Abstract
Health and a vibrant life are sought by everyone. To improve quality of life (QOL), maintain a healthy state, and prevent various diseases, evaluations of the effects of potentially QOL-increasing factors are important. Chronic oxidative stress and inflammation cause deteriorations in central nervous system function, leading to low QOL. In healthy individuals, aging, job stress, and cognitive load over several hours also induce increases in oxidative stress, suggesting that preventing the accumulation of oxidative stress caused by daily stress and daily work contributes to maintaining QOL and ameliorating the effects of aging. Hydrogen has anti-oxidant activity and can prevent inflammation, and may thus contribute to improve QOL. The present study aimed to investigate the effects of drinking hydrogen-rich water (HRW) on the QOL of adult volunteers using psychophysiological tests, including questionnaires and tests of autonomic nerve function and cognitive function. In this double-blinded, placebo-controlled study with a two-way crossover design, 26 volunteers (13 females, 13 males; mean age, 34.4 ± 9.9 years) were randomized to either a group administered oral HRW (600 mL/d) or placebo water (PLW, 600 mL/d) for 4 weeks. Change ratios (post-treatment/pre-treatment) for K6 score and sympathetic nerve activity during the resting state were significantly lower after HRW administration than after PLW administration. These results suggest that HRW may reinforce QOL through effects that increase central nervous system functions involving mood, anxiety, and autonomic nerve function.
Keywords: anxiety, autonomic nerve function, hydrogen-rich water, mood, quality of life
INTRODUCTION
Health and a vibrant life are much craved by everyone. To improve quality of life (QOL), maintain a healthy state, and prevent the onset of various diseases, evaluation of interventional effects for improving QOL is important. The high metabolic rate of the brain results in the generation of disproportionate amounts of reactive oxygen and nitrogen species, leading to increased oxidative stress.1 Increased oxidative stress and lipid peroxidation initiate a cascade of proinflammatory signals, leading to inflammation. Altered homeostasis of oxidation, inflammation, and protein aggregation has been suggested to contribute to the death of neurons, which is directly related to impairments in various cognitive domains. As such, chronic oxidative stress and inflammation may cause deteriorations in the function of the central nervous system, leading to reductions in QOL. Hydrogen has antioxidant activity and can prevent inflammation.2,3,4 The distribution of hydrogen throughout the brain and body indicates actions both in the central and peripheral nervous systems. Previous clinical studies have shown that hydrogen-rich water (HRW) reduces concentrations of markers of oxidative stress in patients with metabolic syndrome,5,6 improves lipid and glucose metabolism in patients with type 2 diabetes,7 improves mitochondrial dysfunction in patients with mitochondrial myopathies, and reduces inflammatory processes in patients with polymyositis/dermatomyositis.8 In another study, exercise-induced declines in muscle function among elite athletes were also improved by administering HRW.9 Although such findings suggest that HRW may help alleviate symptoms of several diseases and increase the physical performance of athletes, the effects of prolonged HRW ingestion on the QOL of individuals in the general population remain unknown.
Some reports have demonstrated that oxidative stress is associated with QOL in patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease and cervical cancer.10,11 During oncological treatment among patients with cervical cancer, antioxidant supplementation was found to be effective in improving QOL.11 In addition, Kang et al.12 reported that treatment with HRW for patients receiving radiotherapy for liver tumors decreased oxidative stress and improved QOL. Although the association between oxidative stress and QOL in healthy individuals is still unclear, aging, job stress, and cognitive load over the course of several hours in healthy individuals have also been found to induce increases in oxidative stress,13,14,15,16 suggesting that preventing the accumulation of oxidative stress caused by daily stress and daily work may contribute to the maintenance of QOL and amelioration of the effects of aging. Continuous HRW intake might therefore be expected to reduce accumulation of oxidative stress, thus helping to prevent decreases in QOL.
The aim of the present study was to investigate the effects of drinking 600 mL of HRW per day for 4 weeks on the QOL of adult volunteers using questionnaires for sleep, fatigue, mood, anxiety, and depression, an autonomic function test, and a higher cognitive function test.
SUBJECTS AND METHODS
Subjects
Thirty-one adult volunteers between 20 and 49 years old participated in this double-blinded, randomized, placebo-controlled study with a two-way crossover design. Exclusion criteria comprised: history of chronic illness; chronic medication or use of supplemental vitamins; employment in shift work; pregnancy; body mass index ≤ 17 or ≥ 29 kg/m2; food allergy; history of smoking; or history of drinking excessive amounts of alcohol (≥ 60 g/day). Shift workers were excluded because the water was administered at breakfast and dinner, the timings of which are irregular among shift workers. In addition, the mental and physical conditions of shift workers can be greatly affected by the shift schedule for the preceding 2 days, which may impact the results obtained from the questionnaires used in this study. Before each experiment, participants were asked to refrain from drinking alcohol, since drinking excessive amounts of alcohol carries significant risks of fluctuations in physical condition. All experiments were conducted in compliance with national legislation and the Code of Ethical Principles for Medical Research Involving Human Subjects of the World Medical Association (the Declaration of Helsinki) and registered to the UMIN Clinical Trials Registry (No. UMIN000022382). The study protocol was approved by the Ethics Committee of Osaka City University Center for Health Science Innovation (OCU-CHSI-IRB No. 4), and all participants provided written informed consent for participation in the study.
Study design
We used a double-blinded, placebo-controlled study with a two-way crossover design, as summarized in Figure 1. After admission to the study, participants were randomized in a double-blinded manner to receive HRW in an aluminum pouch (0.8–1.2 ppm of hydrogen, 300 mL/pouch; Melodian Corporation, Yao, Japan) or placebo water (PLW), representing mineral water from the same source (i.e., same components without hydrogen) in an aluminum pouch (0 ppm of hydrogen, 300 mL/pouch; Melodian Corporation) twice a day for 4 weeks. Fifteen participants were administered PLWfirst, and then HRW. The remaining 16 participants were administered HRWfirst, and then PLW. Participants consumed water within 5 minutes twice a day, at breakfast and dinner in their home, and confirmed the water intake at breakfast and dinner in a daily journal for 4 weeks. We assessed the intake rate of water by checking the daily journal every 4 weeks, on the 2nd and 4th experimental days. No participants reported any difference in taste between HRW and PLW. Previous studies have reported interventional effects of administering HRW to humans at hydrogen concentrations under 1.3 ppm.5,12 We therefore used a similar concentration of 0.8–1.2 ppm in the present study. Absolute volumes (600 mL) of HRW and PLW were provided to participants rather than a volume proportional to body mass, based on previously reported results.5,6,7,12 The duration of supplementation was set based on previous findings with HRW administration for 2–8 weeks.5,12,17 A 4-week washout period was provided between HRW and PLW administrations based on a previous study.8 The day before starting each experiment, participants were told to finish dinner by 21:00, and were required to fast overnight to avoid any influence of diet on concentrations of measured parameters (markers of inflammation and oxidative stress) in blood samples. At 09:00 the next day, participants completed the questionnaires after confirming that they had refrained from drinking alcohol, had finished dinner by 21:00, and had fasted overnight. Autonomic nerve function was measured at 09:30. Cognitive function testing was conducted at 09:45. Blood samples were collected at 10:00. These measurements were performed a total of four times for each participant, before (pre) and after (post) each of the two 4-week administration periods. From 24 hours (the day before the visit day) before each visit for measurements, participants were told to refrain from drinking alcohol or performing strenuous physical activity and to follow their normal diets, drinking habits, and sleeping hours. During the 4-week PLW or HRW administration periods, daily daytime activity (amount of physical exertion) of participants was measured using a pedometer and participants kept a daily journal to record drinking volume and times of PLW or HRW intake, physical condition (e.g., pain, lassitude, and indefinite complaints), sleeping times, etc.
Figure 1.
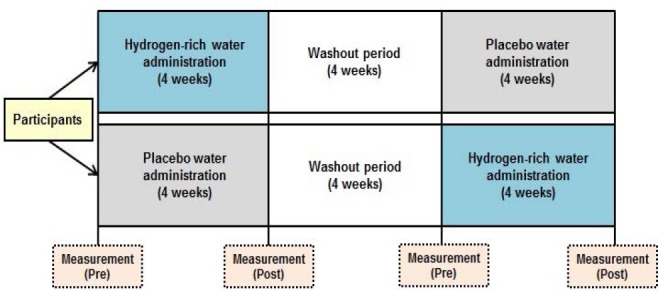
Time course of the experiments.
Note: Participants were randomly divided into two study groups. The experiment consisted of 4 weeks of hydrogen-rich water (HRW) administration or placebo water (PLW) administration, a 4-week washout period, and then another 4 weeks of PLW administration or HRW administration. Before (pre) and after (post) each period of HRW or PLW administration, subjective and objective measurements for quality of life were obtained, such as results for sleep, mood, anxiety, feelings of depression, autonomic nerve function, and cognitive function.
Questionnaire
Severity of fatigue was measured using the Chalder Fatigue Scale (CFS)18 and a modified version of the Osaka City University Hospital Fatigue Scale.19 Mood and anxiety were evaluated using the K6 scale.20 Symptoms of depression were measured using the Center for Epidemiologic Studies Depression Scale.21 General sleepiness and daytime sleepiness scores were calculated using the Pittsburgh Sleep Quality Index (PSQI)22 and the Epworth Sleepiness Scale,23 respectively. The reliability and validity of the Japanese versions of these questionnaires have been confirmed.19,24,25,26,27,28
Autonomic function test
Participants underwent simultaneous electrocardiography and photoplethysmography using a Vital Monitor 302 system (Fatigue Science Laboratory, Osaka, Japan) while sitting quietly with their eyes closed for 3 minutes. These data were analyzed using MemCalc software (GMS, Tokyo, Japan). Frequency analyses for R-R interval variation from electrocardiography and a-a interval variation as the second derivative of photoplethysmography (accelerated plethysmography) were performed using the maximum entropy method, which is capable of estimating the power spectrum density from short time series data, and is adequate for examining changes in heart rate variability under different conditions of short duration.29,30 The power spectrum resolution was 600 Hz. For frequency analyses, the low-frequency component power (LF) was calculated as the power within a frequency range of 0.04–0.15 Hz, and the high-frequency component power (HF) was calculated as that within a frequency range of 0.15–0.4 Hz. HF is vagally mediated,31,32,33 whereas LF originates from a variety of sympathetic and vagal mechanisms.30,34 Some review articles35,36,37 mentioned that LF reflects sympathetic nerve activity and is used as a marker of sympathetic nerve activity in original articles. Before autonomic nerve function testing was conducted for 3 minutes, a practice test was conducted for a period of 1 minute, in accordance with previous studies.38,39,40 The reliability of these tests has been confirmed.41,42
Cognitive function test
Since previous studies have revealed that a switching attention task is useful for evaluating reduced performance under fatigue conditions,43,44,45 we used task E of the modified advanced trail making test (mATMT) as a switching attention task for evaluating executive function.46,47 Circles with numbers (from 1 to 13) or kana (Japanese phonograms, 12 different letters) were shown in random locations on a screen, and participants were required to use a computer mouse to alternately touch the numbers and kana; this task thus required switching attention. When participants touched a target circle, it remained in the same position, but its color changed from black to yellow. Participants were instructed to perform the task as quickly and correctly as possible, and continuously performed this task for 5 minutes. We evaluated three indices of task performance: the total count of correct responses (number of correctly touched numbers and letters); the total count of errors (number of incorrectly touched numbers and letters); and the motivational response (reaction time from a finished trial to the next trial). Based on our previous study,47 before participants performed task E of the mATMT on each experimental day, they practiced for a period of 1 minute. The reliability of this test has been confirmed.43,44
Blood sample analyses
Blood samples were collected from the brachial vein. The amount of blood sampled was 13 mL per experimental day. We thus collected blood samples on four occasions (once per experimental day) in the study. Blood samples for serum analyses were centrifuged at 1,470 × g for 5 minutes at 4°C. The concentration of high-sensitivity C-reactive protein (hs-CRP) in each serum sample was assessed by particle-enhanced immunonephelometry using a BNII analyzer (BN II ProSpec; Siemens, Munich, Germany). Oxidative activity in each serum sample was assessed with the reactive oxygen metabolites-derived compounds (d-ROMs) test (Diacron International, Grosseto, Italy), while anti-oxidative activity was measured with the biological anti-oxidant potential (BAP) test (Diacron International) using a JCABM1650 automated analyzer (JEOL, Tokyo, Japan).48 The concentrations of ROMs are expressed in Carratelli units (1 CARR U = 0.08 mg of hydrogen peroxide/dL).49 The oxidative stress index (OSI) was calculated using the following formula: OSI = C × (d-ROMs/BAP), where C denotes a coefficient for standardization to set the mean OSI in healthy individuals at 1.0 (C = 8.85).45 All supernatants were stored at -80°C until analyzed. Assays for hs-CRP were performed at LSI Medience Corporation (Tokyo, Japan) and those for serum d-ROMs and BAP were performed at Yamaguchi University Graduate School of Medicine.
Daily daytime activity and daily journal
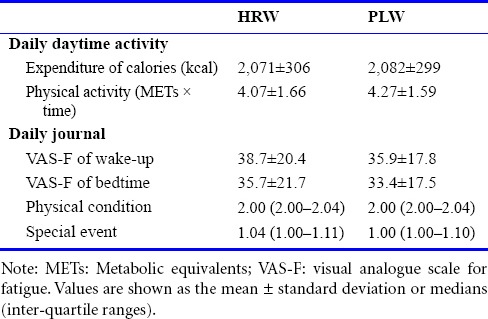
Daily daytime activity, representing the expenditure of calories and amount of physical activity (METs × time) was recorded using an Active style Pro HJA-350IT pedometer (OMRON, Kyoto, Japan). A daily journal was kept for 4 weeks, and included information on fatigue (based on a visual analogue scale from 0, representing “no fatigue”, to 100, representing “total exhaustion”) just after waking up and before bedtime, sleeping times, physical condition (1, good; 2, normal; or 3, bad), and special events (if the day was different from a usual day: 1, no; or 2, yes). We carefully checked the daily journal every four weeks, on the 2nd, 3rd, and 4th experimental days.
Statistical analyses
First, we tested the normality (parametric or non-parametric distributions) of each measured parameter using the Kolmogorov-Smirnov test. Values are presented as the mean ± standard deviation or median and interquartile range based on the results of Kolmogorov-Smirnov test. The Wilcoxon signed-rank test for non-parametric parameters and paired t-test for differences between HRW and PLW administrations after two-way repeated-measurement analysis of variance for parametric parameters were conducted. If significant changes were observed by comparisons within each condition (pre- vs. post-HRW; pre- vs. post-PLW) or between post-treatment values (post-HRW vs. post-PLW), then we compared change ratios between post-HRW/pre-HRW and post-PLW/pre-PLW using the Wilcoxon signed-rank test or paired t-test. All P values were two-tailed, and those less than 0.05 were considered statistically significant. Statistical analyses were performed using IBM SPSS Statistical Package version 20.0 (IBM, Armonk, NY, USA).
RESULTS
General results
During the study, we excluded five participants from data analyses due to symptoms of hay fever, prolonged medication use because of a cold, insufficient intake of HRW or PLW intake (≥ 85%), or a frequency of special events ≤ 15% as recorded in the daily diary. We thus analyzed data from a total of 26 participants (13 females, 13 males; mean age, 34.4 ± 9.9 years; mean body mass index, 21.5 ± 2.6 kg/m2). No side, order, and carry-over effects were observed from the oral administrations of HRW and PLW in any participant.
Questionnaire results
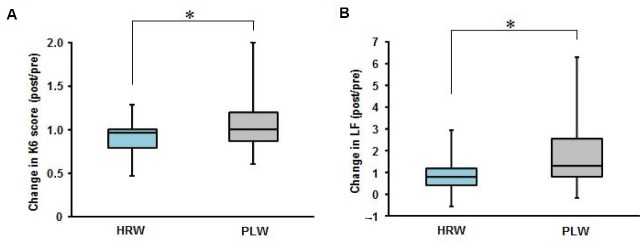
Results from the questionnaires are summarized in Table 1. No questionnaire scores at baseline (pre) showed any significant differences between HRW and PLW administration groups. With HRW administration, scores for K6, CFS, and PSQI were significantly decreased after the 4-week administration period. In addition, the change ratio (post/pre) for K6 score was significantly lower in the HRW administration group than in the PLW administration group (Figure 2). No significant changes were seen in any other questionnaire scores (modified version of the Osaka City University Hospital Fatigue Scale, Center for Epidemiologic Studies Depression Scale or Epworth Sleepiness Scale) after HRW administration and no significant changes in any of the scores were seen after PLW administration. Likewise, these scores did not differ significantly between HRW and PLW after administration.
Table 1.
Changes in parameters related to quality of life due to hydrogen-rich water (HRW) or placebo water (PLW) administration
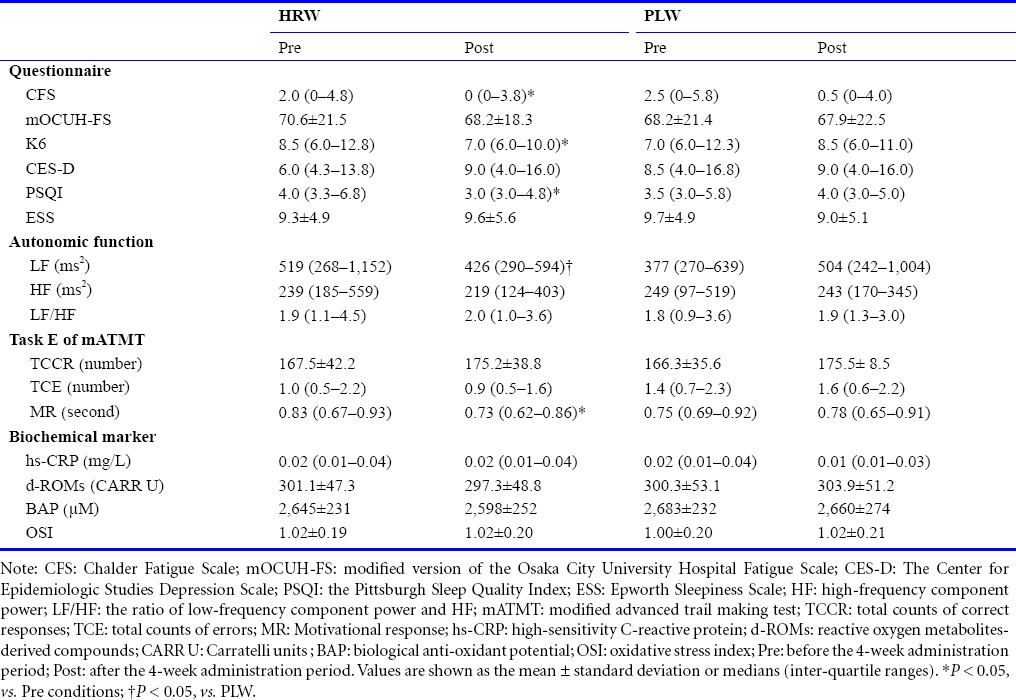
Figure 2.
Comparison of change ratios (post-treatment/pre-treatment) for parameters related to quality of life with administration of hydrogen-rich water (HRW) or placebo water (PLW) for 4 weeks.
Note: Change ratios for K6 score for mood (A) and anxiety and the low-frequency component power (LF) for autonomic nerve function (B). *P < 0.05.
Autonomic function results
Results for the autonomic nerve function are summarized in Table 1. LF, HF, and LF/HF ratio at baseline (pre) did not differ significantly between HRW and PLW administrations, indicating similar autonomic nerve function in the two groups before water intake. Although the HF and LF/HF ratio were not significantly affected by 4-week administrations of HRW or PLW, LF after HRW administration was significantly lower than that after PLW administration. The change ratio (post/pre) for LF was also significantly lower in the HRW administration group than in the PLW administration group (Figure 2).
Cognitive function results
Results for the cognitive function test are shown in Table 1. Motivational response and total counts of correct responses and errors at baseline (pre) did not differ significantly between HRW and PLW administrations, indicating similar cognitive function between groups before water intake. Motivational response after HRW administration was significantly faster than that before HRW administration. The change ratio (post/pre) for motivational response was not significantly different in the HRW administration group than in the PLW administration group. No significant differences in motivational response, total counts of correct responses, or errors after water administration were seen between HRW- and PLW-administered conditions.
Blood sample results
No significant differences were seen in any blood parameters (hs-CRP, d-ROMs, BAP, and OSI) before HRW or PLW administration (Table 1), indicating the comparability of the two groups before water intake. After HRW and PLW administrations, we again found no significant differences in these blood parameters.
Daily daytime activity and daily journal results
The daily expenditure of calories and amount of physical activity during the 4-week administration periods did not differ significantly between HRW and PLW administration conditions (Table 2). Similarly, visual analogue scale scores for fatigue just after waking and before bedtime, sleeping times, physical condition, and counts of special events were comparable between HRW and PLW administration conditions (Table 2), indicating that living habits were successfully controlled during the experimental period in the two groups.
Table 2.
Daily daytime activity and data recorded in the daily journal during the hydrogen-rich water (HRW) or placebo water (PLW) administration period (4 weeks)
DISCUSSION
The present findings suggest that HRW administration for 4 weeks may have improved the QOL of adult volunteers in terms of improved mood and anxiety and reduced activity of the sympathetic nervous system at rest.
In terms of associations between hydrogen and the central nervous system, a report by Ohsawa et al.4 was the first to demonstrate that molecular hydrogen acts, at least in part, as an anti-oxidant as it binds to hydroxyl ions produced in central nervous system injuries. Previous studies have proposed that HRW administration has neuroprotective effects50 and anti-aging effects on periodontal oxidative damage in healthy aged rats.51 In a rat model of Alzheimer's disease, hydrogen-rich saline prevented neuroinflammation and oxidative stress, and improved memory function.52 In terms of the association between HRW and QOL, only one study reported that HRW administration for 6 weeks improved QOL scores in patients treated with radiotherapy for liver tumors.12 Although reports on the effects of HRW administration in healthy populations have not been accumulated, job stress14,15 and acute fatigue caused by mental and physical loading for several hours16,53 have been shown to enhance oxidative stress. As for physical fatigue, in order to alleviate acute physical fatigue in healthy volunteers not including athletes, we have previously demonstrated that treatment with antioxidant supplements is effective.54,55,56 The present study provided new findings that HRW affects not only physical condition but also mental conditions such as mood, anxiety, and autonomic nerve function. One of the advantages of HRW is the ability to cross the blood-brain barrier, offering high potential to reduce oxidative stress in the brain. A previous study in rats found that levels of malondialdehyde, a marker of oxidative stress, were around 4.8-fold higher in the brain than in the blood (plasma).57 These results suggest that HRW may be effective for reducing accumulated oxidative stress in the brain in daily life, potentially contributing to the maintenance of central nervous system activity and preventing decreases in QOL.
In the present study, mood and anxiety levels improved after HRW administration. These negative emotions are also known to be involved in conditions related to oxidative stress; social phobia,58,59 depression,60 anxiety,61,62 and other neuropsychiatric disorders63 have been shown to be associated with increased oxidative stress. Neuroinflammation is also related to fatigue, mood, anxiety, and sleep.64,65,66,67 In older mice, HRW administration succeeded in suppressing depression-like behaviors.68 These findings suggest that administration of HRW for 4 weeks may be effective for controlling such negative emotions by reducing oxidative stress and inflammation of the central nervous system. Increasing evidence suggests that oxidative stress and inflammation in neurons are involved in the pathological manifestations of many neurological and neuropsychiatric disorders, and HRW administration may thus help alleviate the symptoms of these disorders. Previous study revealed that oxidative stress of the brain causes cognitive and motivational deficits in a mouse model of neuropsychiatric disorder (schizophrenia).69 In the present study, motivational response of cognitive function test was improved by prolonged HRW intake, suggesting that a reduction of oxidative stress in the brain by the intake of HRW may increase motivational performance of cognitive task.
Stressors can enhance sympathetic hyperactivity, promote oxidative stress, and boost pro-inflammatory cytokine production.70,71,72 Autonomic nerve function is thus closely associated with oxidative stress and inflammation. Attenuation of sympathetic nervous system activity during the resting state in adult volunteers may therefore be the result of decreases in inflammation and oxidative stress as an effect of prolonged HRW administration. However, the lack of changes in oxidative stress markers noted in the present study after HRW intake for 4 weeks could be due to the low severity of oxidative stress in the participants. Actually, serum d-ROMs (307.1 ± 49.4 CARR U) and BAP (2,549 ± 194 µM) concentrations at the first measurement point in the present study were within normal ranges based on the results of serum d-ROMs (286.9 ± 100.2 CARR U) and BAP (2,541 ± 122 µM) concentrations measured in 312 healthy participants in our previous study.48 However, levels of oxidative stress fluctuate depending on daily work load and stress. In addition, the rat study by García-Niño et al.57 that found malondialdehyde levels around 4.8-fold higher in the brain than in plasma indicate that oxidative stress in the brain is more severe. Daily administration of HRW for 4 weeks may thus contribute to attenuation of and prevention from the cumulative oxidative stress in the brain. Mood, anxiety, and autonomic nerve function could thus potentially be improved. Although the range of sympathetic nerve activity in the present study considers to be normal based on our previous studies,73,74 sympathetic nerve activity also fluctuates depending on daily work load and stress.35 Therefore, lower sympathetic nerve activity of resting state may contribute to suppress an excessive increase in sympathetic nerve activity after the daily work load and stress.
We conducted this study with a limited number of participants. Before our results can be generalized, studies involving larger numbers of participants are essential.
Although we mainly examined the effects of HRW on the central nervous system, we did not directly evaluate the dynamics of inflammation and oxidation in the brain. Neuroimaging studies using positron emission tomography and magnetic resonance imaging are thus underway in our laboratory to identify the mechanisms underlying the effects of HRW intake on the central nervous system that can improve QOL.
In conclusion, HRW administration for 4 weeks in adult volunteers improved mood, anxiety, and autonomic nerve function, suggesting that HRW administration may offer an effective method to reinforce QOL and maintain good health. In a further study, we will try to identify the effects of HRW administration in participants with ongoing stress or chronic fatigue.
Acknowledgments
We would like to thank Ms. Mika Furusawa for her excellent technical assistances and Forte Science Communications for editorial help with this manuscript.
Footnotes
Conflicts of interest
This work was presented at Japanese Society of Fatigue Science, Yamaguchi City, Japan on May 16, 2016. Yasuyoshi Watanabe received funding for the present study from Melodian Corporation. The other authors have no conflicts of interest to declare.
Research ethics
All experiments were conducted in compliance with national legislation and the Code of Ethical Principles for Medical Research Involving Human Subjects of the World Medical Association (the Declaration of Helsinki) and registered to the UMIN Clinical Trials Registry (UMIN000022382). The study protocol was approved by the Ethics Committee of Osaka City University Center for Health Science Innovation (OCU-CHSI-IRB No. 4).
Declaration of participant consent
The authors certify that they have obtained all appropriate participant consent forms. In the form the participants have given their consent for their images and other clinical information to be reported in the journal. The participants understand that their names and initials will not be published and due efforts will be made to conceal their identity, but anonymity cannot be guaranteed.
Data sharing statement
Datasets analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
Plagiarism check
Checked twice by iThenticate.
Peer review
Externally peer reviewed.
Open peer reviewers
Lei Huang, Loma Linda University, USA; Qin Hu, Shanghai Jiao Tong University, China.
REFERENCES
- 1.Starke RM, Chalouhi N, Ali MS, et al. The role of oxidative stress in cerebral aneurysm formation and rupture. Curr Neurovasc Res. 2013;10:247–255. doi: 10.2174/15672026113109990003. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Buchholz BM, Kaczorowski DJ, Sugimoto R, et al. Hydrogen inhalation ameliorates oxidative stress in transplantation induced intestinal graft injury. Am J Transplant. 2008;8:2015–2024. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-6143.2008.02359.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Huang CS, Kawamura T, Toyoda Y, Nakao A. Recent advances in hydrogen research as a therapeutic medical gas. Free Radic Res. 2010;44:971–982. doi: 10.3109/10715762.2010.500328. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Ohsawa I, Ishikawa M, Takahashi K, et al. Hydrogen acts as a therapeutic antioxidant by selectively reducing cytotoxic oxygen radicals. Nat Med. 2007;13:688–694. doi: 10.1038/nm1577. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Nakao A, Toyoda Y, Sharma P, Evans M, Guthrie N. Effectiveness of hydrogen rich water on antioxidant status of subjects with potential metabolic syndrome-an open label pilot study. J Clin Biochem Nutr. 2010;46:140–149. doi: 10.3164/jcbn.09-100. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Song G, Li M, Sang H, et al. Hydrogen-rich water decreases serum LDL-cholesterol levels and improves HDL function in patients with potential metabolic syndrome. J Lipid Res. 2013;54:1884–1893. doi: 10.1194/jlr.M036640. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Kajiyama S, Hasegawa G, Asano M, et al. Supplementation of hydrogen-rich water improves lipid and glucose metabolism in patients with type 2 diabetes or impaired glucose tolerance. Nutr Res. 2008;28:137–143. doi: 10.1016/j.nutres.2008.01.008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Ito M, Ibi T, Sahashi K, Ichihara M, Ito M, Ohno K. Open-label trial and randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, crossover trial of hydrogen-enriched water for mitochondrial and inflammatory myopathies. Med Gas Res. 2011;1:24. doi: 10.1186/2045-9912-1-24. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Aoki K, Nakao A, Adachi T, Matsui Y, Miyakawa S. Pilot study: Effects of drinking hydrogen-rich water on muscle fatigue caused by acute exercise in elite athletes. Med Gas Res. 2012;2:12. doi: 10.1186/2045-9912-2-12. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Ben Moussa S, Rouatbi S, Ben Saad H. Incapacity, handicap, and oxidative stress markers of male smokers with and without COPD. Respir Care. 2016;61:668–679. doi: 10.4187/respcare.04420. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Fuchs-Tarlovsky V, Rivera MA, Altamirano KA, Lopez-Alvarenga JC, Ceballos-Reyes GM. Antioxidant supplementation has a positive effect on oxidative stress and hematological toxicity during oncology treatment in cervical cancer patients. Support Care Cancer. 2013;21:1359–1363. doi: 10.1007/s00520-012-1674-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Kang KM, Kang YN, Choi IB, et al. Effects of drinking hydrogen-rich water on the quality of life of patients treated with radiotherapy for liver tumors. Med Gas Res. 2011;1:11. doi: 10.1186/2045-9912-1-11. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Inal ME, Kanbak G, Sunal E. Antioxidant enzyme activities and malondialdehyde levels related to aging. Clin Chim Acta. 2001;305:75–80. doi: 10.1016/s0009-8981(00)00422-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Casado Á, Castellanos A, López-Fernández ME, et al. Determination of oxidative and occupational stress in palliative care workers. Clin Chem Lab Med. 2011;49:471–477. doi: 10.1515/CCLM.2011.061. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Ishihara I, Nakano M, Ikushima M, et al. Effect of work conditions and work environments on the formation of 8-OH-dG in nurses and non-nurse female workers. J UOEH. 2008;30:293–308. doi: 10.7888/juoeh.30.293. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Fukuda S, Nojima J, Motoki Y, et al. A potential biomarker for fatigue: Oxidative stress and anti-oxidative activity. Biol Psychol. 2016;118:88–93. doi: 10.1016/j.biopsycho.2016.05.005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Ostojic SM, Stojanovic MD. Hydrogen-rich water affected blood alkalinity in physically active men. Res Sports Med. 2014;22:49–60. doi: 10.1080/15438627.2013.852092. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Chalder T, Berelowitz G, Pawlikowska T, et al. Development of a fatigue scale. J Psychosom Res. 1993;37:147–153. doi: 10.1016/0022-3999(93)90081-p. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Fukuda S, Takashima S, Iwase M, Yamaguchi K, Kuratsune H, Watanabe Y. Development and validation of a new fatigue scale for fatigued subjects with and without chronic fatigue syndrome. In: Watanabe Y, Evengård B, Natelson BH, Jason LA, Kuratsune H, editors. Fatigue Science for Human Health. New York: Springer; 2008. pp. 89–102. [Google Scholar]
- 20.Kessler RC, Andrews G, Colpe LJ, et al. Short screening scales to monitor population prevalences and trends in non-specific psychological distress. Psychol Med. 2002;32:959–976. doi: 10.1017/s0033291702006074. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Radloff LS. The CES-D scale: a self-report depression scale for research in the general population. Appl Psychol Meas. 1977;1:385–401. [Google Scholar]
- 22.Buysse DJ, Reynolds CF, 3rd, Monk TH, Berman SR, Kupfer DJ. The Pittsburgh Sleep Quality Index: a new instrument for psychiatric practice and research. Psychiatry Res. 1989;28:193–213. doi: 10.1016/0165-1781(89)90047-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Johns MW. A new method for measuring daytime sleepiness: the Epworth sleepiness scale. Sleep. 1991;14:540–545. doi: 10.1093/sleep/14.6.540. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Doi Y, Minowa M, Uchiyama M, et al. Psychometric assessment of subjective sleep quality using the Japanese version of the Pittsburgh Sleep Quality Index (PSQI-J) in psychiatric disordered and control subjects. Psychiatry Res. 2000;97:165–172. doi: 10.1016/s0165-1781(00)00232-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Furukawa TA, Kawakami N, Saitoh M, et al. The performance of the Japanese version of the K6 and K10 in the World Mental Health Survey Japan. Int J Methods Psychiatr Res. 2008;17:152–158. doi: 10.1002/mpr.257. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Takegami M, Suzukamo Y, Wakita T, et al. Development of a Japanese version of the Epworth Sleepiness Scale (JESS) based on item response theory. Sleep Med. 2009;10:556–565. doi: 10.1016/j.sleep.2008.04.015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Tanaka M, Fukuda S, Mizuno K, et al. Reliability and validity of the Japanese version of the Chalder Fatigue Scale among youth in Japan. Psychol Rep. 2008;103:682–690. doi: 10.2466/pr0.103.3.682-690. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Shima S, Shikano T, Kitamura T. New self-rating scales for depression. Clin Psychiatry. 1985;27:717–723. [Google Scholar]
- 29.Kanaya N, Hirata N, Kurosawa S, Nakayama M, Namiki A. Differential effects of propofol and sevoflurane on heart rate variability. Anesthesiology. 2003;98:34–40. doi: 10.1097/00000542-200301000-00009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Takusagawa M, Komori S, Umetani K, et al. Alterations of autonomic nervous activity in recurrence of variant angina. Heart. 1999;82:75–81. doi: 10.1136/hrt.82.1.75. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Akselrod S, Gordon D, Ubel FA, Shannon DC, Berger AC, Cohen RJ. Power spectrum analysis of heart rate fluctuation: a quantitative probe of beat-to-beat cardiovascular control. Science. 1981;213:220–222. doi: 10.1126/science.6166045. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Pomeranz B, Macaulay RJ, Caudill MA, et al. Assessment of autonomic function in humans by heart rate spectral analysis. Am J Physiol. 1985;248:H151–153. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.1985.248.1.H151. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Malliani A, Pagani M, Lombardi F, Cerutti S. Cardiovascular neural regulation explored in the frequency domain. Circulation. 1991;84:482–492. doi: 10.1161/01.cir.84.2.482. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Appel ML, Berger RD, Saul JP, Smith JM, Cohen RJ. Beat to beat variability in cardiovascular variables: noise or music? J Am Coll Cardiol. 1989;14:1139–1148. doi: 10.1016/0735-1097(89)90408-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Tanaka M, Tajima S, Mizuno K, et al. Frontier studies on fatigue, autonomic nerve dysfunction, and sleep-rhythm disorder. J Physiol Sci. 2015;65:483–498. doi: 10.1007/s12576-015-0399-y. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Montano N, Porta A, Cogliati C, et al. Heart rate variability explored in the frequency domain: a tool to investigate the link between heart and behavior. Neurosci Biobehav Rev. 2009;33:71–80. doi: 10.1016/j.neubiorev.2008.07.006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Perini R, Veicsteinas A. Heart rate variability and autonomic activity at rest and during exercise in various physiological conditions. Eur J Appl Physiol. 2003;90:317–325. doi: 10.1007/s00421-003-0953-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Tajima K, Tanaka M, Mizuno K, Okada N, Rokushima K, Watanabe Y. Effects of bathing in micro-bubbles on recovery from moderate mental fatigue. Ergonomia IJE&HF. 2008;30:134–145. [Google Scholar]
- 39.Mizuno K, Tanaka M, Tajima K, Okada N, Rokushima K, Watanabe Y. Effects of mild-stream bathing on recovery from mental fatigue. Med Sci Monit. 2010;16:Cr8–14. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Mizuno K, Tanaka M, Yamaguti K, Kajimoto O, Kuratsune H, Watanabe Y. Mental fatigue caused by prolonged cognitive load associated with sympathetic hyperactivity. Behav Brain Funct. 2011;7:17. doi: 10.1186/1744-9081-7-17. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Heart rate variability: standards of measurement, physiological interpretation and clinical use. Task Force of the European Society of Cardiology and the North American Society of Pacing and Electrophysiology. Circulation. 1996;93:1043–1065. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Kume S, Nishimura Y, Mizuno K, et al. Music improves subjective feelings leading to cardiac autonomic nervous modulation: a pilot study. Front Neurosci. 2017;11:108. doi: 10.3389/fnins.2017.00108. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Kajimoto O. Development of a method of evaluation of fatigue and its economic impacts. In: Watanabe Y, Evengård B, Natelson BH, Jason LA, Kuratsune H, editors. Fatigue Science for Human Health. New York: Springer; 2008. pp. 33–46. [Google Scholar]
- 44.Mizuno K, Watanabe Y. Neurocognitive impairment in childhood chronic fatigue syndrome. Front Physiol. 2013;4:87. doi: 10.3389/fphys.2013.00087. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45.Mizuno K, Tanaka M, Fukuda S, Imai-Matsumura K, Watanabe Y. Relationship between cognitive functions and prevalence of fatigue in elementary and junior high school students. Brain Dev. 2011;33:470–479. doi: 10.1016/j.braindev.2010.08.012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46.Kawatani J, Mizuno K, Shiraishi S, et al. Cognitive dysfunction and mental fatigue in childhood chronic fatigue syndrome--a 6-month follow-up study. Brain Dev. 2011;33:832–841. doi: 10.1016/j.braindev.2010.12.009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47.Mizuno K, Tanaka M, Fukuda S, Sasabe T, Imai-Matsumura K, Watanabe Y. Changes in cognitive functions of students in the transitional period from elementary school to junior high school. Brain Dev. 2011;33:412–420. doi: 10.1016/j.braindev.2010.07.005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 48.Trotti R, Carratelli M, Barbieri M. Performance and clinical application of a new, fast method for the detection of hydroperoxides in serum. Panminerva Med. 2002;44:37–40. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 49.Nojima J, Motoki Y, Tsuneoka H, et al. ‘Oxidation stress index’ as a possible clinical marker for the evaluation of non-Hodgkin lymphoma. Br J Haematol. 2011;155:528–530. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2141.2011.08719.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 50.Li J, Wang C, Zhang JH, Cai JM, Cao YP, Sun XJ. Hydrogen-rich saline improves memory function in a rat model of amyloid-beta-induced Alzheimer's disease by reduction of oxidative stress. Brain Res. 2010;1328:152–161. doi: 10.1016/j.brainres.2010.02.046. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 51.Matsumoto A, Yamafuji M, Tachibana T, Nakabeppu Y, Noda M, Nakaya H. Oral ‘hydrogen water’ induces neuroprotective ghrelin secretion in mice. Sci Rep. 2013;3:3273. doi: 10.1038/srep03273. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 52.Tomofuji T, Kawabata Y, Kasuyama K, et al. Effects of hydrogen-rich water on aging periodontal tissues in rats. Sci Rep. 2014;4:5534. doi: 10.1038/srep05534. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 53.Watanabe Y, Kuratsune H, Kajimoto O. Desmond Biochemical indices of fatigue for anti-fatigue strategies and products. In: Matthews G, Desmond PA, Neubauer C, Hancoc PA, editors. The Handbook of Operator Fatigue. CRC Press; 2012. pp. 209–224. [Google Scholar]
- 54.Ataka S, Tanaka M, Nozaki S, et al. Effects of Applephenon and ascorbic acid on physical fatigue. Nutrition. 2007;23:419–423. doi: 10.1016/j.nut.2007.03.002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 55.Mizuno K, Tanaka M, Nozaki S, et al. Antifatigue effects of coenzyme Q10 during physical fatigue. Nutrition. 2008;24:293–299. doi: 10.1016/j.nut.2007.12.007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 56.Mizuma H, Tanaka M, Nozaki S, et al. Daily oral administration of crocetin attenuates physical fatigue in human subjects. Nutr Res. 2009;29:145–150. doi: 10.1016/j.nutres.2009.02.003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 57.García-Niño WR, Zatarain-Barrón ZL, Hernández-Pando R, Vega-Garcia CC, Tapia E, Pedraza-Chaverri J. Oxidative stress markers and histological analysis in diverse organs from rats treated with a hepatotoxic dose of Cr(VI): effect of curcumin. Biol Trace Elem Res. 2015;167:130–145. doi: 10.1007/s12011-015-0283-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 58.Atmaca M, Tezcan E, Kuloglu M, Ustundag B, Tunckol H. Antioxidant enzyme and malondialdehyde values in social phobia before and after citalopram treatment. Eur Arch Psychiatry Clin Neurosci. 2004;254:231–235. doi: 10.1007/s00406-004-0484-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 59.Atmaca M, Kuloglu M, Tezcan E, Ustundag B. Antioxidant enzyme and malondialdehyde levels in patients with social phobia. Psychiatry Res. 2008;159:95–100. doi: 10.1016/j.psychres.2002.12.004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 60.Maurya PK, Noto C, Rizzo LB, et al. The role of oxidative and nitrosative stress in accelerated aging and major depressive disorder. Prog Neuropsychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry. 2016;65:134–144. doi: 10.1016/j.pnpbp.2015.08.016. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 61.Arranz L, Guayerbas N, De la Fuente M. Impairment of several immune functions in anxious women. J Psychosom Res. 2007;62:1–8. doi: 10.1016/j.jpsychores.2006.07.030. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 62.Bouayed J, Rammal H, Younos C, Soulimani R. Positive correlation between peripheral blood granulocyte oxidative status and level of anxiety in mice. Eur J Pharmacol. 2007;564:146–149. doi: 10.1016/j.ejphar.2007.02.055. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 63.Pandya CD, Howell KR, Pillai A. Antioxidants as potential therapeutics for neuropsychiatric disorders. Prog Neuropsychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry. 2013;46:214–223. doi: 10.1016/j.pnpbp.2012.10.017. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 64.Nakatomi Y, Mizuno K, Ishii A, et al. Neuroinflammation in patients with chronic fatigue syndrome/myalgic encephalomyelitis: an (1)(1)C-(R)-PK11195 PET study. J Nucl Med. 2014;55:945–950. doi: 10.2967/jnumed.113.131045. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 65.Castanon N, Luheshi G, Laye S. Role of neuroinflammation in the emotional and cognitive alterations displayed by animal models of obesity. Front Neurosci. 2015;9:229. doi: 10.3389/fnins.2015.00229. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 66.Salim S, Chugh G, Asghar M. Inflammation in anxiety. Adv Protein Chem Struct Biol. 2012;88:1–25. doi: 10.1016/B978-0-12-398314-5.00001-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 67.Liu L, Mills PJ, Rissling M, et al. Fatigue and sleep quality are associated with changes in inflammatory markers in breast cancer patients undergoing chemotherapy. Brain Behav Immun. 2012;26:706–713. doi: 10.1016/j.bbi.2012.02.001. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 68.Tian Y, Guo S, Zhang Y, Xu Y, Zhao P, Zhao X. Effects of hydrogen-rich saline on hepatectomy-induced postoperative cognitive dysfunction in old mice. Mol Neurobiol. 2017;54:2579–2584. doi: 10.1007/s12035-016-9825-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 69.Johnson AW, Jaaro-Peled H, Shahani N, et al. Cognitive and motivational deficits together with prefrontal oxidative stress in a mouse model for neuropsychiatric illness. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2013;110:12462–12467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1307925110. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 70.Bierhaus A, Wolf J, Andrassy M, et al. A mechanism converting psychosocial stress into mononuclear cell activation. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2003;100:1920–1925. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0438019100. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 71.Epel ES, Blackburn EH, Lin J, et al. Accelerated telomere shortening in response to life stress. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2004;101:17312–17315. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0407162101. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 72.Steptoe A, Hamer M, Chida Y. The effects of acute psychological stress on circulating inflammatory factors in humans: a review and meta-analysis. Brain Behav Immun. 2007;21:901–912. doi: 10.1016/j.bbi.2007.03.011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 73.Mizuno K, Tajima K, Watanabe Y, Kuratsune H. Fatigue correlates with the decrease in parasympathetic sinus modulation induced by a cognitive challenge. Behav Brain Funct. 2014;10:25. doi: 10.1186/1744-9081-10-25. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 74.Yamaguti K, Tajima S, Kuratsune H. Autonomic dysfunction in chronic fatigue syndrome. Adv Neuroimmune Biol. 2013;4:281–289. [Google Scholar]