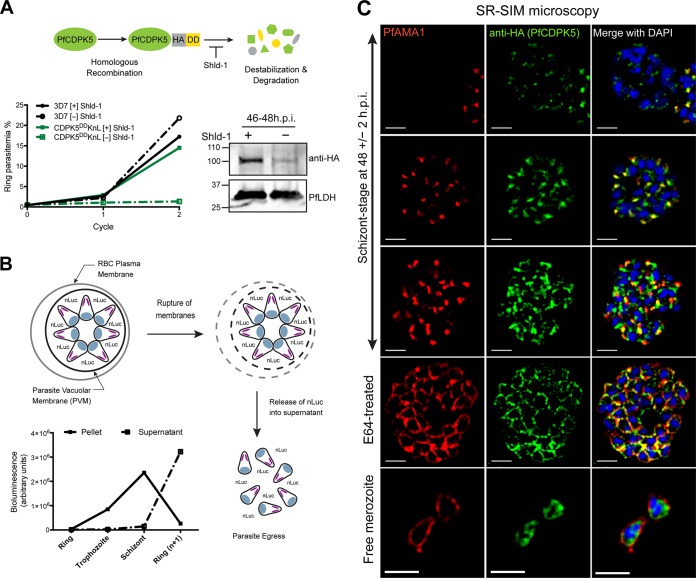
FIG 1 .
Characterization of 3D7-PfCDPK5DDKnL parasites and PfCDPK5 localization. (A, top) Schematic of 3D7-PfCDPK5DDKnL regulation. This parasite strain has two genetic modifications. The destabilizing domain (DD) is fused to the carboxy terminus of PfCDPK5, and the KnL reporter gene is integrated into the genome. The PfCDPK5 fusion protein is stabilized in the presence of Shld-1 and degraded in the absence of Shld-1. (Bottom left) Replication curves of 3D7-PfCDPK5DDKnL and control 3D7 parasites cultured with Shld-1 ([+] Shld-1) and without Shld-1 ([−] Shld-1). Values are means ± standard deviations (SD) (error bars) (n = 3). (Bottom right) Immunoblot of schizont-stage lysates probed with anti-HA (recognizes the epitope tag of PfCDPK5-3HA-DD) and anti-PfLDH (loading control). The positions of molecular mass markers (in kilodaltons) are indicated to the left of the blot. h.p.i., hours post-invasion. (B) Schematic of KnL reporter protein release from 3D7-PfCDPK5DDKnL parasites. The graph shows bioluminescent activity in supernatant and parasite pellets from ring, trophozoite, schizont, and reinvaded parasites. Values are means ± SD (n = 3). (C) Schizonts from [+] Shld-1 3D7-PfCDPK5DDKnL parasites were fixed, probed with anti-HA and anti-PfAMA1 antibodies, and visualized by SR-SIM. Bars, 2 µm.