Abstract
Dicistroviridae is a family of small non-enveloped viruses with monopartite, linear, positive-sense RNA genomes of approximately 8–10 kb. Viruses of all classified species infect arthropod hosts, with some having devastating economic consequences, such as acute bee paralysis virus in domesticated honeybees and taura syndrome virus in shrimp farming. Conversely, the host specificity and other desirable traits exhibited by several members of this group make them potential natural enemies for intentional use against arthropod pests, such as triatoma virus against triatomine bugs that vector Chagas disease. This is a summary of the International Committee on Taxonomy of Viruses (ICTV) Report on the taxonomy of the Dicistroviridae which is available at www.ictv.global/report/dicistroviridae.
Keywords: Dicistroviridae, ICTV Report, taxonomy
Virion
Virions are roughly spherical, with a particle diameter of approximately 30 nm and no envelope (Table 1, Fig. 1). The virions exhibit icosahedral, pseudo-T=3 symmetry and are composed of 60 protomers, each comprising a single molecule of VP1, VP2 and VP3. A smaller protein, VP4, is also present inside the virion and in contact with the genome [1].
Table 1. Characteristics of the family Dicistroviridae.
| Typical member: | cricket paralysis virus (AF218039), species Cricket paralysis virus, genus Cripavirus |
|---|---|
| Virion | Non-enveloped, 30 nm-diameter virions |
| Genome | 8–10 kb of positive-sense, non-segmented RNA |
| Replication | Cytoplasmic within viral replication complexes formed from a variety of host cellular membranes |
| Translation | Directly from genomic RNA, initiated at IRES elements in the 5′ UTR and IGR |
| Host range | Arthropoda |
| Taxonomy | Member of the order Picornavirales. Includes the genera Aparavirus, Cripavirus and Triatovirus, each containing several species |
Fig. 1.
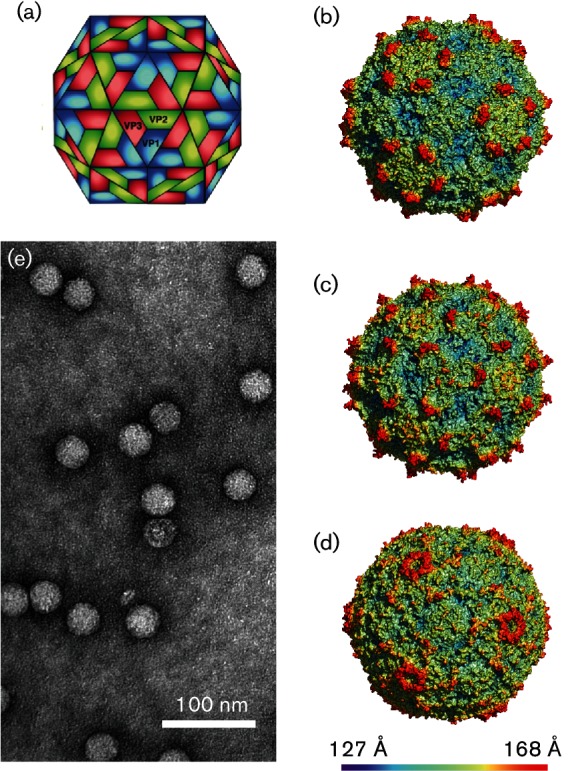
(a) Diagram illustrating the packing of dicistrovirus surface proteins VP1, VP2 and VP3. Renderings (courtesy of A. E. Mechaly) of (b) triatoma virus, (c) Israeli acute bee paralysis virus and (d) cricket paralysis virus (colour scale indicates distance from the particle centre). (e) Negative contrast electron micrograph of purified triatoma virus (courtesy of G. A. Marti).
Genome
The RNA genome is monopartite and contains two main non-overlapping ORFs that are flanked by UTRs and separated by an intergenic region (IGR) (Fig. 2). The 5′-proximal and 3′-proximal ORFs encode non-structural and structural protein precursors, respectively. Components of the non-structural polyprotein include an RNA-dependent RNA polymerase, cysteine protease, RNA helicase and one or more copies of a VPg protein. VPg is covalently linked to the 5′ end of the genome.
Fig. 2.
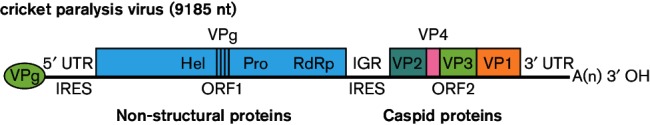
Genome structure of cricket paralysis virus. The RNA genome contains two non-overlapping ORFs separated by an IGR. The 5′ proximal ORF encodes the non-structural proteins: RNA helicase (Hel), cysteine protease (Pro) and RNA-dependent RNA polymerase (RdRp). The structural proteins are encoded by the 3′-proximal ORF.
Replication
Replication occurs exclusively in the cytoplasm of infected cells. Cap-independent translation proceeds directly from two distinct internal ribosomal entry site (IRES) elements located within the 5′-UTR and the IGR. These IRES elements permit production of non-structural proteins early in the infection process before host translation mechanisms are inhibited, and excess molar quantities of structural proteins when capsid proteins are required later. Unusually, the IGR IRES directs translation initiation at a 3′-adjacent non-AUG codon and in the absence of all canonical initiation factors. The conserved three-dimensional structure is crucial to the IGR IRES function [2]. Pseudo-knot and stem-loop structures in the IGR IRES are highly conserved across all members of the family and facilitate interactions with the ribosome [3]. The 5′-UTR IRES is not obviously conserved in sequence or structure across the group. Translation activity of the IGR IRES is comparatively greater than that of the 5′-UTR IRES at late time points [4].
Taxonomy
The family Dicistroviridae is comprised of three genera: Aparavirus, Cripavirus and Triatovirus. Demarcation of the genera is based on phylogenetic divergence and unique characteristics exhibited by the internal ribosomal entry site [2]. Dicistrovirus infections vary considerably in virulence and pathogenicity; the severity of disease ranges from inapparent to lethal. Transmission via ingestion and the alimentary canal feature prominently in dicistrovirus infection acquisition and transmission. Most of the dicistroviruses exhibit a tissue tropism toward some part of the alimentary canal, often replicating in epithelial cells of the gut and subsequently shedding virus particles into the gut lumen where virus accumulates in the faeces and serves as inoculum [5]. Nervous tissue, fat body, epidermal cells and gonads may also support replication of dicistroviruses.
Resources
Full ICTV Online (10th) Report: www.ictv.global/report/dicistroviridae.
Funding information
Production of this summary, the online chapter and associated resources were funded by a grant from the Wellcome Trust (WT108418AIA).
Acknowledgements
Members of the ICTV Report Consortium are Elliot J. Lefkowitz, Andrew J. Davison, Stuart G. Siddell, Peter Simmonds, Michael J. Adams, Donald B. Smith, Richard J. Orton and Nick J. Knowles.
Conflicts of interest
The authors declare that there are no conflicts of interest.
References
- 1.Sánchez-Eugenia R, Goikolea J, Gil-Cartón D, Sánchez-Magraner L, Guérin DM. Triatoma virus recombinant VP4 protein induces membrane permeability through dynamic pores. J Virol. 2015;89:4645–4654. doi: 10.1128/JVI.00011-15. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Jan E. Divergent IRES elements in invertebrates. Virus Res. 2006;119:16–28. doi: 10.1016/j.virusres.2005.10.011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Nakashima N, Uchiumi T. Functional analysis of structural motifs in dicistroviruses. Virus Res. 2009;139:137–147. doi: 10.1016/j.virusres.2008.06.006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Khong A, Bonderoff JM, Spriggs RV, Tammpere E, Kerr CH, et al. Temporal regulation of distinct internal ribosome entry sites of the Dicistroviridae cricket paralysis virus. Viruses. 2016;8:e25. doi: 10.3390/v8010025. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Meeus I, De Miranda JR, De Graaf DC, Wäckers F, Smagghe G. Effect of oral infection with Kashmir bee virus and Israeli acute paralysis virus on bumblebee (Bombus terrestris) reproductive success. J Invertebr Pathol. 2014;121:64–69. doi: 10.1016/j.jip.2014.06.011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


