Abstract
Background
Gonorrhea remains one of the most common sexually transmitted diseases worldwide. Successful treatment has been hampered by emerging resistance to each of the antibiotics recommended as first-line therapies. We retrospectively analyzed the susceptibility of gonorrhea to azithromycin and ceftriaxone using data from the China Gonococcal Resistance Surveillance Programme (China-GRSP) in order to provide evidence for updating the treatment recommendations in China.
Methods and findings
In this study, we included 3,849 isolates collected from patients with a confirmed positive Neisseria gonorrhoeae (N. gonorrhoeae) culture at clinic visits during the period of 1 January 2013 through 31 December 2016 in 7 provinces. Antimicrobial susceptibility testing of gonorrhea isolates using agar dilution was conducted to determine minimum inhibitory concentration (MIC). Resistance to azithromycin (RTA) was defined as MIC ≥ 1.0 mg/l, and decreased susceptibility to ceftriaxone (DSC) was defined as MIC ≥ 0.125 mg/l. The prevalence of isolates with RTA was 18.6% (710/3,827; 95% CI 17.4%–19.8%). The percentage of patients with DSC fluctuated between 9.7% and 12.2% over this period. The overall prevalence of isolates with both RTA and DSC was 2.3% (87/3,827; 95% CI 1.9%–2.8%) and it increased from 1.9% in 2013 to 3.3% in 2016 (chi-squared test for trend, P = 0.03). Study limitations include the retrospective study design and potential biases in the sample, which may overrepresent men with symptomatic infection, coastal residents, and people reporting as heterosexual.
Conclusions
To our knowledge, this is the first national study on susceptibility of N. gonorrhoeae to azithromycin and ceftriaxone in China. Our findings indicate high rates of RTA and DSC from 2013 to 2016. Although dual therapy with azithromycin and ceftriaxone has been recommended by WHO and many countries to treat gonorrhea, reevaluation of this therapy is needed prior to its introduction in China.
In an observational study using data from the China Gonococcal Resistance Surveillance Programme, Yueping Yin estimate rates of reduced susceptibility to WHO-recommended antibiotics for Neisseria gonorrhoeae.
Author summary
Why was this study done?
Antimicrobial resistance in Neisseria gonorrhoeae (N. gonorrhoeae) is a global threat in the control of this infection. China has one of the biggest antimicrobial consumption rates globally. However, China has limited data on antimicrobial resistance in gonorrhea.
Systematic and timely collection and analysis of data on antimicrobial susceptibility of N. gonorrhoeae will inform the development of Chinese treatment guidelines and clinical practice standards.
What did the researchers do and find?
Minimum inhibitory concentrations (MICs) of azithromycin and ceftriaxone were determined for 3,849 clinical isolates from patients with gonorrhea who provided samples during the time period 2013 to 2016 in 7 provinces in China.
Following the Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute criteria, MIC values were used to define isolates as resistant to azithromycin and/or with decreased susceptibility to ceftriaxone.
High prevalence of resistance to azithromycin (18.6%) and decreased susceptibility to ceftriaxone (10.8%) were found in our study population. The prevalence of concomitant resistance to azithromycin and decreased susceptibility to ceftriaxone increased from 1.9% in 2013 to 3.3% in 2016.
What do these findings mean?
N. gonorrhoeae strains resistant to azithromycin and/or with decreased susceptibility to ceftriaxone are prevalent in China, posing a challenge for gonorrhea control.
The results can be used to inform national recommendations for N. gonorrhoeae treatment in China.
Introduction
Gonorrhea, caused by Neisseria gonorrhoeae (N. gonorrhoeae), remains one of the most common sexually transmitted diseases (STDs) worldwide. In 2012, the World Health Organization (WHO) estimated 27 million prevalent and 78 million incident cases of gonorrhea among people 15–49 years old. Of these estimated numbers, 42.5% and 45%, respectively, occurred in the Western Pacific Region. China is the most populous country in this region and contributes substantially to the number of people with gonorrhea [1]. China reports approximately 115,000 new cases of gonorrhea annually. The incidence of gonorrhea has increased in recent years, and the infection has become one of the most common notifiable infectious diseases in the country [2]. Gonorrhea causes urethritis, cervicitis, pharyngitis, and anal infection. If left untreated, it can result in complications such as pelvic inflammatory disease in women [3] and infertility in both men and women [4]. Moreover, it increases the risk for HIV acquisition and transmission [5]. Control of gonorrhea in many countries largely relies on detection of cases followed by therapy to cure the infection and eliminate transmission to others. However, successful treatment has been hampered by emerging resistance to each of the antibiotics recommended as first-line therapies [6]. Latest in this trend are resistance and treatment failures for extended-spectrum cephalosporins, including ceftriaxone and cefixime [7,8]. Monotherapy with ceftriaxone (250 mg intramuscularly in a single dose) for uncomplicated gonococcal infections is still the recommended regimen in the current guidelines in China. To halt the development and spread of resistance, dual therapy consisting of ceftriaxone and azithromycin has been recommended as the first-line therapy in international and national guidelines [9–11]. However, the first treatment failure with dual therapy was reported in 2016 in the United Kingdom [12]. To provide evidence for updating China’s national treatment recommendations for gonorrhea, we analyzed data on the susceptibility to azithromycin and ceftriaxone of N. gonorrhoeae isolates collected in the China Gonococcal Resistance Surveillance Programme (China-GRSP).
Methods
Ethical clearance
The study was approved by the Medical Ethics Committee at the Institute of Dermatology, the Chinese Academy of Medical Sciences & Peking Union Medical College, and the National Center for Sexually Transmitted Disease Control (NCSTD) at Nanjing (approval number 2014-LS-026) for the use of anonymized samples and data collected during routine outpatient services to patients attending local dermatology and/or STD clinics.
Study population
The current study was a retrospective study based on clinical isolates and data of patients with confirmed N. gonorrhoea in the China-GRSP. The China-GRSP was launched by the NCSTD as a collaboration project consisting of a few clinics in 1987. China joined the WHO Western Pacific Gonococcal Antimicrobial Susceptibility Programme (GASP) in 1992 and then expanded China-GRSP to more participating clinics in 9 provinces (Guangdong, Guangxi, Hainan, Zhejiang, Sichuan, Tianjin, Xinjiang, Shanghai, and Chongqing) in 2007. In 2013, China-GRSP started collecting data on azithromycin resistance. At each participating clinic, routine medical consultation was provided to patients. Cultures for N. gonorrhoeae were performed in patients with a positive risk assessment. Data from patients with confirmed N. gonorrhoeae from 1 January 2013 to 31 December 2016 were used in this study. The study focused on 7 provinces (Fig 1); Shanghai and Chongqing were not included in this study because these provinces did not collect data about azithromycin resistance. Selected demographic, behavioral, and clinical characteristics of the participants were extracted from outpatient medical records, i.e., from background information collected during the clinic visits.
Fig 1. Geographic locations of the provinces where N. gonorrhoeae isolates were collected from patients.
The number of isolates from each province is given in parentheses.
Isolation of N. gonorrhoeae
As a patient could be infected at different anatomical sites (cervix/vagina, pharynx, rectum, and urethra), samples from more than 1 site were collected, if indicated. Rectal and pharyngeal samples were generally not obtained from heterosexual males. Samples were inoculated into selective Thayer-Martin (TM) medium and cultured in an incubator at 36°C in 5%–10% CO2 for 24 to 48 hours. With the cultured isolate samples, probable N. gonorrhoeae was identified based on colonial morphology (growth of typical appearing colonies), Gram stain (Gram-negative), and oxidase reaction (oxidase-positive intracellular diplococci in stained smears). Sugar fermentation tests were further performed if the identification was ambiguous. The gonococcal isolates were further sub-cultured from the selective TM medium to a nonselective medium, and the confirmed colonies were suspended in skim milk and frozen to −70°C until shipped to provincial central STD laboratories for antimicrobial susceptibility testing.
Antimicrobial susceptibility testing
Agar dilution antimicrobial susceptibility tests were conducted at the central STD laboratories of the participating provinces according to WHO recommendations [13]. Specifically, the isolates were cultured from frozen stocks onto selective TM medium and sub-cultured on GC medium base agar supplemented with hemoglobin powder and IsoVitaleX Enrichment (BD Diagnostics, Oxford, England) at 36°C with 5% to 10% CO2 for 18 to 20 hours at the central STD laboratories. The colonies were scraped, and suspensions of 107 organisms per milliliter were prepared. Using a multipoint inoculator (104 per point), the suspension was applied to antibiotic-containing medium (GC agar base supplemented with 10% defibrinated sheep blood; Nanjing Bianzhen Biotechnology, Nanjing, China) on a 9-cm diameter plate [14]. The plate was cultured at 36°C with 5% to 10% CO2 for 18 to 24 hours, and the growth of gonococci in different concentrations of antibiotic (0.03, 0.06, 0.125, 0.25, 0.5, 1.0, 2.0, 4.0, and 8.0 mg/l for azithromycin and 0.008, 0.015, 0.03, 0.06, 0.125, 0.25, 0.5, and 1.0 mg/l for ceftriaxone) was observed and recorded. The minimum inhibitory concentration (MIC) was defined as the lowest concentration of an antibiotic that inhibited the growth of gonococci. MIC interpretive criteria were in accordance with the Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute to define resistance or decreased susceptibility [13,15]. For azithromycin, we categorized MIC values as susceptible (MIC ≤ 0.5 mg/l) or resistant (MIC ≥ 1.0 mg/l). For ceftriaxone, we categorized MICs as susceptible (MIC ≤ 0.06 mg/l) or decreased susceptibility (MIC ≥ 0.125 mg/l). For quality assurance, all the central STD laboratories participated in the external quality assurance program of the WHO Western Pacific GASP through the National STD Reference Laboratory in Nanjing.
Statistical analyses
The development of the statistical analysis plan, including changes inspired by peer review, is described in S1 Text. Those patients whose isolates were successfully cultured and for which MICs for azithromycin and/or ceftriaxone were determined were included in the final analyses. In this study, we calculated the prevalence rates and their 95% confidence intervals (CIs) of N. gonorrhoeae resistance to azithromycin (RTA), decreased susceptibility to ceftriaxone (DSC), and both RTA and DSC (RTA/DSC). Age was described as median and 25%–75% interquartile range (IQR) because the age data followed a left-skewed distribution. MIC was described as geometric mean and 95% CI because MICs were multiple values determined by serial dilutions. For MICs determined as above or below a specific value, we used the midpoint value between this specific value and the value of the next higher or lower dilution for calculating the geometric means. Bivariate analyses were conducted by chi-squared test or chi-squared test for trend. Multinomial logistic regression analysis was conducted to explore the associations of variables with being infected with strains of N. gonorrhoeae with RTA, DSC, or RTA/DSC. Variables with a significance level of P < 0.10 in bivariate analyses were included in a multinomial logistic regression model. Adjusted odds ratios (AORs) and 95% CIs were estimated by adjusting for potential confounding factors that were included in the model. P ≤ 0.05 was set as the level of significance. Statistical analysis was done using SPSS for Windows (version 16.0; SPSS, Chicago, Illinois) and MedCalc for Windows (version 16.8; MedCalc Software, Mariakerke, Belgium).
The current study is reported as per Strengthening the Reporting of Observational Studies in Epidemiology (STROBE) guidelines (S1 Checklist).
Results
Baseline characteristics of patients
A total of 3,849 N. gonorrhoeae isolates were collected from 3,849 patients (males, 91.1%; females, 8.9%). Data on repeat infections in individuals were not available due to anonymization of the dataset during the study years. Of the 3,503 males who provided information on sexual orientation (99.9% of the male total), 3,451 (98.5%) were heterosexual and 52 (1.5%) were homosexual or bisexual. The median age was 31 years (IQR 26–40 years) for males and 31 years (IQR 25–43 years) for females. The majority (92.8%) of the participants were of Han ethnicity, and 50.2% were from the provinces along the coast, where more cases of gonorrhea were reported than in other areas [16]. Previous infection with gonorrhea was reported in 15.0% of patients. Among the heterosexual patients, the majority of the isolates were from the urethra (99.4%) in males and the cervix or urethra (96.2%) in females. No patients were found to have a positive N. gonorrhoeae isolate at more than 1 anatomical site.
Azithromycin susceptibility
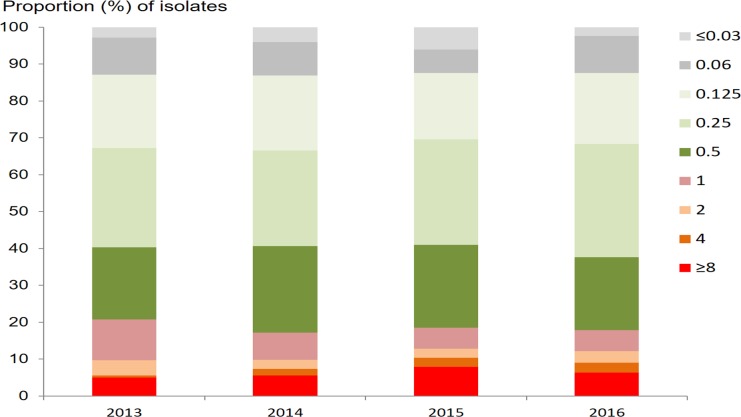
Out of 3,849 N. gonorrhoeae isolates, 3,827 (99.4%) and 3,849 (100.0%) had MIC results for azithromycin and ceftriaxone, respectively. The geometric mean azithromycin MIC was 0.32 mg/l (95% CI 0.31–0.34 mg/l), with a range of ≤0.05 to ≥8 mg/l. The prevalence of RTA (defined as MIC ≥ 1.0 mg/l) was 18.6% (710/3,827; 95% CI 17.4%–19.8%). The proportions of the isolates with different MICs of azithromycin by year are shown in Fig 2. Neither the mean MIC nor the percentage of resistant strains appeared to change during the 2013–2016 study period, remaining between 0.31 mg/l and 0.34 mg/l and between 17.1% and 20.8%, respectively. Multinomial regression analysis (Table 1) indicates that RTA was significantly associated with younger age (AOR 0.99; 95% CI 0.98–1.00; P = 0.043) and being female (AOR 1.50; 95% CI 1.13–2.00; P = 0.005, compared with males).
Fig 2. Proportion of N. gonorrhoeae isolates with different minimum inhibitory concentrations (mg/l) for azithromycin, by year.
Table 1. Associations between resistance to azithromycin or decreased susceptibility to ceftriaxone and demographic and clinical characteristics (multinomial regression analysis*).
| Characteristics | Resistance to azithromycin (MIC ≥ 1.0 mg/l)** | Decreased susceptibility to ceftriaxone (MIC ≥ 0.125 mg/l) | Resistance to azithromycin and decreased susceptibility to ceftriaxone | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Prevalence (n/N) | AOR (95% CI) | Prevalence (n/N) | AOR (95% CI) | Prevalence (n/N) | AOR (95% CI) | |
| Age group (years) | ―― | 0.99 (0.98–1.00)* | ―― | 1.00 (0.98–1.01) | ―― | 0.99 (0.97–1.01) |
| Sex | ||||||
| Male | 17.9 (624/3,486) | Reference | 11.1 (389/3,507) | Reference | 2.2 (77/3,486) | Reference |
| Female | 25.2 (86/341) | 1.50 (1.13–2.00) | 8.2 (28/342) | 0.77 (0.47–1.27) | 2.9 (10/341) | 1.42 (0.71–2.84) |
| Sexual orientation | ||||||
| Heterosexual | 18.6 (699/3,763) | Reference | 10.9 (412/3,784) | Reference | 2.3 (86/3,677) | Reference |
| Homosexual or bisexual | 15.4 (8/52) | 0.77 (0.34–1.74) | 7.7 (4/52) | 0.45 (0.14–1.48) | 1.9 (1/52) | 1.08 (0.14–8.12) |
| Previous gonococcal infection | ||||||
| Yes | 21.2 (122/576) | 1.12 (0.87–1.43) | 7.1 (41/577) | 0.68 (0.45–1.03) | 2.3 (13/576) | 0.78 (0.41–1.46) |
| No | 18.1 (587/3,243) | Reference | 11.5 (374/3,264) | Reference | 2.3 (73/3,243) | Reference |
| Residence along the coast | ||||||
| Yes | 17.1 (331/1,934) | 1.00 (0.83–1.20) | 12.9 (249/1,934) | 1.84 (1.44–2.36) | 1.7 (32/1,902) | 0.56 (0.35–0.88) |
| No | 20.0 (379/1,893) | Reference | 8.8 (168/1,915) | Reference | 2.9 (55/1,838) | Reference |
*Reference value in the multinomial regression analysis: neither resistance to azithromycin nor decreased susceptibility to ceftriaxone.
**22 results for azithromycin MIC are missing.
AOR, adjusted odds ratio; CI, confidence interval; MIC, minimum inhibitory concentration.
Ceftriaxone susceptibility
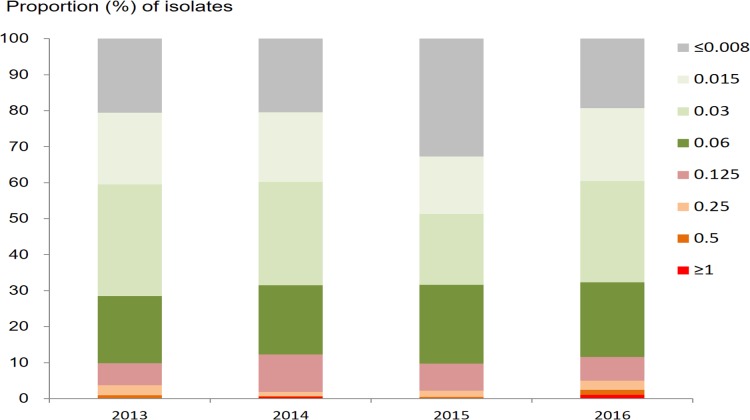
The geometric mean ceftriaxone MIC was 0.025 mg/l (95% CI 0.024–0.026 mg/l), with a range of ≤0.008 to ≥1.0 mg/l. The prevalence of DSC (defined as MIC ≥ 0.125 mg/l) was 10.8% (417/3,849; 95% CI 9.9%–11.9%). The proportions of isolates with different MICs for ceftriaxone are shown by year in Fig 3. The percentage with DSC fluctuated between 9.7% and 12.2% over the period from 2013 to 2016. In the multinomial analysis (Table 1), DSC was significantly associated with residence in areas along the coast (AOR 1.84; 95% CI 1.44–2.36; P < 0.001, compared with residence in other areas).
Fig 3. Proportion of N. gonorrhoeae isolates with different minimum inhibitory concentrations (mg/l) for ceftriaxone, by year.
Resistance to azithromycin and decreased susceptibility to ceftriaxone
The proportion of isolates resistant to azithromycin in those with DSC (21.0%, 87/415; 95% CI 17.3%–25.1%) was not statistically different from the proportion of isolates resistant to azithromycin in those susceptible to ceftriaxone (18.3%, 623/3,412; 95% CI 17.0%–19.6%) (chi-squared = 1.79; P = 0.18; Table 2). The prevalence of isolates with RTA/DSC was 2.3% (87/3,827; 95% CI 1.9%–2.8%). The prevalence increased from 1.9% (18/928; 95% CI 1.2%–3.0%) in 2013 to 3.3% (32/981; 95% CI 2.3%–4.6%) in 2016 (chi-squared for trend = 4.78; P = 0.03) (Fig 4). Multinomial regression analysis (Table 1) indicates that residents in areas along the coast are less likely to be infected with strains with RTA/DSC (AOR 0.56; 95% CI 0.35–0.88; P = 0.013).
Table 2. Number and percentage of isolates susceptible or resistant to azithromycin by susceptibility breakpoints of ceftriaxone.
| Ceftriaxone | Azithromycin* | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Resistant (MIC ≥ 1.0 mg/l) | Susceptible (MIC ≤ 0.5 mg/l) | Total | |
| Susceptible (MIC ≤ 0.06 mg/l) | 623 (18.3%) | 2,789 (81.7%) | 3,412 (100.0%) |
| Decreased susceptibility (MIC ≥ 0.125 mg/l) | 87 (21.0%) | 328 (79.0%) | 415 (100.0%) |
| Total | 710 (18.6%) | 3,117 (81.4%) | 3,827 (100.0%) |
*There were 22 isolates without MIC data for azithromycin.
MIC, minimum inhibitory concentration.
Fig 4. Proportion of N. gonorrhoeae isolates with resistance to azithromycin (MIC ≥ 1.0 mg/l) and decreased susceptibility to ceftriaxone (MIC ≥ 0.125 mg/l) from 2013 to 2016.
MIC, minimum inhibitory concentration.
Discussion
The current study represents, to our knowledge, the first national surveillance on trends of susceptibility of N. gonorrhoeae to azithromycin and ceftriaxone over time in China. In addition, associations between susceptibility data and demographic and clinical characteristics of study participants were examined. Our findings indicate that the rate of dual RTA and DSC increased between 2013 and 2016. The prevalences of N. gonorrhoeae RTA and DSC found in this study in China were higher than those reported in many countries, including in Europe and the Americas [17–27] (Table 3). A high prevalence of RTA or DSC has also been reported in Japan, although the sample size of the available study was relatively small (less than 700 isolates in total over 3 years) [27]. It is unclear whether circulating gonococcal strains with altered susceptibility to the key antibiotic agents in China acquired these mutations through domestic selective pressure or whether the strains have been imported. Antimicrobial resistant gonorrhea was documented first in Asia [28,29], then emerged in other areas in the world. Although azithromycin monotherapy is not recommended for gonorrhea treatment in China, this antibiotic is widely used for treatment of chlamydial infection according to the national STD treatment guidelines [30]. The prevalence of chlamydial infection is much higher than that of gonorrhea both among high-risk groups, such as female sex workers [31,32] and men who have sex with men [33], and in the general population [34] in China. Overuse of macrolides for chlamydia and other infections could facilitate emergence of resistance in N. gonorrhoeae [35]. Studies in China have reported that a high percentage (>50%) of outpatient visits result in prescription of antibiotics [36,37].
Table 3. Prevalence of resistance to azithromycin or decreased susceptibility to ceftriaxone among N. gonorrhoeae isolates collected from 2013 to 2016 in different countries.
| Country/region by year | Resistance to azithromycin (MIC ≥ 1.0 mg/l) | Decreased susceptibility to ceftriaxone (MIC ≥ 0.125 mg/l) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Number of isolates | Percentage | Number of isolates | Percentage | |
| United States | ||||
| 2013 [17] | 5,945 | 3.6 | 5,945 | 0.1 |
| 2014 [17] | 5,093 | 7.1 | 5,093 | 0.1 |
| Canada | ||||
| 2014 [18] | 3,809 | 0.05 | ||
| European Union | ||||
| 2013 [19] | 1,994 | 5.4 | 1,932 | 0.4* |
| 2014 [20] | 2,147 | 7.9 | 2,015 | 0.25* |
| United Kingdom | ||||
| 2013 [21] | 1,750 | 1.6 | 1,750 | 0.2 |
| 2014 [21] | 1,568 | 1.0 | 1,568 | 0.0 |
| 2015 [21] | 1,699 | 9.8 | 1,699 | 0.0 |
| Germany | ||||
| 2010–2015 [22] | 266 | 7.1 | ||
| Australia | ||||
| 2013 [23] | 4,897 | 2.1 | 4,897 | 0.6 |
| 2014 [24] | 4,804 | 2.5 | 4,804 | 0.6 |
| 2015 [25] | 5,411 | 2.6 | 5,411 | 0.1 |
| Zimbabwe | ||||
| 2015–2016 [26] | 388 | 0.0 | ||
| Japan | ||||
| 2013 [27] | 241 | 22.4** | 241 | 31.5** |
| 2014 [27] | 192 | 14.1** | 192 | 32.8** |
| 2015 [27] | 238 | 18.8** | 238 | 29.4** |
| Our study in China | ||||
| 2013–2016 | 3,827 | 18.6 | 3,849 | 10.8 |
*MIC > 0.125 mg/l for ceftriaxone was used in this study.
**These rate data came from personal communication with the corresponding author (Prof. Mitsuru Yasuda, Department of Urology, Gifu University Hospital) of the cited study.
MIC, minimum inhibitory concentration.
WHO and many countries have recommended dual antimicrobial therapy with ceftriaxone plus azithromycin for people with symptomatic and asymptomatic gonorrhea [9–11]. However, despite the high prevalence of DSC (more than 10%) in the current study, treatment failure of ceftriaxone has not been documented in China. It is important that clinicians be on high alert to recognize gonorrhea treatment failures so that they can be reported promptly to public health officials. The high and increasing prevalence of RTA/DSC found in the current study suggests the need for further consideration and validation of an appropriate regimen for treatment of gonorrhea in China.
Socioeconomic, behavioral, and clinical factors associated with antimicrobial resistance have been investigated by previous studies in China and other countries [38–40]. Interestingly, the factors independently associated with RTA and DSC were not the same in our study. Female patients had a higher risk of infection with an azithromycin-resistant strain than males. This finding was consistent with that reported in Amsterdam [41] but different from that reported in Shanghai, where male sex was a significant predictor of tetracycline resistance [38]. Our finding of an association of younger age with RTA is different from that reported in Shanghai, where probable resistance to ceftriaxone was most common among those in older age groups [38]. In addition, in our study, DSC was more likely to occur in areas along the coast, but RTA/DSC was more prevalent in other areas. These associations may be related to transmission dynamics linked to the sexual networks of different populations or in different areas. In addition, the resistance patterns are also dependent on the population seeking care in the sentinel clinics. Further studies on genomic epidemiology and sexual networks among people infected with resistant strains are needed. In contrast to the expected association between previous gonorrhea infection—linked to potential exposure to the antibiotics—and antimicrobial resistance, our study indicated that previous infection with gonorrhea was not associated with risk of RTA or DSC.
There are some potential limitations to this study. First, although the current study was a national surveillance survey with a large number of isolates collected from 7 provinces in China, the sample accounts for roughly only 1% of reported cases of gonorrhea during the study period in the country. Geographically, less than a quarter of the 31 provinces in the country participated in the study, and most of them were located in the economically developed areas along the coast. Moreover, the majority of male participants provided urethral specimens (99.4% of men), and the majority of female participants provided cervical or urethral specimens (96.2% of women). Our sample overrepresents men because men are usually symptomatic and easy to identify for specimen collection. Another concern is that most pharyngeal and anal gonorrhea is asymptomatic, and repeat infections or repeat visits of anonymized patients to clinics during the study period may result in the true number of individuals sampled being smaller than the number of “patients” described here, although this difference is likely to be relatively small. In addition, only a small proportion of the study participants were homosexual or bisexual, and therefore the majority of men did not report any anal or pharyngeal sexual intercourse [42]. All of these potential biases may limit the generalizability of the current study to all people infected with gonorrhea in China. Second, those isolates with MIC > 0.5 mg/l for azithromycin or MIC > 0.125 mg/l for ceftriaxone were not further categorized for susceptibility analysis to identify high-level RTA and/or resistance to ceftriaxone. Third, although molecular typing of N. gonorrhoeae was carried out in a few areas and reported previously [43], it was not performed in the present survey. Future studies should include molecular and genomic analyses to investigate gonorrhea transmission and to track the spread of antimicrobial resistance [44]. With regard to the treatment of gonorrhea in China, the national STD guidelines have not yet been updated to include dual therapy with ceftriaxone plus azithromycin for gonorrhea but recommend the use of azithromycin for treating potential infection with chlamydia among patients infected with gonorrhea. Further studies are needed to look into appropriate doses of ceftriaxone and azithromycin as well as use of other antibiotics in China.
In conclusion, the current study was a national study on the susceptibility of N. gonorrhoeae to azithromycin and ceftriaxone with implications for antibiotic choice for treatment of gonorrhea in China. An increasing trend of isolates with simultaneous RTA and DSC will likely impede the introduction of the currently WHO-recommended dual therapy in China. Therefore, evaluation of the efficacy of the dual therapy and the development of novel treatment strategies are urgently warranted in China. In addition, future resources should be dedicated to enhancing antimicrobial resistance surveillance by increasing both the number of laboratories performing susceptibility testing and the quality of susceptibility tests. The development of rapid diagnostics to promptly detect gonococcal infections and identify antimicrobial resistance is also urgently needed.
Supporting information
(DOC)
(DOCX)
(XLSX)
Acknowledgments
The China-GRSP is a national program coordinated by the NCSTD under the leadership of the National Health and Family Planning Commission in China. The authors wish to acknowledge the staff of the collaborating STD clinics where this study took place, and the participants of this study for their wonderful cooperation.
Abbreviations
- AOR
adjusted odds ratio
- China-GRSP
China Gonococcal Resistance Surveillance Programme
- CI
confidence interval
- DSC
decreased susceptibility to ceftriaxone
- GASP
Gonococcal Antimicrobial Susceptibility Programme
- IQR
interquartile range
- MIC
minimum inhibitory concentration
- NCSTD
National Center for Sexually Transmitted Disease Control
- RTA
resistance to azithromycin
- STD
sexually transmitted disease
- TM
Thayer-Martin
- WHO
World Health Organization
Data Availability
Data of the China GRSP are owned by China's National Center for STD Control and CAMS Institute of Dermatology but the de-identified data in a spreadsheet are provided as a supplemental document.
Funding Statement
YY received funding from The Chinese Academy Medical Sciences (CAMS) Initiative for Innovative Medicine (2016-I2M-3-021). The funders had no role in study design, data collection and analysis, decision to publish, or preparation of the manuscript.
References
- 1.Newman L, Rowley J, Vander Hoorn S, Wijesooriya NS, Unemo M, Low N, et al. Global estimates of the prevalence and incidence of four curable sexually transmitted infections in 2012 based on systematic review and global reporting. PLoS ONE. 2015;10:12:e0143304 doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0143304 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Yang S, Wu J, Ding C, Cui Y, Zhou Y, Li Y, et al. Epidemiological features of and changes in incidence of infectious diseases in China in the first decade after the SARS outbreak: an observational trend study. Lancet Infect Dis. 2017;17:716–25. doi: 10.1016/S1473-3099(17)30227-X [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.McCormack WM. Pelvic inflammatory disease. N Engl J Med. 1994;330:115–9. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199401133300207 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Hook EW 3rd, Handsfield HH. Gonococcal infections in the adult In: Holmes KK, Sparling PF, Mardh PA, Lemon SM, Stamm WE, Piot P, et al. , editors. Sexually transmitted diseases. 3rd ed. New York: McGraw-Hill; 1999. pp. 451–66. [Google Scholar]
- 5.Cohen MS, Hoffman IF, Royce RA, Kazembe P, Dyer JR, Daly CC, et al. Reduction of concentration of HIV-1 in semen after treatment of urethritis: implications for prevention of sexual transmission of HIV-1. AIDSCAP Malawi Research Group. Lancet. 1997;349:1868–73. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Unemo M, Shafer WM. Antimicrobial resistance in Neisseria gonorrhoeae in the 21st century: past, evolution, and future. Clin Microbiol Rev. 2014;27:587–613. doi: 10.1128/CMR.00010-14 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Shimuta K, Unemo M, Nakayama S, Morita-Ishihara T, Dorin M, Kawahata T, et al. Antimicrobial resistance and molecular typing of Neisseria gonorrhoeae isolates in Kyoto and Osaka, Japan, 2010 to 2012: intensified surveillance after identification of the first strain (H041) with high-level ceftriaxone resistance. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2013;57:5225–32. doi: 10.1128/AAC.01295-13 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Ison CA, Hussey J, Sankar KN, Evans J, Alexander S. Gonorrhoea treatment failures to cefixime and azithromycin in England, 2010. Euro Surveill. 2011;16:19833 [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Workowski KA, Bolan GA, Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Sexually transmitted diseases treatment guidelines, 2015. MMWR Recomm Rep. 2015;64(RR-03):1–137. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Bignell C, Unemo M, European STI Guidelines Editorial Board. 2012 European guideline on the diagnosis and treatment of gonorrhoea in adults. Int J STD AIDS. 2013;24:85–92. doi: 10.1177/0956462412472837 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.World Health Organization. WHO guidelines for the treatment of Neisseria gonorrhoeae Geneva: World Health Organization; 2016. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Fifer H, Natarajan U, Jones L, Alexander S, Hughes G, Golparian D, et al. Failure of dual antimicrobial therapy in treatment of gonorrhea. N Engl J Med. 2016;374:2504–6. doi: 10.1056/NEJMc1512757 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.World Health Organization. Manual for the laboratory identification and antimicrobial susceptibility testing of bacterial pathogens of public health concern in the developing world Geneva: World Health Organization; 2003. [Google Scholar]
- 14.Ye S, Su X, Wang Q, Yin Y, Dai X, Sun H. Surveillance of antibiotic resistance of Neisseria gonorrhoeae isolates in China, 1993–1998. Sex Transm Dis. 2002;29:242–5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.US Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Gonococcal Isolate Surveillance Project (GISP) protocol. Atlanta: US Centers for Disease Control and Prevention; 2016. [Google Scholar]
- 16.Gong XD, Yue XL, Jiang N, Teng F, Meng PX, Li J, et al. Epidemiological characteristics and trends of gonorrhea in China from 2000 to 2014. Chin J Dermatol. 2015;48:301–6. [Google Scholar]
- 17.US Centers for Disease Control and Prevention Division of STD Prevention. Sexually transmitted disease surveillance 2014: Gonococcal Isolate Surveillance Project (GISP) supplement and profiles Atlanta: US Centers for Disease Control and Prevention; 2016. [Google Scholar]
- 18.Martin I, Sawatzky P, Liu G, Allen V, Lefebvre B, Hoang L, et al. Decline in decreased cephalosporin susceptibility and increase in azithromycin resistance in Neisseria gonorrhoeae, Canada. Emerg Infect Dis. 2016;22:65–7. doi: 10.3201/eid2201.151247 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Cole MJ, Spiteri G, Jacobsson S, Pitt R, Grigorjev V, Unemo M, et al. Is the tide turning again for cephalosporin resistance in Neisseria gonorrhoeae in Europe? Results from the 2013 European surveillance. BMC Infect Dis. 2015;15:321 doi: 10.1186/s12879-015-1013-x [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.European Centre for Disease Prevention and Control. Gonococcal antimicrobial susceptibility surveillance in Europe, 2014. Stockholm: European Centre for Disease Prevention and Control; 2016. [Google Scholar]
- 21.Public Health England. Surveillance of antimicrobial resistance in Neisseria gonorrhoeae—key findings from the Gonococcal Resistance to Antimicrobials Surveillance Programme (GRASP). London: Public Health England; 2016. [Google Scholar]
- 22.Regnath T, Mertes T, Ignatius R. Antimicrobial resistance of Neisseria gonorrhoeae isolates in south-west Germany, 2004 to 2015: increasing minimal inhibitory concentrations of tetracycline but no resistance to third-generation cephalosporins. Euro Surveill. 2016;21:30335. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Lahra MM, Australian Gonococcal Surveillance Programme. Australian Gonococcal Surveillance Programme annual report, 2013. Commun Dis Intell Q Rep. 2015;39:E137–45. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Lahra MM, Australian Gonococcal Surveillance Programme. Australian Gonococcal Surveillance Programme annual report, 2014. Commun Dis Intell Q Rep. 2015;39:E347–54. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Lahra MM, Enriquez RP, National Neisseria Network. Australian Gonococcal Surveillance Programme annual report, 2015. Commun Dis Intell Q Rep. 2017;41:E60–7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Latif AS, Gwanzura L, Machiha A, Ndowa F, Tarupiwa A, Gudza-Mugabe M, et al. Antimicrobial susceptibility in Neisseria gonorrhoeae isolates from five sentinel surveillance sites in Zimbabwe, 2015–2016. Sex Transm Infect. 2017. May 5 doi: 10.1136/sextrans-2016-053090 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Yasuda M, Hatazaki K, Ito S, Kitanohara M, Yoh M, Kojima M, et al. Antimicrobial susceptibility of Neisseria gonorrhoeae in Japan from 2000 to 2015. Sex Transm Dis. 2017;44:149–53. doi: 10.1097/OLQ.0000000000000556 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Tapsall J. Neisseria gonorrhoeae and emerging resistance to extended spectrum cephalosporins. Curr Opin Infect Dis 2009;22:87–91. doi: 10.1097/QCO.0b013e328320a836 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC). Cephalosporin susceptibility among Neisseria gonorrhoeae isolates—United States, 2000–2010. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep. 2011;60:873–7. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Wang QQ, Liu QZ, Xu JH. Guidelines of sexually transmitted disease prevention and treatment Shanghai: Shanghai Science and Technology Publishing House; 2014. [Google Scholar]
- 31.Su S, Chow EP, Muessig KE, Yuan L, Tucker JD, Zhang X, et al. Sustained high prevalence of viral hepatitis and sexually transmissible infections among female sex workers in China: a systematic review and meta-analysis. BMC Infect Dis. 2016;16:2 doi: 10.1186/s12879-015-1322-0 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Chen XS, Yin YP, Liang GJ, Wang QQ, Jiang N, Liu Q, et al. The prevalences of Neisseria gonorrhoeae and Chlamydia trachomatis infections among female sex workers in China. BMC Public Health. 2013;13:121 doi: 10.1186/1471-2458-13-121 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Fu GF, Jiang N, Hu HY, Mahapatra T, Yin YP, Mahapatra S, et al. The epidemic of HIV, syphilis, chlamydia and gonorrhea and the correlates of sexual transmitted infections among men who have sex with men in Jiangsu, China, 2009. PLoS ONE. 2015;10:3:e0118863 doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0118863 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Parish WL, Laumann EO, Cohen MS, Pan S, Zheng H, Hoffman I, et al. Population-based study of chlamydial infection in China: a hidden epidemic. JAMA. 2003;289:1265–73. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Unemo M1, Shafer WM. Antibiotic resistance in Neisseria gonorrhoeae: origin, evolution, and lessons learned for the future. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2011;1230:E19–28. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.2011.06215.x [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Yin X, Song F, Gong Y, Tu X, Wang Y, Cao S, et al. A systematic review of antibiotic utilization in China. J Antimicrob Chemother. 2013;68:2445–52. doi: 10.1093/jac/dkt223 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Wang J, Wang P, Wang X, Zheng Y, Xiao Y. Use and prescription of antibiotics in primary health care settings in China. JAMA Intern Med. 2014;174:1914–20. doi: 10.1001/jamainternmed.2014.5214 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Trecker MA, Waldner C, Jolly A, Liao M, Gu W, Dillon JA. Behavioral and socioeconomic risk factors associated with probable resistance to ceftriaxone and resistance to penicillin and tetracycline in Neisseria gonorrhoeae in Shanghai. PLoS ONE. 2014;9:2:e89458 doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0089458 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Cole MJ, Spiteri G, Town K, Unemo M, Hoffmann S, Chisholm SA, et al. Risk factors for antimicrobial resistant Neisseria gonorrhoeae in Europe. Sex Transm Infect. 2014;41:723–9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Goldstein E, Kirkcaldy RD, Reshef D, Berman S, Weinstock H, Sabeti P, et al. Factors related to increasing prevalence of resistance to ciprofloxacin and other antimicrobial drugs in Neisseria gonorrhoeae, United States. Emerg Infect Dis. 2012;18:1290–7. doi: 10.3201/eid1808.111202 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Wind CM, Schim van der Loeff MF, van Dam AP, de Vries HJ, van der Helm JJ. Trends in antimicrobial susceptibility for azithromycin and ceftriaxone in Neisseria gonorrhoeae isolates in Amsterdam, the Netherlands, between 2012 and 2015. Euro Surveill. 2017;22:30431 doi: 10.2807/1560-7917.ES.2017.22.1.30431 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Bissessor M, Whiley DM, Lee DM, Snow AF, Fairley CK, Peel J, et al. Detection of Neisseria gonorrhoeae isolates from tonsils and posterior oropharynx. J Clin Microbiol. 2015;53:3624–6. doi: 10.1128/JCM.01647-15 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Chen SC, Yin YP, Dai XQ, Unemo M, Chen XS. First nationwide study regarding ceftriaxone resistance and molecular epidemiology of Neisseria gonorrhoeae in China. J Antimicrob Chemother. 2016;71:92–9. doi: 10.1093/jac/dkv321 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44.De Silva D, Peters J, Cole K, Cole MJ, Cresswell F, Dean G, et al. Whole-genome sequencing to determine transmission of Neisseria gonorrhoeae: an observational study. Lancet Infect Dis. 2016;16:1295–303. doi: 10.1016/S1473-3099(16)30157-8 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
(DOC)
(DOCX)
(XLSX)
Data Availability Statement
Data of the China GRSP are owned by China's National Center for STD Control and CAMS Institute of Dermatology but the de-identified data in a spreadsheet are provided as a supplemental document.