Abstract
Systemic sclerosis (SSc) is a multisystemic autoimmune connective tissue disorder; in the gastrointestinal tract, the esophagus is the most commonly affected organ. Symptoms of esophageal disease are due to gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD) and esophageal motor dysfunction. Since the development of high-resolution manometry (HRM), this method has been preferred for the study of SSc patients with esophageal involvement. Using HRM, classic scleroderma esophagus, defined as absent or ineffective peristalsis of the distal esophagus in combination with a hypotensive lower esophageal sphincter, was found in as many as 55% of SSc patients. Endoscopy is the appropriate test for evaluating dysphagia and identifying evidence and possible complications of GERD. In the therapeutic area, treatment ranges from general supportive measures to the administration of drugs such as proton pump inhibitors and/or prokinetics. However, as many SSc patients do not respond to existing therapies, there is an urgent need for new therapeutic modalities. Buspirone, a 5-hydroxytryptamine 1A receptor agonist, could be a putative therapeutic option, as it was found to exert a significant beneficial effect in SSc patients with esophageal involvement. This review summarizes our knowledge concerning the evaluation and management of esophageal manifestations in SSc patients, including emerging therapeutic modalities.
Keywords: Systemic sclerosis, scleroderma esophagus, high-resolution manometry, 5-HT1A receptor agonist, buspirone
Introduction
Systemic sclerosis (SSc), a connective tissue disease of unknown origin, occurs most frequently in females aged 40-65 years (female:male ratio 8:2). Gastrointestinal tract involvement is very common and the esophagus is the most frequently affected part (up to 90% of patients) [1-4]. The pathogenesis of esophageal involvement in SSc is multifactorial. On the basis of clinical, immunological, and histopathological observations, three pathways have been proposed as being involved in scleroderma: vascular alterations, an abnormal immune response, and disturbances in the regulation of connective tissue metabolism. The pathogenesis of SSc is initiated with vascular endothelial activation (vasculopathy), reflected in recurrent episodes of reperfusion and vasoconstriction, and this progresses to episodic and sustained tissue ischemia with inappropriate immunological and reparative changes. Excessive deposition of collagen and collagen matrix from activated profibrogenic fibroblasts ensues, resulting in fibrosis and replacement of tissue in the skin and multiple internal organs, including the esophagus [5-11].
Symptoms and complications of esophageal dysfunction in SSc
Patients with SSc and esophageal involvement usually report two types of symptoms: due to gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD), such as heartburn and regurgitation, and/or due to esophageal dysmotility, such as dysphagia and chest pain [5,12]. Dysphagia may not only represent a symptom of dysmotility, but could also be the result of Candida esophagitis or of peptic stricture formation due to complicated GERD [13]. Overall, the incidence of esophageal symptoms in SSc has been estimated at between 40% and 80%, even though a percentage of patients are totally asymptomatic despite their documented esophageal disease [5,12-16].
Complications of GERD, such as peptic strictures occur in up to 30% of patients [3,13,17-19], whereas Barrett’s esophagus has been found in up to 37% [13,18-20]. Moreover, GERD may contribute to interstitial lung disease via recurrent micro-aspiration of acid causing bronchoconstriction [21]. Although SSc patients have a risk of developing esophageal carcinoma, the use of proton pump inhibitors (PPIs) has decreased its incidence [22].
Diagnosis
Esophageal involvement can be assessed by the following methods:
Manometry
Classic manometry was, until recently, the gold standard method for the detection and assessment of esophageal dysmotility, especially in the early stages of esophageal involvement in SSc patients. The typical manometric findings include decreased lower esophageal sphincter (LES) pressure and absent or ineffective peristalsis of the distal esophagus [12,19]. The combination of distal aperistalsis and a hypotensive LES is called classic scleroderma esophagus. Since the development of high-resolution manometry (HRM), this method has been preferred for the study of SSc patients [23]. HRM, using multiple closely spaced pressure sensors, allows a better assessment of the whole esophagus and especially of the LES.
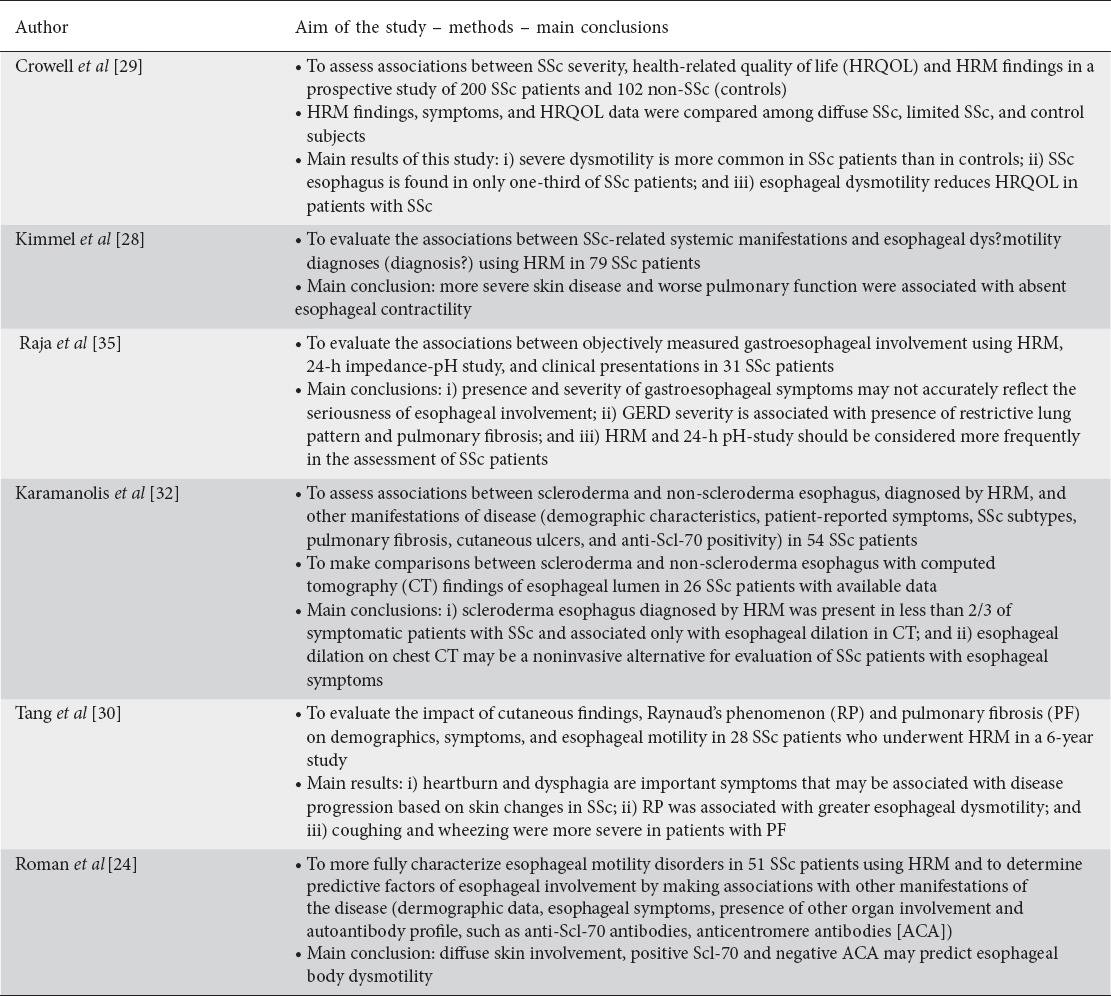
With HRM, the overall frequency of manometric abnormalities reported in SSc patients has been very high, affecting up to 75-80% of them. Hypotensive LES was encountered in more than 50% of patients, whereas esophageal body dysmotility was present in more than 60% of patients. Classic scleroderma esophagus was found in as many as 55% of patients [24-30]. In a well-characterized cohort of patients with SSc, we observed, using recent criteria for esophageal motility diagnosis [31], that classic scleroderma esophagus was the most prevalent contractility pattern in SSc patients [32]. Table 1 summarizes studies demonstrating the importance of HRM.
Table 1.
Studies that evaluated the important role of high-resolution manometry (HRM) in systemic sclerosis (SSc) disease
pH monitoring
Esophageal pH monitoring, with or without impedance, is considered the gold standard for gastroesophageal reflux detection. However, its role in the management of SSc patients is limited and in clinical practice it is only used in patients with resistant reflux symptoms. Thus, only few studies assess pH parameters in patients with SSc. Abnormal pH monitoring has been seen in up to 85% of patients [33-35]. Although the number of reflux events is similar between SSc patients and non-scleroderma patients, a small but well-designed study [36] found that SSc patients showed a greater number of events with longer duration. A recent retrospective study suggested a role of pH monitoring as a prognostic factor in patients with SSc and interstitial lung disease [37]. Esophageal pH monitoring was performed in 10 SSc patients referred for lung transplantation and severe reflux, calculated via a self-administered score of pH monitoring. The authors found that the presence of abnormal pH was a better predictor of survival than abnormal pulmonary function tests. Thus, esophageal pH monitoring should be considered early in SSc patients with early-stage lung disease, as this test could identify those in whom intense anti-reflux therapy should be introduced to prevent GERD and its detrimental effects in patients awaiting lung transplantation.
Endoscopy
Upper endoscopy is the appropriate test for evaluating dysphagia, identifying evidence of GERD, such as esophagitis, and identifying possible reflux complications, such as esophageal stenosis, Barrett’s esophagus and esophageal adenocarcinoma. Esophageal manifestations are more common in SSc patients than in the general population; thus, endoscopy should be performed in patients with SSc, even if they do not report reflux symptoms, as it is well known that symptoms are not predictive for the presence of esophagitis [18]. Prevalence of endoscopic esophagitis has been reported in up to 65% [13,14,18,33], whereas Barrett’s esophagus was found in up to 7% of SSc patients [38]. A recent, prospective study that included fifty SSc patients with Barrett’s esophagus (40 without and 10 with dysplasia) showed an overall 0.7% year rate of progression to adenocarcinoma, not greater than that seen in the general population [39].
Treatment
In general, the treatment is supportive and patients are advised to chew food well, avoid big bites, and use water as complimentary to solid foods. Moreover, in symptomatic SSc patients with esophageal involvement drug administration targeting either GERD symptoms or dysmotility symptoms could be offered.
GERD therapies
PPIs are considered as the standard of care for the treatment of GERD in SSc patients. However, the effective dose of PPIs for alleviating reflux symptoms in SSc patients is still under investigation. Few studies using standard doses of PPIs reported symptomatic improvement and healing of esophagitis [40-42]. Even though PPIs demonstrated a clear short-term benefit, the long-term efficacy of these drugs was not sustained and there was no evidence that progression of esophageal dysfunction was prevented [41]. We have to keep in mind that an estimated 40% of SSc patients showed no response to a standard PPI dose. Thus, a two- to fourfold increase in the daily dose of PPIs, in order to gain better symptom control in patients with a partial response, is common practice [43]. A recent study, involving 148 SSc GERD patients, some of whom showed partial response to PPIs, compared the efficacy of a combination of omeprazole with domperidone, or with alginic acid, in alleviating reflux symptoms. The authors concluded that the addition of domperidone or alginic acid to omeprazole therapy was effective in the majority of non-responsive patients [44]. However, even with this approach, approximately 20% of patients did not respond. This study highlights the necessity for more potent anti-reflux drugs in order to reduce the severity and frequency of reflux symptoms in SSc patients. Endoscopic procedures, such as dilation with balloon dilators, have been proposed for use in patients with peptic strictures related to GERD [43].
Motility therapies
According to the pathophysiology of SSc, motility abnormalities could be among the mechanisms underlying GERD pathogenesis. Thus, various prokinetic drugs have been used in the treatment of SSc patients with esophageal involvement, such as metoclopramide, erythromycin, and cisapride [45-47]. It has been reported that metoclopramide and erythromycin may increase LES pressure in SSc patients [48-50], while cisapride has been shown to increase LES pressure and the amplitude of distal esophageal body peristalsis [45,51]. Based on these results, prokinetics are used in clinical practice. However, experience with the use of prokinetic drugs in SSc patients is bibliographically limited and has had controversial results. Moreover, their use is restricted because of safety profile issues (central nervous system, cardiovascular side effects).
Domperidone, a peripheral dopamine antagonist, is currently the most common prokinetic agent used in clinical practice in patients with SSc, although data regarding its effect on esophageal motility are conflicting [46,47]. A recent study, involving 10 SSc patients who underwent HRM before and after administration of 10 mg domperidone, challenged the drug’s effect on motility. Acute administration of domperidone had no effect upon any manometric parameters compared to the baseline values [52]. Moreover, there is some concern over safety issues, as domperidone has been associated with cases of sudden death due to its cardiac side effects [53,54].
Emerging therapies
Buspirone, an orally available 5-hydroxytryptamine 1A (5-HT1A) receptor agonist, has shown a beneficial effect on esophageal motor function in healthy subjects. Thus, we studied the differences in HRM parameters in 20 SSc patients with esophageal involvement before and after acute administration of 10 mg buspirone. We observed a significant increase in the LES resting pressure in up to 80% of SSc patients, from 9.4±2.6 to 11.5±3.3 mmHg (P=0.0002). Moreover, a non-significant trend (P=0.09) toward an increased amplitude of esophageal body motility was also observed [52].
Based on this result, buspirone was administered in a 4-week open-label study that included SSc patients with symptomatic esophageal involvement despite PPI administration [55]. Twenty-two consecutive SSc patients underwent HRM before and after a 4-week administration of 20 mg of buspirone, so that the efficacy of long-term buspirone administration on esophageal motor dysfunction and on esophageal symptoms could be evaluated. Following buspirone administration for 4 weeks, an increase in the LES resting pressure was observed in 15 (68%) patients, with an enhancement from 7.7±3.9 to 12.2±4.6 mmHg (P<0.00005). In an attempt to identify prognostic factors for the beneficial effect of buspirone, a moderate, but significant, inverse correlation between the increase in LES resting pressure and supra-aortic diameter, measured by chest computed tomography (r=-0.589, P=0.017) was found. Moreover, the severity of heartburn and regurgitation significantly decreased at 4 weeks compared with baseline (P=0.001, and P=0.022, respectively), whereas no significant improvement was found in the severity scores of chest pain and dysphagia. Concerning the safety issues, buspirone was well tolerated by all patients who completed the study and only self-limited adverse effects that did not affect their daily activities were observed.
Surgical management
Anti-reflux procedures, such as Nissen fundoplication, are generally considered suboptimal in SSc patients with reflux symptoms, because of the profound esophageal dysmotility seen in this disease. Indeed, 38-71% of patients who underwent fundoplication developed postoperative dysphagia, even though an improvement in the severity of reflux symptoms and in esophageal acid exposure has been reported after surgical intervention [56-58]. In an attempt to identify a better surgical option for the management of SSc-associated gastroesophageal reflux, a recent review of different surgical series proposed Roux-en-Y gastric bypass as an alternative. The authors showed that patients undergoing Roux-en-Y gastric bypass reported better postoperative GERD-related quality of life and less dysphagia compared with those undergoing fundoplication [59]. However, we have to keep in mind that Roux-en-Y should also be pursued with caution, because of the small intestinal dysmotility in SSc patients and the possibility of bacterial overgrowth.
Fig. 1 demonstrates an algorithm for the therapeutic management of SSc.
Figure 1.
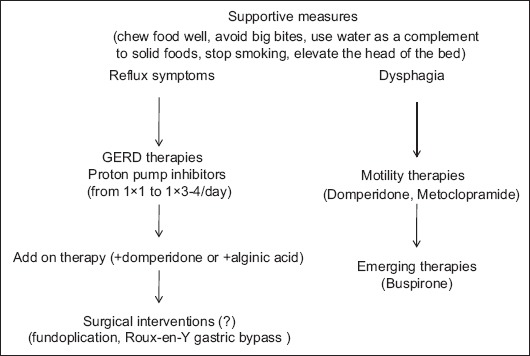
Algorithm for therapeutic approach to SSc patients with esophageal manifestations
SSc, systemic sclerosis; GERD, gastroesophageal reflux disease.
Concluding remarks
Esophageal involvement in SSc is common, occurring in up to 90% of patients. It carries significant morbidity and mortality, which can be improved by its early diagnosis and treatment. Nowadays, HRM is the gold standard method used to identify SSc patients with esophageal motility disorders. Treatment for SSc-induced esophageal impairment, which includes PPIs, prokinetics and endoscopic interventions, is still a challenging process. Buspirone, a 5-HT1A receptor agonist, was found to exert a significant beneficial effect on both manometric and clinical parameters in the treatment of SSc patients with esophageal involvement, creating new data relating to future therapeutic modalities in that category of patients.
Biography
National and Kapodistrian University of Athens, “Laikon” General Hospital, Athens, Greece
Footnotes
Conflict of Interest: None
References
- 1.Varga J, Abraham D. Systemic sclerosis:a prototypic multisystem fibrotic disorder. J Clin Invest. 2007;117:557–567. doi: 10.1172/JCI31139. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Villadsen GE, Storkholm J, Zachariae H, Hendel L, Bendtsen F, Gregersen H. Oesophageal pressure-cross-sectional area distributions and secondary peristalsis in relation to subclassification of systemic sclerosis. Neurogastroenterol Motil. 2001;13:199–210. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-2982.2001.00259.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Clements PJ, Becvar R, Drosos AA, Ghattas L, Gabrielli A. Assessment of gastrointestinal involvement. Clin Exp Rheumatol. 2003;21:S15–S18. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Kirby DF, Chatterjee S. Evaluation and management of gastrointestinal manifestations in scleroderma. Curr Opin Rheumatol. 2014;26:621–629. doi: 10.1097/BOR.0000000000000117. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Ebert EC. Esophageal disease in scleroderma. J Clin Gastroenterol. 2006;40:769–775. doi: 10.1097/01.mcg.0000225549.19127.90. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Treacy WL, Baggenstoss AH, Slocumb CH, Code CF Scleroderma of the esophagus. A correlation of histologic and physiologic finding. Ann Intern Med. 1963;59:351–356. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-59-3-351. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Cohen S. The gastrointestinal manifestations of scleroderma:pathogenesis and management. Gastroenterology. 1980;79:155–166. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Attar A. [Digestive manifestations in systemic sclerosis] Ann Med Interne (Paris) 2002;153:260–264. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Roberts CG, Hummers LK, Ravich WJ, Wigley FM, Hutchins GM. A case-control study of the pathology of oesophageal disease in systemic sclerosis (scleroderma) Gut. 2006;55:1697–1703. doi: 10.1136/gut.2005.086074. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Gilliam AC. Scleroderma. Curr Dir Autoimmun. 2008;10:258–279. doi: 10.1159/000131502. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Gabrielli A, Avvedimento EV, Krieg T. Scleroderma. N Engl J Med. 2009;360:1989–2003. doi: 10.1056/NEJMra0806188. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Ntoumazios SK, Voulgari PV, Potsis K, Koutis E, Tsifetaki N, Assimakopoulos DA. Esophageal involvement in scleroderma:gastroesophageal reflux, the common problem. Semin Arthritis Rheum. 2006;36:173–181. doi: 10.1016/j.semarthrit.2006.08.002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Abu-Shakra M, Guillemin F, Lee P. Gastrointestinal manifestations of systemic sclerosis. Semin Arthritis Rheum. 1994;24:29–39. doi: 10.1016/0049-0172(94)90097-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Ling TC, Johnston BT. Esophageal investigations in connective tissue disease:which tests are most appropriate? J Clin Gastroenterol. 2001;32:33–36. doi: 10.1097/00004836-200101000-00008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Kaye SA, Siraj QH, Agnew J, Hilson A, Black CM. Detection of early asymptomatic esophageal dysfunction in systemic sclerosis using a new scintigraphic grading method. J Rheumatol. 1996;23:297–301. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Harper RA, Jackson DC. Progressive systemic sclerosis. Br J Radiol. 1965;38:825–834. doi: 10.1259/0007-1285-38-455-825. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Orringer MB, Dabich L, Zarafonetis CJ, Sloan H. Gastroesophageal reflux in esophageal scleroderma:diagnosis and implications. Ann Thorac Surg. 1976;22:120–130. doi: 10.1016/s0003-4975(10)63972-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Zamost BJ, Hirschberg J, Ippoliti AF, Furst DE, Clements PJ, Weinstein WM. Esophagitis in scleroderma. Prevalence and risk factors. Gastroenterology. 1987;92:421–428. doi: 10.1016/0016-5085(87)90137-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Weston S, Thumshirn M, Wiste J, Camilleri M. Clinical and upper gastrointestinal motility features in systemic sclerosis and related disorders. Am J Gastroenterol. 1998;93:1085–1089. doi: 10.1111/j.1572-0241.1998.00334.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Katzka DA, Reynolds JC, Saul SH, et al. Barrett's metaplasia and adenocarcinoma of the esophagus in scleroderma. Am J Med. 1987;82:46–52. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(87)90376-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Savarino E, Furnari M, de Bortoli N, et al. Gastrointestinal involvement in systemic sclerosis. Presse Med. 2014;43:e279–e291. doi: 10.1016/j.lpm.2014.03.029. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Segel MC, Campbell WL, Medsger TA, Roumm AD. Systemic sclerosis (scleroderma) and esophageal adenocarcinoma:is increased patient screening necessary? Gastroenterology. 1985;89:485–488. doi: 10.1016/0016-5085(85)90440-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Fox MR, Bredenoord AJ. Oesophageal high-resolution manometry:moving from research into clinical practice. Gut. 2008;57:405–423. doi: 10.1136/gut.2007.127993. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Roman S, Hot A, Fabien N, et al. Réseau Sclérodermie des Hospices Civils de Lyon. Esophageal dysmotility associated with systemic sclerosis:a high-resolution manometry study. Dis Esophagus. 2011;24:299–304. doi: 10.1111/j.1442-2050.2010.01150.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Savariono E, Mei F, Parodi A, et al. Gastrointestinal motility disorder assessment in systemic sclerosis. Rheumatology (Oxford) 2013;52:1095–1100. doi: 10.1093/rheumatology/kes429. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Calderaro DC, de Carvalho MA, Moretzsohn LD. Esophageal manometry in 28 systemic sclerosis Brazilian patients:findings and correlations. Dis Esophagus. 2009;22:700–704. doi: 10.1111/j.1442-2050.2009.01000.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Lahcene M, Oumnia N, Matougui N, Boudjella M, Tebaibia A, Touchene B. Esophageal dismotility in scleroderma:a prospective study of 183 cases. Gastronterol Clin Biol. 2009;33:466–469. doi: 10.1016/j.gcb.2009.01.014. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Kimmel JN, Carlson DA, Hinchcliff M, et al. The association between systemic sclerosis disease manifestations and esophageal high-resolution manometry parameters. Neurogastroenterol Motil. 2016;28:1157–1165. doi: 10.1111/nmo.12813. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Crowell MD, Umar SB, Griffing WL, DiBaise JK, Lacy BE, Vela MF. Esophageal motor abnormalities in patients with scleroderma:heterogeneity, risk factors, and effects on quality of life. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2017;15:207–213. doi: 10.1016/j.cgh.2016.08.034. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Tang DM, Pathikonda M, Harrison M, Fisher RS, Friedenberg FK, Parkman HP. Symptoms and esophageal motility based on phenotypic findings of scleroderma. Dis Esophagus. 2013;26:197–203. doi: 10.1111/j.1442-2050.2012.01349.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Bredenoord AJ, Fox M, Kahrilas PJ, Pandolfino JE, Schwizer W, Smout AJ International High Resolution Manometry Working Group. Chicago classification criteria of esophageal motility disorders defined in high resolution esophageal pressure topography. Neurogastroenterol Motil. 2012;25(Suppl 1):57–65. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2982.2011.01834.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Karamanolis GP, Denaxas K, Panopoulos S, et al. Severe esophageal disease and its associations in systemic sclerosis. Clin Exp Rheumatol. 2017;35(Suppl 106):106:82–85. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Arif T, Masood Q, Singh J, Hassan I. Assessment of esophageal involvement in systemic sclerosis and morphea (localized scleroderma) by clinical, endoscopic, manometric and pH metric features:a prospective comparative hospital based study. BMC Gastroenterol. 2015;15:15–24. doi: 10.1186/s12876-015-0241-2. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Weber P, Ganser G, Frosch M, Roth J, Hülskamp G, Zimmer KP. Twenty-four hour intraesophageal pH monitoring in children and adolescents with scleroderma and mixed connective tissue disease. J Rheumatol. 2000;27:2692–2695. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Raja J, Ng CT, Sujau I, Chin KF, Sockalingam S. High-resolution oesophageal manometry and 24-hour impedance-pH study in systemic sclerosis patients:association with clinical features, symptoms and severity. Clin Exp Rheumatol. 2016;34(Suppl 100):115–121. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Murphy JR, McNally P, Peller P, Shay SS. Prolonged clearance is the primary abnormal reflux parameter in patients with progressive systemic sclerosis and esophagitis. Dig Dis Sci. 1992;37:833–841. doi: 10.1007/BF01300380. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Fisichella PM, Reder NP, Gagermeier J, Kovacs EJ. Usefulness of pH monitoring in predicting the survival status of patients with scleroderma awaiting lung transplantation. J Surg Res. 2014;189:232–237. doi: 10.1016/j.jss.2014.03.025. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Marie I, Ducrotte P, Denis P, Hellot MF, Levesque H. Oesophageal mucosal involvement in patients with systemic sclerosis receiving proton pump inhibitor therapy. Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 2006;24:1593–1601. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2036.2006.03180.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Wipff J, Coriat R, Mascioccchi M, et al. Outcomes of Barrett's esophagus related to systemic sclerosis:a 3-year EULAR Scleroderma Trials and Research prospective follow-up study. Rheumatology. 2011;50:1440–1444. doi: 10.1093/rheumatology/ker110. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Hendel L, Hage E, Hendel J, Stentoft P. Omeprazole in the long-term treatment of severe gastro-oesophageal reflux disease in patients with systemic sclerosis. Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 1992;6:565–577. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2036.1992.tb00571.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Pakozdi A, Wilson H, Black CM, Denton CP. Does long term therapy with lansoprazole slow progression of oesophageal involvement in systemic sclerosis? Clin Exp Rheumatol. 2009;27(3 Suppl 54):5–8. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Muro Y, Sugiura K, Nitta Y, et al. Scoring of reflux symptoms associated with scleroderma and the usefulness of rabeprazole. Clin Exper Rheumatol. 2009;27(3 Suppl 54):15–21. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Hansi N, Thoua N, Carulli M, et al. Consensus best practice pathway of the UK scleroderma study group:gastrointestinal manifestations of systemic sclerosis. Clin Exp Rheumatol. 2014;32(6 Suppl 86):S214–S221. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44.Foocharoen C, Chunlerthith K, Mairiang P, et al. Effectiveness of add-on therapy with domperidone vs alginic acid in proton pump inhibitor partial response gastro-esophageal reflux disease in systemic sclerosis:randomized placebo-controlled trial. Rheumatology (Oxford) 2017;56:214–222. doi: 10.1093/rheumatology/kew216. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45.Sallam H, McNearney TA, Chen JD. Systematic review:pathophysiology and management of gastrointestinal dysmotility in systemic sclerosis (scleroderma) Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 2006;23:691–712. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2036.2006.02804.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46.Di Martino N, Ingrosso M, Fei L, Maffettone V, Landolfi V, Del Genio A. [Behavior of the pressure of the lower esophageal sphincter after intravenous administration of domperidone in normal subjects] Minerva Med. 1985;76:1411–1417. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47.Grande L, Lacima G, Ros E, et al. Lack of effect of metoclopramide and domperidone on esophageal peristalsis and esophageal acid clearance in reflux esophagitis. A randomized, double-blind study. Dig Dis Sci. 1992;37:583–588. doi: 10.1007/BF01307583. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 48.Johnson DA, Drane WE, Curran J, et al. Metoclopramide response in patients with progressive systemic sclerosis. Effect on esophageal and gastric motility abnormalities. Arch Intern Med. 1987;147:1597–1601. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 49.Ramirez-Mata M, Ibañez G, Alarcon-Segovia D. Stimulatory effect of metoclopramide on the esophagus and lower esophageal sphincter of patients of patients with PSS. Arthritis Rheum. 1977;20:30–34. doi: 10.1002/art.1780200105. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 50.Drane WE, Karvelis K, Johnson DA, Curran JJ, Silverman ED. Scintigraphic detection of metoclopramide esophageal stimulation in progressive systemic sclerosis. J Nucl Med. 1987;28:810–815. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 51.Wehrmann T, Caspary WF. [Effect of cisapride on esophageal motility in healthy probands and patients with progressive systemic scleroderma] Klin Wochenschr. 1990;68:602–607. doi: 10.1007/BF01660958. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 52.Karamanolis GP, Panopoulos S, Karlaftis A, et al. Beneficial effect of the 5-HT1A receptor agonist buspirone on esophageal dysfunction associated with systemic sclerosis:A pilot study. United European Gastroenterol J. 2015;3:266–271. doi: 10.1177/2050640614560453. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 53.Gyger G, Baron M. Systemic sclerosis:gastrointestinal disease and its management. Rheum Dis Clin North Am. 2015;41:459–473. doi: 10.1016/j.rdc.2015.04.007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 54.Leelakanok N, Holcombe A, Schweizer ML. Domperidone and risk of ventricular arrhythmia and cardiac death:a systematic review and meta-analysis. Clin Drug Investig. 2016;36:97–107. doi: 10.1007/s40261-015-0360-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 55.Karamanolis GP, Panopoulos S, Denaxas K, et al. The 5-HT1A receptor agonist buspirone improves esophageal motor function and symptoms in systemic sclerosis:a 4-week, open-label trial. Arthritis Res Ther. 2016;18:195. doi: 10.1186/s13075-016-1094-y. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 56.Poirier NC, Taillefer R, Topart P, Duranceau A. Antireflux operations in patients with scleroderma. Ann Thoracic Surg. 1994;58:66–72. doi: 10.1016/0003-4975(94)91073-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 57.Orringer MB, Orringer JS, Dabich L, Zarafonetis CJ. Combined Collis gastroplasty—fundoplication operations for scleroderma reflux esophagitis. Surgery. 1981;90:624–630. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 58.Mansour KA, Malone CE. Surgery for scleroderma of the esophagus:a 12-year experience. Ann Thoracic Surg. 1988;46:513–514. doi: 10.1016/s0003-4975(10)64687-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 59.Kent MS, Luketich JD, Irshad K, et al. Comparison of surgical approaches to recalcitrant gastroesophageal reflux disease in the patient with scleroderma. Ann Thoracic Surg. 2007;84:1710–1715. doi: 10.1016/j.athoracsur.2007.06.025. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


