Abstract
This study examines adverse events for cosmetics in the FDA’s Center for Food Safety and Applied Nutrition’s Adverse Event Reporting System to inform future policymaking to protect consumers.
The US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) defines cosmetics as articles for beautification, cleansing, or altering physical appearance. There have been multiple public health controversies surrounding cosmetics involving lip balms, lipsticks, and eyelash makeups adulterated with prostaglandins. In 2014, the FDA began investigating WEN by Chaz Dean Cleansing Conditioners after directly receiving 127 consumer reports. The FDA later learned the manufacturer had already received 21 000 complaints of alopecia and scalp irritation. The product remains on the market with the FDA currently soliciting additional consumer reports. To encourage greater transparency and more reporting, the FDA’s Center for Food Safety and Applied Nutrition’s Adverse Event Reporting System (CFSAN), a repository of adverse events related to foods, dietary supplements, and cosmetics, was made publically available in 2016. Our objective was to examine adverse events in CFSAN to inform future policymaking.
Methods
We extracted the entire CFSAN data file (2004-2016), including all voluntary submissions by consumers and health care professionals. We categorized all cosmetic-related adverse events by FDA-designated product class. For 5% of entries, no product class was identifiable. We collected self-reported adverse health outcomes (nonserious injury, serious injury, disability, congenital defects, or death) for each event. We used a logit transform to estimate 95% CIs for proportions, and a logistic regression model to compare the proportion of serious adverse health outcomes (serious injury, disability, congenital defect, or death) reported for each product class compared with the global average. Because this study used only publicly available data, it was exempt from Northwestern University institutional review board approval.
Results
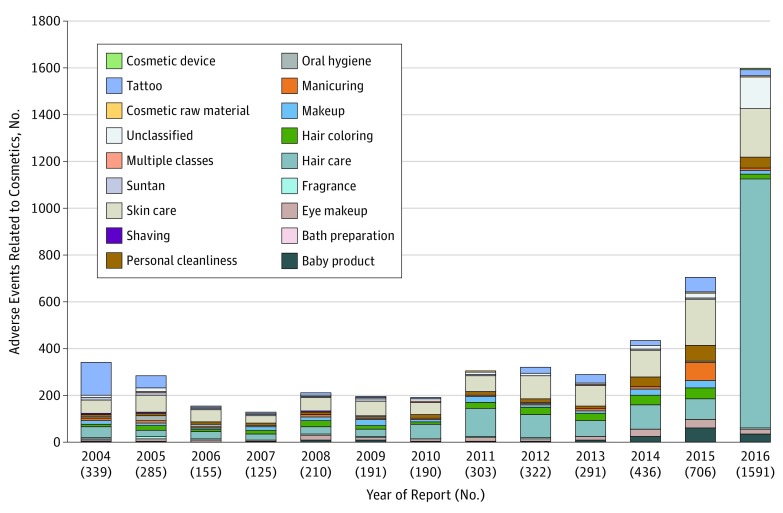
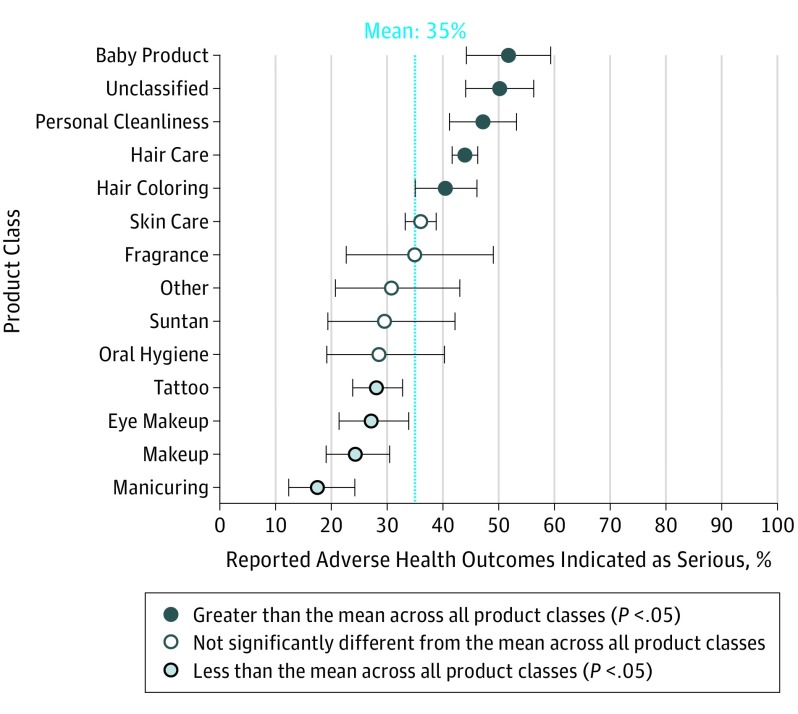
From 2004 to 2016, a total of 5144 events were submitted (an average of 396 events per year). From 2015 (n = 706) to 2016 (n = 1591), there was an increase in adverse events, specifically involving hair care products, compared with the average (Figure 1). Overall, the 3 most commonly implicated products were hair care (n = 1805), skin care (n = 1148), and tattoos (n = 388). Product classes with significantly higher than average (35.0%) reports of serious health outcomes were as follows: baby (51.8%; 95% CI, 44.2%-59.3%), unclassified (50.2%; 95% CI, 44.1%-56.3%), personal cleanliness (47.1%; 95% CI, 41.2%-53.2%), hair care (43.9%; 95% CI, 41.7%-46.2%), and hair coloring products (40.5%; 95% CI, 35.0%-46.1%) (Figure 2).
Figure 1. Adverse Event Reports for Cosmetics and Personal Care Products From 2004 to 2016.
The US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) provides definitions for all product classes. Briefly, skin care products constitute a broad range of items, including cleansing lotions and creams, depilatories, sprays, moisturizers, and anti-wrinkle products. Personal cleanliness products included bath soaps, deodorants, and douches. Baby products included shampoos, lotions, oils, creams, and powders marketed toward newborns and infants. Hair care products, which include shampoos (noncoloring), rinses (noncoloring), hair spray, and hair straighteners, constituted 35% (n = 1805) of all adverse health reports. Skin care products were the next most common source of complaints at 22% (n = 1148). Five percent of products (n = 257) were not classifiable based on the available data. The data label for each year indicates the total number of adverse events reported. On average, 396 cosmetic-related adverse events were sent to the FDA every year. There was a 78% increase in 2015 and a 300% increase in 2016 for adverse event reports compared with the mean across the entire time period (2004-2016). This increase was largely driven by the hair care products class, specifically the WEN product line by Chaz Dean.
Figure 2. Adverse Events Leading to Serious Adverse Health Outcome, a Nonserious Adverse Health Outcome, or a Health System Visit for Cosmetic and Personal Care Product Classes.
A “serious” adverse health outcome was counted whenever a reporter attributed a specific adverse event with any of the following: serious injury, disability, congenital anomaly, or death. We collapsed 5 product types that had 20 or fewer adverse outcomes, which included bath preparation products, shaving products, cosmetic raw materials, cosmetic devices, and multiple category products into the “other” category. The dashed vertical line illustrates the average percentage of reported adverse events across the 14 product types for each of the adverse health outcomes. An orange dot signifies a higher-than-average percentage compared with the mean (P < .05). A purple dot signifies a lower-than-average percentage compared with the mean (P < .05). A black dot signifies no significant difference compared with the average. Error bars indicate 95% CIs. As expected, products with high percentages of serious adverse events also had lower percentages of nonserious adverse events.
Discussion
Better cosmetic surveillance is needed given their ubiquity and lack of a premarket approval pathway. Unlike devices, pharmaceuticals, and dietary supplements, cosmetic manufacturers have no legal obligation to forward adverse events to the FDA; CFSAN reflects only a small proportion of all events. The data suggest that consumers attribute a significant proportion of serious health outcomes to cosmetics. The lack of high-quality data leads to reactionary responses by the FDA subject to consumer pressure as evidenced by the WEN conditioners controversy. The first step to improve cosmetic safety is broader reporting, especially from manufacturers. Greater coordination with other databases (eg, National Poison Data System) may yield useful collateral information.
There are several limitations to this analysis. Although the FDA removes duplicate reports, there is no causality determination and health outcomes are all self-reported. Demographic information is also limited to sex and age. Additional data on medical comorbidities or concomitant product use would be relevant. Finally, we cannot distinguish reports from consumers vs those from health care professionals.
In 2014, the FDA expressed “profound disappointment” with the industry’s draft legislation to modernize cosmetics regulation and refused to invest additional taxpayer dollars for further negotiations. Since then, California’s Senator Diane Feinstein has introduced the Personal Care Products Safety Act (PCPSA) with a coalition of supporters. The bill’s key components include granting the FDA authority to recall unsafe cosmetics, mandatory manufacturer reporting of adverse events, and a yearly safety review of 5 ingredients. However, the law does not provide more investment to the National Toxicology Program for more rigorous scientific testing. For products blurring the line between drug and cosmetic (cosmeceuticals), a form of premarket approval should be considered. Ultimately, PCPSA is a first step in the right direction to protect consumers.
References
- 1.US Food and Drug Administration. EOS lip balm products. 2016. https://www.fda.gov/Cosmetics/ProductsIngredients/Products/ucm490864.htm. Accessed December 9, 2016.
- 2.Monnot AD, Christian WV, Abramson MM, Follansbee MH. An exposure and health risk assessment of lead (Pb) in lipstick. Food Chem Toxicol. 2015;80:253-260. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.US Food and Drug Administration. Potentially harmful “cosmetic” eye product seized. 2007. https://www.fda.gov/ForConsumers/ConsumerUpdates/ucm048964.htm. Accessed March 3, 2017.
- 4.US Food and Drug Administration. WEN by Chaz Dean Cleansing Conditioners. FDA Statement: Investigation of Adverse Event Reports. 2016. https://www.fda.gov/Safety/MedWatch/SafetyInformation/SafetyAlertsforHumanMedicalProducts/ucm511890.htm. November 3, 2016.
- 5.Taylor MR. Letter to the Personal Care Products Council and Independent Cosmetics Manufacturers and Distributors concerning the proposed draft legislation. 2015. https://www.fda.gov/AboutFDA/CentersOffices/OfficeofFoods/CFSAN/CFSANFOIAElectronicReadingRoom/ucm388296.htm. Accessed December 3, 2016.
- 6.Lyon J. Regulating personal care products. JAMA. 2016;316(18):1859. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]