Key Points
Question
What is the association between wait time and 30-day mortality in patients undergoing hip fracture surgery?
Findings
In this retrospective cohort study that included 42 230 adults, wait time longer than 24 hours was associated with higher risk-adjusted likelihood of 30-day mortality (6.5% vs 5.8%).
Meaning
A wait time of 24 hours may represent a threshold of increased risk for delaying hip fracture surgery.
Abstract
Importance
Although wait times for hip fracture surgery have been linked to mortality and are being used as quality-of-care indicators worldwide, controversy exists about the duration of the wait that leads to complications.
Objective
To use population-based wait-time data to identify the optimal time window in which to conduct hip fracture surgery before the risk of complications increases.
Design, Setting, and Participants
Population-based, retrospective cohort study of adults undergoing hip fracture surgery between April 1, 2009, and March 31, 2014, at 72 hospitals in Ontario, Canada. Risk-adjusted restricted cubic splines modeled the probability of each complication according to wait time. The inflection point (in hours) when complications began to increase was used to define early and delayed surgery. To evaluate the robustness of this definition, outcomes among propensity-score matched early and delayed surgical patients were compared using percent absolute risk differences (RDs, with 95% CIs).
Exposure
Time elapsed from hospital arrival to surgery (in hours).
Main Outcomes and Measures
Mortality within 30 days. Secondary outcomes included a composite of mortality or other medical complications (myocardial infarction, deep vein thrombosis, pulmonary embolism, and pneumonia).
Results
Among 42 230 patients with hip fracture (mean [SD] age, 80.1 years [10.7], 70.5% women) who met study entry criteria, overall mortality at 30 days was 7.0%. The risk of complications increased when wait times were greater than 24 hours, irrespective of the complication considered. Compared with 13 731 propensity-score matched patients who received surgery earlier, 13 731 patients who received surgery after 24 hours had a significantly higher risk of 30-day mortality (898 [6.5%] vs 790 [5.8%]; % absolute RD, 0.79; 95% CI, 0.23-1.35) and the composite outcome (1680 [12.2%]) vs 1383 [10.1%]; % absolute RD, 2.16; 95% CI, 1.43-2.89).
Conclusions and Relevance
Among adults undergoing hip fracture surgery, increased wait time was associated with a greater risk of 30-day mortality and other complications. A wait time of 24 hours may represent a threshold defining higher risk.
This cohort study uses health administrative databases in Ontario, Canada, to investigate the optimal timing of hip fracture surgery after which patients’ risk of complications increase.
Introduction
Expedited hip fracture surgery for increasing numbers of patients who may be medically complex and most commonly receive surgery outside regular working hours involves several different medical and surgical specialists, hospital administrators, and allied staff. Despite resources expended toward performing surgery earlier and extensive research on the topic, controversy remains about the acceptable waiting time for treatment. Guidelines from the United States and Canada recommend surgery within 48 hours. The proportion of patients receiving surgery within 36 hours is the quality-of-care indicator used in the United Kingdom, but hospital adherence ranges from 14.7% to 95.3%.
Variable policy and adherence to guidelines are the result, in part, of inconsistent empirical evidence for a time-to-surgery threshold. Confounding by indication may exaggerate the effect of early surgery, with medically complex patients being predisposed to both complications and awaiting optimization prior to surgery. Wait times have also been measured imprecisely in days and arbitrarily divided into early and delayed groups, decreasing statistical power to find differences. The calculation of precise inpatient surgical wait times, in hours rather than days, is possible in Ontario, Canada, for all surgical procedures in the province. The objective of this study was to use these data at the population level to establish a time-to-surgery threshold before the risk of complications increases.
Methods
Data Sources and Setting
A population-based cohort study was conducted using health administrative databases in Ontario, Canada. Ontario residents have their medically necessary health care services, physician and hospital information, and demographic characteristics recorded in these databases. These data are held and linked at the Institute for Clinical Evaluative Sciences (ICES; http://www.ices.on.ca) and have been used previously to study patients with hip fractures (eAppendix A in the Supplement). The study protocol was approved by the Research Ethics Board at Sunnybrook Health Sciences Centre, Toronto, Ontario. Individual patient informed consent is not required for use of encoded administrative health data in Ontario.
Patients
Adults undergoing hip fracture surgery in Ontario between April 1, 2009, and March 31, 2014, were eligible. The beginning of the accrual period was selected when a variable measuring exact surgical wait times was introduced. Accrual ended to allow for 1 year of follow-up (up to the final date March 31, 2015) after the date of initial hospitalization (index date). Similar diagnostic and procedure codes previously used to identify patients with a hip fracture who had experienced complications after orthopedic surgery were retained (eAppendix B in the Supplement).
Non-Ontario residents, those dead on or before their index date, elective hospital admissions, those with prior hip fracture(s) back to 2002, and patients without hospital arrival time data were excluded due to their missing data, potential for misclassification, or both. Other exclusion criteria identified rare cases, unrepresentative of most hip fractures from a clinical perspective: age younger than 45 years, extreme surgical delays (>10 days), and surgery performed by a nonorthopedic surgeon or at a hospital with fewer than 5 hip fracture surgeries during the study period. Hip fractures occurring while patients were in the hospital also were excluded because surgical delays for these patients could not be operationalized using available data (Table 1).
Table 1. Assembly of the Study Cohort in Ontario, Canada Between 2009 and 2014.
| Inclusion and Exclusion Criteria | No. |
|---|---|
| Inclusion criteria | |
| Hip fracture surgical procedures in Ontario during study period | 48 627 |
| Exclusion criteria | |
| Non-Ontario resident | 31 |
| Dead before or on index date | 8 |
| Nonorthopedic surgeon | 351 |
| Prior hip fracture | 1997 |
| Missing emergency presentation time data | 1460 |
| Hip fracture occurring in-hospital | 440 |
| Elective hospital admission | 1002 |
| Low-volume hospital (<5 hip fracture procedures during study period) | 34 |
| Patients aged <45 y | 746 |
| Hip fracture surgery delayed >10 d | 328 |
| Eligible hip fracture fixation procedures (total study cohort size) | 42 230 |
| Eligible treating surgeons | 522 |
| Eligible treating hospitals | 72 |
Main Exposure
The primary independent variable was the wait time for surgery and defined as the total time elapsed from emergency department arrival until surgery (in hours). To capture the time that elapsed during transfer between hospitals, all contiguous hospitalizations from the earliest hospital arrival time to the date and time of surgery were assessed.
Covariates
Patient characteristics previously shown to explain most of the variation in mortality after hip fracture surgery were measured including age, sex, and medical comorbidity (Table 2). Medical comorbidity was estimated using 3 validated tools based on each patient’s health care utilization in the 5 years prior to the index date: (1) the Deyo-Charlson Comorbidity Index classified hospital discharge diagnoses, (2) the Johns Hopkins Collapsed Aggregated Diagnosis Groups categorized hospitalizations and outpatient physician visits, and (3) previously validated algorithms that identified patients with a specific diagnoses (ie, frailty, diabetes, hypertension, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease [COPD], congestive heart failure [CHF], coronary artery disease [CAD], or dementia [eAppendix A in the Supplement]). Associated conditions at the time of hospital presentation also were assessed: osteomyelitis, bone cancer, other fractures, total hip arthroplasty in the prior 5 years, and multiple trauma (defined as an Injury Severity Score ≥16).
Table 2. Baseline Characteristics of 42 230 Patients Undergoing Hip Fracture Surgery in Ontario Between 2009-2014.
| Before Matching, No. (%) | After Matching, No. (%) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ≤24 Hours (n = 14 174) |
>24 Hours (n = 28 056) |
Standardized Mean Differencea | ≤24 Hours (n = 13 731) |
>24 Hours (n = 13 731) |
Standardized Mean Differencea | |
| ED to surgery, mean (SD), h | 15.7 (6.16) | 50.4 (28.8) | 15.7 (6.15) | 48.5 (27.3) | ||
| Demographics | ||||||
| Age, mean (SD), y | 79.9 (11.5) | 81.2 (10.2) | 0.12 | 80.1 (11.3) | 80.1 (10.7) | 0.01 |
| Women | 10 172 (71.8) | 19 587 (69.8) | 0.04 | 9866 (71.9) | 9806 (71.4) | 0.01 |
| Income Quintile | ||||||
| Lowest | 3145 (22.2) | 6358 (22.7) | 0.01 | 3040 (22.1) | 3054 (22.2) | 0 |
| 2 | 2873 (20.3) | 5719 (20.4) | 0 | 2807 (20.4) | 2793 (20.3) | 0 |
| 3 | 2715 (19.2) | 5276 (18.8) | 0.01 | 2657 (19.4) | 2654 (19.3) | 0 |
| 4 | 2698 (19.0) | 5388 (19.2) | 0 | 2624 (19.1) | 2609 (19.0) | 0 |
| Highest | 2679 (18.9) | 5174 (18.4) | 0.01 | 2603 (19.0) | 2621 (19.1) | 0 |
| Missing | 64 (0.5) | 141 (0.5) | 0.01 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Rural residence | 1123 (7.9) | 2488 (8.9) | 0.03 | 1098 (8.0) | 1056 (7.7) | 0.01 |
| Missing | 86 (0.6) | 199 (0.7) | 0.01 | |||
| Comorbidity | ||||||
| Associated conditions | ||||||
| Injury severity score ≥16b | 129 (0.9) | 200 (0.7) | 0.02 | 108 (0.8) | 107 (0.8) | 0 |
| Bone cancer | 50 (0.4) | 126 (0.4) | 0.02 | 47 (0.3) | 60 (0.4) | 0.02 |
| Osteomyelitis | NR | 17 (0.1) | 0.02 | NR | NR | 0.02 |
| Other fractures | 655 (4.6) | 1391 (5.0) | 0.02 | 625 (4.6) | 671 (4.9) | 0.02 |
| Total hip arthroplasty within 5 y prior | 111 (0.8) | 250 (0.9) | 0.01 | 107 (0.8) | 111 (0.8) | 0 |
| Specific comorbidities | ||||||
| Frail | 2141 (15.1) | 5079 (18.1) | 0.08 | 2102 (15.3) | 2069 (15.1) | 0.01 |
| Diabetes | 3831 (27.0) | 8626 (30.7) | 0.08 | 3733 (27.2) | 3726 (27.1) | 0 |
| Hypertension | 10 711 (75.6) | 22 593 (80.5) | 0.12 | 10 448 (76.1) | 10 489 (76.4) | 0.01 |
| Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease | 2437 (17.2) | 5702 (20.3) | 0.08 | 2380 (17.3) | 2305 (16.8) | 0.01 |
| Congestive heart failure | 2396 (16.9) | 7171 (25.6) | 0.21 | 2347 (17.1) | 2359 (17.2) | 0 |
| Coronary artery disease | 848 (6.0) | 2271 (8.1) | 0.08 | 831 (6.1) | 851 (6.2) | 0.01 |
| Dementia | 3962 (28.0) | 8384 (29.9) | 0.04 | 3872 (28.2) | 3719 (27.1) | 0.02 |
| Deyo-Charlson scorec | ||||||
| 0 | 2298 (16.2) | 4514 (16.1) | 0 | 2237 (16.3) | 2194 (16.0) | 0.01 |
| 1 | 1910 (13.5) | 4056 (14.5) | 0.03 | 1865 (13.6) | 1855 (13.5) | 0 |
| 2 | 1093 (7.7) | 2692 (9.6) | 0.07 | 1071 (7.8) | 1095 (8.0) | 0.01 |
| 3 or more | 1628 (11.5) | 4595 (16.4) | 0.14 | 1595 (11.6) | 1555 (11.3) | 0.01 |
| No admission within 5yrs prior | 7245 (51.1) | 12 199 (43.5) | 0.15 | 6963 (50.7) | 7032 (51.2) | 0.01 |
| John Hopkins CADG | ||||||
| Acute minor | 12 150 (85.7) | 24 675 (87.9) | 0.07 | 11 796 (85.9) | 11 857 (86.4) | 0.01 |
| Acute major | 12 768 (90.1) | 25 857 (92.2) | 0.07 | 12 384 (90.2) | 12 463 (90.8) | 0.02 |
| Likely to recur | 10 591 (74.7) | 21 509 (76.7) | 0.05 | 10 284 (74.9) | 10 235 (74.5) | 0.01 |
| Asthma | 897 (6.3) | 1991 (7.1) | 0.03 | 875 (6.4) | 854 (6.2) | 0.01 |
| Chronic medical unstable | 9766 (68.9) | 21 170 (75.5) | 0.15 | 9502 (69.2) | 9767 (71.1) | 0.04 |
| Chronic medical stable | 11 508 (81.2) | 23 484 (83.7) | 0.07 | 11 199 (81.6) | 11 185 (81.5) | 0 |
| Chronic specialty stable | 1542 (10.9) | 3249 (11.6) | 0.02 | 1510 (11.0) | 1595 (11.6) | 0.02 |
| Eye dental | 4113 (29.0) | 8641 (30.8) | 0.04 | 4002 (29.1) | 4073 (29.7) | 0.01 |
| Chronic specialty unstable | 3556 (25.1) | 7369 (26.3) | 0.03 | 3458 (25.2) | 3490 (25.4) | 0.01 |
| Psychosocial | 8079 (57.0) | 16 789 (59.8) | 0.06 | 7867 (57.3) | 7838 (57.1) | 0 |
| Prevention, administration | 7079 (49.9) | 14 645 (52.2) | 0.05 | 6874 (50.1) | 6918 (50.4) | 0.01 |
| Pregnancy | 48 (0.3) | 94 (0.3) | 0 | 45 (0.3) | 51 (0.4) | 0.01 |
| Fracture Characteristics | ||||||
| Fracture type | ||||||
| Femoral neck | 7039 (49.7) | 14 169 (50.5) | 0.02 | 6796 (49.5) | 6809 (49.6) | 0 |
| Intertrochanteric | 6275 (44.3) | 12 269 (43.7) | 0.01 | 6102 (44.4) | 6078 (44.3) | 0 |
| Subtrochanteric | 860 (6.1) | 1618 (5.8) | 0.01 | 833 (6.1) | 844 (6.1) | 0 |
| Fixation | ||||||
| Sliding hip screw or cannulated screws | 6754 (47.7) | 12 362 (44.1) | 0.07 | 6476 (47.2) | 6501 (47.3) | 0 |
| Arthroplasty | 5068 (35.8) | 11 180 (39.8) | 0.08 | 4958 (36.1) | 4950 (36.0) | 0 |
| Intramedullary nail | 2352 (16.6) | 4514 (16.1) | 0.01 | 2297 (16.7) | 2280 (16.6) | 0 |
| Surgery duration, mean (SD), min | 102.16 (45.41) | 107.68 (42.83) | 0.13 | 102.00 (41.19) | 102.73 (38.98) | 0.02 |
| Timing of surgery, No. (%) | ||||||
| Evening or weekend | 10 388 (73.3) | 19 426 (69.2) | 0.09 | 10 071 (73.3) | 9800 (71.4) | 0.04 |
| Working hours | 3668 (25.9) | 8307 (29.6) | 0.08 | 3547 (25.8) | 3788 (27.6) | 0.04 |
| Overnight | 118 (0.8) | 323 (1.2) | 0.03 | 113 (0.8) | 143 (1.0) | 0.02 |
| Hospital and Surgeon Characteristics | ||||||
| Hospital type | ||||||
| Academic | 3479 (24.5) | 8688 (31.0) | 0.14 | 3379 (24.6) | 3387 (24.7) | 0 |
| Large community (≥400 beds) | 4991 (35.2) | 10 949 (39.0) | 0.08 | 4963 (36.1) | 4945 (36.0) | 0 |
| Medium community (<400 beds) | 5603 (39.5) | 8138 (29.0) | 0.22 | 5389 (39.2) | 5399 (39.3) | 0 |
| Missing | 101 (0.7) | 281 (1.0) | 0.03 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Hospital hip fracture volume the prior year, mean (SD) | 243.9 (106.6) | 253.4 (115.0) | 0.09 | 252.8 (139.2) | 253.8 (138.1) | 0.01 |
| Hospital daily urgent surgery volume in the prior year, mean (SD) | 4.28 (2.47) | 4.64 (2.67) | 0.14 | 4.27 (2.44) | 4.33 (2.61) | 0.02 |
| Surgeon years in practice, mean (SD) | 12.6 (9.36) | 12.6 (9.76) | 0.01 | 12.6 (9.36) | 12.6 (9.72) | 0 |
| Surgeon hip fracture volume in the prior year, mean (SD), y | 40.20 (22.09) | 39.90 (22.21) | 0.01 | 40.32 (22.15) | 40.40 (22.44) | 0 |
| Other Characteristics | ||||||
| Transfer from any health care institution | 3608 (25.5) | 8824 (31.5) | 0.13 | 3529 (25.7) | 3515 (25.6) | 0 |
| Discharge disposition | ||||||
| Home | 3690 (26.0) | 5407 (19.3) | 0.16 | 3527 (25.7) | 3000 (21.8) | 0.09 |
| Long-term or complex continuing care | 3680 (26.0) | 7668 (27.3) | 0.03 | 3606 (26.3) | 3498 (25.5) | 0.02 |
| Palliative or deceased | 526 (3.7) | 1657 (5.9) | 0.1 | 515 (3.8) | 689 (5.0) | 0.06 |
| Rehabilitation | 5044 (35.6) | 9941 (35.4) | 0 | 4912 (35.8) | 5032 (36.6) | 0.02 |
| Other | 1234 (8.7) | 3383 (12.1) | 0.11 | 1171 (8.5) | 1512 (11.0) | 0.08 |
| Year | ||||||
| 2009 | 2590 (18.3) | 5258 (18.7) | 0.01 | 2555 (18.6) | 2398 (17.5) | 0.03 |
| 2010 | 2552 (18.0) | 5587 (19.9) | 0.05 | 2498 (18.2) | 2657 (19.4) | 0.03 |
| 2011 | 2703 (19.1) | 5592 (19.9) | 0.02 | 2535 (18.5) | 2608 (19.0) | 0.01 |
| 2012 | 2998 (21.2) | 5645 (20.1) | 0.03 | 2909 (21.2) | 2875 (20.9) | 0.01 |
| 2013 | 3331 (23.5) | 5974 (21.3) | 0.05 | 3234 (23.6) | 3193 (23.3) | 0.01 |
Abbreviation: CADG, collapsed aggregated diagnosis groups; ED, emergency department; NR, not reportable according to privacy guidelines.
Differences of 0.1 or more represent meaningful differences in covariates between groups.
The Injury Severity Score is a measure of the severity of traumatic injury and ranges from 0 (least severe) to 75 (most severe).
Deyo-Charlson score is a measure of patient comorbidity (prior to their hip fracture) and ranges from 0 (lowest mortality risk) to 3 or more (highest mortality risk). Patients may also be classified as having no prior hospital admissions.
Median neighborhood household income quintile was used as a proxy for socioeconomic status. Patients directly transferred from other health care institutions (long-term care, for example), each patient’s discharge disposition, and those residing in rural areas were identified. Each procedure’s type, duration, and timing (working hours, weekdays between 7 am and 5 pm; evening or weekend, 5 pm to 12 am on a weekday or 7 am to 12 pm over the weekend; or overnight, any day from 12 am to 7 am) were recorded.
Index surgeon- and hospital-related factors were assigned at time of each patient’s operation. These included (1) years since each surgeon’s Canadian orthopedic certification (surgeon experience) and (2) the number of hip fracture procedures performed in the year preceding the index event (surgeon and hospital volume). Each hospital’s capacity for performing nonelective surgery was operationalized as the mean daily number of any nonelective (or urgent) procedures performed at the hospital, orthopedic or otherwise, in the year preceding the index event. Hospitals were also categorized as either academic or community based on their membership in the Council of Academic Hospitals of Ontario (http://www.cahohospitals.com). Community hospitals were further classified as large (≥400 beds) or small to medium (<400 beds).
Outcomes
The primary outcome was mortality within 30 days of being admitted for hip fracture surgery. A 30-day observation window is the most common follow-up period measured in literature and considers the temporal association between surgical delay and the development of complications. Longer follow-up at 90 and 365 days was considered in secondary analyses.
Medical complications within 30, 90, and 365 days, as well as a composite of mortality or any medical complication, were assessed as secondary outcomes. Medical complications considered were myocardial infarction, deep vein thrombosis, pulmonary embolism, and pneumonia. Surgical complications (hardware removal and postoperative hip dislocation) presumed to be unrelated to wait times were assessed as negative tracer outcomes intended to test the specificity of the findings (see the Sensitivity Analyses section).
Statistical Analysis
Risk-adjusted, restricted cubic splines with 4 knots were used to model the probability of complications according to the time elapsed from emergency department arrival to surgery. Any nonlinear relationship between surgical delay and each outcome could be assessed using spline regression, which makes no underlying assumptions about a functional form. Rather than arbitrarily dividing patients into early and delayed surgery groups, the association between surgical delay and mortality was graphically represented to visualize an inflection point (in hours), if one existed, when complications began to rise. At time thresholds around the area of inflection, the area under the receiver operating characteristic curve was calculated for adjusted logistic regression models relating surgical delay to 30-day mortality. The time (in hours) producing the maximum area under the curve increase was selected as the threshold to dichotomize time and classify patients as receiving either early or delayed surgery. To further evaluate the robustness of this definition, early and delayed patients were matched 1:1 without replacement on the logit of propensity scores.
Restricted cubic spline, logistic regression, and propensity score models were all adjusted for the same covariates: age, sex, year, income quintile, rurality, transfer from any health care institution, medical comorbidity, fracture and surgery type, Injury Severity Score, surgeon volume and experience, hospital volume and type, and surgery duration. Variables thought to be confounders based on existing literature and clinical judgment were included. Mediators of delay unrelated to mortality (such as surgery timing) and common effects of the relationship between delay and mortality (such as discharge disposition) were not included as variables in the models. Missing data, which was less than 1% for all variables considered, were excluded from regression models.
Baseline cohort characteristics were reported as means (SDs) and proportions as appropriate and compared using standardized mean differences to avoid identifying spurious statistical associations in the large administrative data set. Standardized differences of more than 0.1 were considered indicative of imbalance. The McNemar test compared outcomes in early and delayed groups after matching and generalized estimating equations (GEEs) calculated percent absolute risk differences (% absolute risk difference [RD], with 95% CIs).
Sensitivity Analyses
Several prespecified sensitivity analyses were conducted. Splines were generated in patient subgroups stratified by sex, medical comorbidity, hospital type, and timing of presentation to determine whether the identified time threshold was consistent across patient subgroups. Prespecified falsification hypotheses tested specificity of the findings. Because medication data were only available for patients older than 65 years in the Ontario databases, a sensitivity analysis restricted to these patients adjusted for blood thinner prescriptions within the year before surgery.
Two post hoc sensitivity analyses were also conducted. Prolonged wait times may indicate medical, rather than administrative, reasons for delay and even greater confounding. Therefore, an analysis restricted to patients’ receiving surgery within 36 hours was conducted to assess the association between wait times and complications in a subgroup with less potential for unmeasured confounding. As an indicator of residual confounding in the delayed group, the relationship between matching status (matched or unmatched) and mortality in delayed group patients was also explored.
All analyses were performed at ICES using SAS statistical software version 9.3 and Enterprise Guide version 6.1 (SAS Institute Inc) and a 2-sided type I error probability of .05.
Results
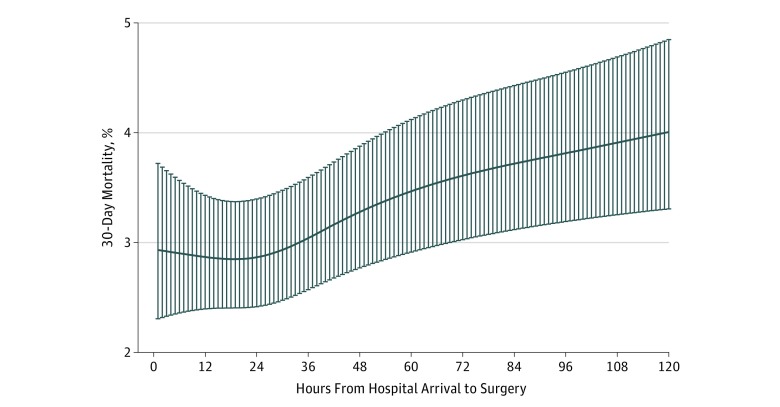
There were a total of 42 230 patients who met inclusion (Table 1) and were treated by 522 orthopedic surgeons at 72 Ontario hospitals. Their mean (SD) age was 80.1 (10.7) years, and 70.5% were women (Table 2). The mean (SD) time to surgery was 38.8 (28.8) hours. Adjusted splines modeled an area of inflection around 24 hours when the risk of developing complications began to increase, irrespective of the outcome or follow-up period assessed (Figure 1 and Figure 2). Surgical complications (dislocation, hardware removal) were not related to wait time (Figure 2). The maximum area under the curve increase occurred when using 24 hours to classify patients into early or delayed surgery groups compared with 6-, 12-, 18-, 30- and 36-hour thresholds (eAppendix D in the Supplement). Delayed hip fracture surgery was therefore defined as surgery occurring more than 24 hours after emergency department arrival.
Figure 1. Probability of the Primary Outcome According to Wait Times for Surgery as a Continuous Variable.
Probabilities (95% CIs) models used restricted cubic splines adjusting for age, sex, year, income quintile, rurality, transfer from any health care institution, Deyo-Charlson score, history of frailty, diabetes, heart failure, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, myocardial infarction, or hypertension, fracture and surgery type, Injury Severity Score, surgeon volume and experience, hospital volume and type, and surgery duration. Analysis conducted among 41 186 of 42 230 patients. C statistic was 0.756. Variance inflation factors were 4 or less for included variable included, indicating an absence of collinearity. Probabilities of the primary outcome according to wait times for surgery are presented for patients with average fracture, physician, and hospital system characteristics in the cohort.
Figure 2. Probability of the Primary, Secondary, and Negative Tracer Outcomes (Involving Hardware Removal and Hip Dislocation).
Probabilities (95% CIs) models used restricted cubic splines. Variables in the adusted models are listed in the “Outcomes” section of the Methods and in Figure 1. Analysis conducted among 41 186 of 42 230 patients. Probabilities of each outcome according to wait times for surgery are presented for the patient with average fracture, physician, and hospital system characteristics in the cohort.
According to this definition, 14 174 patients (33.6%) received early surgery and 28 056 patients (66.4%) received delayed surgery. Before matching, patients receiving delayed surgery were significantly more likely to be men, have medical comorbidity, arrive from other health care institutions, and be treated at academic or higher-volume centers (Table 2). There were 13 731 ( ≅ 97%) patients in the early surgery group matched to those in the delayed group, and covariates were balanced between groups after matching (including those variables with missing categories).
Of the 13 731 matched patients who received hip fracture surgery after 24 hours, 898 patients (6.5%) died within 30 days vs 790 patients (5.8%) of 13 731 who received surgery within 24 hours, for an absolute risk difference of 0.79% (95% CI, 0.23%-1.35%); 166 (1.2%) vs 96 (0.7%) had pulmonary embolism, for an absolute risk difference of 0.51% (95% CI, 0.28%-0.74%); 160 (1.2%) vs 107 (0.8%) had myocardial infarction, for an absolute risk difference of 0.39% (95% CI, 0.15%-0.62%); and 637 (4.6%) vs 506 (3.7%) had pneumonia, for an absolute risk difference of 0.95% (95% CI, 0.48%-1.43%). For the composite outcome, 1680 patients (12.2%) vs 1383 (10.1%) died within 30 days for an absolute risk difference of 2.16% (95% CI, 1.43%-2.89%). Outcomes remained significant at 90 and 365 days (Table 3).
Table 3. Primary and Secondary Outcomes After Matchinga.
| Outcome | No. (%) of Patients | Absolute Risk Difference, % (95% CI) | P Valueb | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ≤24 Hours (n = 13 731) |
>24 Hours (n = 13 731) |
|||
| Primary Outcome | ||||
| 30-d Mortality | 790 (5.8) | 898 (6.5) | 0.79 (0.23 to 1.35) | .006 |
| Secondary Outcomes | ||||
| Mortality, d | ||||
| 90 | 1463 (10.7) | 1649 (12.0) | 1.35 (0.61 to 2.10) | <.001 |
| 365 | 2654 (19.3) | 2971 (21.6) | 2.31 (1.47 to 3.25) | <.001 |
| Pulmonary embolism, d | ||||
| 30 | 96 (0.7) | 166 (1.2) | 0.51 (0.28 to 0.74) | <.001 |
| 90 | 118 (0.9) | 191 (1.4) | 0.53 (0.28 to 0.78) | <.001 |
| 365 | 152 (1.1) | 228 (1.7) | 0.55 (0.28 to 0.83) | <.001 |
| Deep venous thrombosis, d | ||||
| 30 | 111 (0.8) | 136 (1.0) | 0.18 (−0.04 to 0.40) | .11 |
| 90 | 169 (1.2) | 190 (1.4) | 0.15 (−0.11 to 0.42) | .26 |
| 365 | 255 (1.9) | 259 (1.9) | 0.03 (−0.29 to 0.35) | .86 |
| Pneumonia, d | ||||
| 30 | 506 (3.7) | 637 (4.6) | 0.95 (0.48 to 1.43) | <.001 |
| 90 | 671 (4.9) | 800 (5.8) | 0.94 (0.41 to 1.47) | <.001 |
| 365 | 1101 (8.0) | 1245 (9.1) | 1.05 (0.39 to 1.71) | .002 |
| Myocardial infarction, d | ||||
| 30 | 107 (0.8) | 160 (1.2) | 0.39 (0.15 to 0.62) | .001 |
| 90 | 126 (0.9) | 181 (1.3) | 0.40 (0.15 to 0.65) | .002 |
| 365 | 184 (1.3) | 231 (1.7) | 0.34 (0.06 to 0.63) | .02 |
| Composite outcome, dc | ||||
| 30 | 1383 (10.1) | 1680 (12.2) | 2.16 (1.43 to 2.89) | <.001 |
| 90 | 2153 (15.7) | 2492 (18.1) | 2.47 (1.59 to 3.34) | <.001 |
| 365 | 3568 (26.0) | 4009 (29.2) | 3.21 (2.17 to 4.25) | <.001 |
| Negative tracer outcomes, dd | ||||
| Hardware removal | ||||
| 30 | 54 (0.4) | 47 (0.3) | −0.05 (−0.19 to 0.09) | .49 |
| 90 | 156 (1.1) | 140 (1.0) | −0.12 (−0.36 to 0.13) | .35 |
| 365 | 384 (2.8) | 347 (2.5) | −0.27 (−0.65 to 0.11) | .16 |
| Postoperative hip dislocation | ||||
| 30 | 24 (0.2) | 28 (0.2) | 0.05 (−0.07 to 0.13) | .58 |
| 90 | 43 (0.3) | 43 (0.3) | 0 (−0.13 to 0.13) | >.99 |
| 365 | 59 (0.4) | 54 (0.4) | −0.04 (−0.19 to 0.12) | .64 |
Greedy matching occurred 1:1 on the logit of a propensity score with a caliper of 0.2 × SD; 96.9% of eligible patients who found matches.
P values were calculated using the McNemar test.
Mortality and other medical complications.
Surgical complications presumed to be unrelated to wait times were assessed as negative tracer outcomes intended to test the specificity of the findings.
Mortality due to deep venous thrombosis was not significantly different between groups at 30 days with 136 patients (1.0%) who did not undergo surgery for more than 24 hours vs 111 patients (0.8%) who received it within 24 hours for an absolute risk difference of 0.18% (95% CI, −0.04% to 0.40%). The same held true at 90 days with 190 patients (1.4%) vs 169 patients (1.2%) for an absolute risk difference of 0.15% (95% CI, −0.11% to 0.42%) and at 365 days 259 (1.9%) vs 255 (1.9%) for an absolute risk difference of 0.03% (95% CI, −0.29% to 0.35%).
The relationships between wait times and complications were robust to stratification among different patient subgroups, including among patients without comorbidity and those receiving surgery within 36 hours, for whom confounding by indication should not play a role (eAppendices C and G in the Supplement). There was no significant difference in surgical complications (negative tracer outcomes) between groups (Table 3). Sensitivity analysis restricted to patients older than 65 years and adjusting for antiplatelet or anticoagulant medications also produced equivalent results (eAppendix E in the Supplement). Although unmatched patients in the delayed group were more medically complex than matched patients, adjusted regression found no significant association between matching status and 30-day mortality indicating no residual confounding in the matched delayed group (eAppendix F in the Supplement).
Discussion
Among adults undergoing hip fracture surgery in Ontario, Canada, increased wait time was associated with a greater risk of 30-day mortality and other complications. Although several studies have linked wait times for hip fracture surgery to mortality and morbidity, inconsistent evidence for a time-to-surgery threshold has translated to variable guideline recommendations and compliance with wait time benchmarks.
This is the first study, to our knowledge, to analyze time as a continuous variable in hours and empirically identify a time-to-surgery threshold associated with increased complications after hip fracture. The primary finding pertains to increasing numbers of patients experiencing hip fractures and the different medical and surgical specialists treating them: a wait time of 24 hours may represent a threshold defining higher risk because complications increased when surgery was delayed after this time, irrespective of the complication, follow-up period, or patient subgroup assessed. Preoperative optimization is often required for patients with a hip fracture and can feasibly be performed within the proposed timeframe. Because wait times for hip fracture surgery are already used worldwide as quality indicators to assess hospital performance, the results of this study may inform existing hip fracture care guidelines and policies.
Targeting surgery within 24 hours represents a significant change in practice because 66% of the patients in this study did not receive surgery within this timeframe. Hip fracture prioritization must also be balanced with the needs of patients on waiting lists for other surgical procedures. Because time to surgery rather than timing of surgery is associated with increased risk, continuing to conduct hip fracture operations during evenings and weekends may help reduce wait times for hip fracture surgery without conflicting with elective operations. However, other performance improvement efforts will be required, as well as future work that identifies where these efforts would be most successfully targeted. Although effect modification was not observed in subgroup analyses, given the practical challenges of further reducing existing thresholds, future work may continue trying to identify a subset most in need of urgent surgery.
This study has several strengths. First, a population-based sample from Ontario’s diverse population of approximately 13.5 million was used. Findings are generalizable to other jurisdictions, including the United States and Europe, where operating room resources are limited and patients are required to wait for hip fracture surgery. Second and third, the study was conducted in a public health care system where patients can be followed up for complications even if they present elsewhere in the system and surgical delays are mostly related to administrative rather than patient factors.
Fourth, rather than arbitrarily dividing patients into early and delayed surgery groups, exact time-to-surgery data (in hours) and spline regression were used to empirically define a threshold for increased risk. Observational research is required to determine a time-to-surgery threshold because investigators likely consider it unethical and impractical to allocate patients to increasing thresholds of delayed surgery in this way. The Hip Fracture Accelerated Surgical Treatment and Care Track (HIP ATTACK) trial will compare standard of care treatment to surgery performed much earlier than this (ie, within 6 hours of hospital arrival) and may provide important estimates of the effect of early surgery in the absence of confounding by indication. However, the study will not assess whether delays greater than 6 hours but less than the standard of care are acceptable.
Limitations
This study also has several limitations. First, since medically complex patients are predisposed to both complications and awaiting optimization prior to surgery, several analyses were performed to mitigate the influence of confounding. Comparisons between early and delayed surgery groups after matching were balanced across more than 30 covariates, which included detailed measures of preexisting medical comorbidity. The absence of effect modification in several important clinical scenarios was also demonstrated in subgroup analyses, including those restricted to patients without comorbidity and those receiving surgery within 36 hours for whom surgical delays should be administrative. However, the finding that increased wait time is associated with increased risk may still be influenced by unmeasured factors.
Second, other complications were not considered that may be clinically important in this population and potentially related to waiting for surgery, such as major bleeding. Outcomes were chosen based on their being (1) important clinical priorities, (2) plausibly related to the primary exposure, and (3) identifiable by validated codes (see eAppendix B in the Supplement). Future study is required to assess whether misclassification of fat embolism as pulmonary embolism, the more salient diagnosis, may explain the significant difference observed in pulmonary embolism between groups, whereas a difference in deep vein thrombosis was not detected. Although patient reported outcomes were not assessed, it may be assumed that expedited hip fracture surgery is patient centered and would be appreciated by patients and their families, other processes of care being equal. Third, patients with nonoperative hip fracture were also not considered because those who died waiting for surgery could not be distinguished from those for whom nonoperative treatment was indicated. However, experiencing a major complication while waiting for surgery precluded the former patients from entering the cohort, leading to more conservative estimates of the effect of waiting for surgery.
Conclusions
Among adults undergoing hip fracture surgery, increased wait time was associated with a greater risk of 30-day mortality and other complications. A wait time of 24 hours may represent a threshold defining higher risk. Because two-thirds of patients did not receive surgery within this timeframe, performance improvement is warranted.
eAppendix A. Data sources
eAppendix B. Database codes
eAppendix C. Empirically derived surgical delay threshold – spline regression
eAppendix D. Results of quality assessment per study
eAppendix E. Diagnostic performance of serological tests – test combinations
eReferences F. Adjusting for antiplatelet and/or anticoagulant prescriptions
eAppendix G. Subgroup analysis of those undergoing surgery within 36 hours
References
- 1.Leslie WD, O’Donnell S, Lagacé C, et al. ; Osteoporosis Surveillance Expert Working Group . Population-based Canadian hip fracture rates with international comparisons. Osteoporos Int. 2010;21(8):1317-1322. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Pincus D, Desai SJ, Wasserstein D, et al. . Outcomes of after-hours hip fracture surgery. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2017;99(11):914-922. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Buse GL, Bhandari M, Sancheti P, et al. ; Hip Fracture Accelerated Surgical Treatment and Care Track (HIP ATTACK) Investigators . Accelerated care versus standard care among patients with hip fracture: the HIP ATTACK pilot trial. CMAJ. 2014;186(1):E52-E60. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Dy CJ, McCollister KE, Lubarsky DA, Lane JM. An economic evaluation of a systems-based strategy to expedite surgical treatment of hip fractures. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2011;93(14):1326-1334. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Simunovic N, Devereaux PJ, Sprague S, et al. . Effect of early surgery after hip fracture on mortality and complications: systematic review and meta-analysis. CMAJ. 2010;182(15):1609-1616. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.ACS TQIP Best Practices in Management of Orthopaedic Trauma 2015; https://www.facs.org/quality-programs/trauma/tqip/best-practice. Accessed July 11, 2016.
- 7.Canadian Institute for Health Information Wait times for priority procedures in Canada, 2017. Ottawa, ON: CIHI; 2017. http://www.boneandjointcanada.com.
- 8.Royal College of Physicians National Hip Fracture Database Annual Report 2015. London, England: Royal College of Physicians; 2015. [Google Scholar]
- 9.Salas M, Hofman A, Stricker BH. Confounding by indication: an example of variation in the use of epidemiologic terminology. Am J Epidemiol. 1999;149(11):981-983. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Ryan DJ, Yoshihara H, Yoneoka D, Egol KA, Zuckerman JD. Delay in hip fracture surgery: an analysis of patient-specific and hospital-specific risk factors. J Orthop Trauma. 2015;29(8):343-348. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Fu MC, Boddapati V, Gausden EB, Samuel AM, Russell LA, Lane JM. Surgery for a fracture of the hip within 24 hours of admission is independently associated with reduced short-term post-operative complications. Bone Joint J. 2017;99-B(9):1216-1222. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Bretherton CP, Parker MJ. Early surgery for patients with a fracture of the hip decreases 30-day mortality. Bone Joint J. 2015;97-B(1):104-108. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Nyholm AM, Gromov K, Palm H, Brix M, Kallemose T, Troelsen A; Danish Fracture Database Collaborators . Time to surgery is associated with thirty-day and ninety-day mortality after proximal femoral fracture: a retrospective observational study on prospectively collected data from the Danish Fracture Database Collaborators. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2015;97(16):1333-1339. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Sayers A, Whitehouse MR, Berstock JR, Harding KA, Kelly MB, Chesser TJ. The association between the day of the week of milestones in the care pathway of patients with hip fracture and 30-day mortality: findings from a prospective national registry—the National Hip Fracture Database of England and Wales. BMC Med. 2017;15(1):62. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Dawson NV, Weiss R. Dichotomizing continuous variables in statistical analysis: a practice to avoid. Med Decis Making. 2012;32(2):225-226. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Frood J, Johnson T. Improving measures of hip fracture wait times: a focus on Ontario. Healthc Q. 2010;13(4):16-18. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Sheehan KJ, Sobolev B, Guy P, et al. ; Canadian Collaborative Study on Hip Fractures . Constructing an episode of care from acute hospitalization records for studying effects of timing of hip fracture surgery. J Orthop Res. 2016;34(2):197-204. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Schilling PL, Bozic KJ. Development and validation of perioperative risk-adjustment models for hip fracture repair, total hip arthroplasty, and total knee arthroplasty. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2016;98(1):e2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Deyo RA, Cherkin DC, Ciol MA. Adapting a clinical comorbidity index for use with ICD-9-CM administrative databases. J Clin Epidemiol. 1992;45(6):613-619. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Weiner JP, Abrams C The Johns Hopkins ACG System: technical reference guide version 10.0. 2011. https://www.healthpartners.com/ucm/groups/public/@hp/@public/documents/documents/cntrb_035024.pdf. Accessed November 2, 2017.
- 21.Agabiti N, Picciotto S, Cesaroni G, et al. ; Italian Study Group on Inequalities in Health Care . The influence of socioeconomic status on utilization and outcomes of elective total hip replacement: a multicity population-based longitudinal study. Int J Qual Health Care. 2007;19(1):37-44. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Kralj B. Measuring “Rurality” for Purposes of Health Care Planning: An Empirical Measure for Ontario. Toronto, ON: Ontario Medical Association; 2005. [Google Scholar]
- 23.Sheehan KJ, Sobolev B, Guy P, et al. ; Canadian Collaborative Study of Hip Fractures . In-hospital mortality after hip fracture by treatment setting. CMAJ. 2016;188(17-18):1219-1225. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Moja L, Piatti A, Pecoraro V, et al. . Timing matters in hip fracture surgery: patients operated within 48 hours have better outcomes: a meta-analysis and meta-regression of over 190,000 patients. PLoS One. 2012;7(10):e46175. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Prasad V, Jena AB. Prespecified falsification end points: can they validate true observational associations? JAMA. 2013;309(3):241-242. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Marrie RA, Dawson NV, Garland A. Quantile regression and restricted cubic splines are useful for exploring relationships between continuous variables. J Clin Epidemiol. 2009;62(5):511-7.e1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Ravi B, Jenkinson R, Austin PC, et al. . Relation between surgeon volume and risk of complications after total hip arthroplasty: propensity score matched cohort study. BMJ. 2014;348:g3284. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Austin PC. Comparing paired vs non-paired statistical methods of analyses when making inferences about absolute risk reductions in propensity-score matched samples. Stat Med. 2011;30(11):1292-1301. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Austin PC. Optimal caliper widths for propensity-score matching when estimating differences in means and differences in proportions in observational studies. Pharm Stat. 2011;10(2):150-161. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Brookhart MA, Schneeweiss S, Rothman KJ, Glynn RJ, Avorn J, Stürmer T. Variable selection for propensity score models. Am J Epidemiol. 2006;163(12):1149-1156. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Austin PC. Balance diagnostics for comparing the distribution of baseline covariates between treatment groups in propensity-score matched samples. Stat Med. 2009;28(25):3083-3107. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Pincus D, Gomes T, Hellings C, et al. . A population-based assessment of the drug interaction between levothyroxine and warfarin. Clin Pharmacol Ther. 2012;92(6):766-770. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.McIsaac DI, Abdulla K, Yang H, et al. . Association of delay of urgent or emergency surgery with mortality and use of health care resources: a propensity score-matched observational cohort study. CMAJ. 2017;189(27):E905-E912. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Uzoigwe CE, Burnand HGF, Cheesman CL, Aghedo DO, Faizi M, Middleton RG. Early and ultra-early surgery in hip fracture patients improves survival. Injury. 2013;44(6):726-729. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Sheehan KJ, Sobolev B, Chudyk A, Stephens T, Guy P. Patient and system factors of mortality after hip fracture: a scoping review. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2016;17(1):166. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Juurlink D, Preyra C, Croxford R, et al. . Canadian Institute for Health Information Discharge Abstract Database: A Validation Study. Toronto, ON: Institute for Clinical Evaluative Sciences; 2006. [Google Scholar]
- 37.Aggarwal A, Harris IA, Naylor JM. Patient preferences for emergency or planned hip fracture surgery: a cross-sectional study. J Orthop Surg Res. 2016;11(1):120. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
eAppendix A. Data sources
eAppendix B. Database codes
eAppendix C. Empirically derived surgical delay threshold – spline regression
eAppendix D. Results of quality assessment per study
eAppendix E. Diagnostic performance of serological tests – test combinations
eReferences F. Adjusting for antiplatelet and/or anticoagulant prescriptions
eAppendix G. Subgroup analysis of those undergoing surgery within 36 hours