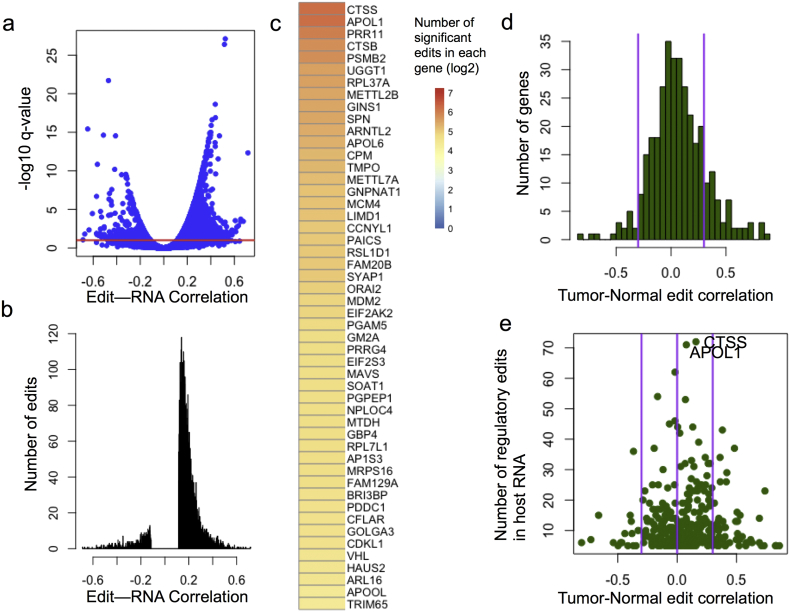
Fig. 2.
Landscape of regulatory RNA editing sites in LUAD. (A) Plot showing the distribution of RNA editing site-mRNA abundance correlation and the significance of the association. The red line denotes q-value < 0.1 significance threshold. Histogram of regulatory RNA editing sites' association to RNA abundance (B). Genes are ranked by the number of predicted regulatory RNA editing sites within their RNA molecule, and the top 50 are shown in (C). Edits are grouped by their host gene and RNA editing site-RNA spearman correlations are compared between tumor and normal (D). Genes with high Tumor-normal regulatory RNA editing site correlation have regulatory RNA editing sites with similar regulatory potential in both tumor and normal. The tumor-normal edit correlation is plotted against the number of regulatory edits in each host RNA molecule (E).