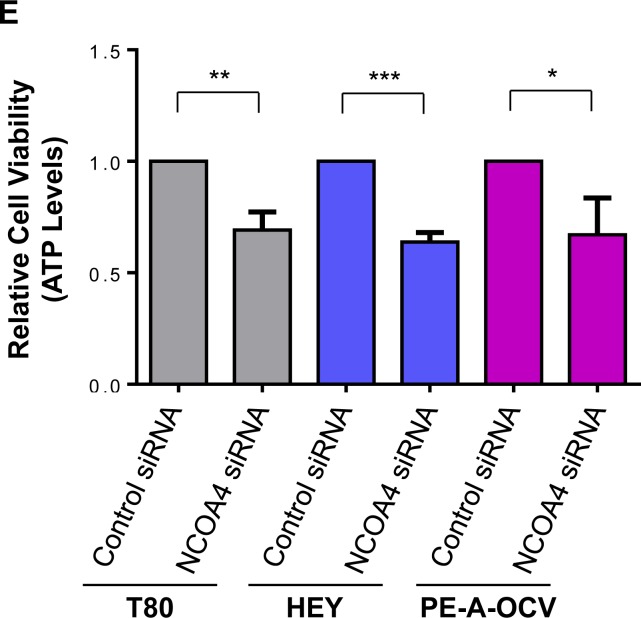
Figure 3. NCOA4 knockdown reduces cellular viability in T80, HEY, and PE-A-OCV cells.
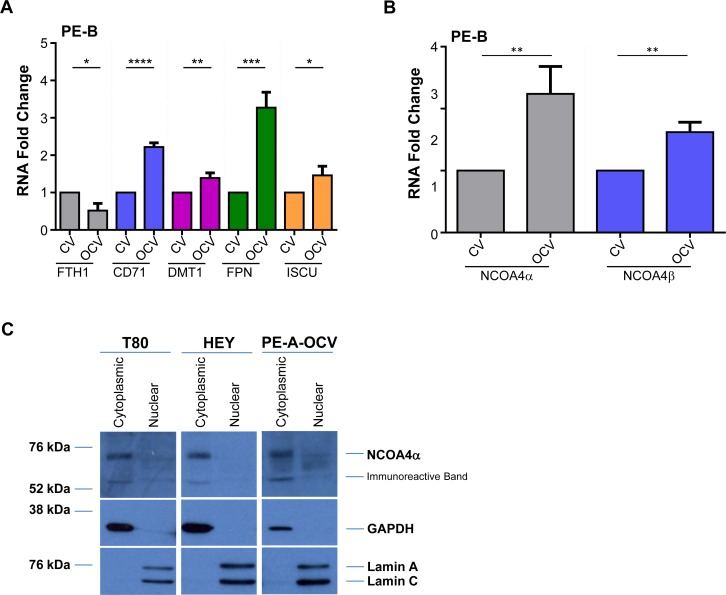
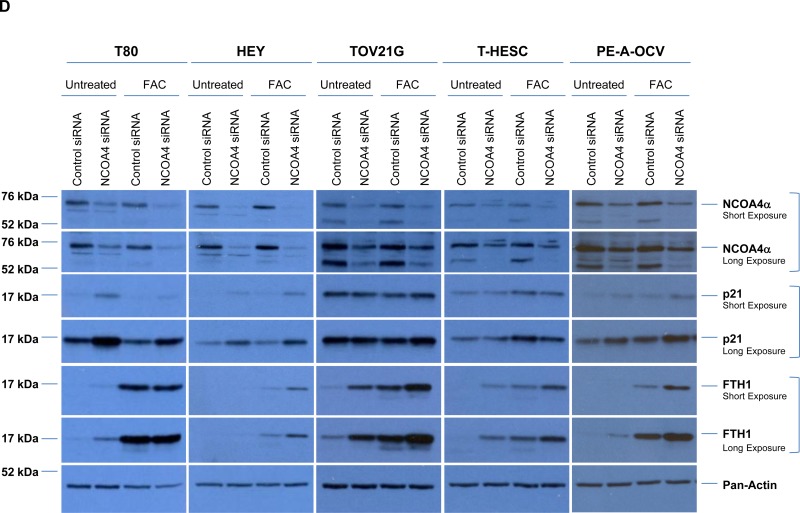
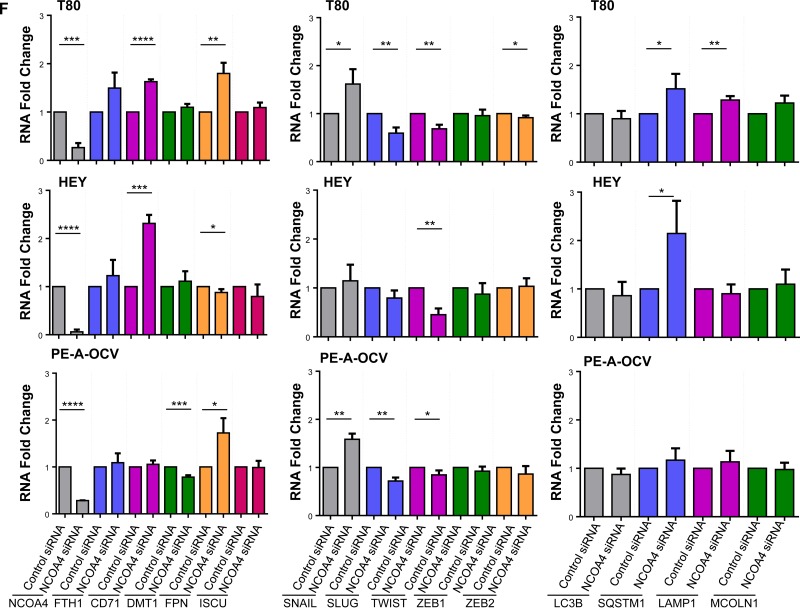
Transcript levels for (A) genes in the iron pathway including (B) NCOA4α and NCOA4β were assessed via real-time PCR using RNA extracted from the second batch of PE-B-CV and PE-B-OCV cells. Three independent experiments were performed. (C) Western analyses of cytoplasmic and nuclear fractions from T80, HEY, and the first batch of PE-A-OCV cells were performed using the indicated antibodies. Data shown is representative of three independent experiments. (D) Cell lysates from NCOA4 siRNA treated T80, HEY, TOV21G, T-HESC, and the second batch of PE-A-OCV (treated for 18 hours with 250 μM FAC) were analyzed by western blotting using the indicated antibodies. Data shown are representative of three independent experiments. (E) Cellular viability (via ATP measurements) was assessed upon NCOA4 knockdown in T80, HEY, and the second batch of PE-A-OCV (2nd batch) cells. Three independent experiments were performed. (F) Using RNA isolated from T80, HEY and the second batch of PE-A-OCV treated with NCOA4 siRNA, transcript levels for genes in the iron, EMT, lysosome/autophagy pathways were measured via real-time PCR. Three independent experiments were performed.