Abstract
The wound healing is a complex process wherein inflammation, proliferation and regeneration evolve according to a spatio‐temporal pattern from the activation of coagulation cascade to the formation of a plug clot including fibrin matrix, blood‐borne cells and cytokines/growth factors. Creating environments conducive to tissue repair, the haemoderivatives are commonly proposed for the treatment of hard‐to‐heal wounds. Here, we explored in vitro the intrinsic regenerative potentialities of a leucocyte‐ and platelet‐rich fibrin product, known as CPL‐MB, defining the stemness grade of cells sprouting from the haemoderivative. Using highly concentrated serum‐based medium to simulate wound conditions, we isolated fibroblast‐like cells (CPL‐CMCs) adhering to plastic and showing stable in vitro propagation, heterogeneous stem cell expression pattern, endothelial adhesive properties and immunomodulatory profile. Due to their blood derivation and expression of CXCR4, CPL‐CMCs have been suggested to be immature cells circulating in peripheral blood at quiescent state until activation by both coagulation event and inflammatory stimuli such as stromal‐derived factor 1/SDF1. Expressing integrins (CD49f, CD103), vascular adhesion molecules (CD106, CD166), endoglin (CD105) and remodelling matrix enzymes (MMP2, MMP9, MMP13), they showed a transendothelial migratory potential besides multipotency. Taken together, our data suggested that a standardized, reliable and economically feasible blood product such as CPL‐MB functions as an artificial stem cell niche that, under permissive conditions, originate ex vivo immature cells that could be useful for autologous stem cell‐based therapies.
Keywords: circulating multipotent cells, haemoderivatives, in vivo guided regeneration, autologous cell therapies
Introduction
Over the last three decades, the enormous progress in cell processing technology has enhanced a general shift from heterologous to autologous stem cell‐based therapies. In the prospect of having biomaterials and bioactive surgical additives with predictable outcome in regenerative medicine, several techniques have been developed to process peripheral blood and to obtain products useful for controlling inflammation and enforcing the physiological events of haemostasis and wound healing 1, 2, 3, 4. Depending on their contents of platelets, leucocytes and fibrin architecture, they are commonly classified into four families: (i) pure platelet‐rich plasma (P‐PRP, in liquid or gel form); (ii) leucocyte‐ and platelet‐rich plasma (L‐PRP, in liquid or gel form); (iii) pure platelet‐rich fibrin (P‐PRF); and (iv) leucocyte‐ and platelet‐rich fibrin (L‐PRF) 5. Among them, L‐PRF offers overall higher amounts of released TGF‐β1, a sustained, long‐term release of growth factors (VEGF, IGF1, PDGF‐AB) and cytokines (IL‐1β), and stronger induction of cell migration in vitro 6. Obtained by different production methods and devices, the haemoderivatives demonstrate to be beneficial for tissues with restricted blood supply, slow cell turnover, limited extracellular matrix restoration facilitating the recruitment, proliferation and maturation of cells participating in regeneration. They are commonly used in clinics for numerous medical applications including (i) the healing of recalcitrant ulcers and burns; (ii) the stimulation of tissue regeneration in dentistry, implantology, and maxillofacial and plastic surgery; (iii) the treatment of knee osteoarthritis; and (iv) the repair of musculoskeletal tissue, tendon, and ligament lesions 1, 7, 8. To date, the intrinsic regenerative potentialities of L‐PRP have been commonly attributed to platelet‐ and leucocyte‐derived factors (coagulation factors, growth factors and cytokines) and fibrin matrix that synergistically orchestrate the recruitment of stem cells or progenitor cells following an inflammatory response driven by neutrophils, M1‐polarized macrophages and T lymphocytes (early‐phase), and M2 macrophages (late‐phase) 9. A growing body of evidence demonstrates that the contribution of L‐PRF to in vivo angiogenesis and vasculogenesis at injury site is mediated by intrinsically carried haematopoietic stem cells (HSCs) (CD34+) and endothelial progenitor cells (EPCs) (CD34+/VEGR‐2+/CD133+) 10. Although fibroblast‐like multipotent cells with proliferative and multidifferentiative properties have been identified in human peripheral blood 11, 12, 13, to date, no evidence about their presence has been reported in L‐PRF products. As the discovery of multipotent stem cells in L‐PRF products could have important implications for the future of regenerative medicine confirming (i) the active role of the haemoderivatives in the so‐called in vivo guided regeneration and (ii) the development of a standardized method to extract autologous stem cells, in this study, a leucocyte–platelet‐concentrated membrane, prepared according to the Caloprisco protocol 10 and called CLP‐MB, has been cultured in vitro to characterize the stemness grade of sprouted cells under permissive conditions.
Materials and methods
Haemoderivatives
Following the Italian standards of quality assurance, leucocyte‐ and platelet‐rich fibrin membranes (CLP‐MB) were prepared at the Immunohematology and Transfusion Medicine Department, San Martino Hospital of Belluno, Italy. Under Italian ethic committee authorization and informed consent, ten male volunteer donors were submitted to a multicomponent apheresis procedure, and blood samples were processed according to the procedure published by Caloprisco et al. 10. In Table 1, haematologic values of blood samples and blood derivatives are reported.
Table 1.
Haematologic values of blood samples before apheresis (pre‐AP) and at final phase of concentrated leucocyte/platelet membrane (CPL‐MB)
| Patient | Phase | RBC (×106/μl) | PLT (×103/μl) | WBC (×103/μl) | NE (×103/μl) | LY (×103/μl) | MO (×103/μl) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 |
pre‐AP CLP‐MB |
5.23 0.58 |
183 1452 |
6.58 22.40 |
4.70 4.85 |
1.10 9.22 |
0.60 10.17 |
| 2 |
pre‐AP CLP‐MB |
4.46 0.37 |
249 1511 |
6.27 23.20 |
4.40 2.80 |
1.40 16.00 |
0.30 3.60 |
| 3 |
pre‐AP
CLP‐MB |
5.53 0.37 |
184 1464 |
4.36 17.60 |
2.70 0.80 |
1.30 12.80 |
0.30 4.00 |
| 4 |
pre‐AP
CLP‐MB |
5.40 0.39 |
185 1700 |
6.38 30.00 |
3.20 0.80 |
1.90 21.20 |
0.60 8.00 |
| 5 |
pre‐AP CLP‐MB |
4.18 0.30 |
206 1800 |
4.66 18.00 |
2.90 1.20 |
1.10 12.40 |
0.30 4.00 |
| 6 |
pre‐AP CLP‐MB |
4.96 0.53 |
171 1801 |
4.26 29.40 |
2.30 2.70 |
1.50 20.30 |
0.30 6.20 |
| 7 |
pre‐AP CLP‐MB |
4.87 1.06 |
153 1502 |
3.47 30.80 |
1.60 1.60 |
1.40 22.30 |
0.40 6.90 |
| 8 |
pre‐AP CLP‐MB |
5.13 0.55 |
188 1808 |
3.12 21.00 |
1.60 1.20 |
1.00 13.30 |
0.40 6.50 |
| 9 |
pre‐AP CLP‐MB |
5.33 0.64 |
234 1508 |
4.04 25.20 |
1.60 3.20 |
1.6 15.40 |
0.50 6.60 |
| 10 |
pre‐AP CLP‐MB |
4.33 0.28 |
199 1794 |
4.58 23.25 |
2.10 0.60 |
1.80 17.10 |
0.50 5.55 |
RBC: red blood cells; PTL: platelets; WBC: total leucocytes; NE: neutrophils; LY: lymphocytes; MO: monocytes. The representative data of RBC, PLT and leucocytes from CPL‐MB are reported in bold.
Isolation of fibroblast stem‐like cells
Rounded patches of CPL‐MB were prepared and seeded in polystyrene culture dishes (BD, Franklin Lakes, NJ, USA) preconditioned with foetal bovine serum (Invitrogen‐Thermo Fisher Scientific, Waltham, MA, USA). Thus, samples were maintained at 37°C, 95% humidity and 5% CO2, in proliferation culture medium [Alpha‐modified Eagle's medium (α‐MEM) without nucleosides, 50% foetal bovine serum, 1% antibiotic solution, 1% Glutamax (all from Invitrogen Thermo Fisher Scientific, Inc)]. When cell sprouting was observed, CPL‐MB patches were discarded, and culture medium was changed with fresh one every 2 days. Cell expansion was performed for 21 days before detecting fibroblastoid cells (CPL‐CMCs) with proliferative potential. At 80% confluence, CPL‐CMC cells were detached using 0.02% EDTA/0.25% trypsin solution, and subcultures were seeded (5 × 103 cells/cm2) in proliferation culture medium containing 16.5% FBS. In alternative to commercial FBS, autologous serum has been suggested to be used in the perspective of clinical use of CPL‐CMCs. During cell isolation and expansion phases, the samples were daily observed by optical microscope DM/IL (Leica, Wetzlar, Germany), and pictures were taken with Nikon Digital Sight Ds‐SMCc camera (Nikon Corporation, Tokyo, Japan). In order to correlate the activation of circulating multipotent cells to the inflammatory environment promoted by haemoderivatives, the expression of TNFα, IL‐10, Wnt3a, TGFβ1, CD206 was investigated by Western blot in cells sprouted from CPL‐MB. In parallel, the expression pattern of CPL‐MB was used as a reference.
Proteomic analysis of CPL‐derived adherent cells
Using antibodies reported in Table 2, Western blot analysis was performed on total protein extract of CLP membranes and cells isolated from early (inflammatory cells) and late (CLP‐CMCs) sprouted populations. The protein extraction was carried out using a RIPA buffer containing 0.25% TWEEN®20 (Sigma‐Aldrich, St. Louis, MO, USA). After quantification using BCA Protein Assay Reagent Kit (Thermo Fisher Scientific, Inc.), 20 μg of total protein extracts from each sample was separated by reducing SDS‐PAGE (Bio‐Rad Laboratories Inc., Hercules, CA, USA) and then electrophoretically transferred to 0.45‐μm nitrocellulose membrane (Immunological Sciences, Rome, Italy). The immunoblot was performed by incubating samples overnight at 4°C with primary antibodies against CD206, TGFβ1, Wnt3a, IL‐10, TNFα (Table 2). After washing with 0.25% TWEEN®20 in PBS, the membranes were treated for 1 h with peroxidase‐conjugated secondary goat antimouse and anti‐rabbit antibodies (Immunological Sciences) and then developed using enhanced chemiluminescence substrate (Immunological Sciences). The immunoreactive sites were visualized using VersaDoc Imaging System (Bio‐Rad Laboratories Inc.). The protein expression level was normalized to glyceraldehyde 3‐phosphate dehydrogenase/GAPDH housekeeping protein (EMD Millipore, Billerica, MA, USA) and quantified by ImageLab processing software (Bio‐Rad Laboratories Inc.). Data from three independent experiments were reported as a ratio within the target protein and relative housekeeping protein expression.
Table 2.
Antibodies used for flow cytometry analysis, Western blot and immunofluorescence
| Primary antibodies | Manufacturing company |
|---|---|
| FITC mouse anti‐human CD11c | BD Biosciences |
| APC mouse anti‐human CD13 | BD Biosciences |
| PE mouse anti‐human CD14 | Santa Cruz Biotecnology, Inc |
| FITC mouse anti‐human CD29 | Santa Cruz Biotecnology, Inc |
| PE mouse anti‐human CD31 | BD Biosciences |
| PE‐Cy5 mouse anti‐human CD33 | BD Biosciences |
| PE‐Cy7 mouse anti‐human CD34 | BD Biosciences |
| Rabbit anti‐human CD38 | Santa Cruz Biotecnology, Inc |
| PE mouse anti‐human CD40 | BD Biosciences |
| PE mouse anti‐human CD44 | Santa Cruz Biotecnology, Inc |
| PE mouse anti‐human CD45 | Santa Cruz Biotecnology, Inc |
| FITC mouse anti‐human CD49f | ImmunoTools |
| PE mouse anti‐human CD73 | BioLegend, Inc |
| PE‐Cy5 mouse anti‐human CD80 | BD Biosciences |
| APC mouse anti‐human CD86 | BD Biosciences |
| FITC mouse anti‐human CD90 | Santa Cruz Biotecnology, Inc |
| Mouse anti‐human CD103 | Santa Cruz Biotecnology, Inc |
| PE mouse anti‐human CD105 | Santa Cruz Biotecnology, Inc |
| FITC mouse anti‐human CD106 | Acris Antibodies GmbH |
| APC mouse anti‐human CD133/1 | Miltenyi Biotec |
| PE mouse anti‐human CD133/2 | Miltenyi Biotec |
| FITC mouse anti‐human CD146 | Santa Cruz Biotecnology, Inc |
| FITC mouse anti‐human CD166 | Santa Cruz Biotecnology, Inc |
| Rabbit anti‐human CD206 | Santa Cruz Biotecnology, Inc |
| PE mouse anti‐human PDGFRβ | BD Biosciences |
| FITC mouse anti‐human VEGFR2 | R&D Systems, Inc. |
| Rabbit anti‐human FGFR1 | Santa Cruz Biotecnology, Inc |
| APC mouse anti‐human FGFR2 | R&D Systems, Inc. |
| Rabbit anti‐human EGFR | Santa Cruz Biotecnology, Inc |
| FITC mouse anti‐human NG2 | Santa Cruz Biotecnology, Inc |
| Rabbit anti‐human VE‐cadherin | Santa Cruz Biotecnology, Inc |
| Mouse anti‐human αSMA | EMD Millipore |
| Mouse anti‐human vimentin | Santa Cruz Biotecnology, Inc |
| Rabbit anti‐human vWF | Abcam |
| Mouse anti‐human FVIII | Abcam |
| Rabbit anti‐human TGFβ1 | Santa Cruz Biotecnology, Inc |
| Rabbit anti‐human Wnt3a | Immunological Sciences |
| Rabbit anti‐human IL‐10 | Immunological Sciences |
| Rabbit Anti‐human TNFα | Immunological Sciences |
| PE mouse anti‐human CXCR4 | Santa Cruz Biotecnology, Inc |
| Rabbit anti‐human Frizzled 1 | Acris Antibodies GmbH |
| PE mouse anti‐human Frizzled 2 | Santa Cruz Biotecnology, Inc |
| Goat anti‐human Frizzled 3 | Santa Cruz Biotecnology, Inc |
| Goat anti‐human Frizzled 9 | Santa Cruz Biotecnology, Inc |
| PE mouse anti‐human SEEA4 | BD Biosciences |
| Alexa Fluor® 488 mouse anti‐human TLR4 | Bioss Antibodies |
| Rabbit anti‐human SIRPα | eBiosciences |
| FITC mouse anti‐human GR‐1/Ly6G | BD Biosciences |
| PE‐Cy7 mouse anti‐human HLA‐ABC | BD Biosciences |
| PE‐Cy5 mouse anti‐human HLA DR | BD Biosciences |
| Secondary antibodies | |
|---|---|
| PE goat antimouse | Santa Cruz Biotecnology, Inc |
| PE goat anti‐rabbit | Santa Cruz Biotecnology, Inc |
| PE donkey anti‐goat | Santa Cruz Biotecnology, Inc |
| Alexa Fluor® 488 antimouse | EMD Millipore |
| Isotype controls | |
|---|---|
| FITC Isotype Control | Santa Cruz Biotechnology, Inc; BD Biosciences; ImmunoTools; Acris Antibodies GmbH; R&D Systems, Inc |
| PE Isotype Control | Santa Cruz Biotechnology, Inc; BD Biosciences; BioLegend, Inc; Miltenyi Biotec |
| PE‐Cy5 Isotype Control | BD Biosciences |
| PE‐Cy7 Isotype Control | BD Biosciences |
| APC Isotype Control | R&D Systems, Inc.; Miltenyi Biotec. |
| Alexa Fluor® 488 Isotype Control | Bioss Antibodies |
Proliferation capacity of CPL‐CMCs
The proliferation rate of CPL‐CMCs was evaluated culturing for 16 consecutive passages and seeding in triplicate each generation at a density of 5 × 103 cells/cm2. After 24 hrs, the cells were detached using EDTA/trypsin solution and counted with a hemocytometer. The average number of cells and standard deviation (SD) for each passage was used to define the doubling population time (DPT).
Stemness gene profile
The expression of OCT4, NANOG, SOX2, KLF4, NOTCH, STAT3 and REX1 was investigated by quantitative PCR (qPCR) in subcultures evolving from 4th generation to 20th generations, using oligonucleotides (Thermo Fisher Scientific, Inc.) listed in Table 3. Reverse transcription and amplification reaction were carried out using SensiFAST™ SYBR® One‐Step kit (Bioline Inc., London, UK) and AriaMx Real‐time PCR System (Agilent Technology, Santa Clara, CA, USA). For statistical significance of data, three independent analyses of each target per subpopulation were performed preparing multiple technical replicates. The hypoxanthine phosphoribosyltransferase 1/HPRT1 housekeeping gene was considered as control. For quantification of gene expression level, the comparative CT method (2−ΔCt) was used.
Table 3.
Oligonucleotides used for RT‐PCR and qPCR analysis (F = forward; R = reverse)
| Genes | Primer sequences | Accession | Amplicon length |
|---|---|---|---|
| TGFA |
F: CACACTCAGTTCTGCTTCCA R: GTGATGGCCTGCTTCTTCT |
NM_003236.3 | 151 bp |
| TGFB1 |
F: CGTGGAGCTGTACCAGAAATAC R: CTAAGGCGAAAGCCCTCAAT |
NM_000660.6 | 158 bp |
| LIF |
F: TCTGCACTGGAAACATGGG R: CTGATCTGGTTCATGAGGTTGT |
NM_002309.4 | 104 bp |
| IL1A |
F: AGTGAGACCAACCTCCTCTT R: ACACCCAGTAGTCTTGCTTTG |
NM_000575.4 | 108 bp |
| IL1B |
F: ATGGACAAGCTGAGGAAGATG R: CCCATGTGTCGAAGAAGATAGG |
NM_000576.2 | 114 bp |
| IL4 |
F: CACCGAGTTGACCGTAACA R: CTTCCATGGTGGCTGTAGAA |
NM_000589.3 | 138 bp |
| IL6 |
F: GAGCTGTGCAGATGAGTACAA R: GGACTGCAGGAACTCCTTAAA |
NM_000600.4 | 190 bp |
| IL10 |
F: GCTGGAGGACTTTAAGGGTTAC R: GATGTCTGGGTCTTGGTTCTC |
NM_000572.2 | 105 bp |
| IL12 |
F: ATTCCAGAGAGACCTCTTTCATAAC R: CTTGAACTCCACCTGGTACATC |
NM_000882.3 | 124 bp |
| TNFA |
F: CCAGGGACCTCTCTCTAATCA R: TCAGCTTGAGGGTTTGCTAC |
FJ795028.1 | 106 bp |
| TNFR1 |
F: GGACAGGGAGAAGAGAGATAGT R: TGGACAGTCATTGTACAAGTAGG |
AH003016.2 | 115 bp |
| TNFR2 |
F: TGCATCGTGAACGTCTGTAG R: GGAATCTGTGTCTCCCATTGT |
NM_001066.2 | 84 bp |
| REX1 |
F: GAGATGGAGTAAGGAGGGAGAT R: ATGGACAAGCTGAGGAAGATG |
NM_174900.3 | 105 bp |
| SOX2 |
F: ATTCCAGAGAGACCTCTTTCATAAC R: TACCTTTCTGCCCGTGAAGTGGAT |
NM_003106.3 | 191 bp |
| STAT3 |
F: AAAGACAGCTACGTGGGTGACGAA R: AGAACCTGCAGGAGGCAGAAGAAT |
NM_213662.1 | 175 bp |
| NOTCH |
F: AGGATCACACAGGTGGCCCATATT R: AGCTAAAGCAGCAGCAAACTTCGG |
NM_017617.3 | 112 bp |
| OCT4 |
F: TCGAGGAATTGCTCAAAGTGCTGG R: ACACCAACGGCTGGAAGCTAAATC |
NM_002701.4 | 102 bp |
| KLF4 |
F: GAAGATGCGCAGCAGCGAGAATTT R: ACTTTCTCCTGTCCGTCATTGGCT |
NM_004235.4 | 106 bp |
| NANOG |
F: AGAATATGCACCAGGCCGAAGAGT R: AGCTAAGAGTCTTTGGTGCTGGCT |
NM_024865.2 | 106 bp |
| TUBβ3 |
F: ACAACGAGGCCTCTTCTCACAAGT R: ATACTCCTCACGCACCTTGCTGAT |
NM_006086.3 | 225 bp |
| vWF |
F: ACTCAGTGCATTGGTGAGGATGGA R: TCGGACACACTCATTGATGAGGCA |
NM_000552.4 | 842 bp |
| CD31 |
F: ACTGGACAAGAAAGAGGCCATCCA R: TCCTTCTGGATGGTGAAGTTGGCT |
NM_000442.4 | 677 bp |
| HPRT1 |
F: ATGGACAGGACTGAACGTCTTGCT R: TTGAGCACACAGAGGGCTACAATG |
NM_000194.2 | 79 bp |
Immunophenotyping of CPL‐CMCs
Using anti‐human antibodies reported in Table 2, subcultures from 4th to 20th generations were analysed by flow cytometry (FCM) for the expression of typical markers related to stemness, lineage commitment, cell–ECM interactions and enzyme/signalling molecules. Flow cytometry analysis was performed with FACSCanto II Flow cytometer (BD Biosciences, CA, USA) and FACS Diva software (BD). Data were reported as mean percentage of positive cells and relative mean fluorescence intensity (MFI) calculated on n = 3 replicas of each sample for all target markers. Samples treated with only secondary antibodies or isotype control antibodies (Table 2) were prepared as references.
Differentiative plasticity of CPL‐CMCs
CLP‐CMCs were seeded at 1.5 × 104 cells/cm2 and induced to differentiate under the conditions described below. In parallel, cultures in proliferation medium were prepared as controls. After 7 and 14 days, the analysis by cytochemistry, immunofluorescence, PCR, WB and FCM was performed to confirm the lineage‐specific differentiation. In all experiments, resting cells were used as reference. Antibodies and oligonucleotides are reported in Table 2 and Table 3, respectively. For gene expression analysis, the housekeeping HPRT1 was considered for normalization of data.
Adipogenic induction
The stimulation was performed with DMEM high‐glucose medium (Sigma‐Aldrich) supplemented with 10% FBS (Invitrogen‐Thermo Fisher Scientific, Inc), 1% antibiotic solution (Sigma‐Aldrich) and adipogenic supplements (1 mM dexamethasone, 0.5 mM 3‐isobutyl‐1‐methylxanthine, 10 mg/ml insulin, 60 mM indomethacin) (all from Sigma‐Aldrich). After 3, 7 and 14 days from induction, the adipogenic commitment was evaluated detecting the expression of perilipin/PLIN1 and leptin/LEP genes by qPCR. In parallel, samples were fixed with 10% formalin solution (Sigma‐Aldrich) and stained with Oil Red O solution (5 mg/ml in isopropanol) (Sigma‐Aldrich) to verify the presence of cytoplasmic lipid droplets. Nuclei were counterstained with haematoxylin (Sigma‐Aldrich) according to the standard procedure.
Myogenic induction
Subconfluent (~90%) CLP‐CMCs were grown in standard medium supplemented with 100 ng/ml IGF (ImmunoTools, Friesoythe, Germany) and 200 μM ascorbic acid (Sigma‐Aldrich Co.). At different time‐points (3, 7, 14 days), myogenic differentiation was verified by qPCR investigating the expression of genes related to early (myogenic differentiation 1/MYOD1), intermediate (myogenin/MYOG) and late (tropomyosin 1/TPM1) differentiation phases. At 14 days from induction, the expression of vimentin was evaluated by immunofluorescence to detect the formation of syncytium‐like structures.
Neurogenic induction
Neurogenic differentiation was induced in subconfluent (~60%) cells using DMEM/F‐12 medium (Thermo Fisher Scientific, Inc.) supplemented with 2% FBS, 50 U/ml penicillin, 50 μg/ml streptomycin and 0.1% dimethyl sulphoxide (DMSO) (all from Sigma‐Aldrich). After 3 and 7 days, the samples were submitted to the analysis of brain‐derived neurotrophic factor/BDNF, nerve growth factor/NGF, tubulin beta 3 class III/TUBB3 and synaptophysin/SYP by qPCR.
Endothelial induction
CLP‐CMCs (2x104cells/cm2) were seeded on 24‐well plates coated with 0.5 ml of Matrigel (diluted 1:10 in standard medium) (BD Bioscience) and cultured in a humid atmosphere with 5% CO2. At 3 and 7 days from induction, the gene expression of platelet endothelial cell adhesion molecule/CD31 was analysed by one‐step reverse transcriptase–PCR (Qiagen, Hilden, Germany). In parallel, we evaluated the formation of capillary‐like structures by optical microscopy using an inverted microscope Motic AE2000 (Motic®, Wetzlar, Germany) equipped with Nikon DS‐L1 camera (Nikon, Düsseldorf, Germany), and the expression of blood‐clotting protein factor VIII/FVIII by immunofluorescence. Finally, to better explore the endothelial potential of CLP‐CMC cells, extracellular vesicles/exosomes (EVs/exs) were isolated using Cell Culture‐Nanovesicles kit (Biofield Innovation Srl, Padova, Italy) from conditioned media according to the manufacturer's protocol. After labelling with PKH26 Red Fluorescent Cell Linker Kit for General Cell Membrane Labeling (Sigma‐Aldrich), all samples were characterized by FCM for size, using as reference polystyrene beads supplied in Flow Cytometry Size Calibration Kit (Molecular Probes, Inc, Eugene, OR), and expression of CD9 or CD63 by indirect staining, according to the Pospichalova protocol 14. Moreover, we analysed by WB the expression of tetraspanin family protein/CD9, FVIII, Wnt3a ligand. Extracellular vesicles/exosomes from resting cells were considered as reference. For excluding cells from the analysis, cis‐Golgi marker/GM‐130 was considered as staining control. All antibodies used are listed in Table 2.
Statistical analysis
It was performed with paired Student's t‐test, and results were considered significant when P < 0.05.
Results
Isolation and growth of human CPL‐CMC cells
The study included 10 male volunteers under therapy with haemoderivatives for impaired wound healing. After 21 days from seeding, all samples showed an active cell sprouting with spindle‐ or flat‐like shaped cells at early‐phase and cells with fibroblastic morphology at late‐phase (Fig. 1A). Accordingly, a different expression pattern of the inflammatory cytokine TNFα and the protective molecule IL‐10 was observed (Fig. 1A), suggesting a possible correlation among in vivo regeneration following the implantation of CLP‐MB and the in vitro development of cells with anti‐inflammatory functionality, proliferative activity and high grade of stemness. In particular, CPL‐CMC subcultures from 4th to 20th generation demonstrated a doubling population time of 21 ± 1.85 hrs, which was significantly shorter than that of other multipotent cells 12, 13 isolated from human peripheral blood (Fig. 1B). During in vitro short and prolonged expansion, a high positive expression of transcription factors NANOG, SOX2, KLF4, STAT3 was detected (Fig. 1C), suggesting a high stemness grade of CPL‐CMCs. In parallel, normal karyotype of 46 chromosomes with no aneuploidy, tetraploidy or other visible abnormalities was verified (data not shown).
Figure 1.
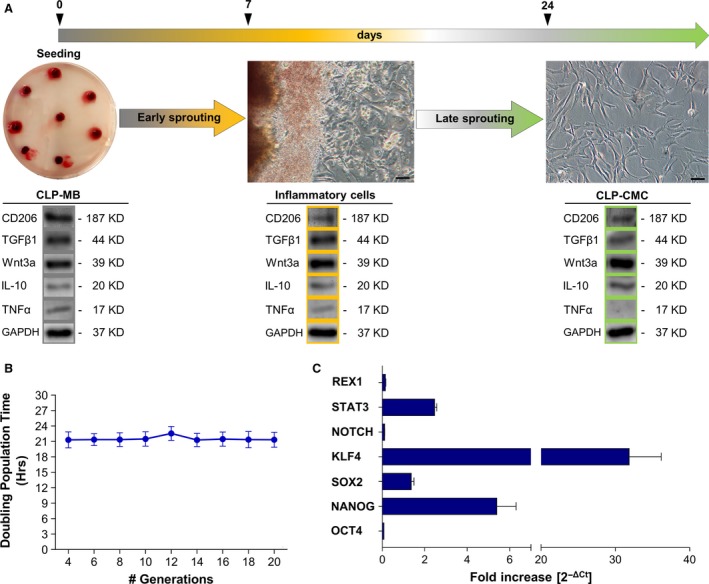
Compared to other blood‐derived stem cell populations, CLP‐CMCs have a distinctive stemness signature. Morphological study and stemness characterization of human CLP‐CMCs. (A) Optical microscopy image of CLP‐MB and CLP‐CMC sprouted cells at early and late‐phases during 21 days of in vitro culturing. Scale bar: 25 μm. (B) Calculation of doubling population time (DPT) over a total of 16 divisions. (C) Gene expression analysis of pluripotency markers by quantitative PCR in cells grown in proliferative medium. The comparative CT method (2−ΔCt ± S.D) was used to quantify the gene expression level. HPRT was considered as housekeeping gene.
Multipotency of CPL‐CMCs
By FACS analysis, the immunophenotypic profile of CMC was determined (Fig. 2). Interestingly, all populations extracted from CPL membranes showed an almost homogenous expression of CD44/HCELL, CD49f and CD184/CXCR4 (Fig. 2A) that are markers related to bone marrow derivation 15, multipotency 16 and migratory potentialities 17. As expected, several markers typically expressed in multipotent stem cells or mediating transendothelial migration, angiogenic potentiality, cell–matrix and cell–cell interactions, and finally immune properties were detected in CPL‐CMCs. They included CD13, CD73, CD105, SSEA4, NG2 as stem cell markers; CD106, CD144, CD146, CD166, von Willebrand factor/vWF as endothelial stem/progenitor phenotype cues; and CD11b, CD18, CD103 as adhesion molecules (Fig. 2B). Glycolipids 18, such as NG2, and heparan sulphate proteoglycans 19, such as syndecan‐1/SDC1 20, 21 and perlecan/PLC 21, are critical environmental regulators of haematopoietic and mesenchymal stem cell niches. As reported in Fig. 2B, CPL‐CMC cells showed to express SDC1 and PLC that, together with CD34 and CD38, were assumed as indicative of both adhesive properties to endothelium and possible derivation from bone marrow. Other markers such as CD14, CD29, CD31, CD45, CD90, CD117, CD133, PDGFRβ were not detected (Fig. 2B). Moreover, CPL‐CMCs demonstrated by FCM to possess immune properties and engraftment potential expressing tetraspanin CD9 22, TGFβ 23 and SIRPα 24 (Fig. 2B). For CD9, a role in migration, adhesion and homing is also considered 25, 26. The null expression of HLA Class II and the low level of HLA Class I confirmed the potentialities of CPL‐CMCs for both allogeneic and autologous therapies 27. Taken together, our collected data demonstrated distinctive immunophenotypic properties of CPL‐CMCs as compared to other blood‐derived stem cell populations.
Figure 2.
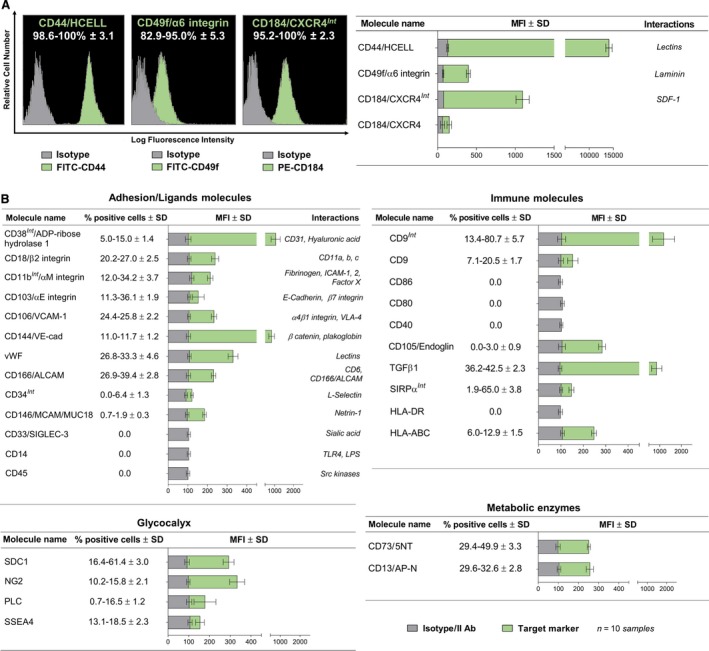
CLP‐CMCs proliferate in vitro without reaching replicative senescence and growth arrest. FCM characterization of CLP‐CMC subcultures under proliferative conditions. Data are reported as mean percentage of positive cells and relative mean fluorescence intensity (MFI) calculated on n = 3 replicas of each sample for all target markers. Samples treated with only secondary antibodies or isotype control antibodies were used as references.
Responsiveness of CPL‐CMC cells to environmental stimuli
As reported in Fig. 3A, CPL‐CMCs showed by WB the expression of numerous growth factors, including EGF, FGF, neurotrophins and Wnt ligands. The synthesis of pro‐ and anti‐inflammatory cytokines (Fig. 3B), receptors of TNFα (Fig. 3B) and matrix remodelling enzymes such as MMP‐2, MMP‐9 and MM‐P13 (Fig. 3C) was detected at mRNA level.
Figure 3.
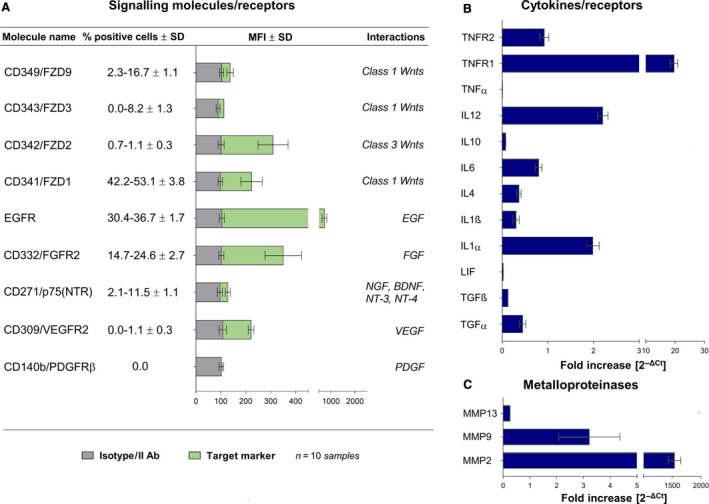
High responsivity to Wnt signals, growth factors, neurotrophins and potential migratory activity are observed in CLP‐CMCs. (A) Evaluation of CLP‐CMC responsivity to environmental stimuli by FCM. (B) Gene expression analysis of immune properties and matrix remodelling enzymes by qPCR.
Differentiative potentialities of CPL‐CMCs
After specific differentiation induction, the plasticity of CMCs towards adipogenic, myogenic and neurogenic lineages was demonstrated evaluating the gene expression of lineage‐specific markers (Fig. 4A, Fig. 5A, Fig. 6A), the accumulation of lipid droplets (Fig. 4B), the acquisition of cell‐orientated distribution (Fig. 5B) and the assembling of cytoskeleton components (Fig. 6B). CPL‐CMCs displayed the gene expression of CD31 (Fig. 7A), an increased protein expression of CD166 and vWF (Fig. 7B) and the formation of capillary‐like network structures (Fig. 7C). The acquired endothelial‐like phenotype was furtherly confirmed by the protein expression of FVIII together with EGF and vWF, in CD9‐tagged mixed population of extracellular vesicles and exosomes (Fig. 7D). In parallel, resting cells cultured on polystyrene culture dishes showed elongated morphology at maximum confluence (Fig. 7C) and expressed Wnt3a by Evs/exs (Fig. 7D).
Figure 4.
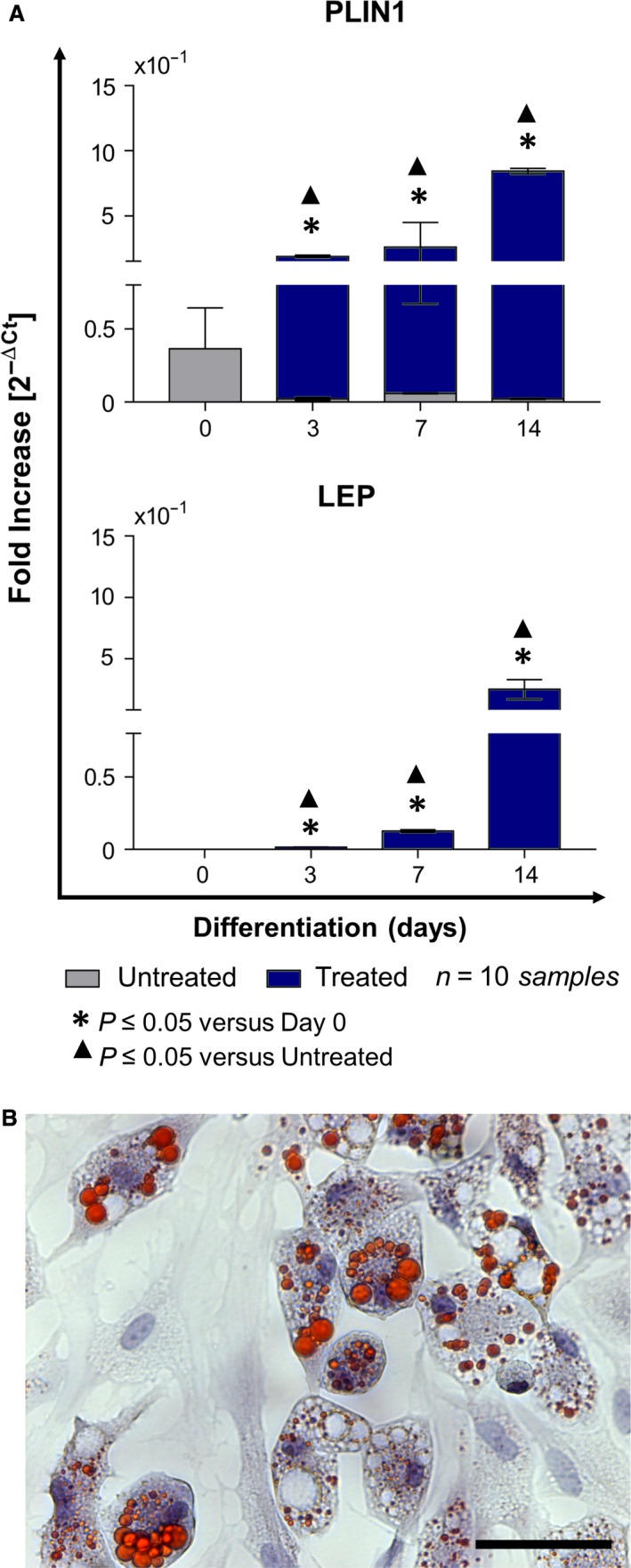
Under permissive in vitro conditions, CLP‐CMCs acquire adipocyte‐like phenotype. (A) Gene expression analysis of perilipin/PLIN1 and leptin/LEP. (B) Detection of cytoplasmic lipid droplets by Oil Red O staining. Nuclei were counterstained with haematoxylin. Scale bar: 25 μm.
Figure 5.
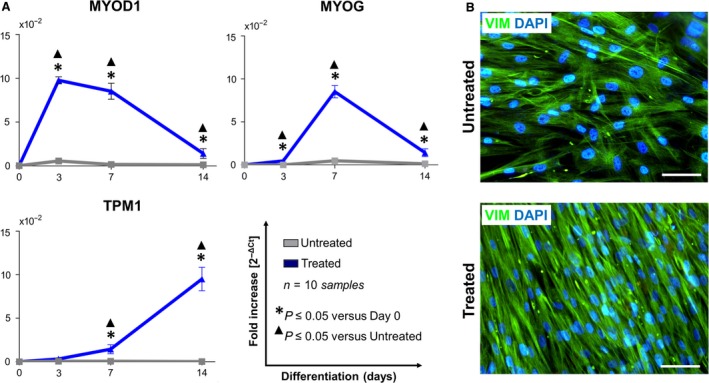
CLP‐CMCs have a potential to undergo myogenic‐like commitment. (A) qPCR analysis of MYOD1, myogenin/MYOG) and tropomyosin/TPM1. (B) Immunofluorescence detection of vimentin. Nuclei were counterstained with Fluoro‐Gel II solution containing DAPI. Scale bar: 25 μm.
Figure 6.
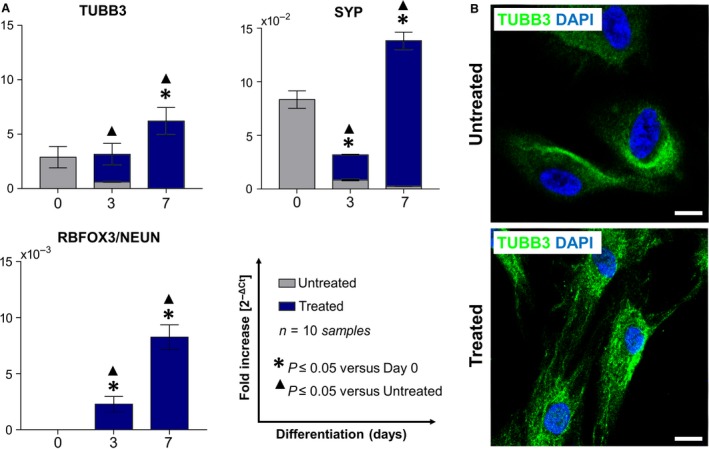
Neurogenic differentiative ability of CLP‐CMCs is demonstrated in vitro. (A) qPCR analysis of ß‐tubulin isotype III/TUBB3, synaptophysin/SYP and neuronal nuclear antigen RBFOX3/NEUN). (B) Immunofluorescence detection of TUBB3. Nuclei were counterstained with Fluoro‐Gel II solution containing DAPI. Scale bar: 10 μm.
Figure 7.
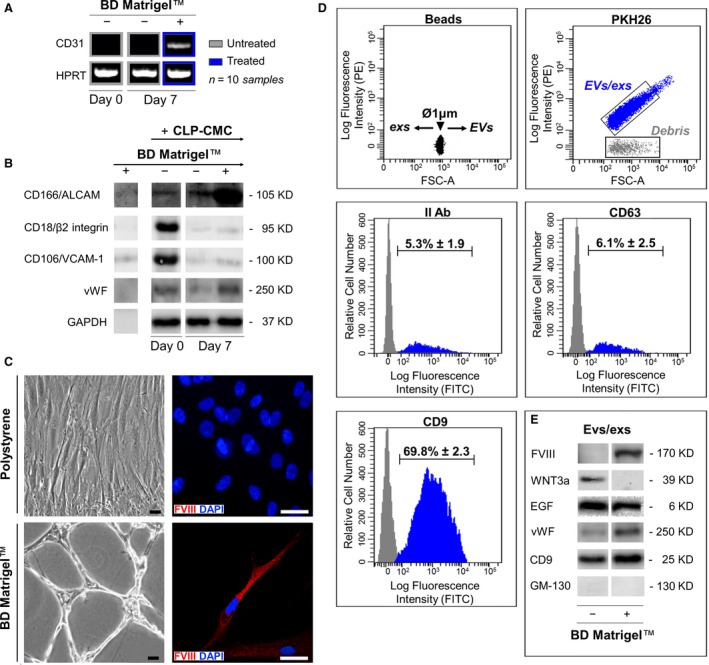
In comparison with resting cells (−), CLP‐CMCs respond to the stimulation with BD MatrigelTM (+) acquiring endothelial‐like phenotype. (A) Analysis of CD31 gene by one‐step RT‐PCR. (B) WB analysis of vascular adhesion molecules (CD18, CD106, CD166), vWF and GAPDH housekeeping protein. (C) Optical microscopy (left side) and immunofluorescence (right side) detecting FVIII in cells counterstained with DAPI. Scale bar: 25 μm. (D) FCM characterization of PKH26‐tagged extracellular vesicles/exosomes [isolated from the conditioned culture media of CLP‐CMCs stimulated with BD MatrigelTM (+) or resting cells (−). The vesicles were discriminated by size, using polystyrene beads as reference, and by expression of characteristic markers, CD9 and CD63. (E) WB analysis of FVIII, WNT3a, EGF, vWF, CD9 in extracellular vesicles/exosomes isolated from the conditioned culture media of CLP‐CMCs stimulated with BD MatrigelTM (+) or resting cells (−). To verify the absence of cells, the expression of cis‐Golgi marker/GM‐130 was considered as negative control.
Discussion
Offering the cellular, physical and chemical cues implicated in haemostatic response and tissue restoration, the haemoderivatives show great potentials for regenerative medicine 28.
Opening new perspectives in autologous stem cell research, L‐PRF products prepared according to Caloprisco's method 10 have been found to deliver stem cell‐like cells with unique phenotypic features, functionality and differentiative potentialities in comparison with endothelial/haematopoietic progenitors 29, 30, mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs) 27, 31, 32, embryonic‐like stem cells 11, 33, 34, 35, 36 and circulating multipotent cells 12, 13, 25, 37. Isolated by minimal in vitro manipulation of CPL membranes, CMC cells showed fibroblast‐like morphology, long‐lasting proliferative activity and high expression of CD44/HCELL, CD49f and CXCR4. The overlapping expression of embryonic (SSEA‐4), mesenchymal (CD13, CD105, CD106, CD73, CD146), haematopoietic (CD38, CD34) and endothelial (CD144, CD166, vWF) stem cell markers highlighted the presence of distinct immature subsets. Moreover, specific immunomodulatory (CD9, SIRPα, pro‐ and anti‐inflammatory cytokines) properties and receptors for Wnt ligands (FZD1/2/3/9), growth factors (EGFR, FGFR2, p75, VEGFR2) and inflammatory stimuli (TNFR1/2) confirmed high environmental responsiveness of CPL‐CMCs. Lacking integrin β1, CD90 and PDGFRβ, CMC cells showed distinct immunophenotype and origin in comparison with circulating multipotent progenitor cells 12, 38 and perivascular multipotent progenitor cells 22, 39. Primed by the interaction with fibrin matrix and P‐selectins on activated platelets 40, 41, the immunophenotypic heterogeneity of CPL‐CMCs has been suggested to reflect a dynamic equilibrium between the acquired responsivity to extracellular signals and the retained self‐renewal potential 42. Based on the expression profile of adhesion molecules (CAMs) and glycolipids/proteoglycans, the physiological and regulatory processes underlying the trafficking of CLP‐CMCs in peripheral blood were defined as similar to those of leucocytes.
Likely haematopoietic stem and progenitor cells, CLP‐CMCs displayed the specialized glycoform of CD44 known as HCELL, suggesting to have a possible haematopoietic origin, bone marrow derivation and transendothelial migration potential. As reported by Sackstein 15, the cell migration from vascular to extravascular compartments develops by two different mechanisms: the canonical multistep process and the so‐called step 2‐bypass pathway. In the canonical pathway, following the initial tethering/rolling contact of blood‐borne cells with endothelium, CXCR4 binds to its cognate ligand CXCL1/SDF‐1, thereby triggering G protein‐coupled VLA‐4 activation, with subsequent firm adhesion and transmigration. In the ‘step 2‐bypass pathway’, the activation of VLA‐4 occurs via G protein‐mediated mechanosignaling after HCELL binding to E‐selectin and/or CD44 interaction with endothelial HA. As suggested by the intracellular expression of CXCR4, the extravasation of CPL‐CMCs is likely to progress by the canonical pathway.
The stemness signature of CPL‐CMCs was further confirmed by both the gene expression of the key components of self‐renewal machinery (NANOG, SOX2, KLF4, STAT3) 43, 44, 45 and the almost homogenous expression of CD49f 46, that is known for transducing survival signals, mediating endothelial progenitor cell migration/adhesion and enhancing multipotency through OCT4, SOX2 and NANOG 12, 43. Collectively, our data pointed out that the self‐renewal of CPL‐CMCs could be regulated likely in embryonic stem cells wherein KLF4 connects STAT3 activation with NANOG expression after interacting with SOX2 and OCT4 45.
A growing body of evidence suggests that L‐PRF products, including CPL‐MB, are attractive biomaterials for regenerative medicine due to their ability to promote in vivo a guided tissue regeneration by ‘endogenous cell homing’. Our findings add a novel aspect to the complex picture of stem cell research demonstrating that CPL‐MB functions as a reservoir of autologous stem cells that could be isolated under permissive conditions by culturing ex vivo the haemoderivatives. Currently, apart from HSC transplantation for haematologic diseases, the clinical experience with somatic stem cell therapy appears promising but still restricted by biological questions about the safety of cell manufacturing, the route of administration, the irreversibility of treatment and the not predictable long‐term survival of engrafted cells 47, 48. Due to these limitations, and considering that, during in vitro expansion of multipotent stem cells, the homing molecules could be lost causing a significant reduction in cell migratory efficiency 49, 50, 51, circulating endogenous stem/progenitor cells could represent a valid and alternative source of immature cells for medical autologous applications 52. Responding to a temporally defined sequence of instructive cues mostly derived from platelets, haematopoietic and not haematopoietic cells from CPL membranes shape a co‐ordinated progression from inflammation to regenerative‐like phases, mimicking the response of living tissues to injury 53, 54, 55, 56. One of the key findings of our study was the recognition of CLP‐CMCs as cells expressing striking morphological and immunophenotypic similarities to alternatively activated M2 macrophages 57 and myeloid angiogenic cells (MACs) 58. Showing an elongated/spindle shape and the expression of mannose receptor/CD206, IL‐10, TGFβ1 and Wnt3a 59, 60, CPL‐CMC cells have been suggested to function by dampening inflammatory responses, scavenging cellular debris and promoting angiogenesis. Furthermore, the engagement of CD206 signalling could be also involved in the cell trafficking of CPL‐CMCs through the stimulated production of MMPs (i.e. MMP‐2, MMP‐9) and matrix remodelling 61. Indeed, in the early‐phase of in vitro culture, CPL membranes showed a significant cell sprouting, thus indirectly suggesting that a proteolytic activity and fibrinolysis were active. The fibrinolytic system, with its main player plasmin, plays a crucial role in cell migration, bioavailability of growth factors and regulation of other protease systems during inflammation and tissue regeneration 28, 62. As the internalization and the degradation of plasminogen activator require the mannose receptor 63, it is likely that CPL‐CMCs could modulate the process of fibrinolysis within CPL membranes for regulating their proliferation, differentiation 62, 64, 65 and migration 61.
Finally, based on their abilities to respond to differentiative stimuli, a broad range of medical applications of CLP‐CMCs could have been suggested, including the treatment of (i) blood disorders, such as haemophilia 66; and (ii) defects of adipose tissue, skeletal muscle and nervous system 67.
Conclusion
As a direct evolution of fibrin glue technologies, autologous platelet preparations are a new generation of biomaterials used in regenerative medicine for improving tissue healing. In this study, we demonstrated that the leucocyte‐ and platelet‐rich fibrin product called CPL‐MB functions not only as a reservoir of bioactive factors (PDGF, TGF‐β, VEGF, fibrinogen, fibronectin and vitronectin), useful to recruit stem cells to wound site, but acts also as an artificial stem cell niche containing haematopoietic and multipotent cells, similarly to bone marrow and perivascular niches. Our in vitro model provides the first evidence that multipotent cells could be mobilized to peripheral blood under physiological conditions and not only under stress conditions (i.e. inflammation, tissue damage, stimulation by drugs or growth factors), as commonly reported. Likely the haematopoietic stem cell niche, CPL‐MB results as a complex milieu that regulates, by structural and bioactive factors, the survival, expansion, differentiation and transendothelial migration of immature cells. Although a growing body of evidence suggests the existence of multipotent cells in peripheral blood, to date, the use of blood as an alternative source of autologous stem cells in regenerative medicine is limited by several important questions concerning the predictability of successful isolation and ex vivo expansion by a standardized protocol. Produced according to Italian standards of quality assurance and Caloprisco's method, CPL‐MB could represent a valid strategy to bypass the intrinsic heterogeneity of blood samples and to normalize the cell content of blood derivatives for obtaining autologous cells with a defined stemness signature.
Conflict of interest
The authors indicated no potential conflict of interests.
Author contributions
D.L.R. and P.P.P.: involved in the study conception and design; D.L.R.: involved in the data analysis and interpretation, manuscript writing and final approval of manuscript; B.T. and S.S.: involved in the collection and assembly of data and contributed to manuscript writing; B.A., P.I. and C.S.: contributed to the preparation and quality control of CLP‐MB; A.A.: contributed to scientific and financial support; C.C.: contributed to collection and assembly of data; and C.M.T. and P.P.P.: contributed to data interpretation and final approval of manuscript.
Acknowledgements
This study was supported by Foundation for Biology and Regenerative Medicine, Tissue Engineering and Signaling (TES) ONLUS (Padova, Italy), Associazione Volontari Italiani del Sangue/A.V.I.S. Regionale Veneto (Treviso, Italy) and Associazione Bellunese Volontari del Sangue/A.B.V.S (Belluno, Italy).
References
- 1. Burnouf T, Goubran HA, Chen T‐M, et al Blood‐derived biomaterials and platelet growth factors in regenerative medicine. Blood Rev. 2013; 27: 77–89. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2. Marenzi G, Riccitiello F, Tia M, et al Influence of Leukocyte‐ and Platelet‐Rich Fibrin (L‐PRF) in the healing of simple postextraction sockets: a split‐mouth study. Biomed Res Int. 2015; 2015: 369273, 6 pages. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3. Dohan Ehrenfest DM, Pinto NR, Pereda A, et al The impact of the centrifuge characteristics and centrifugation protocols on the cells, growth factors, and fibrin architecture of a leukocyte‐ and platelet‐rich fibrin (L‐PRF) clot and membrane. Platelets. 2017; 2: 1–14. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4. Castro AB, Meschi N, Temmerman A, et al Regenerative potential of leucocyte‐ and platelet‐rich fibrin. Part A: intra‐bony defects, furcation defects and periodontal plastic surgery. A systematic review and meta‐analysis. J Clin Periodontol. 2017; 44: 67–82. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5. Dohan Ehrenfest DM, Bielecki T, Mishra A, et al In search of a consensus terminology in the field of platelet concentrates for surgical use: platelet‐rich plasma (PRP), platelet‐rich fibrin (PRF), fibrin gel polymerization and leukocytes. Curr Pharm Biotechnol. 2012; 13: 1131–7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6. Schär MO, Diaz‐Romero J, Kohl S, et al Platelet‐rich concentrates differentially release growth factors and induce cell migration in vitro. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2015; 473: 1635–43. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7. Bielecki T, Dohan Ehrenfest DM. Leukocyte‐ and platelet‐rich Plasma (L‐PRP)/fibrin (L‐PRF) in medicine ‐ past, present, future. Curr Pharm Biotechnol. 2012; 13: i–ii. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8. Masoudi E, Ribas J, Kaushik G, et al Platelet‐rich blood derivatives for stem cell‐based tissue engineering and regeneration. Curr Stem Cell Reports. 2016; 2: 33–42. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9. Hart J. Inflammation 1: its role in the healing of acute wounds. J Wound Care. 2002; 11: 205–9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10. Caloprisco G, Borean A, De Angeli S, et al New method to produce hemocomponents for regenerative use from peripheral blood: integration among platelet growth factors monocytes and stem cells. Transfus Apher Sci. 2010; 42: 117–24. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11. Kucia MJ, Wysoczynski M, Wu W, et al Evidence that very small embryonic‐like stem cells are mobilized into peripheral blood. Stem Cells. 2008; 26: 2083–92. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12. Cesselli D, Beltrami AP, Rigo S, et al Multipotent progenitor cells are present in human peripheral blood. Circ Res. 2009; 104: 1225–34. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13. Scapin G, Bertalot T, Vicentini N, et al Neuronal commitment of human circulating multipotent cells by carbon nanotube‐polymer scaffolds and biomimetic peptides. Nanomedicine (Lond). 2016;. https://doi.org/10.2217/nnm-2016-0150. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14. Pospichalova V, Svoboda J, Dave Z, et al Simplified protocol for flow cytometry analysis of fluorescently labeled exosomes and microvesicles using dedicated flow cytometer. J Extracell Vesicles. 2015; 4: 25530, 15 pages. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15. Sackstein R. The biology of CD44 and HCELL in hematopoiesis: the “step 2‐bypass pathway” and other emerging perspectives. Curr Opin Hematol. 2011; 18: 239–48. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16. Yu K‐R, Yang S‐R, Jung J‐W, et al CD49f enhances multipotency and maintains stemness through the direct regulation of OCT4 and SOX2. Stem Cells. 2012; 30: 876–87. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17. Kucia M, Reca R, Miekus K, et al Trafficking of normal stem cells and metastasis of cancer stem cells involve similar mechanisms: pivotal role of the SDF‐1‐CXCR4 axis. Stem Cells. 2005; 23: 879–94. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18. Gang EJ, Bosnakovski D, Figueiredo CA, et al SSEA‐4 identifies mesenchymal stem cells from bone marrow. Blood. 2007; 109: 1743–51. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19. Rodgers KD, San Antonio JD, Jacenko O. Heparan sulfate proteoglycans: a GAGgle of skeletal‐hematopoietic regulators. Dev Dyn. 2008; 237: 2622–42. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20. Corless CL, Mendoza A, Collins T, et al Colocalization of thrombospondin and syndecan during murine development. Dev Dyn. 1992; 193: 346–58. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21. Chen X‐D, Dusevich V, Feng JQ, et al Extracellular matrix made by bone marrow cells facilitates expansion of marrow‐derived mesenchymal progenitor cells and prevents their differentiation into osteoblasts. J Bone Miner Res. 2007; 22: 1943–56. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22. Crisan M, Chen C‐W, Corselli M, et al Perivascular multipotent progenitor cells in human organs. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2009; 1176: 118–23. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23. Haak‐Frendscho M, Wynn TA, Czuprynski CJ, et al Transforming growth factor‐beta 1 inhibits activation of macrophage cell line RAW 264.7 for cell killing. Clin Exp Immunol. 1990; 82: 404–10. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24. Saito Y, Ellegast JM, Rafiei A, et al Peripheral blood CD34 + cells efficiently engraft human cytokine knock‐in mice. Blood. 2016; 128: 1829–33. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25. Meng X, Ichim TE, Zhong J, et al Endometrial regenerative cells: a novel stem cell population. J Transl Med. 2007; 5: 57, 10 pages. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26. Leung KT, Chan KYY, Ng PC, et al The tetraspanin CD9 regulates migration, adhesion, and homing of human cord blood CD34 + hematopoietic stem and progenitor cells. Blood. 2011; 117: 1840–50. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27. Murphy MB, Moncivais K, Caplan AI. Mesenchymal stem cells: environmentally responsive therapeutics for regenerative medicine. Exp Mol Med. 2013; 45: e54, 16 pages. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28. de Boer HC, Verseyden C, Ulfman LH, et al Fibrin and activated platelets cooperatively guide stem cells to a vascular injury and promote differentiation towards an endothelial cell phenotype. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2006; 26: 1653–9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29. Medina RJ, Barber CL, Sabatier F, et al Endothelial progenitors: a consensus statement on nomenclature. Stem Cells Transl Med. 2017; 6: 1316–20. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30. Challen GA, Boles NC, Chambers SM, et al Distinct hematopoietic stem cell subtypes are differentially regulated by TGF‐beta1. Cell Stem Cell. 2010; 6: 265–78. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31. Caplan AI. Adult mesenchymal stem cells for tissue engineering versus regenerative medicine. J Cell Physiol. 2007; 213: 341–7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32. Kögler G, Sensken S, Airey JA, et al A new human somatic stem cell from placental cord blood with intrinsic pluripotent differentiation potential. J Exp Med. 2004; 200: 123–35. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33. Ratajczak MZ, Zuba‐Surma EK, Machalinski B, et al Very Small Embryonic‐Like (VSEL) stem cells: purification from adult organs, characterization, and biological significance. Stem Cell Rev. 2008; 4: 89–99. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34. Zuba‐Surma EK, Kucia M, Ratajczak J, et al “Small stem cells” in adult tissues: very small embryonic‐like stem cells stand up!. Cytom Part A. 2009; 75A: 4–13. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35. Ratajczak MZ. A novel view of the adult bone marrow stem cell hierarchy and stem cell trafficking. Leukemia. 2015; 29: 776–82. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36. De Miguel MP, Arnalich Montiel F, Lopez Iglesias P, et al Epiblast‐derived stem cells in embryonic and adult tissues. Int J Dev Biol. 2009; 53: 1529–40. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37. Bockeria L, Bogin V, Bockeria O, et al Endometrial regenerative cells for treatment of heart failure: a new stem cell enters the clinic. J Transl Med. 2013; 11: 56, 8 pages. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38. Roufosse CA, Direkze NC, Otto WR, et al Circulating mesenchymal stem cells. Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 2004; 36: 585–97. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39. Crisan M, Yap S, Casteilla L, et al A perivascular origin for mesenchymal stem cells in multiple human organs. Cell Stem Cell. 2008; 3: 301–13. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40. Koedam JA, Cramer EM, Briend E, et al P‐selectin, a granule membrane protein of platelets and endothelial cells, follows the regulated secretory pathway in AtT‐20 cells. J Cell Biol. 1992; 116: 617–25. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41. Ma Y‐Q, Plow EF, Geng J‐G. P‐selectin binding to P‐selectin glycoprotein ligand‐1 induces an intermediate state of alphaMbeta2 activation and acts cooperatively with extracellular stimuli to support maximal adhesion of human neutrophils. Blood. 2004; 104: 2549–56. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42. Graf T, Stadtfeld M. Heterogeneity of embryonic and adult stem cells. Cell Stem Cell. 2008; 3: 480–3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43. Loh Y‐H, Wu Q, Chew J‐L, et al The Oct4 and Nanog transcription network regulates pluripotency in mouse embryonic stem cells. Nat Genet. 2006; 38: 431–40. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44. Matsuda T, Nakamura T, Nakao K, et al STAT3 activation is sufficient to maintain an undifferentiated state of mouse embryonic stem cells. EMBO J. 1999; 18: 4261–9. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45. Zhang P, Andrianakos R, Yang Y, et al Kruppel‐like factor 4 (Klf4) prevents embryonic stem (ES) cell differentiation by regulating Nanog gene expression. J Biol Chem. 2010; 285: 9180–9. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46. Yu K‐R, Yang S‐R, Jung J‐W, et al CD49f enhances multipotency and maintains stemness through the direct regulation of OCT4 and SOX2. Stem Cells. 2012; 30: 876–87. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47. Herberts CA, Kwa MSG, Hermsen HPH. Risk factors in the development of stem cell therapy. J Transl Med. 2011; 9: 29, 14 pages. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 48. Mousavinejad M, Andrews PW, Shoraki EK. Current biosafety considerations in stem cell therapy. Cell J. 2016; 18: 281–7. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 49. Steingen C, Brenig F, Baumgartner L, et al Characterization of key mechanisms in transmigration and invasion of mesenchymal stem cells. J Mol Cell Cardiol. 2008; 44: 1072–84. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 50. Tondreau T, Meuleman N, Stamatopoulos B, et al In vitro study of matrix metalloproteinase/tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinase production by mesenchymal stromal cells in response to inflammatory cytokines: the role of their migration in injured tissues. Cytotherapy. 2009; 11: 559–69. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 51. Devine SM, Cobbs C, Jennings M, et al Mesenchymal stem cells distribute to a wide range of tissues following systemic infusion into nonhuman primates. Blood. 2003; 101: 2999–3001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 52. Chen F‐M, Wu L‐A, Zhang M, et al Homing of endogenous stem/progenitor cells for in situ tissue regeneration: promises, strategies, and translational perspectives. Biomaterials. 2011; 32: 3189–209. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 53. Zhou D, Huang C, Lin Z, et al Macrophage polarization and function with emphasis on the evolving roles of coordinated regulation of cellular signaling pathways. Cell Signal. 2014; 26: 192–7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 54. Mosser DM, Edwards JP. Exploring the full spectrum of macrophage activation. Nat Rev Immunol. 2008; 8: 958–69. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 55. Lawrence T, Natoli G. Transcriptional regulation of macrophage polarization: enabling diversity with identity. Nat Rev Immunol. 2011; 11: 750–61. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 56. Lee Y‐L, Lee L‐W, Su C‐Y, et al Virally inactivated human platelet concentrate lysate induces regulatory T cells and immunosuppressive effect in a murine asthma model. Transfusion. 2013; 53: 1918–28. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 57. Ferrari G, Mavilio F. Myogenic stem cells from the bone marrow: a therapeutic alternative for muscular dystrophy? Neuromuscul Disord. 2002; 12(Suppl 1): S7–10. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 58. Medina RJ, O'Neill CL, O'Doherty TM, et al Myeloid angiogenic cells act as alternative M2 macrophages and modulate angiogenesis through interleukin‐8. Mol Med. 2011; 17: 1045–55. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 59. Geem D, Medina‐Contreras O, Kim W, et al Isolation and characterization of dendritic cells and macrophages from the mouse intestine. J Vis Exp. 2012; 63: e4040, 6 pages. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 60. Cosín‐Roger J, Ortiz‐Masiá D, Calatayud S, et al M2 macrophages activate WNT signaling pathway in epithelial cells: relevance in ulcerative colitis. PLoS ONE. 2013; 8: e78128, 12 pages. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 61. Almalki SG, Agrawal DK. Effects of matrix metalloproteinases on the fate of mesenchymal stem cells. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2016; 7: 129, 12 pages. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 62. Heissig B, Lund LR, Akiyama H, et al The plasminogen fibrinolytic pathway is required for hematopoietic regeneration. Cell Stem Cell. 2007; 1: 658–70. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 63. Allavena P, Chieppa M, Monti P, et al From pattern recognition receptor to regulator of homeostasis: the double‐faced macrophage mannose receptor. Crit Rev Immunol. 2004; 24: 179–92. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 64. Gong Y, Hoover‐Plow J. The plasminogen system in regulating stem cell mobilization. J Biomed Biotechnol. 2012; 2012: 1–7. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 65. Andronicos NM, Chen EI, Baik N, et al Proteomics‐based discovery of a novel, structurally unique, and developmentally regulated plasminogen receptor, Plg‐RKT, a major regulator of cell surface plasminogen activation. Blood. 2010; 115: 1319–30. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 66. Fomin ME, Togarrati PP, Muench MO. Progress and challenges in the development of a cell‐based therapy for hemophilia A. J Thromb Haemost. 2014; 12: 1954–65. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 67. Muller‐Sieburg CE, Sieburg HB, Bernitz JM, et al Stem cell heterogeneity: implications for aging and regenerative medicine. Blood. 2012; 119: 3900–7. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


