. 2010;16:991–1006. doi: 10.1261/rna.1947110. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Kloster MB, Bilgrau AE, Rodrigo-Domingo M, Bergkvist KS, Schmitz A, Sønderkær M, Bødker JS, Falgreen S, Nyegaard M, Johnsen HE, et al. A model system for assessing and comparing the ability of exon microarray and tag sequencing to detect genes specific for malignant B-cells. BMC Genomics. 2012;13:596. doi: 10.1186/1471-2164-13-596. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Mastrokolias A, den Dunnen JT, van Ommen GB, 't Hoen PA, van Roon-Mom WM. Increased sensitivity of next generation sequencing-based expression profiling after globin reduction in human blood RNA. BMC Genomics. 2012;13:28. doi: 10.1186/1471-2164-13-28. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Gonorazky H, Liang M, Cummings B, Lek M, Micallef J, Hawkins C, Basran R, Cohn R, Wilson MD, MacArthur D, Marshall CR, et al. RNAseq analysis for the diagnosis of muscular dystrophy. Ann Clin Transl Neurol. 2015;3:55–60. doi: 10.1002/acn3.267. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Lesluyes T, Pérot G, Largeau MR, Brulard C, Lagarde P, Dapremont V, Lucchesi C, Neuville A, Terrier P, Vince-Ranchère D, et al. RNA sequencing validation of the Complexity INdex in SARComas prognostic signature. Eur J Cancer. 2016;57:104–111. doi: 10.1016/j.ejca.2015.12.027. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Chandrasekharappa SC, Lach FP, Kimble DC, Kamat A, Teer JK, Donovan FX, Flynn E, Sen SK, Thongthip S, Sanborn E, et al. Massively parallel sequencing, aCGH and RNA-Seq technologies provide a comprehensive molecular diagnosis of Fanconi anemia. Blood. 2013;121:e138–e148. doi: 10.1182/blood-2012-12-474585. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.O'Hurley G, Busch C, Fagerberg L, Hallström BM, Stadler C, Tolf A, Lundberg E, Schwenk JM, Jirström K, Bjartell A, et al. Analysis of the human prostate-specific proteome defined by transcriptomics and antibody-based profiling identifies TMEM79 and ACOXL as two putative, diagnostic markers in prostate cancer. PLoS One. 2015;10:e0133449. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0133449. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Endsley MP, Moyle-Heyrman G, Karthikeyan S, Lantvit DD, Davis DA, Wei JJ, Burdette JE. Spontaneous transformation of murine oviductal epithelial cells: A model system to investigate the onset of fallopian-derived tumors. Front Oncol. 2015;5:154. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2015.00154. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Katayama S, Skoog T, Jouhilahti EM, Siitonen HA, Nuutila K, Tervaniemi MH, Vuola J, Johnsson A, Lönnerberg P, Linnarsson S, et al. Gene expression analysis of skin grafts and cultured keratinocytes using synthetic RNA normalization reveals insights into differentiation and growth control. BMC Genomics. 2015;16:476. doi: 10.1186/s12864-015-1671-5. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44.Wang Z, Gerstein M, Snyder M. RNA-Seq: A revolutionary tool for transcriptomics. Nat Rev Genet. 2009;10:57–63. doi: 10.1038/nrg2484. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45.Swindell WR, Remmer HA, Sarkar MK, Xing X, Barnes DH, Wolterink L, Voorhees JJ, Nair RP, Johnston A, Elder JT, Gudjonsson JE. Proteogenomic analysis of psoriasis reveals discordant and concordant changes in mRNA and protein abundance. Genome Med. 2015;7:86. doi: 10.1186/s13073-015-0208-5. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46.Stone RC, Du P, Feng D, Dhawan K, Rönnblom L, Eloranta ML, Donnelly R, Barnes BJ. RNA-Seq for enrichment and analysis of IRF5 transcript expression in SLE. PLoS One. 2013;8:e54487. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0054487. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47.Shi L, Zhang Z, Yu AM, Wang W, Wei Z, Akhter E, Maurer K, Costa Reis P, Song L, Petri M, Sullivan KE. The SLE transcriptome exhibits evidence of chronic endotoxin exposure and has widespread dysregulation of non-coding and coding RNAs. PLoS One. 2014;9:e93846. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0093846. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]