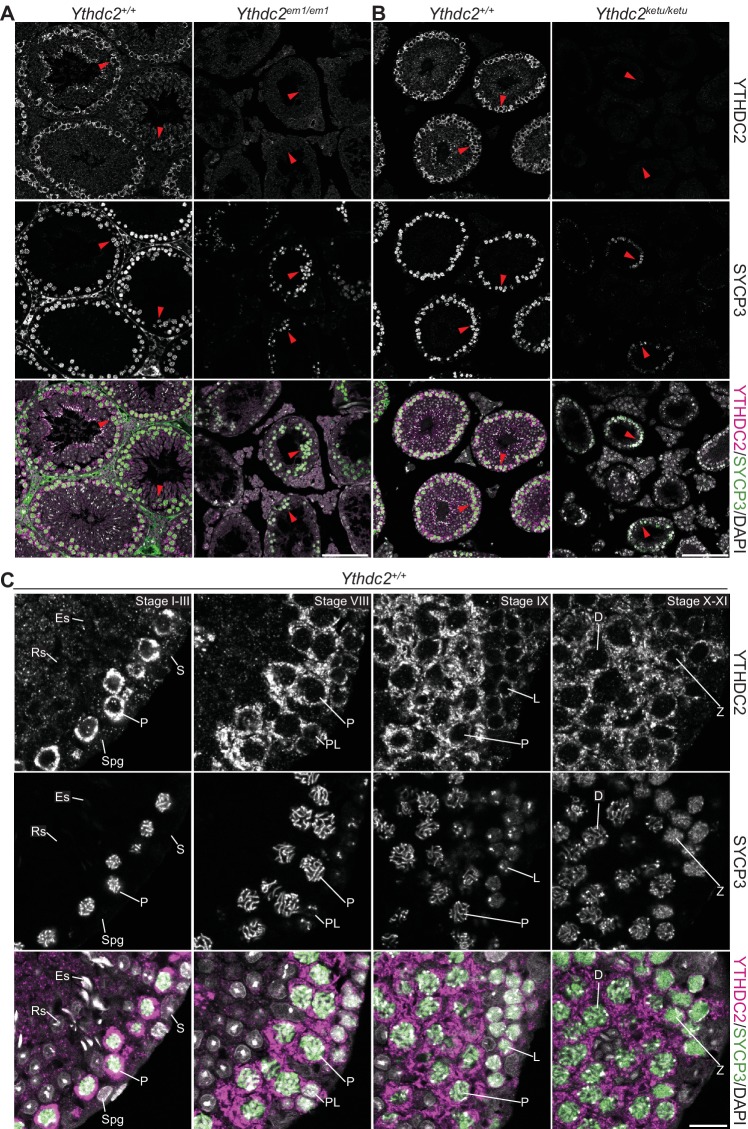
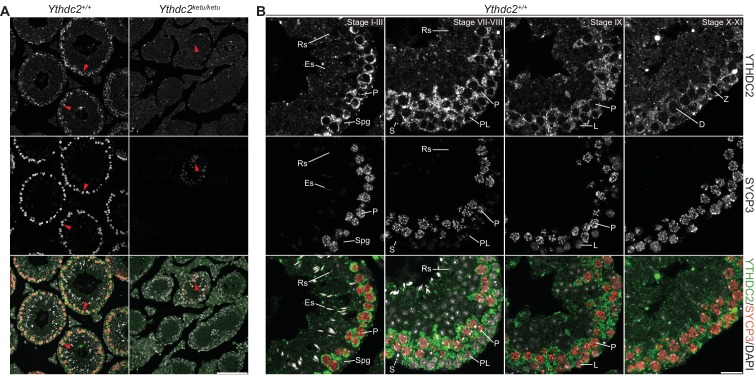
Figure 7. YTHDC2 localization in wild-type and mutant testes.
(A and B) YTHDC2 and SYCP3 immunofluorescence on testis sections from 2-month-old Ythdc2em1/em1, Ythdc2ketu/ketu, and their wild-type littermates. Arrowheads indicate SYCP3-positive spermatocytes. Scale bars represent 100 μm. (C) YTHDC2 and SYCP3 immunofluorescence on testis sections from an adult B6 male. Approximate seminiferous epithelial cycle stages (based on SYCP3 and DAPI staining patterns) are provided. S, Sertoli cell; Spg, spermatogonia; L, leptotene spermatocyte; Z, zygotene spermatocyte; P, pachytene spermatocyte; D, diplotene spermatocyte; RS, round spermatid; ES, elongating spermatid. Scale bar represents 15 μm.