Abstract
Background
Low temperature is a crucial factor influencing plant growth and development. The chlorophyll precursor, 5-aminolevulinic acid (ALA) is widely used to improve plant cold tolerance. However, the interaction between H2O2 and cellular redox signaling involved in ALA-induced resistance to low temperature stress in plants remains largely unknown. Here, the roles of ALA in perceiving and regulating low temperature-induced oxidative stress in tomato plants, together with the roles of H2O2 and cellular redox states, were characterized.
Results
Low concentrations (10–25 mg·L− 1) of ALA enhanced low temperature-induced oxidative stress tolerance of tomato seedlings. The most effective concentration was 25 mg·L− 1, which markedly increased the ratio of reduced glutathione and ascorbate (GSH and AsA), and enhanced the activities of superoxide dismutase, catalase, ascorbate peroxidase, dehydroascorbate reductase, and glutathione reductase. Furthermore, gene expression of respiratory burst oxidase homolog1 and H2O2 content were upregulated with ALA treatment under normal conditions. Treatment with exogenous H2O2, GSH, and AsA also induced plant tolerance to oxidative stress at low temperatures, while inhibition of GSH and AsA syntheses significantly decreased H2O2-induced oxidative stress tolerance. Meanwhile, scavenging or inhibition of H2O2 production weakened, but did not eliminate, GSH- or AsA- induced tomato plant tolerance to oxidative stress at low temperatures.
Conclusions
Appropriate concentrations of ALA alleviated the low temperature-induced oxidative stress in tomato plants via an antioxidant system. The most effective concentration was 25 mg·L− 1. The results showed that H2O2 induced by exogenous ALA under normal conditions is crucial and may be the initial step for perception and signaling transmission, which then improves the ratio of GSH and AsA. GSH and AsA may then interact with H2O2 signaling, resulting in enhanced antioxidant capacity in tomato plants at low temperatures.
Electronic supplementary material
The online version of this article (10.1186/s12870-018-1254-0) contains supplementary material, which is available to authorized users.
Keywords: 5-Aminolevulinic acid, Tomato, Chilling, Oxidative stress, Hydrogen peroxide, Redox state
Background
As an economically important crop, tomatoes (Solanum lycopersicum L.) are widely cultivated [1]. However, as a tropical and subtropical plant, tomato plant growth, development, and production are also negatively influenced by low temperatures (0 °C–15 °C) [2]. The low temperature (8 °C–15 °C) is widespread during the tomato production under protected cultivation in winter and early spring in China, which seriously restrict the normal production of tomatoes. Plants perceive and defend against the cold temperatures using a range of mechanisms, including the regulation of gene expression [3], redox state [4], and complex signaling [5, 6]. Beyond the limit of cold tolerance, reactive oxygen species (ROS) excessively accumulate [7]. ROS include hydroxyl radicals (·OH), superoxide anions (O2−), singlet oxygen (1O2) and hydrogen peroxide (H2O2) [8–10]. As strong oxidizers, high levels of ROS have pernicious effects that result in DNA damage, lipid peroxidation, protein denaturation, a decline in photosynthesis, enzyme activity impairment, and cell death [11, 12]. Consequently, maintaining moderate levels of ROS is essential in protecting against diverse abiotic and biotic stresses.
Maintaining a delicate balance between ROS generation and removal is important for plants, which is principally accomplished by antioxidant defence system [13, 14]. The main antioxidant defense system involves the ascorbate-glutathione (AsA-GSH) cycle, which consists of two dominating nonenzymatic antioxidants, reduced glutathione and ascorbate (GSH and AsA), and four enzymes [ascorbate peroxidase (APX), monodehydroascorbate reductase (MDHAR), dehydroascorbate reductase (DHAR) and glutathione reductase (GR)]. Together with these four enzymes, GSH and AsA reduce ROS via spontaneous biochemical reactions [8, 15]. In addition, superoxide dismutase (SOD) and catalase (CAT) also play key roles in antioxidant systems [16].
However, moderate oxidative stress and oxidative signaling are also essential to maintain plant growth and development [17–19]. For example, H2O2 generated by NADPH oxidases encoded by the respiratory burst oxidase homologue1 (RBOH1) genes, play critical roles in tomato plant responses to oxidative stress as a signaling [20, 21]. ROS may also induce the regulation of groups of genes with protective functions [22], and crosstalk with endogenous phytohormones such as abscisic acid, gibberellins, salicylic acid, jasmonic acid, and ethylene, to regulate protective responses in plants under oxidative stress [4, 23]. The 5-aminolevulinic acid (ALA), an essential biosynthetic precursor of all tetrapyrrole compounds [24, 25], can also maintain moderate ROS levels via antioxidases and antioxidants [26–29]. However, few studies have focused on the interaction between H2O2 and cellular redox signaling in ALA-induced resistance to oxidative stress in plants at low temperatures.
In this study, low temperature perception and stress tolerance in both ALA-treated and untreated leaves of tomato plants were investigated by determining the roles and interactions of H2O2, glutathione, and ascorbate redox signaling induced by ALA at low temperatures.
Methods
Plant culture and experimental design
Tomato plants (cv. Jinpeng no. 1) sensitive to low temperature stress were used in this study. The seeds were germinated at 28 °C in petri dishes which lined with moistened filter paper. The germinated seeds were then sown in 50-well plates filled with a mixture of peat, perlite and vermiculite (2:1:1, v/v/v) and grown in a controlled environment greenhouse at Northwest Agriculture & Forestry University. The seedlings were transplanted into plastic pots (10 cm × 10 cm, one seedling per pot) containing the same mixture medium when the fourth true leaf was fully expanded. Plants were then placed in growth chambers at a temperature of 25 °C/18 °C (day/night), relative humidity of 65% ± 5%, and a photoperiod of 10.5 h [photosynthetic photonflux density (PPFD), 350 μmol·m− 2 s− 1] + 1.5 h (PPFD, 50 μmol·m− 2 s− 1)/12 h (day/night). Each plant was irrigated once every two days with 100 mL distilled water and fertilized at every other occasion with 100 mL of a 50% concentration of Hoagland nutrient solution. The experiments began when the fifth true leaves were completely expanded, and a total of 45 plants for each treatment were analyzed.
To explore the effects of ALA on plant tolerance to low temperature, tomato plants were first sprayed with distilled water (control) or 0, 1, 5, 10, 25, 50, or 100 mg·L− 1 ALA (Sigma Aldrich, St. Louis, MO, USA) solution. The selection of ALA concentrations was based on the studies of Korkmaz et al. [30], Ali et al. [31] and our preliminary experiments. Each plant was treated with 6 mL (according to our preliminary experiment results) of ALA solution or distilled water on both sides 1.5 h before the night, and a few drops of surfactant (Tween 20) were added to enhance adherence. Twelve hours later, the control plants were still under normal conditions as previously mentioned, while other plants were subjected to low temperature at 15 °C/8 °C (day/night) under the same light and humidity regime as previously mentioned. After 24 h, the degree of stress tolerance was assessed by measuring changes in the net photosynthetic rate (Pn), malondialdehyde (MDA) content, and relative electrical conductivity (REC), and the plant growth indexes were measured after 6 days. With the same processing time and conditions as mentioned above, the H2O2 content, maximal quantum yield of PSII photochemistry (Fv/fm), and the antioxidase and antioxidants were determined in plants treated with distilled water or 25 mg·L− 1 ALA under normal condition (Control and ALA) or low temperature (LT and LT + ALA).
A level of 25 mg·L− 1 ALA was used in the following experiments. To study the effects of H2O2 on plants induced by ALA, the plants were treated with distilled water or 25 mg·L− 1 ALA under normal conditions. The transcripts of RBOH1 and levels of H2O2 were then measured during the next 24 h.
To determine the roles of H2O2, GSH, and AsA in ALA-induced tolerance against oxidative stress at low temperatures, the tomato leaves were pretreated with 5 mM dimethylthiourea (DMTU, a H2O2 and O2− scavenger) [32, 33], 100 μM diphenyleneiodonium (DPI, an inhibitor of oxidative burst and NADPH oxidases which generates H2O2) [2, 32], 1 mM buthionine sulfoximine (BSO, an inhibitor of GSH biosynthesis) [32, 34], or 1 mM acriflavine (AF, an inhibitor of AsA biosynthesis). After 8 h, the leaves were sprayed with 25 mg·L− 1 ALA, 5 mM H2O2 [35], 5 mM GSH, or 1 mM AsA. Twelve hours later, the plants were exposed to low temperatures. After 24 h low temperatures, the MDA content and REC were measured.
In addition, we applied the compound inhibitors to further examine the interaction between H2O2, GSH, and AsA with the same treatments and index measurement as described above.
Measurement of plant growth indexes
After the height and stem diameter of each plant were measured, the plants were washed with distilled water, topical moisture was removed, and the plants were dissected into shoots and roots. The fresh weights of dissected tissues were determined, and then the dry weights were obtained after drying for 15 min at 105 °C and then 75 °C for 72 h. There were seven independent biological replicates for each independent treatment, and three independent experiments were performed.
Measurement of Pn, Fv/fm, MDA, and REC
Pn was measured with a portable photosynthesis system LI-6400 (LI-COR Inc., USA). Fv/fm was measured according to the methods of Pérez-Bueno et al. [36] with the Open FluorCam FC 800-O and analyzed using the Fluorcam7 software (PSI, Brno, Czech Republic). The level of membrane lipid peroxidation in leaves was valuated by measuring the MDA content as described by Hodges et al. [37]. The REC was measured according to Zhou and Leul [38].
Measurement of H2O2 content
The H2O2 content in tomato leaves was estimated according to the method of Willekens et al. [39]. Mixed 800 mL extracted sample with 400 mL reaction buffer (pH 4.4) containing 4 mM 2, 2′-azino-di (3-ethylbenzthiazoline-6-sulfonic acid) and 100 mM potassium acetate, 400 mL deionized water and 0.25 U of horseradish peroxidase (HRP). The H2O2 content was determined by measuring the absorbance at 412 nm.
Histochemical staining of O2− was carried out as described by Jabs et al. [40] and the histochemical staining of H2O2 was fulfilled according to the methods of Thordal- Christensen et al. [41].
Measurements of antioxidant enzyme extracts and activities
For the measurement of SOD (EC 1.15.1.1) activities, one unit of SOD activity was defined as the amount of enzyme needed 50% inhibition of the decrease of nitro blue tetrazolium (NBT), as monitored at 560 nm [42].
CAT (EC 1.11.1.6) activity was measured by monitoring the decreases of H2O2 at 240 nm for 2 min. DHAR (EC 1.8.5.1) activity was assayed by monitoring the changes of ascorbate at 265 nm for 3 min. GR (EC 1.6.4.2) activity was assayed by monitoring the decrease of NADPH at 340 nm for 3 min. APX (EC 1.11.1.11) activity was assayed by monitoring the decreases of ascorbate at 290 nm for 2 min. MDHAR (EC 1.6.5.4) activity was assayed by monitoring the decreases of NADPH at 340 nm for 3 min. The methods above were described according to Noctor et al. [35].
Measurements of glutathione and ascorbate levels
The glutathione content was assayed by monitoring the changes of 2-nitro-5-thiobenzoic acid absorbance at 412 nm for 5 min. The ascorbate content was assayed by monitoring the changes of ascorbate at 265 nm for 5 min [35].
RNA extraction and qRT-PCR analyses
Total RNA was extracted from tomato leaves using the Plant RNA Kit (OmegaBio-Tek, Doraville, GA, USA) according to the supplier’s instructions. The total RNA was then reverse-transcribed using a PrimeScript TM RT reagent kit with a gDNA Eraser (Takara, Shiga, Japan), following the manufacturer’s instructions. The gene specific primers of RBOH1 for qRT-PCR were as follows; (forward, 5′-CGGAACAGGCAACGGTGTA-3′; reverse, 5′-TGCGAAATCGGAACGATAAA- 3′) and for the actin gene were (forward, 5′-GGGATGGAGAAGTTTGGTGGTGG-3′; reverse, 5′-CTTCGACCAAGGGATGGTGTAGC-3′), which was used as an internal control.
Statistical analysis
All data were analysed with SAS 8.0 software (SAS Institute, Cary, NC, USA) using Duncan’s multiple- range test at a significance level of P < 0.05.
Results
The effects of ALA concentrations on tomato membrane lipid peroxidation, Pn, and growth under low temperature stress
Compared to the control, low temperatures increased the levels of both MDA and REC, and decreased the level of Pn, while ALA treatment at low concentrations (10–25 mg·L− 1) dramatically decreased the levels of both MDA and REC, and increased the level of Pn at low temperatures. At the optimal concentration of 25 mg·L− 1 ALA, MDA and REC were 21.1% and 39.3% lower, respectively, and Pn was 97.5% higher than that of plants not treated with ALA under low temperature (A0) (Fig. 1). In addition, treatment with ALA significantly improved the plant growth of tomatoes compared with A0 plants (Additional file 1: Table S1). The protective effect of ALA against low temperature stress was attenuated when treated with ALA concentrations either higher or lower than 25 mg·L− 1 (Fig. 1).
Fig. 1.
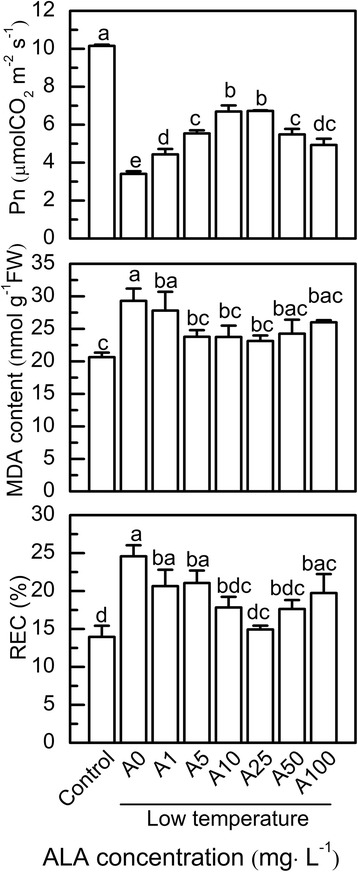
ALA alleviation of low temperature-induced oxidative stress was dose dependent. Data are expressed as the mean ± standard error of three independent biological replicates. Different letters above the bars indicate a significant difference of P < 0.05
The effects of ALA on the RBOH1 expression and H2O2 accumulation, and Fv/fm in tomato plants under low temperature stress
Under control conditions, ALA treatment upregulated the RBOH1 expression and increased the H2O2 content of plants (Fig. 2a). Low temperature increased the RBOH1 expression and the level of H2O2, and resulted in the highest levels among all treatments (Fig. 2a), while the Fv/fm significantly declined (Fig. 2b). However, treatment with ALA at low temperatures reduced RBOH1 expression and H2O2 content by 17.9% and 23.5%, respectively (Fig. 2a), while the level of Fv/fm increased by 8.8% (Fig. 2b), as compared to the untreated low temperature-stressed plants (LT).
Fig. 2.
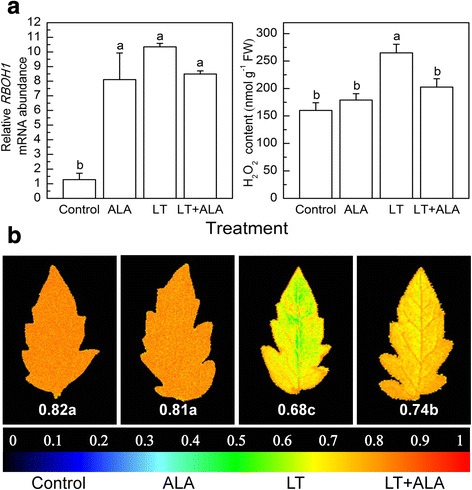
ALA reduced the RBOH1 transcription and H2O2 levels, and improved the Fv/fm at low temperature. a RBOH1 transcription levels (the levels in control plants at 0 h was normalized as 1) and H2O2 content; b Images of the Fv/fm, the false color code depicted at the bottom of the image ranges from 0 (black) to 1(red). Data are expressed as the mean ± standard error of three independent biological replicates. Different letters above the bars indicate a significant difference at P < 0.05
Compared with the control, ALA treatment had no distinct effect on O2− and H2O2 histochemical staining, but low temperatures caused a remarkable accumulation of O2− and H2O2 in leaves and mesophyll cells, which were alleviated by ALA treatment at low temperatures (LT + ALA) (Additional file 2: Figure S1).
To verify the roles of H2O2 in plants induced by ALA, plants treated with ALA under normal conditions for 12 h showed an upregulation of RBOH1 transcripts and H2O2 content of 203.0% and 22.7%, respectively (Fig. 3).
Fig. 3.
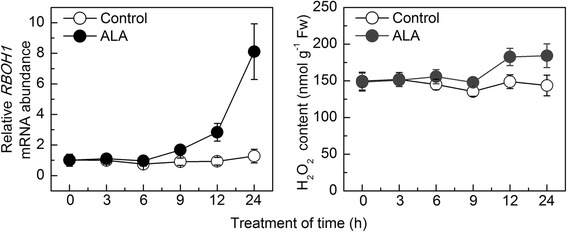
ALA induced upregulation of RBOH1 transcription levels and accumulation of H2O2 content under normal conditions. The RBOH1 transcription levels in control plants at 0 h was normalized as 1. Data are expressed as the mean ± standard error of three independent biological replicates
The effects of ALA on antioxidation in tomato plants under low temperature stress
Under normal conditions, ALA treatment had no significant effects on the antioxidases and antioxidants (Fig. 4, Table 1). However, low temperature stress significantly enhanced the activities of SOD, APX, MDHAR, and DHAR, and the ratio of AsA/DHA, while the activities of CAT and GR and the ratio of GSH/ GSSG were greatly reduced as compared to the control (Fig. 4, Table 1). Treatment with ALA at low temperatures significantly increased the activities of SOD, APX, DHAR, and GR, and the ratio of GSH/GSSG by 14.8%, 42.6%, 33.9%, 113.5%, and 120.3%, respectively, but decreased the activity of MDHAR by 23.2% compared with untreated low temperature-stressed plants (LT) (Fig. 4, Table 1).
Fig. 4.
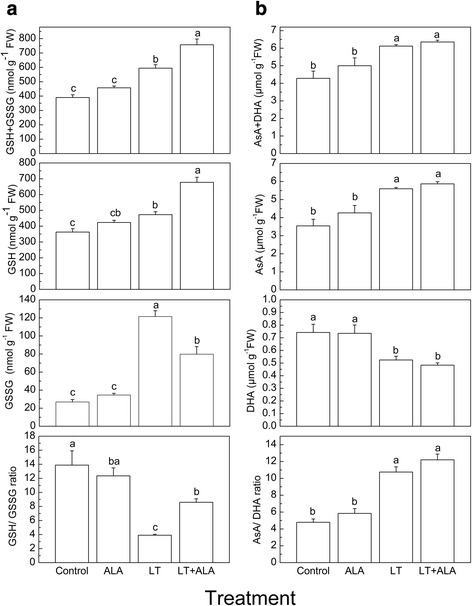
ALA regulated the redox status of glutathione and ascorbate to inhibit low temperature-induced oxidative stress. a Content of GSH + GSSG, GSH, and GSSG, and the ratio of GSH/GSSG; b Content of AsA + DHA, AsA, and DHA, and the ratio of AsA/DHA. Data are expressed as the mean ± standard error of three independent biological replicates. Different letters above the bars indicate a significant difference at P < 0.05
Table 1.
The activities of antioxidant enzymes in tomato leaves induced by ALA
| Treatment | SOD activity (unit mg− 1 prot) | CAT activity (μmol mg− 1 prot min− 1) | APX activity (μmol mg− 1 prot min− 1) | GR activity (nmol mg− 1 prot min− 1) | MDHAR activity (nmol mg− 1 prot min− 1) | DHAR activity (nmol mg− 1 prot min− 1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Control | 8.12 ± 0.33c | 105.72 ± 7.72a | 1.70 ± 0.12c | 62.97 ± 7.38ba | 393.72 ± 42.09b | 198.14 ± 6.73c |
| ALA | 8.73 ± 0.56cb | 98.56 ± 3.96ba | 1.62 ± 0.17c | 70.35 ± 9.33a | 397.26 ± 45.58b | 213.81 ± 17.61c |
| LT | 9.92 ± 0.32b | 76.43 ± 6.69c | 2.35 ± 0.28b | 20.2 ± 1.84c | 615.68 ± 29.78a | 461.11 ± 27.8b |
| LT + ALA | 11.39 ± 0.48a | 85.57 ± 2.73bc | 3.34 ± 0.14a | 43.13 ± 4.34b | 472.68 ± 43.14b | 617.55 ± 48.94a |
Data are expressed as the mean ± standard error of three independent biological replicates. Different letters indicate a significant difference at P < 0.05
The effects of H2O2, GSH, and AsA on ALA-induced antioxidation on tomato plant tolerance to low temperature stress
At low temperatures, application of H2O2, GSH, or AsA dramatically reduced the MDA content by 30.3%, 36.0% and 34.2%, respectively, and decreased REC by 38.5%, 44.5%, and 38.1%, respectively, compared with the application of H2O in tomato plants (Fig. 5). However, pretreatment of the tomato leaves with DMTU, DPI, BSO, or AF mostly eliminated the ALA-induced tolerance to oxidative stress under low temperature (Fig. 5).
Fig. 5.
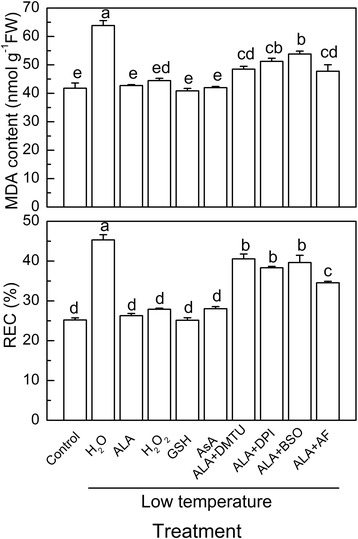
Involvement of H2O2, GSH, and AsA in ALA-induced oxidative stress tolerance at low temperatures. Data are expressed as the mean ± standard error of three independent biological replicates. Different letters above the bars indicate a significant difference at P < 0.05
To further characterize the interactions among H2O2, AsA, and GSH in defending against low temperature stress, the effects of BSO, AF, DMTU, and DPI on H2O2, AsA, and GSH-induced low temperature tolerance were determined. Pretreatment with BSO or AF largely reduced the alleviated effect of H2O2 on the oxidative stress-induced increase of MDA levels and REC at low temperatures (Fig. 6). In contrast, pretreatment with DMTU or DPI partially blocked the GSH- or AsA-induced oxidative stress tolerances at low temperatures (Fig. 6).
Fig. 6.
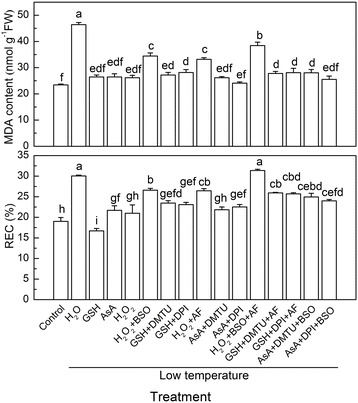
The relationships among H2O2, GSH, and AsA in the inhibition of low temperature-induced oxidative stress. Data are expressed as the mean ± standard error of three independent biological replicates. Different letters above the bars indicate a significant difference at P < 0.05
Discussion
Exogenous ALA induces defense against low temperature-induced oxidative stress in tomato plants
Many studies showed that application of high concentrations of ALA could induce the generation of free tetrapyrroles, such as protochlorophyllide (Pchlide). Meanwhile, free tetrapyrroles generated highly reactive singlet oxygen which was the trigger of severe oxidative stress [25, 43]. In contrast, low concentrations of ALA alleviated oxidative stress in many crops, such as peppers [30], soybeans [44], melons [45] and oilseed rape [46]. In the present study, the results showed that low temperatures caused severe oxidative stress by generating O2− that was converted to H2O2, while pretreatment with ALA alleviated the oxidative damages from the low temperature stress (Additional file 2: Figure S1). Notably, the effects of ALA on coping with oxidative stress and improving plant growth were much weaker at concentrations above or below 25 mg·L− 1 (Fig. 1, Additional file 1: Table S1). This might be due to the dual effects of ALA that caused ROS accumulation with excessive free tetrapyrroles [43], or removed ROS by antioxidation [29], suggesting that the mode of action of ALA on plants was dose dependent.
The AsA-GSH cycle plays key roles in ALA-induced defenses against oxidative stress at low temperatures
Plants accumulating free tetrapyrroles can induce photooxidative damage [25]. However, there is no evidence to suggest that ALA directly scavenges ROS (O2− and H2O2). The reduction of ROS by ALA might therefore be dependent on reactions of antioxidant systems. O2− could be rapidly converted into H2O2 by SOD [12], which could then be converted to H2O or O2 by a GSH and/or a AsA regenerating cycle and/or CAT [47]. In the present study, GSH and AsA levels and the activities of some key enzymes (APX, GR, and DHAR) involved in the AsA-GSH cycle and SOD were dramatically increased, the activity of CAT was only slightly enhanced, and the activity of MDHAR was significantly decreased with ALA treatment under low temperature compared with untreated low temperature-stressed plants (LT) (Table 1, Fig. 4). These results suggested that O2− was reduced to H2O2 by SOD, which was then scavenged by the CAT and the AsA-GSH cycle induced by ALA. With AsA as a substrate, APX played a direct role, and the AsA regeneration was mainly catalyzed by increased activity of DHAR, but not MDHAR, from DHA to AsA [47]. Overall, the results showed that the AsA-GSH cycle induced by ALA eliminated excessive H2O2 in tomato plants at low temperatures.
The interaction between H2O2 signaling and the glutathione and ascorbate redox states is essential for ALA-induced oxidative stress perception and tolerance at low temperatures
It is well-known that ROS plays critical roles in mediating signal transmission in plants [48]. The upregulation of RBOH1 expression induced by ALA caused H2O2 generation under normal conditions (Fig. 3) [20], suggesting that ALA might induce plant perception and self-protective mechanisms via intensive H2O2 signaling, which subsequently alleviated the oxidative stress at low temperatures.
Regarding peroxide metabolism and their regeneration, GSH and AsA are interdependently associated [49]. Our studies showed that treatment with GSH and AsA induced tomatoes tolerance to oxidative stress at low temperatures, while pretreatment with AF and BSO largely blocked the ALA-induced resistance against oxidative stress (Fig. 5). Cellular GSH and AsA are reductants involved in the defense against ROS, and are also known to affect signaling intensities, as well as transmitting information from environmental stresses to their respective targets (stress-related genes, phytohormone levels, or regulatory proteins) [49–51]. Pretreatment with ALA might therefore induce initial defense mechanisms via H2O2 signaling and the interaction with other signaling compounds, such as GSH and AsA [4, 52], to induce resistance to oxidative stress at low temperatures [7]. In addition, GSH is a transmitter of intracellular ROS signaling, while enough of the AsA pool and a high AsA/DHA ratio might play a minor role in ROS signaling via the GSH redox cycle [53], and via phytohormones, and gene expressions [49]. The results therefore suggested that the increases in GSH and AsA were essential for H2O2-induced tolerance to low temperature-induced oxidative stress (Fig. 6).
Taken together, intensive H2O2 signaling induced by pretreatment with ALA may mediate the redox status of glutathione and ascorbate to perceive the oxidative stress and subsequent resistance at low temperatures. In addition, GSH and AsA may interact with H2O2 signaling and other phytohormones, to induce a series of relevant gene expressions, resulting in an enhanced antioxidant capacity in tomato plants at low temperatures.
Conclusions
Exogenous ALA alleviated the low temperature-induced oxidative stress in tomato plants via an antioxidant system, and the most effective concentration of ALA was 25 mg·L− 1. Pretreatment with ALA under normal conditions may induce initial plant perception and signaling transmission via elevated H2O2 signaling, which then activates defense mechanisms by glutathione and ascorbate redox signaling, inducing plant resistance to oxidative stress at low temperatures. In addition, glutathione and ascorbate redox signaling may interact with H2O2 to regulate the protective responses.
Additional files
Table S1. The effects of ALA concentrations on the growth of tomato seedlings under low temperature stress. Data are expressed as the mean ± standard error of seven independent biological replicates. Different letters indicate a significant difference at P < 0.05. (DOCX 15 kb)
Figure S1. Histochemical staining of the effects of ALA on ROS accumulation. O2− (a) and H2O2 (b) in tomato leaves and mesophyll cells. The photographs were obtained using an Olympus motorized system microscope (BX51, Olympus, Tokyo, Japan) at 1000× magnifications. Bar = 20 μm. (JPEG 3465 kb)
Acknowledgements
We thank Hao Li, Dalong Zhang, Xiaojing Li, and Jianyu Yang (College of Horticulture, Northwest Agriculture & Forestry University) for their technical assistance.
Funding
This work was supported by grants from the National High-tech R&D Program of China (863 Program) (No. 2013AA103004) and the China Agriculture Research System (No. CARS-23-C-05). The funders had no role in the experiment design, data analysis, decision to publish, or preparation of the manuscript.
Availability of data and materials
The datasets analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
Abbreviations
- AF
Acriflavine
- APX
Ascorbate peroxidase
- AsA
Reduced ascorbate
- BSO
Buthionine sulfoximine
- CAT
Catalase
- DHA
Dehydroascorbate
- DHAR
Dehydroascorbate reductase
- DMTU
Dimethylthiourea
- DPI
Diphenyleneiodonium
- Fv/fm
Maximal quantum yield of PSII photochemistry
- GR
Glutathione reductase
- GSH
Reduced glutathione
- GSSG
Oxidized glutathione
- H2O2
Hydrogen peroxide
- MDHAR
Monodehydroascorbate reductase
- O2−
Superoxide anions
- Pn
Net photosynthesis rate
- ROS
Reactive oxygen species
- SOD
Superoxide dismutase
Authors’ contributions
TL, XH, and JL designed the experiments and wrote the manuscript. TL, JZ, JZ, and QD performed the experiments. TL, QD, and XH analyzed the data. All authors have read and approved the final version of the manuscript.
Ethics approval and consent to participate
Not applicable
Consent for publication
Not applicable
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Footnotes
Electronic supplementary material
The online version of this article (10.1186/s12870-018-1254-0) contains supplementary material, which is available to authorized users.
Contributor Information
Tao Liu, Email: liutao19851352@163.com.
Xiaohui Hu, Email: hxh1977@163.com.
Jiao Zhang, Email: 18829355005@163.com.
Junheng Zhang, Email: balance811@163.com.
Qingjie Du, Email: duqj91@163.com.
Jianming Li, Phone: +86-29-87082613, Email: lijianming66@163.com.
References
- 1.Li JM, Hu LP, Zhang L, Pan XB, Hu XH. Exogenous spermidine is enhancing tomato tolerance to salinity-alkalinity stress by regulating chloroplast antioxidant system and chlorophyll metabolism. BMC Plant Biol. 2015;15:303. doi: 10.1186/s12870-015-0699-7. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Chen M, Thelen JJ. ACYL-LIPID DESATURASE2 is required for chilling and freezing tolerance in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell. 2013;25:1430–1444. doi: 10.1105/tpc.113.111179. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Chinnusamy V, Zhu J, Zhu JK. Cold stress regulation of gene expression in plants. Trends Plant Sci. 2007;12(10):444–451. doi: 10.1016/j.tplants.2007.07.002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Mhamdi A, Han Y, Noctor G. Glutathione-dependent phytohormone responses: teasing apart signaling and antioxidant functions. Plant Signal Behav. 2013;8(5):e24181. doi: 10.4161/psb.24181. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Eremina M, Rozhon W, Poppenberger B. Hormonal control of cold stress responses in plants. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2016;73:797–810. doi: 10.1007/s00018-015-2089-6. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Puyaubert J, Baudouin E. New clues for a cold case: nitric oxide response to low temperature. Plant Cell Environ. 2014;37:2623–2630. doi: 10.1111/pce.12329. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Knight MR, Knight H. Low-temperature perception leading to gene expression and cold tolerance in higher plants. New Phytol. 2012;195:737–751. doi: 10.1111/j.1469-8137.2012.04239.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Gill SS, Tuteja N. Reactive oxygen species and antioxidant machinery in abiotic stress tolerance in crop plants. Plant Physiol Biochem. 2010;48:909–930. doi: 10.1016/j.plaphy.2010.08.016. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Reczek CR, Chandel NS. ROS-dependent signal transduction. Curr Opin Plant Biol. 2015;33:8–13. doi: 10.1016/j.ceb.2014.09.010. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Schieber M, Chandel NS. ROS function in redox signaling and oxidative stress. Curr Biol. 2014;24(10):453–462. doi: 10.1016/j.cub.2014.03.034. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Bose J, Rodrigo-Moreno A, Shabala S. ROS homeostasis in halophytes in the context of salinity stress tolerance. J Exp Bot. 2014;65(5):1241–1257. doi: 10.1093/jxb/ert430. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Willems P, Mhamdi A, Stael S, Storme V, Kerchev P, Noctor G, Gevaert K, Van Breusegem F. The ROS wheel: refining ROS transcriptional footprints. Plant Physiol. 2016;171:1720–1733. doi: 10.1104/pp.16.00420. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Dietz KJ, Mittler R, Noctor G. Recent progress in understanding the role of reactive oxygen species in plant cell signaling. Plant Physiol. 2016;171:1535–1539. doi: 10.1104/pp.16.00938. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Dutilleu C, Garmier M, Noctor G, Mathieu C, Chétrit P, Foyer CH, Rd P. Leaf mitochondria modulate whole cell redox homeostasis, set antioxidant capacity, and determine stress resistance through altered signaling and diurnal regulation. Plant Cell. 2003;15:1212–1226. doi: 10.1105/tpc.009464. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Nahar K, Hasanuzzaman M, Alam MM, Fujita M. Exogenous spermidine alleviates low temperature injury in mung bean(Vigna radiata L.) seedlings by modulating ascorbate-glutathione and glyoxalase pathway. Int J Mol Sci. 2015;16:30117–30132. doi: 10.3390/ijms161226220. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Meng JF, Xu TF, Wang ZZ, Fang YL, Xi ZM, Zhang ZW. The ameliorative effects of exogenous melatonin on grape cuttings under water-deficient stress: antioxidant metabolites, leaf anatomy, and chloroplast morphology. Journal Pineal Res. 2014;57:200–212. doi: 10.1111/jpi.12159. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Baxter A, Mittler R, Suzuki N. ROS as key players in plant stress signalling. J Exp Bot. 2014;65(5):1229–1240. doi: 10.1093/jxb/ert375. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Shu S, Gao P, Li L, Yuan YH, Sun J, Guo SR. Abscisic acid-induced H2O2 accumulation enhances antioxidant capacity in pumpkin-grafted cucumber leaves under ca(NO3)2 stress. Front Plant Sci. 2016;7:1489. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2016.01489. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Noctor G. Lighting the fuse on toxic TNT an enzyme that helps control reactive oxidants sensitizes plants to TNT pollution. Science. 2015;349:1052–1053. doi: 10.1126/science.aad0941. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Zhou J, Xia XJ, Zhou YH, Shi K, Chen ZX, Yu JQ. RBOH1-dependent H2O2 production and subsequent activation of MPK1/2 play an important role in acclimation-induced cross-tolerance in tomato. J Exp Bot. 2014;65(2):595–607. doi: 10.1093/jxb/ert404. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Zhou J, Wang J, Shi K, Xia XJ, Zhou YH, Yu JQ. Hydrogen peroxide is involved in the cold acclimation-induced chilling tolerance of tomato plants. Plant Physiol Biochem. 2012;60:141–149. doi: 10.1016/j.plaphy.2012.07.010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Foyer CH, Shigeoka S. Understanding oxidative stress and antioxidant functions to enhance photosynthesis. Plant Physiol. 2011;155:93–100. doi: 10.1104/pp.110.166181. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Saxena I, Srikanth S, Chen Z. Cross talk between H2O2 and interacting signal molecules under plant stress response. Front Plant Sci. 2016;7:570. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2016.00570. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.An YY, Li J, Duan CH, Liu LB, Sun YP, Cao RX, Wang LJ. 5-aminolevulinic acid thins pear fruits by inhibiting pollen tube growth via Ca2+-ATPase-mediated Ca2+ efflux. Front Plant Sci. 2016;7:121. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2016.00121. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Apitz J, Nishimura K, Schmied J, Wolf A, Hedtke B, van Wijk KJ, Grimm B. Posttranslational control of ALA synthesis includes GluTR degradation by Clp protease and stabilization by GluTR-binding protein. Plant Physiol. 2016;170:2040–2051. doi: 10.1104/pp.15.01945. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Akram NA, Ashraf M, Al-Qurainy F. Aminolevulinic acid-induced changes in some key physiological attributes and activities of antioxidant enzymes in sunflower (Helianthus annuus L.) plants under saline regimes. Sci Hortic. 2012;142:143–148. doi: 10.1016/j.scienta.2012.05.007. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Akram NA, Ashraf M. Regulation in plant stress tolerance by a potential plant growth regulator, 5-aminolevulinic acid. Journal Plant Growth Regul. 2013;32:663–679. doi: 10.1007/s00344-013-9325-9. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Sun XE, Feng XX, Li C, Zhang ZP, Wang LJ. Study on salt tolerance with YHem1 transgenic canola (Brassica napus) Physiol Plantarum. 2015;154:223–242. doi: 10.1111/ppl.12282. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Ali B, Xu X, Gill RA, Yang S, Ali S, Tahir M, Zhou W. Promotive role of 5-aminolevulinic acid on mineral nutrients and antioxidative defense system under lead toxicity in Brassica napus. Ind Crop Prod. 2014;52:617–626. doi: 10.1016/j.indcrop.2013.11.033. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Korkmaz A, Korkmaz Y, Demirkıran AR. Enhancing chilling stress tolerance of pepper seedlings by exogenous application of 5-aminolevulinic acid. Environ Exp Bot. 2010;67:495–501. doi: 10.1016/j.envexpbot.2009.07.009. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Ali B, Tao QJ, Zhou YF, Gill RA, Ali S, Rafiq MT, Xu L, Zhou WJ. 5-Aminolevolinic acid mitigates the cadmium-induced changes in Brassica napus as revealed by the biochemical and ultra-structural evaluation of roots. Ecotox Environ Safe. 2013;92:271–280. doi: 10.1016/j.ecoenv.2013.02.006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Li H, He J, Yang XZ, Li X, Luo D, Wei CH, Ma JX, Zhang Y, Yang JQ, Zhang X. Glutathione-dependent induction of local and systemic defense against oxidative stress by exogenous melatonin in cucumber (Cucumis sativus L.) Journal Pineal Res. 2016;60:206–216. doi: 10.1111/jpi.12304. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Xia XJ, Zhou YH, Ding J, Shi K, Asami T, Chen Z, Yu JQ. Induction of systemic stress tolerance by brassinosteroid in Cucumis sativus. New Phytol. 2011;191:706–720. doi: 10.1111/j.1469-8137.2011.03745.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Jiang YP, Cheng F, Zhou YH, Xia XJ, Mao WH, Shi K, Chen Z, Yu JQ. Cellular glutathione redox homeostasis plays an important role in the brassinosteroid-induced increase in CO2 assimilation in Cucumis sativus. New Phytol. 2012;194:932–943. doi: 10.1111/j.1469-8137.2012.04111.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Noctor G, Mhamdi A, Foyer CH. Oxidative stress and antioxidative systems: recipes for successful data collection and interpretation. Plant Cell Environ. 2016;39:1140–1160. doi: 10.1111/pce.12726. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Pérez-Bueno ML, Pineda M, Díaz-Casado E, Barón M. Spatial and temporal dynamics of primary and secondary metabolism in Phaseolus vulgaris challenged by Pseudomonas syringae. Physiol Plant. 2015;153:161–174. doi: 10.1111/ppl.12237. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Hodges DM, DeLong JM, Forney FC, Prange RK. Improving the thiobarbituric acid-substances assay for estimating lipid peroxidation in plant tissues containing anthocyanin and other inerfering compounds. Planta. 1999;207:604–11. doi: 10.1007/s004250050524. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Zhou WJ, Leul M. Uniconazole-induced alleviation of freezing injury in relation to changes in hormonal balance, enzyme activities and lipid peroxidation in winter rape. Plant Growth Regul. 1998;26:41–47. doi: 10.1023/A:1006004921265. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Willekens H, Chamnongpol S, Davey M, Schraudner M, Langebartels C, Van Montagu M, Inzé D, Van Camp W. Catalase is a sink for H2O2 and is indispensable for stress defence in C3 plants. EMBO J. 1997;16(16):4806–4816. doi: 10.1093/emboj/16.16.4806. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Jabs T, Dietrich RA, Dangl JL. Initiation of runaway cell death in an Arabidopsis mutant by extracellular superoxide. Science. 1996;273:1853–1856. doi: 10.1126/science.273.5283.1853. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Thordal-Christensen H, Zhang Z, Wei Y, Collinge DB. Subcellular localization of H2O2 in plants. H2O2 accumulation in papillae and hypersensitive response during the barley-powdery mildew interaction. Plant J. 1997;11:1187–1194. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-313X.1997.11061187.x. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Giannopolitis CN, Ries SK. Superoxide dismutases I. Occurrence in higher plants. Plant Physiol. 1977;59:309–314. doi: 10.1104/pp.59.2.309. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.op den Camp RGL, Przybyla D, Ochsenbein C, Laloi C, Kim C, Danon A, Wagner D, Hideg E, Gobel C, Feussner I, Nater M, Apel K. Rapid induction of distinct stress responses after the release of singlet oxygen in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell. 2003;15:2320–2332. doi: 10.1105/tpc.014662. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44.Balestrasse KB, Tomaro ML, Batlle A, Noriega GO. The role of 5-aminolevulinic acid in the response to cold stress in soybean plants. Phytochemistry. 2010;71:2038–2045. doi: 10.1016/j.phytochem.2010.07.012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45.Wang LJ, Jiang WB, Huang BJ. Promotion of 5-aminolevulinic acid on photosynthesis of melon (Cucumis melo) seedlings under low light and chilling stress conditions. Physiol Plant. 2004;121:258–264. doi: 10.1111/j.0031-9317.2004.00319.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46.Ali B, Gill RA, Yang S, Gill MB, Farooq MA, Liu D, Daud MK, Ali S, Zhou WJ. Regulation of cadmium-induced proteomic and metabolic changes by 5-aminolevulinic acid in leaves of Brassica napus L. PLoS One. 2015;10(4):e0123328. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0123328. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47.Mittler R. Oxidative stress, antioxidants and stress tolerance. Trends Plant Sci. 2002;7(9):405–410. doi: 10.1016/S1360-1385(02)02312-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 48.Miller G, Schlauch K, Tam R, Cortes D, Torres MA, Shulaev V, Dang JL, Mittler R. The plant NADPH oxidase RBOHD mediates rapid systemic signaling in response to diverse stimuli. Sci Signal. 2009;2(84):1–10. doi: 10.1126/scisignal.2000448. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 49.Foyer CH, Noctor G. Ascorbate and glutathione: the heart of the redox hub. Plant Physiol. 2011;155:2–18. doi: 10.1104/pp.110.167569. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 50.May MJ, Vernoux T, Leaver C, Montagu MV, Inze´ D. Glutathione homeostasis in plants: implications for environmental sensing and plant development. J Exp Bot. 1998;49(321):649–667. [Google Scholar]
- 51.Ball L, Accotto GP, Bechtold U, Creissen G, Funck D, Jimenez A, Kular B, Leyland N, Mejia-Carranza J, Reynolds H, Karpinski S, Mullineaux PM. Evidence for a direct link between glutathione biosynthesis and stress defense gene expression in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell. 2004;16:2448–2462. doi: 10.1105/tpc.104.022608. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 52.Noctor G, Foyer CH. Intracellular redox compartmentation and ROS-related communication in regulationand signaling. Plant Physiol. 2016;171:1581–1592. doi: 10.1104/pp.16.00346. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 53.Han Y, Mhamdi A, Chaouch S, Noctor G. Regulation of basal and oxidative stress-triggered jasmonic acid-related gene expression by glutathione. Plant Cell Environ. 2013;36:1135–1146. doi: 10.1111/pce.12048. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Table S1. The effects of ALA concentrations on the growth of tomato seedlings under low temperature stress. Data are expressed as the mean ± standard error of seven independent biological replicates. Different letters indicate a significant difference at P < 0.05. (DOCX 15 kb)
Figure S1. Histochemical staining of the effects of ALA on ROS accumulation. O2− (a) and H2O2 (b) in tomato leaves and mesophyll cells. The photographs were obtained using an Olympus motorized system microscope (BX51, Olympus, Tokyo, Japan) at 1000× magnifications. Bar = 20 μm. (JPEG 3465 kb)
Data Availability Statement
The datasets analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.


