This randomized clinical trial examines whether monthly high-dose vitamin D supplementation prevents cardiovascular disease in the general population.
Key Points
Question
Does monthly high-dose vitamin D supplementation prevent cardiovascular disease?
Findings
In a randomized clinical trial that included 5108 participants from the community, the cumulative incidence of cardiovascular disease for a median follow-up period of 3.3 years was 11.8% among participants given 100 000 IU of vitamin D3 monthly and 11.5% among those given placebo.
Meaning
Monthly high-dose vitamin D supplementation did not prevent cardiovascular disease and should not be used for this purpose.
Abstract
Importance
Cohort studies have reported increased incidence of cardiovascular disease (CVD) among individuals with low vitamin D status. To date, randomized clinical trials of vitamin D supplementation have not found an effect, possibly because of using too low a dose of vitamin D.
Objective
To examine whether monthly high-dose vitamin D supplementation prevents CVD in the general population.
Design, Setting, and Participants
The Vitamin D Assessment Study is a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial that recruited participants mostly from family practices in Auckland, New Zealand, from April 5, 2011, through November 6, 2012, with follow-up until July 2015. Participants were community-resident adults aged 50 to 84 years. Of 47 905 adults invited from family practices and 163 from community groups, 5110 participants were randomized to receive vitamin D3 (n = 2558) or placebo (n = 2552). Two participants retracted consent, and all others (n = 5108) were included in the primary analysis.
Interventions
Oral vitamin D3 in an initial dose of 200 000 IU, followed a month later by monthly doses of 100 000 IU, or placebo for a median of 3.3 years (range, 2.5-4.2 years).
Main Outcomes and Measures
The primary outcome was the number of participants with incident CVD and death, including a prespecified subgroup analysis in participants with vitamin D deficiency (baseline deseasonalized 25-hydroxyvitamin D [25(OH)D] levels <20 ng/mL). Secondary outcomes were myocardial infarction, angina, heart failure, hypertension, arrhythmias, arteriosclerosis, stroke, and venous thrombosis.
Results
Of the 5108 participants included in the analysis, the mean (SD) age was 65.9 (8.3) years, 2969 (58.1%) were male, and 4253 (83.3%) were of European or other ethnicity, with the remainder being Polynesian or South Asian. Mean (SD) baseline deseasonalized 25(OH)D concentration was 26.5 (9.0) ng/mL, with 1270 participants (24.9%) being vitamin D deficient. In a random sample of 438 participants, the mean follow-up 25(OH)D level was greater than 20 ng/mL higher in the vitamin D group than in the placebo group. The primary outcome of CVD occurred in 303 participants (11.8%) in the vitamin D group and 293 participants (11.5%) in the placebo group, yielding an adjusted hazard ratio of 1.02 (95% CI, 0.87-1.20). Similar results were seen for participants with baseline vitamin D deficiency and for secondary outcomes.
Conclusions and Relevance
Monthly high-dose vitamin D supplementation does not prevent CVD. This result does not support the use of monthly vitamin D supplementation for this purpose. The effects of daily or weekly dosing require further study.
Trial Registration
clinicaltrials.gov Identifier: ACTRN12611000402943
Introduction
The possibility that UV radiation, through a mechanism that involves vitamin D, may protect against cardiovascular disease (CVD) was initially proposed in 1981. Results from recent meta-analyses have confirmed that people with low vitamin D status have increased risk of CVD. Several pathophysiologic mechanisms could explain this inverse association.
Confirmation of the vitamin D–CVD hypothesis requires evidence from randomized clinical trials (RCTs) of vitamin D supplementation, which is limited for the general population. The Women’s Health Initiative found no benefit from a vitamin D supplement (combined with calcium) against CVD, although the intiative has been criticized because of its very low vitamin D3 dose (400 IU/d) and poor adherence. Another population-based RCT reported a nonsignificant 10% reduction in CVD incidence from a 4-monthly 100 000-IU vitamin D3 dose. Secondary analysis of a large trial of fracture prevention in participants with a previous fracture found that vitamin D3 (800 IU/d) did not protect against myocardial infarction or stroke but reduced cardiac failure events by 25%, although the reduction was smaller (18%) and nonsignificant when combined with previous studies.
Given the limited (and mixed) RCT evidence on vitamin D supplementation and CVD, we performed a large RCT with recruitment from the general population. To address concerns about the low dose and low adherence in prior studies, we chose a monthly high-dose vitamin D supplement to determine whether it would decrease the incidence of CVD compared with placebo.
Methods
Study Design
The Vitamin D Assessment study is a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial with the primary aim to evaluate the efficacy of monthly vitamin D supplementation in reducing the incidence of CVD. The study was approved by the New Zealand Multi-region Ethics Committee in Wellington in October 2010 and registered with the Australian New Zealand Clinical Trials Registry in April 2011. Full details of the study methods have been published. The trial protocol can be found in Supplement 1.
Inclusion criteria were age of 50 to 84 years, ability to give written informed consent, resident in Auckland, New Zealand, at recruitment, and anticipated residence in New Zealand for the 4-year study period. Exclusion criteria were current use of vitamin D supplements, including cod-liver oil (>600 IU/d if aged 50-70 years; >800 IU/d if aged 71-84 years); diagnosis of psychiatric disorders that would limit ability to comply with the study protocol; history of hypercalcemia, nephrolithiasis, sarcoidosis, parathyroid disease, or gastric bypass surgery; enrolled in another study, which could affect participation; or baseline corrected serum calcium level greater than 10.0 mg/dL (to convert to millimoles per liter, multiply by 0.25).
Recruitment of Participants and Baseline Interview
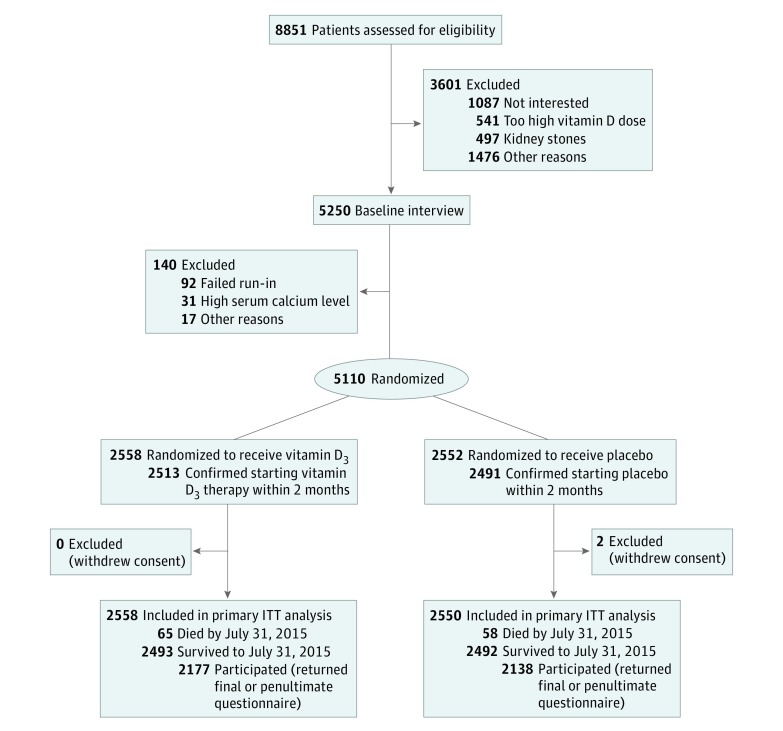
Participants were recruited in Auckland, where 94% of the population is registered with family practices. Most participants were recruited from 55 practices. Beginning in March 2011, a personalized letter was mailed to their homes (n = 47 905) that invited participation in the study, and of 8688 replies, 5107 individuals remained interested and were eligible for baseline interviews. An additional 163 potential participants from ethnic minority community groups were assessed, and 143 were eligible for baseline interviews. A total of 5250 individuals attended the baseline interview (Figure 1) at The University of Auckland from April 5, 2011, through November 6, 2012.
Figure 1. Flow Diagram for the Vitamin D Assessment Study.
ITT indicates intention-to-treat.
The interview included collecting information on written informed consent, sociodemographic status (age, sex, self-reported race/ethnicity, highest educational level, and current employment), lifestyle (current tobacco smoking, alcohol drinking during the past 12 months, and usual leisure-time physical activity and sun exposure during the past 3 months), intake of vitamin D or calcium supplements, current medication prescribed by a physician, and medical history told by a physician (including hypertension, coronary heart disease, cardiac failure, cardiac arrhythmia, hyperlipidemia, stroke, venous thrombosis, and diabetes). Height was measured to the nearest 0.1 cm and weight to the nearest 0.1 kg (in light clothing without shoes). Brachial blood pressure was measured after 30 minutes of rest with an OMRON T9P oscillometric device (OMRON Healthcare Europe BV) on 3 occasions with approximately 30 seconds between readings while the patient was seated. A nonfasting blood sample was collected to screen for hypercalcemia, with the remaining serum aliquoted and stored at −80°C for later measurement of 25 hydroxyvitamin D [25(OH)D] and lipid levels.
Randomization
After the baseline interview, participants were mailed a run-in questionnaire with a masked placebo capsule. After exclusions for nonreturn of the questionnaire within 4 weeks (with confirmation of taking the capsule) or hypercalcemia (corrected serum calcium level >10.0 mg/dL), from June 3, 2011, through January 23, 2013, a total of 5110 people (4972 from practices and 138 from the community) were randomized to the treatment groups (Figure 1). Random assignment was made to 1 of the 2 treatment groups in random block sizes of 8, 10, or 12, within race/ethnic group and 5-year age strata. Treatment was allocated automatically using computer generation by a study biostatistician (A.W.S.), and all other staff and participants were masked.
Intervention
Vitamin D3 (2.5 mg or 100 000 IU) or placebo soft-gel oral capsules (Tishcon Corporation) were mailed to participants’ homes. Two capsules were sent in the first mail delivery after randomization (ie, 200 000-IU bolus or placebo), followed with a 2.5-mg (100 000–IU) capsule of vitamin D3 (or placebo) sent a month later and thereafter monthly. The aim was to increase the serum 25(OH)D concentrations throughout the year to 32 to 40 ng/mL (to convert to nanomoles per liter, multiply by 2.496), which observational studies at that time suggested was optimal for health (although subsequent research suggests a lower optimal threshold). A monthly 100 000-IU vitamin D dose was chosen because of pharmacokinetic evidence indicating that this maintains serum 25(OH)D levels above 35 ng/mL for a month after ingestion.
Capsules initially were mailed monthly to participants, along with a 1-page questionnaire (and reply-paid envelope), which recorded self-reported adherence and monitored retention. Monthly mailings of capsules continued until June 2013, and then, from July 2013 onward, for cost reasons, 4 capsules were mailed every 4 months with monthly reminders (by email or letter) to participants to take their monthly capsule. Questionnaires continued to be mailed monthly until November 2013 and then were sent 4 times monthly with 4 capsules from March 2014 onward.
Follow-up and Outcomes
The Ministry of Health allocates all New Zealand residents a unique National Health Index number, which was used to track deaths and hospital discharges (both with International Statistical Classification of Diseases and Health Related Problems, Tenth Revision [ICD-10] coding), and dispensed prescriptions (including generic name, dose, amount, and frequency) for all participants during the follow-up period, which ended July 31, 2015. These data were used to define CVD outcomes, alone or in combination with data about prior CVD from the baseline interview (eTable 1 in Supplement 2).
The CVD outcomes (developed by study researchers [R.S., C.M.M.L., L.T., K.-T.K., C.A.C.]) were included regardless of history of the same disease if they were given an A code (primary reason for hospitalization or death) for the following diseases: chronic ischemic heart disease (ICD-10 code I25), pulmonary embolism (ICD-10 code I26), other pulmonary diseases (ICD-10 code I27), inflammatory cardiac conditions (ICD-10 codes I30.1, I31-I41), conduction disorders (ICD-10 codes I44, I45), cardiac arrest (ICD-10 code I46), arrhythmias (ICD-10 codes I47-I49), ill-defined heart disease (ICD-10 code I51), diseases of the arteries (ICD-10 codes I70-I79), and diseases of the veins, including venous thrombosis (ICD-10 codes I80-I82). For other CVDs, we also included discharges with B codes (secondary reasons for hospitalization) in combination with baseline interview or prescription data. Acute myocardial infarction was defined as ICD-10 code I21, with either an A code regardless of prior myocardial infarction or a B code for participants with no prior myocardial infarction. Angina was defined as ICD-10 code I20 (A or B code) or initiation of nitrate therapy (≥2 prescriptions of glyceryl trinitrate or isosorbide mononitrate) after the baseline interview in participants who did not report a history of angina at the baseline interview. In participants who did not report a history of heart failure at the baseline interview, heart failure was defined as initiation after the baseline interview of treatment with loop diuretics, which are used specifically for this disease (≥2 prescriptions of furosemide or bumetanide) or A or B code for ICD-10 codes I11.0, I50.0, I50.1, and I50.9, and cardiomyopathy was defined as A or B code for ICD-10 codes I25.5, I42.0, and I42.7 through I42.9 (as defined previously). Stroke was defined as A or B code for ICD-10 codes I61 through I67 in participants who did not report a history of stroke at baseline interview. Hypertension was included as an outcome because of its inclusion in a previous cohort study of vitamin D and CVD and previous RCTs of vitamin D supplementation. It was defined as A or B code for ICD-10 codes I10 through I15 (not otherwise included in the above ICD-10 codes) in participants who did not report that they were undergoing treatment for hypertension at baseline. The primary outcome of all CVD events combined (ICD-10 codes I10-I82) was based on the above disease definitions. Prespecified secondary disease outcomes were based on the cardiovascular pathophysiologic findings associated with vitamin D deficiency and observational epidemiologic studies. The outcomes listed in the original study protocol, which did not differentiate between A- and B-coded events and did not include mention of prescriptions to define specific diseases, were refined between the end of follow-up (July 2015) and breaking of the randomization code (February 2016), based on analyses of the Ministry of Health databases since the start of the study by other cardiovascular epidemiologists in our department, to include relevant CVD events that received a B code.
Corrected serum calcium level was measured at baseline, and serum total cholesterol and high-density lipoprotein cholesterol levels were measured in aliquots collected at baseline and stored at −80°C on an Advia 2400 analyzer (Siemens Healthcare Diagnostics). Serum 25(OH)D level, combining vitamins D2 and D3, was measured in baseline aliquots stored frozen by liquid chromatography–tandem mass spectrometry (ABSciex API 4000) with 12.7% interassay coefficient of variation in a local laboratory participating in the Vitamin D External Quality Assessment Scheme program (www.deqas.org). In a 10% random sample, 438 of 515 invited participants (85.0%) agreed to return at 6, 12, 24, and 36 months for collection of additional blood samples to measure corrected calcium (on fresh blood) and 25(OH)D levels (in stored blood samples, measured in the same batch for each participant).
Statistical Analysis
We estimated that a cohort of participants aged 50 to 84 years with a similar age, sex, and race/ethnic distribution as the 2006 New Zealand Census and with similar mortality and hospital discharge rates as for New Zealand would have an annual CVD event rate (for hospital discharges and mortality) of 6%. Assuming that the event rate among healthy volunteers was 80% of this, a sample of 5000 persons followed up for 4 years has a greater than 80% power (5% significance level) to detect a 20% reduction in CVD events.
Analysis of the primary outcome (CVD) was conducted on an intention-to-treat basis made possible by the National Health Index number to identify CVD events regardless of whether participants continued to participate actively in the study by returning the home questionnaire. The Cox proportional hazards regression model, with robust sandwich variance estimates, was used to compare the time to first CVD event in the 2 treatment groups and to calculate CVD hazard ratios (HRs) in the placebo group. Deaths from non-CVD causes were censored.
The treatment group differences in 25(OH)D levels were tested for change over time with a general linear model with repeated time using an unstructured correlation matrix. Where indicated, season-adjusted (deseasonalized) values were calculated for each participant from their individual baseline 25(OH)D concentration and date of blood sample collection by using a sinusoidal model with values derived from baseline values for all participants. Vitamin D deficiency was defined as having a deseasonalized 25(OH)D level less than 20 ng/mL. Analyses were performed using SAS statistical software, version 9.3 (SAS Institute). All statistical tests were 2-tailed with a 5% level of significance.
Results
Baseline Characteristics, Recruitment, and Follow-up
Figure 1 shows the number of individuals assessed for eligibility (n = 8851), randomized (n = 5110), and included in the primary analysis (n = 5108), after excluding 2 participants (both placebo) who withdrew consent after being randomized. Among the 5108 patients analyzed, the mean (SD) age was 65.9 (8.3) years, 2969 (58.1%) were male, and 4253 (83.3%) were of European or other race/ethnicity, with the remainder being Polynesian or South Asian. A total of 2618 participants (51.3%) were in paid employment. Only 320 (6.3%) currently smoked tobacco, and 2173 (42.5%) were ex-smokers; 408 (8.0%) were taking vitamin D supplements (within study eligibility criteria), and 252 (4.9%) were taking calcium supplements. The observed mean (SD) baseline 25(OH)D concentration was 25.3 (9.5) ng/mL, and the deseasonalized level was 26.5 (9.0) ng/mL. Baseline characteristics were similar between the vitamin D and placebo groups (Table 1).
Table 1. Baseline Comparison of the Vitamin D and Placebo Groupsa.
| Variable | Vitamin D (n = 2558) |
Placebo (n = 2550) |
|---|---|---|
| Age, y | ||
| 50-59 | 571 (22.3) | 567 (22.2) |
| 60-69 | 1112 (43.5) | 1108 (43.5) |
| 70-79 | 716 (28.0) | 722 (28.3) |
| 80-84 | 159 (6.2) | 153 (6.0) |
| Males | 1512 (59.1) | 1457 (57.1) |
| Race/ethnicity | ||
| Maori | 137 (5.4) | 135 (5.3) |
| Pacific Islander | 168 (6.6) | 166 (6.5) |
| South Asian | 126 (4.9) | 123 (4.8) |
| European or other | 2127 (83.2) | 2126 (83.4) |
| Highest educational levelb | ||
| Primary school | 53 (2.1) | 42 (1.6) |
| Secondary school | 1091 (42.7) | 1036 (40.6) |
| Tertiary | 1412 (55.2) | 1470 (57.7) |
| In paid employmentb | ||
| Yes | 1301 (50.9) | 1317 (51.6) |
| No | ||
| Retired | 1041 (40.7) | 1018 (39.9) |
| House duties | 34 (1.3) | 51 (2.0) |
| Other | 177 (6.9) | 161 (6.3) |
| Tobacco smokingb | ||
| Current | 164 (6.4) | 156 (6.1) |
| Past | 1101 (43.0) | 1072 (42.0) |
| Never | 1286 (50.3) | 1317 (51.6) |
| Alcohol drinkingb | ||
| Current | 2177 (85.1) | 2211 (86.7) |
| Past | 224 (8.8) | 183 (7.2) |
| Never | 151 (5.9) | 154 (6.0) |
| Vigorous physical activity, h/wk | ||
| None | 1015 (39.7) | 1018 (39.9) |
| 1-2 | 609 (23.8) | 585 (22.9) |
| >2 | 804 (31.4) | 832 (32.6) |
| Refused or do not know | 130 (5.1) | 115 (4.5) |
| Sun exposure, h/db | ||
| <1 | 350 (13.7) | 369 (14.5) |
| 1-2 | 1562 (61.1) | 1559 (61.1) |
| >2 | 611 (23.9) | 588 (23.1) |
| Take supplements | ||
| Vitamin Dc | 208 (8.1) | 200 (7.8) |
| Calcium | 125 (4.9) | 127 (5.0) |
| Past medical conditions told by a physician | ||
| Hypertension | 955 (37.3) | 930 (36.5) |
| Angina | 166 (6.5) | 187 (7.3) |
| Myocardial infarction | 168 (6.6) | 162 (6.4) |
| Heart failure | 39 (1.5) | 45 (1.8) |
| Irregular heartbeat | 346 (13.5) | 318 (12.5) |
| Stroke, including transient ischemic attack | 50 (2.0) | 31 (1.2) |
| Thrombosis | 45 (1.8) | 37 (1.5) |
| Diabetes | 265 (10.4) | 239 (9.4) |
| Anthropometry, mean (SD) | ||
| Weight, kg | 81.3 (16.5) | 81.2 (16.0) |
| Body mass indexd | 28.4 (5.1) | 28.5 (5.1) |
| Blood pressure, mean (SD), mm Hg | ||
| Systolic | 139 (19) | 139 (19) |
| Diastolic | 78 (10) | 78 (10) |
| Pulse rate, mean (SD), /min | 63.5 (10.0) | 63.0 (10.3) |
| Cholesterol level, mean (SD) | ||
| Total cholesterol level, mg/dL | 185 (42) | 189 (42) |
| HDL-C level, mg/dL | 54 (15) | 54 (15) |
| Cholesterol ratio | 3.6 (0.9) | 3.6 (0.9) |
| Corrected serum calcium level, mean (SD), mg/dL | 9.2 (0.4) | 9.2 (0.4) |
| 25-Hydroxyvitamin D level | ||
| Observed level, mean (SD), ng/mL | 25.5 (9.5) | 25.2 (9.4) |
| <20 ng/mL, observed | 746 (29.2) | 788 (30.9) |
| <20 ng/mL, deseasonalized | 612 (23.9) | 658 (25.8) |
Abbreviation: HDL-C, high-density lipoprotein cholesterol.
SI conversion factors: to convert total cholesterol and HDL-C levels to millimoles per liter, multiply by 0.0259; calcium to millimoles per liter, multiply by 0.25; and 25-hydroxyvitamin D to nanomoles per liter, multiply by 2.496.
Data are presented as number (percentage) of patients unless otherwise indicated.
Percentages do not total 100.0% because of missing or don’t know responses.
A dosage of 600 IU/day or less if aged 50 to 70 years and 800 IU/day or less if aged 71 to 84 years.
Calculated as weight in kilograms divided by height in meters squared.
Nearly all participants confirmed (by questionnaire within 2 months of randomization) that they had started taking the study capsule (vitamin D, 2513 [98.2%]; placebo, 2491 [97.6%]), and only 21 (0.8%) of the 2558 patients in the vitamin D group and 49 (1.9%) of the 2550 patients in the placebo group never confirmed this at any time during the follow-up period (median, 3.3 years; range, 2.5-4.2 years). By the end of follow-up, 123 participants (2.4%) had died, whereas 4032 (78.9%) returned the final July 2015 questionnaire, and an additional 283 (5.5%) returned the penultimate March 2015 questionnaire, confirming that of those still alive (4315 [86.6%]) were actively participating during the last five months of follow-up.
25(OH)D Levels During Follow-up
Mean observed 25(OH)D concentrations are given in Table 2 for the randomly selected participants who returned to have blood samples obtained. These concentrations were greater than 20 ng/mL higher in the treated group compared with the placebo group in the blood samples collected at 6 months, up to 36 months of follow-up; these findings confirm the high adherence reported in the home questionnaires, which was 84.9% in the vitamin D group and 82.9% in the placebo group (83.9% overall, 168 667 capsules reported having been taken during 200 936 person-months). Mean (SD) corrected serum calcium levels throughout the follow-up period were similar for the vitamin D vs placebo groups (9.2 [0.4] vs 9.2 [0.4] mg/dL at 6, 12, and 24 months and 9.6 [0.4] vs 9.6 [0.4] mg/dL at 36 months). Only 1 person developed hypercalcemia (corrected serum calcium level >10.4 mg/dL), which was from primary hyperparathyroidism; the participant continued taking the study capsule, which after unmasking, was revealed to be placebo. In the total sample, no statistically significant difference was found in the number of deaths between the vitamin D (n = 65) and placebo groups (n = 58, P = .53).
Table 2. Observed Mean (SD) Serum 25(OH)D Levels at Baseline and Follow-up at 6, 12, 24, and 36 Months.
| Period | Vitamin D | Placebo | Change From Baseline (Vitamin D – Placebo), Mean (95% CI) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| No. of Patients | 25(OH)D Level, Mean (SD), ng/mL | No. of Patients | 25(OH)D Level, Mean (SD), ng/mL | ||
| Baseline | 225 | 24.4 (9.6) | 216 | 24.4 (9.6) | NA |
| 6-mo Follow-up | 190 | 51.7 (16.8) | 182 | 30.0 (12.4) | 20.8 (18.4-23.6) |
| 12-mo Follow-up | 201 | 47.7 (18.0) | 198 | 24.0 (11.2) | 23.2 (20.4-26.0) |
| 24-mo Follow-up | 191 | 52.9 (15.6) | 194 | 26.4 (10.8) | 26.4 (24.0-28.9) |
| 36-mo Follow-up | 171 | 54.1 (16.0) | 163 | 26.4 (11.6) | 27.6 (24.8-30.5) |
Abbreviations: 25(OH)D, 25-hydroxyvitamin D; NA, not applicable.
SI conversion factor: To convert 25(OH)D to nanomoles per liter, multiply by 2.496.
Outcomes
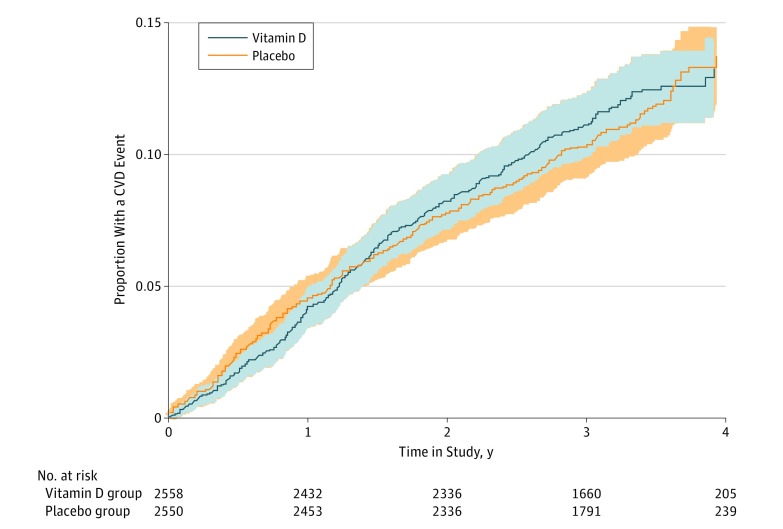
As expected, baseline 25(OH) concentration categories were inversely associated with CVD risk during follow-up in the placebo group after adjusting for demographic covariates (eTable 2 in Supplement 2). Numbers of participants with 1 or more CVD event (the primary outcome) during follow-up in the vitamin D and placebo groups, along with HRs adjusted for age, sex, and race/ethnicity, are given in Table 3. No significant difference was found in the percentage for all CVD events combined between the vitamin D (11.8%) and placebo (11.5%) groups (HR, 1.02; 95% CI, 0.87-1.20). Similar results were seen in vitamin D–deficient participants (HR, 1.00; 95% CI, 0.74-1.35) and when participants were categorized by previous CVD (Table 3). No difference was found between the vitamin D and placebo groups in the time to first CVD event during follow-up (Figure 2) or in the frequency of disease-specific secondary outcomes (Table 3).
Table 3. Proportion of Participants Having a Cardiovascular Disease Event During Follow-up and Hazard Ratios Adjusting for Age, Sex, and Race/Ethnicitya.
| Cardiovascular Disease (ICD-10 Code) | No. (%) of Events | Hazard Ratio (95% CI) | P Value (Wald χ2) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Vitamin D (n = 2558) |
Placebo (n = 2550) |
|||
| Primary end point (I10-I82)b | ||||
| All | 303 (11.8) | 293 (11.5) | 1.02 (0.87-1.20) | .81 |
| 25(OH)D level <20 ng/mLc | 80 (13.1) | 88 (13.4) | 1.00 (0.74-1.35) | .99 |
| Previous cardiovascular diseased | 214 (16.9) | 202 (16.5) | 1.01 (0.83-1.22) | .93 |
| No previous cardiovascular disease | 89 (6.9) | 91 (6.9) | 0.99 (0.74-1.33) | .96 |
| Secondary end points | ||||
| Hypertension (I10-I15) | 34 (1.3) | 40 (1.6) | 0.84 (0.53-1.33) | .45 |
| Myocardial infarction (I21, I22) | 28 (1.1) | 31 (1.2) | 0.90 (0.54-1.50) | .68 |
| Angina (I20) | 45 (1.8) | 31 (1.2) | 1.43 (0.90-2.26) | .13 |
| Heart failure, including cardiomyopathye | 69 (2.7) | 57 (2.2) | 1.19 (0.84-1.68) | .34 |
| Arrhythmias (I47-I49) | 45 (1.8) | 48 (1.9) | 0.93 (0.62-1.39) | .71 |
| Chronic IHD and arteriosclerosis (I25, I70-I79) | 21 (0.8) | 17 (0.7) | 1.22 (0.64-2.33) | .54 |
| Stroke, hemorrhage, infarct, other (I61-I67) | 26 (1.0) | 27 (1.1) | 0.95 (0.55-1.62) | .84 |
| Venous thrombosis, including pulmonary embolism (I26, I80-I8) | 11 (0.4) | 15 (0.6) | 0.74 (0.34-1.61) | .45 |
| Other cardiovascular diseasef | 24 (0.9) | 27 (1.1) | 0.88 (0.51-1.52) | .65 |
Abbreviations: 25(OH)D, 25-hydroxyvitamin D; ICD-10, International Statistical Classification of Diseases and Health Related Problems, Tenth Revision; IHD, ischemic heart disease.
Placebo group values were used for the HRs.
Includes 33 deaths from cardiovascular disease (18 in the vitamin group and 15 in the placebo group).
On the basis of deseasonalized concentrations: 612 participants in the vitamin D group and 658 in the placebo group.
Previous hypertension, myocardial infarction, angina, heart failure, arrhythmia, stroke, or venous thrombosis.
ICD-10 codes I11.0, I25.5, I42.0, I42.7, I42.8, I42.9, I50.0, I50.1, and I50.9.
Other diseases in primary end point, including cardiovascular deaths (unspecified): 8 in the vitamin D group and 7 in the placebo group.
Figure 2. Proportion of Participants With a Cardiovascular Disease (CVD) Event During Follow-up.
Shaded areas indicate 95% CIs.
Discussion
The results of this large population-based RCT indicate that vitamin D supplementation given in the dose and frequency we used does not prevent CVD, and the findings are consistent with previous RCTs of vitamin D supplementation and mendelian randomization studies. However, it remains possible that monthly doses of vitamin D are less effective in preventing disease than daily or weekly doses. Recommendation for the desired frequency of vitamin D dosing has changed from when our study began, at which time it was considered that a bolus dose of vitamin D would be stored as vitamin D for later conversion to 25(OH)D and that monthly dosing was frequent enough to avoid any increase in the catabolism of the active metabolite (1,25-dihydroxyvitamin D) in nonrenal tissues. In contrast, recent reviews have concluded that vitamin D is more accessible for internalization into cells than 25(OH)D, and in our study, vitamin D would only have been in the blood circulation for several days after each monthly dose because of its shorter half-life. Other trials, which are giving vitamin D monthly (eg, D-Health, The International Polycap Study 3) or daily (eg, Vitamin D and Omega-3 Trial), will help clarify whether dosing frequency is important.
Our results do not support the findings from observational studies that report an inverse association between 25(OH)D and CVD, which could be explained by residual confounding from other lifestyle risk factors. It is possible that 25(OH)D concentrations are a surrogate marker of sun exposure, which may have other health effects entirely separate from vitamin D. Thus, we caution against closure of this topic, given the descriptive epidemiologic findings on inverse associations between solar radiation and CVD with regard to season, latitude, and altitude.
Strengths and Limitations
Our study has several strengths that enhance the validity of the conclusions. First, we had a high retention rate, with 87% still participating actively in the final follow-up period. Second, we had high adherence, with 84% of capsules reported taken in questionnaires, confirmed by the high serum 25(OH)D concentrations in the vitamin D group of the measured subgroup (Table 2). Third, the mean 25(OH)D concentration greater than 40 ng/mL in the vitamin D group confirmed the adequacy of the vitamin D dose, particularly the greater than 20-ng/mL difference compared with the placebo arm.
Our study also has some potential limitations. The event rate was lower than expected, as was the follow-up time, which decreased the number of expected events from 890 to the 596 observed; therefore, the power to detect a 20% reduction was 75% (5% significance), which is equivalent to 80% power to detect a 21% reduction. However, this is unlikely to have changed our main conclusion because our point estimate of effect for the primary end point was close to 1 (Table 3), supporting a null finding. The study had much less power to detect benefits for the subgroup with vitamin D deficiency and for preventing specific CVD outcomes, such as heart failure, as reported in previous RCTs. Our funding only allowed for median follow-up of 3.3 years, and we cannot exclude possible longer-term beneficial effects from vitamin D supplementation. Our outcome measures were not adjudicated, but this is an unlikely explanation for our null findings because the validity of our outcome is indicated by the expected associations with risk factors in the placebo group (eTable 2 in the Supplement) and by research indicating that the CVD hospitalization data from the Ministry of Health have good agreement with the Framingham risk factor equation in Europeans. Furthermore, we were unable to identify participants who emigrated during the study. However, our inability to record overseas CVD events is unlikely to have changed our findings because the number of CVD events not recorded is likely to have been small based on our annual 4% incidence rate, whereas the number of participants who emigrated is likely to have been small based on the high retention rate in the final study period (when 87% of participants returned questionnaires).
Conclusions
This study found that monthly high-dose vitamin D supplementation does not prevent CVD. The effects of daily or weekly dosing on CVD risk require further study.
Trial Protocol
eTable 1. ViDA CVD Outcomes Based on Ministry of Health Hospital Discharge (A* and B# codes) and Dispensed Prescription Data: Primary End point I10-I82
eTable 2. Hazard Ratios of Cardiovascular Disease During Follow-up Associated With Baseline 25-Hydroxyvitamin D (25(OH)D) Concentration and Demographic Variables in the Placebo Group, Adjusted for All Other Variables in the Table
References
- 1.Scragg R. Seasonality of cardiovascular disease mortality and the possible protective effect of ultra-violet radiation. Int J Epidemiol. 1981;10(4):337-341. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Wang L, Song Y, Manson JE, et al. Circulating 25-hydroxy-vitamin D and risk of cardiovascular disease: a meta-analysis of prospective studies. Circ Cardiovasc Qual Outcomes. 2012;5(6):819-829. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Schöttker B, Jorde R, Peasey A, et al. ; Consortium on Health and Ageing: Network of Cohorts in Europe and the United States . Vitamin D and mortality: meta-analysis of individual participant data from a large consortium of cohort studies from Europe and the United States. BMJ. 2014;348:g3656. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Norman PE, Powell JT. Vitamin D and cardiovascular disease. Circ Res. 2014;114(2):379-393. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Hsia J, Heiss G, Ren H, et al. ; Women’s Health Initiative Investigators . Calcium/vitamin D supplementation and cardiovascular events. Circulation. 2007;115(7):846-854. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Wactawski-Wende J, Kotchen JM, Anderson GL, et al. ; Women’s Health Initiative Investigators . Calcium plus vitamin D supplementation and the risk of colorectal cancer. N Engl J Med. 2006;354(7):684-696. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Newmark HL, Heaney RP. Calcium, vitamin D, and risk reduction of colorectal cancer. Nutr Cancer. 2006;56(1):1-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Trivedi DP, Doll R, Khaw KT. Effect of four monthly oral vitamin D3 (cholecalciferol) supplementation on fractures and mortality in men and women living in the community: randomised double blind controlled trial. BMJ. 2003;326(7387):469. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Ford JA, MacLennan GS, Avenell A, Bolland M, Grey A, Witham M; RECORD Trial Group . Cardiovascular disease and vitamin D supplementation: trial analysis, systematic review, and meta-analysis. Am J Clin Nutr. 2014;100(3):746-755. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Scragg R, Waayer D, Stewart AW, et al. The Vitamin D Assessment (ViDA) Study: design of a randomized controlled trial of vitamin D supplementation for the prevention of cardiovascular disease, acute respiratory infection, falls and non-vertebral fractures. J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol. 2016;164:318-325. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Institute of Medicine Dietary Reference Intakes for Calcium and Vitamin D. Washington, DC: Institute of Medicine; 2011. [Google Scholar]
- 12.Ministry of Health New Zealand Enrollment in a primary health organisation. http://www.health.govt.nz/our-work/primary-health-care/about-primary-health-organisations/enrolment-primary-health-organisation. Accessed May 25, 2016.
- 13.Wareham NJ, Jakes RW, Rennie KL, et al. Validity and repeatability of a simple index derived from the short physical activity questionnaire used in the European Prospective Investigation into Cancer and Nutrition (EPIC) study. Public Health Nutr. 2003;6(4):407-413. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Scragg R, Jackson R, Holdaway IM, Lim T, Beaglehole R. Myocardial infarction is inversely associated with plasma 25-hydroxyvitamin D3 levels: a community-based study. Int J Epidemiol. 1990;19(3):559-563. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Bischoff-Ferrari HA, Giovannucci E, Willett WC, Dietrich T, Dawson-Hughes B. Estimation of optimal serum concentrations of 25-hydroxyvitamin D for multiple health outcomes. Am J Clin Nutr. 2006;84(1):18-28. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Scragg R, Sowers M, Bell C; Third National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey . Serum 25-hydroxyvitamin D, diabetes, and ethnicity in the Third National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey. Diabetes Care. 2004;27(12):2813-2818. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Black PN, Scragg R. Relationship between serum 25-hydroxyvitamin d and pulmonary function in the third national health and nutrition examination survey. Chest. 2005;128(6):3792-3798. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Scragg R, Sowers M, Bell C. Serum 25-hydroxyvitamin D, ethnicity, and blood pressure in the Third National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey. Am J Hypertens. 2007;20(7):713-719. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Sohl E, de Jongh RT, Heymans MW, van Schoor NM, Lips P. Thresholds for serum 25(OH)D concentrations with respect to different outcomes. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2015;100(6):2480-2488. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Ilahi M, Armas LA, Heaney RP. Pharmacokinetics of a single, large dose of cholecalciferol. Am J Clin Nutr. 2008;87(3):688-691. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Wells S, Riddell T, Kerr A, et al. Cohort profile: the PREDICT Cardiovascular Disease Cohort in New Zealand Primary Care (PREDICT-CVD 19) [published online December 20, 2015]. Int J Epidemiol. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Demant MN, Gislason GH, Køber L, Vaag A, Torp-Pedersen C, Andersson C. Association of heart failure severity with risk of diabetes: a Danish nationwide cohort study. Diabetologia. 2014;57(8):1595-1600. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Beveridge LA, Struthers AD, Khan F, et al. ; D-PRESSURE Collaboration . Effect of vitamin d supplementation on blood pressure: a systematic review and meta-analysis incorporating individual patient data. JAMA Intern Med. 2015;175(5):745-754. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Schnatz PF, Manson JE. Vitamin D and cardiovascular disease: an appraisal of the evidence. Clin Chem. 2014;60(4):600-609. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Wang TJ. Vitamin D and cardiovascular disease. Annu Rev Med. 2016;67:261-272. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Statistics New Zealand 2006. New Zealand Census. Mortality and Demographic Data. http://www.health.govt.nz/nz-health-statistics/health-statistics-and-data-sets/mortality-and-demographic-data-series. Accessed February 24, 2017.
- 27.New Zealand Ministry of Health Hospital Event Data and Stats. http://www.health.govt.nz/nz-health-statistics/health-statistics-and-data-sets/hospital-event-data-and-stats Accessed February 24, 2017.
- 28.Sachs MC, Shoben A, Levin GP, et al. Estimating mean annual 25-hydroxyvitamin D concentrations from single measurements: the Multi-Ethnic Study of Atherosclerosis. Am J Clin Nutr. 2013;97(6):1243-1251. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Jorde R, Schirmer H, Wilsgaard T, et al. Polymorphisms related to the serum 25-hydroxyvitamin D level and risk of myocardial infarction, diabetes, cancer and mortality: the Tromsø Study. PLoS One. 2012;7(5):e37295. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Afzal S, Brøndum-Jacobsen P, Bojesen SE, Nordestgaard BG. Genetically low vitamin D concentrations and increased mortality: Mendelian randomisation analysis in three large cohorts. BMJ. 2014;349:g6330. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Heaney RP, Armas LA, Shary JR, Bell NH, Binkley N, Hollis BW. 25-Hydroxylation of vitamin D3: relation to circulating vitamin D3 under various input conditions. Am J Clin Nutr. 2008;87(6):1738-1742. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Vieth R. How to optimize vitamin D supplementation to prevent cancer, based on cellular adaptation and hydroxylase enzymology. Anticancer Res. 2009;29(9):3675-3684. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Hollis BW, Wagner CL. Clinical review: the role of the parent compound vitamin D with respect to metabolism and function: why clinical dose intervals can affect clinical outcomes. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2013;98(12):4619-4628. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Heaney RP, Armas LA. Quantifying the vitamin D economy. Nutr Rev. 2015;73(1):51-67. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Meyer HE, Holvik K, Lips P. Should vitamin D supplements be recommended to prevent chronic diseases? BMJ. 2015;350:h321. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Manson JE, Bassuk SS, Lee IM, et al. The VITamin D and OmegA-3 TriaL (VITAL): rationale and design of a large randomized controlled trial of vitamin D and marine omega-3 fatty acid supplements for the primary prevention of cancer and cardiovascular disease. Contemp Clin Trials. 2012;33(1):159-171. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Holick MF. Biological effects of sunlight, ultraviolet radiation, visible light, infrared radiation and vitamin D for health. Anticancer Res. 2016;36(3):1345-1356. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Marti-Soler H, Gonseth S, Gubelmann C, et al. Seasonal variation of overall and cardiovascular mortality: a study in 19 countries from different geographic locations. PLoS One. 2014;9(11):e113500. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Müller-Nordhorn J, Binting S, Roll S, Willich SN. An update on regional variation in cardiovascular mortality within Europe. Eur Heart J. 2008;29(10):1316-1326. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Burtscher M. Effects of living at higher altitudes on mortality: a narrative review. Aging Dis. 2013;5(4):274-280. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Donneyong MM, Hornung CA, Taylor KC, et al. Risk of heart failure among postmenopausal women: a secondary analysis of the randomized trial of vitamin D plus calcium of the women’s health initiative. Circ Heart Fail. 2015;8(1):49-56. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Riddell T, Wells S, Jackson R, et al. Performance of Framingham cardiovascular risk scores by ethnic groups in New Zealand: PREDICT CVD-10. N Z Med J. 2010;123(1309):50-61. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Trial Protocol
eTable 1. ViDA CVD Outcomes Based on Ministry of Health Hospital Discharge (A* and B# codes) and Dispensed Prescription Data: Primary End point I10-I82
eTable 2. Hazard Ratios of Cardiovascular Disease During Follow-up Associated With Baseline 25-Hydroxyvitamin D (25(OH)D) Concentration and Demographic Variables in the Placebo Group, Adjusted for All Other Variables in the Table