Abstract
With cancer stem cells (CSCs) became the research hotspot, emerging studies attempt to reveal the functions of these special subsets in tumorigenesis. Although various approaches have been used in CSCs researches, only a few could really reflect or simulate the microenvironment in vivo. At present, CSCs theories are still difficult to apply for clinical remedy because CSCs subpopulations are always hard to identify and trace. Thus an ideal approach for clinicians and researchers is urgently needed. Circulating tumor cells (CTCs), as the method of noninvasive-liquid biopsy, could be detected in the peripheral blood (PB) from many tumors and even could be treated as procurators for CSCs deeper researches from patient-derived sample. However, CTCs, as a diagnostic marker, also raise much controversy over theirs clinical value. Mechanisms causing CTCs to shed from the tumor have not been fully characterized, thus it is unclear whether CTCs represent the entire makeup of cancer cells in the tumor or only a subset. The heterogeneity of CTCs also caused different clinical outcomes. To overcome these unsolved problems, recently, CTC researches are not just depend on enumerations, whereas those CTC subsets that could expand in vitro may play a pivotal role in the metastatic cascade. Here, we retrospect the CTC developmental history and discourse upon the enrichment of viable CTCs in functional assays, probe the further avenue at the crossroad.
Keywords: Circulating tumor cells, Culture, Expansion, Function
Background
For decades, tumor formation and development has been regarded as a mysterious issue, compelling scientists to seek the mechanism of origin. Much evidence hinted that some small subpopulations of tumorigenic cells were the causation of tumor recurrence and metastasis, but it may be difficult to draw definitive conception because of the lack of rigorous model and effective methods to identify these special subpopulations. Since 1960, when the Philadelphia (Ph) chromosome and its unique association with chronic myeloid leukaemia (CML) were discovered [1], evidence has been found that the appearance of clonal chromosomal aberrations caused abnormal cell proliferation in bone marrow. These pathological cells could be the culprit of tumorigenesis. Further research also found that these cells (Ph+) were always detected in circulation [2]. From then, cells with special markers had been noticed by researchers. The concept of cancer stem cell (CSCs) began to appear in the mid-1990s by isolating rare cells in the blood of patient with leukemia, these cells were capable to grow into a new leukemia when injected into mice [3]. The early discoveries contributed CSCs to become the hotspot and thus diverse CSC models were emerged subsequently. Many studies provided proof for the CSC hypotheses and managed to address and deduct the process of tumor initiation and development. Unfortunately, these relative hypotheses had not got the final conclusion [4–7], none could perfectly illustrate the details of every step in tumorigenesis and its relapse. It is still unknown about which CSCs paradigm is really suitable for modern clinical therapy. And now to solve these unsettled arguments, more researchers expect to focus on a single-cell level, which could have more convincing to reveal mechanisms of CSC. Therefore, the development of single-cell diagnostic methods is flourishing these years. Circulating tumor cells (CTCs) in the peripheral blood (PB) from different types of tumors are increasingly detected by various methods. However, the mechanisms causing CTCs to shed from the tumor have not been fully characterized, thus it is unclear whether CTCs represent the entire makeup of cancer cells in the tumor or only a subpopulation [8]. Nevertheless those CTC subsets, with CSCs feature, could expand in vitro may play a pivotal role in the metastatic cascade.
The viable CTCs with CSCs feature for functional analysis
Since the CellSearch system was designed to detect detached tumor cells in PB, CTCs enumeration was thought to be an important method in the clinic relevance [9]. However, there were some limitations for CTC applications. The one was that the released CTCs number in different tumor types were quite disparity [10]. For example, inflammatory breast cancer (IBC) is characterized by high vascularity and increased microvessel density which may increase the chance for the CTCs release [11]. The higher incidence of CTC has also existed in SCLC patients with COPD, the inflammatory conditions and accumulation of airway macrophages which construct particular niches and enhance the invasive ability of CTCs to degrade the extracellular matrix (ECM) in early stage [10, 12] than other cancer types.. Apparently, a threshold of 3–5 CTCs/7.5 ml blood has been defined by the CellSearch system for prognostic stratification [10], which seems not compatible with all cancer patients. Other limitations were that enriched CTCs could not accurately cover the whole population and not all CTCs detected are clinically relevant [13]. Many isolated methods for CTCs relied on either defined surface marker or differences in the size of individual cell populations [13–16]. But CTCs are not a homogeneous group that can be captured by a set of identical markers or the same physicochemical properties. A few CTCs could remain the vitality in a very hostile environment during circulation [13, 14, 17, 18] by fusing with bone marrow-derived cells or altering the phenotype that could protect and hide them from the immune system attack. The methods based on the CD45 marker- even be considered that only express in mature mononuclear blood cells, was found that could even be appeared in CTCs by adhering to platelets or recruiting macrophages [10, 19]. And assumed epithelial markers, such as EpCAM, could also miss the CTCs subsets with low or absent expression [20] and inevitably cause decreased detection of CTCs that had undergone epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT), an important alteration involved in metastasis [13]. Contrary to transient disseminated tumor cells (DTC), these altered CTCs may be the key subsets which could manifest CSC features and significantly correlated to treatment response [15, 21–23]. In order to overcome these limitations, some specific markers that have a high specificity were used to define certain tumor types, such as mammaglobin for breast cancer and prostate-specific antigen (PSA) for prostate cancer. Nevertheless, these markers could be also downregulated during dedifferentiation of tumor cells [24] or absent in some particular CTCs due to the heterogeneity and plasticity [15]. These dynamic changes hindered CTC as a biomarker for clinical applications. For extending the understanding of relevant CTCs involved in metastasis, fortunately, the molecular technologies had integrated into CTCs identification by single-cell analyses such as RNA or exon sequencing [25, 26], which could be used to perform quantitative gene expression profiling for special CTCs and potentially guide patient management [26]. However, although studies of molecular characterization did identify different CTC subpopulations within a single blood sample, they had not addressed the biology of CTCs due to the scarcity of CTCs in the PB [25, 27]. To solve this issue, techniques on CTCs expansion both in vitro and in vivo had appeared (Fig. 1). The “viable CTCs”, which were enriched and isolated by label-free methods based on biophysical rather than biochemical properties, became the important role in experimental functional assays. One study reported that isolated human CTCs from murine blood showed an enhanced aggressive phenotype under hypoxic environment in vitro and in vivo [28]. The produced viable CTCs from xenografts in mouse manifested more biologic activity for functional researches. Other study also defined that qualified enrichment of viable CTCs must include some important parameters, such as capture efficiency, enrichment rate and even cell viability [29]. Recently, several groups have achieved a huge harvest in the expansion of CTCs from cancer patients. Two papers reported patient-derived CTCs culture for 6 months [30] and 1 year [31] respectively. Sufficient viable CTCs as a procurator for CSCs functional analyses could provide more biological information. But the next challenging obstacles had also existed. Many researchers concerned issues that were the efficient establishment of human-CTC cultures and the value for clinical applications. Recent years, the study reported that CTCs with CSCs phenotype derived from colorectal cancer patients could be designed to test drug sensitivity and integrate a personalized approach to clinical utility [25]. And then, much more CTC-platform provided the practicability on separation of viable CTCs by subsequent short-term growth in culture [27, 32–34] for functional test of CTC lines. Success in culturing human CTCs would overcome the difficulty of characterizing these rare cells and could extend new potential therapeutic strategy (Fig. 2).
Fig. 1.
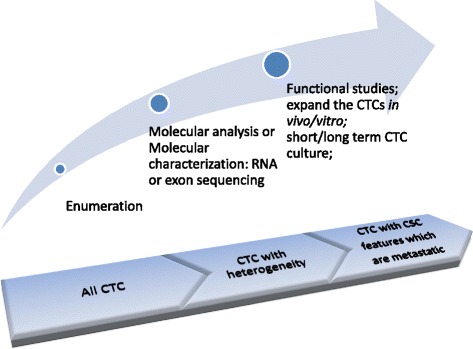
CTC researches undergone the three stages CTC enumerations include various subsets such as dormant cells, apoptotic cells, and even normal hemopoietic stem cells, only depend on enumeration is not suitable for clinical evaluation. Whereas, further the studies in molecular characterization by RNA or exon sequencing could explain CTC heterogeneity, expanded CTCs could be the special subsets not only for deeper molecular-level researches but for functional analyses and guide the clinical therapy
Fig. 2.
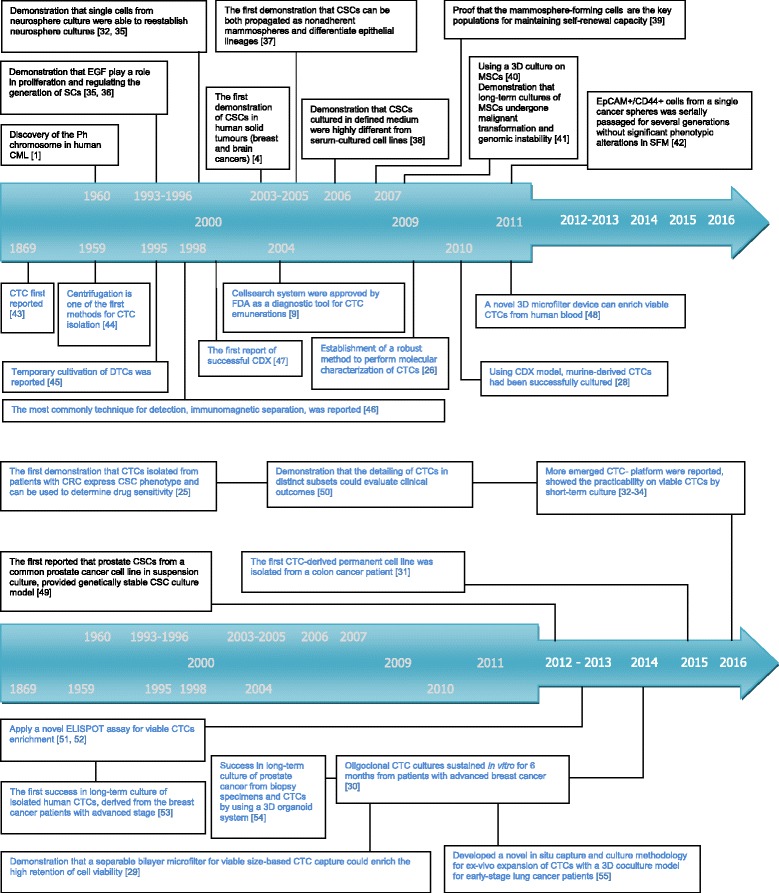
The most influential events contributing to the causal relationship between CSCs and CTCs The fonts in black indicate events related to CSCs [1, 4, 32, 56, 57, 62–68]. The fonts in blue indicate events related to CTCs [9, 26, 28–34, 48, 54, 69–78]. And recent years, many evidence showed the inextricable connection between CSCs and CTCs, the expanded CTCs subsets are always used as a tool to reflect intrinsic characteristic of CSCs [25, 77, 78]. The abbreviations in Fig. 2: stem cells (SCs); mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs); serum-free medium (SFM); disseminated tumor cells (DTC); CTC-derived xenografts (CDX) [35–39, 43–48, 51, 52, 54]
Functional analysis of CTCs revealed modern individual treatment
Traditional CSC models suggested that there were intratumor heterogeneity in the primary site due to some special tumor cells get gene mutations which were able to become CSCs subpopulations and resulted in the tumor recurrence, metastasis or chemical drugs resistant. Current opinion even believed that these CSCs subpopulations were not immutable [16, 35–38]. Theoretically, under different environmental stress, CSCs and non-CSCs subpopulations were in a dynamic conversion [16]. Owing to the challenge of identify CSCs subpopulations, CTCs as a “monitoring method” were often used to study on the heterogeneity of CSCs in patient-derived samples in real-time. Some researchers had found CTCs and parental cells or primary tumor cells [28, 39] with some similarity such as hypoxia response both enhanced aggressive phenotype [23, 28] and others had found some differences in mutant gene [40] which could lead CTCs to acquire more aggressive behaviors. These researches showed that CTCs not only acted as an intermediate, they also as the potential precursor cells of metastasis [41] during the movement of tumor cells from the primary site to a distant location and the establishment of a new cancer growth. Different environmental stresses lead to different fates of CTCs. Some special CTCs could survive by some phenotypic and functional alteration to resistant environmental stress [42]. More aggressive CTCs could become potentially tumor-initiating cells, but they were unique and heterogeneous cell populations by their relation to a series of biological processes, such as EMT or mesenchymal-epithelial transition (MET), differed from the CSC-like cells in primary site as many researches previous described [35, 43–45]. These potentially tumor-initiating cells may not only infiltrate into distant sites, and also recruit some immunosuppressive cells, particularly tumor-associated macrophages (TAMs) to create a defensive shield and build the secondary niches [10, 12, 19]. The different cellular and intracellular interactions could cause totally different antitumor immune responses and metastatic prognoses [42, 45]. It could partially explain the source of heterogeneity of tumor metastasis and development in clinic. Recently a study investigated the different regrowth of the same CSCs population in primary and metastatic sites from a mouse model of colorectal cancer [46]. The authors found that the specific stem-cell subpopulation were eliminated by Lgr5+ target therapy in both primary and metastatic sites, but when the drugs treatment ceased, the two sites had different outcomes. In primary site, the tumor increased in the size and the specific stem-cell population reappeared, but in the metastatic site, there was no relapsed [46]. It could be explained that these CTCs, which had migrated through the bloodstream, could more contribute to act as the role of tumor-initiating cells and to drive metastasis formation, rather than act as the role of CSCs, which must have more self-renewal ability to maintain metastasis growth [46]. Conversely in primary site, the other cells may have the reversible ability and fulfilled stem-cell functions to fuel tumor regrowth [46, 47]. Thus, the target therapy might be more effective on metastatic site than primary site. Besides the difference between CTCs and primary tumor cells, the heterogeneity also exists in different CTC subpopulations. Malara N et al. even showed different biological behaviors in two expanded CTCs (eCTCs) subpopulations derived from patients with colon cancer. The eCTCs subpopulation expressed CXCR4+CK20+ were not tumorigenic but able to disseminate, and the other subpopulation expressed CD45−CD133+ were more tumorigenic. Patients with different prevalence of CTCs had different clinical outcomes [48]. Thus, on these basis of the CTCs heterogeneous composition, many researchers now do believe that traditional clinical treatment strategies might not be useful to patients with metastasis, because these treatment strategies often based on the pathological and molecular characterization of the primary tumor [49]. As current functional researches showed, CTCs should provide more useful resources for the mechanisms of metastasis formation [41]. The detailing of sufficient eCTCs in distinct subsets, by qualitative and quantitative measurement, might be useful to better define a personalized metastatic risk score [48] and lead to a better way in identification and isolation of metastasis-initiator cells for further clinical individual treatment decision regarding drug resistance [27] or prognosis [17].
The expanded methods of CTCs for clinical individual application
CSCs are known to be highly chemo-resistant [50] and more tumorigenic capacity under special microenvironment such as hypoxia-inducible condition [51]. They are always the key subsets that cause the treatment failed in whole tumor disease. Many researchers attempted to use the viable eCTCs to extend the knowledge of CSCs and figure out the process of metastasis formation. The methods that could get the more qualified eCTCs for reliable study are very crucial. CTC- derived xenograft (CDX) models is one of the expanded methods in vivo. Ameri, K et al. [28] using CDX to build a murine- derived CTCs model, showed that CTCs had an enhanced aggressive phenotype under chronic hypoxia. Their results revealed the micro-environmental stress could select for cells with phenotypes alterations and contributes to increased metastases. Successful CDX models could not only better mimic biological environment, it also recapitulate each individual patient’s cancer pathology and yield results more predictive of subsequent activity in patients [52]. However, using human cell line to generate murine-derived CTCs had its inevitable defects, because these CTCs from immunodeficient mice were not perfectly adequate for human [52]. For example, taken CTCs from cardiac puncture rather than from venous sampling, the most important differences are: i 2-7 ml blood is the minimal volume to human but is lethal to mouse, thus the enriched CTCs numbers are not on the same scale, CTCs in equal volume from mouse must be significantly higher than human. ii The sites that CTCs were directly punctured from heart means cardiogenic derived circulation in mouse, differed from peripheral venous and arterial circulation [53] in patients. And after that, although various studies reported that xenografts of CTCs were successful in many solid tumors, it should be also noted that many CDXs could be only obtained from advanced stage patients with high CTC counts, and even these xenotransplantation in vivo must take a long time [52].
The extended methods of CTCs in vitro were also reported. Many researchers suggested that the short term-eCTCs could distinguish from healthy or inflammation-derived cells that were isolated and unable to survive and expand [27, 48]. However, the maintenance of CTC culture in vitro from human blood samples is a complicated task, because many CTCs have limited proliferation ability and senesced after a few cell divisions in many cultural conditions such as adherent monolayer culture [30]. Lack of efficient conditions for eCTCs in vitro had become a bottleneck in clinic applications. Nevertheless, one study reported a microfluidic technology, human-CTC culture after enrichment by CTCiChip [54] showed the practicability of ex-vivo short term eCTCs in clinical trials. CTCs could be isolated and expanded from blood samples of early stage lung cancer patients, including patients with stage I [54]. In order to facilitate CTC expansion, the authors used a 3D co-culture condition, they introduced tumor associated fibroblasts to construct a tumor microenvironment [54]. Therefore, their expanded approach had high success rates to further characterize the biology of CTCs. And the long-term CTC cultures in vitro were reported by Min Y et al. They established oligoclonal CTC cultures sustained for > 6 months. CTCs were isolated from six of 36 patients with metastatic luminal subtype breast cancers [30]. In their serum free culture condition, the isolated CTCs could be maintained as suspended status and could form multi-cellular clusters, which were also named spheroids [55]. The eCTCs as non-adherent spheres may properly reflect intrinsic properties of CSCs that remain viable in the bloodstream after loss of attachment to basement membrane [30]. Spheroid culture of CTCs as a representative in vitro could reflect CTC cluster formation and growth in vivo [55]. Similar report was published by Cayrefourcq L et al. - the first CTC-derived permanent cell line isolated from the blood of a colon cancer patient, these CTCs had been cultured for more than 1 year [31]. It is a wealth of current functional researches on the biology of CTCs and raise the new perspective for drug testing in vitro and in vivo. But these long-term culture must also require high CTC counts from the advanced stage patients and were low success rate. Notably, there were another phenomenon might explain the low success rate. In Fan X et al.’s paper, the authors studied on 2 common prostate cancer cell lines named LNCaP and PC3 as research tools. Their results showed that PC3 could be formed spheres in suspension culture but LNCaP were failed [56] in the same condition. This suggested that different tumor cell lines, due to their different growth biology, could not either survive or expand in same culture mediums and environments in vitro. Thus, to better understanding CTCs biology from different origins, researchers must consider the merits and drawbacks in different culture conditions and approaches for clinical individual therapy (Table 1).
Table 1.
Merits and drawbacks in three different methods for CTCs expansion
| Method | CDX | Short term | Long term |
|---|---|---|---|
| CTC number | High | Low | High |
| Patient origin | Advanced stage only | Early and advanced stage | Advanced stage only |
| Condition | Experimental animal | 10% FCS medium | Defined serum-free medium |
| Sample origin | Organ-vasculature circulation | Peripheral venous or arterial circulation | Peripheral venous or arterial circulation |
| Character | Tumorigenic capacity evaluation; complex procedure and individual difference | Differentiation and limited proliferation ability with significant phenotypic alterations | Phenotype stable; maintaining the tumorigenicity in non-adherent status |
| Research purpose | Simulate microenvironment in vivo | Expand enough CTCs for downstream analyses | Enrich and expand CTCs to establish patient-derived cell lines for long-term research |
| Cost | High | Cheap | Moderate |
| Culture cycle | Several months | 1-2 weeks | Several months −1 year |
| Successful rate | Low | Moderate | Low |
Optimize the current approaches of CTCs culture
Before strategies of CTC culture apply for clinical management, some problems should be concerned to address properly. The further characterization of the expanded CTC-derived cell lines must be required to define clearly, such as CTCs proliferated as tumor spheres always cultured in serum-free medium which were far from the conditions in vivo. How they differed from cells cultured from primary tumor biopsies or directly implanted into mouse models are concerned issues [30]. The other key technical problems are how to maintain CTCs phenotype and composition of population stable in culture. Some reports even hint that normal human mesenchymal stem cells (hMSC) are prone to genomic change and subsequent malignant transformation in long term culture [57]. Thus, CTC culture may be also meet the same situation that caused the genomic instability under various environmental stresses, especially long-term culture. 3D biomaterial for co-culture is an ideal way to solve this problem, which could maximize to mimic tumor physical and biochemical microenvironment by adding the different culture ingredients, i.e. growth factors, hormones, serums, matrix components, and growth factors. It also could facilitate CTC expansion [54]. Thus, 3D biomaterial could be considered to integrate the different culture methods for more realistic drug responses [58]. Furthermore, define and modify culture media supplements properly for different tumor cell lines are much important for CTC culture (Table 2).
Table 2.
Various formulas of culture for different sample-derived CSCs and CTCs
| Purpose | Cell origin | Culture material | Cell seeded concentration | Initial treatment | Medium | Added ingredients | Environment | Culture cycle | ref |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CSC/SC Sphere formation | Bladder cancer cells | Ultra-low attachment surface (Corning) | 6 × 103 cells/well | 6-well plates | Serum-free DMEM/F12 (Gibco) | 20 ng/mL EGF(Invitrogen), 20 ng/mL bFGF (Invitrogen), 1% N2 (Invitrogen), 2% B27 (Invitrogen) and 1% penicillin-streptomycin (Hyclone) | 2 w | [79] | |
| Pancreatic Cancer KPCL Cell Line | Ultra-low attachment plates (Corning) | Tumor tissue minced | Promote organoid formation in serum-free for 3 days | Serum-free DMEM/F12 | 0.5% methylcellulose, 1% N2 (Invitrogen), 2% B27 (Invitrogen), 20 ng/ml recombinant human EGF (Miltenyi Biotec) and 20 ng/ml recombinant human FGF-2 (Miltenyi Biotec), 5 μg/ml heparin (Sigma) and 1% penicillin/streptomycin (Invitrogen) | 3 d | [80] | ||
| Kidney cancer cell lines ACHN /CAKI-1 RCC | Ultra-low attachment plates (Corning) | 500 cells/well | 96-well plate; 100 μl SFDM/well; add 25 μl SFDM /well /day | Serum-free defined media (SFDM) low-glucose (1 g/l) DMEM | L-Glutamine, sodium pyruvate, Penicillin/Streptomycin (Wisent Inc), 20 ng/ml basic FGF, 20 ng/ml EGF, and B27 (Invitrogen, Grand Island, USA) | 3 w | [81] | ||
| Brain metastases tumor | Ultra-low attachment surface (Corning) | 200 to 2 cells /well (limiting dilution) | 100 μL of cNSC media in a 96-well plate | Complete NSC (cNSC) media | Complete NSC media is comprised of NSC basal media (1% N2 [Gibco], 0.2% 60 μg/mL N-acetylcystine, 2% neural survival factor-1 [Lonza], 1% HEPES, and 6 mg/mL glucose in 1:1 DMEM/F12 [Gibco]), supplemented with 1× antibiotic–antimycotic (Wisent), 20 ng/mL human epidermal growth factor (Sigma),20 ng/mL basic fibroblast growth factor (Invitrogen), and 10 ng/mL leukemia inhibitory factor (Chemicon) | 37 °C, 5% CO2 |
7 d | [82] | |
| Mammary gland stem cells | Low-attachment culture plate (Corning) | Serial dilution; 5-2000/well | 96-well plate; | MM+ medium | DMEM/F12 supplemented with 2% calf serum, 10 mmol/L HEPES, 20 ng/mL epidermal growth factor (EGF), 10 μg/mL insulin, 5% bovine serum albumin, 1:50 B27 (Invitrogen), 20 ng/mL, basic fibroblast growth factor (bFGF), and 10 μg/mL heparin and 100 μg/mL penicillin/streptomycin | 7 d | [67] | ||
| Breast organoids | 50-mm low attachment plat (Corning) | 2.5 × 105 cells/well | Dissociated into single cells after 6–8 h into 6-well plates | Serum free DMEM/F12 media | 10 ng/ml hEGF, 1 mg/ml hydrocortisone, 10 mg/ml insulin, 20 ng/ml bFGF, 4 ng/ml heparin (Sigma Aldrich), B27 (Invitrogen) supplemented with antibiotics | 7 d | [83, 84] | ||
| HCC1806/MCF10A | Ultra-low attachment plates(Corning) | 5 × 103 cells/well | Mammary epithelial growth medium (MEBM) | Serum-free mammary epithelial growth medium (MEBM) (Lonza), supplemented with B27 (Invitrogen), 20 ng/mL EGF and 20 ng/mL bFGF (BD Biosciences), and 4 μg/mL heparin (Sigma). | 10–14 d | [85] | |||
| Brain tumor cell lines | Cells grown as monolayers were transfered into serum-free medium | DMEM high glucose (Sigma) | Serum free stem cell medium: DMEM/F12 (70/30%), 2% B27 (Invitrogen), 5 ng/mL heparin (Sigma), supplemented with 20 ng/mL human recombinant epidermal growth factor (hrEGF; Invitrogen), and 20 ng/mL human basic recombinant fibroblast growth factor (bFGF; BD Bioscience) | 37 °C, 5% CO2 | 4–5 w | [86] | |||
| Gastric cancer cell (patient- derived) | A single cell in 96-well plate | Samples were subjected to mechanical /enzymatic dissociation | Neurobasal-A medium (Gibco, Camarillo, CA) | Neurobasal-A medium (Gibco, Camarillo, CA) supplemented with 2 mM L-glutamine, 120 lg/ml of penicillin, 100 lg/ml of streptomycin, B27, 50 ng/ml of EGF, and 50 ng/ml of FGF-2. For differentiation, 5% FCS was added to the media instead of growth factors. | 10 days | [68] | |||
| PC3 human prostate cancer cells | 100 cm2 culture dishes | 1000 cells/ml | DMEM/F12 | Serum-free DMEM/F12 medium containing 20 ng/ml epidermal growth factor (EGF; R and D Systems, Minneapolis, MN), 5μg/ml insulin, 0.4% bovine serum albumin (Sigma, St. Louis, MO), and 2% B27 (Invitrogen, Carlsbad, CA) | 37 °C; humidified atmosphere; 5% CO2 | [56] | |||
| CSC 3D culture | GBM6 cell line | 3D CHA scaffold culture | 50,000 cells /scaffold; 12-well plates | DMEM | DMEM supplemented with 2.5% FBS and 1% penicillin/streptomycin | 37 °C humidified atmosphere 5% CO2 | 14 d | [87] | |
| CTC culture | Patients with metastatic CRC (stage IV) | Ultralow attachment plates (Corning) | N/A | In 24-well plates | M12 medium (1 mL/well) | M12 medium contains advanced DMEM/F12 (Gibco), 2 mmol/L of L-glutamine, 100 Unit/mL of penicillin and streptomycin, N2 supplement (Gibco), 20 ng/mL of epidermal growth factor (R&D) and 10 ng/mL of fibroblast growth factor-basic (R&D) | 3 w (5 × 106 cells) | [25] | |
| Patients with breast cancer | N/A | 24- or 6-well plates for further growth, and subsequently into T75 tissue culture flasks | DMEM/F12 | Stem cell culture medium (DMEM/F12 containing 5 mg/ml insulin, 0.5 mg/ml hydrocortisone, 2% B27, 20 ng/ml EGF, and 20 ng/ml FGF-2) for the first seven days, then switched to EpiCult-C medium from day 8 (STEMCELL Technologies Inc.) with 10% FBS and 1% penicillin/streptomycin and continued to grow in this medium until day 21. The medium used from day 22 on was DMEM/F12 plus 10% FBS and 1% penicillin/streptomycin solution (Regular M) | 37 °C, 5% CO2, | 0-7;8-21;>22d | [77] | ||
| Patients with colon tumor | N/A | DMEM/F12 | Sphere medium used was DMEM/F12- Heparin 0.5 U/ml, EGF 50 ng/ml, FGF 25 ng/ml, BSA 1%, penicillin–streptomycin solution 1%. | 14 d (short term) | [48] | ||||
| Patients with colon tumor | Non adherent plates | N/A | Culture in 24 well and into T25 flasks for culture expansion | DMEM/F12; RPMI1640 | DMEM/F12 containing insulin (20 μg/mL), 1% N2 complement, epithelial growth factor (EGF: 20 ng/mL), L-Glutamine (2 mM), fibroblast growth factor-2 (FGF2: 10 ng/mL) and 2% foetal calf serum for the first days (Medium 1). After a few weeks, the CTC culture was switched to another appropriate culture medium to improve the CTC cell growth (Medium 2: RPMI1640, Growth factors: EGF and FGF-2, Insuline-Transferine-Selenium supplement, L-Glutamine) under normoxic conditions (5% CO2) | Hypoxic conditions; 2% O2; 37 °C | A few months obtained billions of tumor cells | [31] | |
| Patients with lung cancer (early stage) | 3D material: Collagen; matrigel; fibroblasts | N/A | 3D co: a mix of collagen and matrigel and fibroblasts 3D mono: cultured only with gel; 2D co: cultured only with fibroblasts 2D mono: without any gel nor fibroblasts | RPMI1640 | RPMI1640 (10% FBS and 1% Penicillin/Streptomycin) maintained under different culture conditions and cultured up to 7 days on the chip: 3Dco; 3Dmono; 2Dco; 2Dmono | 14 d | [54] | ||
| Patients with head and neck tumor | Non adherent spheroid microplates (Thermo Scientific, USA) | N/A | Isolated CTCs were cultured in 96F well | DMEM/F12 | Culture medium containing Advanced DMEM/F12 with the following additives: 50 ng/mL EGF (Sigma), 5% v/v R-spondin 1, 10% v/v Noggin, 10 ng/mL FGF10 (Peprotech), 1 ng/ml FGF2 (Peprotech), 10 nM Nicotinamide (Acros), 0.5 μM A83–01 (Tocris), 10 μM SB202190 (Sigma Aldrich), 10 μM Y-27632 (Selleck Chemical), 1X B27 Additive (Invitrogen), 1.25 mM N-Acetyl-L-cysteine (Sigma-Aldrich), 2 nM Glutamax(Invitrogen), 10 mM HEPES (Sigma Aldrich), 1:100 v/v Primocin (Invivogen) | 2% O2; 5% CO2; 37 °C | 14 d | [32] | |
| Patients with pancreatic/urothelial/urinary bladder/ prostate Cancer | N/A | 6-well cultivation plate | RPMI1640 | Isolated CTCs by size-based separation methodMetaCell®, and grown in FBS-enriched RPMI1640 (10%) for a minimum of 3-6 days; | 37 °C, 5% CO2 | 14 d | [17, 33, 88–92] |
Conclusions
Many studies have thought CTCs as a noninvasive method could provide a new perspective [59], but only enumeration is not sufficient [15, 60], it may only reflect relative tumor burden or leakiness of tumor-associated vasculature [40]. The quantification of CTCs with their viability are of high value for clinical evaluation, these CTCs with potential CSCs feature generally represent the tumor metastases and could be as procurators to facilitate real-time monitoring during systemic therapies by sequential peripheral blood sampling. But researchers must also keep an eye on those dormant CTCs in PB. A few of them may become the precursors of metastases in distant sites which offer appropriate conditions for them [61]. Thus, the optimal culture conditions for CTC expansion will need to be also considered for these special CTCs subsets. By utilizing different 3D biomaterials to improve culture microenvironment are the better options, it could screen out the more pertinent CTCs subsets and acquire more realistic information for strategy of personal therapy.
Acknowledgements
Not applicable
Funding
Not applicable
Availability of data and materials
Not applicable
Abbreviations
- CDX
CTC-derived xenografts
- CSCs
Cancer stem cells
- CTCs
Circulating tumor cells
- DTC
Disseminated tumor cells
- ECM
Extracellular matrix
- eCTCs
Expanded CTCs
- EMT
Epithelial-Mesenchymal Transition
- IBC
Inflammatory breast cancer
- MET
Mesenchymal-Epithelial Transition
- MSCs
Mesenchymal stem cells
- PB
Peripheral blood
- Ph
Philadelphia chromosome
- SCs
Stem cells
- SFM
Serum-free medium
- TAMs
Tumor-associated macrophages
- TICs
Tumor-initiation cells
Authors’ contributions
Luo YT wrote and edited the manuscript, Cheng J revised the manuscript and gave critical review of the manuscript, Feng X, He SJ and Wang YW contributed to language editing, Huang Q gave suggestions and gave revisions. All authors read and approved the final version of the manuscript.
Ethics approval and consent to participate
Not applicable
Consent for publication
Not applicable
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Contributor Information
Y. T. Luo, Email: seiyaterran@sohu.com
J. Cheng, Email: ajinch@163.com
X. Feng, Email: fxngtg@163.com
S. J. He, Email: he-si-jia@163.com
Y. W. Wang, Email: wywxrbnm@163.com
Q. Huang, Email: qianh2011@126.com
References
- 1.Nowell P, Hungerford D. A minute chromosome in human chronic granulocytic leukemia. Science. 1960;132:1497. doi: 10.1126/science.144.3623.1229. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Hea LR. Persistent mitosis of transfused homologous leukocytes in children receiving antileukemic therapy. Science. 1963;142:1305–1311. doi: 10.1126/science.142.3597.1305. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Lapidot T, Sirard C, Vormoor J, Murdoch BTH. A cell initiating human acute myeloid leukaemia after transplantation into SCID mice. Nature. 1994;367:645–648. doi: 10.1038/367645a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Nguyen LV, Vanner R, Dirks P, Eaves CJ. Cancer stem cells: an evolving concept. Nat Rev Cancer. 2012;12:133–143. doi: 10.1038/nrc3184. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Shackleton M, Quintana E, Fearon ER, Morrison SJ. Heterogeneity in cancer: cancer stem cells versus clonal evolution. Cell. 2009;138:822–829. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2009.08.017. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Bjerkvig R, Tysnes BB, Aboody KS, Najbauer J, Terzis AJ. The origin of the cancer stem cell:current controversies and new insights. Nat Rev Cancer. 2005;5:899–904. doi: 10.1038/nrc1740. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Avgustinova A, Benitah SA. The epigenetics of tumour initiation: cancer stem cells and their chromatin. Curr Opin Genet Dev. 2016;36:8–15. doi: 10.1016/j.gde.2016.01.003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Qin Z, Ljubimov VA, Zhou C, Tong Y, Liang J. Cell-free circulating tumor DNA in cancer. Chinese journal of cancer. 2016;35:36. doi: 10.1186/s40880-016-0092-4. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Cristofanilli M, Budd GT, Ellis MJ, Stopeck A. Circulating tumor cells, disease progression, and survival in metastatic breast cancer. N Engl J Med. 2004;351:781–791. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa040766. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Hamilton G, Rath B. Circulating tumor cell interactions with macrophages: implications for biology and treatment. Transl Lung Cancer Res. 2017;6(4):418–430. doi: 10.21037/tlcr.2017.07.04. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Pierga JY, Bidard FC, Autret A, Petit T, Andre F, Dalenc F, Levy C, Ferrero JM, Romieu G, Bonneterre J, et al. Circulating tumour cells and pathological complete response: independent prognostic factors in inflammatory breast cancer in a pooled analysis of two multicentre phase II trials (BEVERLY-1 and -2) of neoadjuvant chemotherapy combined with bevacizumab. Ann Oncol. 2017;28(1):103–109. doi: 10.1093/annonc/mdw535. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Hamilton G, Rath B, Klameth L, Hochmair MJ. Small cell lung cancer: recruitment of macrophages by circulating tumor cells. Oncoimmunology. 2015;5(3):e1093277. doi: 10.1080/2162402X.2015.1093277. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Leong SM, Tan KM, Chua HW, Tan D, Fareda D, Osmany S, Li MH, Tucker S, Koay ES. Sampling circulating tumor cells for clinical benefits: how frequent? J Hematol Oncol. 2015;8:75. doi: 10.1186/s13045-015-0174-9. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Pesta M, Kulda V, Narsanska A, Fichtl J, Topolcan O. May CTC technologies promote better cancer management? EPMA J. 2015;6:1. doi: 10.1186/s13167-014-0023-x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Nel I, David P, Gerken GG, Schlaak JF, Hoffmann AC. Role of circulating tumor cells and cancer stem cells in hepatocellular carcinoma. Hepatol Int. 2014;8:321–329. doi: 10.1007/s12072-014-9539-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Yang F, Xu J, Tang L, Guan X. Breast cancer stem cell: the roles and therapeutic implications. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2017;74:951–966. doi: 10.1007/s00018-016-2334-7. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Kolostova K, Cegan M, Bobek V. Circulating tumour cells in patients with urothelial tumours: enrichment and in vitro culture. Canadian Urological Association journal. 2014;8:E715–E720. doi: 10.5489/cuaj.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Meyer CP, Pantel K, Tennstedt P, Stroelin P, Schlomm T, Heinzer H, Riethdorf S, Steuber T. Limited prognostic value of preoperative circulating tumor cells for early biochemical recurrence in patients with localized prostate cancer. Urol Oncol. 2016;34:235 e11–235 e16. doi: 10.1016/j.urolonc.2015.12.003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Liu Q, Liao Q, Zhao Y. Myeloid-derived suppressor cells (MDSC) facilitate distant metastasis of malignancies by shielding circulating tumor cells (CTC) from immune surveillance. Med Hypotheses. 2016;87:34–39. doi: 10.1016/j.mehy.2015.12.007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Mu Z, Benali-Furet N, Uzan G, Znaty A, Ye Z, Paolillo C, Wang C, Austin L, Rossi G, Fortina P, et al. Detection and characterization of circulating tumor associated cells in metastatic breast cancer. Int J Mol Sci. 2016;17(10):1665. doi: 10.3390/ijms17101665. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Li M, Zhang B, Zhang Z, Liu X, Qi X, Zhao J, Jiang Y, Zhai H, Ji Y, Luo D. Stem cell-like circulating tumor cells indicate poor prognosis in gastric cancer. Biomed Res Int. 2014;2014:981261. doi: 10.1155/2014/981261. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Bidard FC, Proudhon C, Pierga JY. Circulating tumor cells in breast cancer. Mol Oncol. 2016;10:418–430. doi: 10.1016/j.molonc.2016.01.001. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Noman MZ, Messai Y, Muret J, Hasmim M, Chouaib S. Crosstalk between CTC, immune system and hypoxic tumor microenvironment. Cancer microenvironment: official journal of the International Cancer Microenvironment Society. 2014;7:153–160. doi: 10.1007/s12307-014-0157-3. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Alix-Panabières C, Pantel K. Challenges in circulating tumour cell research. Nat Rev Cancer. 2014;14(9):623–631. doi: 10.1038/nrc3820. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Grillet F, Bayet E, Villeronce O, Zappia L. Circulating tumour cells from patients with colorectal cancer have cancer stem cell hallmarks in ex vivo culture. Gut. 2016; 10.1136/gutjnl-2016-311447. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- 26.Sieuwerts AM, Kraan J, Bolt-de Vries J, van der Spoel P, Mostert B, Martens JW, Gratama JW, Sleijfer S, Foekens JA. Molecular characterization of circulating tumor cells in large quantities of contaminating leukocytes by a multiplex real-time PCR. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2009;118:455–468. doi: 10.1007/s10549-008-0290-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Khoo BL, Lee SC, Kumar P, Tan TZ, Warkiani ME, Ow SG, Nandi S, Lim CT, JP T. Short-term expansion of breast circulating cancer cells predicts response to anti-cancer therapy. Oncotarget. 2015;6:15578–15593. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.3903. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Ameri K, Luong R, Zhang H, Powell AA, Montgomery KD, Espinosa I, Bouley DM, Harris AL, Jeffrey SS. Circulating tumour cells demonstrate an altered response to hypoxia and an aggressive phenotype. Br J Cancer. 2010;102:561–569. doi: 10.1038/sj.bjc.6605491. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Zhou MD, Hao S, Williams AJ, Harouaka RA, Schrand B, Rawal S, Ao Z, Brenneman R, Gilboa E, Lu B, et al. Separable bilayer microfiltration device for viable label-free enrichment of circulating tumour cells. Sci Rep. 2014;4:7392. doi: 10.1038/srep07392. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Yu M, Bardia A, Aceto N, Bersani F, Madden MW, Donaldson MC, Desai R, Zhu H, Comaills V, Zheng Z, et al. Ex vivo culture of circulating breast tumor cells for individualized testing of drug susceptibility. Science. 2014;345:216–220. doi: 10.1126/science.1253533. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Cayrefourcq L, Mazard T, Joosse S, Solassol J, Ramos J, Assenat E, Schumacher U, Costes V, Maudelonde T, Pantel K, et al. Establishment and characterization of a cell line from human circulating colon cancer cells. Cancer Res. 2015;75:892–901. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-14-2613. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Kulasinghe A, Perry C, Warkiani ME, Blick T, Davies A. Short term ex-vivo expansion of circulating head and neck tumour cells. Oncotarget. 2016;7:60101–60109. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.11159. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Kolostova K, Matkowski R, Gurlich R, Grabowski K, Soter K, Lischke R, Schutzner J, Bobek V. Detection and cultivation of circulating tumor cells in gastric cancer. Cytotechnology. 2016;68:1095–1102. doi: 10.1007/s10616-015-9866-9. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Laget S, Broncy L, Hormigos K, Dhingra DM, BenMohamed F, Capiod T, Osteras M, Farinelli L, Jackson S, Paterlini-Brechot P. Technical insights into highly sensitive isolation and molecular characterization of fixed and live circulating tumor cells for early detection of tumor invasion. PLoS One. 2017;12:e0169427. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0169427. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Klevebring D, Rosin G, Ma R, Lindberg J, Czene K, Kere J, Fredriksson I, Bergh J, Hartman J. Sequencing of breast cancer stem cell populations indicates a dynamic conversion between differentiation states in vivo. Breast cancer research : BCR. 2014;16:R72. doi: 10.1186/bcr3687. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Iliopoulos D, Hirsch HA, Wang G, Struhl K. Inducible formation of breast cancer stem cells and their dynamic equilibrium with non-stem cancer cells via IL6 secretion. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2011;108:1397–1402. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1018898108. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Fessler E, Dijkgraaf FE, De Sousa EMF, Medema JP. Cancer stem cell dynamics in tumor progression and metastasis: is the microenvironment to blame? Cancer Lett. 2013;341:97–104. doi: 10.1016/j.canlet.2012.10.015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Vermeulen L, de Sousa e Melo F, Richel DJ, Medema JP. The developing cancer stem-cell model: clinical challenges and opportunities. The Lancet Oncology. 2012;13:e83–e89. doi: 10.1016/S1470-2045(11)70257-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Gallaher J, Babu A, Plevritis S, Anderson AR. Bridging population and tissue scale tumor dynamics: a new paradigm for understanding differences in tumor growth and metastatic disease. Cancer Res. 2014;74:426–435. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-13-0759. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Miyamoto DT, Lee RJ, Stott SL, Ting DT, Wittner BS, Ulman M, Smas ME, Lord JB, Brannigan BW, Trautwein J, et al. Androgen receptor signaling in circulating tumor cells as a marker of hormonally responsive prostate cancer. Cancer Discov. 2012;2:995–1003. doi: 10.1158/2159-8290.CD-12-0222. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Wang H, Stoecklein NH, Lin PP, Gires O. Circulating and disseminated tumor cells: diagnostic tools and therapeutic targets in motion. Oncotarget. 2017;8:1884–1912. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.12242. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Jie XX, Zhang XY, CJ X. Epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition, circulating tumor cells and cancer metastasis: mechanisms and clinical applications. Oncotarget. 2017; 10.18632/oncotarget.18277. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- 43.Ravasio R, Ceccacci E, Minucci S. Self-renewal of tumor cells: epigenetic determinants of the cancer stem cell phenotype. Curr Opin Genet Dev. 2016;36:92–99. doi: 10.1016/j.gde.2016.04.002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44.Zhang JX, Chen ZH, Xu Y, Chen JW, Weng HW, Yun M, Zheng ZS, Chen C, Wu BL, Li EM, et al. Downregulation of MicroRNA-644a promotes esophageal Squamous cell carcinoma aggressiveness and stem cell-like phenotype via Dysregulation of PITX2. Clinical cancer research : an official journal of the American Association for Cancer Research. 2017;23:298–310. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-16-0414. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45.Visvader JE, Lindeman GJ. Cancer stem cells: current status and evolving complexities. Cell Stem Cell. 2012;10(6):717–728. doi: 10.1016/j.stem.2012.05.007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46.de Sousa e Melo F, Kurtova AV, Harnoss JM, Kljavin N, Hoeck JD, Hung J, Anderson JE, Storm EE, Modrusan Z, Koeppen H, et al. A distinct role for Lgr5+ stem cells in primary and metastatic colon cancer. Nature. 2017;543(7647):676–680. doi: 10.1038/nature21713. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47.Shimokawa M, Ohta Y, Nishikori S, Matano M, Takano A, Fujii M, Date S, Sugimoto S, Kanai T, Sato T. Visualization and targeting of LGR5+ human colon cancer stem cells. Nature. 2017;545:187–192. doi: 10.1038/nature22081. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 48.Malara N, Trunzo V, Foresta U, Amodio N, De Vitis S, Roveda L, Fava M, Coluccio M, Macri R, Di Vito A, et al. Ex-vivo characterization of circulating colon cancer cells distinguished in stem and differentiated subset provides useful biomarker for personalized metastatic risk assessment. J Transl Med. 2016;14:133. doi: 10.1186/s12967-016-0876-y. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 49.Gkountela S, Szczerba B, Donato C, Aceto N. Recent advances in the biology of human circulating tumour cells and metastasis. ESMO Open. 2016;1:e000078. doi: 10.1136/esmoopen-2016-000078. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 50.Deshmukh A, Deshpande K, Arfuso F, Newsholme P, Dharmarajan A. Cancer stem cell metabolism: a potential target for cancer therapy. Mol Cancer. 2016;15:69. doi: 10.1186/s12943-016-0555-x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 51.Li Z, Bao S, Wu Q, Wang H, Eyler C, Sathornsumetee S, Shi Q, Cao Y, Lathia J, McLendon RE, et al. Hypoxia-inducible factors regulate tumorigenic capacity of glioma stem cells. Cancer Cell. 2009;15:501–513. doi: 10.1016/j.ccr.2009.03.018. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 52.Lai Y, Wei X, Lin S, Qin L, Cheng L, Li P. Current status and perspectives of patient-derived xenograft models in cancer research. J Hematol Oncol. 2017;10:106. doi: 10.1186/s13045-017-0470-7. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 53.Jiao LR, Apostolopoulos C, Jacob J, Szydlo RNJ. Unique localization of circulating tumor cells in patients with hepatic metastases. J Clin Oncol Off J Am Soc Clin Oncol. 2009;27:6160–6165. doi: 10.1200/JCO.2009.24.5837. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 54.Zhang Z, Shiratsuchi H, Lin J, Chen G, Reddy RM, Azizi E, Fouladdel S, Chang AC, Lin L, Jiang H, et al. Expansion of CTCs from early stage lung cancer patients using a microfluidic co-culture model. Oncotarget. 2014;5:12383–12397. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.2592. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 55.Braunholz D, Saki M, Niehr F, Öztürk M, Borràs Puértolas B, Konschak R, Budach V, Tinhofer I. Spheroid culture of head and neck cancer cells reveals an important role of EGFR Signalling in anchorage independent survival. PLoS One. 2016;11:e0163149. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0163149. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 56.Fan X, Liu S, Su F, Pan Q, Lin T. Effective enrichment of prostate cancer stem cells from spheres in a suspension culture system. Urol Oncol. 2012;30:314–318. doi: 10.1016/j.urolonc.2010.03.019. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 57.Rosland GV, Svendsen A, Torsvik A, Sobala E, McCormack E, Immervoll H, Mysliwietz J, Tonn JC, Goldbrunner R, Lonning PE, et al. Long-term cultures of bone marrow-derived human mesenchymal stem cells frequently undergo spontaneous malignant transformation. Cancer Res. 2009;69:5331–5339. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-08-4630. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 58.Bielecka ZF, Maliszewska-Olejniczak K, Safir IJ, Szczylik C, Czarnecka AM. Three-dimensional cell culture model utilization in cancer stem cell research. Biol Rev Camb Philos Soc. 2017;92:1505–1520. doi: 10.1111/brv.12293. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 59.Smerage JB, Barlow WE, Hortobagyi GN, Winer EP, Leyland-Jones B, Srkalovic G, Tejwani S, Schott AF, O'Rourke MA, Lew DL, et al. Circulating tumor cells and response to chemotherapy in metastatic breast cancer: SWOG S0500. Journal of clinical oncology : official journal of the American Society of Clinical Oncology. 2014;32:3483–3489. doi: 10.1200/JCO.2014.56.2561. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 60.Lu SH, Tsai WS, Chang YH, Chou TY, Pang ST, Lin PH, Tsai CM, Chang YC. Identifying cancer origin using circulating tumor cells. Cancer biology & therapy. 2016;17:430–438. doi: 10.1080/15384047.2016.1141839. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 61.Schindlbeck C, Andergassen U, Jueckstock J, Rack B, Janni W, Jeschke U. Disseminated and circulating tumor cells in bone marrow and blood of breast cancer patients: properties, enrichment, and potential targets. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 2016;142(9):1883–1895. doi: 10.1007/s00432-016-2118-3. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 62.Weiss S, Reynolds BA, Vescovi AL, Morshead C, Craig CG. Der Kooy Dv. Is there a neural stem cell in the mammalian forebrain? Trends Neurosci. 1996;19:387–393. doi: 10.1016/S0166-2236(96)10035-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 63.Vescovi AL, Reynolds BA, Fraser DD, S W. bFGF regulates the proliferative fate of unipotent (neuronal) and bipotent (neuronal/astroglial) EGF-generated CNS progenitor cells. Neuron. 1993;11:951–966. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(93)90124-A. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 64.Ponti D, Costa A, Zaffaroni N, Pratesi G, Petrangolini G, Coradini D, Pilotti S, Pierotti MA, Daidone MG. Isolation and in vitro propagation of Tumorigenic breast cancer cells with stem/progenitor cell properties. Cancer Res. 2005;65:5506–5511. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-05-0626. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 65.Lee J, Kotliarova S, Kotliarov Y, Li A, Su Q, Donin NM, Pastorino S, Purow BW, Christopher N, Zhang W, et al. Tumor stem cells derived from glioblastomas cultured in bFGF and EGF more closely mirror the phenotype and genotype of primary tumors than do serum-cultured cell lines. Cancer Cell. 2006;9:391–403. doi: 10.1016/j.ccr.2006.03.030. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 66.Liao MJ, Zhang CC, Zhou B, Zimonjic DB, Mani SA, Kaba M, Gifford A, Reinhardt F, Popescu NC, Guo W, et al. Enrichment of a population of mammary gland cells that form mammospheres and have in vivo repopulating activity. Cancer Res. 2007;67:8131–8138. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-06-4493. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 67.Wang W, Itaka K, Ohba S, Nishiyama N, Chung UI, Yamasaki Y, Kataoka K. 3D spheroid culture system on micropatterned substrates for improved differentiation efficiency of multipotent mesenchymal stem cells. Biomaterials. 2009;14:2705–2715. doi: 10.1016/j.biomaterials.2009.01.030. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 68.Han ME, Jeon TY, Hwang SH, Lee YS, Kim HJ, Shim HE, Yoon S, Baek SY, Kim BS, Kang CD, et al. Cancer spheres from gastric cancer patients provide an ideal model system for cancer stem cell research. Cellular and molecular life sciences : CMLS. 2011;68:3589–3605. doi: 10.1007/s00018-011-0672-z. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 69.Ashworth TR. A case of cancer in which cells similar to those in the tumors were seen in the blood after death. Aus Medj. 1869;14:146–149. [Google Scholar]
- 70.Seal SH. Silicone flotation: a simple quantitative method for the isolation of free-floating cancer cells from the blood. Cancer biology & therapy. 1959;12:590–595. doi: 10.1002/1097-0142(195905/06)12:3<590::aid-cncr2820120318>3.0.co;2-n. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 71.Alix-Panabieres C, Bartkowiak K, Pantel K. Functional studies on circulating and disseminated tumor cells in carcinoma patients. Mol Oncol. 2016;10:443–449. doi: 10.1016/j.molonc.2016.01.004. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 72.Racila E, Euhus D, Weiss AJ, Rao CJM. Detection and characterization of carcinoma cells in the blood. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1998;95:4589–4594. doi: 10.1073/pnas.95.8.4589. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 73.Pretlow TG, Schwartz S, Giaconia JM, Wright AL, Grimm HA, Edgehouse NL, Murphy JR, Markowitz SD, Jamison JM, Summers JL, et al. Prostate cancer and other Xenografts from cells in peripheral blood of patients. Cancer Res. 2000;60:4033–4036. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 74.Zheng S, Lin HK, Lu B, Williams A, Datar R, Cote RJ, Tai YC. 3D microfilter device for viable circulating tumor cell (CTC) enrichment from blood. Biomed Microdevices. 2011;13:203–213. doi: 10.1007/s10544-010-9485-3. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 75.Deneve E, Riethdorf S, Ramos J, Nocca D, Coffy A, Daures JP, Maudelonde T, Fabre JM, Pantel K, Alix-Panabieres C. Capture of viable circulating tumor cells in the liver of colorectal cancer patients. Clin Chem. 2013;59:1384–1392. doi: 10.1373/clinchem.2013.202846. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 76.Alix-Panabières C. EPISPOT assay: detection of viable DTCs/CTCs in solid tumor patients. Recent Results Cancer Res. 2012;195:69–76. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-28160-0_6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 77.Zhang L, Ridgway LD, Wetzel MD, Ngo J, Yin W, Kumar D, Goodman JC, Groves MD, Marchetti D. The identification and characterization of breast cancer CTCs competent for brain metastasis. Sci Transl Med. 2013;5:180ra48. doi: 10.1126/scitranslmed.3005109. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 78.Gao D, Vela I, Sboner A, Iaquinta PJ, Karthaus WR, Gopalan A, Dowling C, Wanjala JN, Undvall EA, Arora VK, et al. Organoid cultures derived from patients with advanced prostate cancer. Cell. 2014;159:176–187. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2014.08.016. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 79.Yang Z, Li C, Fan Z, Liu H, Zhang X, Cai Z, Xu L, Luo J, Huang Y, He L, et al. Single-cell sequencing reveals variants in ARID1A, GPRC5A and MLL2 driving self-renewal of human bladder cancer stem cells. Eur Urol. 2017;71:8–12. doi: 10.1016/j.eururo.2016.06.025. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 80.Dosch JS, Ziemke EK, Shettigar A, Rehemtulla A, Sebolt-Leopold JS. Cancer stem cell marker phenotypes are reversible and functionally homogeneous in a preclinical model of pancreatic cancer. Cancer Res. 2015;75:4582–4592. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-14-2793. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 81.Lichner Z, Saleh C, Subramaniam V, Seivwright A, Prud'homme GJ, Yousef GM. miR-17 inhibition enhances the formation of kidney cancer spheres with stem cell/ tumor initiating cell properties. Oncotarget. 2014;6:5567–5581. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.1901. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 82.Nolte SM, Venugopal C, McFarlane N, Morozova O, Hallett RM, O'Farrell E, Manoranjan B, Murty NK, Klurfan P, Kachur E, et al. A cancer stem cell model for studying brain metastases from primary lung cancer. J Natl Cancer Inst. 2013;105:551–562. doi: 10.1093/jnci/djt022. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 83.Paranjape AN, Mandal T, Mukherjee G, Kumar MV, Sengupta K, Rangarajan A. Introduction of SV40ER and hTERT into mammospheres generates breast cancer cells with stem cell properties. Oncogene. 2012;31:1896–1909. doi: 10.1038/onc.2011.378. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 84.Dey D, Saxena M, Paranjape AN, Krishnan V, Giraddi R, Kumar MV, Mukherjee G, Rangarajan A. Phenotypic and functional characterization of human mammary stem/progenitor cells in long term culture. PLoS One. 2009;4:e5329. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0005329. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 85.Lombardo Y, Filipovic A, Molyneux G, Periyasamy M. Nicastrin regulates breast cancer stem cell properties and tumor growth in vitro and in vivo. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2012;109:16558–16563. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1206268109. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 86.Hussein D, Punjaruk W, Storer LC, Shaw L, Othman R, Peet A, Miller S, Bandopadhyay G, Heath R, Kumari R, et al. Pediatric brain tumor cancer stem cells: cell cycle dynamics, DNA repair, and etoposide extrusion. Neuro-Oncology. 2011;13:70–83. doi: 10.1093/neuonc/noq144. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 87.Wang K, Kievit FM, Erickson AE, Silber JR, Ellenbogen RG, Zhang M. Culture on 3D Chitosan-Hyaluronic acid scaffolds enhances stem cell marker expression and drug resistance in human Glioblastoma cancer stem cells. Advanced healthcare materials. 2016;5:3173–3181. doi: 10.1002/adhm.201600684. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 88.Kolostova K, Matkowski R, Jędryka M, Soter K. The added value of circulating tumor cells examination in ovarian cancer staging. Am J Cancer Res. 2015;5:3363–3375. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 89.Kolostova K, Spicka J, Matkowski R, Bobek V. Isolation, primary culture, morphological and molecular characterization of circulating tumor cells in gynecological cancers. Am J Transl Res. 2015;7:1203–1213. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 90.Kolostova K, Pinkas M, Jakabova A, Pospisilova E, Svobodova P. Molecular characterization of circulating tumor cells in ovarian cancer. Am J Cancer Res. 2016;6:973–980. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 91.Bobek V, Gurlich R, Eliasova P, Kolostova K. Circulating tumor cells in pancreatic cancer patients: enrichment and cultivation. World J Gastroenterol. 2014;20:17163–17170. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v20.i45.17163. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 92.Kolostova K, Zhang Y, Hoffman RM, Bobek V. In vitro culture and characterization of human lung cancer circulating tumor cells isolated by size exclusion from an orthotopic nude-mouse model expressing fluorescent protein. J Fluoresc. 2014;24:1531–1536. doi: 10.1007/s10895-014-1439-3. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Data Availability Statement
Not applicable


