Abstract
Objectives
The space available within the female pelvis is determined by the morphology of all bony components constituting the pelvic skeleton. Although several studies have investigated the impact of hip-bone structural variations in on parturition, the potential effects of commonly occurring lumbosacral transitional vertebrae (LSTV) variations have been underreported. This descriptive morphometric study reports dimensions of the female sacrum associated LSTV variations and suggests their probable mechanistic effects on normal labor.
Methods
One hundred and twelve female osteological sacral specimens with LSTV were examined for the type of transitional anomaly. Position, height, and surface areas of the auricular surfaces, interauricular distances, sacral heights, S1 body width and upper surface areas, and articulating areas of S1 facets were measured and compared with data from non-transitional samples.
Results
Female LSTV predominantly presented as accessory L5-S1 articulations (unilateral and bilateral) and degrees of lumbarization (separation of the first sacral segment). Since some of these alterations were found to be significantly associated with changes in sacral size, these features, in conjunction with cranial shift of the auricular surfaces, may be associated with overall in dorsal pelvic dimensions.
Conclusions
Structural alterations identified in female LSTV sacrum may change dorsal pelvic dimensions and thus, the availability of dorsal pelvic space, potentially altering the biomechanics of normal labor.
Keywords: Facets, Pelvis, Parturition, Lumbosacral Vertebrae
Introduction
Lumbosacral transitional vertebrae (LSTV) affect around 12% of the global population and are most commonly seen in females.1-3 The spectrum of these transitions include: (a) accessory L5-S1 articulations between the transverse elements, (b) unilateral/bilateral L5-S1 fusions (sacralization), or (c) partial/complete separation between S1-S2 elements (lumbarization).4,5 Such variations alter the overall size of the sacrum, the position and surface areas of the auricular surface, and the orientation of superior articular facets of the sacrum.4,6,7
Dimensions of the pelvic cavity play a major role in the progression and outcome of parturition.8 The space available within the pelvic cavity is clinically assessed by routine obstetric measurements obtained for linear dimensions across the planes mostly at the pelvic inlet, mid-pelvic cavity, and pelvic outlet.9-11 At all these levels, linear dimensions are measured in the anteroposterior, transverse, and oblique planes.8-10 Although a combination of dimensional assessments help to predict the ease of passage of the fetal head during parturition, the ease of engagement of the fetal head is generally determined by the position and projection of the sacral promontory into the dorsal pelvic inlet. This factor determines the availability of the conjugate lengths at the pelvic inlet. Variability of the position of the promontory (and the craniocaudal dimension of the dorsal pelvis) can be associated with variability of the number of sacral segments as seen in LSTV anomalies.
Evidence suggesting a cause-effect relationship between obstructed labor and specific spinal and pelvic deformities is available in the literature.8,11-13 However, potential effects of anatomical alterations in the female pelvis resulting from LSTV (and associated variabilities in the position of the sacral auricular surfaces) on labor have scarcely been reported. Archeological studies have, however, documented cases of possible fetomaternal fatalities attributed to maternal LSTV.7,14,15 Specifically, in context of mid-labor forward sagittal tilting (nutation) of the sacrum facilitating flexion-rotation of the fetal head in the dorsal pelvic space, and thus the role of sacral dimensions, are not yet clearly elucidated.9,16
This study investigates the implications of LSTV on the dorsal pelvic dimensions in females and discusses potential complications of such anomalies in parturition, topics that few studies have objectively discussed.17-19
Methods
A total of 112 female sacra catalogued in large cohort of osteological sacral samples were studied for LSTV structural anomalies. The samples selected for measurements represent population samples obtained from dried adult Indian female cadavers donated to medical institutions across central and southern regions of India. Samples with complete ossification of the growth plates and free from major structural damage were selected for measurements after identification of LSTV characteristics of accessory articulation on the ala of the sacrum, additional/partial segments (> 5 = sacralization) or less/partial sacral segments (< 5 = lumbarization). Samples were also screened and grouped according to the position of their auricular surfaces4:
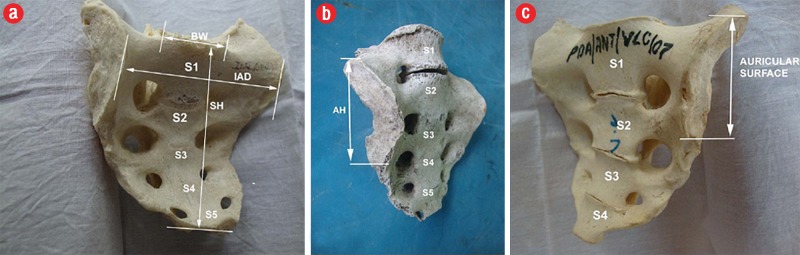
Type I [Figure 1a] typical/normal; auricular surface extending between the level of the upper border of the body of S1 segment and the mid-S3 segment,
Type II [Figure 1b] high up; auricular surface situated between a level higher than the upper border of the S1 segment and not extending beyond the lower limit of S2, and
Type III [Figure 1c] low down; auricular surface spanning between the mid-segment of S1 and the lower portion of S3.
Figure 1.
(a) Five-segment female sacrum showing parameters included in the study. (b) Female sacrum showing partial lumbarization, and separation of S1 with type III /low down auricular surface. (c) Female sacrum with complete lumbarization. Note the four segments in the body and the higher position (type II) of the auricular surface (shown within the arrows). SH: sacral height; BW: body width; IAD: interauricular distance.
Samples were measured for linear dimensions [Figure 1] and surface areas:
Sacral height (SH)
Interauricular distance (IAD)
Sacral body width (BW)
Mean auricular height (AH)
Articular surface area (ASA)
L5 superior body surface area (BSA)
Facet surface area (FSA)
The size and orientation of the superior facet articulating surfaces on the S1 were noted. Facets were considered rudimentary if the FSA measured < 1.00 cm2. In case of unilateral small facets, these areas were considered rudimentary if they possessed < 40% area of the contralateral facet. Presence of FSAs < 1.00 cm2 on both sides was considered bilaterally rudimentary. The numbers for these cut-off measurements were obtained from earlier published data showing that a 1.00 cm2 area represented < 50% surface area value of the average normative surface area of S1 articular facets.4,6 Additionally, specimens with < 1.00 cm2 facet area or < 40% area compared to the contralateral facet have been documented to present features of LSTV and load-bearing imbalances at the L5-S1 junction.4,6,7,20 Comparisons of LSTV with the normal/typical measurements were performed using the Student’s t-test and has been reported for the female samples in this study. Such comparisons are available across larger mixed gender samples in other published studies.21,22
Results
Seventy-eight (69.6%) specimens were found to be non-LSTV [Table 1]. The remaining 34 samples (30.3%) presented traits of L5-S1 transitions. Thirteen (38.2%) LSTV samples demonstrated unilateral L5-S1 accessory articulation, nine (26.4%) bilateral L5-S1 accessory articulations, four (11.7%) uni- or bilateral complete sacralizations [Figure 2a], and eight (23.5%) specimens were completely lumbarized. Majority of the bones possessed type I/normal/typical or type II/high up auricular surfaces [Table 1].
Table 1. Distribution of LSTV in female osteological sacral samples, the type of auricular surface and the type of facets. Number of samples identified as female = 112. Normal/typical = 78; sacrum with LSTV = 34.
| Female n = 112 |
Type I (normal/typical) n = 38 |
Type II (high up) n = 36 |
Type III (low down) n = 4 |
Unilateral rudimentary facets |
Bilateral rudimentary facets |
|
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Normal/typical n = 78 |
78/112 (69.6%) |
38/78 | 36/78 | 4/78 | 1/78 | 1/78 |
| Unilateral accessory L5-S1 articulation n = 13 |
13/34 (38.2%) |
2/38 | 11/36 | 0/4 | 6/13 | 2/13 |
| Bilateral accessory L5-S1 articulation n = 9 |
9/34 (26.4%) |
2/38 | 7/36 | 0/4 | 3/9 | 4/9 |
| Sacralized L5 n = 4 |
4/34 (11.7%) |
1/38 | 0/36 | 3/4 | 1/4 | 1/4 |
| Lumbarized S1 n = 8 |
8/34 (23.5%) |
1/38 | 5/36 | 2*/4 | 4/8 | 1/8 |
LSTV:lumbosacral transitional vertebrae. *partial lumbarization.
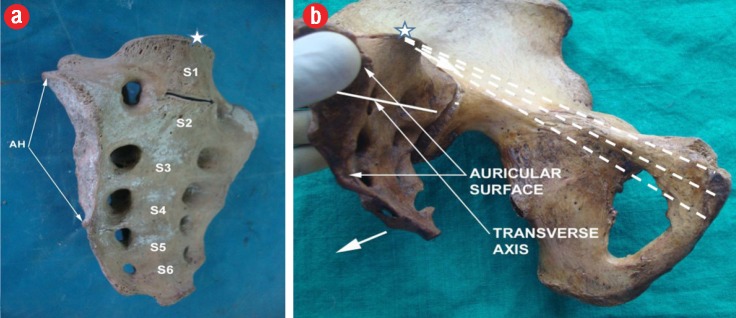
Figure 2.
(a) Complete sacralization of L5 with the sacrum forming the S1 segment. Note the lower position of the auricular surface (type III). (b) The transverse axis for sacral nutation (horizontal bold line); the moments of sacral rotation in the sagittal plane are denoted by two short, thick arrows. The sacral promontory at the dorsal aspect of the pelvic inlet is marked by asterisk, and the three measured conjugates are represented by dashed lines.
Only four samples showed type III/low down auricular surfaces. Type I sacra rarely showed any LSTV variation except four specimens presenting accessory articulations, one sacralization and one lumbarization. Most type II variants presented unilateral or bilateral LSTV accessory articulations and a few showed the feature of complete lumbarization of the S1 sacral segment. Type III sacral specimen exhibited only three sacralization and two cases of partial (unilateral) lumbarization of the first sacral segment.
Most of the sacra with lumbosacral accessory articulations and S1 lumbarization demonstrated rudimentary facets, as reported earlier.6
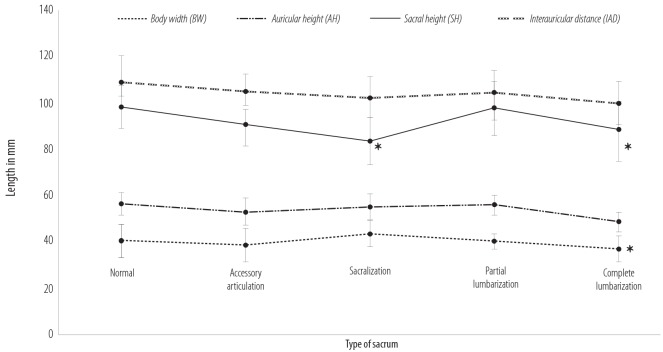
The linear parameters reported here demonstrate different group-specific mean values [Table 2] [Figure 3]. The differences in (a) SH, (b) IAD, (c)sacral BW, and (d) mean AH demonstrated a gradual and bidirectional change in parameters from the normal/typical variants (i.e., dimensions were seen to increase with features of sacralization and decrease with lumbarization).
Table 2. Mean values (in mm) and comparisons of linear parameters between normal/typical and transitional L5-S1 variations in female sacra. Standard deviations are provided in parenthesis.
| Linear dimensions | Normal/typical sacra n = 78 |
Sacra with accessory articulation n = 13 |
Sacra with complete and bilaterally fused L5 n = 9 |
Sacra with partial lumbarization of S1 n = 2 |
Sacra with complete lumbarization of S1 n = 8 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SH | 98.0 ± 9.2 | 90.2 ± 8.6 | SH 97.5 ± 10.6 SH+L5 110.7 ± 09.4 SH-L5 83.4 ± 10.1* |
97.3 ± 11.7 | 87.8 ± 13.2* |
| IAD | 108.7 ± 11.0 | 104.2 ± 7.6 | 102.2 ± 8.5 | 104.1 ± 14.8 | 99.5 ± 9.0 |
| BW | 40.3 ± 7.0 | 38.6 ± 7.2 | 43.5 ± 6.0 | 40.1 ± 3.1 | 36.6 ± 5.6* |
| AH | 56.2 ± 4.6 | 53.0 ± 5.7 | 54.8 ± 5.4 | 55.8 ± 4.2 | 48.6 ± 4.3 |
SH: sacral height; IAD: interauricular distance; BW: sacral body width; AH: auricular height. *Significant at p < 0.050.
Figure 3.
Linear dimensions of linear parameters showing values measured in the normal and different types of sacral transitional anomalies. *Significant at p < 0.050 when compared with typical sacrum data.
Normal/typical SH measured 98.0±9.2 mm, with sacralization measured 110.7±09.4 mm. Sacra with complete separation of the S1 (lumbarization) were relatively shorter (SH = 87.8±13.2 mm; p < 0.050). The five-segment SHs in the sacralized specimen measured 97.5±10.6 mm. However, on inclusion of the fifth lumbar vertebrae in the measurement (SH+L5), the SH measured 110.7±09.4 mm, and mean height of the same sacrum without the inclusion of the fifth lumbar vertebra measured 83.4±10.1 mm (p < 0.050). The parameter IAD indicated the overall width of the sacrum [Table 2] and indicated that all female specimen measured wider than their lengths. The IAD with complete lumbarization measured the least (99.5±9.0 mm) in comparison to the other LSTV groups. The width of the sacral body above the first sacral segment (BW) demonstrated a similar distribution as that seen with IAD. The BW was the least with complete lumbarization (36.6±5.6 mm; p < 0.050). The mean AH in the normal/typical specimen measured 56.2±4.6 mm, the maximum value measured across all groups. The minimum value of this parameter was found with complete lumbarization, 48.6±4.3 mm. Sacralized samples with additional L5 segments incorporated into the sacral body measured 54.8±5.4 mm. These LSTV ASA values were comparable to the non-LSTV auricular surface heights. Despite the overall increased SH, the mean values seen in the sacralized samples (110.7±09.4 mm), the auricular surface heights were comparable to the normal/typical type I variants. Most lumbarized female specimens screened were associated with accessory lumbosacral articulations (7/8 samples). Surface area measurements on the sacrum demonstrate different group-specific mean values measured in the normal and different types of sacral transitional anomalies [Figure 4]. Only the ASA parameter in the partially lumbarized female specimen demonstrated a statistical significantly alteration in that surface area.
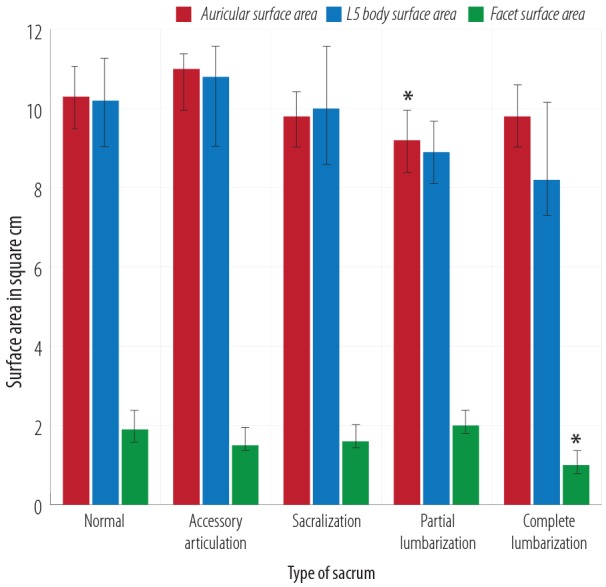
Figure 4: Surface area measurements on the sacrum showing values measured in the normal and different types of sacral transitional anomalies. *Significant at p < 0.050 when compared with typical sacrum data.
Discussion
Pelvic dimensions may vary with stature, gender, or ethnicity.23 These differences may be attributable to the size of hip-bones or the sacrum, which determines the availability of space for fetal descent through the maternal pelvis.8,10,12,20,24 Given the changes identified with LSTV and the varying size of the female sacrum, associated changes in the dorsal pelvic dimensions may complicate normal labor.
More specifically, lumbarization may reduce overall dorsal pelvic space and diminish effective sagittal flexion of the mid-pelvic fetal head. Since higher percentages of LSTV have been documented in the female population, the significance of the observations made in this study may not be overemphasized.1,2,18 Though this study did not objectively test and compare real-time kinetics of labor in normal/typical and probable LSTV-associated pelvic alterations, it discusses next the potential obstetric implications of the changing sacral dimensions and auricular surface position.4,25
Two varieties (unilateral or bilateral L5-S1 accessory articulations and features of incomplete lumbarization of S1) are associated with a type II (high up) position of the auricular surface. In such a situation, additionally, the overall height and width of the sacrum are lesser than the measured typical or standard variants. A shorter sacrum may feature changes in the ventral curvature of the dorsal pelvis and may accordingly impede initial flexion and later extension of the face through the birth canal. Significantly smaller IADs detected in such sacrum may suggest diminished transverse dimensions at the pelvic inlet. Additionally, a slightly forward sacral promontory in such cases may play a critical role in limiting the available anteroposterior diameter for engagement of the fetal head.7,8,12,14,15
Complete lumbarization presents similar effects of significantly smaller SH due to a loss in the number of sacral segments and, hence, present a comparatively reduced anterior curvature of the posterior pelvic wall.22 Additionally, higher auricular surfaces seen in these samples may result in a cranial shift of the transverse axis of sagittal nutation of the sacrum. This phenomenon may create more space for the fetus inside the pelvis as well as at the pelvic exit to expedite labor [Figure 2].9 However, the smaller overall linear dimensions seen, especially with complete lumbarization of the S1, may delay the progress of labor depending on the dynamics of fetal head engagement secondary to the altered patterns of lumbosacral mobility at the new L6-S1 lumbosacral junction.5,26 Accordingly, abnormal L6-S1 stress patterns and joint dysfunctions may unfavorably affect childbirth.
Finally, sacrum with a sacralization may present as complete L5 sacralization with bilateral higher position (type III) auricular surfaces, or unilateral (partial) lumbarization with one-sided high and one-sided low auricular surfaces.21,22 Such a phenomenon may alter the dynamics of sacroiliac relaxation and sacral nutation patterns during labor. This study reports higher SH values with sacralization, which may result in a larger dorsal concavity. More significantly, complete sacralization most likely can result in a high sacral promontory position due to the natural assimilation of the L5 as the extra sacral segment. Also, an increase in transverse dimensions (IAD and BW) in such cases is suggestive of larger transverse diameters at the pelvic inlet and a cranial shift of sacral promontory. It is important to note that despite the extra segment, the auricular surface remains at a lower position (type III) within the overall sacral corpus. Accordingly, the transverse axis of sacral rotation is pushed inferiorly. This phenomenon may limit the full range of the posterior nutation [Figure 2b] of the sacrum, thereby compromising the availability of dorsal pelvic space for the fetal head to flex as it descends mid-way through the pelvis. Additionally, larger osseous auricular surfaces (ASA and larger sacroiliac joint size) resulting from addition of extra sacral segments may limit the range of sagittal rotation. A pelvis with partial lumbarization or incomplete sacralization usually present two different levels of auricular surfaces on either side that, along with increased SH and IADs, can further complicate the normal dynamics of human parturition.4,8,12,18
Conclusion
Since the sacrum forms an important element of the articulated pelvis, either objective or incidental detection of LSTV variations in pregnancy may warrant evaluation of the potential impact on the progress of labor.
Disclosure
The authors declared no conflicts of interest. No funding was received for this study.
References
- 1.Bron JL, van Royen BJ, Wuisman PI. The clinical significance of lumbosacral transitional anomalies. Acta Orthop Belg 2007. Dec;73(6):687-695. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Castellvi AE, Goldstein LA, Chan DP. Lumbosacral transitional vertebrae and their relationship with lumbar extradural defects. Spine (Phila Pa 1976) 1984. Jul-Aug;9(5):493-495. 10.1097/00007632-198407000-00014 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Delport EG, Cucuzzella TR, Kim N, Marley J, Pruitt C, Delport AG. Lumbosacral transitional vertebrae: incidence in a consecutive patient series. Pain Physician 2006. Jan;9(1):53-56. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Mahato NK. Association of rudimentary sacral zygapophyseal facets and accessory and ligamentous articulations: Implications for load transmission at the L5-S1 junction. Clin Anat 2010. Sep;23(6):707-711. 10.1002/ca.21009 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Tini PG, Wieser C, Zinn WM. The transitional vertebra of the lumbosacral spine: its radiological classification, incidence, prevalence, and clinical significance. Rheumatol Rehabil 1977. Aug;16(3):180-185. 10.1093/rheumatology/16.3.180 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Mahato NK. Disc spaces, vertebral dimensions, and angle values at the lumbar region: a radioanatomical perspective in spines with L5-S1 transitions: clinical article. J Neurosurg Spine 2011. Oct;15(4):371-379. 10.3171/2011.6.SPINE11113 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Willis A, Oxenham MF. A case of maternal and perinatal death in Neolithic Southern Vietnam, c. 2100–1050 BCE. Int J Osteoarchaeol 2013;23(6):676-684 . 10.1002/oa.1296 [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Spörri S, Hänggi W, Braghetti A, Vock P, Schneider H. Pelvimetry by magnetic resonance imaging as a diagnostic tool to evaluate dystocia. Obstet Gynecol 1997. Jun;89(6):902-908. 10.1016/S0029-7844(97)00148-8 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Stokes IA, Iatridis JC. Mechanical conditions that accelerate intervertebral disc degeneration: overload versus immobilization. Spine (Phila Pa 1976) 2004. Dec;29(23):2724-2732. 10.1097/01.brs.0000146049.52152.da [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Morgan MA, Thurnau GR, Fishburne JI., Jr The fetal-pelvic index as an indicator of fetal-pelvic disproportion: a preliminary report. Am J Obstet Gynecol 1986. Sep;155(3):608-613. 10.1016/0002-9378(86)90288-7 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Young J. Relaxation of the Pelvic Joints in Pregnancy: Pelvic Arthropathy of Pregnancy. BJOG 1940;47(5):493-524 . 10.1111/j.1471-0528.1940.tb08842.x [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Spörri S, Thoeny HC, Raio L, Lachat R, Vock P, Schneider H. MR imaging pelvimetry: a useful adjunct in the treatment of women at risk for dystocia? AJR Am J Roentgenol 2002. Jul;179(1):137-144. 10.2214/ajr.179.1.1790137 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Taneja R, Dighe M, Kanal KM, Richardson ML, Mitsumori LM, Dubinsky TJ. Utility of multiplanar and three-dimensional reconstructions from computed tomography performed for maternal indications for visualizing fetal anatomy and estimating gestational age. J Comput Assist Tomogr 2011. Jul-Aug;35(4):446-453. 10.1097/RCT.0b013e3182206f40 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Sibley LM, Armelagos GJ, Van Gerven DP. Obstetric dimensions of the true pelvis in a medieval population from Sudanese Nubia. Am J Phys Anthropol 1992. Dec;89(4):421-430. 10.1002/ajpa.1330890403 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Skippen MW. Obstetric practice and cephalopelvic disproportion in Glasgow between 1840 and 1900. 2009, University of Glasgow. [Google Scholar]
- 16.Henske WC. Relaxation of the pelvic joints in pregnancy. Am J Obstet Gynecol 1936;31(4):721-722 . 10.1016/S0002-9378(36)90496-9 [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Derry DE. On the Sexual and Racial Characters of the Human Ilium. J Anat 1923. Oct;58(Pt 1):71-83. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Tague RG. Variation in pelvic size between males and females. Am J Phys Anthropol 1989. Sep;80(1):59-71. 10.1002/ajpa.1330800108 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Tague RG. Variation in pelvic size between males and females in nonhuman anthropoids. Am J Phys Anthropol 1995. Jul;97(3):213-233. 10.1002/ajpa.1330970302 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Powell MC, Worthington BS, Buckley JM, Symonds EM. Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) in obstetrics. I. Maternal anatomy. Br J Obstet Gynaecol 1988. Jan;95(1):31-37. 10.1111/j.1471-0528.1988.tb06477.x [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Mahato NK. Complete sacralization of L5 vertebrae: traits, dimensions, and load bearing in the involved sacra. Spine J 2010. Jul;10(7):610-615. 10.1016/j.spinee.2010.04.012 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Mahato NK. Morphological traits in sacra associated with complete and partial lumbarization of first sacral segment. Spine J 2010. Oct;10(10):910-915. 10.1016/j.spinee.2010.07.392 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Davivongs V. The Pelvic Girdle of the Australian Aborigine; Sex Differences and Sex Determination. Am J Phys Anthropol 1963. Dec;21:443-455. 10.1002/ajpa.1330210403 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Thoms H. Relaxation of the symphysis pubis in pregnancy. J Am Med Assoc 1936;106(16):1364-1366 . 10.1001/jama.1936.02770160022007 [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Mahato N. Assessment of pelvic dimensions and evaluation of new morphometric indices for determination of sex in human hip bones. Aust J Forensic Sci 2010;42(2):123-135 . 10.1080/00450610903258094 [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Farfan HF, Sullivan JD. The relation of facet orientation to intervertebral disc failure. Can J Surg 1967. Apr;10(2):179-185. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]