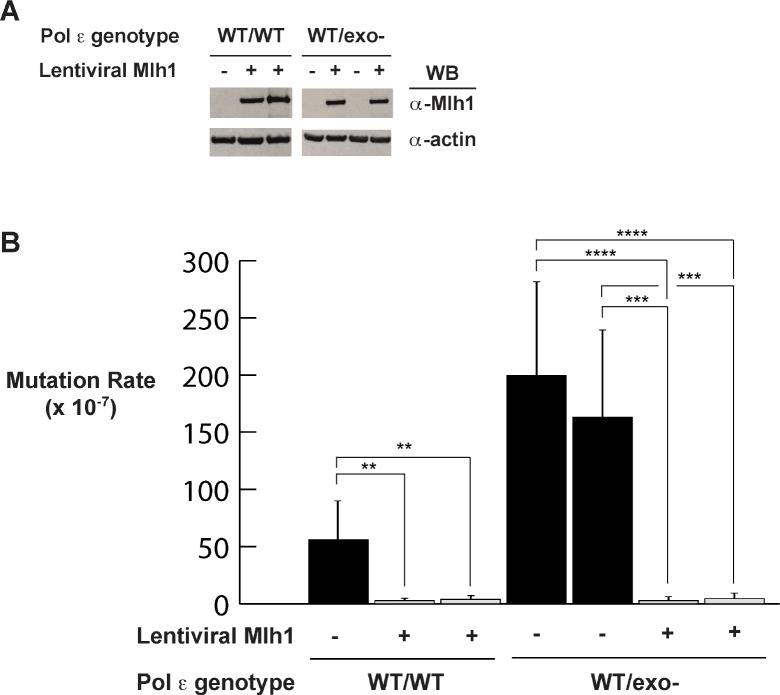
Figure 3. Mismatch repair suppresses exonuclease-deficient Pol ε-induced mutation rate increase.
(A) Lentivirus encoding human Mlh1 was generated and used to infect parental cells with wild type Pol ε and cells heterozygous for Pol ε exonuclease deficiency. Cell lysates were probed by Western blot using antibodies against Mlh1 and β-actin. (B) Mutation rates were measured by fluctuation analysis as described in the Methods using the Ma-Sandri-Sarkar Maximum Likelihood Estimator. Twelve independent isolates from each of two parental (wt/wt) and two heterozygous cell lines (wt/exo-) expressing Mlh1 were used. 95% confidence intervals are shown. Pol εwt/wt Mlh1+ Clone 1 Mutation Rate = 1.7 × 10−7, SEM = 0.72 × 10−7, p=0. 0046. Pol εwt/wt Mlh1+ Clone 2 Mutation Rate = 2.5 × 10−7, SEM = 1.1 × 10−7, p=0.0053. Pol εwt/exo- Mlh1+ Clone 1 Mutation Rate = 2.3 × 10−7, SEM = 0.81 × 10−7, p<0.0001 (vs. Pol εwt/exo- Mlh1- Clone 1) and p=0.0003 (vs. Pol εwt/exo- Mlh1- Clone 2). Pol εwt/exo- Mlh1+ Clone 2 Mutation Rate = 3 × 10−7, SEM = 1.3 × 10−7, p<0.0001 (vs. Pol εwt/exo- Mlh1- Clone 1) and p=0.0003 (vs. Pol εwt/exo- Mlh1- Clone 2). Mutation Rates for Pol εwt/exo- Mlh1+ Clone 1 and Clone 2 were not significantly different (p=0.6485). Mutation rates from cells lacking mismatch repair (from Figure 1A) are shown for comparison.