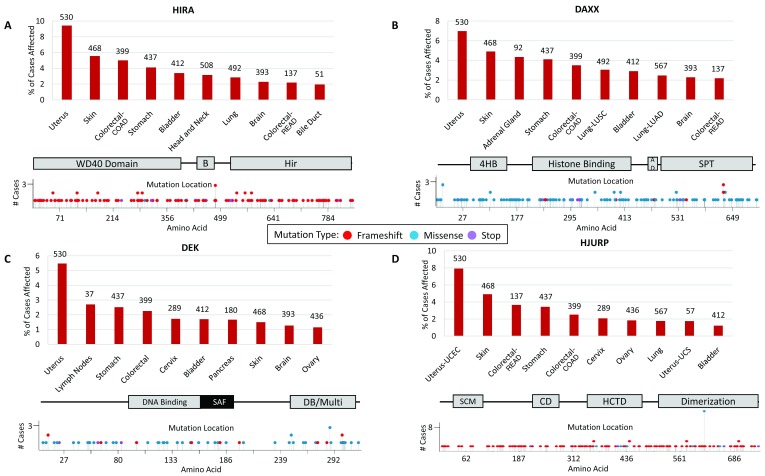
Figure 2. Mutations in H3 variant chaperones occur in many cancer types.
A. Percentage of cases affected by HIRA mutations in multiple cancer types obtained from The Cancer Genome Atlas (TCGA) analysis. Numbers listed above each bar represent total number of cases analyzed. TCGA cancer types listed in order from left to right include uterine corpus endometrial carcinoma (UCEC), skin cutaneous melanoma (SKCM), colon adenocarcinoma (COAD), stomach adenocarcinoma (STAD), urothelial bladder carcinoma (BLCA), head–neck squamous cell carcinoma (HNSC), lung squamous cell carcinoma (LUSC), glioblastoma multiforme (GBM), rectum adenocarcinoma (READ), and cholangiocarcinoma (CHOL). Locations of mutations within the HIRA protein. HIRA protein domains include a WD-40 repeat-containing domain, the B-domain (B) necessary for binding to Asf1, and the conserved Hir domain. B. DAXX mutations as above. TCGA cancer types listed in order from left to right include UCEC, SKCM, adrenocortical carcinoma (ACC), STAD, COAD, LUSC, BLCA, lung adenocarcinoma (LUAD), GBM, and READ. DAXX protein domains include the four-helix bundle (4HB) necessary for ATRX binding, a histone-binding domain, an acidic domain, and the Ser/Pro/Thr-rich region. C. DEK oncogene mutations listed as above. TCGA cancer types listed in order from left to right include UCEC, diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLBC), STAD, COAD, cervical squamous cell carcinoma and endocervical adenocarcinoma (CESC), BLCA, pancreatic adenocarcinoma (PAAD), SKCM, GBM, and ovarian cancer (OV). DEK protein domains shown include a DNA-binding domain, the scaffold attachment factor-box (SAF), and a DNA-binding and multimerization domain. D. HJURP mutations listed as above. TCGA cancer types listed in order from left to right include UCEC, SKCM, READ, STAD, COAD, CESC, OV, LUAD, uterine carcinosarcoma (UCS), and BLCA. HJURP protein domains include the SCM3 domain, the conserved domain (CD), the HJURP C-terminal domain (HCTD) responsible for centromere targeting, and the dimerization domain.