Abstract
Background:
Atherosclerosis-induced vascular disorders are major causes of death in most western countries. During the development of atherosclerotic lesions, foam cell formation is essential and formed through the expression of CD36 and the peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma (PPAR-γ).
Objective:
To investigate whether dansameum extract (DSE) could show anti-atherosclerotic effect through down-regulating cellular redox state including CD36 and PARP-γ expression in oxidative low-density lipoprotein (oxLDL)-treated RAW264.7 cells and on differentiated foam cells in ApoE Knockout (ApoE-/-) mice.
Materials and Methods:
The Korean polyherbal medicine DSE was prepared from three plants in the following proportions: 40 g of Salvia miltiorrhiza root, 4 g of Amomumxanthioides fruit, and 4 g of Santalum album lignum. The immunohistochemistry and reverse transcription-polymerase chain reaction was used for analysis of protein and mRNA involved in foam cell formation.
Results:
We first showed that effects of DSE on foam cell formation in both oxLDL-induced RAW264.7 cells and in blood vessels from apolipoprotein E deficientApoE-/- mice with high fat diet-fed. DSE treatment significantly reduced the expression of CD36 and PPAR-γ in oxLDL-stimulated RAW264.7 cells and ApoE-/-mice, in the latter case by regulating heme oxygenase-1. Furthermore, DSE treatment also reduced cellular lipid content in vitro and in vivo experiments.
Conclusion:
Our data suggest that DSE may have anti-atherosclerotic properties through regulating foam cell formation.
SUMMARY
Dansameum extract (DSE) Regulates the expression of CD36 and peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma in oxidative low-density lipoprotein-stimulated RAW264.7 Cells and ApoE Knockout (ApoE Knockout [ApoE-/-]) mice
DSE Regulates Cholesterol Levels in the Serum of ApoE-deficient (ApoE-/-) mice
DSE Reduced the Formation of Foam Cells by Regulating heme oxygenase-1 in ApoE-/- mice with high fat diet-fed.
Abbreviations used: DSE: Dansameum extract, PPAR-γ: Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor γ, HO-1: Heme oxygenase-1, CVD: Cardiovascular diseases
Keywords: CD36, Dansameum, foam cell, heme oxygenase-1, peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma
INTRODUCTION
Atherosclerosis, a leading cause of vascular diseases such as stroke and myocardial infarction, can be fatal.[1,2,3] It is associated with the accumulation of plaques resulting from changes in lipid metabolism of the blood vessels wall.[4,5] Therefore, controlling lipid metabolism is a therapeutic goal for early-stage atherosclerosis.[5,6]
The initial development of atherosclerosis occurs following injury and damage to the endothelial cells of blood vessels. It also accompanies metabolic syndrome and hyperlipidemia.[7] CD36, which mediates the transformation of macrophages into foam cells is activated by oxidized low-density lipoprotein (oxLDL).[8] The signal cascade downstream of CD36 is mediated by the activation of peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma (PPAR-γ) which is involved in energy balance and the regulation of adipocyte differentiation.[9] In addition, the activation of extracellular signal-regulated kinase, nuclear factor erythroid 2-related factor 2 (Nrf2), and heme oxygenase (HO)-1 pathways play an important role in regulating CD36-mediated lipid uptake.[10,11,12] Therefore, differentiation of foam cells by controlling these transcription factors may be a major goal for inhibiting the development of early atherosclerosis.
Although numerous research and preclinical studies on the treatment of vascular disease have been conducted, no clinical trials have been performed. Thus, complementary medicine represents an alternative therapeutic approach to traditional medicine based on clinical experience. Dansameum extract (DSE) has been prescribed for hearing problems and to promote blood flow.[13] The composition of DSE has been reported in many studies. DSE has been demonstrated to promote various biological effects, such as anti-inflammation, antioxidant, antithrombotic, and fibrinolysis effects. Tanshinone I, tanshinone IIA, cryptotanshinone, dihydrotanshinone, and salvianolic acid B have been reported as the active compounds of DSE.[14,15,16,17,18,19,20,21,22]
However, the ability of DSE to maintain redox homeostasis in oxLDL-induced converted foam cells has not been established. The molecular mechanism of atherosclerosis in apolipoprotein E-deficient (ApoE-/-) mouse aorta involves with CD36-and PPAR-γ-mediated differentiation of macrophages.[23,24] Therefore, we investigated whether DSE could exert anti-atherosclerotic effect through down-regulating cellular redox state, including CD36 and PARP-γ expression in oxLDL-treated RAW264.7 cells and on foam cells in ApoE-/-mice.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Materials and reagents
Fetal bovine serum (FBS) and Dulbecco's modified Eagle's medium containing high glucose concentrations (DMEM) were purchased from Gibco-BRL (Grand Island, NY, USA). Cell culture plasticware was purchased from SPL Life Sciences (Gyeonggi-Do, Korea). Total RNA isolation kits (RNAgents) were purchased from Promega (Madison, WI, USA).
Superscript II reverse transcription, Cholesterol E kit BC108-E, and Vectastain ABC kits were purchased from Invitrogen (Carlsbad, CA, USA), YD Diagnostics (Yongin, Kyunggi-do, Korea), and Vector Labs (Burlingame, CA, USA), respectively. The following antibodies were used: Murine anti-mouse CD36 (Santa Cruz Biotechnology, Inc., Santa Cruz, CA, USA), murine anti-mouse PPAR-γ (Santa Cruz Biotechnology), and murine anti-heme oxygenase-1 (HO-1) (Santa Cruz Biotechnology). Tanshinone IIA and salvianolic acid were obtained from ChemFaces (Wuhan, China), and rosmarinic acid from Sigma-Aldrich (St. Louis, MO, USA). Other chemical reagents were obtained from Sigma-Aldrich.
Plant material and dansameum extract extraction
The Korean polyherbal medicine DSE was prepared from three plants in the following proportions: 40 g of Salvia miltiorrhiza root, 4 g of Amomumxanthioides fruit, and 4 g of Santalum album lignum. These components were purchased from Dongguk University Gyeongju Hospital (Gyeongju, Korea) and authenticated by Professors Kibong Kim and Sun-Young Park. DSE (48 g) was blended, and the crude powder was processed in 500 mL of sterile deionized water at 100°C for 3 h. The aqueous extract was concentrated to 50 mL at 60°C under vacuum in a rotary evaporator, and lyophilized by freeze-drying at −60°C (yield, 9.1%).
High-performance liquid chromatography-based Analysis
High-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC)-based fingerprinting was performed using an Agilent 1200 series system (Agilent Technologies, Santa Clara, CA, USA) with a binary solvent delivery pump, a vacuum degasser, a diode-array detector, and Agilent Chem Station software. Separation was performed using a Phenomenex Geminin NX-C18 column (3.5 μm × 4.6 mm × 250 mm). The mobile phase consisted of 0.1% (v/v) acetonitrile and 0.5% (v/v) formic acid in water, and a flow rate of 0.8 mL/min was used. A standard solution containing tanshinone IIA, salvianolic acid, and rosmarinic acid was prepared by dissolving these compounds in distilled water (10 mg/100 mL) and filtering through a 0.45 μm membrane filter, after which HPLC was performed.
Cell culture
Murine RAW264.7 cells were purchased from the Korean Cell Line Bank (Seoul, Korea) and cultured in DMEM containing 10% FBS and 1% penicillin-streptomycin at 37°C in a 5% CO2 atmosphere. For all experiments, subculture was performed until the cells were 70%–80% confluent.
Immunocytochemistry
Protein expression of CD36 and PPAR-γ was analyzed by immunocytochemistry. Briefly, the cells were fixed on a slide with 4% paraformaldehyde for 10 min at room temperature, and then the slide was placed in 0.25% Triton-X100 in phosphate-buffered saline (PBS) for 10 min. The slide was then blocked using PBS containing 5% BSA for 1 h, followed by overnight incubation with primary antibody at 4°C. It was then washed twice with PBS. A Vectastain ABC kit was used to induce avidin–biotin complex formation in accordance with the manufacturer's instructions. Immunostaining was performed using 0.05% DAB, and the slides were counterstained with hematoxylin. The intensity of expressed proteins was analyzed using Image J software (NIH, Bethesda, MD, USA). Immunostained cells were counted in 20 randomly selected fields at a magnification of ×400 under a microscope (Nikon Eclipse Ti, Nikon Instruments, Inc., Tokyo, Japan), and the percentage of positive cells was calculated as the number of positive cells/total number of cells ×100%.
Reverse transcription-polymerase chain reaction
Total RNA was isolated from the RAW264.7 cells using a total RNA isolation kit. First-strand cDNA was synthesized from 0.5 μg of total RNA using the Superscript II reverse transcription system following the manufacturer's instructions. Polymerase chain reactions (PCRs) were performed using primers for mouse CD36 (sense, 5’-GAG CCC ACA GTT CCG ATC A-3’; antisense, 5’-CTG GGA GTT GGC GAG AAA AC-3’), PPAR-γ primer (sense, 5’-CGA AGA TGC CAT TCT GGC-3’; antisense, 5’-GTC TTT CCT GTC AAG ATC G-3’), and β-actin (sense, 5’-GGA GAA GAT CTG GCA CCA CACC-3’; antisense, 5’-CCT GCT TGC TGA TCC ACA TCT GCT GG-3’). PCRs consisted of 30 cycles of denaturation at 95°C for 10 s, annealing at 50°C for 30 s, and elongation at 72°C for 1 min. PCR products were separated on 1% agarose gels, and the band intensities of amplified cDNAs were compared after visualization under UV light.
Lipid uptake assay
To evaluate lipid uptake in oxLDL-stimulated RAW264.7 cells, we first performed Oil Red O staining in vitro. Briefly, RAW264.7 cells (2 × 103 cells/well) were seeded in an 8-chamber slide and incubated in DMEM containing 10% FBS. After the cells had reached 70% confluence, they were pretreated with oxLDL for 2 h and then treated with DSE (0.5–2.0 mg/mL) for 12 h, while control cells were not exposed to DSE. Following this, the cells were washed with PBS and fixed with 2% paraformaldehyde for 10 min. After washing with PBS, the cells were stained with filtered Oil Red O solution (60% Oil Red O dye and 40% water) (Sigma-Aldrich) at room temperature for 15 min. Next, for Oil Red O staining of aortic tissue, frozen sections (5 μm thick) were fixed with 10% formaldehyde. Serial cryosections of tissue adjacent were treated with propylene glycol for 2 min, Oil Red O solution for 6 min, 85% propylene glycol for 1 min, and hematoxylin for 1 min. The intensity of Oil Red O staining was analyzed using Image J software.
Animal experiment
Six-week-old male ApoE-/-mice (18-20 g) on a C57Bl/6 background were purchased from the Jackson Laboratory (Bar Harbor, ME, USA). All procedures involving animals were approved by the Institutional Animal Care and Use Committee of Dongguk University (IACUC number: 2014-010) and conducted according to the NIH Guide for the Care and Use of Laboratory Animals. Mice were individually housed in stainless steel cages with ad libitum access to water and food. To test the vascular protective effect of DSE, the animals were randomly divided into three different groups (n = 10/group): A control (CON) group fed a regular chow (AIN 93G), a diet-induced obesity (AE) group fed a high-fat diet (60% fat; 20% carbohydrates; 20% protein), and a DSE-treated (DT) group fed a high fat diet and orally administered daily with 240 mg/kg/day DSE in normal saline for 12 weeks.
Cholesterol assay
Total serum cholesterol was measured using a Cholesterol E kit according to the manufacturer's instructions.
Immunohistochemistry
All mice were deeply anesthetized by intraperitoneal injection of sodium pentobarbital (25 μg/10 g of body weight). Mice were perfused and fixed with 10% formalin for 4 min. Tissue samples were prepared using routine procedures for cryosection. Sections (5 μm thick) were placed in 0.3% hydrogen peroxide for 3 min to block endogenous peroxidase activity, and then blocked with 5% goat serum for 1 h. Sections were then incubated for 72 h at 4°C in 3% goat serum containing murine anti-mouse CD36 (1:100), murine anti-mouse PPAR-γ (1:100), or murine anti-HO-1 (1:100), followed by three washes with PBS. A Vectastain ABC kit was used to induce avidin–biotin complex formation in accordance with the manufacturer's instructions. Immunostaining analysis was performed using a substrate solution of 0.05% DAB, and the slides were counterstained with hematoxylin. Sections were examined using a light microscope (Olympus BX50; Olympus Co. Ltd., Tokyo, Japan) at ×200 magnification.
Data analysis
Data are expressed as the mean ± standard error of at least three independent experiments and were analyzed using GraphPad Prism (Prism 4.00 for Windows, GraphPad, San Diego, CA, USA). Differences between two groups were identified using Student's t-test, while one-way analysis of variance, accompanied by Tukey's test, was used for multiple comparisons. P < 0.05 was considered as statistical significance.
RESULTS
Dansameum extract regulates the expression of CD36 and peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma in oxidative low-density lipoprotein-stimulated RAW264.7 cells
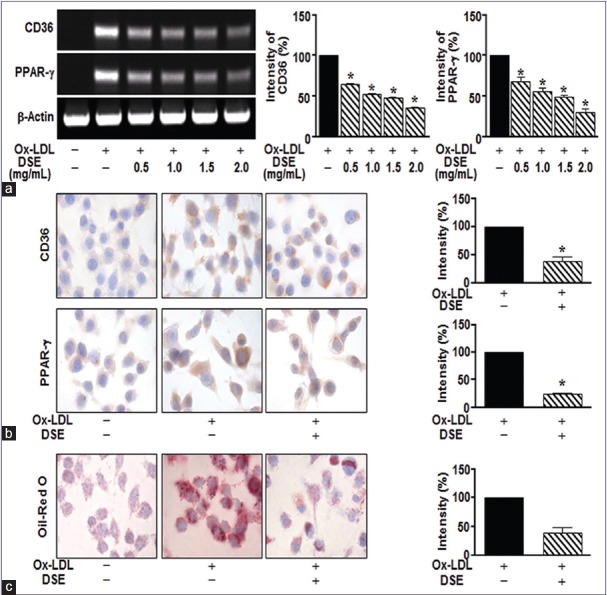
Numerous studies show that CD36 and PPAR-γ in oxLDL-stimulated macrophages mediate the development of atherosclerotic lesions.[8] Therefore, modulation of CD36 and PPAR-γ activity may be a suitable therapeutic approach for atherosclerosis. To investigate the effect of DSE in oxLDL-stimulated RAW264.7 cells, we first examined the expression of CD36 and PPAR-γ in oxLDL-stimulated RAW264.7 cells by immunocytochemistry and reverse transcription-polymerase chain reaction. Treatment with oxLDL (5 μg/mL) induced the expression of CD36 and PPAR-γ, whereas DSE significantly reduced this response, up to a maximum at 2 mg/mL [Figure 1a and b]. Next, we evaluated the degree of oxLDL-induced accumulation of lipids using Oil Red O staining. As shown in Figure 1c, DSE (2 mg/mL) significantly inhibited oxLDL-induced lipid uptake [Figure 1c].
Figure 1.
Dansameum extract regulates the expression of CD36 and peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma in oxidative low-density lipoprotein-stimulated RAW264.7 Cells. Raw264.7 cells were pretreated with oxidative low-density lipoprotein (50 μg/mL) for 2 h. The cells were incubated in the absence or presence of dansameum extract (0.5–2.0 mg/mL) for 12 h. (a) CD36 and peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma mRNA levels, analyzed by reverse transcription-polymerase chain reaction. (b) Cells immunostained for CD36 and peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma. (c) Raw264.7 cells stained with Oil Red O solution. These results represent the mean ± standard error from three independent experiments. *P < 0.05 versus oxidative low-density lipoprotein -stimulated group
Dansameum extract regulates the expression of CD36 and peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma in ApoE knockout mice
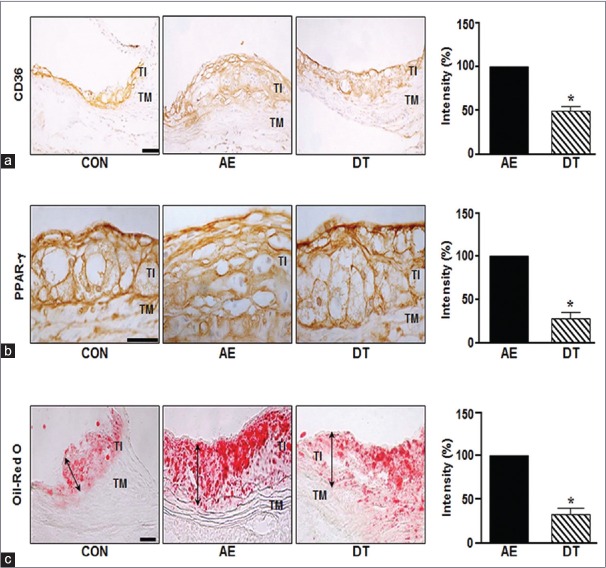
Our IHC data showed that atherosclerotic lesions contained high levels of CD36 and PPAR-γ in AE mice. As shown in Figure 2a and 2b, the protein expression of CD36 and PPAR-γ were also significantly higher in the aorta of AE group mice than control mice. DSE-treated DT mice were significantly reduced CD36 and PPAR-γ (to 50.4% and 71% for CD36 and PPAR-γ, respectively). Next, we tested whether DSE could reduce the accumulation of lipids in the aorta of ApoE-/-mice. The increased intensity of Oil Red O staining visible in the aortas from a diet-induced obesity (AE) group mice was inhibited by DSE administration [Figure 2c].
Figure 2.
Dansameum extract regulates the expression of CD36 and peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma in ApoE knockout mice. ApoE knockout mice were fed a high fat diet and/or treated with a dansameum extract extract for 12 weeks. Sections (TI: Tunica intima, TM: Tunica media, CON: Chow-fed, AE: High fat diet-fed, DT: High fat diet-fed and treated with dansameum extract) were prepared from mouse aortas. (a and b) Immunohistochemical analysis of aortic sinus, performed using anti-CD36 and anti- peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma antibodies. (c) Oil red O staining of aortic tissue. The red color indicates lipid. The graph shows the intensity of OIL RED O staining. These results represent the mean ± standard error of three independent experiments. *P < 0.05 versus AE group
Dansameum extract regulates cholesterol levels in the serum of ApoE-deficient ApoE knockout mice
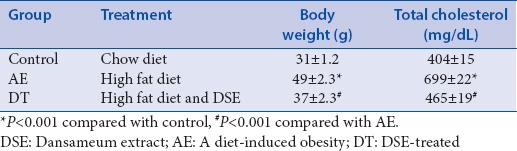
DSE has been reported to have various functions including blood flow improvement and prevents oxidative stress, anti-inflammatory, and antioxidant properties.[13,14,15,16] In addition, DSE inhibits platelet aggregation and promotes fibrinolysis in several studies.[10,11] Their previous studies suggest that cholesterol could be regulated by DSE. Table 1 shows the total cholesterol levels and body weight of the three groups of mice after 12 weeks of treatment. AE mice had the highest body weight and total cholesterol levels among these groups. And, DSE significantly reduced both body weight and total cholesterol.
Table 1.
The effects of dansameum extract treatment for 12 weeks on body weight and serum total cholesterol in apolipoprotein E deficient mice in high fat diet-fed
Dansameum extract reduced the formation of foam cells by regulating heme oxygenase-1 in ApoE knockoutmice with high fat diet-fed
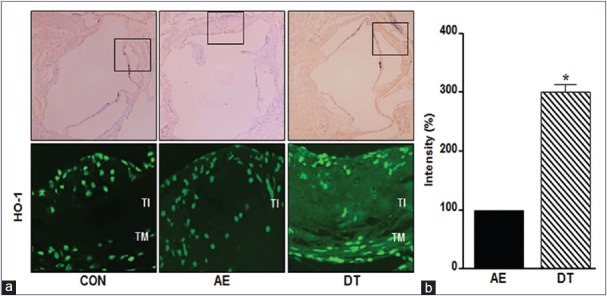
During the early stage of atherosclerosis, pro-oxidant and pro-atherogenic stimulation such as oxLDL enhances HO-1 expression in vascular tissue.[25,26] Therefore, the formation of foam cells is accompanied by the induction of HO-1 during the development of atherosclerosis. As shown in Figure 3, HO-1 protein was slightly lower in the aortas of AE group mice than in those of CON group mice, but it was increased 2-fold in DT mice compared with the AE group.
Figure 3.
Dansameum extract reduced the formation of foam cells by regulating heme oxygenase-1 in ApoE knockout mice with high fat diet-fed. (a) ApoE knockout mice were fed a high fat diet and/or treated with dansameum extract for 12 weeks. Aortic tissues were fixed with 40% formalin. The tissues (TI: Tunica intima, TM: Tunica media, CON: Chow-fed, AE: High fat diet-fed, DT: High fat diet-fed and treated with dansameum extract) were immunostained with anti- heme oxygenase-1 antibody. The upper photographs show the whole aortic sinus. The box shows the location of the lower photograph. (b) Intensity of heme oxygenase-1 immunostaining. Intensity are analyzed as mean ± standard error (n = 6). *P < 0.05 versus AE group
Chromatogram analysis of dansameum extract composition
As shown in Figure 4, the composition of DSE was determined using HPLC analysis. We also detected three major peaks in DSE, representing rosmarinic acid, tanshinone IIA, and salvianolic acid, at 24.37, 25.00, and 47.37 min, respectively, of the HPLC-spectrum.
Figure 4.
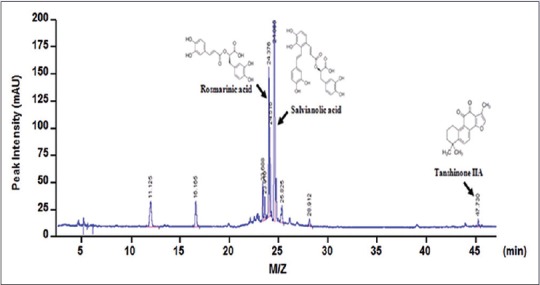
Chromatogram analysis of three components of dansameum extract). (a) High performance liquid chromatography chromatogram of dansameum extract at 254 nm. The chemical structures and arrows indicate rosmarinic acid (23.37 min), salvianolic acid (25.00 min), and tanshinone IIA (47.37 min). M/Z: Mass to charge ratio
DISCUSSION
Chronic atherosclerosis is associated with increased foam cell formation in the vascular intima, resulting from increased accumulation of cholesterol and lipids.[27] Recently, alternative medicine and natural foods have been gaining attention in the treatment of atherosclerosis.[28,29,30] In the present study, we found that DSE can exert inhibitory effect on atherosclerosis through reduction of lipid accumulation, which is associated with foam cell formation. DSE has been reported to inhibit platelet aggregation and promote fibrinolysis in several studies.[21,22] Our results showed that DSE regulates the expression of CD36 and PPAR-γ in oxLDL-stimulated RAW264.7 cells and in the aorta of ApoE-/-mice. Furthermore, treatment of ApoE-/-mice with DSE for 12 weeks significantly inhibited the development of early-stage atherosclerosis.
As DSE has been prescribed for the regulation of blood flow and stasis in previous studies, we evaluated whether DSE regulates lipid uptake or lipid-induced atherosclerotic lesions. Three active compounds of DSE, namely, rosmarinic acid, salvianolic acid, and tanshinone IIA have been reported to exert antioxidant and anti-inflammatory properties, and are considered effective components for diverse diseases, including platelet aggregation and cerebral infarction.[17,18,19,20,21] We determined these three components in the DSE sample used in our study by HPLC analysis [Figure 4].
As described above, we evaluated whether the active compounds of DSE could regulate foam cell formation in ApoE-/-mice. We hypothesized that DSE regulates oxLDL-mediated foam cell formation by inducing HO-1 expression. oxLDL induces the accumulation of Nrf2, a component of a key signaling pathway, resulting in the upregulation of CD36 as well as the downstream transcription factor PPAR-γ. HO-1 has been reported to protect against oxidative stress in cardiovascular disorders such as hypertension and neointima formation after vascular injury.[31] Our results showed that DSE administration to ApoE-/-mice increased HO-1 expression. Moreover, DSE significantly reduced CD36 and PPAR-γ expression in vitro and in vivo.
Although atherosclerotic development in ApoE-/-mice is induced by a high-fat diet, inhibition of CD36 expression can reduce atherosclerosis.[32] In addition, the formation of plaques in the arterial walls is induced by monocyte to macrophage differentiation, which is mediated CD36.[8] Our results suggest that DSE induces HO-1 expression and downregulates CD36 signal, thereby suppressing the development of early-stage atherosclerosis. Feeding the mice with a western diet for 12 weeks increased body weight and total cholesterol. DSE administration prevented these effects by upregulating HO-1 expression and consequently downregulating CD36 and PPAR-γ expression. Therefore, DSE may be an effective treatment option in the early and developmental phases of atherosclerosis.
CONCLUSION
The results of our study suggest that DSE exerts anti-atherosclerotic effect by regulating the expression of HO-1, CD36, and PPAR-γ, and it inhibits the differentiation of macrophages into foam cells. Consequently, DSE reduces the development of early atherosclerotic lesions and lipid accumulation in the aorta in ApoE-/-mice fed a high-fat diet. Therefore, DSE may be effective in the prevention of atherosclerosis.
Financial support and sponsorship
Nil.
Conflicts of interest
There are no conflicts of interest.
Acknowledgments
This study was supported by a Biomedical Research Institute Grant (2015-18) from Pusan National University Hospital.
REFERENCES
- 1.Chen X, Zhou L, Zhang Y, Yi D, Liu L, Rao W, et al. Risk factors of stroke in Western and Asian countries: A systematic review and meta-analysis of prospective cohort studies. BMC Public Health. 2014;14:776. doi: 10.1186/1471-2458-14-776. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Gerber Y, Myers V, Goldbourt U, Benyamini Y, Scheinowitz M, Drory Y, et al. Long-term trajectory of leisure time physical activity and survival after first myocardial infarction: A population-based cohort study. Eur J Epidemiol. 2011;26:109–16. doi: 10.1007/s10654-010-9523-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Schuett KA, Lehrke M, Marx N, Burgmaier M. High-risk cardiovascular patients: Clinical features, comorbidities, and interconnecting mechanisms. Front Immunol. 2015;6:591. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2015.00591. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Buttari B, Profumo E, Businaro R, Saso L, Capoano R, Salvati B, et al. Oxidized haemoglobin-driven endothelial dysfunction and immune cell activation: Novel therapeutic targets for atherosclerosis. Curr Med Chem. 2013;20:4806–14. doi: 10.2174/09298673113209990162. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Choy PC, Siow YL, Mymin D, Karmin O. Lipids and atherosclerosis. Biochem Cell Biol. 2004;82:212–24. doi: 10.1139/o03-085. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Zhao J, Zhu H, Wang S, Ma X, Liu X, Wang C, et al. Naoxintong protects against atherosclerosis through lipid-lowering and inhibiting maturation of dendritic cells in LDL receptor knockout mice fed a high-fat diet. Curr Pharm Des. 2013;19:5891–6. doi: 10.2174/1381612811319330008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Ross R. The pathogenesis of atherosclerosis: A perspective for the 1990s. Nature. 1993;362:801–9. doi: 10.1038/362801a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Park YM. CD36, a scavenger receptor implicated in atherosclerosis. Exp Mol Med. 2014;46:e99. doi: 10.1038/emm.2014.38. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Hajri T, Hall AM, Jensen DR, Pietka TA, Drover VA, Tao H, et al. CD36-facilitated fatty acid uptake inhibits leptin production and signaling in adipose tissue. Diabetes. 2007;56:1872–80. doi: 10.2337/db06-1699. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Aubouy A, Olagnier D, Bertin G, Ezinmegnon S, Majorel C, Mimar S, et al. Nrf2-driven CD36 and HO-1 gene expression in circulating monocytes correlates with favourable clinical outcome in pregnancy-associated malaria. Malar J. 2015;14:358. doi: 10.1186/s12936-015-0888-8. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Zhou D, Samovski D, Okunade AL, Stahl PD, Abumrad NA, Su X, et al. CD36 level and trafficking are determinants of lipolysis in adipocytes. FASEB J. 2012;26:4733–42. doi: 10.1096/fj.12-206862. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.D’Archivio M, Scazzocchio B, Filesi C, Varì R, Maggiorella MT, Sernicola L, et al. Oxidised LDL up-regulate CD36 expression by the nrf2 pathway in 3T3-L1 preadipocytes. FEBS Lett. 2008;582:2291–8. doi: 10.1016/j.febslet.2008.05.029. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Jeong HJ, Choi Y, Kim MH, Kang IC, Lee JH, Park C, et al. Rosmarinic acid, active component of Dansam-Eum attenuates ototoxicity of cochlear hair cells through blockage of caspase-1 activity. PLoS One. 2011;6:e18815. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0018815. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Matkowski A, Zielińska S, Oszmiański J, Lamer-Zarawska E. Antioxidant activity of extracts from leaves and roots of Salvia miltiorrhiza Bunge, S. Przewalskii Maxim. and S. Verticillata L. Bioresour Technol. 2008;99:7892–6. doi: 10.1016/j.biortech.2008.02.013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Wang JH, Wang J, Choi MK, Gao F, Lee DS, Han JM, et al. Hepatoprotective effect of Amomum xanthoides against dimethylnitrosamine-induced sub-chronic liver injury in a rat model. Pharm Biol. 2013;51:930–5. doi: 10.3109/13880209.2013.770040. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Santha S, Dwivedi C. Anticancer effects of Sandalwood (Santalum album) Anticancer Res. 2015;35:3137–45. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Kuang P, Wu W, Zhu K. Evidence for amelioration of cellular damage in ischemic rat brain by radix salviae miltiorrhizae treatment – Immunocytochemistry and histopathology studies. J Tradit Chin Med. 1993;13:38–41. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Wu W, Kuang P, Li Z. Protective effect of radix Salviae miltiorrhizae on apoptosis of neurons during focal cerebral ischemia and reperfusion injury. J Tradit Chin Med. 1997;17:220–5. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Lo CJ, Lin JG, Kuo JS, Chiang SY, Chen SC, Liao ET, et al. Effect of salvia miltiorrhiza bunge on cerebral infarct in ischemia-reperfusion injured rats. Am J Chin Med. 2003;31:191–200. doi: 10.1142/S0192415X03000916. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Adams JD, Wang R, Yang J, Lien EJ. Preclinical and clinical examinations of Salvia miltiorrhiza and its tanshinones in ischemic conditions. Chin Med. 2006;1:3. doi: 10.1186/1749-8546-1-3. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Zhou L, Zuo Z, Chow MS. Danshen: An overview of its chemistry, pharmacology, pharmacokinetics, and clinical use. J Clin Pharmacol. 2005;45:1345–59. doi: 10.1177/0091270005282630. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Chan TY. Interaction between Warfarin and danshen (Salvia miltiorrhiza) Ann Pharmacother. 2001;35:501–4. doi: 10.1345/aph.19029. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Ditiatkovski M, Toh BH, Bobik A. GM-CSF deficiency reduces macrophage PPAR-gamma expression and aggravates atherosclerosis in ApoE-deficient mice. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2006;26:2337–44. doi: 10.1161/01.ATV.0000238357.60338.90. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Kuchibhotla S, Vanegas D, Kennedy DJ, Guy E, Nimako G, Morton RE, et al. Absence of CD36 protects against atherosclerosis in ApoE knock-out mice with no additional protection provided by absence of scavenger receptor A I/II. Cardiovasc Res. 2008;78:185–96. doi: 10.1093/cvr/cvm093. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Min KJ, Cho KH, Kwon TK. The effect of oxidized low density lipoprotein (oxLDL)-induced heme oxygenase-1 on LPS-induced inflammation in RAW 264.7 macrophage cells. Cell Signal. 2012;24:1215–21. doi: 10.1016/j.cellsig.2012.02.001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Orozco LD, Kapturczak MH, Barajas B, Wang X, Weinstein MM, Wong J, et al. Heme oxygenase-1 expression in macrophages plays a beneficial role in atherosclerosis. Circ Res. 2007;100:1703–11. doi: 10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.107.151720. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Allahverdian S, Chehroudi AC, McManus BM, Abraham T, Francis GA. Contribution of intimal smooth muscle cells to cholesterol accumulation and macrophage-like cells in human atherosclerosis. Circulation. 2014;129:1551–9. doi: 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.113.005015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Balzer J, Rassaf T, Heiss C, Kleinbongard P, Lauer T, Merx M, et al. Sustained benefits in vascular function through flavanol-containing cocoa in medicated diabetic patients a double-masked, randomized, controlled trial. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2008;51:2141–9. doi: 10.1016/j.jacc.2008.01.059. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Sumner MD, Elliott-Eller M, Weidner G, Daubenmier JJ, Chew MH, Marlin R, et al. Effects of pomegranate juice consumption on myocardial perfusion in patients with coronary heart disease. Am J Cardiol. 2005;96:810–4. doi: 10.1016/j.amjcard.2005.05.026. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Seyed MA, Jantan I, Bukhari SN, Vijayaraghavan K. A comprehensive review on the chemotherapeutic potential of piceatannol for cancer treatment, with mechanistic insights. J Agric Food Chem. 2016;64:725–37. doi: 10.1021/acs.jafc.5b05993. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Kim YM, Pae HO, Park JE, Lee YC, Woo JM, Kim NH, et al. Heme oxygenase in the regulation of vascular biology: From molecular mechanisms to therapeutic opportunities. Antioxid Redox Signal. 2011;14:137–67. doi: 10.1089/ars.2010.3153. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Febbraio M, Podrez EA, Smith JD, Hajjar DP, Hazen SL, Hoff HF, et al. Targeted disruption of the class B scavenger receptor CD36 protects against atherosclerotic lesion development in mice. J Clin Invest. 2000;105:1049–56. doi: 10.1172/JCI9259. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]