Abstract
Background
The liver disease is one of the most important traditional public health problems in Egypt. Oxidative stress is attributed to such pathological condition that further contributes to the initiation and progression of liver injury. In the present study, we have investigated if the strong antioxidant power of Nicotinamide (NA), Vitamin B2 (VB2), and Vitamin C (VC) can ameliorate TAA-induced oxidative stress-mediated liver injury in the rats.
Methods
Thirty-six albino rats were divided into six groups: Control group; TAA group (IP injection with TAA at a dosage of 200 mg/Kg three times a week for two months); TAA + NA group (rats administered with NA at a dosage of 200 mg/kg daily besides TAA as in the control); TAA + VB2 group (rats administered with vitamin B2 at a dosage of 30 mg/kg daily besides injection with TAA); TAA + VC group (rats administered with vitamin C at a dosage of 200 mg/kg daily along with injection of TAA). TAA + NA + VB + VC group (rats administered the with the three vitamins daily in TAA pre-injected at the respective doses described above).
Results
Treatment of rats with TAA led to a significant elevation of aspartate aminotransferase (AST), alanine aminotransferase (ALT), alkaline phosphatase (ALP), lactate dehydrogenase (LDH), total bilirubin, cholesterol, triglycerides, low-density lipoprotein (LDL) and tumor necrosis factor-alpha (TNF-α) in the serum samples. Moreover, malondialdehyde (MDA), hydroxyproline and nitic oxide (NO) were also significantly increased in the TAA-treated rats, while reduced glutathione (GSH), superoxide dismutase (SOD) and catalase (CAT) were significantly compromised in the hepatic samples. Rats administered with NA, VB2, and VC as individually or in combination ameliorated the deleterious effects of TAA that was confirmed by histopathology. However, the combination of the three vitamins was found more effective as compared to each of the vitamins.
Conclusion
Our work demonstrates that NA, VB2, and VC cross-talk with each other that act as a more potent biochemical chain of antioxidant defense against TAA-induced toxicities in vivo.
Keywords: Hepatotoxicity, Thioacetamide, Nicotinamide, Vitamin B2, Vitamin C, Inflammatory markers, Lipid profile, Oxidative stress
Background
Egypt has been a hot spring of academic research under tropical medicine programs. Due to such medical problems, the confronting physicians have been facing the complications of hepatic fibrosis and cirrhosis because of schistosomiasis and chronic viral infections. It led many of the prominent hepatologists to establish clinical liver centers in entire Egypt region [1]. Four over three decades, many investigators have been trying to find efficient and long-lasting clinical solutions for liver diseases.
Thioacetamide (TAA) is a thio-sulfur-containing compound, which has been frequently used in leather, motor fuel, textile, paper, food, and beverage industries since long [2]. Administration of one dose of TAA leads to acute hepatic toxicity, while chronic exposure causes hepatic cirrhosis and possible development of liver tumors. The metabolic activation of TAA by cytochrome P450 generates TAA-intermediates, and reactive oxygen species (ROS) that can further covalently bind to biologically significant molecules and increase cellular oxidative stress, lipid peroxidation, and deplete glutathione [3]. Nicotinamide (NA), is a precursor of essential coenzymes for numerous reactions in the body [4]. Although NA is known to prevent or treat pellagra [5], it has other pharmacological actions as an antioxidant [6], and antinociceptive [7]. Nicotinamide, the amide derivative of vitamin B3, has been shown to exhibit a number of anti-inflammatory properties including inhibition of inducible NO synthase (iNOS) [8], free radical scavenging [9], suppression of MHC class II expression [10] and intracellular adhesion molecule ICAM-1 expression on endothelial cells [11]. NA is changed to nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide by the aid of enzymes. These cellular pathways are essential for energy metabolism and may directly influence normal physiology, as well as disease progression [12]. For example, NA has been shown to protect against bleomycin-induced Pulmonary Fibrosis [13], and doxorubicin-induced nephrotoxicity [14].
Riboflavin (VB2) is the central component of the cofactors Flavin adenine dinucleotide (FAD). VB2 plays a key role in cellular function, growth, development and energy metabolism [15]. It is effective in preventing migraine [16] and reduces hepatocellular injury following liver ischemia through its role in lowering hepatic inducible nitric oxide synthase and nitric oxide [17]. VB2 can act against oxidative stress, especially lipid peroxidation and oxidative injury. It is reported that riboflavin protects the body against oxidative stress by glutathione redox cycling beside conversion of the reduced riboflavin to the oxidized form among other possible mechanisms [18, 19]. Vitamin C (VC) is the most important radical scavenging antioxidant in extracellular fluids [20] Vitamin C (ascorbic acid) is a six-carbon lactone is called an antioxidant because, by donating its electrons, it prevents other compounds from being oxidized [21]. VC has been reported to attenuate hepatic damage and can act synergistically with other vitamins in the management of oxidative stress [22]. Vitamin C was reported to form a synergy with other agents to protect the liver. One of the obvious synergies is between vitamin C and vitamin E that ameliorated ethanol-induced hepatotoxicity via normalization of transaminases, lipid peroxidation [23] and endogenous antioxidants [24].
Thus, this study aimed to investigate hepatoprotective activities of nicotinamide, vitamin B2, and vitamin C, separately or in combination, against thioacetamide-induced liver damage, hyperlipidemia and oxidative stress in rats. The hepatoprotective activity was assessed using liver function tests, lipid profile, hepatic oxidative stress parameters, inflammatory markers and hydroxyproline as hepatic fibrosis marker.
Methods
Chemicals
TAA, NA, vitamin B2 and vitamin C were purchased from Sigma-Aldrich Corporation (St Louis, MO, USA). Remaining all chemicals were of analytical grade from authentic companies of International repute.
Animals
The study was performed on six weeks’ old male albino rats weighing 120–150 g, obtained from the Egyptian Holding Company for Biological Products and Vaccines, Cairo, Egypt. The animals were kept in an environment with controlled temperature (25 °C), humidity (45–55%), and photoperiod (12-h/12-h light/dark cycle). All the animals under study had free access to chow diet and water. All animal care protocols were by the Research Ethics Committee, National Research Centre, Egypt.
Experimental design
The rats were sorted into six groups, each containing eight rats as follows:
Group I: Control rats without any treatment.
Group II: Rats injected IP with TAA at a dosage of 200 mg/Kg [25] thrice a week for two months.
Group III: Rats administered with NA at a dosage of 200 mg/kg [26] daily and injected with 200 mg/Kg of TAA IP thrice a week for two months.
Group IV: Rats administered with vitamin B2 at a dosage of 30 mg/kg [27] daily and injected with 200 mg/Kg of TAA IP thrice a week for two months.
Group V: Rats administered with vitamin C at a dosage of 200 mg/kg [28, 29] daily and injected with 200 mg/Kg of TAA IP thrice a week for two months.
Group VI: Rats administered with all three of the previous vitamins daily and injected with 200 mg/Kg of TAA IP thrice a week for two months. The ratio of a multivitamin was performed as previously described [30].
Samples collection
Blood samples were collected from each group by puncture of the retro-orbital venous sinus, into heparinized tubes under light ether anesthesia weekly. The blood was centrifuged at 1200×g for 10 min to separate plasma which was stored at − 40 °C. After collection of the blood samples, the animals from all the groups were autopsied under light ether anesthesia. The liver was removed from its surrounding tissues, placed into tubes and washed with normal saline (cold) and kept at − 40 °C. The liver tissues were homogenized in a cold potassium phosphate buffer (0.05 M, pH 7.4) and centrifuged at 3000 rpm for 10 min at 4 °C. The resulting supernatant of tissue homogenate was used for determination of the oxidative stress parameters.
Biochemical and inflammatory parameters assay
Serum AST, ALT, ALP, LDH, total bilirubin, total protein, cholesterol, triglycerides, LDL and HDL concentrations were determined calorimetrically using the commercial kits (Salucea Company, Netherlands). Moreover, hepatic MDA, GSH, CAT, SOD and NO were determined calorimetrically using kits manufactured by Bio-diagnostic, Egypt. Plasma TNF-α and hepatic hydroxyproline were determined by enzyme-linked immunoassay by the kits from R&D Systems (USA) and Koma Biotechnology (Seoul, Korea) respectively.
Histological studies
At the end of the experiment, a portion of a liver from each of the sacrificed rat was fixed in 10% buffered formalin and processed for paraffin sectioning after dehydrating them in various concentrations of alcohol, cleared with xylol and embedded in paraffin blocks. Sections of about 5 μm thickness were stained with hematoxylin and eosin (H&E) for histological study.
Statistical analysis
Data have been presented as mean ± S.E.M and analyzed by one-way ANOVA followed by least significant difference (LSD) using SPSS software (version 20.0, SPSS Inc., Chicago, IL).
Results
Liver function tests
The mean values illustrated in Table 1 showed a significant elevation of plasma AST, ALT, ALP, LDH and total bilirubin in rats treated with TAA only, while total protein decreased compared to the control. These effects on liver function parameters associated with injection with TAA were alleviated when the rats were also treated with NA, VB2 or VC, with a significant decrease in the liver enzyme levels and bilirubin and an increase in total protein. Administration of all three vitamins together had a more profound effect in mitigating the adverse parameters than when the rats were treated with just one of the vitamins.
Table 1.
Effect of Nicotinamide, Vitamin B2 and Vitamin C on liver function parameters in plasma of thioactamide treated rats
| Treatment Parameter | Control | TAA | TAA + NA | TAA + VB2 | TAA + VC | TAA + NA,VB2,VC |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AST(U/l) | 46.53 ± 1.08 | 269.36 ± 11.75a | 137.64 ± 6.83a,b | 142.43 ± 7.76a,b | 170.34 ± 7.33a,b | 95.17 ± 4.59a,b,c |
| ALT(U/l) | 23.17 ± 1.34 | 153.46 ± 8.63a | 114.56 ± 4.78a,b | 109.89 ± 9.32a,b | 94.57 ± 3.21a,b | 65.46 ± 1.96a,b,c |
| ALP(U/l) | 150.46 ± 10.06 | 676.35 ± 21.67a | 470.48 ± 26.41a,b | 418.34 ± 15.68a,b | 580.41 ± 19.73a,b | 242.00 ± 15.47a,b,c |
| LDH | 212.55 ± 8.69 | 802.40 ± 4.75a | 512.07 ± 18.67a,b | 450.82 ± 14.25a,b | 478.16 ± 17.56a,b | 275.44 ± 12.49a,b,c |
| Total bilirubin(mg/dl) | 0.43 ± 0.01 | 0.91 ± 0.03a | 0.63 ± 0.01a,b | 0.70 ± 0.04a,b | 0.66 ± 0.03a,b | 0.54 ± 0.02a,b,c |
| Total protein(g/dl) | 7.34 ± 1.58 | 5.27 ± 0.10a | 5.88 ± 0.19a,b | 6.09 ± 0.27a,b | 6.47 ± 0.34a,b | 7.55 ± 0.10a,b,c |
aSignificant difference from control
bSignificant difference from TAA group
cSignificant difference from TAA + NA, TAA + VB2, TAA + VC
Lipid profile
TAA injection resulted in a significant increase in the plasma level of cholesterol, triglycerides, and LDL, while HDL decreased significantly (Table 2). Treating the rats with TAA and NA, VB2 or VC, however, resulted in the changes in these parameters being reversed to some extent. Once again, a greater degree of improvement was noticed when the three vitamins were combined.
Table 2.
Effect of Nicotinamide,Vitamin B2 and Vitamin C on plasma lipid profile of rats treated with thioacetamide
| Control | TAA | TAA + NA | TAA + VB2 | TAA + VC | TAA + NA,VB2, VC | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cholesterol(mg/dl) | 70.33 ± 3.45 | 158.58 ± 5.67a | 135.11 ± 4.39a,b | 114.37 ± 7.01a,b | 102.44 ± 3.12a,b | 84.37 ± 2.49a,b,c |
| Triglycerides (mg/dl) | 64.58 ± 3.16 | 190.86 ± 8.23a | 159.11 ± 4.23a,b | 140.27 ± 3.55a,b | 96.75 ± 2.81a,b | 72.60 ± 5.36b,c |
| HDL (mg/dl) | 33.62 ± 1.38 | 26.09 ± 1.43a | 31.96 ± 1.02 | 30.25 ± 0.78 | 30.43 ± 1.54 | 32.48 ± 2.57 |
| LDL(mg/dl) | 49.72 ± 1.62 | 100.83 ± 3.58a,b | 70.39 ± 3.08a,b | 76.00 ± 2.51a,b | 66.42 ± 2.81a,b | 53.17 ± 1.94b,c |
aSignificant difference from control (P
bSignificant difference from TAA group
cSignificant difference from TAA + NA, TAA + VB2, TAA + VC
Oxidative stress parameters
The data relating to hepatic oxidative stress markers are summarized in Table 3 and show a significant decrease in hepatic GSH, CAT, and SOD in the TAA group, but a marked increase in hepatic MDA, NO, Hydroxyproline and plasma TNF-α. These changes were significantly reversed in rats treated with the three vitamins in combination.
Table 3.
Effect of Nicotinamide, Vitamin b2 and Vitamin C on hepatic MDA (nmol/mg), GSH (μmol/g tissue), catalase (U/g tissue), SOD (U/g tissue), NO (nmol/g,Hydroxyproline (Ug/g tissue) and plasma TNF-α (Pg/ml)
| Control | TAA | TAA + NA | TAA + VB2 | TAA + VC | TAA + NA,VB2,VC | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MDA | 6.43 ± 0.23 | 11.78 ± 0.45a | 8.59 ± 0.42a,b | 9.04 ± 0.47a,b | 8.16 ± 0.32a,b | 7.35 ± 0.16a,b,c |
| GSH | 32.78 ± 1.06 | 19.68 ± .0.30a | 23.79 ± 0.51a,b | 23.55 ± 1.02a,b | 25.82 ± 0.54a,b | 29.48 ± 0.49b,c |
| Catalase | 503.17 ± 30.00 | 266.84 ± 22.57a | 400.46 ± 20.33a,b | 370.16 ± 12.93a,b | 395.00 ± 18.71a,b | 468.52 ± 8.75b,c |
| SOD | 275.43 ± 8.41 | 131.73 ± 6.98a | 200.17 ± 11.07a,b | 180.00 ± 4.51a,b | 188.72 ± 9.12a,b | 249.84 ± 8.26b,c |
| NO | 65.78 ± 3.18 | 127.34 ± 6.38a | 80.67 ± 3.74a,b | 93.08 ± 4.11a,b | 88.71 ± 3.53a,b | 74.96 ± 2.56b |
| H.Prol | 112.47 ± 6.32 | 763.71 ± 21.49a | 426.85 ± 10.65a,b | 512.67 ± 17.53a,b | 459.27 ± 13.89a,b | 342.79 ± 8.29a,b,c |
| TNF-α | 12.42 ± 0.25 | 76.28 ± 1.03a | 44.90 ± 0.56a,b | 60.85 ± 0.52a,b | 53.67 ± 0.36a,b | 36.42 ± 0.11a,b,c |
aSignificant difference from control
bSignificant difference from TAA group
cSignificant difference from TAA + NA, TAA + VB2, TAA + VC
Histopathological investigation of the liver
Control hepatic tissue
Figure 1 shows the typical structure of the hepatic tissues with normal polygonal hepatocytes and normal blood sinusoids.
Fig. 1.
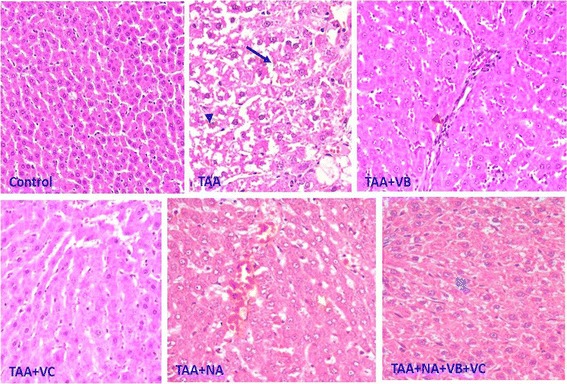
Representative photos of the hepatic tissues from the control and the various treated groups. Arrow: Dilated sinusoids; Black arrow head: Vacuolated hepatocytes; Red arrow head: Inflammatory cell infiltration; Yellow arrow head: Vesiculated nucleus; Blue arrow head: Normal nucleus
The effect of TAA
Histopathological examination of hepatic sections from TAA rats revealed the presence of vacuolated hepatocytes with degenerated nuclei and irregular and damaged cell membranes. Disturbed and dilated blood sinusoids were also clearly observed along with fibroblasts distributed extensively through the hepatic tissue of this group. Moreover, mitotic figures were also noted in some hepatic sections (Fig. 1).
The effect of combining TAA with treatment with VB
The sections from this group showed an increased number of irregular hepatocytes with degenerated nuclei. Disturbed and narrowed blood sinusoids, frequently infiltrated with inflammatory cells, were also a prominent feature in the liver sections of these rats, along with fibroblasts extensively distributed through the hepatic tissue (Fig. 1).
The effect of combining TAA with treatment with VC
The general structure of the hepatic tissue in this group was markedly improved. Hepatocytes with faint cytoplasm but with healthy nuclei were arranged in hepatic cords creating narrow blood sinusoids (Fig. 1).
The effect of combining TAA with treatment with NA
Histological examination of different sections from rats of this group revealed that there was a marked improvement in the distribution of hepatocytes relative to the hepatic blood sinusoids. On the other hand, hepatocytes appeared with vesiculated nuclei showing partially degenerated chromatin materials.
The effect of combining TAA with treatment with VC and VB
Although there was an apparent improvement in the general hepatic architecture, many pathological signs could still be observed in the sections of this group. Some hepatocytes appeared vacuolated, and the blood sinusoids were narrow and disturbed in comparison with those in the control sections (Fig. 1).
Discussion
Liver disease has been one of the traditionally major health issues in Egypt for a long time. The primary causes of liver disease are schistosomiasis (from the 1950s until the 1980s) and hepatitis C virus (1990s). Here, we used TAA to induce an experimental model of liver damage to mimic the pathophysiological symptoms of acute human liver diseases. TAA causes hepatic fibrosis through liver cell membrane injury, which in turn, causes a marked increase in enzymes levels. In the present study, TAA caused a significant increase in ALT, AST, ALT, LDH and bilirubin levels versus to the control the ones. Elevation of the activity of liver enzymes after TAA administration indicates cellular leakage, loss of structural and functional integrity of the liver [31].
We have previously reported several natural products with antioxidant and anti-inflammatory properties in vivo studies with promising results [32–35]. The present investigation has shown that rats treated with TAA have increased hepatic Nitric oxide (NO) and plasma TNF-α. Although NO is an important signaling molecule; yet its excess production results in the formation of peroxynitrite which is a very invasive cellular oxidant [36]. It is interesting, therefore to report that both these parameters were effectively countered in the animals administered with NA, VB2 or VC in the present study.
Lots of literature on anti-oxidative therapy and antioxidants have been proposed to prevent and treat liver diseases [37] highlighting the curative properties of antioxidants in such ailments. Specifically, treatment of TAA rats with NA improved the activities of liver enzymes and the histopathological structure of the liver. Earlier, we have reported that NA exerts a hepatoprotective effect against a high-fat ethanol diet and acetaminophen-induced acute liver injury [38]. Besides, it is documented that NA benefits both dams and pups; hence it merits evaluation for preventing or treating Preeclampsia complication in human pregnancies [39]. Furthermore, NA has been effective in ameliorating many oxidative stress-induced pathological conditions [40].
Similarly, VC also normalized the increased activity of liver enzymes in the plasma samples confirming its hepatoprotective effects in the present investigation. Studies have shown that this vitamin has hepato-protective properties due to its antioxidative properties, that gets better in synergy with other agents. The co-administration of ascorbic acid with alpha-tocopherol acetate and sodium selenate ameliorated ethanol-induced liver damage in rats [41]. The vitamin is believed to normalize the liver function parameters like ALT, AST, LDH, ALP, some endogenous antioxidants as well as blood hydroperoxide and malondialdehyde in the livers of carbon tetrachloride intoxicated rats [42, 43]. Besides, it has shown restoration and reconstitution of the polyfunctional, long-lived T-cells in the diabetic rats [44]. Furthermore, the vitamin is the most important hydrophilic antioxidant with high efficiency of free radical scavenging in vivo [45]. However, the mechanism involved appears to be ascorbyl radical reacting with other free radicals to stop their propagation [46].
It is documented that VB2 significantly improves serum and the histological parameters of hepatocellular damage and neutrophil infiltration following liver ischemia in mice [17]. Recently, many studies have also demonstrated that irradiated riboflavin protects the cisplatin-induced oxidative stress-mediated hepatotoxicity and nephrotoxicity in rodent based studies [47–50]. Furthermore, VB2 and UV light together were able to reduce the titer of MERS-CoV in human plasma products to a non-detecting level suggesting that the combination may lower the risk of transfusion transmission of MERS-CoV [51]. In this study treatment of rats with the three vitamins in combination led to a more pronounced alleviation of the effects of the liver injury induced by TAA. We have previously found that folic acid and melatonin as a combination was superior to using them individually regarding recovering hepatic function and structure [51]. In the present data, TAA administration resulted in a significant reduction in the plasma levels of a total protein that might be indicative of injury in the hepatocytes and excessive destruction of proteins including antioxidant enzymes and cellular reducing powers including SH-protein bond production or alterations in RNA sequences in the target tissues. An increase in ALP activity and bilirubin level after TAA treatment reflects the pathological change in the biliary flow in the animals. Likewise, their suppression in the rats treated with NA, VB2, and VC as combination suggests possible stabilization of the biliary dysfunction. Furthermore, TAA also enhanced the extent of lipid peroxidation, liver fibrosis and cirrhosis accompanied by the morphological and many other biochemical alterations resembling that of the human disease [52, 53]. Therefore, it is logical to say that TAA caused the cellular damage by inhibiting the activity of the antioxidant enzymes in the present study [54]. The combination of three vitamins significantly decreased liver hydroxyproline content in TAA-treated rats, which may be due to a decline in the accumulation of fibrotic tissue in the liver. Our findings are in accord with many earlier studies emphasizing the role of oxidative stress in the mechanisms of liver fibrosis and cirrhosis [55]. The antioxidant enzymes (SOD and CAT) as well as reducing power GSH were found significantly improved in the liver homogenates of the rats treated with TAA followed by the three-vitamins combination as compared to the control. The improvement of all these parameters seems to restore the structural and functional integrity of the target organs in the animals [56].
Hyperlipidaemia is a vascular risk factor associated with atherosclerosis, coronary artery diseases, cerebral vascular disease and peripheral disease. The present investigation showed that the three vitamin combination inhibits the increase in cholesterol, triglycerides and LDL levels in TAA treated rats. However, the combination increased the HDL level. Our study showed that TAA toxicity stimulated hypercholesterolemia with hypertriglyceridemia. VC may hinder the development of atherosclerosis and prevent the onset of acute coronary events by several molecular mechanisms. The vitamin also helps in maintaining arterial wall integrity that can alter cholesterol metabolism by modulating the conversion of cholesterol into bile acids, while it affects plasma triglyceride levels via modulation by lipoprotein lipase activity [57]. The vitamin has also been shown to protect HDL cholesterol from lipid oxidation. It, therefore, allows for reverse cholesterol transport involving the removal of unesterified cholesterol from extrahepatic cell membranes into esterified ones via lecithin: cholesterol acyltransferase [58]. Apart from these, another vitamin taken under the present study, nicotinamide has been reported to decrease serum cholesterol, triglycerides and free fatty acids in the fasting rat [59]. Moreover, NA induced up-regulation of tumor necrosis factor-α (TNF-α) transcription and interleukin-6 (IL-6). Both the cytokines are with lipolytic properties, thereby increasing free fatty acid release [60].
All the three vitamins have an excellent antioxidant and anti-inflammatory properties. Upon their co-administration in TAA pre-treated rodents, they decreased the oxidative stress that further improved cellular structure and functionality. The diminished liver function markers and cholesterol, LDL and TNF-α concomitant with enhanced activity of antioxidant enzymes (SOD and CAT) and replenishment of the cellular reducing power (GSH) are vivid indicators of recovery of tissue damage. The improvement in all these parameters indicates that the cellular, molecular and structural damage incurred by TAA were alleviated by the combination of the vitamins. As each vitamin has a different degree of antioxidant and anti-inflammatory properties, their respective combination gives a different level of outcome after the treatment. However, when all the vitamins were administered together, they showed a synergistic ameliorative effect against the TAA-induced toxic insults in vivo (Fig. 2).
Fig. 2.

Showing putative mechanism of TAA-toxicity amelioration by the proposed combination of the vitamins
Conclusions
The present study entails the combination of NA, VB2, and VC has stronger antioxidant and anti-inflammatory power as compared to the individual potential of the vitamins against TAA-induced toxicity. The three vitamins exert the protective effects through their antioxidant, antifibrosis and anti-inflammatory properties that consequently restore the structure and functionality of the target organs. Hence, anti-oxidative therapy mainly comprising of natural antioxidants represents a reasonable therapeutic approach for the prevention and treatment of oxidative stress-mediated liver diseases.
Acknowledgments
The authors extend their appreciation to the Deanship of Scientific Research at King Saud University for funding the work through the research group Project no. RG-1436-004.
Funding
We declare at this moment the role of the Deanship of Scientific Research at King Saud University in the design of the study and collection, analysis, and interpretation of data and in writing the manuscript.
Availability of data and materials
All data generated or analyzed during this study are included in this published article.
Abbreviations
- CAT
Catalase
- GSH
Glutathione
- HDL
High density lipoprotein
- LDL
Low density lipoprotein
- MDA
Malondialdehyde
- NA
Nicotinamide
- NO
Nitric oxide
- S.E.M.
Tumour necrosis factor-alpha (TNF-α), Standard error of mean
- SOD
Superoxide dismutase
- TAA
Thioacetamide
- VB2
Vitamin B2
- VC
Vitamin C
Authors’ contributions
SB prepared the introduction and conducted the animal care, analyzed the biochemical data, prepared the results, figures, and the oxidative stress tests. HE designed this study, supervised the practical work and finalized the manuscript. SM revised the manuscript. IA provided the chemicals and contributed to the final revision. IH designed the mechanism diagramme and checked English grammar, text, organization, and typesetting of the paper. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Ethics approval and consent to participate
The study was approved by ethical committee of Zoology Department, King Saud University, Riyadh.
Consent for publication
The authors declare that there is no any individual person’s data in any form (including individual details, images or videos).
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Contributor Information
Samir A. E. Bashandy, Email: bashandys@hotmail.com
Hossam Ebaid, Email: hossamebaid@yahoo.com.
Sherif A. Abdelmottaleb Moussa, Email: hebaid@yahoo.com
Ibrahim M. Alhazza, Email: imalhazza@hotmail.com
Iftekhar Hassan, Email: iftekharhassan2002@gmail.com.
Abdulaziz Alaamer, Email: mebaid@yahoo.com.
Jameel al Tamimi, Email: jtamimi1010@gmail.com.
References
- 1.Strickland GT. Liver disease in Egypt: hepatitis C superseded schistosomiasis as a result of iatrogenic and biological factors. Hepatology. 2006;43(5):915–922. doi: 10.1002/hep.21173. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Watson RR, Preedy V. Bioactive food as dietary interventions for liver and gastrointestinal disease. 1. USA: Academic Press, Elsevier Inc; 2012. [Google Scholar]
- 3.Pallottini V, Martini C, Bassi AM, Romano P, Nanni G, Trentalance A. Rat HMG-CoA reductase activation in thioacetamide-induced liver injury is related to an increased reactive oxygen species content. J Hepatol. 2006;44(2):368–374. doi: 10.1016/j.jhep.2005.06.011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Rolfe HM. A review of nicotinamide: treatment of skin diseases and potential side effects. Cosmetic Dermat. 2014;13:324–328. doi: 10.1111/jocd.12119. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Hegyi J, Schwartz RA, Hegyi V. Pellagra: dermatitis, dementia, and diarrhea. Int Dermatol. 2004;43:1–5. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-4632.2004.01959.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Abd Allah OM, El-Din S, El Debakey AF. Effect of combined Fenofibrate and nicotinamide on oxidative stress and inflammatory cytokines involved in cisplatin-induced nephrotoxicity in rats. American Pharmacol Toxicol. 2014;9:206–222. doi: 10.3844/ajptsp.2014.206.222. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Godin AM, Ferreira WC, Rocha LS, Seniuk JT. Antinociceptive and anti-inflammatory activities of nicotinamide and its isomers in different experimental models. Pharmacol Biochem Behavior. 2011;99:782–788. doi: 10.1016/j.pbb.2011.07.003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Andersen HU, Jorgensen KH, Egeberg J, Mandrup-Poulsen T, Nerup J. Nicotinamide prevents interleukin-1 effects on accumulated insulin release and nitric oxide production in rat islets of Langerhans. Diabetes. 1994;43:770–777. doi: 10.2337/diab.43.6.770. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Burkart V, Koike T, Brenner HH, Kolb H. Oxygen radicals generated by the enzyme xanthine oxidase lyse rat pancreatic islet cells in vitro. Diabetologia. 1992;35:1028–1034. doi: 10.1007/BF02221677. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Otsuka A, Hanafusa T, Miyagawa J, Kono N, Tarui S. Nicotinamide and 3-aminobenzamide reduce interferon-gamma-induced class II MHC (HLA-DR and -DP) molecule expression on cultured humanendothelial cells and fibroblasts. Immunopharmacol Immunotoxicol. 1991;13:263–280. doi: 10.3109/08923979109019705. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Hiromatsu Y, Sato M, Tanaka K, Ishisaka N, Kamachi J, Nonaka K. Inhibitory effects of nicotinamide on intercellular adhesion molecule-1 expression on cultured human thyroid cells. Immunology. 1993;80:330–332. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Hara N, Yamada K, Shibata T, Osago H, Hashimoto T, Tsuchiya M. Elevation of cellular NAD levels by nicotinic acid and involvement of nicotinic acid phosphoribosyltransferase in human cells. Biol Chem. 2007;282:24574–24582. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M610357200. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Mikaili P, Hemmati AA, Khodayar MJ, Ghafurian M, Rashidi I. Evaluation of the effects of nicotinamide on the bleomycin-induced pulmonary fibrosis in rat. Int Animal Vet Advan. 2011;3:330–336. [Google Scholar]
- 14.Ayla S, Seckin I, Tanriverdi G, Cengiz M, Eser M, Soner BC, Oktem G. Doxorubicin induced nephrotoxicity: protective effect of nicotinamide. International Journal of Cell Biology. 2011:1–9. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- 15.Said HM, Ross AC. Riboflavin. In: Ross AC, Caballero B, Cousins RJ, Tucker KL, Ziegler TR, editors. Modern nutrition in health and disease. 11. Baltimore, MD: Lippincott Williams & Wilkins; 2014. pp. 325–330. [Google Scholar]
- 16.Sherwood M, Goldman RD. Effectiveness of riboflavin in pediatric migraine prevention. Can Fam Physician. 2014;60:244–246. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Sanches SC, Ramalho LN, Mendes-Braz M, Terra VA. Riboflavin (vitamin B-2) reduces hepatocellular injury following liver ischaemia and reperfusion in mice. Food Chem Toxico. 2014;67:65–71. doi: 10.1016/j.fct.2014.02.013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Ashoori M, Saedisomeolia A. Riboflavin (vitamin B2) and oxidative stress: a review. British Nutrition. 2014;111:1985–1991. doi: 10.1017/S0007114514000178. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Hassan I, Chibber S, Naseem I. Ameliorative effect of riboflavin on the cisplatin induced nephrotoxicity and hepatotoxicity under photoillumination. Food Chem Toxicol. 2010;48(8–9):2052–2058. doi: 10.1016/j.fct.2010.05.004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Popovic LM, Mitic NR, Miric D, Bisevac B, Miric M, Popovic B. Influence of vitamin C supplementation on oxidative stress and neutrophil inflammatory response in acute and regular exercise. Oxid Med Cell Long. 2015:1–7. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- 21.Padayatty SJ, Katz A, Wang Y, Eck P, Kwon O, Lee J-H, et al. Vitamin C as an antioxidant: evaluation of its role in disease prevention. J Am Coll Nutr. 2003;22(1):18–35. doi: 10.1080/07315724.2003.10719272. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Layachi N, Kechrid Z. Combined protective effect of vitamins C and E on cadmium induced oxidative liver injury in rats. Afric Biotechnol. 2012;11:16013–16020. doi: 10.5897/AJB12.2665. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Oyinbo CA, Dare WN, Okogun GRA, An-yanwu LC, Ibeabuchi NM, Noronha CC, Okanlawon OA. The Hepatoprotective effect of vitamin C and E on hepatotoxicity induced by ethanol in Sprague Dawley rats. Pak J Nutr. 2006;5(6):507–511. doi: 10.3923/pjn.2006.507.511. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Yanadarg Y, Ozsoy-Sacan O, Ozdil S, Bolkent S. Combined effects of vitamin C, vitamin E, and sodium Selenate supplementation on absolute ethanol-induced injury in various organs of rats. Int J Toxicol. 2007;26(6):513–23. [DOI] [PubMed]
- 25.Elhaggagy AA, Alsaggaf S, Amin HA. The preventive and therapeutic role of curcumin in liver cirrhosis. Life Science Journal. 2014;11(10):328–338. [Google Scholar]
- 26.John CM, Ramasamy R, Al Naqeeb G, Al-Nuaimi AH, Adam A. Nicotinamide supplementation protects gestational diabetic rats by reducing oxidative stress and enhancing immune responses. Curr Med Chem. 2012;19:5181–5186. doi: 10.2174/092986712803530449. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Al-Harbi NO, Imam F, Nadeem A, Al-Harbi MM. Riboflavin attenuates lipopolysaccharide-induced lung injury in rats. Toxicol Mech Methods. 2015;25:417–423. doi: 10.3109/15376516.2015.1045662. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Farshid AA, Tamaddonfard E, Ranjbar S. Oral administration of vitamin C and histidine attenuate cyclophosphamide-induced hemorrhagic cystitis in rats. Indian Pharmacol. 2013;45:126–129. doi: 10.4103/0253-7613.108283. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Chen TM, Subeq YM, Lee RP, Chiou TW, Hsu BG. Single dose intravenous thioacetamide administration as a model of acute liver damage in rats. Int Exp Pathol. 2008;89:223–231. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2613.2008.00576.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Ebaid H, Hassanein KA, El-Feki MA. The undenatured whey protein enhanced wound healing in mice. J Egyp Germ Society Zool. 2005;40:2–27. [Google Scholar]
- 31.Ebaid H, Salem A, Sayed A, Metwalli A. Whey protein enhances normal inflammatory responses during cutaneous wound healing in diabetic rats. Lipids Health Dis. 2011;10:235. doi: 10.1186/1476-511X-10-235. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Ebaid H, Hassan I, Bashandy S, Taha NA, Mahmood A, Alomar S, Alhazza I, Mashaly A, Rady A. Zinc improves the immune function and the proliferation of lymphocytes in Cadmium-treated rats. Cent Eur Immunol. 2014;39:441–448. doi: 10.5114/ceji.2014.47726. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Bashandy SA, El Awdan SA, Ebaid H, Alhazza IM. Antioxidant Potential of Spirulina platensis Mitigates Oxidative Stress and Reprotoxicity Induced by Sodium Arsenite in Male Rats. Oxid Med Cell Long. 2016, 2016:7174351. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- 34.Fouda MM, Abdel-Mohsen AM, Ebaid H, Hassan I, Al-Tamimi J, Abdel-Rahman RM, Metwalli A, Alhazza I, Rady A, El-Faham A, Jancar J. Wound healing of different molecular weight of hyaluronan; in-vivo study. Int Biol Macromol. 2016;89:582–591. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2016.05.021. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Al Basher G, Ebaid H, Ajarem J, Abu-Taweel G. Impairment of active avoidance learning and sensory motor reflexes in mice offspring induced by perinatal acute toxic exposure to selenium. Afric Pharmacy Pharmacol. 2011;5:1389–1397. doi: 10.5897/AJPP11.271. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Medina J, Moreno-Otero R. Pathophysiological basis for antioxidant therapy in chronic liver disease. Drugs. 2005;65:2445–2461. doi: 10.2165/00003495-200565170-00003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Hassanin KM, Hashem KS, Abdel-Kawi SH. Hepatoprotective Effects of vitamin C and micronized vitamin C against paracetamol induced hepatotoxicity in rats: a comparative study. Int Biochem Biotechnol. 2013;2:474–483. [Google Scholar]
- 38.Li F, Fushima T, Oyanagi G, Townley-Tilson HD, Sato E, Nakada H, Oe Y, Hagaman JR, Wilder J, Li M, Sekimoto A. Nicotinamide benefits both mothers and pups in two contrasting mouse models of preeclampsia. Proc Natl Acad Sci. 2016;(47):13450–5. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- 39.Mahmoud YI, Mahmoud AA. Role of nicotinamide (vitamin B3) in acetaminophen-induced changes in rat liver: Nicotinamide effect in acetaminophen-damged. Exp Toxicol Pathol. 2016;68:345–354. doi: 10.1016/j.etp.2016.05.003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Ozdil S, Bolkent S, Yanardag R, Arda-Pirincci P. Protective effects of ascorbic acid, dl-alpha-tocopherol acetate, and sodium Selenate on ethanol-induced liver damage of rats. Biol Trace Element Res. 2011;97:149–162. doi: 10.1385/BTER:97:2:149. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Bashandy S, Omara E, Ebaid H, Amin M, Soliman M. Role of zinc as an antioxidant and anti-inflammatory to relieve cadmium oxidative stress induced testicular damage in rats. Asian Pac J Trop Biomed. 6(12):1056–64
- 42.Bashandy SA, Alwasel SH. Carbon tetrachloride–induced hepatotoxicity and nephrotoxicity in rats: protective role of vitamin C. Pharmacol Toxicol. 2011;6:283–92.
- 43.Badr G, Bashandy S, Ebaid H, Mohany M, Sayed D. Vitamin C supplementation reconstitutes polyfunctional T cells in streptozotocin-induced diabetic rats. Eur Nutr. 2012;51:623–633. doi: 10.1007/s00394-011-0176-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44.Lykkesfeldt J. Determination of ascorbic acid and dehydroascorbic acid in biological samples by high-performance liquid chromatography using subtraction methods: reliable reduction with tris[2-carboxyethyl]phosphine hydrochloride. Anal Biochem. 2000;15:89–93. doi: 10.1006/abio.2000.4592. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45.Oroian M, Escriche I. Antioxidants: characterization, natural sources, extraction and analysis. Food Res Int. 2015;74:10–36. doi: 10.1016/j.foodres.2015.04.018. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46.Liu S, Li S, Wang B, Lin X, Wu Y, Liu H, Qu X, Dai J, X1 Z, Zhou H. Scleral cross-linking using riboflavin UVA irradiation for the prevention of myopia progression in a Guinea pig model: blocked axial extension and altered scleral microstructure. PLoS One. 2016;(9):0165792. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- 47.Keil SD, Bowen R, Marschner S. Inactivation of Middle East respiratory syndrome coronavirus (MERS-CoV) in plasma products using a riboflavin-based and ultraviolet light-based photochemical treatment. Transfusion. 2016;(12):2948–52. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- 48.Hassan I, Chibber S, Naseem I. Vitamin B2: a promising adjuvant in cisplatin based chemoradiotherapy by cellular redox management. Food Chem Toxicol. 2013;59:715–723. doi: 10.1016/j.fct.2013.07.018. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 49.Hassan I, Chibber S, Khan AA, Naseem I. Riboflavin ameliorates cisplatin induced toxicities under Photoillumination. PLoS One. 2012;7(5):e36273. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0036273. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 50.Ebaid H, Bashandy SA, Alhazza IM, Rady A, El-Shehry S. Folic acid and melatonin ameliorate carbon tetrachloride-induced hepatic injury, oxidative stress and inflammation in rats. Nutr Metab (Lond) 2013;10:20. doi: 10.1186/1743-7075-10-20. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 51.Abdalfattah AA, El-Ebiary AA, Hantash EM. Study of the effects of melatonin on experimentally induced hepatic Fibrogenesis in rats. Intern Advanced Res. 2016;4:1187–1197. [Google Scholar]
- 52.Li X, Benjamin IS, Alexander B. Reproducible production of thioacetamide-induced macronodular cirrhosis in the rat with nomortality. Hepato. 2002;36:488–493. doi: 10.1016/S0168-8278(02)00011-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 53.Sarkar MK, Sil PC. Hepatocytes are protected by herb Phyllanthus Niruri protein isolate against thioacetamide toxicity. Pathophysiology. 2007;14:113–120. doi: 10.1016/j.pathophys.2007.08.001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 54.Wang H, Wei W, Wang NP. Melatonin ameliorates carbon tetrachloride-induced hepatic fibrogenesis in rats via inhibition of oxidative stress. Life Sci 200577:1902–1915. [DOI] [PubMed]
- 55.Masella R, Di Benedetto R, Vari R, Filesi C, Giovannini C. Novel mechanisms of natural antioxidant compounds in biological systems: involvement of glutathione and glutathione-related enzymes. Nutr Biochem. 2005;16:577–586. doi: 10.1016/j.jnutbio.2005.05.013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 56.Villacorta L, Azzi A, Zingg JM. Regulatory role of vitamins E and C on extracellular matrix components of the vascular system. Molecular Asp Med. 2007;28:507–537. doi: 10.1016/j.mam.2007.05.002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 57.Hillstrom RJ, Yacapin-Ammons AK, Lynch SM. Vitamin C Inhibits lipid oxidation in human HDL. J Nutr. 2003;133(10):3047–3051. doi: 10.1093/jn/133.10.3047. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 58.Dalton C, VanTrabert TC, Dwyer JX. Relationship of nicotinamide and nicotinic acid to hypolipidemia. Biochem Pharmacol. 1970;19(9):2609–2619. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(70)90011-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 59.Choi S, Yoon H, Oh KS, Oh YT, Kim YI, Kang I, Youn JH. Widespread effects of nicotinic acid on gene expression in insulin-sensitive tissues: implications for unwanted effects of nicotinic acid treatment. Metabolism. 2011;60:134–144. doi: 10.1016/j.metabol.2010.02.013. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 60.Plomgaard P1, Fischer CP, Ibfelt T, Pedersen BK, van Hall G. Tumor necrosis factor-alpha modulates human in vivo lipolysis. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2008;93:543-9. [DOI] [PubMed]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Data Availability Statement
All data generated or analyzed during this study are included in this published article.


