Abstract
The ubiquitin E3 ligase DELTEX1 (DTX1) is specifically downregulated in gastric cancer tissues, and expression of DTX1 is linked to better prognoses and survival in gastric cancer. Cellular FLICE inhibitory protein (c-FLIP) is known for its pivotal role in the resistance of cancer cells to death receptor-induced cell death. Here, we show that DTX1 is an E3 ligase for c-FLIP in gastric cancer cells. DTX1 promoted c-FLIP downregulation. Overexpression of DTX1 sensitized gastric cancer cells to TRAIL-induced apoptosis, whereas DTX1-knockdown attenuated apoptosis induction. DTX1 binds c-FLIPL and directs it into the endosome-lysosomal pathway for proteasome-independent degradation. Moreover, induction of DTX1 in AGS cells by geldanamycin conferred susceptibility of those cells to TRAIL-induced apoptosis. Our results reveal a tumor-suppressive role for DTX1 and suggest a new approach to increasing TRAIL efficacy by raising DTX1 levels in gastric cancer therapy. DTX1 also enhanced c-FLIP degradation and FasL-induced and TRAIL-induced apoptosis in T cells, suggesting that DTX1 constitutes one of the physiological mechanisms regulating c-FLIP stability.
Introduction
Gastric cancer cells are characterized by their resistance to apoptosis induction by death receptors. Gastric cancer has one of the world’s leading cancer mortality rates, with a poor 5-year survival rate1–3. Advanced stages of gastric cancer show local invasion, peritoneal dissemination, and hepatic or para-aortic lymph node metastasis. Surgery remains the curative therapy, but is limited to non-metastatic gastric cancer. The efficacy of chemotherapy for gastric cancer is poor due to multidrug resistance (MDR). Therefore, identification of novel biomarkers and development of new therapeutics for gastric cancer are one of the demanding priorities.
The Death receptor (DR) agonist TRAIL has been explored for its efficacy to induce apoptosis in different types of cancers4–6, including gastric cancer7,8. Like other death receptors, engagement of TRAIL receptors (DR4 and DR5) by TRAIL results in the formation of death-inducing signaling complexes (DISC) containing FADD and procaspase-89–12. Procaspase-8 undergoes autoproteolytic cleavage to generate active caspase-8 at DISC, leading to activation of downstream caspases and irreversible cell damage. Cellular FLICE-inhibitory protein (c-FLIP) is a master anti-apoptotic factor that suppresses death receptor-induced apoptosis by interfering with the processing of procaspase-8 at DISC9–15. c-FLIP also inhibits necrosis and autophagy16–18. c-FLIP is partly accountable for the failure of TRAIL receptor agonists in clinical attempts to treat cancers4,19, so it is a target for cancer therapy19–21. Expression of c-FLIP is induced by activation signaling, including NF-κB22, Akt, and ERK13,19,22–24. Levels of c-FLIP protein are subjected to regulation by two ubiquitin E3 ligases, ITCH and CBL, through the promotion of polyubiquitination and subsequent proteosomal degradation of c-FLIP25,26.
TRAIL receptors and the downstream effector caspase-8 are intact in gastric cancer cells27,28. However, gastric cancers are generally resistant to TRAIL-induced cell death, and induction of TRAIL-mediated cytotoxicity always requires co-stimulation with a sensitizing reagent. c-FLIP is upregulated in gastric cancer and is associated with metastasis and tumor progression29,30. As in other types of cancer, c-FLIP contributes to the resistance to TRAIL-induced apoptosis in gastric cancer31–34. We have previously shown that Helicobacter pylori enhances the susceptibility to TRAIL-induced apoptosis in gastric cancer cells by downregulation of c-FLIP34.
Deltex (DTX) is a target of Notch, and is composed of Notch-binding WWE domains at the N-terminus, followed by a proline-rich motif, and a C-terminal RING finger domain35,36. DTX1 confers ligand-independent activation of Notch by directing the ubiquitination and endosomal entry of Notch37,38. Similar to the E3 ligases Itch and Cbl-b39, DTX1 is a target of NFAT and is involved in T cell tolerance40,41. We recently found that DTX1 promotes the degradation of PKCθ and PLC-γ in a way similar to ITCH and Cbl-b42.
In the present study, we show that DTX1 is specifically downregulated in gastric cancer and is critical for the resistance of gastric cancer cells to TRAIL-induced cell death. DTX1 binds to c-FLIP and promotes degradation of c-FLIP through the endosome-lysosomal pathway. Re-introduction of DTX1 into gastric cancer cells increased TRAIL-induced apoptosis and also reduced c-FLIP. In addition, a treatment that increased DTX1 expression also sensitized gastric cancer to TRAIL treatment. Our results suggest that induction of DTX1 could be a new approach to enhancing the benefits of TRAIL-mediated cancer therapy. We also found that DTX1 enhanced c-FLIP degradation and Fas-induced and TRAIL-induced apoptosis in T cells, indicating that DTX1 constitutes one of the physiological mechanisms regulating c-FLIP stability.
Results
DTX1 expression is negatively correlated with gastric cancer progression
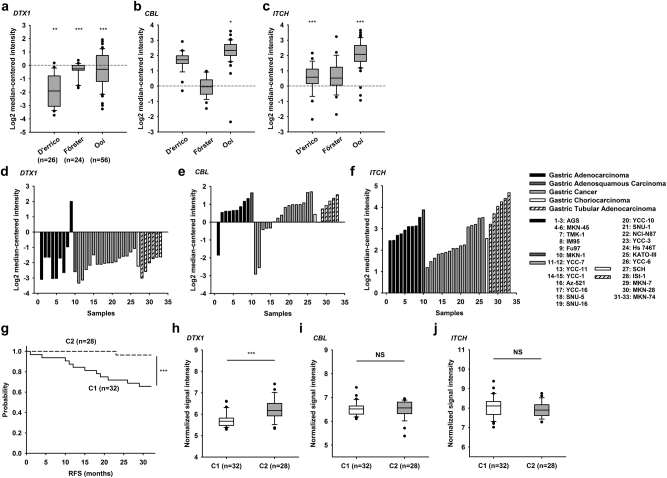
We found that expression of the ubiquitin E3 ligase DELTEX1 (DTX1) is reduced in gastric adenocarcinoma tissues from patients (Fig. 1a). In contrast, expression of ITCH and CBL, the ubiquitin E3 ligases that have been shown to promote polyubiquitination and proteosomal degradation of c-FLIP25,26, are normal or increased in the same gastric cancer tissues (Fig. 1b, c)43–45. In another analysis of human gastric cancer cell lines45, expression of DTX1 is reduced in most of the gastric cancer cell lines examined (Fig. 1d). Expression of CBL is variable in different gastric cancer cell lines, whereas the expression of ITCH is increased in the same group of gastric cancer cell lines (Fig. 1e, f), suggesting that the ITCH-mediated and CBL-mediated c-FLIP degradation processes are not operational in gastric cancer. Gene expression-based prognosis risk score analyses in gastric cancer have also shown that gastric cancer tissues from relapse-free survival (RFS) patients46 expressed higher levels of DTX1 mRNA (Fig. 1g, h). This is in contrast to no correlation being found between the expression of CBL or ITCH and the RFS of gastric cancer patients (Fig. 1i, j). Therefore, DTX1 is downregulated in gastric cancer tissues and DTX1 expression is negatively correlated with gastric cancer progression.
Fig. 1. DTX1is downregulated in gastric cancer andDTX1is correlated with relapse-free survival.
a–c DTX1 expression is lower while CBL and ITCH expressions are normal or elevated in gastric intestinal type adenocarcinoma. Expression of DTX1 (a), CBL (b), and ITCH (c) mRNA in human gastric cancer tissue versus normal43–45. All three databases contain patients presenting with gastric intestinal type adenocarcinoma. The numbers of patient samples in each database are indicated in Fig. 1a. *P ≤ 0.05, **P ≤ 0.01, ***P ≤ 0.001 by Student’s t-test (gastric intestinal type adenocarcinoma vs normal). Data were taken from Oncomine (www.oncomine.org). d–f DTX1 expression (d) is mostly downregulated, whereas CBL (e) and ITCH (f) expressions are mostly increased in different human gastric cancer cell lines. The names and types of the human gastric cancer cell lines from Ooi et al.45 are indicated at right. g–j Higher DTX1 expression in a gastric cancer cluster with better relapse-free survival (RFS). Kaplan–Meier plots (g) of two gastric cancer clusters of different relapse-free survival (RFS)46. P = 0.001 by the log-rank test. Analysis of DTX1 (h), CBL (i), and ITCH (j) expression between C1 and C2 clusters. ***P ≤ 0.001 by Student’s t-test NS, not significant.
DTX1 promotes c-FLIP downregulation and TRAIL-induced apoptosis in gastric cancer cells
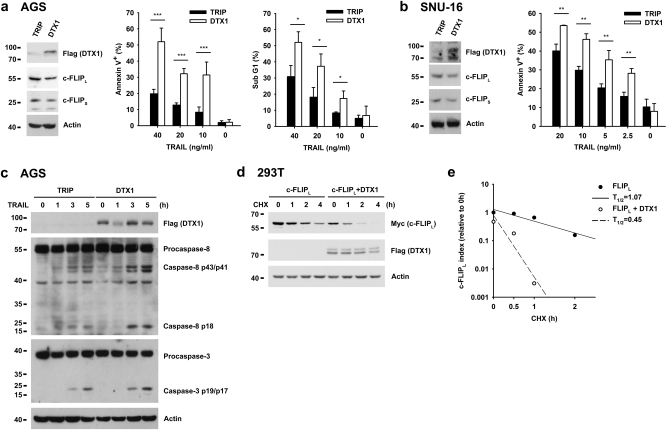
DTX1 is a ubiquitin E3 ligase that is functionally analogous to ITCH and CBL in T cell anergy40,42. Since ITCH and CBL stimulate c-FLIP downregulation, we examined the possible effect of DTX1 on levels of c-FLIPL. We found that overexpression of DTX1 in human gastric adenocarcinoma AGS cells decreased the levels of c-FLIPL and c-FLIPS (Fig. 2a). Consistent with a reduction in c-FLIP, DTX1-expressing AGS cells were more sensitive to apoptosis induced by TNF-related apoptosis-inducing ligand (TRAIL) (Fig. 2a). In another gastric cancer cell line, SNU-16, DTX1 expression also reduced the protein levels of FLIPL and c-FLIPS, with a concomitant increase in TRAIL-induced cell death (Fig. 2b). This effect was accompanied by enhanced activation of pro-caspase-8 into p43 and p18 in DTX1-expressing AGS cells (Fig. 2c). Enhanced formation of active caspase-3 was also found in TRAIL-stimulated DTX1-expressing AGS cells (Fig. 2c).
Fig. 2. DTX1 sensitizes TRAIL-induced apoptosis via c-FLIP downregulation.
a DTX1 enhances TRAIL-induced apoptosis in AGS cells. The levels of Flag-DTX1, c-FLIPL and c-FLIPS in control (TRIP) and DTX1-expressing AGS cells were determined (left). Control and DTX1-expressing AGS cells were treated with TRAIL. Cell death, as established from the Annexin V+ population and sub-G1 cell fraction, were quantitated 5 and 24 h after TRAIL treatment, respectively. Values are mean ± SD of triplicates in an experiment. *P ≤ 0.05, **P ≤ 0.01, ***P ≤ 0.001. The experiment was independently repeated three times. b DTX1 promotes TRAIL-induced cell death in SNU-16 cells. Control (TRIP) and DTX1-expressing SNU-16 cells were treated with TRAIL at the indicated concentrations. The Annexin V+ population and levels of c-FLIPL, c-FLIPS, and DTX1 in control and DTX1-expressing SNU-16 cells were determined as in (a). Values are mean ± SD of a triplicate experiment. Experiments were independently repeated three times with similar results. c DTX1 enhances activation of caspase-8 and caspase-3. Control (TRIP) and DTX1-expressing AGS cells were treated with 20 ng/ml TRAIL. The levels of procaspase-8, processed caspase-8, procaspase-3, and active caspase-3 at the indicated time-points were analyzed by Western blot. The experiment was independently repeated three times with comparable results. d, e DTX1 decreases FLIPL protein stability. c-FLIPL-Myc was transfected with or without DTX1-Flag into 293T cells. After 24 h, transfected cells were treated with cycloheximide (CHX, 50 ng/ml) for the indicated time-points. Cell lysates were prepared and the contents of c-FLIPL-Myc and DTX1-Flag were determined c. The protein levels of c-FLIPL were quantitated by densitometer. The c-FLIPL protein level at time zero was set as 1. The half-life of c-FLIPL protein was calculated as (d)
DTX1 expression did not affect mRNA expression of c-FLIP (Supplementary Fig. 1a), nor did it affect the levels of Mcl-1, Bcl-2, or caspase-8 (Supplementary Fig. 1b). Even though total concentrations of the TRAIL receptors DR4 and DR5 were increased in DTX1-expressing AGS cells, cell surface levels of DR4 and DR5 remained unchanged (Supplementary Fig. 1b). In contrast, DTX1 increased c-FLIPL protein instability (Fig. 2d), with co-expression of DTX1 decreasing the half-life of c-FLIPL protein by 50% (Fig. 2e).
SNU-16 cells are different from AGS cells due to their detectable expression levels of endogenous DTX1, allowing us to address the role of DTX1 by its knockdown. Levels of FLIPL and c-FLIPS proteins were increased in DTX1-knockdown SNU-16 cells, consistent with a reduction in TRAIL-induced apoptosis (Supplementary Fig. 2). Together, these results suggest that DTX1 enhances DR-induced apoptosis through downregulation of FLIPL.
DTX1 interacts with c-FLIPL
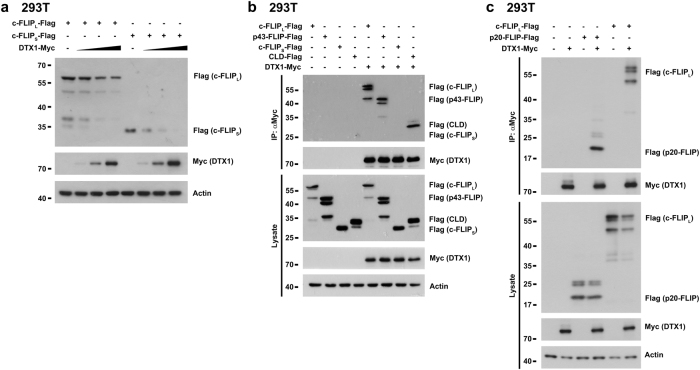
We next examined how DTX1 regulates the stability of c-FLIP protein. We found that DTX1 promoted downregulation of c-FLIPL-FLAG and c-FLIPS-FLAG in 293T cells (Fig. 3a). Immunoprecipitation of DTX1-myc brought down c-FLIPL-FLAG and p43 c-FLIPL-FLAG, but not c-FLIPS-FLAG (Fig. 3b). The c-FLIP caspase-like domain (CLD) was identified as the DTX1-interacting region, evidenced by the ability of DTX1 to bind the CLD (Fig. 3b). We further demonstrated that p20 of the CLD was pulled down by DTX1 (Fig. 3c), suggesting that p20 of the CLD is the region on c-FLIP that binds DTX1. Therefore, DTX1 binds c-FLIPL but does not interact with c-FLIPS. We then investigated how DTX1 enhances the down-regulation of c-FLIPS in 293T cells (Fig. 3a). Only c-FLIPL was expressed in 293T cells (Supplementary Fig. 3a). When transfected in higher amounts into 293T cells, c-FLIPS was resistant to DTX1-mediated downregulation (Supplementary Fig. 3b), in agreement with the inability of c-FLIPS to bind DTX1. However, c-FLIPS-FLAG was downregulated by DTX1 when it was co-expressed with c-FLIPL-FLAG (Supplementary Fig. 3c). Immunoprecipitation of DTX1-myc also pulled down c-FLIPS-FLAG when c-FLIPL-FLAG was co-expressed (Supplementary Fig. 3d). In addition, on introduction of c-FLIPS-FLAG alone, it was found to associate with endogenous c-FLIPL in 293T cells (Supplementary Fig. 3e). These results suggest that intracellular hetero-dimerization of c-FLIPS with c-FLIPL leads to susceptibility of both c-FLIPS and c-FLIPL to DTX1-mediated downregulation in vivo (Fig. 2a, b).
Fig. 3. DTX1 binds c-FLIPLand promotes c-FLIPLdownregulation.
a DTX1 promotes c-FLIP degradation. 293T cells were transfected with c-FLIPL-Flag (200 ng) or c-FLIPS-Flag (2 ng) with increasing amounts of DTX1-Myc. The levels of DTX1, c-FLIPL and c-FLIPS were determined 24 h after transfection. b The caspase-like domain of c-FLIP binds DTX1. DTX1-Myc, c-FLIPL, c-FLIP-p43, c-FLIPS and the caspase-like domain (CLD) were transfected into 293T cells as indicated. Cell lysates were prepared 24 h later and were immunoprecipitated by anti-Myc. The presence of DTX1 and different forms of c-FLIP in the precipitates and lysates were determined by anti-Myc and anti-Flag. c The p20 region in the CLD of c-FLIP binds DTX1. DTX1-Myc, c-FLIPL, and c-FLIP-p20 were transfected into 293T cells as indicated. The levels of DTX1 and different forms of c-FLIP in lysates and anti-Myc immunoprecipitates were determined by anti-Myc and anti-Flag. Experiments (a–c) were independently repeated three times with similar results
DTX1 promotes c-FLIPL degradation by the endosome-lysosome-dependent pathway
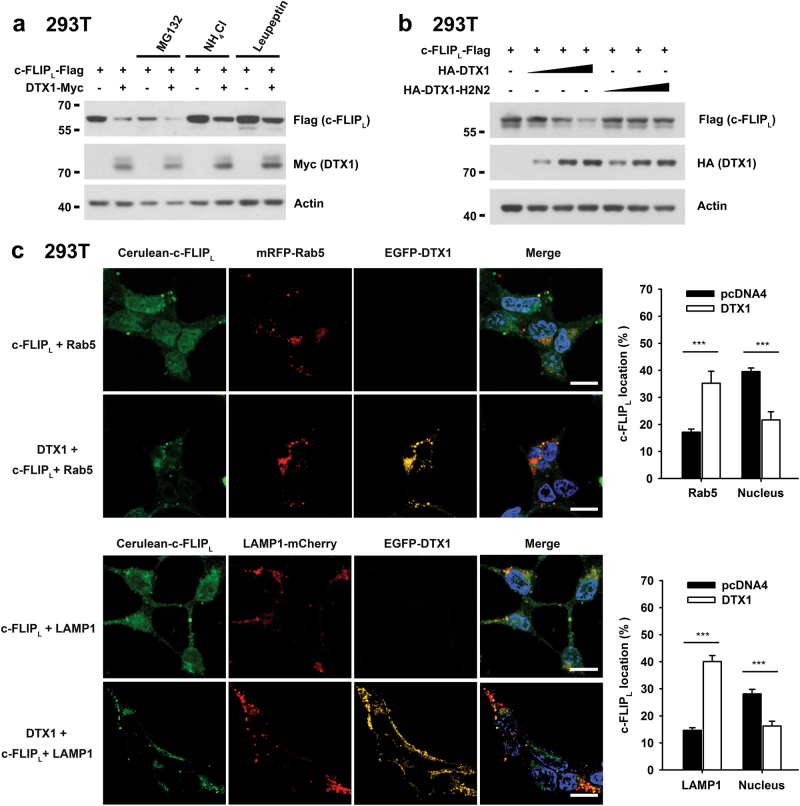
DTX1-mediated c-FLIPL degradation was not prevented by addition of the proteosome inhibitor MG132 (Fig. 4a), suggesting that proteasomes are not involved in this process. Addition of NH4Cl or leupeptin partially protected c-FLIPL from DTX1-induced degradation (Fig. 4a), indicating the involvement of endosome-lysosomal pathways. To further determine the requirement of E3 ligase activity of DTX1 in c-FLIP degradation, we used DTX1 with mutation at E3 ligase active sites (H453N and H456N, H2N2) and found that DTX1-H2N2 was unable to downregulate c-FLIPL (Fig. 4b).
Fig. 4. DTX1 directs c-FLIPL into the endosome-lysosomal degradation pathway.
a DTX1-induced c-FLIPL degradation was inhibited by NH4Cl and Leupeptin. DTX1-Myc and/or c-FLIPL-Flag were transfected into 293T cells. After 24 h, cells were untreated, or treated with MG132 (2.5 μM), NH4Cl (25 mM), or Leupeptin (100 μg/ml) for 8 h. The levels of c-FLIPL-Flag and DTX1-Myc were determined. b Mutation at the RING finger abolishes the ability of DTX1 to downregulate c-FLIPL. 293T cells were transfected with c-FLIPL-Flag with increasing amounts of HA-DTX1 or HA-DTX1-H2N2 (H453N, H456N). The levels of DTX1 and c-FLIPL were determined 24 h after transfection. c DTX1 directs c-FLIPL into endosome–lysosome compartments. 293T cells were transfected with mRFP-Rab5, LAMP1-mCherry, Cerulean-c-FLIPL, or EGFP-DTX1 as indicated. After 24 h, 293T cells were seeded onto polylysine-coated glass coverslips and allowed to attach for another 18 h. Cells were fixed and then mounted in DAPI-Fluoromount-G (Southern Biotechnology Associates). The images of EGFP, Cerulean, mRed, mCherry, and DAPI were obtained under a Zeiss LSM 780 confocal microscope (Zeiss). Experiments were independently repeated three times with similar results. Co-localization of Cerulean-c-FLIPL with mRFP-Rab5 or LAMP1-mCherry in 40–50 cells was calculated using WCIF ImageJ software. Scale bars, 10 μm, ***P ≤ 0.001
c-FLIPL alone was evenly distributed in the nucleus and cytoplasm, without apparent co-localization with the early endosome marker Rab5 (Fig. 4c). Co-expression of DTX1 and c-FLIPL resulted in a significant increase in c-FLIPL and Rab5 co-localization (Fig. 4c), suggesting that entry of c-FLIPL into endosomal compartments is promoted by the c-FLIPL-DTX1 association. Similarly, c-FLIPL was not located in lysosomes when expressed alone, yet the presence of DTX1 enhanced co-localization of c-FLIPL with the lysosomal marker LAMP (Fig. 4c). Together, these results suggest that DTX1 directs c-FLIPL into endosomal and lysosomal compartments for c-FLIP degradation.
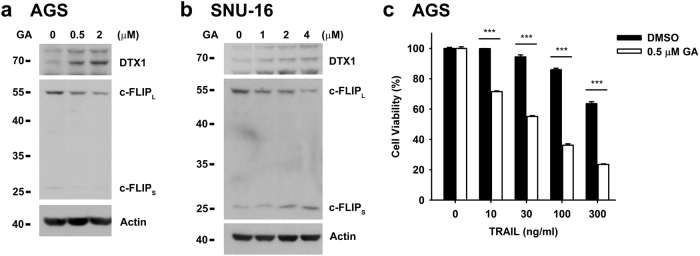
Geldanamycin decreases the protein level of c-FLIP and enhances TRAIL sensitivity
We next examined whether the DTX1-mediated downregulation of c-FLIP contributes to sensitization of cancer cells to TRAIL-induced cell death. Geldanamycin (GA) induces c-FLIPL degradation and cellular apoptosis in human lung cancer cells47. Treatment of AGS and SNU-16 cells with GA for 24 h also resulted in c-FLIPL downregulation (Fig. 5a, b). Addition of GA also enhanced the ability of TRAIL to induce cell death in AGS cells (Fig. 5c). We found that GA treatment led to increased DTX1 protein levels in AGS and SNU-16 cells (Fig. 5a, b). Notably, GA treatment did not affect the expression of DTX1 or c-FLIP mRNA (Supplementary Fig. 4).
Fig. 5. Geldanamycin decreases the protein level of c-FLIP and enhances TRAIL sensitivity.
a, b Geldanamycin (GA) promotes c-FLIPL degradation. AGS cells (a) or SNU-16 (b) cells were treated with GA at the indicated concentrations for 24 h. The levels of DTX1, c-FLIPL, and c-FLIPS were determined by immunoblotting. c GA sensitizes AGS cells to TRAIL-induced apoptosis. AGS cells were treated with 0.5 μM GA overnight and then incubated with TRAIL for 24 h. Cell viability was determined by MTT assay. Values are means ± standard deviations of three independent experiments. ***P ≤ 0.001
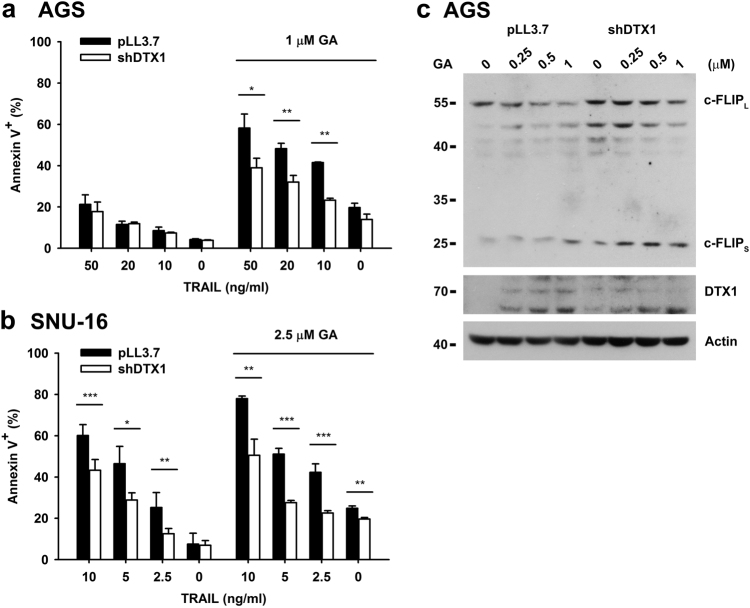
We then examined whether DTX1 was involved in GA-induced TRAIL sensitivity and c-FLIP degradation. DTX1-knockdown did not affect apoptosis induced by TRAIL alone in AGS cells, likely due to low DTX1 expression (Fig. 6a), but DTX1-deficiency reduced apoptosis triggered by TRAIL plus GA (Fig. 6a). The celldeath triggered by the combination of TRAIL and GA was similarly attenuated by DTX1-knockodwn in SNU-16 cells (Fig. 6b). GAinduced c-FLIP degradation was prevented by DTX1-knockdown in AGS cells (Fig. 6c). These results suggest that the GA-induced c-FLIP degradation was partly attributable to the induction of DTX1, leading to enhanced sensitivity of gastric cancer cells to TRAIL treatment. Together, our results suggest that increased DTX1 enhances TRAIL-triggered apoptosis in gastric cancer cells partly by downregulation of c-FLIP.
Fig. 6. Geldanamycin enhances TRAIL-induced apoptosis through DTX1-mediated c-FLIPLdegradation.
a, b DTX1 knockdown reduces GA-enhanced TRAIL sensitivity. Control (pLL3.7) and DTX1-knockdown (shDTX1) AGS cells (a) or SNU-16 cells (b) were incubated with GA overnight followed by TRAIL treatment for 5 h. Apoptosis was determined by Annexin V/PI staining. Values are means ± standard deviations of an experiment with triplicate (a) or three independent experiments (b). *P ≤ 0.05, **P ≤ 0.01, ***P ≤ 0.001. Experiment (a) was repeated three times with similar results. c DTX1-knockdown attenuates GA-induced c-FLIPL degradation. Control (pLL3.7) and DTX1-knockdown (shDTX1) AGS cells were treated with GA overnight. The levels of DTX1, c-FLIPL, and c-FLIPS were determined. Experiments (c) was independently repeated three times with similar results
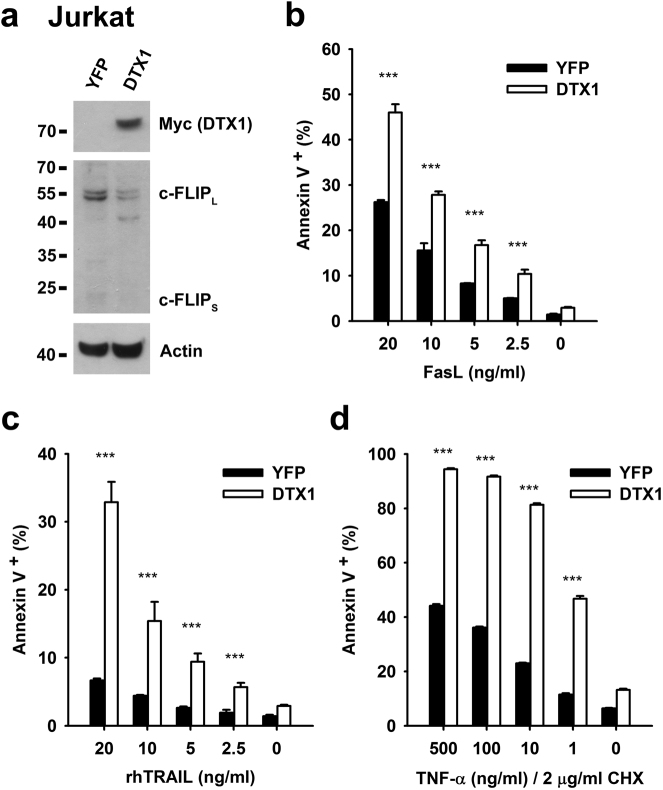
DTX1 enhances FasL-induced and TRAIL-induced apoptosis in T cells
The involvement of DTX1 in c-FLIP degradation is not limited to gastric cancer cells. We used Dtx1−/− T cells to examine the role of DTX1 in c-FLIP downregulation. c-FLIP was barely detectable in naïve WT T cells or Dtx1−/− T cells. TCR stimulation induced the expression of c-FLIP, and DTX1-deficiency increased CD3-triggered c-FLIP expression (Supplementary Fig. 5). Activated Dtx1−/− T cells were more resistant to FasL-induced apoptosis. We further explored whether overexpression of DTX1 increased the sensitivity of T lymphoma to death receptor-induced cell death by targeting c-FLIPL for degradation. DTX1 expression reduced the levels of c-FLIP in Jurkat cells (Fig. 7a). Increased DTX1 expression was indeed accompanied by enhanced FasL-induced apoptosis and TRAIL-triggered cell death in Jurkat cells (Fig. 7b, c). In addition, increased DTX1 expression promoted TNF-α-induced apoptosis in Jurkat cells in the presence of cycloheximide (Fig. 7d). Thus, DTX1 promotes DR-induced cell death in normal T cells and in T lymphoma. DTX1-promoted c-FLIP instability represents one of the physiological mechanisms that regulate c-FLIP protein.
Fig. 7. DTX1-overexpression enhances FasL-induced, TRAIL-induced and TNF-α-induced apoptosis in Jurkat cells.
a Reduced c-FLIP levels in DTX1-overexpressing Jurkat cells. The levels of c-FLIPL, c-FLIPS, and DTX1(Myc) in control (YFP) and DTX1-expressing Jurkat cells were determined. b–d Control (YFP) and DTX1-expressing Jurkat cells were treated with FasL b, TRAIL c, or TNF-α d at the indicated concentrations. The extent of apoptosis was analyzed 6 h later by flow cytometry with Annexin V staining. Data are mean ± SD of a triplicate experiment. Experiments were independently repeated three times with similar results. ***P ≤ 0.001. The experiment was independently repeated twice with comparable results
Discussion
Here, we report a new finding that DTX1 is an E3 ligase for c-FLIP in gastric cancer cells. The presence of DTX1 profoundly reduced the protein stability of c-FLIP (Fig. 2d, e). We have previously demonstrated that DTX1, similar to Cbl-b and Itch, promotes PKCθ and PLC-γ degradation in anergic Th1 cells42. In addition, as for Cbl-b and Itch39, DTX1 induced PKCθ degradation by directing it to the endocytic pathway for lysosomal degradation. We illustrate that DTX1 promotes c-FLIPL protein downregulation by similarly directing c-FLIPL into the endosome-lysosomal pathway for degradation (Fig. 4). Consequently, DTX1 expression enhanced the susceptibility of gastric cancer cells to TRAIL-induced apoptosis (Fig. 2a, b), whereas DTX1 downregulation increased the resistance to TRAIL-triggered cell death (Supplementary Fig. 2).
We have demonstrated that DTX1 interacts with c-FLIPL but not with c-FLIPS, and reveal that the p20 region of the caspase-like domain in c-FLIPL is the DTX-association domain (Fig. 3b, c). Binding of DTX1 to c-FLIPL leads to c-FLIPL degradation. Notably, expression of DTX1 led to a reduction of both c-FLIPL and c-FLIPS levels in AGS, SNU-16, and Jurkat cells (Figs 2a, b and 7a). A likely cause for the downregulation of c-FLIPS in these cancer cells is that c-FLIPL is hetero-dimerized with c-FLIPS in vivo and that the binding of DTX1 to c-FLIPL induces the degradation of c-FLIPL-c-FLIPS dimers. c-FLIPS was associated with the endogenous c-FLIPL in 293T cells (Supplementary Fig. 3e). This is further supported by the fact that DTX1 is co-expressed with c-FLIPL and c-FLIPS dimers in 293T cells, resulting in downregulation of both c-FLIPL and c-FLIPS (Fig. 3a, Supplementary Fig. 3c), and by the observation that c-FLIPS is associated with DTX1 under co-expression of c-FLIPL (Supplementary Fig. 3d).
DTX1 was downregulated in most of our gastric cancer samples (Fig. 1). Increased expression of c-FLIP in DTX1-deficient cells suggests that DTX1 downregulation confers resistance to TRAIL-induced apoptosis in gastric cancer cells. This finding, together with the negative correlation between cancer prognoses and DTX1 expression levels (Fig. 1g, h), suggest that manipulation of DTX1 could be beneficial in therapies against gastric cancer. We propose that reagents that can stimulate the expression of DTX1 may enhance the susceptibility of gastric cancer to TRAIL treatment.
Interaction with HSP90 contributes to the protein stability of c-FLIP. HSP90 also recruits c-FLIP to DISC to inhibit TRAIL-induced cell death48. HSP-90 inhibitors are known to exhibit inhibitory effects on multiple signaling pathways in cancer cells49. These inhibitors act synergistically with TRAIL to induce cell death in various cancers50–52. As reported for gastric cancer53, we found that addition of GA augmented TRAIL-induced apoptosis (Fig. 5). We have further demonstrated that DTX1 partly mediates the enhancing effect of GA on TRAIL-induced apoptosis (Figs 5 and 6). Knockdown of DTX1 partly reversed the enhancing effect of GA in AGS and SNU-16 cells (Fig. 6). Even though the exact molecular mechanism requires further investigation, it should be noted that other deltex family members (DTX2, DTX3, DTX4) are also associated with HSP90.
Our results suggest variability in the recruitment of a specific E3 ligase and in the mechanistic process of c-FLIP degradation in different cell types. Itch mediates c-FLIPL ubiquitination and degradation in conjunction with JNK signaling in hepatocytes and fibroblasts25. CBL has been shown to promote c-FLIPS degradation in non-small cell lung carcinoma cells via mTORC2-dependent signaling26. Here, we found that DTX1 enhances c-FLIPL downregulation in gastric cancer cells and lymphomas via an endosome-lysosomal pathway. Given the vast heterogeneity between different tumors, selection of E3 ligases for c-FLIP degradation is likely determined by the availability of the given E3 ligase and the signaling within tumor microenvironments. We also illustrate that c-FLIP protein levels are regulated by DTX1 in normal T cells (Supplementary Fig. 5), suggesting that DTX1 represents one of the physiological mechanisms controlling c-FLIP stability. It should be noted that the effect of DTX1-deficiency was not overwhelming (Supplementary Figs. 2 and 5), suggesting that DTX1 contributes to but is unlikely to be the only regulator of c-FLIP protein instability.
In summary, we identify DTX1, but not CBL or ITCH, as the E3 ligase regulating c-FLIP protein stability in gastric cancer cells. In addition, we show that DTX1 joins ITCH and CBL as another E3 ligase controlling c-FLIP under physiological conditions. Different c-FLIP degradation pathways are likely to have cancer type-dependent mechanisms, yet to be determined. We have also demonstrated that gastric cancer cells, which are relatively resistant to TRAIL treatment, become susceptible to TRAIL-induced cell death in the presence of DTX1. Our results suggest that a combination of TRAIL with compounds that increase DTX1 expression could be a new approach for gastric cancer therapy.
Materials and methods
Reagents
Recombinant human TRAIL and anti-His were obtained from R&D Systems (Minneapolis, MN). MG132, propidium iodide (PI), 3-(4,5-dimethyl-thiazol-2-yl)-2,5-diphenyl tetrazolium bromide (MTT), and anti-Flag-HRP were purchased from Sigma (St. Louis, MO). Rabbit anti-DTX1 polyclonal antiserum against GST-Deltex1 was generated as described9. The following antibodies were obtained from Santa Cruz Biotech (Santa Cruz, CA): anti-caspase-3 (H-277), anti-DR4 (H130), anti-DR5 (N-19), anti-Mcl-1 (S-19), and anti-Bcl-2 (N-19). Annexin V-Cy5 was obtained from Biovision (Mountain View, CA). Anti-Myc (9B11), anti-caspase-8 (1C12), and anti-active caspase-3 (D175) were purchased from Cell Signaling (Beverly, MA). Anti-actin (clone C4) and anti-β-tubulin (clone AA2) were purchased from Millipore (Temecula, CA). Anti-human FLIP mAb (NF6) was purchased from AdipoGen (San Diego, CA). Horseradish peroxidase-conjugated secondary antibodies were purchased from Jackson ImmunoResearch Laboratories. WesternBright ECL HRP substrate was obtained from Advansta Corporation (Menlo Park, CA). Dapi-Fluoromount-GTM was obtained from SouthernBiotech (Birmingham, AL). Protein G Mag SepharoseTM Xtra was obtained from GE Healthcare (Piscataway, NJ).
Analysis of cancer gene microarray database
The publicly-accessible Oncomine cancer microarray database (Compendia Biosciences; Ann Arbor, MI, USA; www.oncomine.com) was used to examine the expression of DTX1 in human gastric cancer tissue and cancer cell lines. D’Errico et al. (GEO accession GSE13911)43, Förster et al. (GEO accession GSE22377)44, and Ooi et al. (GEO accession GSE15459)45 datasets were used to compare DTX1, ITCH, and CBL expression levels between cancer and normal tissues. The Ooi et al. (GEO accession GSE15455)45 dataset was used to compare expression levels of DTX1, ITCH, and CBL among a panel of cell lines that represent adenocarcinoma, adenosquamous carcinoma, choriocarcinoma, and tubular adenocarcinoma of gastric cancer.
Hierarchical clustering analysis of gene expression data from 65 human primary tumor tissue samples and six gastrointestinal stromal tumor tissue samples was used to determine gene expression with gastric cancer outcomes46. Primary microarray data (GEO accession GSE13891) were used to compare DTX1, ITCH, and CBL expression levels between C1 and C2 clusters.
Cell culture and transfection
AGS and SNU-16 cells were cultured in RPMI 1640 medium with 10% FCS (Life Technologies-Invitrogen), 10 mM glutamine, 100 U/ml penicillin, 100 μg/ml streptomycin, and 20 mM 2-ME. DMEM (Life Technologies) was used in the culture of 293T cells. Transfection of 293T cells was performed by using OmicsFect In Vitro Transfection Reagent (Omics Biotechnology, Taiwan).
DTX1 overexpression and knockdown
For overexpression of DTX1, mouse DTX1 cDNA (a gift from Dr. Hideyuki Okano, Keiko University, Tokyo, Japan) was tagged with FLAG and subcloned into pTRIP-IRES-GFP to generate pTRIP-DTX1-IRES-GFP. 293T cells were transfected with pTRIP-IRES-GFP or pTRIP-c-FLIP-IRES-GFP, psPAX2, and pMD2G, and the lentivirus-containing culture supernatants were harvested 48 h after transfection. AGS and SNU-16 cells were infected with recombinant lentivirus, and GFP-expressing cells were isolated by sorting on a FACSAriaII SORP system (BD Biosciences). The c-FLIP p20 (198–376) fragment was isolated by PCR using forward primer 5′ ATG TCA AAT AAC TTC AGG CTC C and reverse primer 5′ ATC CAC CTC CAA GAG GCT GC. A full-length 2XHA-DTX1 (H453N and H456N, H2N2) mutant was generated40 and subcloned into pcDNA4 for expression in 293T cells.
For DTX1 knockdown, human DTX1-specific shRNA was subcloned into pLentiLox vector (pLL3.7; a gift from Dr. Luk Van Parijs, Massachusetts Institute of Technology, Cambridge, MA). The sequence of the human DTX1-specific shRNA was 5′-GAA GTT CAC CGC AAG AGG A-3′. Lentiviruses were harvested from culture supernatants of 293T cells transfected with pLL3.7 or pLL3.7-shDTX1, psPAX2, and pMD2.G. AGS and SNU-16 cells were infected with recombinant lentivirus, and GFP-expressing cells were sorted 48 h post-infection on a FACSAriaII SORP system (BD Biosciences, Mountain View, c-FLIP mouse [18] was a gift of Dr. You-Wen He (Duke University Medical Center, Durham NC). Mice with T cell-specific knockout of c-FLIP were generated by crossing of c-FLIP mouse with Cd4-Cre mouse. Mouse experiments were conducted with approval from the Institutional Animal Care and Use Committee, Academia Sinica. CA).
Apoptosis and cell viability assays
Several different methods were used to measure apoptosis and viability. After TRAIL treatment for 5–6 h, cells were stained with Annexin V-Cy5 and propidium iodide (PI), and annexin V+ populations were quantified by flow cytometry. After TRAIL treatment for 24 h, cells were stained with PI in hypotonic solution (50 mg/ml PI, 0.1% sodium citrate, 0.1% Triton X-100) overnight at 4 °C. Fractions of cells with sub-G1 DNA content were quantified using CellQUEST software on a FACSCalibur flow cytometer (BD Biosciences). For viability determination, AGS cells were plated in 96-well plates for 24 h before treatment. After TRAIL treatment, the cells were incubated with 0.5 mg/ml MTT in complete medium for 2 h. The surviving cells converted MTT to generate a purple-colored formazan product when dissolved in dimethyl sulfoxide (DMSO). The intensity of formazan product was measured by absorbance at 490 nm using SOFTmax PRO 4.3.1 LS software accompanying an Emax microtiter plate reader (Molecular Device, Sunnyvale, CA). Cell viability was calculated by dividing the absorbance of treated cells by that of the control. For measurement of caspase activation, control and DTX1-expressing cells were treated with 20 ng/ml TRAIL. The levels of procaspase-8, procaspase-3, processed caspase-8 (p43/41, p18) and processed caspase-3 (p19/17) were determined by immunoblots.
Surface staining
For staining of cell surface DR4 and DR5, AGS cells were incubated with anti-DR4 or anti-DR5 in PBS containing 2% FBS for 2 h. After washing with PBS, cells were stained with allophycocyanin-conjugated anti-Rabbit IgG or anti-Goat IgG, and analyzed on a FACSCalibur flow cytometry system.
Quantitative PCR
Total RNA from AGS cells was isolated using TRIzol (Invitrogen). cDNAs were prepared and analyzed for the expression of DTX1, c-FLIPL and c-FLIPS on a LightCycler 480 Real-Time PCR System (Roche). The PCR protocol was 95 °C for 10 min, followed by 45 cycles of 95 °C for 10 s, 60 °C annealing for 10 s, and 72 °C extension for 8 s. The PCR primers were: human DTX1, forward, 5′CAG CCG CCT GGG AAG ATG GAG TT-3′ and reverse, 5′-TGG ATG CCT GTG GGG ATG TCA TAG AC-3′; human c-FLIPL, forward, 5′-CCT AGG AAT CTG CCT GAT AAT CGA-3′ and reverse, 5′-TGG GAT ATA CCA TGC ATA CTG AGA TG-3′; human c-FLIPS, forward, 5′-GCA GCA ATC CAA AAG AGT CTC A -3′ and reverse, 5′-ATT TCC AAG AAT TTT CAG ATC AGG A-3′.
Immunoprecipitation
Cells were washed and lysed in whole cell extract (WCE) buffer (25 mM HEPES pH 7.4, 300 mM NaCl, 1.5 mM MgCl2, 0.2 mM EDTA pH 8.0, 0.1% Triton X-100, 0.5 mM DTT, 1× Complete protease inhibitor (EDTA-free, Roche)). Two hundred and fifty microgram whole cell lysate was incubated with antibodies, as indicated in each figure, on a rotating shaker overnight at 4 °C. Five microliter of Protein G Mag Sepharose was added and the samples were incubated at 4 °C for 1 h. The Protein G Mag Sepharose was washed repeatedly with 1 ml of WCE buffer. The beads were mixed with 1 × SDS-PAGE sample buffer and boiled at 100 °C for 5 min. Pull-down complex and total lysates were analyzed in 10% SDS-PAGE and transferred to polyvinylidene difluoride (PVDF) membranes (Millipore). The membranes were blocked with 5% skimmed milk for 1 h and probed with an appropriate antibody, followed by incubation with a HRP-conjugated secondary antibody. The protein bands were visualized by the ECL detection system.
Protein stability determination
c-FLIPL-Myc was transfected with or without DTX1-Flag in 293T cells. Cells were treated with cycloheximide (CHX, 50 ng/ml) for the indicated timeframes. Cell lysates were prepared and contents of c-FLIPL-Myc and DTX1-Flag were quantitated. The direct effect of DTX1 on c-FLIPL protein levels was examined by transfecting 293T cells with c-FLIPL or c-FLIPS in the presence of increasing amounts of DTX1. The levels of DTX1, c-FLIPL and c-FLIPS were determined 24 h after transfection. To identify the inhibitor of c-FLIP degradation, DTX1-Myc and/or c-FLIPL-Flag were transfected into 293T cells, and cells were treated with or without MG132 (2.5 μM), NH4Cl (25 mM), or leupeptin (100 μg/ml). The levels of c-FLIPL-Flag and DTX1-Myc were determined 8 h later.
Fluorescence protein constructs and confocal imaging
pmRFP-Rab5 was obtained from Addgene (Addgene plasmid 14437). pcDNA4-EGFP-DTX1 and pcDNA4-LAMP1-mCherry were generated as described previously9. To generate pcDNA4-cerulean-c-FLIPL, cerulean fragments were amplified by PCR from Cerulean-GalT (Addgene plasmid 11930) with HindIII/EcoRI and cloned into pcDNA4-c-FLIPL-Myc with HindIII/EcoRI to create a translational fusion construct.
293T cells (1 × 106) transduced with mRFP-Rab5 or LAMP1-mCherry were transfected with cerulean-c-FLIPL and EGFP-DTX1. 24 h after transfection, cells were re-seeded on a 22 × 22 mm glass coverslip and allowed to attach for another 18 h. Cells were fixed in 2% paraformaldehyde in PBS for 15 min at 37 °C and permeabilized with 0.3% Triton X-100 for 10 min at room temperature. Cells were mounted in Dapi-Fluoromount-GTM (SouthernBiotech, Birmingham, AL) and observed under a Zeiss LSM 780 confocal microscope.
Image acquisition
Images were observed under a Zeiss LSM 780 confocal microscope with a plan-Apochromat 63×/1.4 Oil DIC objective lens at room temperature. Samples were mounted in Dapi-Fluoromount-GTM. EGFP and Cerulean fluorescence proteins were excited by an argon laser (488 nm). EGFP fluorescence was collected in the range of 490 to 550 nm. Cerulean fluorescence was collected in the range of 445 to 489 nm. mRFP and mCherry fluorescence proteins were excited by a HeNe laser (594 nm) and emissions were collected with a 545 nm long-pass filter. DAPI-bound DNA was excited by a diode laser (405 nm) and fluorescence was collected in the range of 405 to 470 nm. The pinholes were as follows: Ch1–55 μm (blue), Chs1–54 μm (orange), Ch2–55 μm (red), and Chs1–55 μm (green). Images were acquired by a digital AxioCam (Zeiss) microscope camera using Carl Zeiss software Zen 2.1 (black).
Electronic supplementary material
Acknowledgements
We thank Ms. Yamin Lin of the FACS Core and Shu-Mei Huang of the Confocal Core of the Institute of Molecular Biology, Academia Sinica for cell sorting and confocal microscopy, and Dr. John O’Brien for editing the manuscript. This work was supported by grant MOST 105-2321-B-001-065 from the Ministry of Science and Technology and an Academia Sinica Investigator Award from Academia Sinica, Taiwan, R.O.C.
Author contributions
T.S.H.: acquisition, analysis and interpretation of data, statistical analyses; S.T.M.: data acquisition; P.N.H.: material support and study concept; M.Z.L.: study concept and design, supervision of the study, drafting of the manuscript.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Footnotes
Edited by T Kaufmann
Edited by T. Kaufmann
Publisher's note: Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary information
The online version of this article (10.1038/s41419-017-0165-6) contains supplementary material.
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
References
- 1.Ferlay J, et al. Cancer incidence and mortality worldwide: sources, methods and major patterns in GLOBOCAN 2012. Int. J. Cancer. 2015;136:E359–E386. doi: 10.1002/ijc.29210. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Corso S, Giordano S. How can gastric cancer molecular profiling guide future therapies? Trends Mol. Med. 2016;22:534–544. doi: 10.1016/j.molmed.2016.05.004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Van Cutsem E, Sagaert X, Topal B, Haustermans K, Prenen H. Gastric cancer. Lancet. 2016;388:2654–2664. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(16)30354-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Ashkenazi A. Targeting the extrinsic apoptotic pathway in cancer: lessons learned and future directions. J. Clin. Invest. 2015;125:487–489. doi: 10.1172/JCI80420. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Lim B, et al. Targeting TRAIL in the treatment of cancer: new developments. Expert Opin. Ther. Targets. 2015;19:1171–1185. doi: 10.1517/14728222.2015.1049838. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.von Karstedt S, Montinaro A, Walczak H. Exploring the TRAILs less travelled: TRAIL in cancer biology and therapy. Nat. Rev. Cancer. 2017;17:352–366. doi: 10.1038/nrc.2017.28. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Qiao L, Wong BC. Targeting apoptosis as an approach for gastrointestinal cancer therapy. Drug Resist. Updat. 2009;12:55–64. doi: 10.1016/j.drup.2009.02.002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Huang Y, et al. sTRAIL-iRGD is a promising therapeutic agent for gastric cancer treatment. Sci. Rep. 2017;7:579. doi: 10.1038/s41598-017-00688-6. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Strasser A, Jost PJ, Nagata S. The many roles of FAS receptor signaling in the immune system. Immunity. 2009;30:180–192. doi: 10.1016/j.immuni.2009.01.001. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Wilson NS, Dixit V, Ashkenazi A. Death receptor signal transducers: nodes of coordination in immune signaling networks. Nat. Immunol. 2009;10:348–355. doi: 10.1038/ni.1714. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Lavrik IN, Krammer PH. Regulation of CD95/Fas signaling at the DISC. Cell Death Differ. 2012;19:36–41. doi: 10.1038/cdd.2011.155. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Green DR, Llambi F. Dell death signaling. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Biol. 2015;7:a006080. doi: 10.1101/cshperspect.a006080. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Budd RC, Yeh WC, Tschopp J. cFLIP regulation of lymphocyte activation and development. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2006;6:196–204. doi: 10.1038/nri1787. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Hughes MA, et al. Co-operative and hierarchical binding of c-FLIP and Caspase-8: a unified model defines how c-FLIP isoforms differentially control cell fate. Mol. Cell. 2016;61:834–849. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2016.02.023. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Schleich K, et al. Molecular architecture of the DED chains at the DISC: regulation of procaspase-8 activation by short DED proteins c-FLIP and procaspase-8 prodomain. Cell Death Differ. 2016;23:681–694. doi: 10.1038/cdd.2015.137. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Feoktistova M, et al. cIAPs block Ripoptosome formation, a RIP1/caspase-8 containing intracellular cell death complex differentially regulated by cFLIP isoforms. Mol. Cell. 2011;43:449–463. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2011.06.011. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Oberst A, et al. Catalytic activity of the caspase-8-FLIPL complex inhibits RIPK3-dependent necrosis. Nature. 2011;471:363–367. doi: 10.1038/nature09852. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.He MX, He YW. A role for c-FLIPL in the regulation of apoptosis, autophagy, and necroptosis in T lymphocytes. Cell Death Differ. 2013;20:188–197. doi: 10.1038/cdd.2012.148. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Fulda S. Targeting extrinsic apoptosis in cancer: Challenges and opportunities. Semin. Cell. Dev. Biol. 2015;39:20–25. doi: 10.1016/j.semcdb.2015.01.006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Safa AR, Pollok KE. Targeting the anti-apoptotic protein c-FLIP for cancer therapy. Cancers. 2011;3:1639–1671. doi: 10.3390/cancers3021639. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Shirley S, Micheau O. Targeting c-FLIP in cancer. Cancer Lett. 2013;332:141–150. doi: 10.1016/j.canlet.2010.10.009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Yeh JH, Hsu SC, Han SH, Lai MZ. Mitogen activated protein kinase kinase antagonized FADD-mediated apoptosis by induced FLIP expression. J. Exp. Med. 1998;188:1795–1802. doi: 10.1084/jem.188.10.1795. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Micheau O, Lens S, Gaide O, Alevizopoulos K, Tschopp J. NF-κB signals induce the expression of c-FLIP. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2001;21:5299–5305. doi: 10.1128/MCB.21.16.5299-5305.2001. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Kreuz S, Siegmund D, Scheurich P, Wajant H. NF-κB inducers upregulate cFLIP, a cycloheximide-sensitive inhibitor of death receptor signalling. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2001;21:3964–3973. doi: 10.1128/MCB.21.12.3964-3973.2001. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Chang L, et al. The E3 ubiquitin ligase itch couples JNK activation to TNFalpha-induced cell death by inducing c-FLIP(L) turnover. Cell. 2006;124:601–613. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2006.01.021. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Zhao L, Yue P, Khuri FR, Sun SY. mTOR complex 2 is involved in regulation of Cbl-dependent c-FLIP degradation and sensitivity of TRAIL-induced apoptosis. Cancer Res. 2013;73:1946–1957. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-12-3710. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Koyama S, Koike N, Adachi S. Expression of TNF-related apoptosis-inducing ligand (TRAIL) and its receptors in gastric carcinoma and tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes: a possible mechanism of immune evasion of the tumor. J. Cancer Res. Clin. Oncol. 2002;128:73–79. doi: 10.1007/s004320100292. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Kanehara I, Nakata B, Hirakawa K. Caspase-8 is scarcely silenced and its activity is well correlated with the anticancer effect of tumor necrosis factor-related apoptosis-inducing ligand in gastric cancer cells. Oncol. Rep. 2005;14:1249–1253. doi: 10.3892/or.14.5.1249. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Lee SH, et al. Increased expression of FLIP, an inhibitor of Fas-mediated apoptosis, in stomach cancer. APMIS. 2003;111:309–314. doi: 10.1034/j.1600-0463.2003.1110203.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Zhou XD, et al. Overexpression of cellular FLICE-inhibitory protein (FLIP) in gastric adenocarcinoma. Clin. Sci. 2004;106:397–405. doi: 10.1042/CS20030238. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Nam, S. Y. et al. Upregulation of FLIP(S) by Akt, a possible inhibition mechanism of TRAIL-induced apoptosis in human gastric cancers. Cancer Sci.94, 1066–1073. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- 32.Wang W, et al. Programmed cell death 4 (PDCD4) mediates the sensitivity of gastric cancer cells to TRAIL-induced apoptosis by down-regulation of FLIP expression. Exp. Cell. Res. 2010;316:2456–2464. doi: 10.1016/j.yexcr.2010.05.027. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Belkhiri A, Zhu S, Chen Z, Soutto M, El-Rifai W. Resistance to TRAIL is mediated by DARPP-32 in gastric cancer. Clin. Cancer Res. 2012;18:3889–3900. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-11-3182. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Lin WC, et al. Helicobacter pylori sensitizes TNF-related apoptosis-inducing ligand (TRAIL)-mediated apoptosis in human gastric epithelial cells through regulation of FLIP. Cell Death Dis. 2014;5:e1109. doi: 10.1038/cddis.2014.81. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Matsuno K, Diederich RJ, Go MJ, Blaumueller CM, Artavanis-Tsakonas S. DTX acts as a positive regulator of Notch signaling through interactions with the Notch ankyrin repeats. Development. 1995;121:2633–2644. doi: 10.1242/dev.121.8.2633. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Kishi N, et al. Murine homologs of DTX define a novel gene family involved in vertebrate Notch signaling and neurogenesis. Int. J. Dev. Neurosci. 2001;19:21–35. doi: 10.1016/S0736-5748(00)00071-X. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Hori K, et al. Drosophila Deltex mediates Suppressor of Hairless-independent and late-endosomal activation of Notch signaling. Development. 2004;131:5527–5537. doi: 10.1242/dev.01448. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Hori K, Sen A, Kirchhausen T, Artavanis-Tsakonas S. Synergy between the ESCRT-III complex and Deltex defines a ligand-independent Notch signal. J. Cell. Biol. 2011;195:1005–1015. doi: 10.1083/jcb.201104146. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Heissmeyer V, et al. Calcineurin imposes T cell unresponsiveness through targeted proteolysis of signaling proteins. Nat. Immunol. 2004;5:255–265. doi: 10.1038/ni1047. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Hsiao HW, et al. Deltex1 is a target of the transcription factor NFAT that promotes T cell anergy. Immunity. 2009;31:72–83. doi: 10.1016/j.immuni.2009.04.017. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Hsiao HW, et al. Deltex1 antagonizes HIF-1α and sustains the stability of regulatory T cells in vivo. Nat. Commun. 2015;6:6353. doi: 10.1038/ncomms7353. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Hsu TS, Hsiao HW, Wu PJ, Liu WH, Lai MZ. Deltex1 promotes protein kinase Cθ degradation and sustains Casitas B-lineage lymphoma expression. J. Immunol. 2014;193:1672–1680. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.1301416. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.D’Errico M, et al. Genome-wide expression profile of sporadic gastric cancers with microsatellite instability. Eur. J. Cancer. 2009;45:461–469. doi: 10.1016/j.ejca.2008.10.032. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44.Förster S, Gretschel S, Jöns T, Yashiro M, Kemmner W. THBS4, a novel stromal molecule of diffuse-type gastric adenocarcinomas, identified by transcriptome-wide expression profiling. Mod. Pathol. 2011;24:1390–1403. doi: 10.1038/modpathol.2011.99. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45.Ooi CH, et al. Oncogenic pathway combinations predict clinical prognosis in gastric cancer. PLoS Genet. 2009;5:e1000676. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1000676. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46.Cho JY, et al. Gene expression signature–based prognostic risk score in gastric cancer. Clin. Cancer Res. 2011;17:1850–1857. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-10-2180. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47.Wang Q, et al. Down-regulation of cellular FLICE-inhibitory protein (Long Form) contributes to apoptosis induced by Hsp90 inhibition in human lung cancer cells. Cancer Cell. Int. 2012;12:54. doi: 10.1186/1475-2867-12-54. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 48.Panner A, Murray JC, Berger MS, Pieper RO. Heat shock protein 90alpha recruits FLIPS to the death-inducing signaling complex and contributes to TRAIL resistance in human glioma. Cancer Res. 2007;67:9482–9489. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-07-0569. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 49.Whitesell L, Lin NU. Hsp90 as a platform for the assembly of more effective cancer chemotherapy. Biochim. Biophys. Acta. 2012;1823:756–766. doi: 10.1016/j.bbamcr.2011.12.006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 50.Vasilevskaya IA, O’Dwyer PJ. 17-Allylamino-17-demethoxygeldanamycin overcomes TRAIL resistance in colon cancer cell lines. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2005;70:580–589. doi: 10.1016/j.bcp.2005.05.018. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 51.Wang X, et al. 17-allylamino-17-demethoxygeldanamycin synergistically potentiates tumor necrosis factor-induced lung cancer cell death by blocking the nuclear factor-kappaB pathway. Cancer Res. 2006;66:1089–1095. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-05-2698. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 52.Henrich CJ, et al. Withanolide E sensitizes renal carcinoma cells to TRAIL-induced apoptosis by increasing cFLIP degradation. Cell Death Dis. 2015;6:e1666. doi: 10.1038/cddis.2015.38. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 53.Chen H, Li LQ, Pan D. Geldanamycin induces apoptosis in human gastric carcinomas by affecting multiple oncogenic kinases that have synergic effects with TNF-related apoptosis-inducing ligand. Oncol. Lett. 2015;10:3732–3736. doi: 10.3892/ol.2015.3807. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.