Fig. 1.
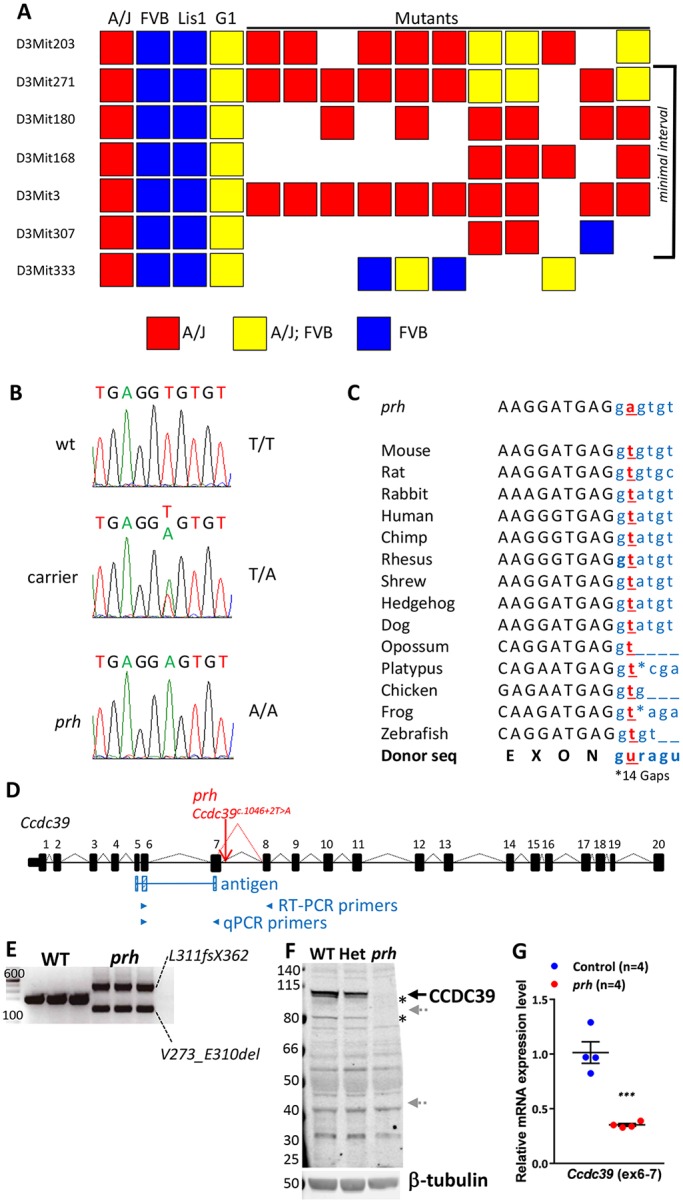
The prh mutation (chr3:g.33731448A>T) is at a conserved mRNA splicing donor site within Ccdc39 intron 7 (Ccdc39c.930+2T>A). (A) Genetic map of the region containing prh bounded proximally by D3Mit271 and distally by D3Mit307. (B) Sanger sequencing traces of the genomic DNA showing a homozygous chr3:g.33731448A>T change in the prh sequence. (C) The conserved splice donor site sequence (AGguragu) within Ccdc39 intron 7 in 14 different species from the UCSC genome database and nucleotide change found in prh (Ccdc39c.930+2T>A, red). Protein coding and intronic sequences are shown in black upper and blue lower case, respectively. (D) The wild-type Ccdc39 gene (from the UCSC genome database) and with the prh mutation. (E) RT-PCR on P1 brain showing two abnormal Ccdc39 transcripts, but no native isoform of Ccdc39, in the prh mutants. DNA size marker (left, bp). (F) Western blotting with CCDC39 antibody on P8 brain lysate from wild type (WT), heterozygous (Het) and prh mutant. CCDC39 protein was not found in the prh mutants and was reduced in the heterozygotes. No shorter protein products are detected of the size predicted to be encoded by the abnormal Ccdc39 mRNAs (∼99 kDa and ∼40 kDa, gray arrows). The CCDC39 isoforms are also missing in the prh mutant (asterisks). β-tubulin, loading control. (G) Quantitative RT-PCR on P1 brain RNA showing reduced Ccdc39 mRNA levels in the prh mutants. The locations of qPCR primers are indicated in D. ***P<0.001.
