In the article titled “4-Phenylbutyric Acid Attenuates Pancreatic Beta-Cell Injury in Rats with Experimental Severe Acute Pancreatitis” [1], the authors made a mistake in the process of analysis by using the recommended concentrations of reference standard which should be diluted by 20 times to be the actual concentrations.
Therefore, in the “3.3. Serum Insulin, TNF-α, IL-1β, and Glucose Levels” section, the text reading “Spearman correlation analysis revealed that serum levels of insulin were positively correlated with TNF-α (r = 0.8052, P < 0.05) and IL-1β (r = 0.7661, P < 0.05) and showed significantly negative correlation between serum insulin levels and serum glucose levels (r = −0.7600, P < 0.05) (Figure 5)” should be corrected as follows.
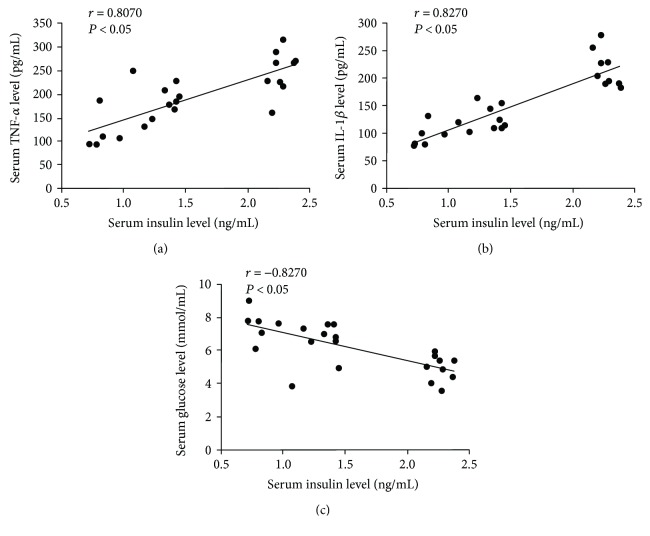
Figure 5.
The correlations of serum insulin with TNF-α, IL-1β, and glucose were analyzed using Spearman correlation test. (a) Spearman correlation between insulin and TNF-α; (b) Spearman correlation between insulin and IL-1β; (c) Spearman correlation between insulin and glucose.
“Spearman correlation analysis revealed that serum levels of insulin were positively correlated with TNF-α (r = 0.8070, P < 0.05) and IL-1β (r = 0.8270, P < 0.05) and showed significantly negative correlation between serum insulin levels and serum glucose levels (r = −0.7191, P < 0.05) (Figure 5).”
In addition, the raw data for Figures 4(a) and 5 are included in the Supplementary Materials (available here) and the figures should be corrected as follows.
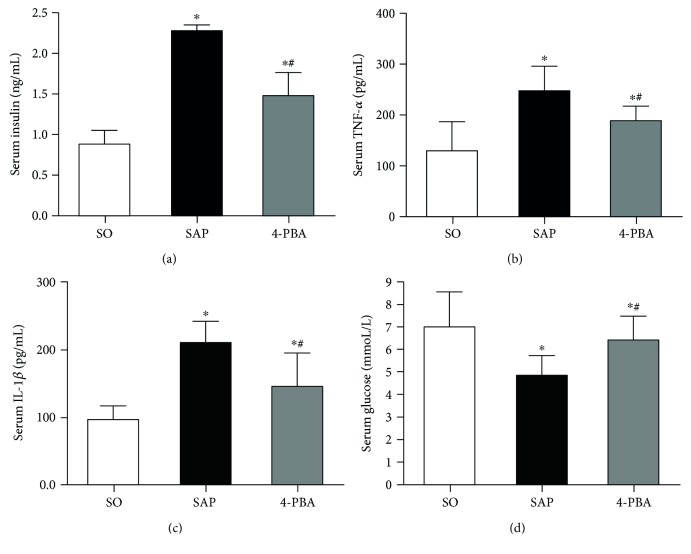
Figure 4.
Effects of 4-phenylbutyric acid on insulin, inflammatory cytokine, and glucose production in serum. (a) Insulin; (b) TNF-α; (c) IL-1β; (d) glucose. Each value represents the mean ± standard deviation. ∗ P < 0.05 versus SO group; # P < 0.05 versus SAP group.
Supplementary Materials
Table 1: serum levels of insulin, TNF-α, IL-1β, and glucose in rats.
References
- 1.Hong Y.-p., Guo W.-y., Wang W.-x., et al. 4-Phenylbutyric acid attenuates pancreatic beta-cell injury in rats with experimental severe acute pancreatitis. International Journal of Endocrinology. 2016;2016:11. doi: 10.1155/2016/4592346.4592346 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Table 1: serum levels of insulin, TNF-α, IL-1β, and glucose in rats.