Abstract
The increasing number of clinical conditions that involve a pathological contribution from the complement system — many of which affect the kidneys — has spurred a regained interest in therapeutic options to modulate this host defence pathway. Molecular insight, technological advances, and the first decade of clinical experience with the complement-specific drug eculizumab, have contributed to a growing confidence in therapeutic complement inhibition. More than 20 candidate drugs that target various stages of the complement cascade are currently being evaluated in clinical trials, and additional agents are in preclinical development. Such diversity is clearly needed in view of the complex and distinct involvement of complement in a wide range of clinical conditions, including rare kidney disorders, transplant rejection and haemodialysis-induced inflammation. The existing drugs cannot be applied to all complement-driven diseases, and each indication has to be assessed individually. Alongside considerations concerning optimal points of intervention and economic factors, patient stratification will become essential to identify the best complement-specific therapy for each individual patient. This Review provides an overview of the therapeutic concepts, targets and candidate drugs, summarizes insights from clinical trials, and reflects on existing challenges for the development of complement therapeutics for kidney diseases and beyond.
A decade ago, the field of complement therapeutics experienced a watershed moment with the introduction of the first complement-specific drug, the anti-C5 antibody, eculizumab, into the clinic1,2. In 2007, the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) approved eculizumab (trade name Soliris) for treatment of the orphan disease paroxysmal nocturnal haemoglobinuria (PNH)3. Subsequent approval of eculizumab for the similarly rare kidney disease atypical haemolytic uraemic syndrome (aHUS) in 2011 (REF. 4) further raised awareness of the complement system as a promising therapeutic target for inflammatory disorders, particularly those affecting the kidney5. Deregulated or excessive complement activation is now recognized as a key pathogenic driver in a wide spectrum of immune-mediated and inflammatory diseases, ranging from haematological and ocular pathologies to cancer and ageing-related neuroinflammatory and neurodegenerative disorders6,7.
The therapeutic and commercial success of eculizumab, together with profound changes in the perception and knowledge of the complement system and its roles in health and disease7,8, has led to a veritable renaissance of complement-targeted drug discovery. Several drug candidates have now reached late-stage clinical development for various disorders, and dozens more are in development pipelines9,10. In addition, potential indications for therapeutic complement inhibition are rapidly increasing in number and complexity7. Despite the encouraging progress in drug discovery, some technical challenges and important strategic questions remain, such as the appropriate selection of therapeutic targets and patient populations in each disorder, and particularly under which circumstances modulation of the complement system, which is an important host defence pathway, would be advised.
In this Review, we describe the physiological and pathophysiological implications of complement activation and the consequences for kidney-related and other diseases, summarize the approaches taken to develop the next generation of complement therapeutics, and discuss progress and challenges in the field. The growing number of complement-mediated pathologies, in conjunction with the absence or limited availability of effective treatment options, has prompted the consideration of a broad therapeutic arsenal that can rationally exploit the versatility of targets within the complement cascade. Moreover, the multifaceted nature of this cornerstone system of innate immunity further emphasizes the need for the development of therapeutic interventions that will likely maximize clinical responses without compromising tissue immunosurveillance. Clearly, the complement field is assimilating a wealth of new knowledge that redefines complement as a clinical entity in many diseases. With a heightened awareness of new complement-based therapeutic modalities, this game-changing period is anticipated to lead to more comprehensive and disease-tailored therapeutic strategies with greater promise for clinical translation.
The role of complement in host defence
Complement is a critical part of the host defence machinery that, together with the contact and coagulation systems and the various branches of innate and adaptive immunity, helps to maintain barrier functions and protect against microbial invasion after injury11. The role of complement is to detect, tag and eliminate microbial intruders with almost immediate reactivity but sufficient specificity to avoid damaging host cells7,12 (FIG. 1a). This reactivity and specificity is achieved via a series of circulating pattern recognition proteins (PRPs) that sense pathogen-associated molecular patterns (PAMPs) and initiate the complement cascade.
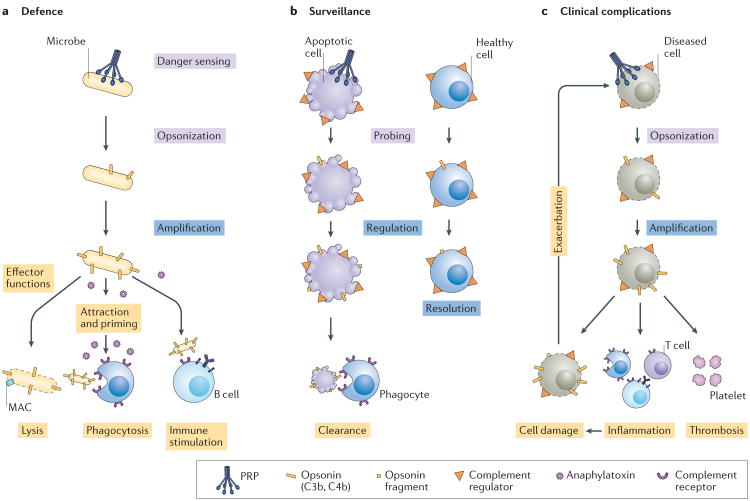
Figure 1. Complement involvement in host defence, immune surveillance and disease processes.
a | Sensing of microbial intruders by pattern recognition proteins (PRPs) of the complement system leads to opsonization (tagging) of the microorganisms with C3b and/or C4b. In the absence of regulators on the microbial surface, this initial opsonization is rapidly amplified via C3 convertases, leading to the initiation of various effector functions, including cell damage or lysis via the membrane attack complex (MAC), chemoattraction and immune cell activation by anaphylatoxins, shuttling and phagocytosis of opsonized microorganisms via complement receptors and the stimulation of cellular and/or adaptive immune responses. b | Immune surveillance by complement has a role in housekeeping functions, such as the clearance of apoptotic cells following controlled activation of the cascade. Attack of healthy host cells by complement is typically prevented by a set of complement regulators that rapidly resolve bystander activation or probing. c | Cell injury and/or genetic alterations can lead to excessive activation or insufficient regulation of complement. Dysregulated opsonization and generation of complement effectors can contribute to thrombo-inflammatory complications and lead to additional cell damage, which can in turn further activate complement and exacerbate the adverse effects.
The surveillance, immunomodulatory and effector functions of complement are elicited through a tightly coordinated network of interactions involving three canonical pathways of activation: the classical pathway, alternative pathway and lectin pathway. The classical pathway is initiated by binding of PRPs to immune complexes, whereas the lectin pathway is initiated by binding of PRPs to aberrant carbohydrate structures that are exposed on foreign, damaged or necrotic cells. The alternative pathway amplifies the initial response and maintains a low level of activity through a tick-over mechanism. The alternative pathway might also have a role in initiation of the complement cascade, but the question of whether an initiating PRP acts in this pathway is not yet resolved7,13. In settings such as thromboinflammation, complement can be activated via non-canonical routes that bypass these three pathways, for example, by serine proteases with promiscuous enzymatic activity in the intracellular space or in the vasculature14.
Upon recognition of foreign surfaces, PRP-associated serine proteases cleave soluble complement components that are covalently deposited on the activating surface and form C3 convertase complexes. Subsequent convertase- mediated cleavage of the abundant plasma protein C3 leads to opsonization of the foreign particle with the activation fragment C3b. This opsonin can form new C3 convertases and thereby amplify opsonization, inducing several effector functions7,12. C3b and its degradation products serve as ligands for a variety of complement receptors that mediate transport of opsonized particles to immune organs, facilitate phagocytosis and/or stimulate adaptive immune responses15. In addition, progressive opsonization induces the formation of C5 convertases that activate C5 and initiate the generation of pore-forming membrane attack complexes (MACs) that lyse susceptible microorganisms or damage cells. Convertase-mediated activation of C3 and C5 also liberates the anaphylatoxins C3a and C5a, respectively, which act as potent immune modulators and/or chemo-attractants that recruit immune cells to sites of activation and orchestrate downstream immune responses. The orthologous C4a protein, which is released from C4 during activation of the classical pathway and the lectin pathway, can activate proteinase-activated receptor 1 (PAR1) and PAR4, which are expressed on several cell types, including platelets and endothelial cells16. This mechanism likely contributes to crosstalk between the complement, coagulation and endothelial barrier systems16,17. The extensive crosstalk between complement effector molecules and components of other host defence systems has mostly emerged during the past 2 decades and is considered to be critical for mounting a successful defence against microbial intruders and accumulating cellular debris7,8,18. Thereby, complement provides an important layer of protection, especially during the critical phase in the early stages of life when the adaptive immune system is still developing.
The role of complement in host defence has long been acknowledged, but increasing evidence indicates that the powerful sensing and effector capabilities of this system are also utilized in the immunoediting of host cells during tissue development and repair as well as during the clearance of debris7. Similar to PAMPs, damage-associated molecular patterns (DAMPs) can raise an initial complement response that is typically kept in check by complement regulators on the host cell surface. Ideally, this response leads to controlled opsonization that facilitates silent clearance via recognition by complement receptors without invoking danger signalling (FIG. 1b). Although this process was first described for the removal of immune complexes and apoptotic cells19,20, fascinating discoveries point to an involvement of complement in the editing of non-immune cells, for example, in synaptic pruning during brain development21,22.
For many decades, complement was perceived to be a blood-borne immune system that was solely located in the intravascular space, with the entire spectrum of its components synthesized almost exclusively in the liver. Reports in the 1980s documented the presence of a functionally intact intracellular complement pool within lymphocytes and other cell types23–25, but the broader implications of this finding remained obscure. Renewed interest in intracellular complement in the past 5 years led to the identification of C3-mediated and C5-mediated activation and signalling events in the intracellular space26. Intracellular complement might be involved in the homeostasis and development of T cells, among other roles, but the implications for disease and therapy remain to be further explored26. Hence, complement exerts housekeeping functions and helps to coordinate defensive responses that reach beyond protection against microbial intruders.
Complement as a therapeutic target
In view of the important defence functions of the complement cascade, pharmacological intervention might seem unwise. Unfortunately, however, vulnerability to erroneous activation and dysregulation renders the complement system an important risk factor for many diseases7 (FIG. 1c). In principle, complement can be triggered by any foreign, diseased or otherwise altered surface, and host cells are occasionally opsonized owing to bystander activation or low background turnover (tick-over). A panel of potent complement regulators, both in the circulation and tethered to host cell surfaces, normally controls complement activation at the level of initiation, convertase-mediated opsonization and MAC formation27 (FIG. 1b). Successful immune surveillance by complement critically relies on the balance between activation and regulation as well as on discrimination between self and non-self surfaces. Any disruption of this balance that leads to improperly controlled opsonization and effector generation may have severe adverse clinical consequences7,12,27 (FIG. 1c).
Although beneficial for host defence, crosstalk between the complement system and other immune and homeostatic pathways (for example, the coagulation and kinin systems) might exacerbate the adverse outcomes of inappropriate complement activation by fuelling events contributing to inflammation, thrombosis and host cell injury7,18. Moreover, host cell damage often results in new triggers for complement activation (such as DAMPs) and creates a vicious cycle. Some cells and organs, including the eyes and kidneys, seem to be particularly affected by complement-mediated damage, with implications for diseases ranging from aHUS and C3 glomerulopathy (C3G) to lupus nephritis (LN) and IgA nephropathy.
In many debilitating, life-threatening diseases, the benefits of targeting the complement system to reduce inflammation and cell or tissue damage might outweigh the risks of weakening a layer of host defence, especially in adult patients with functioning adaptive immune systems. The early involvement of complement in disease processes makes this system an attractive target for early intervention in many diseases, as complement inhibition could potentially prevent exacerbation and triggering of downstream inflammatory pathways9. However, the rationale for therapeutically modulating complement and the optimal point of intervention needs to be carefully assessed for each disorder. Profound knowledge of the underlying pathological processes is critical to enable optimal target and drug selection for each indication.
Indications for complement therapies
Owing to a steady stream of data from large genetic studies, increasing awareness of complement in the clinical community, and improved diagnostic tools and disease models, the number of complement-mediated diseases has rapidly expanded over the past 10 years. In contrast to many other pathways in which alterations lead to a narrow and well-defined set of diseases, disorders with known or suspected complement involvement cover an exceptionally broad range, including tissue- specific, systemic, acute and chronic disorders of the inflammatory, autoimmune, age-related, biomaterial-induced and neurodegenerative spectrum7.
Despite the diversity and complexity in pathologies associated with imbalanced complement, the mechanistic involvement of complement in disease processes follows a few major principles7 (FIG. 2). An overwhelming number of activating triggers, such as PAMPs in the case of sepsis or DAMPs in trauma, can lead to systemic inflammatory response syndrome (SIRS), in which the severe and sudden reaction of complement and other defence pathways causes homeostatic imbalance, hyper-acute inflammation and tissue damage that can lead to organ dysfunction and death. In the case of complement involvement, too much of a protective response can lead to an adverse outcome. In transplant-induced and bio-material-induced inflammation, complement recognizes non-self surfaces that are exposed to blood or tissue fluid and invokes an appropriate but unwanted response28–30. The subsequent adverse reactions might have a negative impact on the quality of life of the patient and on the lifetime and function of the foreign component, and can in extremis lead to rejection of the material, cell or organ.
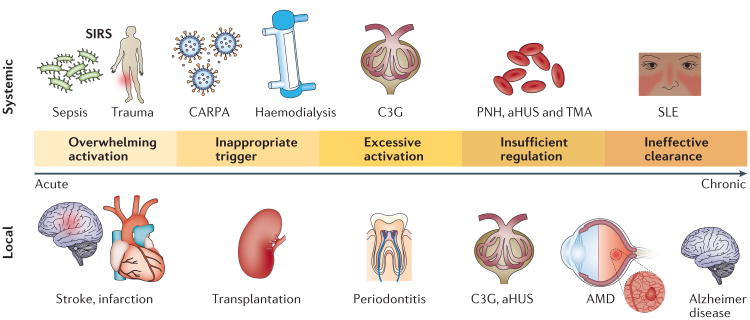
Figure 2. Major mechanisms of the pathogenic involvement of complement in systemic and local disorders.
Even when the complement system is operating normally, adverse activation can be triggered after exposure to massive amounts of pathogen, damage-associated stimuli or foreign surfaces such as transplanted organs or biomaterials. In many chronic disorders, genetic alterations lead to a systemic or local imbalance of complement that can contribute to inflammation, thrombosis and tissue damage. Ineffective removal of apoptotic cells, debris or immune complexes owing to the clearing capacity of the complement system being exceeded or deficiencies in complement components can induce or exacerbate autoimmune and neurodegenerative diseases. aHUS, atypical haemolytic uraemic syndrome; AMD, age-related macular degeneration; C3G, C3 glomerulopathy; CARPA, complement activation-related pseudo allergy; PNH, paroxysmal nocturnal haemoglobinuria; SIRS, systemic inflammatory response syndrome; SLE, systemic lupus erythematosus; TMA, thrombotic microangiopathy.
In addition to acute inflammatory conditions, complement drives several chronic disorders, such as PNH, aHUS and age-related macular degeneration (AMD). The majority of these disorders are at least partially mediated by unbalanced complement activation due to alterations in complement genes and proteins, including mutations, polymorphisms, deletions and deficiencies. Polymorphisms can lead to gain-of-function alterations of complement activators or loss-of-function alterations of complement regulators, and may impair the self-recognition capabilities of soluble complement regulators such as factor H (FH). The distinct combination of complement alterations in an individual, sometimes referred to as the complotype, often determines the fitness of his or her complement system and his or her susceptibility to certain diseases31.
The normally beneficial actions of complement aimed at removing immune complexes, apoptotic cells and debris can lead to adverse reactions when debris or plaque can no longer be removed, resulting in constant complement activation that contributes to an inflammatory microenvironment. Prominent examples of this principle are age-related disorders such as Alzheimer disease, atherosclerosis and AMD32,33. In addition, insufficient clearance of apoptotic cells and/or immune complexes owing to deficiencies in early complement components is considered to be a key contributor to autoimmune diseases such as systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE)19,20.
Kidney-related disorders
The pronounced susceptibility of the kidney to complement- mediated injury has been largely attributed to its unique anatomical and functional features that seem to be conducive to complement activation. Similar to the eyes, which are also particularly susceptible to disorders driven by imbalanced complement activation, the kidneys are characterized by a prominent, compartment-dividing membrane, the glomerular basement membrane, that lacks complement regulators and may be prone to attack upon damage of the covering cell layer7. Several other factors such as the high local concentration of complement components due to renal ultrafiltration, local variations in pH that influence the activation potential of complement, and disruption or vulnerability of the glycocalyx lining the endothelial wall might increase the susceptibility of the kidneys to complement-induced damage7,34. The pathogenic processes that underlie complement-mediated kidney disorders are, however, highly diverse.
Haemolytic uraemic syndrome
aHUS is a rare, severe form of thrombotic microangiopathy (TMA) that is characterized by thrombocytopenia, haemolytic anaemia and acute kidney injury with endothelial lesions that often lead to end-stage renal disease (ESRD)35. The presence of one or more genetic alterations in components of the alternative pathway of complement activation greatly increases susceptibility to aHUS, and genetic abnormalities leading to complement dysregulation are identified in approximately 60% of patients35. The disease may be precipitated by a number of triggers, including viral and bacterial infections, drugs, pregnancy, transplantation and systemic diseases. The interplay between the complement, coagulation and endothelial barrier systems seems to be particularly important in aHUS pathogenesis17, and eculizumab is the treatment of choice (BOX 1).
Box 1. Complement therapeutics in aHUS and C3G.
Atypical haemolytic uraemic syndrome
In atypical haemolytic uraemic syndrome (aHUS), generation of the membrane attack complex (MAC) and pro-inflammatory C5a via the terminal pathway seem to drive the disease process35,200. Consequently, anti-C5 therapy using eculizumab has emerged as the gold-standard treatment. Whether continuous eculizumab treatment is necessary is debated as aHUS often manifests in flares and treatment costs are high201,202.
Moreover, pharmacokinetic or pharmacodynamic breakthrough can occur and might affect treatment outcome. Alternative treatment options for aHUS would therefore be welcome. A phase II proof-of-concept study of the C5a receptor 1 (C5aR1) antagonist avacopan in aHUS gave promising results, and multi-centre trials of this agent are eagerly awaited171. Although the mode of action is not yet clear, OMS721, an antibody targeting mannose-binding lectin-associated serine protease 2 (MASP2), has also shown promising results in aHUS trials and is being further developed for this indication117,203. Little is known about the potential benefits of taming opsonization in aHUS by inhibiting complement at the level of complement C3 or the C3 convertase.
C3 glomerulopathies
Eculizumab has been evaluated in C3 glomerulopathy (C3G), but only a fraction of patients benefit from the therapy41,121. This finding is not surprising, as C3G is driven by excessive convertase-mediated complement activation in the circulation, with deposition of C3 activation fragments in the glomerular tissue39,41. Inhibition of C3 activation therefore seems to be the obvious therapeutic strategy41,121, and proof-of-concept trials with the convertase inhibitor CR1 and in vitro studies with the C3 inhibitor Cp40 have shown promising results144,204. Several drug candidates, including inhibitors of C3, factor D and MASP2, have also entered clinical development, and it will be important to determine which approach confers the most benefit for each subgroup of patients. C5-mediated effector generation also has a role in C3G and might be particularly important in patients who respond to eculizumab. The C5aR1 antagonist avacopan has been successfully used in a patient with refractory C3G, and clinical development programmes have been announced for this indication205. Insight from clinical trials is urgently needed to help define therapeutic strategies and hopefully lead to the first treatment options for C3G.
In contrast to aHUS, typical HUS has a well-defined infectious aetiology and is most commonly attributed to Escherichia coli strains that produce Shiga toxins, which trigger severe endothelial injury and vascular inflammation35. An involvement of complement in typical HUS and other TMAs such as thrombotic thrombo cytopenic purpura or transplant-related TMA has been suggested36,37 but is not as well established as for aHUS and the therapeutic implications remain unclear. Although eculizumab was reported to be beneficial in patients with Shiga toxin-producing E. coli (STEC)-HUS during a food-related epidemic in Germany, the precise involvement of complement and the true clinical impact of anti-C5 therapy in this disease remain controversial35,37. Results from an ongoing, controlled phase III trial of eculizumab in paediatric patients with STEC-HUS are highly anticipated35,38.
C3 glomerulopathies
Another rare spectrum of kidney diseases that are primarily mediated by complement dysregulation are the C3Gs, which include dense deposit disease and C3 glomerulonephritis39. Despite a similar set of complement proteins being affected by genetic alterations, the exact profiles and the pathological consequences of C3G are distinct from those observed in aHUS39,40 (BOX 1). C3G is primarily driven by excessive complement turnover in the circulation due to convertase-stabilizing autoantibodies, which manifests in massive deposition of C3 activation fragments in the kidney (mostly on the glomerular basement membrane in the case of dense deposit disease). Currently, no approved treatment options for C3G exist, and patients rely on symptomatic measures that include immunosuppression, antihypertensive drugs and maintenance with frequent haemodialysis39,41.
Haemodialysis
Although a life-saving intervention for many patients with ESRD and other kidney impairment, haemodialysis can exacerbate inflammation and contribute to cardiovascular disease and other complications28. In particular, recognition of the materials used in the haemodialysis filter and extracorporeal circuit as foreign surfaces by complement can lead to adverse reactions30. Although the switch from cellulose-based to synthetic polymer haemodialysis filters in the 1980s led to a substantial reduction in filter-induced complement activation, studies in the past decade have shown that a substantial amount of complement is still activated during haemodialysis sessions28,42. Complement inhibition might therefore be an easily applicable approach to eliminate an inflammatory trigger in haemodialysis. Given the complexity of the processes involved and the inflammatory state of the patients, finding suitable end points to evaluate the efficacy of such therapy may be challenging.
Transplantation
Many patients undergoing haemo-dialysis are on waiting lists for kidney transplantation. Those fortunate enough to receive a transplant may face a series of potential complications, many of which are partially related to complement activation7,29,43. Elevated complement activation markers have been detected in deceased donor organs and have been linked to unfavourable outcomes in transplant recipients44. The unavoidable ischaemia that occurs during organ explantation and storage leads to hypoxic damage of endothelial cells, with exposure of neoepitopes that may trigger complement activation during reperfusion in the recipient and contribute to ischaemia-reperfusion injury (IRI).
Antibody-mediated rejection (AMR) due to sensitization and/or mismatches in the ABO blood group profiles or HLA profiles between donor and recipient is perhaps the most feared complication after transplantation. AMR is becoming rare owing to improved screening and treatment procedures but can lead to rapid loss of the transplanted organ, largely as a result of complement-mediated damage upon massive triggering of the classical pathway by anti-ABO or anti-HLA antibodies29,43,45.
Transplant-related complications were among the first indications considered for complement therapeutics, but this strategy continues to encounter obstacles (BOX 2). Nevertheless, successful interference in AMR and other complement-induced adverse effects could potentially enable transplantation across compatibility barriers or even across species barriers. Indeed, the use of transgenic pigs expressing human complement regulators is among the most promising paths in xenotransplantation research46.
Box 2. Complement therapeutics in transplantation.
Complement has roles in many transplantation-related complications, including inflammatory priming of the donor and recipient, ischaemia-reperfusion injury of the graft, and acute, chronic and cellular rejection29,43,45. Despite encouraging data from experimental and preclinical studies, these concepts have not yet been successfully translated into therapeutic intervention.
The challenges in developing complement inhibitors for use in solid-organ transplantation are demonstrated by the history of eculizumab use in this setting43,206. A proof-of-concept study in a mouse heart transplantation model of antibody-mediated rejection (AMR) demonstrated that antibody therapy targeting complement C5 could not only prevent AMR but also induce accommodation60. The approval of eculizumab for use in paroxysmal nocturnal haemoglobinuria enabled first-in-human studies in transplantation43,207. In a seminal open-label, single-centre trial, eculizumab reduced the incidence of acute AMR after kidney transplantation in comparison to a historic control group (7% versus 44%)208. A follow-up study did not, however, show a beneficial effect of eculizumab on chronic rejection, and the incidence of transplant glomerulopathy was comparable in the eculizumab and control groups after extended treatment43,208,209. Several controlled clinical trials were initiated to investigate eculizumab use for various aspects of transplantation-related complications. Despite initial promise, some of these studies did not reach their primary end points, and others were terminated owing to insufficient efficacy210–212.
The current lack of success with complement therapeutics in transplantation illustrates the complexity and heterogeneity of the underlying processes. Patient stratification, tailored study design and selection of distinct targets might prove to be critical for the success of the approach. Several trials with eculizumab and plasma protease C1 inhibitor are ongoing, and the results of a large clinical study using Mirococept are eagerly awaited147. As the arsenal of promising candidate molecules reaching clinical stages increases, the goal of using complement drugs to prevent transplantation-related complications is becoming more achievable.
Diabetic nephropathy
Complement activation might be a major contributor to diabetic nephropathy, which is the leading cause of ESRD in developed countries47. The accumulation of advanced glycation end-products may trigger PRP-initiated complement activation47,48, and plasma hyperglycaemia has been reported to affect the inhibitory capacity of some complement regulators such as CD59, which controls MAC formation49. High levels of C3 and increased levels of complement activation markers such as soluble MACs have been reported in patients with type 1 diabetes50. Although elevated plasma levels of C3 were associated with diabetes incidence in a population-based cohort study spanning more than 15 years, whether C3 upregulation is causally related to the disease is not yet clear51. Dysregulation of the complement system in patients with diabetes could potentially contribute to renal damage and ESRD, but the exact mechanisms, contributions and therapeutic implications are still being investigated.
IgA nephropathy
The immune-complex mediated disease IgA nephropathy is caused by aberrant glycosylation of IgA molecules, which are subsequently recognized by antiglycan autoantibodies52. Glomerular immune-complex deposits can lead to complement activation, which causes podocyte damage either directly or indirectly via activation of mesangial cells and stimulation of cytokines and other downstream immune mediators. A number of complement therapeutics are currently in clinical trials for patients with IgA nephropathy (see below).
Lupus nephritis
A similar mechanism to that described for IgA nephropathy might underlie LN, which is a common clinical manifestation and major cause of morbidity in SLE53. Depending on the exact location of immune-complex deposition, complement activation may contribute to several classes of LN and cause renal cell damage, vascular lesions and TMA53. Promising data from case studies suggest a potential benefit of eculizumab in LN, particularly in patients with TMA54.
ANCA-associated vasculitis
Another example of the spectrum of autoimmune diseases with kidney involvement in which complement has a pathogenic role is anti-neutrophil cytoplasmic antibody (ANCA)-associated vasculitis (AAV)55. In this disease, priming of neutrophils induces the translocation of proteins such as myeloblastin or myeloperoxidase to the cell surface. These proteins are then recognized by autoantibodies, leading to the activation of complement and other host defence systems and the release of effector molecules such as C5a55,56. This release in turn activates neutrophils and therefore results in a vicious cycle that exacerbates the disease, with potentially life-threatening consequences. Complement is centrally involved in the pathology of AAV, and blockage of the C5a signalling axis has emerged as a promising treatment option, as discussed below55.
Complement-targeting therapeutics
Even within the spectrum of kidney-related disorders highlighted above, an enormous variety of underlying complement mechanisms, pathways and components exists. When considering all of the other potential indications for complement therapeutics, including less explored frontiers such as cancer and neurological diseases, the diversity and complexity widens substantially. This broad scope of indications and pathological mechanisms necessitates a tailored approach to the treatment of individual diseases. Although the first complement drugs have reached the clinic, an urgent need remains for a diverse set of inhibitors. Fortunately, several promising candidate drugs that target various stages of the complement cascade (FIG. 3) are in development (TABLES 1,2)9,10.
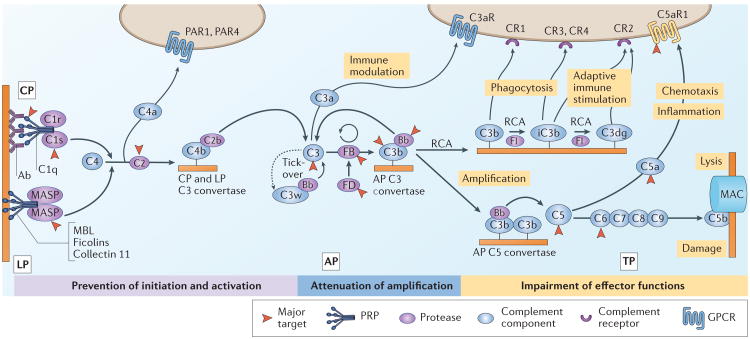
Figure 3. Therapeutic intervention in the complement cascade.
The complement cascade is initiated via pattern recognition proteins (PRPs) of the classical pathway (CP) and lectin pathway (LP) or via tick-over of the alternative pathway (AP). Formation of C3 convertases by any route leads to cleavage of C3 and opsonization of the activating surface with C3b. The AP also drives amplification of the initial complement response as C3b interacts with factor B (FB) and factor D (FD) to form new convertases. Insufficiently restricted opsonization enables generation of AP C5 convertases that cleave C5 and initiate the terminal pathway (TP), which leads to formation of membrane attack complexes (MACs). Regulator of complement activation (RCA) family proteins attenuate convertase assembly and shape immune responses by acting as cofactors for the regulatory protease factor I (FI) that degrades C3b to iC3b and C3dg. C3b and its degradation products bind to complement receptors and stimulate phagocytosis and/or immune signalling. The release of anaphylatoxins (C3a and C5a) during complement activation mediates the attraction and priming of immune cells and helps to orchestrate downstream inflammatory responses. Therapeutic complement inhibition can be achieved by preventing initiation in a pathway-specific manner, by controlling the activation and amplification of the response at the level of C3 or at the level of the CP and LP C3 convertase or by modulating specific effector pathways or functions. Major targets for complement therapeutics include C3, C5 and C5a receptor 1 (C5aR1). Ab, antibody; Bb, cleavage product formed from the degradation of FB; C2b, cleavage product formed from the degradation of C2; C3aR, C3a receptor; C3w, hydrolysed C3 (C3[H2O]); C4a, cleavage product formed from the degradation of C4; C4b, cleavage product formed from the degradation of C4; CR1–4, complement receptor type 1–4; C5b, cleavage product formed from the degradation of C5; GPCR, G protein-coupled receptor; MASP, mannose-binding lectin-associated serine protease; MBL, mannose-binding lectin; PAR1, proteinase-activated receptor 1; PAR4, proteinase-activated receptor 4.
Table 1. Examples of complement-targeted candidate drugs in preclinical development.
| Target | Drug candidate (company) | Entity | Suggested indications |
|---|---|---|---|
| C1q | ANX005, ANX007 (Annexon) | Antibody | Alzheimer disease, Huntington disease, glaucoma |
| C1s | BIVV020 (Bioverativ) | Antibody | Cold agglutinin disease |
| MASP3 | OMS906 (Omeros) | Antibody | Alternative pathway-driven diseases |
| C2 | PRO-02 (Broteio/Argen-x) | Antibody | Ischaemia–reperfusion injury |
| FB | FB inhibitor (Novartis) | Small molecule | NA |
| FD | FD inhibitor (Novartis) | Small molecule | NA |
| ACH-5228 and others (Achillion) | Small molecule | AMD and/or GA, C3 glomerulopathy, IC-MPGN | |
| FD inhibitor (Ra Pharma) | Peptide | AMD and/or GA, orphan renal diseases | |
| FH | 5C6, compsorbin (Amyndas) | Peptide | Transplant and/or biomaterial-induced inflammation |
| C3 | AMY-103 (Amyndas) | Peptide | NA |
| Convertases | AMY-201; also known as mini-FH (Amyndas) | Protein | NA |
| C5 | SOBI005 (Sobi) | Protein | C5-driven diseases |
| Oral C5 inhibitor (Ra Pharma) | Peptide | PNH, gMG, LN, CNS diseases | |
| Long-acting coversin (Akari) | Protein | NA | |
| ISU305 (ISU ABXIS) | Antibody* | PNH | |
| Mubodina (Adienne) | Antibody | Typical haemolytic uraemic syndrome | |
| C5a | IFX-2, IFX-3 (InflaRx) | Antibody | NA |
| C5aR1 | ALS-205 (Alsonex) | Peptide | ALS, Alzheimer disease, Huntington disease |
| DF2593A (Dompé) | Small molecule | Inflammatory and neuropathic pain | |
| IPH5401 (Innate Pharma) | Antibody | Immuno-oncology indications | |
| C6 | Regenemab (Regenesance) | Antibody | PNH, gMG, ALS |
| C6-LNA (Regenesance) | Oligonucleotide | Multiple sclerosis |
Information in the table is based on public announcements of development programmes. ALS, amyotrophic lateral sclerosis; AMD, age-related macular degeneration; C1q, complement C1q; C1s, complement C1s; C2, complement C2; C3, complement C3; C5, complement C5; C5a, anaphylatoxin formed from the degradation of complement C5; C5aR1, C5a receptor 1; C6, complement C6; FB, factor B; FD, factor D; FH, factor H; CNS, central nervous system; GA, geographic atrophy; gMG, generalized myasthenia gravis; IC-MPGN, immune complex membranoproliferative glomerulonephritis; LN, lupus nephritis; MASP3, mannose-binding lectin-associated serine protease 3; NA, not available; PNH, paroxysmal nocturnal haemoglobinuria.
Biosimilar of eculizumab.
Table 2. Complement therapeutics in clinical trials.
| Target | Drug candidate (Company) | Entity | Clinical trial(s) | Indication(s) | Refs | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Phase | Trial number | |||||
| C1s | BIVV009 (Bioverativ) | Antibody | I | NCT02502903 | Cold agglutinin disease | 110 |
| MASP2 | OMS721 (Omeros) | Antibody | II | NCT02222545 | Thrombotic microangiopathies | 213 |
| NCT02682407 | IgA nephropathy, LN, MN, C3G | 116 | ||||
| III | NCT03205995 | aHUS | 117 | |||
| Properdin | CLG561 (Novartis) | Antibody | II | NCT02515942* | AMD and/or GA | 78 |
| C3 | AMY-101 (Amyndas) | Peptide | I | NCT03316521 | C3G | 163 |
| II | NA | C3G, PNH, ABOi kidney transplantation, peridontitis | 214 | |||
| APL-1 (Apellis) | Peptide | I | NA | COPD | 215 | |
| APL-2 (Apellis) | Peptide | I | NCT02588833 | PNH | 156 | |
| NCT02264639 | PNH (add-on therapy) | 155 | ||||
| NCT02461771‡ | AMD (CNV) | 216 | ||||
| II | NCT02503332 | AMD and/or GA | 217 | |||
| NCT03226678 | wAIHA, CAD | 159 | ||||
| APL-9 (Apellis) | Peptide | I | ACTRN12616000862448 | PNH | 160 | |
| FB | IONIS-FB-LRx (Ionis, GSK) | Oligonucleotide | I | 2015-001837-25 | AMD and/or GA | 141 |
| FD | Lampalizumab (Genentech) | Antibody | II | NCT02288559 | AMD and/or GA | 130 |
| III | NCT02745119 | AMD and/or GA | 218 | |||
| NCT02247531 | AMD and/or GA | 132 | ||||
| NCT02247479 | AMD and/or GA | 133 | ||||
| ACH-4471 (Achillion) | Small molecule | II | NCT03053102 | PNH | 125 | |
| Convertases | Mirococept (MRC) | Protein | III | ISRCTN49958194 | Transplantation | 147,148 |
| C5 | Ravulizumab; also known as ALXN1210 (Alexion) | Antibody | I/II | NCT02598583 | PNH | 219 |
| II | NCT02605993 | PNH | 220 | |||
| III | NCT02946463 | PNH (naive) | 103 | |||
| NCT03056040 | PNH (treated) | 104 | ||||
| NCT02949128 | aHUS (naive) | 102 | ||||
| Tesidolumab; also known as LFG316 (Novartis and MorphoSys) | Antibody | I | NCT02878616‡ | Transplantation | 221 | |
| II | NCT02763644 | Transplant-associated microangiopathy | 76 | |||
| NCT01527500‡ | AMD and/or GA | 222 | ||||
| NCT02515942* | AMD | 78 | ||||
| NCT02534909 | PNH | 75 | ||||
| NCT01526889 | Uveitis and/or panuveitis | 77 | ||||
| SKY59; also known as RG6107 and RO7112689 (Chugai and Roche) | Antibody | I/II | NCT03157635 | PNH | 223 | |
| REGN3918 (Regeneron) | Antibody | I | NCT03115996 | PNH | 82 | |
| ABP959 (Amgen) | Antibody§ | I | ACTRN12616000509460 | PNH, aHUS | 71 | |
| GNR-045 (Generium) | Antibody§ | I | ECU-PNH-I | PNH | 224 | |
| Coversin (Akari) | Protein | II | NCT02591862 | PNH | 89 | |
| RA101495 (Ra Pharma) | Peptide | II | NCT03030183 | PNH (poor responders) | 96 | |
| NCT03078582 | PNH | 95 | ||||
| Zimura (Ophthotech) | Oligonucleotide | II | NCT02397954‡ | IPCV | 85 | |
| II/III | NCT02686658 | AMD | 86 | |||
| Cemdisiran (Alnylam) | Oligonucleotide | I/II | NCT02352493 | PNH | 98 | |
| II | NA | aHUS | 101 | |||
| C5a | ALXN1007 (Alexion) | Antibody | II | NCT02245412‖ | GVHD | 225 |
| NCT02128269‖ | APS | 226 | ||||
| IFX-1 (InflaRx) | Antibody | II | NCT02246595‡ | Sepsis | 227 | |
| NCT02866825‡ | SIRS, complex cardiac surgery | 228 | ||||
| NCT03001622 | Hidradenitis suppurativa | 229 | ||||
| C5aR1 | Avacopan; also known as CCX168 (ChemoCentryx) | Small molecule | II | NCT02464891‖ | aHUS | 172 |
| NCT02384317‡ | IgA nephropathy | 173 | ||||
| III | NCT02994927 | A AV | 169 | |||
The table includes ongoing, completed and terminated trials from 2012 onwards. Completed trials are not listed when the development has progressed to the next phase for the same indication. AAV, anti-neutrophil cytoplasmic-antibody-associated vasculitis; aHUS, atypical haemolytic uraemic syndrome; ABOi, ABO incompatible; AMD, age-related macular degeneration; APS, antiphospholipid syndrome; C1s, complement C1s; C3, complement C3; C3G, C3 glomerulopathy; C5, complement C5; C5a, anaphylatoxin formed from the degradation of complement C5; C5aR1, C5a receptor 1; FB, factor B; FD, factor D; CNV, choroidal neovascularization; COPD, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease; GA, geographic atrophy; GVHD, graft versus host disease; IPCV, idiopathic polypoidal choroidal vasculopathy; LN, lupus nephritis; MASP2, mannose-binding lectin-associated serine protease 2; MN, membranous nephropathy; NA, not available; PNH, paroxysmal nocturnal haemoglobinuria; SIRS, systemic inflammatory response syndrome; wAIHA, warm autoimmune haemolytic anaemia.
CLG561 and tesidolumab were used as a combination therapy in the same trial.
Completed trial.
Biosimilar antibody of eculizumab.
Terminated trial.
The current surge in complement-targeted drug discovery may seem to be a sudden phenomenon but has been a long time coming. The potential of therapeutically modulating the complement system was recognized as early as the middle of the past century, and several drug candidates ranging from serine protease inhibitors to engineered regulators were developed but did not reach the clinic. Technical hurdles, the selection of complex indications with ill-defined involvement of complement, and concerns about the safety of the approach often served as major roadblocks on the path to reaching the market1,9,10.
Eculizumab and biosimilars
Eculizumab has undeniably been the motor of the renewed interest in complement-targeted therapy during the past decade. This fully humanized monoclonal antibody (mAb) binds to C5 and prevents its proteolytic cleavage by C5 convertases into the bio active fragments C5a and C5b2. By blocking the generation of the potent complement effectors C5a and the MAC, eculizumab abrogates downstream inflammatory and cell-damaging effects that contribute to pathology in several complement-mediated disorders.
The first mAb against murine C5 was developed 3 decades ago, with an anti-human C5 mAb emerging in 1991 (REFS 57,58). After initial proof-of- concept studies with the murine C5-blocking mAb BB5.1 (REFS 57,59), Alexion developed a primate and human C5-specific mAb and, finally, the humanized antibody eculizumab60,61. Alexion benefited from orphan drug initiatives, which facilitated the successful marketing of eculizumab to treat PNH. In contrast to the more prevalent but highly complex disorders that were initially considered as potential indications for eculizumab, such as rheumatoid arthritis, the pathomechanism of PNH is tightly linked to complement activation. In this disease, acquired somatic mutations in genes responsible for membrane anchor synthesis result in clonal populations of blood cells that lack two complement regulators, among other membrane proteins. Affected erythrocytes have increased susceptibility to (bystander) complement attack, which leads to their MAC-mediated lysis (intravascular haemolysis) and contributes to thrombotic complications. By impairing C5 activation and subsequent formation of the MAC, eculizumab prevents intravascular haemolysis in most patients with PNH and profoundly changed the hitherto limited options for therapy62. With the exception of an increased risk of meningococcal infections, which is curtailed by mandatory vaccination, eculizumab showed an overall beneficial safety profile during clinical trials and long-term post-approval observations63,64, thereby raising confidence in the therapeutic approach.
Among the many potential follow-up indications for eculizumab, aHUS stood out as the most promising in clinical evaluation studies, and market authorization was granted by the FDA in 2011 (REF. 5). Meanwhile, the off-label use of eculizumab identified several other potential indications, and clinical trials are ongoing for indications ranging from transplantation to refractive generalized myasthenia gravis (gMG)10,65 (TABLE 3). This chronic neuromuscular autoimmune disease became the third approved indication for the antibody in 2017, as the European Medicines Agency and the FDA both granted corresponding extensions66. In a phase III clinical trial in patients with anti-acetylcholine receptor antibody-positive gMG, an ultra-rare form of the disease with a lack of treatment modalities, eculizumab resulted in substantial improvement in several disease scores despite narrowly missing the primary end point67–69.
Table 3. Approved complement therapeutics in clinical use.
| Target | Drug (company) | Entity | Approved indications | Indication extension trials | Refs | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Indication | Phase | Trial number | |||||
| Serine proteases including C1r, C1s and MASPs | Cinryze (Shire) | Protein | HAE | Transplantation | I | NCT02435732 | 230 |
| III | NCT02547220 | 231 | |||||
| Cetor (Sanquin) | Protein | HAE | Trauma or sepsis | III | NCT01275976* | 232 | |
| Transplantation | II | NCT02251041 | 233 | ||||
| Berinert (CSL Behring) | Protein | HAE | Transplantation | I/II | NCT02134314 | 234 | |
| II | NCT02936479 | 235 | |||||
| Ruconest; also known as conestat alfa (Pharming) | Protein | HAE | Contrast-induced nephropathy | II | NCT02869347 | 236 | |
| C5 | Soliris; also known as eculizumab (Alexion) | Antibody | PNH, aHUS, gMG | Cold agglutinin disease | II | NCT01303952‡ | 237 |
| Membranoproliferative glomerulonephritis | II | NCT02093533 | 238 | ||||
| Guillain–Barré syndrome | II | NCT02493725‡ | 239 | ||||
| Transplantation | II | NCT01567085 | 240 | ||||
| NCT01919346 | 241 | ||||||
| NCT01895127* | 211 | ||||||
| NCT01399593* | 212 | ||||||
| II/III | NCT02145182‡ | 242 | |||||
| NCT01106027 | 243 | ||||||
| STEC-HUS | III | NCT02205541 | 38 | ||||
| gMG | III | NCT02301624 | 244 | ||||
| NCT01997229‡ | 69 | ||||||
| Neuromyelitis optica | III | NCT01892345 | 245 | ||||
aHUS, atypical haemolytic uraemic syndrome; C1r, complement C1r; C1s, complement C1s; C5, complement C5; gMG, generalized myasthenia gravis; HAE, hereditary angioedema; MASPs, mannose-binding lectin-associated serine proteases; PNH, paroxysmal nocturnal haemoglobinuria; STEC-HUS, haemolytic uraemic syndrome related to Shiga toxin-producing Escherichia coli.
Terminated trial.
Completed trial.
Despite these successes, three main caveats exist to the clinical use of eculizumab. First, the exceptionally high cost of the drug, which can exceed US$500,000 annually per patient, puts pressure on health care systems and severely restricts availability in certain markets70. With patent protection on eculizumab expiring, several biosimilar specialists are waiting to introduce their own brands of the anti-C5 antibody (TABLES 1,2). For example, Amgen has initiated clinical trials with an eculizumab biosimilar for PNH71, and the involvement of local competitors such as the Russian company Generium provides evidence of the effort to make the drug available to markets that do not currently benefit from anti-C5 therapies owing to economic restrictions. Second, the dose scheme and pharmacokinetics of eculizumab typically require a biweekly administration as slow infusion, which may impose a substantial treatment burden for patients. Third, not all patients respond equally well to the treatment, even those with the approved indications.
Among patients with PNH, a very small number do not respond owing to a point mutation in the eculizumab epitope on C5 (Arg885His)72, but at least one-third remain transfusion-dependent despite eculizumab therapy62. A potential factor that might contribute to this insufficient clinical response is extravascular haemolysis. Although eculizumab prevents MAC formation and intravascular haemolysis, PNH erythrocytes continue to be opsonized by C3 fragments, which could lead to recognition by complement receptors on phagocytic cells and extravascular haemolysis via erythrophagocytosis, as shown in in vitro studies62,73. Insufficient dosing and/or pharmacodynamic breakthrough could also potentially contribute to insufficient responses to eculizumab62,74. Indeed, an in vitro study showed that at high levels of complement activation, eculizumab alone was not sufficient to protect PNH erythrocytes from lysis; the addition of a second C5 inhibitor or an agent controlling upstream activation at the convertase level was required for full blockade74. The clinical availability of additional complement inhibitors for the treatment of PNH and other disorders is therefore an important goal.
Next-generation C5 inhibitors
Inspired by the success of eculizumab, many pharmaceutical companies are developing alternative anti-C5 treatments (TABLES 1,2). Novartis was among the first to introduce a fully human anti-C5 antibody, termed tesidolumab, which is under clinical evaluation for use alone or in combination with an antibody (CLG561) that blocks properdin (a positive complement regulator that acts by stabilizing the alternative pathway C3 convertase) for indications ranging from AMD and PNH to TMA and transplantation75–78.
Another anti-C5 mAb, SKY59 (developed as a collaboration between Roche and Chugai), has been engineered to have a long half-life by combining pH-dependent C5 binding with improved recycling through the neonatal Fc receptor (FcRn)79. Interaction with FcRn increases the plasma circulation of SKY59 by creating an intracellular protein pool that is protected from lysosomal degradation and is therefore recycled more efficiently to the extracellular space80.
Regeneron entered an anti-C5 antibody (REGN3918) into phase I trials for PNH in 2017 (REFS 81,82), but no details have been announced about the nature and/or potential benefits of this agent. In addition, a minibody against C5 termed mubodina has been in preclinical development by Adienne for several years. Interestingly, mubodina seems to be the only drug candidate considered for treating typical HUS rather than aHUS83.
In addition to antibodies, C5-targeted drug development efforts involve a diverse set of molecules ranging from peptides and proteins to aptamers. Although these alternative entities do not necessarily provide a clear benefit compared with antibodies in terms of target inhibition, they could potentially be used to target distinct sites on C5 that are not affected by polymorphisms and might have advantages relating to their production cost and pharmacokinetic profiles, including the potential for oral administration.
Zimura (Ophthotech), an aptamer-based C5 inhibitor that has been in clinical development for many years, is currently being evaluated for retinal diseases, including wet and dry forms of AMD84–86. A tick-derived protein with dual activity against C5 and leukotriene B4, termed coversin87, has reached phase II clinical trials in patients with PNH who are resistant to eculizumab and is scheduled for another phase II aHUS trial in 2017 (REFS 88,89). In addition to PNH and aHUS, the manufacturer Akari included Guillain–Barré syndrome, bullous pemphigoid and rare eye diseases as potential indications for coversin and announced the preclinical development of a long-acting form based on PASylation technology88,90. Another protein-based C5 inhibitor in preclinical stages is the affibody SOBI005 (Sobi). In contrast to its predecessor (SOBI002), which was associated with transient adverse events that led to termination of a clinical trial91,92, SOBI005 is fused to the Fc fragment of IgG1 rather than to an albumin-binding entity as a strategy to increase its half-life.
Ra Pharma is developing a macrocyclic peptide, RA101495, that binds C5 with high affinity and allosterically inhibits convertase-mediated cleavage93. After receiving orphan drug designation for PNH, Ra advanced RA101495 to phase II trials using a once-daily subcutaneous self-administration scheme94–96. Ra has also announced development programmes for gMG and LN94 and published preclinical data with a related C5 inhibitor (RA101295) that conferred significant protection from multi-organ failure and reduced mortality in a non-human primate model of bacterial sepsis97.
Alnylam has taken an alternative C5 blocking approach by targeting the gene rather than the protein. Cemdisiran (ALN-CC5) is a hepatocyte-targeted RNA interference therapeutic that impairs C5 synthesis by the liver after subcutaneous administration. Phase I/II trials of cemdisiran as a monotherapy in PNH showed that the agent did not completely inhibit haemolysis, indicating a potential contribution of locally produced C5 in the pathogenesis of the disease98,99. Future trials might therefore focus on combined treatment with cemdisiran and eculizumab in patients who have insufficient responses to eculizumab alone99,100. Alnylam has also announced the initiation of a phase II trial with cemdisiran as a monotherapy in aHUS101.
Finally, Alexion is currently evaluating a second-generation anti-C5 antibody termed ravulizumab (ALXN1210) in phase III trials for PNH and aHUS102–104. By introducing mutations to the eculizumab protein sequence, the plasma residence of the antibody could be markedly increased through pH-dependent lysosomal release, thereby reducing C5-mediated clearance, and through increased FcRn binding105. Preliminary data have shown that in contrast to the biweekly administration necessary with eculizumab, the dose interval of ravulizumab may be extended to 8 weeks to reduce the treatment burden67,105. The effect of the introduction of ravulizumab on the status of eculizumab will be interesting, and how the availability of this new agent might affect the development of eculizumab biosimilars and other C5-targeting compounds is unclear.
Preventing initiation
Although C5 has a key role in the generation of potent complement effectors, it might not necessarily be the ideal therapeutic target for many indications, including PNH62. In C3G, cumulative evidence from case reports and a small clinical trial with off-label use of eculizumab suggests that the effects of anti-C5 therapy are limited owing to the strong involvement of C3 activation in many patients41,106 (BOX 1). Upstream inhibition of complement at the level of initiation or amplification might be necessary in some indications, whereas the tailored blockade of an individual effector such as C5a may be sufficient in others. Fortunately, the complement cascade offers multiple points of intervention (FIG. 3), several of which have already been translated into therapeutic concepts9,10 (FIG. 4). In general, these interventions can be classified into three major functional categories: prevention of complement initiation; attenuation of convertase-mediated amplification; and blockade of one or several effector functions. Therapeutic inhibition at the stage of complement initiation might enable blockade of one activation pathway while preserving the protective activity of the other pathways, but such an approach will require detailed knowledge of the exact disease mechanism.
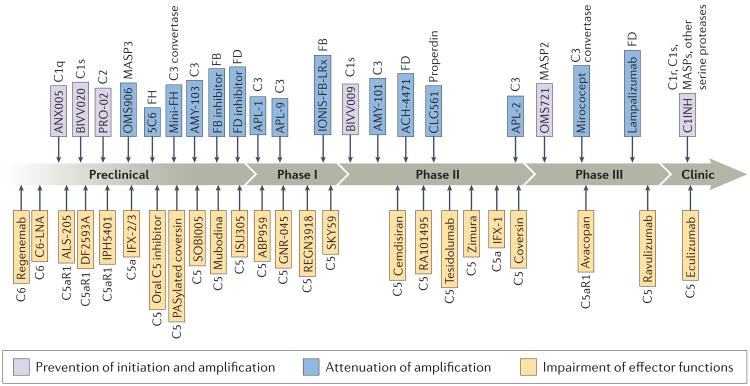
Figure 4. The complement drug development pipeline.
Complement-targeted drugs and drug candidate that are in preclinical or clinical development as of September 2017 are shown. This schematic is based on publications, conference abstracts and publicly available information on company websites. The major target is listed next to each drug name. In the preclinical section, drug candidates are ordered according to target, and their position does not reflect the stage of development. In the phase I through phase III sections, drugs are ordered according to the start date of the clinical trial; only the most advanced trial is indicated for each candidate drug. C1q, complement C1q; C1s, complement C1s; C2, complement C2; C3, complement C3; C5, complement C5; C5a, anaphylatoxin formed from the degradation of complement C5; C5aR1, C5a receptor 1; FB, factor B; FD, factor D; FH, factor H; MASP, mannose-binding lectin-associated serine protease.
Classical pathway
The classical pathway may be considered a target when antibody-mediated complement activation is involved in disease pathogenesis. The PRP of this pathway, the multivalent protein C1q, recognizes antibody patches (IgM or hexameric IgG) on surfaces upon which associated serine proteases (C1r and C1s) are activated. C1s then cleaves C4 and complement C2 to form classical pathway C3 convertases on the activating surface, which initiates C3 cleavage and downstream complement processes.
Under physiological conditions, C1s activity is controlled by plasma protease C1 inhibitor (C1INH). Plasma-purified C1INH has been registered in some European markets since 1997, so it could be considered the first clinical complement inhibitor, but this member of the serine protease inhibitor family is not specific for C1s; it also inhibits additional serine proteases of the complement, coagulation and other systems107. Indeed, the current indication for C1INH preparations, C1INH-deficiency with hereditary angioedema, is primarily related to the kinin system rather than the complement system. The therapeutic efficacy of C1INH on inhibiting complement is uncertain and remains to be defined in clinical settings108. The broad specificity of C1INH might, however, be advantageous in diseases with complex involvement of defence pathways, and several clinical trials covering indications from trauma to transplantation are ongoing (TABLE 3).
Drug candidates specific for classical pathway components have also emerged in development pipelines. Annexon is developing blocking anti-C1q anti bodies (ANX005, ANX007) that prevent classical pathway activation and are being considered as treatment options for ocular and neurological indications109. The humanized antibody BIVV009 (Bioverativ), on the other hand, is directed against C1s. In May 2017, following phase Ib trials110, the FDA granted BIVV009 breakthrough therapy designation for the treatment of cold agglutinin disease111, a rare form of autoimmune haemolytic anaemia that lacks treatment options. The company also announced the preclinical development of a next- generation C1s antibody for subcutaneous administration with less frequent dosing111.
Lectin pathway
Though evolutionarily older than the classical pathway, the lectin pathway seems to be more complex and was only described during the past 3 decades112,113. Five PRPs have been identified, including mannose-binding lectin (MBL), ficolins 1–3 and collectin 11 (REF. 113). These PRPs recognize different carbohydrate and/or acetylation patterns and circulate in complex with MBL-associated serine proteases (MASPs). Similar to the classical pathway, surface recognition by PRPs leads to the activation of MASPs, which convert C4 and C2 to form a C3 convertase.
In the past 10 years, involvement of the lectin pathway has been described in several diseases, in particular those involving IRI. Promising results have been obtained with inhibition of this pathway in models of myocardial or gastrointestinal IRI114, and evidence of lectin pathway activation in donor organs following ischaemic damage has ignited interest in the role of this pathway in renal transplantation115.
To our knowledge, no drug development programme is currently targeting PRPs of the lectin pathway; however, C1INH inhibits MASPs, and Omeros is developing inhibiting antibodies for MASP2 (OMS721) and MASP3 (OMS906) (TABLE 2). The anti-MASP2 mAb OMS721 is being evaluated in a phase III trial for aHUS and a phase II trial for several renal indications, including C3G and LN116,117 (TABLE 2). Use of OMS721 in IgA nephropathy received orphan drug and breakthrough therapy designation from the FDA in 2017, and phase III trials are planned for this indication118. The clinical progress of anti-MASP2 treatment in aHUS has attracted particular attention, as little direct evidence suggests that the lectin pathway has a major role in the pathology of this disease. The possibility exists, therefore, that crosstalk functions of MASP2 might contribute to the therapeutic effect of OMS721 in aHUS (BOX 1).
A comparatively new approach to lectin pathway inhibition aims to block the serine protease C2, which forms part of the C3 convertase in both the classical and lectin pathways and is directly involved in C3 cleavage. The C2-blocking antibody PRO-02 (Prothix/Broteio) may inhibit C3 activation and is currently being investigated as a potential therapy for auto immune haemolytic anaemia, IRI-mediated disorders and transplantation119.
Attenuating amplification
The alternative pathway has a critical role in amplifying the complement response independent of the initiating pathway and in exacerbating inflammatory pathologies7. When a C3b molecule is deposited on an activating surface, either by classical and lectin pathway C3 convertases or as a result of bystander effects or tick-over, the subsequent binding of the serine proteases factor B (FB) and factor D (FD) leads to the assembly of the alternative pathway C3 convertase (C3bBb complex) that cleaves C3 into C3a and additional C3b, which can participate in the formation of new convertases. In many settings, this amplification loop is the major source of opsonization and feeds all effector arms of the complement system, including inflammatory and adaptive signalling, phagocytosis and the formation of C5 convertases with subsequent MAC assembly7,12 (FIG. 3). Controlling the destructive power of the alternative pathway is, therefore, considered to be critical in both physiological and therapeutic contexts.
Healthy human cells are protected from the effects of the alternative pathway C3 convertase by a series of inhibitors of the regulator of complement activation (RCA) family27. These regulators are composed of 4–30 complement control protein (CCP) domains and are either membrane-bound (complement receptor type 1 (CR1), membrane cofactor protein (CD46), complement decay-accelerating factor (CD55)) or circulate as soluble plasma proteins (FH, C4b-binding protein (C4BP)). RCA family proteins act by destabilizing the C3 convertase and/or by serving as cofactors for the regulatory protease factor I (FI) that degrades C3b to fragments that cannot participate in convertase formation; CD55 accelerates convertase decay and CD46 enables opsonin degradation, whereas CR1, FH and C4BP exert both actions27. The C3b degradation products iC3b and C3dg cannot form new convertases but mediate important signalling functions via the phagocytic integrin receptors CR3 and CR4 as well as adaptive immune stimulation through CR2, which forms part of the B cell co-receptor complex12,15. C3 therefore acts as a dynamic functional hub that serves both as a substrate of the convertase and as a source for opsonins that drive convertase formation and immune signalling15.
Convertase inhibitors
The process of C3 activation offers various points of potential therapeutic intervention120,121. In principle, the action of the alternative pathway C3 convertases can be prevented by blocking any element that contributes to C3 convertase assembly or function, with the participating serine proteases of particular interest. FD has emerged as an attractive target owing to its comparatively low plasma concentration, high specificity and bottleneck role in convertase assembly. Novartis has developed small-molecule FD inhibitors inspired by kallikrein blockers that bind to the catalytic site of FD, are orally bioavailable and appear to distribute into ocular tissue, with potential implications for AMD therapy122,123. Similarly, Achillion has introduced small FD inhibitors, one of which, ACH-4471, has been assessed in preclinical PNH and aHUS models124 and is currently being evaluated in phase II clinical trials in an orally administered form125. Programmes for ACH-4471 in C3G and for next- generation FD inhibitors (such as ACH-5228) for oral and/or ophthalmic use are in the Achillion pipeline126.
Among the FD-targeting strategies, the anti-FD antibody fragment lampalizumab (Genentech) has progressed the furthest towards clinical use. In contrast to small-molecule FD inhibitors, which block the catalytic centre of the enzyme, lampalizumab binds to an exosite of FD and prevents conversion of the pro-convertase C3bB to the mature form C3bBb127,128. The high plasma turnover of FD and other pharmacokinetic challenges limit the systemic use of lampalizumab129; however, this agent has been evaluated for intravitreal use in patients with geographic atrophy associated dry forms of AMD. In phase II studies130, lampalizumab treatment resulted in a 20% reduction in the progression of retinal lesions in the overall patient cohort, with a 44% reduction in a subgroup carrying polymorphisms in the genes for both FH and FI131. Two large phase III trials of lampalizumab for geographic atrophy in AMD with identical study designs were initiated in 2014 (REFS 132,133). The treatment did not reach the primary end point in the first of these studies, and results from the second are anticipated in November 2017 (REF. 134). To what extent a newly described FD bypass mechanism through which plasma kallikrein may contribute to the activation of the alternative pathway C3 proconvertase in the absence of FD might affect the results of the lampalizumab trials or of FD inhibition in general remains to be explored135,136.
Rather than inhibiting the catalytic or proconvertase-binding functions of FD, Omeros is focusing on blocking the synthesis of mature FD using an anti-MASP3 mAb (OMS906)137. The rationale for this approach is that MASP3 has a role in the conversion of pro-FD to FD138,139. To date, no preclinical data on this strategy are available.
Although anti-FB antibodies that prevent convertase formation have previously been developed, current FB-targeting interventions focus on different strategies120. Ionis has developed an oligonucleotide drug (IONIS-FB-LRx) that reduces the production of FB and thereby affects alternative pathway convertase formation. This drug showed dose-dependent reduction of FB levels up to 50% after subcutaneous administration in a phase I trial140,141, and plans for phase II trials have been announced142. Novartis has also initiated development efforts towards small-molecule, and likely orally available, FB inhibitors, but no clinical trials have been announced.
Engineered regulators
Therapeutic control of excessive convertase activity can be accomplished using RCA-type regulators, which destabilize the convertase complex and degrade C3b27,120. Even in the early days of complement-targeted drug discovery, engineered regulators were among the most commonly developed candidates. For example, an extracellular form of CR1 comprising all 30 CCP domains was one of the first complement drugs to reach clinical trials (TP10, Avant)143 and showed promise in a compassionate clinical trial for C3G (CDX1135, Celldex)144. However, both CDX1135 and the opsonin-targeted FH derivative TT30 (Taligen/Alexion)145 have now been discontinued, leaving two candidates originating from academic research efforts in the clinical pipelines.
One of these regulator-based agents, Mirococept, is composed of three extracellular domains of CR1 fused to a lipopeptide tag that enables tethering to endothelial cells upon perfusion of organ transplants146. This cytotopic drug showed beneficial safety profiles after systemic administration and organ perfusion in phase I and phase IIb trials, and a large clinical study in kidney transplantation is ongoing in the UK147,148.
The engineered regulator mini-FH (AMY-201; Amyndas) is designed to exert its inhibitory activity on diseased host cells after systemic administration149. This agent consists of the regulatory and surface-recognizing segments of FH connected by a peptide linker. Despite its reduced size in comparison to FH, the binding of mini-FH to opsonins is maintained or even improved, resulting in high efficacy in preclinical models of PNH74,149. Amyndas is also developing a peptide- based entity, compsorbin (5C6), that can be coated to biomaterials and cells, for example, the endothelium of transplanted organs, to recruit endogenous FH and therefore protect against complement attack150,151.
Compstatin analogues
C3 inhibitors based on compstatin, a cyclic peptide with strong affinity and selectivity for human and primate C3 (REF. 152), protect the C3 substrate rather than affect the C3 convertase153. Upon binding to a functionally important site on C3, compstatin analogues impair the binding of the protein to the assembled convertases independent of their origin. In this way, compstatin-based drugs prevent propagation and amplification of complement activation and effector generation after initiation via the classical, lectin or alternative pathways153. Discovery of the compstatin family of inhibitors and most of their preclinical development is firmly rooted in academic research, with the initial compound described in 1996 (REFS 152,153). A second-generation compstatin analogue (4(1MeW)7W, also known as POT-4 and APL-1)154 and pegylation derivatives have been licensed by the University of Pennsylvania, USA, to Apellis, which is currently conducting clinical trials with a pegylated form of this analogue (APL-2) in AMD and PNH using intravitreal and subcutaneous administration, respectively. Following positive results in two small phase Ib trials155,156 in which the drug rapidly normalized disease markers in newly diagnosed patients and in treated patients with suboptimal responses to eculizumab157, APL-2 received fast track designation for PNH by the FDA, and Apellis announced plans for phase III trials in late 2017 (REF. 157). The primary end point was also reached in a phase II study in patients with AMD and geographic atrophy, in whom a significant reduction in the rate of lesion growth was observed upon monthly intravitreal injection with APL-2 (REF. 158). In addition, APL-2 has entered phase II clinical trials for warm autoimmune haemolytic anaemia and cold agglutinin disease159. Another derivative, termed APL-9, which consists of a tridecapeptide linked to a polyethylene glycol (PEG) moiety via a dipeptide spacer, has been registered for phase I trials160, but details about the exact nature of this compound have not yet been disclosed.
Continuous development of the compstatin scaffold for increased target affinity, inhibitory efficacy and pharmaco kinetic properties resulted in the analogue Cp40, which showed efficacy in various preclinical models ranging from PNH, C3G and haemodialysis to periodontal disease153,161. With a target affinity in the sub-nanomolar range, almost 6,000-fold greater than that of the first-generation compstatin, and an extended plasma half-life of more than 50 hours, Cp40 is well suited for prolonged therapeutic administration153,161. The unique pharmacokinetic profile of Cp40 eliminates the need for further peptide modifications such as pegylation, thus eliminating the risk of related adverse events at high doses or PEG-specific immune responses over extended dosing periods. Furthermore, the pharmaco kinetic behaviour of Cp40 potentially enables fast recovery of complement activity in the case of adverse effects and may have implications for tissue distribution, dosing and administration in a disease-tailored context. As the production costs of unmodified Cp40 are expected to be lower than that of pegylated peptides, this agent has the potential to form the basis of an efficacious and affordable C3-targeted therapy. After receiving orphan drug designation for C3G and PNH162, a Cp40-based drug candidate (AMY-101, Amyndas) completed phase I trials in 2017 with development plans for these indications as well as for ABO-incompatible kidney transplantation and periodontal disease, among others163. Finally, fourth-generation compstatin analogues (for example, AMY-103) are being developed by Amyndas at preclinical stages.
Blocking effector functions
Therapeutic strategies that act upstream of C5 activation to prevent opsonization and generation of C3 effectors also influence C5 effectors by impairing the formation of C5 convertases. These comprehensive strategies might have advantages over C5-directed therapies. Situations exist, however, in which an even more effector-directed strategy could be considered.
Targeting C5a signaling
Targeting the C5a signalling axis could be particularly beneficial owing to the powerful chemotactic, cell-stimulating and pro-inflammatory functions of this anaphylatoxin164. Although C5a binds to two receptors of the G protein-coupled receptor (GPCR) family, C5a receptor 1 (C5aR1) primarily exerts the known effector functions (FIG. 3). Therapeutic antagonism of C5aR1 has long been considered a promising strategy, but initial clinical trials with C5aR1 antagonists often showed limited efficacy in selected indications, such as AMD. Following promising results in models of neurological diseases, including Alzheimer disease and Huntington disease32,165, ALS-205 (Alsonex), a derivative of the pioneering peptide-based C5aR1 antagonist PMX53 (REFS 164,166), has entered the clinical development arena.
In animal models, C5aR1 blockade ameliorated small vessel inflammation and ANCA-associated glomerulonephritis by reducing the activation of phagocytic cells (neutrophils) and the production of reactive oxygen species, two main effector pathways contributing to AAV pathology56,167. ChemoCentryx is developing an orally available small-molecule C5aR1 antagonist, avacopan, which has now reached phase III trials for the treatment of AAV168–170. Avacopan has received orphan drug designation for C3G and aHUS and is being developed for both indications171,172. In addition, open-label phase II trials of avacopan in IgA nephropathy have been completed, but the results have not yet been published and no further development has been announced173.
The preclinical drug candidate DF2593A (Dompé) reportedly binds to a distinct pocket on C5aR1 and acts as an allosteric modulator of the receptor174; inflammatory and neuropathic pain are listed as potential indications. Innate Pharma is currently focusing preclinical development efforts on an antibody (IPH-5401) to block C5aR1 activity175. Interestingly, IPH-5401 seems to be the only complement-targeted drug candidate with potential immuno-oncology-related indications. Owing to the complex yet powerful interplay of C5a with immunosuppressive pathways in the tumour microenvironment, C5aR1-modulating approaches could potentially be used in combination with checkpoint inhibitors (for example, antibody therapy targeting programmed cell death protein 1) to reverse tumour immunosuppression, reinstate antitumour immunity and enable more durable clinical responses6.
An alternative strategy to prevent C5a signalling is to neutralize C5a in the circulation. This approach is the concept behind the anti-C5a antibody IFX-1, which is being developed by InflaRx176. Although this agent was originally targeted towards sepsis and conditions related to SIRS, current clinical development programmes focus on AAV and hidradenitis suppurativa, a painful chronic inflammatory condition that affects hair follicles177. In addition to IFX-1, InflaRx lists a next-generation anti-C5a antibody with a higher degree of humanization and an altered pharmacokinetic profile (IFX-2) in its pipelines178.
Preventing membrane attack complex assembly
Inhibiting the C5a–C5aR1 axis does not affect MAC formation, but the first drug candidates aiming at preventing the assembly of this cell-damaging pore complex have reached preclinical stages. Upon activation of C5 by a convertase, the resulting C5b rapidly interacts with the plasma proteins C6 and C7 to form a tri-molecular complex that can insert into membranes (although the majority is inactivated in solution). Once tethered to the membrane, C5b–C7 recruits C8 and several copies of C9 to form the MAC179. Regenesance is developing an anti-C6 antibody, regenemab, and C6 antisense inhibitors as part of its preclinical programme. Regenemab is aimed at PNH as the initial indication, whereas the antisense strategy is aimed at multiple sclerosis.
Other approaches
The plethora of drug candidates listed above covers the range of officially communicated complement-targeted programmes at preclinical and clinical stages. However, a similar wealth of innovative approaches are being developed in the discovery programmes of pharmaceutical companies and in academic laboratories9. Efforts are also underway to engage complement activation and effector function through therapeutic antibodies in cancer and autoimmune diseases as well as in anti-infective therapy180. Complement-mediated cytotoxicity drives the molecular mechanism of rituximab and similar anti bodies, some of which are used to treat autoimmune kidney diseases such as LN53,181. Novel insights into antibody-mediated complement activation have led to technical advances, such as the development of hexabodies, which form activating antibody clusters and induce a stronger complement-mediated effector response against targeted cells than do conventional antibodies182,183. The clinical application of directed complement-mediated cytotoxi city strategies for therapeutic purposes, for example, to kill tumour cells in the setting of cancer immunotherapy, is expected to increase in the future.
Evolving challenges
Despite the current activity and gratifying progress in complement-targeted drug discovery, substantial challenges remain. The types and implications of the challenges encountered in the development of complement therapeutics have changed considerably in the past decade1,9,10,65. In the early days of complement drug discovery, barriers to progress were primarily related to theoretical considerations and extrapolation of potential adverse effects from the clinical presentations of patients with complement deficiencies. Aspects that were initially considered to be prohibitive for the success of the approach, such as pharmacokinetic challenges and difficulties in assessing drug safety, are now viewed in a more experience-based and, ultimately, more positive manner. The emerging concept is that pharmacokinetic and safety considerations have to be assessed in the right context and separately for each approach and indication9.
The complement system offers many potential drug targets (for example, serine proteases and GPCRs), most of which are readily and abundantly available in the circulation or on cell surfaces1. However, several peculiarities of the complement system require tailored drug design approaches. Unlike most other biological systems, complement is driven by protein–protein interactions and conformational conversions that are difficult to target using traditional medicinal chemistry approaches1,184. The biotherapeutic revolution, enabling the development of drugs based on engineered proteins, peptides and particularly antibodies, has therefore had a profound impact on complement drug discovery. Indeed, the approved inhibitors and most of the candidates in preclinical and clinical development (FIG. 4; TABLES 1–3) are considered to be biologics.
Administration and pharmacokinetics
Potential disadvantages of biologics typically relate to their pharmacokinetic properties, such as a short half-life and a lack of oral bioavailability that often necessitates parenteral administration, and the high plasma levels and comparatively rapid turnover of some complement proteins add to these challenges9,10. Parenteral administration is not, however, considered a limitation for several potential indications that require stationary treatment, such as transplantation and haemodialysis. Moreover, C1INH and many of the biologic drug candidates can be given subcutaneously with the potential for patient self-administration. For example, in non-human primates, repetitive subcutaneous administration of compstatin Cp40 every 12 hours was sufficient to maintain target-saturating drug concentrations185,186. In the case of filter-induced complement activation during a 4-hour haemodialysis session, a single bolus injection of Cp40 efficiently prevented C3 activation in a non-human primate model42,187. Local administration of a complement therapeutic may often circumvent pharmacokinetic issues observed during systemic use. For example, after intra venous administration, the AMD therapeutic lampalizumab is rapidly eliminated and plasma levels of FD increase, whereas the drug shows a largely extended residence and efficacy after direct administration into the eye as the target compartment129,131.
Therapeutic interference at the genetic level to reduce the production rather than to inhibit the activity of complement components is an alternative strategy to provide long-term control of complement activation. However, as illustrated by the limited efficacy of ALN-CC5 monotherapy for the prevention of haemolysis in patients with PNH99,100, blocking the hepatic synthesis of complement proteins may not always be sufficient, and complement produced locally by the tissue and invading immune cells should also be considered. Finally, the development of small-molecule candidates such as FB and FD inhibitors and C5aR1 antagonists brings the field closer to the first orally available complement drugs, which are highly anticipated for the treatment of chronic diseases.
Safety concerns
Given the role of complement in host defence, concerns about the potential adverse effects of therapeutically modulating the complement cascade need be taken seriously but should be assessed in the right context for each indication and drug. Initial discussions primarily relied on theoretical considerations and observations in patients with primary complement deficiencies. Indeed, an increased risk of severe and fulminant infections, especially with Neisseria meningitidis and a few species of encapsulated bacteria (such as Streptococcus pneumoniae), has been well documented in patients with complement deficiencies188,189. This susceptibility typically varies depending on the particular deficiency, with a lack of terminal pathway components mainly predisposing to neisserial infection, whereas C3 deficiency often leads to a broader range of susceptibilities188,189. Consistent with the concept that complement and other innate immune processes are particularly important during the period in which adaptive immunity is being shaped, the infectious risk in patients with complement deficiencies has been reported to gradually subside as they approach adulthood188–190. Alongside debates regarding whether the inherited absence of complement functions affects baseline immune responses in affected individuals, these considerations raise the question of whether the manifestations of primary complement deficiencies are an adequate indicator of the safety of complement therapeutics. Fortunately, data from clinical studies and therapeutic experience are now providing more reliable insights into the safety of various approaches.
The favourable safety data obtained during the growing clinical use of eculizumab has contributed to a new confidence in therapeutic complement inhibition. Owing to their increased risk of neisserial infection, patients starting eculizumab therapy have to be thoroughly vaccinated. Even after vaccination, susceptibility to this severe complication remains substantial, and patients have to be carefully monitored for signs of infection191. Similar measures will likely apply to other anti-C5 therapies, whereas additional vaccinations against encapsulated bacteria may need to be considered for drugs acting at the level of C3 activation. In the case of infectious complications during complement-targeting treatment, antibiotic therapy or treatment interruption can be considered.
Notably, even inhibition of C3 activation does not completely abrogate pathogen-targeted complement mechanisms; C4b opsonization of cells via the classical and lectin pathways can still occur, and a FD inhibitor still allowed substantial bactericidal activity against meningococci in the serum of vaccinated patients192,193. The minimum amount of complement activity that is required to confer substantial antimicrobial protection has not been determined; however, case reports in patients with C3 nephritic factor (an autoantibody that stabilizes the alternative pathway C3 convertase and therefore results in increased cleavage of C3) and no history of recurring infections suggest that C3 levels as low as 15% of the normal range are protective194,195. Similarly, studies in a Swedish family with a functional deficiency in C3 show that even complete absence of alternative-pathway-mediated C3 activation does not translate into a uniform clinical manifestation, including infection risk196. The period and extent of complement inhibition must therefore have a critical role in any safety assessment9. Short-term treatment, such as a single bolus of compstatin Cp40 at the beginning of a haemodialysis session, will not have a lasting effect on infection risk. Similarly, the local administration of complement drugs in a specific tissue or compartment might not notably affect systemic complement activity, as has been shown for lampalizumab129.
Overall, insight from clinical use and trial data suggest that aspects of microbial safety remain important but typically can be controlled to enable assessment of complement-targeting therapeutics in clinical trials. In adult patients with normal adaptive immune responses, the increased risk of infection seems to be limited and can be managed by prophylactic anti-infective measures such as vaccines. The residual risk has to be carefully weighed against the severity of the disease. Thus far, complement-targeted therapy is considered primarily in severe, debilitating disorders with limited or no treatment options, which may often justify taking additional measures to control a potentially increased risk of infection. In some cases, reducing complement-mediated inflammation and tissue damage may have a beneficial effect on containing pathogens, as suggested by proof-of-concept studies in periodontal disease197. Indeed, C3−/− mice showed a reversal of periodontitis-associated dysbiosis, and treatment of non-human primates with naturally occurring periodontal disease with the C3 inhibitor Cp40 markedly decreased inflammation and improved clinical parameters197,198.
The choice of the target level of treatment, that is, initiation, amplification or effector function, is expected to influence the overall risk profile of complement-targeted agents9,10,120,121. However, in the absence of long-term clinical data from inhibitors targeting C3 or other upstream and downstream components, a direct comparison of the safety profiles of these agents with that of eculizumab therapy is not possible. Experimental and preclinical data need to be considered with care but may provide valuable insight. For example, experimental studies employing models of neisserial infection in whole blood from immunized patients showed that specific blockade of the alternative pathway using FD inhibitors might increase neisserial infection risk to a lesser extent than anti-C5 therapy as the full range of classical-pathway-mediated effector functions remain intact, at least in patients with intact adaptive immunity192. Whether therapeutic blockade of individual complement proteins could lead to other complications observed in complement-deficient patients, such as an increased risk of developing SLE-type disorders in the absence of certain classical pathway components189, is even less explored. Several compounds targeting almost all stages of complement activation are currently being evaluated in clinical trials (TABLE 2), and the outcomes of these studies are expected to shed more light on these critical questions.
Patient and target selection
As the number of candidate drugs in clinical pipelines increases, the choice of the appropriate target and corresponding drug will become ever more important. C5 will remain an important point of intervention, but the assessment of drugs interfering at upstream, central and downstream levels of the complement cascade in clinical trials provides important insight into the potential benefits and limitations of each strategy. Approaches that target C3 activation might be particularly efficacious in complex disorders involving several initiation pathways and/or massive opsonization, such as C3G, whereas drugs that target the classical pathway might be more beneficial for indications driven by antibody recognition, such as autoimmune haemolytic anaemia. Even in aHUS, the comparison of distinct strategies targeting C5, C5aR1 or MASP2 currently in clinical trials, and future approaches acting at the level of C3 activation, may eventually produce alternative and tailored options for patients and provide important insight into disease processes (BOX 1). Ideally, a choice of alternative complement inhibitors is expected to benefit patients, might alleviate pressure on health-care systems and could make the strategy available to additional markets. Moreover, as was the case with eculizumab, the off-label use of complement drugs might suggest expansion into new indications.
The unique opportunity provided by multiple treatment options also bears challenges, particularly concerning selection of the patient cohort that might benefit most from a specific approach. A Phase II trial of lampalizumab (anti-FD) in AMD demonstrated that even in a disease with clear complement involvement, only a fraction of patients may fully benefit from a certain treatment130,131,199. In this trial, patients carrying polymorphisms in both FI and FH experienced a substantially greater reduction in the progression of retinal lesions than that seen in those who carried only the FH polymorphism131. On the basis of this insight, the FI polymorphism was considered an important biomarker and was included as an assessment parameter in phase III trials of the drug131–133. In view of the failure to reach the clinical end point in one of these trials (the Spectri study)132,134, the utility of the FI biomarker might be reinvestigated. Nevertheless, as the number of complement therapeutics increases, defining criteria and identifying biomarkers or genetic profiles for selecting patients to be enrolled in clinical trials will become increasingly important. Careful patient selection is key to enabling important benefits of complement therapeutics to be translated into positive results in clinical trials. Further research on the genetic and molecular factors that define complement-mediated disease will therefore remain critical. Similarly, an increasing need exists for sensitive, reproducible and comparable diagnostic tools to select patients and reliably monitor the success of therapeutic approaches65.
Conclusions
The field of complement-targeted drug discovery has undergone profound changes over the past 5 decades, with many twists, turns and near dead-ends. Similar to the complement system itself, the concept of inhibiting this host defence pathway is unique and challenging in many aspects. Rather than focusing on a single target and one distinct disease area, therapeutic complement inhibition should be considered a versatile platform technology that can be applied to a variety of distinct clinical conditions that are related to exposure of host defence pathways to foreign, damaged or altered cells. Although the renaissance of complement-targeted therapy was largely driven by a single drug (eculizumab) and a limited number of diseases (PNH, aHUS and AMD), the current interest in clinical candidates ranging from small molecules, peptides and oligonucleotides to engineered regulators and antibodies, and the diversity of rare and common disorders of the autoimmune, inflammatory, foreign body-induced and age-related spectrum, indicate a great sustainability of this therapeutic approach.
As complement therapeutics have been approved for the treatment of kidney diseases, awareness of the role of complement in these diseases has increased among nephrologists, and such awareness might lead to a further expansion of potential indications. Anti-C5 therapy has emerged as the gold-standard for aHUS treatment, and the field is moving closer to providing therapeutic options for patients with disorders such as AAV, C3G and LN and to protect against the adverse effects of haemodialysis and transplantation. In the future, the greatest challenge may be to identify the optimal targets, diagnostic tools and patient populations to translate promising preclinical data into clinical benefits. Close collaboration between nephrologists, complement specialists, drug discovery experts and providers of diagnostic services in the clinic and laboratory will therefore be essential for the success of treating renal diseases with complement-targeted drugs. A decade after the approval of eculizumab, complement drug discovery is approaching another watershed moment, and exciting developments are anticipated in the next 10 years.
Key points.
Technological advances and the clinical experience with eculizumab have led to a new confidence in therapeutic strategies that target the complement system
Several candidate drugs aimed at a wide range of targets and indications have shown promising efficacy in preclinical studies and early clinical trials, and are now moving into late-stage clinical development
The number of potential indications for complement therapeutics, including kidney disorders, is growing owing to new genetic and molecular insights as well as clinical data
Given the pathological heterogeneity between and even within indications for complement-specific therapies, careful patient stratification will be essential to pave the way towards new therapeutic options
The field of complement drug discovery has already overcome several hurdles, and the growing clinical experience will help to assess the remaining and emerging challenges
Acknowledgments
The authors' work was supported by grants from the US National Institutes of Health (AI068730, AI030040) and the US National Science Foundation (grant No. 1423304), from the Swiss National Science Foundation (grant 31003A_176104) and by funding from the European Community's Seventh Framework Programme, under grant agreement number 602699 (DIREKT).
Abbreviations
- Immunoediting
Complement-mediated immunoediting is a tightly regulated process by which complement tags (opsonizes) and subsequently spares or eliminates host cells, depending on the magnitude and quality of complement responses in distinct pathophysiological contexts. This process might involve other immune-related mechanisms and influences cell-specific or tissue-specific homeostatic and developmental pathways (for example, cell lineage commitment or turnover during development) as well as tissue regeneration and repair
- Synaptic pruning
The selective elimination of excess or unwanted synapses in the central nervous system during normal brain development and in age-related progressive neurological disorders. This process is mainly mediated by brain mononuclear phagocytic cells (that is, microglia) and reactive astrocytes
- Accommodation
In transplantation medicine, accommodation describes an acquired resistance of a transplanted organ to damage caused by complement, antibodies and other immune effector mechanisms
- Biosimilar
A biomedical product, such as a therapeutic antibody, that shares a high degree of structural and functional similarity with a product that is already clinically approved. Similar to small-molecule generic drugs, biosimilars are typically introduced once the patent protection of the original product expires
- Extravascular haemolysis
The process by which erythrocytes are eliminated through phagocytosis in the spleen, liver or bone marrow
- Pharmacodynamic breakthrough
A situation in which the inhibitory capacity of a complement-targeted therapeutic is exhausted owing to excessive complement activation, for example, as a result of acute infection or other triggers. Pharmacodynamic breakthrough might lead to a flare of disease symptoms despite continuous treatment
- Minibody
An engineered antibody fragment consisting of two single-chain variable fragments linked by a dimer of CH3 (and sometimes also CH2) domains of an antibody
- Aptamers
Short biopolymer sequences, typically of oligonucleotide (single-stranded RNA or DNA) or peptide origin, which are selected from a large, random sequence pool on the basis of their ability to bind a molecular target with high specificity
- Affibody
A small engineered protein based on the protein A scaffold from Staphylococcus aureus. Combinatorial variation of key residues in the scaffold enables the generation of affibody proteins that mimic antibodies by binding various targets with high affinity
- Macrocyclic peptide
Nonlinear peptides of natural or synthetic origin that form ring structures containing several peptide residues. Macrocyclic peptides often have distinct properties from their linear counterparts, and many are being developed as therapeutic inhibitors of protein–protein interactions
- Exosite
In an enzyme, an exosite is a functionally important area of the protein that is distinct and often distant from the active or catalytic site. Exosites might, for example, mediate the binding of substrates or cofactors and might constitute interesting targets for inhibitors of protein–protein interactions, such as antibodies
- Cytotopic drug
A drug that is targeted to and acts on a cell surface owing to a tethering moiety
- HexaBodies
Engineered therapeutic antibodies with strong complement-mediated cytotoxic potential due to their increased propensity to form hexameric clusters on target surfaces such as cancer cells
Footnotes
Author contributions: All authors researched the data for the article, contributed to discussions of the content, wrote the text and reviewed or edited the article before submission.
Competing interest statement: J.D.L. is the founder of Amyndas Pharmaceuticals, which is developing complement inhibitors (including third-generation compstatin analogues such as AMY-101). J.D.L. and D.R. are inventors of patents or patent applications that describe the use of complement inhibitors for therapeutic purposes, some of which are developed by Amyndas Pharmaceuticals. J.D.L. is also the inventor of the compstatin technology licensed to Apellis Pharmaceuticals (4(1MeW)7W, also known as POT-4 and APL-1) and pegylated derivatives such as APL-2. D.R. has received speaker's honoraria from Alexion and Novartis. The other authors declare no competing interests.
Publisher's note: Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
References
- 1.Ricklin D, Lambris JD. Complement-targeted therapeutics. Nat Biotechnol. 2007;25:1265–1275. doi: 10.1038/nbt1342. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Rother RP, Rollins SA, Mojcik CF, Brodsky RA, Bell L. Discovery and development of the complement inhibitor eculizumab for the treatment of paroxysmal nocturnal hemoglobinuria. Nat Biotechnol. 2007;25:1256–1264. doi: 10.1038/nbt1344. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Center for Drug Evaluation and Research. Application number: 125166, approval letter. Food and Drug Administration. 2007 https://www.accessdata.fda.gov/drugsatfda_docs/nda/2007/125166s0000_APPROV.
- 4.Center for Drug Evaluation and Research. Application number: 125166s172, approval letter. Food and Drug Administration. 2011 https://www.accessdata.fda.gov/drugsatfda_docs/bla/2011/125166Orig1s172-2.pdf.
- 5.Fakhouri F, Fremeaux-Bacchi V. Thrombotic microangiopathy: eculizumab for atypical haemolytic uraemic syndrome: what next? Nat Rev Nephrol. 2013;9:495–496. doi: 10.1038/nrneph.2013.150. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Reis ES, Mastellos DC, Ricklin D, Mantovani A, Lambris JD. Complement in cancer: untangling an intricate relationship. Nat Rev Immunol. 2017 doi: 10.1038/nri.2017.97. http://dx.doi.org/10.1038/nri.2017.97. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- 7.Ricklin D, Reis ES, Lambris JD. Complement in disease: a defence system turning offensive. Nat Rev Nephrol. 2016;12:383–401. doi: 10.1038/nrneph.2016.70. This Review provides detailed insight into the mechanisms that drive the involvement of complement in various disease processes, including in renal disorders. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Ricklin D, Hajishengallis G, Yang K, Lambris JD. Complement: a key system for immune surveillance and homeostasis. Nat Immunol. 2010;11:785–797. doi: 10.1038/ni.1923. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Ricklin D, Lambris JD. New milestones ahead in complement-targeted therapy. Semin Immunol. 2016;28:208–222. doi: 10.1016/j.smim.2016.06.001. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Morgan BP, Harris CL. Complement, a target for therapy in inflammatory and degenerative diseases. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2015;14:857–877. doi: 10.1038/nrd4657. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Ricklin D, Lambris JD. Preformed mediators of defense — gatekeepers enter the spotlight. Immunol Rev. 2016;274:5–8. doi: 10.1111/imr.12497. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Merle NS, Church SE, Fremeaux-Bacchi V, Roumenina LT. Complement system part I — molecular mechanisms of activation and regulation. Front Immunol. 2015;6:262. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2015.00262. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Blatt AZ, Pathan S, Ferreira VP. Properdin: a tightly regulated critical inflammatory modulator. Immunol Rev. 2016;274:172–190. doi: 10.1111/imr.12466. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Ekdahl KN, et al. Dangerous liaisons: complement, coagulation, and kallikrein/kinin cross-talk act as a linchpin in the events leading to thromboinflammation. Immunol Rev. 2016;274:245–269. doi: 10.1111/imr.12471. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Ricklin D, Reis ES, Mastellos DC, Gros P, Lambris JD. Complement component C3 — the “Swiss army knife” of innate immunity and host defense. Immunol Rev. 2016;274:33–58. doi: 10.1111/imr.12500. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Wang H, Ricklin D, Lambris JD. Complement-activation fragment C4a mediates effector functions by binding as untethered agonist to protease-activated receptor 1 and 4. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2017;114:10948–10953. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1707364114. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Roumenina LT, Rayes J, Frimat M, Fremeaux-Bacchi V. Endothelial cells: source, barrier, and target of defensive mediators. Immunol Rev. 2016;274:307–329. doi: 10.1111/imr.12479. This review describes the intricate relationship between humoral host defence systems, such as complement and coagulation, and endothelial cells, with a particular focus on aHUS and other diseases. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Merle NS, Noe R, Halbwachs-Mecarelli L, Fremeaux-Bacchi V, Roumenina LT. Complement system part II: role in immunity. Front Immunol. 2015;6:257. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2015.00257. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Martin M, Blom AM. Complement in removal of the dead — balancing inflammation. Immunol Rev. 2016;274:218–232. doi: 10.1111/imr.12462. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Scott D, Botto M. The paradoxical roles of C1q and C3 in autoimmunity. Immunobiology. 2016;221:719–725. doi: 10.1016/j.imbio.2015.05.001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Hong S, et al. Complement and microglia mediate early synapse loss in Alzheimer mouse models. Science. 2016;352:712–716. doi: 10.1126/science.aad8373. This seminal paper on synaptic pruning by the complement system provides an excellent example of the immunoediting role of complement in physiological and pathophysiological situations. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Stephan AH, Barres BA, Stevens B. The complement system: an unexpected role in synaptic pruning during development and disease. Annu Rev Neurosci. 2012;35:369–389. doi: 10.1146/annurev-neuro-061010-113810. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Lambris JD, Dobson NJ, Ross GD. Release of endogenous C3b inactivator from lymphocytes in response to triggering membrane receptors for beta 1H globulin. J Exp Med. 1980;152:1625–1644. doi: 10.1084/jem.152.6.1625. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Sundsmo JS. Expression of complement on human peripheral blood lymphocytes. Fed Proc. 1980;39:1200. This paper marks an important early milestone in the recognition of complement as a system with intracellular relevance. [Google Scholar]
- 25.Sundsmo JS. The leukocyte complement system. Fed Proc. 1982;41:3094–3098. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Freeley S, Kemper C, Le Friec G. The “ins and outs” of complement-driven immune responses. Immunol Rev. 2016;274:16–32. doi: 10.1111/imr.12472. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Schmidt CQ, Lambris JD, Ricklin D. Protection of host cells by complement regulators. Immunol Rev. 2016;274:152–171. doi: 10.1111/imr.12475. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Ekdahl KN, Soveri I, Hilborn J, Fellstrom B, Nilsson B. Cardiovascular disease in haemodialysis: role of the intravascular innate immune system. Nat Rev Nephrol. 2017;13:285–296. doi: 10.1038/nrneph.2017.17. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Sacks SH, Zhou W. The role of complement in the early immune response to transplantation. Nat Rev Immunol. 2012;12:431–442. doi: 10.1038/nri3225. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Ekdahl KN, et al. Innate immunity activation on biomaterial surfaces: a mechanistic model and coping strategies. Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2011;63:1042–1050. doi: 10.1016/j.addr.2011.06.012. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Harris CL, Heurich M, Rodriguez de Cordoba S, Morgan BP. The complotype: dictating risk for inflammation and infection. Trends Immunol. 2012;33:513–521. doi: 10.1016/j.it.2012.06.001. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Brennan FH, Lee JD, Ruitenberg MJ, Woodruff TM. Therapeutic targeting of complement to modify disease course and improve outcomes in neurological conditions. Semin Immunol. 2016;28:292–308. doi: 10.1016/j.smim.2016.03.015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Patzelt J, Verschoor A, Langer HF. Platelets and the complement cascade in atherosclerosis. Front Physiol. 2015;6:49. doi: 10.3389/fphys.2015.00049. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Thurman JM. Complement in kidney disease: core curriculum 2015. Am J Kidney Dis. 2015;65:156–168. doi: 10.1053/j.ajkd.2014.06.035. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Fakhouri F, Zuber J, Fremeaux-Bacchi V, Loirat C. Haemolytic uraemic syndrome. Lancet. 2017;390:681–696. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(17)30062-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Meri S. Complement activation in diseases presenting with thrombotic microangiopathy. Eur J Intern Med. 2013;24:496–502. doi: 10.1016/j.ejim.2013.05.009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Noris M, Mescia F, Remuzzi G. STEC-HUS, atypical HUS and TTP are all diseases of complement activation. Nat Rev Nephrol. 2012;8:622–633. doi: 10.1038/nrneph.2012.195. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.US National Library of Medicine. 2017 doi: 10.1080/15360280801989377. ClinicalTrials.gov https://clinicaltrials.gov/show/NCT02205541. [DOI] [PubMed]
- 39.Zipfel PF, et al. The role of complement in C3 glomerulopathy. Mol Immunol. 2015;67:21–30. doi: 10.1016/j.molimm.2015.03.012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Noris M, Remuzzi G. Glomerular diseases dependent on complement activation, including atypical hemolytic uremic syndrome, membranoproliferative glomerulonephritis, and C3 glomerulopathy: core curriculum 2015. Am J Kidney Dis. 2015;66:359–375. doi: 10.1053/j.ajkd.2015.03.040. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Nester CM, Smith RJ. Complement inhibition in C3 glomerulopathy. Semin Immunol. 2016;28:241–249. doi: 10.1016/j.smim.2016.06.002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.DeAngelis RA, Reis ES, Ricklin D, Lambris JD. Targeted complement inhibition as a promising strategy for preventing inflammatory complications in hemodialysis. Immunobiology. 2012;217:1097–1105. doi: 10.1016/j.imbio.2012.07.012. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Fremeaux-Bacchi V, Legendre CM. The emerging role of complement inhibitors in transplantation. Kidney Int. 2015;88:967–973. doi: 10.1038/ki.2015.253. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44.Damman J, et al. Systemic complement activation in deceased donors is associated with acute rejection after renal transplantation in the recipient. Transplantation. 2011;92:163–169. doi: 10.1097/TP.0b013e318222c9a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45.Stegall MD, Chedid MF, Cornell LD. The role of complement in antibody-mediated rejection in kidney transplantation. Nat Rev Nephrol. 2012;8:670–678. doi: 10.1038/nrneph.2012.212. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46.Cooper DK, Ekser B, Ramsoondar J, Phelps C, Ayares D. The role of genetically engineered pigs in xenotransplantation research. J Pathol. 2016;238:288–299. doi: 10.1002/path.4635. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47.Flyvbjerg A. The role of the complement system in diabetic nephropathy. Nat Rev Nephrol. 2017;13:311–318. doi: 10.1038/nrneph.2017.31. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 48.Fortpied J, Vertommen D, Van Schaftingen E. Binding of mannose-binding lectin to fructosamines: a potential link between hyperglycaemia and complement activation in diabetes. Diabetes Metab Res Rev. 2010;26:254–260. doi: 10.1002/dmrr.1079. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 49.Acosta J, et al. Molecular basis for a link between complement and the vascular complications of diabetes. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2000;97:5450–5455. doi: 10.1073/pnas.97.10.5450. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 50.Phieler J, Garcia-Martin R, Lambris JD, Chavakis T. The role of the complement system in metabolic organs and metabolic diseases. Semin Immunol. 2013;25:47–53. doi: 10.1016/j.smim.2013.04.003. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 51.Borne Y, et al. Complement C3 associates with incidence of diabetes, but no evidence of a causal relationship. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2017 doi: 10.1210/jc.2017-00948. http://dx.doi.org//10.1210/jc.2017-00948. [DOI] [PubMed]
- 52.Lai KN, et al. IgA nephropathy. Nat Rev Dis Primers. 2016;2:16001. doi: 10.1038/nrdp.2016.1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 53.Yu F, Haas M, Glassock R, Zhao MH. Redefining lupus nephritis: clinical implications of pathophysiologic subtypes. Nat Rev Nephrol. 2017;13:483–495. doi: 10.1038/nrneph.2017.85. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 54.Sciascia S, et al. Expanding the therapeutic options for renal involvement in lupus: eculizumab, available evidence. Rheumatol Int. 2017;37:1249–1255. doi: 10.1007/s00296-017-3686-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 55.Chen M, Jayne DRW, Zhao MH. Complement in ANCA-associated vasculitis: mechanisms and implications for management. Nat Rev Nephrol. 2017;13:359–367. doi: 10.1038/nrneph.2017.37. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 56.Schreiber A, et al. C5a receptor mediates neutrophil activation and ANCA-induced glomerulonephritis. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2009;20:289–298. doi: 10.1681/ASN.2008050497. Elucidation of the involvement of complement in the pathology of AAV in this study provided an important starting point for the therapeutic use of C5aR1 antagonists in this disorder. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 57.Frei Y, Lambris JD, Stockinger B. Generation of a monoclonal antibody to mouse C5 application in an ELISA assay for detection of anti-C5 antibodies. Mol Cell Probes. 1987;1:141–149. doi: 10.1016/0890-8508(87)90022-3. This paper describes the first monoclonal antibody against (murine) C5, thereby spearheading the development of therapeutic anti‑C5 antibodies such as eculizumab. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 58.Wurzner R, et al. Inhibition of terminal complement complex formation and cell lysis by monoclonal antibodies. Complement Inflamm. 1991;8:328–340. doi: 10.1159/000463204. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 59.Wang Y, Rollins SA, Madri JA, Matis LA. Anti-C5 monoclonal antibody therapy prevents collagen-induced arthritis and ameliorates established disease. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 1995;92:8955–8959. doi: 10.1073/pnas.92.19.8955. This seminal proof‑of‑concept study demonstrates the therapeutic benefit of anti‑C5 therapy. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 60.Wang H, et al. Inhibition of terminal complement components in presensitized transplant recipients prevents antibody-mediated rejection leading to long-term graft survival and accommodation. J Immunol. 2007;179:4451–4463. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.179.7.4451. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 61.Rinder CS, et al. Blockade of C5a and C5b-9 generation inhibits leukocyte and platelet activation during extracorporeal circulation. J Clin Invest. 1995;96:1564–1572. doi: 10.1172/JCI118195. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 62.Risitano AM, Marotta S. Therapeutic complement inhibition in complement-mediated hemolytic anemias: past, present and future. Semin Immunol. 2016;28:223–240. doi: 10.1016/j.smim.2016.05.001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 63.Hillmen P, et al. Long-term safety and efficacy of sustained eculizumab treatment in patients with paroxysmal nocturnal haemoglobinuria. Br J Haematol. 2013;162:62–73. doi: 10.1111/bjh.12347. This study contributes to the regained confidence in complement targeting strategies by providing further evidence of a beneficial safety profile of therapeutic complement inhibition at the level of C5 in a chronic disease setting. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 64.Licht C, et al. Efficacy and safety of eculizumab in atypical hemolytic uremic syndrome from 2-year extensions of phase 2 studies. Kidney Int. 2015;87:1061–1073. doi: 10.1038/ki.2014.423. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 65.Ricklin D, Barratt-Due A, Mollnes TE. Complement in clinical medicine: clinical trials, case reports and therapy monitoring. Mol Immunol. 2017;89:10–21. doi: 10.1016/j.molimm.2017.05.013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 66.Alexion Pharmaceuticals. FDA approves Soliris® (eculizumab) for the treatment of patients with generalized myasthenia gravis (GMG) Alexion Pharmaceuticals. 2017 http://news.alexion.com/press-release/product-news/fda-approves-soliris-eculizumab-treatment-patients-generalized-myasthenia.
- 67.Alexion Pharmaceuticals. Alexion reports second quarter 2017 results. Alexion Pharmaceuticals. 2017 http://news.alexionpharma.com/press-release/financial-news/alexion-reports-second-quarter-2017-results.
- 68.Alexion Pharmaceuticals. New data from phase 3 REGAIN study of eculizumab (Soliris®) in patients with refractory generalized myasthenia gravis (GMG) presented at ICNMD annual congress. Alexion Pharmaceuticals. 2016 http://news.alexionpharma.com/press-release/product-news/new-data-phase-3-regain-study-eculizumab-soliris-patients-refractory-gene.
- 69.US National Library of Medicine. 2017 doi: 10.1080/15360280801989377. ClinicalTrials.gov https://clinicaltrials.gov/show/NCT01997229. [DOI] [PubMed]
- 70.Coyle D, Cheung MC, Evans GA. Opportunity cost of funding drugs for rare diseases: the cost-effectiveness of eculizumab in paroxysmal nocturnal hemoglobinuria. Med Decis Making. 2014;34:1016–1029. doi: 10.1177/0272989X14539731. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 71.Amgen. A randomized, double-blind, single-dose, 3-arm, parallel group study to determine the pharmacokinetic similarity of ABP 959 and eculizumab (Soliris®) in healthy male subjects. Australian New Zealand Clinical Trials Registry. 2016 https://www.anzctr.org.au/Trial/Registration/TrialReview.aspx?id=369851.
- 72.Nishimura J, et al. Genetic variants in C5 and poor response to eculizumab. N Engl J Med. 2014;370:632–639. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa1311084. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 73.Lin Z, et al. Complement C3dg-mediated erythrophagocytosis: implications for paroxysmal nocturnal hemoglobinuria. Blood. 2015;126:891–894. doi: 10.1182/blood-2015-02-625871. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 74.Harder MJ, et al. Incomplete inhibition by eculizumab: mechanistic evidence for residual C5 activity during strong complement activation. Blood. 2017;129:970–980. doi: 10.1182/blood-2016-08-732800. This landmark study provides the first mechanistic insight into the clinical observation that anti-C5 therapies can be exhausted under conditions of extensive complement activation, leading to pharmacodynamic breakthrough. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 75.US National Library of Medicine. 2015 doi: 10.1080/15360280801989377. ClinicalTrials.gov https://clinicaltrials.gov/show/NCT02534909. [DOI] [PubMed]
- 76.US National Library of Medicine. 2017 doi: 10.1080/15360280801989377. ClinicalTrials.gov https://clinicaltrials.gov/show/NCT02763644. [DOI] [PubMed]
- 77.US National Library of Medicine. 2017 doi: 10.1080/15360280801989377. ClinicalTrials.gov https://clinicaltrials.gov/show/NCT01526889. [DOI] [PubMed]
- 78.US National Library of Medicine. 2017 doi: 10.1080/15360280801989377. ClinicalTrials.gov https://clinicaltrials.gov/show/NCT02515942. [DOI] [PubMed]
- 79.Fukuzawa T, et al. Long lasting neutralization of C5 by SKY59, a novel recycling antibody, is a potential therapy for complement-mediated diseases. Sci Rep. 2017;7:1080. doi: 10.1038/s41598-017-01087-7. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 80.Roopenian DC, Akilesh S. FcRn: the neonatal Fc receptor comes of age. Nat Rev Immunol. 2007;7:715–725. doi: 10.1038/nri2155. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 81.Regeneron. Regeneron reports second quarter 2017 financial and operating results. Regeneron Pharmaceuticals. 2017 http://newsroom.regeneron.com/releasedetail.cfm?ReleaseID=1035825.
- 82.US National Library of Medicine. 2017 doi: 10.1080/15360280801989377. ClinicalTrials.gov https://clinicaltrials.gov/show/NCT03115996. [DOI] [PubMed]
- 83.Adienne Pharma & Biotech. MUBODINA. Adienne. 2017 http://www.adienne.com/rnd/molecules-in-development/mubodina.
- 84.Ophthotech. Ophthotech expands focus with development for ophthalmic orphan diseases. Ophthotech. 2017 http://investors.ophthotech.com/releasedetail.cfm?ReleaseID=1034437.
- 85.US National Library of Medicine. 2017 doi: 10.1080/15360280801989377. ClinicalTrials.gov https://clinicaltrials.gov/show/NCT02397954. [DOI] [PubMed]
- 86.US National Library of Medicine. 2017 doi: 10.1080/15360280801989377. ClinicalTrials.gov https://clinicaltrials.gov/show/NCT02686658. [DOI] [PubMed]
- 87.Nunn MA, et al. Complement inhibitor of C5 activation from the soft tick Ornithodoros moubata. J Immunol. 2005;174:2084–2091. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.174.4.2084. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 88.Akari Therapeutics. Akari therapeutics demonstrates positive response with coversin in ongoing phase 2 PNH trial and in additional clinical targets. Akari Therapeutics. 2017 http://akaritx.com/wp-content/uploads/2017/04/2017-04-24-Akari-announces-positive-Interim-Data-From-Phase-II-PNH-and-Corporate-Update.pdf.
- 89.US National Library of Medicine. 2017 doi: 10.1080/15360280801989377. ClinicalTrials.gov https://clinicaltrials.gov/show/NCT02591862. [DOI] [PubMed]
- 90.Kuhn N, Schmidt CQ, Schlapschy M, Skerra A. PASylated coversin, a C5-specific complement inhibitor with extended pharmacokinetics, shows enhanced anti-hemolytic activity in vitro. Bioconjug Chem. 2016;27:2359–2371. doi: 10.1021/acs.bioconjchem.6b00369. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 91.Berglund MM, Stromberg P. The clinical potential of affibody-based inhibitors of C5 for therapeutic complement disruption. Expert Rev Proteomics. 2016;13:241–243. doi: 10.1586/14789450.2016.1148604. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 92.US National Library of Medicine. 2015 doi: 10.1080/15360280801989377. ClinicalTrials.gov https://clinicaltrials.gov/show/NCT02083666. [DOI] [PubMed]
- 93.Ricardo A, et al. Preclinical evaluation of RA101495, a potent cyclic peptide inhibitor of C5 for the treatment of paroxysmal nocturnal hemoglobinuria [abstract] Blood. 2015;126:939. [Google Scholar]
- 94.Pharma Ra. Ra pharmaceuticals receives orphan drug designation from the U. S. FDA for RA101495 for the treatment of paroxysmal nocturnal hemoglobinuria. Ra Pharma. 2017;2290097 http://ir.rapharma.com/phoenix.zhtml?c=254447&p=irol-newsArticle&ID= [Google Scholar]
- 95.US National Library of Medicine. 2017 doi: 10.1080/15360280801989377. ClinicalTrials.gov https://clinicaltrials.gov/show/NCT03078582. [DOI] [PubMed]
- 96.US National Library of Medicine. 2017 doi: 10.1080/15360280801989377. ClinicalTrials.gov https://clinicaltrials.gov/show/NCT03030183. [DOI] [PubMed]
- 97.Keshari RS, et al. Inhibition of complement C5 protects against organ failure and reduces mortality in a baboon model of Escherichia coli sepsis. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2017 doi: 10.1073/pnas.1706818114. http://dx.doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1706818114. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- 98.US National Library of Medicine. 2017 doi: 10.1080/15360280801989377. ClinicalTrials.gov https://clinicaltrials.gov/show/NCT02352493. [DOI] [PubMed]
- 99.Alnylam Pharmaceuticals. Alnylam reports initial ALN-CC5 results in patients with paroxysmal nocturnal hemoglobinuria (PNH) from ongoing phase 1/2 study. Alnylam Pharmaceuticals. 2016 http://investors.alnylam.com/releasedetail.cfm?ReleaseID=975341.
- 100.Hill A, et al. A subcutaneously administered investigational RNAi therapeutic (ALN-CC5) targeting complement C5 for treatment of PNH and complement-mediated diseases: preliminary phase 1/2 study results in patients with PNH. Blood. 2016;128:3891. [Google Scholar]
- 101.Alnylam Pharmaceuticals. Alnylam initiates phase 2 clinical study of cemdisiran (ALN-CC5) in patients with atypical hemolytic-uremic syndrome (aHUS) Alnylam Pharmaceuticals. 2017 http://investors.alnylam.com/releasedetail.cfm?ReleaseID=1041647.
- 102.US National Library of Medicine. 2017 doi: 10.1080/15360280801989377. ClinicalTrials.gov https://clinicaltrials.gov/show/NCT02949128. [DOI] [PubMed]
- 103.US National Library of Medicine. 2017 doi: 10.1080/15360280801989377. ClinicalTrials.gov https://clinicaltrials.gov/show/NCT02946463. [DOI] [PubMed]
- 104.US National Library of Medicine. 2017 doi: 10.1080/15360280801989377. ClinicalTrials.gov https://clinicaltrials.gov/show/NCT03056040. [DOI] [PubMed]
- 105.Sheridan D, et al. Design and preclinical characterization of ALXN1210: a next generation anti-C5 monoclonal antibody with improved pharmacokinetics and duration of action. Immunobiology. 2016;221:1158. [Google Scholar]
- 106.Bomback AS, et al. Eculizumab for dense deposit disease and C3 glomerulonephritis. Clin J Am Soc Nephrol. 2012;7:748–756. doi: 10.2215/CJN.12901211. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 107.Zeerleder S. C1-inhibitor: more than a serine protease inhibitor. Semin Thromb Hemost. 2011;37:362–374. doi: 10.1055/s-0031-1276585. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 108.Nielsen EW, et al. Effect of supraphysiologic levels of C1-inhibitor on the classical, lectin and alternative pathways of complement. Mol Immunol. 2007;44:1819–1826. doi: 10.1016/j.molimm.2006.10.003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 109.Chakradhar S. The road less traveled: start-ups invest in novel approaches against neurodegeneration. Nat Med. 2016;22:11–13. doi: 10.1038/nm0116-11. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 110.US National Library of Medicine. 2017 doi: 10.1080/15360280801989377. ClinicalTrials.gov https://clinicaltrials.gov/show/NCT02502903. [DOI] [PubMed]
- 111.Bioverativ. Bioverativ completes acquisition of True North Therapeutics. Bioverativ. 2017 https://www.bioverativ.com/newsroom/bioverativ-completes-acquisition-of-true-north-therapeutics.aspx.
- 112.Fujita T. Evolution of the lectin-complement pathway and its role in innate immunity. Nat Rev Immunol. 2002;2:346–353. doi: 10.1038/nri800. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 113.Garred P, et al. A journey through the lectin pathway of complement-MBL and beyond. Immunol Rev. 2016;274:74–97. doi: 10.1111/imr.12468. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 114.Schwaeble WJ, et al. Targeting of mannan-binding lectin-associated serine protease-2 confers protection from myocardial and gastrointestinal ischemia/reperfusion injury. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2011;108:7523–7528. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1101748108. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 115.Farrar CA, Zhou W, Sacks SH. Role of the lectin complement pathway in kidney transplantation. Immunobiology. 2016;221:1068–1072. doi: 10.1016/j.imbio.2016.05.004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 116.US National Library of Medicine. 2017 doi: 10.1080/15360280801989377. ClinicalTrials.gov https://clinicaltrials.gov/show/NCT02682407. [DOI] [PubMed]
- 117.US National Library of Medicine. 2017 doi: 10.1080/15360280801989377. ClinicalTrials.gov https://clinicaltrials.gov/show/NCT03205995. [DOI] [PubMed]
- 118.Omeros. FDA grants orphan drug designation to Omeros' OMS721 for treatment of IgA nephropathy. Omeros. 2017 http://investor.omeros.com/phoenix.zhtml?c=219263&p=irol-newsArticle_Print&ID=2292002.
- 119.Boross P, Yildiz C, Simons PJ, Boon L, Hack CE. A monoclonal antibody against complement C2, as a novel complement inhibitor. Altant Conference 2016: Innate Host Defence Utrecht, Netherlands. 2016 [Google Scholar]
- 120.Ricklin D, Lambris JD. Therapeutic control of complement activation at the level of the central component C3. Immunobiology. 2016;221:740–746. doi: 10.1016/j.imbio.2015.06.012. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 121.Mastellos DC, Reis ES, Ricklin D, Smith RJ, Lambris JD. Complement C3-targeted therapy: replacing long-held assertions with evidence-based discovery. Trends Immunol. 2017;38:383–394. doi: 10.1016/j.it.2017.03.003. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 122.Maibaum J, et al. Small-molecule factor D inhibitors targeting the alternative complement pathway. Nat Chem Biol. 2016;12:1105–1110. doi: 10.1038/nchembio.2208. This paper describes the successful development of small molecule inhibitors of FD. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 123.Vulpetti A, et al. Structure-based library design and fragment screening for the identification of reversible complement factor D protease inhibitors. J Med Chem. 2017;60:1946–1958. doi: 10.1021/acs.jmedchem.6b01684. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 124.Yuan X, et al. Small-molecule factor D inhibitors selectively block the alternative pathway of complement in paroxysmal nocturnal hemoglobinuria and atypical hemolytic uremic syndrome. Haematologica. 2017;102:466–475. doi: 10.3324/haematol.2016.153312. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 125.US National Library of Medicine. 2017 doi: 10.1080/15360280801989377. ClinicalTrials.gov https://clinicaltrials.gov/show/NCT03053102. [DOI] [PubMed]
- 126.Achillion Pharmaceuticals. Achillion reports second quarter 2017 financial results and proof-of-concept with a first-in-class, oral factor D inhibitor. Achillion Pharmaceuticals. 2017 http://ir.achillion.com/releasedetail.cfm?ReleaseID=1036547.
- 127.Forneris F, et al. Structures of C3b in complex with factors B and D give insight into complement convertase formation. Science. 2010;330:1816–1820. doi: 10.1126/science.1195821. This seminal study provides structural insight into the formation and functional determinants of the alternative pathway C3 convertase and facilitated the development of convertase-targeted therapeutics. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 128.Katschke KJ., Jr Inhibiting alternative pathway complement activation by targeting the factor D exosite. J Biol Chem. 2012;287:12886–12892. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M112.345082. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 129.Loyet KM, et al. Complement inhibition in cynomolgus monkeys by anti-factor d antigen-binding fragment for the treatment of an advanced form of dry age-related macular degeneration. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2014;351:527–537. doi: 10.1124/jpet.114.215921. In this important preclinical study of the anti-FD antibody lampalizumab, the researchers elucidate important aspects of local and systemic administration of a complement inhibitor considered for AMD treatment. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 130.US National Library of Medicine. 2017 doi: 10.1080/15360280801989377. ClinicalTrials.gov https://clinicaltrials.gov/show/NCT02288559. [DOI] [PubMed]
- 131.Yaspan BL, et al. Targeting factor D of the alternative complement pathway reduces geographic atrophy progression secondary to age-related macular degeneration. Sci Transl Med. 2017;9:eaaf1443. doi: 10.1126/scitranslmed.aaf1443. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 132.US National Library of Medicine. 2017 doi: 10.1080/15360280801989377. ClinicalTrials.gov https://clinicaltrials.gov/show/NCT02247531. [DOI] [PubMed]
- 133.US National Library of Medicine. 2017 doi: 10.1080/15360280801989377. ClinicalTrials.gov https://clinicaltrials.gov/show/NCT02247479. [DOI] [PubMed]
- 134.Genentech. Genentech provides update on first lampalizumab phase III study for geographic atrophy, an advanced form of age-related macular degeneration. Genentech. 2017 https://www.gene.com/media/press-releases/14681/2017-09-08/genentech-provides-update-on-first-lampa.
- 135.Irmscher S, et al. Kallikrein represents an independent complement activator. Mol Immunol. 2017;89:140–140. [Google Scholar]
- 136.Zhang YZ, et al. Activation of alternative complement pathway without complement factor D. Mol Immunol. 2017;89:173–173. [Google Scholar]
- 137.Omeros. Single dose of Omeros' lead MASP-3 inhibitor OMS906 shows multi-week blockade of the alternative pathway. Omeros. 2016 http://investor.omeros.com/phoenix.zhtml?c=219263&p=irol-newsArticle_Print&ID=2221301.
- 138.Dobo J, et al. MASP-3 is the exclusive pro-factor D activator in resting blood: the lectin and the alternative complement pathways are fundamentally linked. Sci Rep. 2016;6:31877. doi: 10.1038/srep31877. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 139.Sekine H, Takahashi M, Iwaki D, Fujita T. The role of MASP-1/3 in complement activation. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2013;735:41–53. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4614-4118-2_3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 140.McCaleb M, et al. Systemic pharmacodynamic efficacy of a complement factor B antisense oligonucleotide in preclinical and phase 1 clinical studies. Invest Ophthalmol Visual Sci. 2017;58:1952. [Google Scholar]
- 141.Isis Pharmaceuticals. A masked, placebo-controlled, dose-escalation, phase 1 study to assess the safety, tolerability, pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of single doses of ISIS 696844 administered subcutaneously to healthy volunteers. National Health Service. 2015 https://www.hra.nhs.uk/planning-and-improving-research/application-summaries/research-summaries/phase-1-sadmad-study-with-subcutaneous-isis-696844/
- 142.Ionis Pharmaceuticals. Ionis to independently advance inotersen and IONIS-FB-L Rx. Ionis Pharmaceuticals. 2017 http://ir.ionispharma.com/news-releases/news-release-details/ionis-independently-advance-inotersen-and-ionis-fb-l-rx.
- 143.Lazar HL, et al. Beneficial effects of complement inhibition with soluble complement receptor 1 (TP10) during cardiac surgery: is there a gender difference? Circulation. 2007;116:183–188. doi: 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.106.677914. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 144.Zhang Y, et al. Soluble CR1 therapy improves complement regulation in C3 glomerulopathy. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2013;24:1820–1829. doi: 10.1681/ASN.2013010045. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 145.Risitano AM, et al. The complement receptor 2/factor H fusion protein TT30 protects paroxysmal nocturnal hemoglobinuria erythrocytes from complement-mediated hemolysis and C3 fragment. Blood. 2012;119:6307–6316. doi: 10.1182/blood-2011-12-398792. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 146.Smith GP, Smith RA. Membrane-targeted complement inhibitors. Mol Immunol. 2001;38:249–255. doi: 10.1016/s0161-5890(01)00047-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 147.Kassimatis T, et al. A double-blind randomised controlled investigation into the efficacy of Mirococept (APT070) for preventing ischaemia reperfusion injury in the kidney allograft (EMPIRIKAL): study protocol for a randomised controlled trial. Trials. 2017;18:255. doi: 10.1186/s13063-017-1972-x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 148.King's College London. EMPIRIKAL — a double blind randomized controlled investigation into the efficacy of Mirococept (APT070) for preventing ischaemia-reperfusion injury in the kidney allograft (EMPIRIKAL) National Health Service. 2013 doi: 10.1186/s13063-017-1972-x. https://www.hra.nhs.uk/planning-and-improving-research/application-summaries/research-summaries/empirikal/ [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- 149.Schmidt CQ, et al. Rational engineering of a minimized immune inhibitor with unique triple-targeting properties. J Immunol. 2013;190:5712–5721. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.1203548. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 150.Nilsson PH, et al. Autoregulation of thromboinflammation on biomaterial surfaces by a multicomponent therapeutic coating. Biomaterials. 2013;34:985–994. doi: 10.1016/j.biomaterials.2012.10.040. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 151.Wu YQ, et al. Protection of nonself surfaces from complement attack by factor H-binding peptides: implications for therapeutic medicine. J Immunol. 2011;186:4269–4277. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.1003802. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 152.Sahu A, Kay BK, Lambris JD. Inhibition of human complement by a C3-binding peptide isolated from a phage-displayed random peptide library. J Immunol. 1996;157:884–891. This paper provides the first description of C3 inhibitors of the compstatin family, of which several derivatives are currently in clinical development and evaluation. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 153.Mastellos DC, et al. Compstatin: a C3-targeted complement inhibitor reaching its prime for bedside intervention. Eur J Clin Invest. 2015;45:423–440. doi: 10.1111/eci.12419. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 154.Katragadda M, Magotti P, Sfyroera G, Lambris JD. Hydrophobic effect and hydrogen bonds account for the improved activity of a complement inhibitor, compstatin. J Med Chem. 2006;49:4616–4622. doi: 10.1021/jm0603419. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 155.US National Library of Medicine. 2017 doi: 10.1080/15360280801989377. ClinicalTrials.gov https://clinicaltrials.gov/show/NCT02264639. [DOI] [PubMed]
- 156.US National Library of Medicine. 2017 doi: 10.1080/15360280801989377. ClinicalTrials.gov https://clinicaltrials.gov/show/NCT02588833. [DOI] [PubMed]
- 157.Apellis Pharmaceuticals. Positive data from APL-2 studies show rapid and durable improvements in LDH and hemoglobin levels in PNH. Apellis Pharmaceuticals. 2017 http://www.apellis.com/pdfs/APL-2PressReleaseClinicalUpdateFINALv5-170629.pdf.
- 158.Apellis Pharmaceuticals. Apellis pharmaceuticals announces that APL-2 met its primary endpoint in a phase 2 study in patients with geographic atrophy, an advanced form of age-related macular degeneration. Apellis Pharmaceuticals. 2017 http://www.apellis.com/pdfs/PressRelease FILLY 12 Month Results FINAL FINAL 170823.pdf.
- 159.US National Library of Medicine. 2017 doi: 10.1080/15360280801989377. ClinicalTrials.gov https://clinicaltrials.gov/show/NCT03226678. [DOI] [PubMed]
- 160.Apellis Pharmaceuticals. Phase 1, double-blind, randomized, placebo-controlled, single ascending dose study of subcutaneous APL-9 in healthy volunteers. Apellis Pharmaceuticals. 2017 https://www.anzctr.org.au/Trial/Registration/TrialReview.aspx?id=370988.
- 161.Qu H, et al. New analogs of the clinical complement inhibitor compstatin with subnanomolar affinity and enhanced pharmacokinetic properties. Immunobiology. 2013;218:496–505. doi: 10.1016/j.imbio.2012.06.003. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 162.Amyndas Pharmaceuticals. Amyndas' lead candidate AMY-101 receives orphan drug status from the FDA and the EMA for the treatment of C3 glomerulopathy. FiercePharma. 2016 http://www.fiercepharma.com/press-releases/amyndas-lead-candidate-amy-101-receives-orphan-drug-status-fda-and-ema-trea.
- 163.US National Library of Medicine. 2017 doi: 10.1080/15360280801989377. ClinicalTrials.gov https://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT03316521. [DOI] [PubMed]
- 164.Hawksworth OA, Li XX, Coulthard LG, Wolvetang EJ, Woodruff TM. New concepts on the therapeutic control of complement anaphylatoxin receptors. Mol Immunol. 2017;89:36–43. doi: 10.1016/j.molimm.2017.05.015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 165.Cukier-Meisner E. Complementary ALS play. Biocentury. 2017 https://www.biocentury.com/biocentury/emerging-company-profile/2017-07-11/why-alsonex-targeting-complement-system-c5a-treat-als.
- 166.Finch AM, et al. Low-molecular-weight peptidic and cyclic antagonists of the receptor for the complement factor C5a. J Med Chem. 1999;42:1965–1974. doi: 10.1021/jm9806594. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 167.Xiao H, et al. C5a receptor (CD88) blockade protects against MPO-ANCA GN. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2014;25:225–231. doi: 10.1681/ASN.2013020143. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 168.Jayne DR, et al. Randomized trial of C5a receptor inhibitor Avacopan in ANCA-associated vasculitis. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2017;28:2756–2767. doi: 10.1681/ASN.2016111179. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 169.US National Library of Medicine. 2017 doi: 10.1080/15360280801989377. ClinicalTrials.gov https://clinicaltrials.gov/show/NCT02994927. [DOI] [PubMed]
- 170.US National Library of Medicine. 2016 doi: 10.1080/15360280801989377. ClinicalTrials.gov https://clinicaltrials.gov/show/NCT02222155. [DOI] [PubMed]
- 171.ChemoCentryx. ChemoCentryx reports second quarter 2017 financial results and recent highlights. ChemoCentryx. 2017 http://ir.chemocentryx.com/releasedetail.cfm?ReleaseID=1036588.
- 172.US National Library of Medicine. 2017 doi: 10.1080/15360280801989377. ClinicalTrials.gov https://clinicaltrials.gov/show/NCT02464891. [DOI] [PubMed]
- 173.US National Library of Medicine. 2016 doi: 10.1080/15360280801989377. ClinicalTrials.gov https://clinicaltrials.gov/show/NCT02384317. [DOI] [PubMed]
- 174.Moriconi A, et al. Targeting the minor pocket of C5aR for the rational design of an oral allosteric inhibitor for inflammatory and neuropathic pain relief. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2014;111:16937–16942. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1417365111. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 175.Innate Pharma. Innate Pharma strengthens its proprietary pipeline with the acquisition of anti-C5aR, a first-in-class clinical-stage antibody, from novo Nordisk A/S. Innate Pharma. 2017 http://www.innate-pharma.com/en/news-events/press-releases/innate-pharma-strengthens-its-proprietary-pipeline-acquisition-anti-c5ar-first-class-clinical-stage-antibodyfrom-novo-nordisk/s.
- 176.Riedemann NC, et al. Controlling the anaphylatoxin C5a in diseases requires a specifically targeted inhibition. Clin Immunol. 2017;180:25–32. doi: 10.1016/j.clim.2017.03.012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 177.InflaRx. InflaRx Reports Topline Phase IIa Clinical Results of IFX-1 for the Treatment of Hidradenitis Suppurativa. InflaRx. 2017 http://www.inflarx.de/Home/Investors/Press-Releases/09-2017--InflaRx-Reports-Topline-Phase-IIa-Clinical-Results-of-IFX-1-for-the-Treatment-of-Hidradenitis-Suppurativa0.html.
- 178.InflaRx. The InflaRx technology. InflaRx. 2017 http://www.inflarx.de/Home/Research---Development/Technology.html.
- 179.Morgan BP. The membrane attack complex as an inflammatory trigger. Immunobiology. 2016;221:747–751. doi: 10.1016/j.imbio.2015.04.006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 180.Taylor RP, Lindorfer MA. Cytotoxic mechanisms of immunotherapy: harnessing complement in the action of anti-tumor monoclonal antibodies. Semin Immunol. 2016;28:309–316. doi: 10.1016/j.smim.2016.03.003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 181.Cassia M, Alberici F, Gallieni M, Jayne D. Lupus nephritis and B-cell targeting therapy. Expert Rev Clin Immunol. 2017;13:951–962. doi: 10.1080/1744666X.2017.1366855. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 182.de Jong RN, et al. A novel platform for the potentiation of therapeutic antibodies based on antigen-dependent formation of IgG hexamers at the cell surface. PLoS Biol. 2016;14:e1002344. doi: 10.1371/journal.pbio.1002344. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 183.Diebolder CA, et al. Complement is activated by IgG hexamers assembled at the cell surface. Science. 2014;343:1260–1263. doi: 10.1126/science.1248943. In this landmark paper, the researchers describe the structural base of antibody recognition by complement on cell surfaces; their findings have important implications for the design of therapeutic antibodies that induce complement-mediated cytotoxicity. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 184.Gros P, Milder FJ, Janssen BJ. Complement driven by conformational changes. Nat Rev Immunol. 2008;8:48–58. doi: 10.1038/nri2231. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 185.Primikyri A, et al. Method development and validation for the quantitation of the complement inhibitor Cp40 in human and cynomolgus monkey plasma by UPLC-ESI-MS. J Chromatogr B Analyt Technol Biomed Life Sci. 2017;1041–1042:19–26. doi: 10.1016/j.jchromb.2016.12.004. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 186.Risitano AM, et al. Peptide inhibitors of C3 activation as a novel strategy of complement inhibition for the treatment of paroxysmal nocturnal hemoglobinuria. Blood. 2014;123:2094–2101. doi: 10.1182/blood-2013-11-536573. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 187.Reis ES, et al. Therapeutic C3 inhibitor Cp40 abrogates complement activation induced by modern hemodialysis filters. Immunobiology. 2015;220:476–482. doi: 10.1016/j.imbio.2014.10.026. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 188.Audemard-Verger A, et al. Infections revealing complement deficiency in adults: a french nationwide study enrolling 41 patients. Medicine (Baltimore) 2016;95:e3548. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000003548. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 189.Reis ES, Falcao DA, Isaac L. Clinical aspects and molecular basis of primary deficiencies of complement component C3 and its regulatory proteins factor I and factor H. Scand J Immunol. 2006;63:155–168. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3083.2006.01729.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 190.Lachmann PJ, Smith RA. Taking complement to the clinic — has the time finally come? Scand J Immunol. 2009;69:471–478. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3083.2009.02258.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 191.McNamara LA, et al. High risk for invasive meningococcal disease among patients receiving eculizumab (Soliris) despite receipt of meningococcal vaccine. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep. 2017;66:734–737. doi: 10.15585/mmwr.mm6627e1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 192.Konar M, Granoff DM. Eculizumab treatment and impaired opsonophagocytic killing of meningococci by whole blood from immunized adults. Blood. 2017;130:891–899. doi: 10.1182/blood-2017-05-781450. This article provides insight into the mechanisms by which neisserial infections might occur in vaccinated patients receiving anti-C5 treatment and specifically into why targeting alternative pathway activation might confer advantages in this context. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 193.Wang J, et al. Using an in vitro xenoantibody-mediated complement-dependent cytotoxicity model to evaluate the complement inhibitory activity of the peptidic C3 inhibitor Cp40. Clin Immunol. 2016;162:37–44. doi: 10.1016/j.clim.2015.11.002. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 194.Egan M, Sullivan K, Frazer-Abel A, Cunningham-Rundles C. A healthy female with C3 hypocomplementemia and C3 Nephritic Factor. Clin Immunol. 2016;169:14–15. doi: 10.1016/j.clim.2016.06.001. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 195.Gewurz AT, Imherr SM, Strauss S, Gewurz H, Mold C. C3 nephritic factor and hypocomplementaemia in a clinically healthy individual. Clin Exp Immunol. 1983;54:253–258. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 196.Sfyroera G, et al. Rare loss-of-function mutation in complement component C3 provides insight into molecular and pathophysiological determinants of complement activity. J Immunol. 2015;194:3305–3316. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.1402781. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 197.Hajishengallis G, et al. Complement inhibition in pre-clinical models of periodontitis and prospects for clinical application. Semin Immunol. 2016;28:285–291. doi: 10.1016/j.smim.2016.03.006. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 198.Maekawa T, et al. Inhibition of pre-existing natural periodontitis in non-human primates by a locally administered peptide inhibitor of complement C3. J Clin Periodontol. 2016;43:238–249. doi: 10.1111/jcpe.12507. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 199.US National Library of Medicine. 2016 doi: 10.1080/15360280801989377. ClinicalTrials.gov https://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT01229215. [DOI] [PubMed]
- 200.Thurman JM, Nester CM. All things complement. Clin J Am Soc Nephrol. 2016;11:1856–1866. doi: 10.2215/CJN.01710216. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 201.Sahutoglu T, et al. Can eculizumab be discontinued in aHUS? Case report and review of the literature. Medicine (Baltimore) 2016;95:e4330. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000004330. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 202.Nester CM, et al. Atypical aHUS: state of the art. Mol Immunol. 2015;67:31–42. doi: 10.1016/j.molimm.2015.03.246. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 203.Omeros. Omeros to present results from dose-ranging stage of OMS721 clinical trial in atypical hemolytic uremic syndrome at World Congress of Nephrology. Omeros. 2017 http://investor.omeros.com/phoenix.zhtml?c=219263&p=irol-newsArticle&id=2256515.
- 204.Zhang Y, et al. Compstatin analog Cp40 inhibits complement dysregulation in vitro in C3 glomerulopathy. Immunobiology. 2015;220:993–998. doi: 10.1016/j.imbio.2015.04.001. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 205.ChemoCentryx. ChemoCentryx reports improvement in renal physiology and stabilization of kidney function following treatment with orally administered complement inhibitor CCX168 (Avacopan) in patient with fefractory C3 glomerulopathy. ChemoCentryx. 2016 http://ir.chemocentryx.com/releasedetail.cfm?ReleaseID=995869.
- 206.Johnson CK, Leca N. Eculizumab use in kidney transplantation. Curr Opin Organ Transplant. 2015;20:643–651. doi: 10.1097/MOT.0000000000000249. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 207.Jager NM, Poppelaars F, Daha MR, Seelen MA. Complement in renal transplantation: the road to translation. Mol Immunol. 2017;89:22–35. doi: 10.1016/j.molimm.2017.05.014. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 208.Stegall MD, et al. Terminal complement inhibition decreases antibody-mediated rejection in sensitized renal transplant recipients. Am J Transplant. 2011;11:2405–2413. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-6143.2011.03757.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 209.Cornell LD, Schinstock CA, Gandhi MJ, Kremers WK, Stegall MD. Positive crossmatch kidney transplant recipients treated with eculizumab: outcomes beyond 1 year. Am J Transplant. 2015;15:1293–1302. doi: 10.1111/ajt.13168. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 210.Alexion Pharmaceuticals. Alexion provides update on phase 2 clinical trial with eculizumab in antibody mediated rejection (AMR) in living-donor kidney transplant recipients. Alexion Pharmaceuticals. 2015 http://news.alexionpharma.com/press-release/company-news/alexion-provides-update-phase-2-clinical-trial-eculizumab-antibody-mediat.
- 211.US National Library of Medicine. 2017 doi: 10.1080/15360280801989377. ClinicalTrials.gov https://clinicaltrials.gov/show/NCT01895127. [DOI] [PubMed]
- 212.US National Library of Medicine. 2017 doi: 10.1080/15360280801989377. ClinicalTrials.gov https://clinicaltrials.gov/show/NCT01399593. [DOI] [PubMed]
- 213.US National Library of Medicine. 2017 doi: 10.1080/15360280801989377. ClinicalTrials.gov https://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT02222545. [DOI] [PubMed]
- 214.Amyndas Pharmaceuticals. Clinical trials. Amyndas Pharmaceuticals. 2017 http://amyndas.com/clinical-trials/
- 215.US Securities and Exchange Commission. 2017 https://www.sec.gov/Archives/edgar/data/1492422/000119312515342824/d23325ds1.htm.
- 216.US National Library of Medicine. 2016 doi: 10.1080/15360280801989377. ClinicalTrials.gov https://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT02461771. [DOI] [PubMed]
- 217.US National Library of Medicine. 2016 doi: 10.1080/15360280801989377. ClinicalTrials.gov https://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT02503332. [DOI] [PubMed]
- 218.US National Library of Medicine. 2017 doi: 10.1080/15360280801989377. ClinicalTrials.gov https://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT02745119. [DOI] [PubMed]
- 219.US National Library of Medicine. 2017 doi: 10.1080/15360280801989377. ClinicalTrials.gov https://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT02598583. [DOI] [PubMed]
- 220.US National Library of Medicine. 2017 doi: 10.1080/15360280801989377. ClinicalTrials.gov https://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT02605993. [DOI] [PubMed]
- 221.US National Library of Medicine. 2017 doi: 10.1080/15360280801989377. ClinicalTrials.gov https://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT02878616. [DOI] [PubMed]
- 222.US National Library of Medicine. 2017 doi: 10.1080/15360280801989377. ClinicalTrials.gov https://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT01527500. [DOI] [PubMed]
- 223.US National Library of Medicine. 2017 doi: 10.1080/15360280801989377. ClinicalTrials.gov https://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT03157635. [DOI] [PubMed]
- 224.Clinical Research Register. 2017 Clinicaltrialsregister.ru http://clinicaltrialsregister.ru/search/index1.php?q=ECU-PNH-I&s=
- 225.US National Library of Medicine. 2017 doi: 10.1080/15360280801989377. ClinicalTrials.gov https://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT02245412. [DOI] [PubMed]
- 226.US National Library of Medicine. 2017 doi: 10.1080/15360280801989377. ClinicalTrials.gov https://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT02128269. [DOI] [PubMed]
- 227.US National Library of Medicine. 2016 doi: 10.1080/15360280801989377. ClinicalTrials.gov https://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT02246595. [DOI] [PubMed]
- 228.US National Library of Medicine. 2017 doi: 10.1080/15360280801989377. ClinicalTrials.gov https://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT02866825. [DOI] [PubMed]
- 229.US National Library of Medicine. 2017 doi: 10.1080/15360280801989377. ClinicalTrials.gov https://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT03001622. [DOI] [PubMed]
- 230.US National Library of Medicine. 2017 doi: 10.1080/15360280801989377. ClinicalTrials.gov https://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT02435732. [DOI] [PubMed]
- 231.US National Library of Medicine. 2017 doi: 10.1080/15360280801989377. ClinicalTrials.gov https://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT02547220. [DOI] [PubMed]
- 232.US National Library of Medicine. 2015 doi: 10.1080/15360280801989377. ClinicalTrials.gov https://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT01275976. [DOI] [PubMed]
- 233.US National Library of Medicine. 2015 doi: 10.1080/15360280801989377. ClinicalTrials.gov https://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT02251041. [DOI] [PubMed]
- 234.US National Library of Medicine. 2017 doi: 10.1080/15360280801989377. ClinicalTrials.gov https://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT02134314. [DOI] [PubMed]
- 235.US National Library of Medicine. 2016 doi: 10.1080/15360280801989377. ClinicalTrials.gov https://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT02936479. [DOI] [PubMed]
- 236.US National Library of Medicine. 2017 doi: 10.1080/15360280801989377. ClinicalTrials.gov https://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT02869347. [DOI] [PubMed]
- 237.US National Library of Medicine. 2017 doi: 10.1080/15360280801989377. ClinicalTrials.gov https://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT01303952. [DOI] [PubMed]
- 238.US National Library of Medicine. 2017 doi: 10.1080/15360280801989377. ClinicalTrials.gov https://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT02093533. [DOI] [PubMed]
- 239.US National Library of Medicine. 2017 doi: 10.1080/15360280801989377. ClinicalTrials.gov https://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT02493725. [DOI] [PubMed]
- 240.US National Library of Medicine. 2017 doi: 10.1080/15360280801989377. ClinicalTrials.gov https://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT01567085. [DOI] [PubMed]
- 241.US National Library of Medicine. 2017 doi: 10.1080/15360280801989377. ClinicalTrials.gov https://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT01919346. [DOI] [PubMed]
- 242.US National Library of Medicine. 2017 doi: 10.1080/15360280801989377. ClinicalTrials.gov https://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT02145182. [DOI] [PubMed]
- 243.US National Library of Medicine. 2017 doi: 10.1080/15360280801989377. ClinicalTrials.gov https://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT01106027. [DOI] [PubMed]
- 244.US National Library of Medicine. 2017 doi: 10.1080/15360280801989377. ClinicalTrials.gov https://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT02301624. [DOI] [PubMed]
- 245.US National Library of Medicine. 2017 doi: 10.1080/15360280801989377. ClinicalTrials.gov https://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT01892345. [DOI] [PubMed]