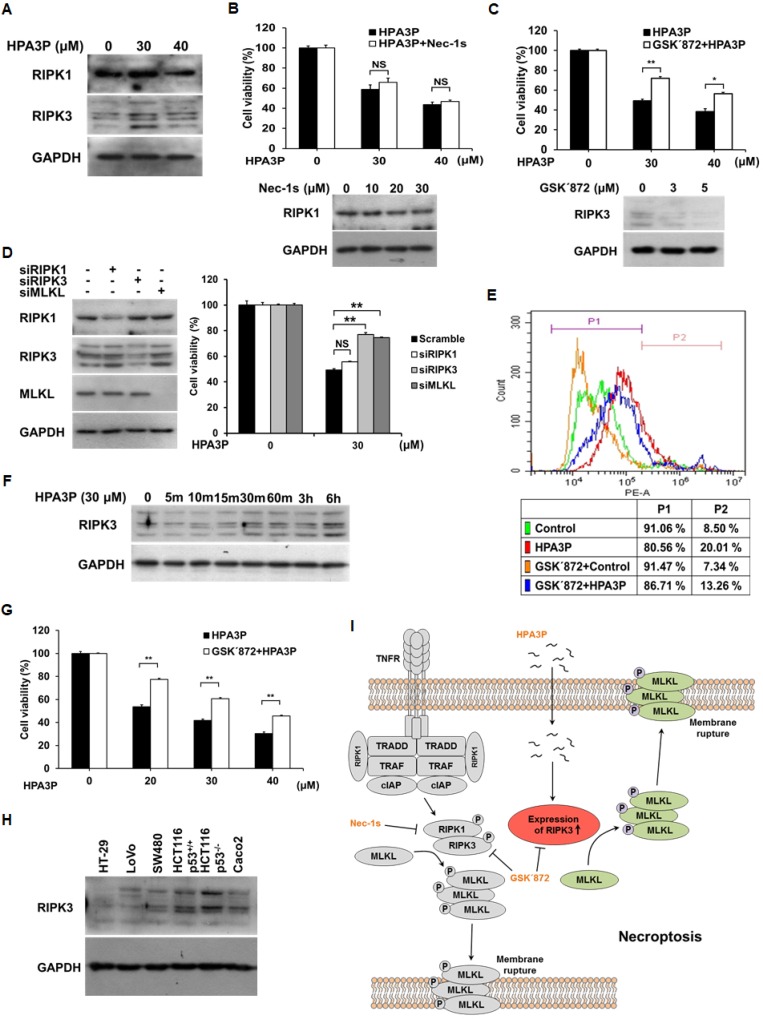
Figure 5. Low concentrations of HPA3P induce RIPK3-dependent necroptosis in HCT116 p53+/+ cells.
(A) HCT116 p53+/+ cells were treated with HPA3P for 6 h. The cell lysates were analysed for RIPK1 and RIPK3 expression by western blotting. The cells were pretreated with 30 μM Nec-1s (B) or 3 μM GSK΄872 (C) for 2 h and (D) transfected with negative-control (scramble), RIPK1, RIPK3, and MLKL siRNA for 24 h. The cells were subsequently treated with HPA3P. HPA3P-induced cytotoxicity was measured by MTT assay. (B–D) The cells were treated with Nec-1s or GSK΄872, and transfected with siRNA for 24 h. The cell lysates were analysed by western blot analysis. (E) The cells were treated with 3 μM GSK΄872 for 2 h and subsequently treated with 30 μM HPA3P for 6 h. The cells were stained with PI for flow cytometric analysis. (F) The cells were treated with 30 μM HPA3P for the indicated times. RIPK3 expression was analysed by western blotting. (G) The cells were pretreated with 3 μM GSK΄872 for 2 h and then treated with HPA3P for 24 h. Cell viability was measured by MTT assay. *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01 indicate a significant difference between the indicated groups. NS, not significant. (H) The colon cancer cell lysates used in this study were analysed by western blotting. (I) Schematic diagram of HPA3P-induced necroptosis.