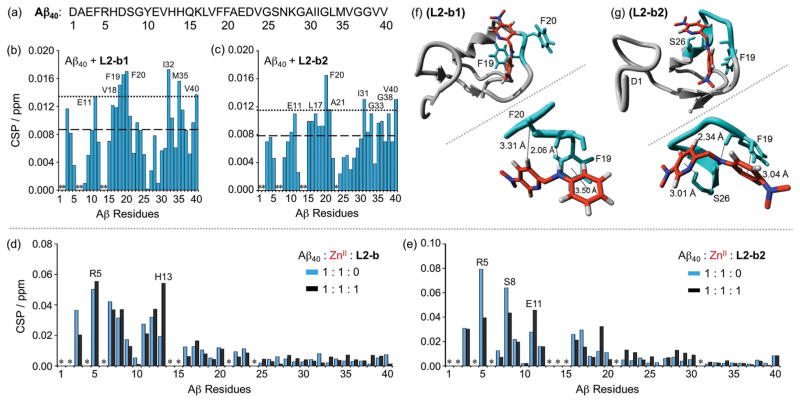
Figure 4.
Interactions of L2-b, L2-b1, or L2-b2 with metal-free or ZnII-treated Aβ40 monomer. (a) Amino acid sequence of Aβ40. Plots of the chemical shift perturbation (CSP) determined through 2D 1H–15N SOFAST-HMQC NMR spectra of uniformly 15N-labeled monomeric Aβ40 upon titration with (b) L2-b1 or (c) L2-b2. The average CSP (dashed line) with standard deviation (dotted line) is presented. *Residues could not be resolved for analysis. Conditions: [Aβ40] = 80 μM; [L2-b1 or L2-b2] = 0 or 800 μM; 20 mM phosphate buffer, pH 7.4, 50 mM NaCl; 7 % D2O (v/v); 10 °C. Plots of the CSP obtained from 2D 1H–15N SOFAST-HMQC NMR spectra of uniformly 15N-labeled monomeric Aβ40 upon addition of ZnII without (blue) and with (black) (d) L2-b or (e) L2-b2. *Residues could not be resolved for analysis. Conditions: [Aβ40] = 80 μM; [ZnCl2] = 80 μM; [L2-b or L2-b2] = 80 μM; 20 mM phosphate buffer, pH 7.4, 50 mM NaCl; 7% v/v D2O. MD simulations showing interactions of (f) L2-b1 or (g) L2-b2 with monomeric Aβ40. Possible sites and energy of interactions of Aβ40 (PDB 1BA4) with L2-b1 or L2-b2 after all-atom MD simulations are summarized. The zoomed-in view (right, below) of each binding site with residues showing interaction distances labeled in & with dashed lines (additional MD simulations data in Supporting Information, Figure S5).